Theme 1 Economics | Quizlet
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
What is a positive statement
A statement that is objective
What is a normative statement
statement that is opinion
What is the basic economic problem?
Although wants are infinite, needs are finite and limited
What are the 4 factors of production
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
What does a PPF diagram show
The maximum combination of capital and consumer goods that the economy can produce with its current resources and technology
What are capital goods
Goods that are produced in order to aid the production of consumer goods
What are consumer goods
Goods that are demanded and bought by households and individuals
What is specialisation
When a country or firm specialises in producing a small range of goods.
Why is it important for countries to specialise
In order to ensure all factors of production including workers, undertake the tasks they are best a
What did Adam smith state
Specialisation can increase labour productivity
What are the advantages of specialisation
Labour productivity increase
Higher quality of goods and services
Workers only need to be trained to do one task
Disadvantages of specialisation
Poor quality of work, as the work is boring
No industrial training so structural employment is likely.
Advantages of specialisation for a country
Comparative advantage leads to greater output worldwide
Disadvantages of specialisation for a country
Countries become dependant on one export (LEDCs reliance on agriculture)
High interdependence which can be impacted by war
What is a free market economy
Individuals can make own choices and own factors of production, no government intervention, decisions are based on satisfaction and profit
what was the invisible hand, who propogated the theory
resources are moved out of production of a good when the consumer no longer wants it, the market allocated resources to everyone's benefit (Adam smith)
advantages of free market economy
consumer sovereignty
high motivation (potential for reward)
firms are in competition so they are productively efficient
disadvantages of free market economy
high inequality
lack of merit goods and no control of demerit goods
risk of monopolies
what is a command economy
all factors of production expect labour are owned by the government, and labour is directed by government
no private property
what is a mixed economy
both free market mechanism and government planning allocate a significant amount of resources
what is the governments role in a mixed economy
creating a framework of rules (preventing monopoly abuse)
redistributes income (taxation and benefits)
produce public and merit goods (streetlights)
what are the underlying assumptions of rational economic decision making
customers aim to maximise utility
producers aim to maximise profit
governments aim to maximise wellfare
what is a movement along the demand curve
a movement from a to b (A-B is extension, B-A is a contraction)
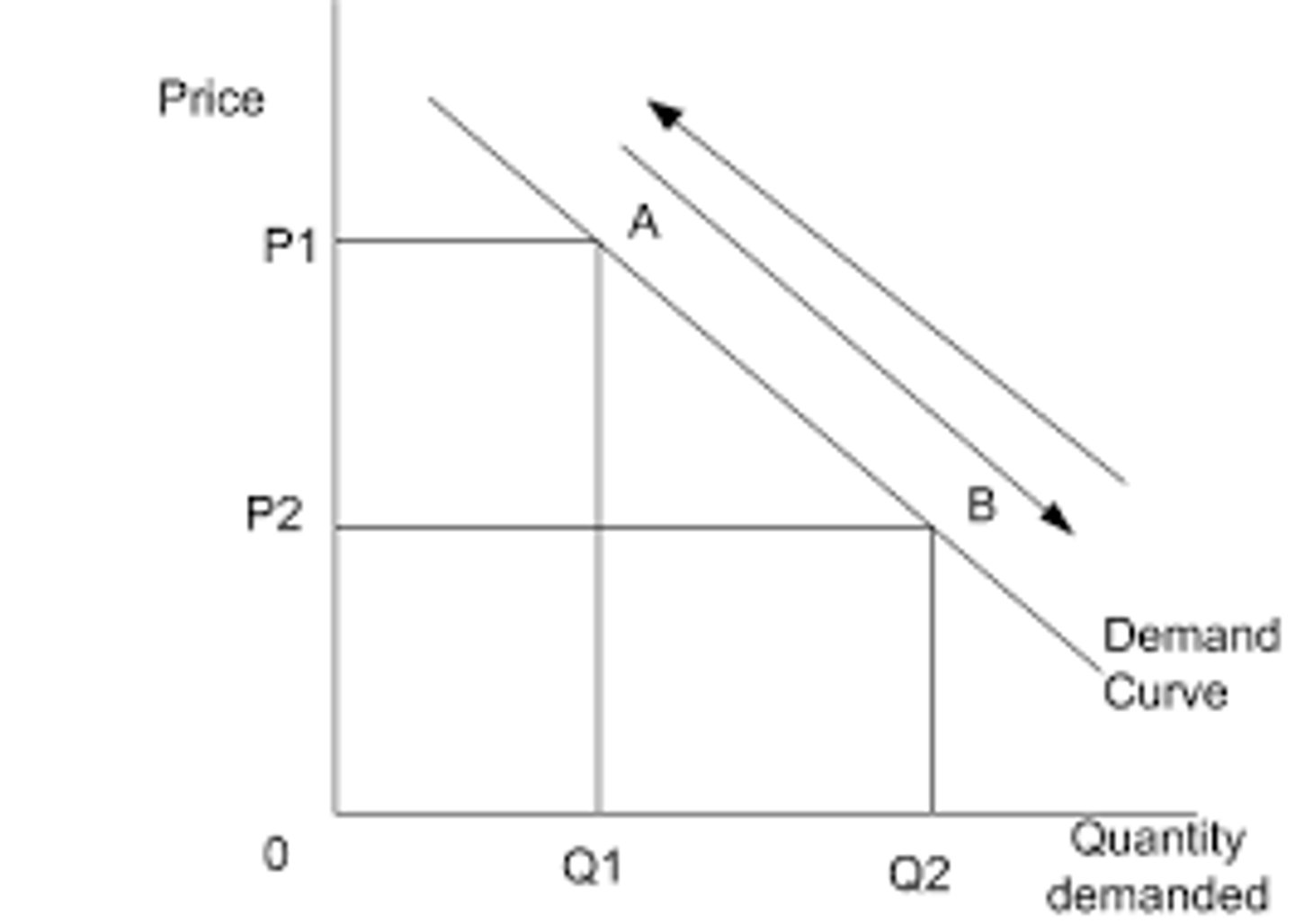
what causes a movement along the demand curve
a change in the price of a good
how can the law of diminishing marginal utility be explained on a graph
demand curve slopes downward showing inverse relationship between price and quantity
What do we have to assume in order to predict or explain how people spend their money
Assume they behave rationally and spend money according to what gives them the greatest satisfaction or welfare
What's the difference between total utility and marginal utility
Total represents the satisfaction gained by customer as result of their overall consumption of a good (eg. Satisfaction from eating whole bar of chocolate)
Marginal represents the change in satisfaction from the consumption of the next unit of a good (increased satisfaction from eating another bar of chocolate)
What is the law of diminishing marginal utility
As more of a good is consumed, each additional unit provides less additional satisfaction
Why does the law of diminishing marginal utility explain why the demand curve slopes downward
If more of a good is consumed there is less satisfaction derived from the good, this means that consumers are less willing to pay high prices at high quantities since they aren't getting as much satisfaction
What is another reason the demand curve slopes downward
In order to maximise satisfaction with income, consumers need to spend so that satisfaction gained per penny is as high as possible. So curve is downward sloping because if price rises marginal utility per penny failed so consumers buy less of the good
Define price elasticity of demand
Responsiveness of demand to a change in the price of a good
What is the formula for PED
%change in QD/% change in price
What are most values of PED and why
Negative, since a rise in price leads to a fall in output
PED = 1, is called what
Unitary elastic, QD changes by same percentage as price
PED is bigger than 1, this means what
Relatively elastic, QD changes by larger percentage than price so demand is relatively response to price
PED is smaller than 1, this means what
QD changes by smaller percentage than price so demand is relatively unresponsive to price.
PED=0, this means what
A change in price has no effect on output, so demand is unresponsive to price
Give 3 factors that influence PED
Availability of substitutes (people can switch to similar products if prices rise)
Necessity
How large a % of total expenditure the good makes up (small percentage means price change is inconsequential)
Why is PED significant
Determines the burden of tax, on wether it lies with consumers or producers
What happens to the incidence of tax if the demand curve is elastic
Lower burden of tax for consumers, higher burden for producers
What happens to incidence of tax if demand curve is inelastic
Lower burden of tax for producers, higher burden of tax for consumers
What happens to revenue if PED is inelastic
Decrease in price leads to an increase in revenue, vice versa
Define income elasticity of demand
Responsiveness of demand to a change in income
What is the formula for YED
%change in quantity demanded/%change in income
What is the good called when YED is less than 0, and give an example
Inferior good, rise in income leads to fall in demand for good. Tesco value goods
What happens to revenue if PED is inelastic
Increase in price leads to increase in revenue
What is the good called when YED is more than 0
Normal good, rise in income leads to rise in demand for good. Dining out or clothing
What is the good called when YED is more than 1, and give an example
Luxury goods, type of normal good, luxury clothing or sports cars
Why is YED significant for businesses
So businesses know how sales will be affected by changes in income of the population
May also impact the type of goods a firm produces, in prosperity firms may produce more luxury goods
Define cross elasticity of demand (xed)
The responsiveness of demand for one product to the change in price of another
give the formula for xed
%change in quanitity demanded of A/% change in price of B
what does it mean when xed is greater than 0
substitutes, increase in the price of good B will lead to increase in demand of good A. Coke and pepsi
what does it mean when xed is smaller than 0
Complementary goods, increase in the price of good B will decrease demand for Good A. DVD's and DVD players
what does it mean when XED=0
unrelated good, change in price of good a has no impact on good B
why do firms need to be aware of XED
so they are aware of firms producing complimentary goods, they need to know how price changes from other firms will affect them and adjust accordingly.
Define supply
Supply is the ability and the willingness to provide a good or service at a particular price at a given time.
What causes a movement along the supply curve from A to B
A change in price
What is the result of an extension in supply
An increase in QS and P
What is the result of a contraction in supply
A decrease in QS and P
What is joint supply and how can it impact market supply
Production of one good automatically leads to another, production of beef leads to leather
If price of beef rises then farmers kill more cows which leads to more leather
What is competitive supply and how can it impact market supply
Production of one good prevents supply of another
If price of beef rises then farmers kill cows which means they can't produce milk, which causes decrease in supply of milk
Give me 5 conditions of supply
Cost of production
Weather
Technology
Price of other goods
Government legislation
Why does the supply curve slope upward?
If prices are higher firms will increase production to take advantage of high profits. If prices are lower firms will cut back on unprofitable production.
Define price elasticity of supply
The responsiveness of supply to a change in price
What is the formula for PES
%change in quantity supplied/%change in price
What is PES=1
Unitary elastic, quantity supply changes by the same as percentage as price
What is it when PES is bigger than 1
Relatively elastic, QS changes by larger percentage than price so supply is relatively responsive to price
What is it when PES is less than 1
Relatively inelastic, QS changes by a smaller percentage than price, so supply is relatively unresponsive to price
What is perfectly elastic PES
PES=infinity
What is perfectly inelastic PES
PES=0
Give me 3 factors affecting PES
Stocks (if stockpile of goods is available then when price rises they may just use the stockpile)
Working below full capacity
Availability of factors of production (labour may need training so can't be insta increased, number of doctors can't instantly increase)
Define short run
Short Run: The short run refers to a period during which some factors of production, such as plant capacity or labor, are fixed and cannot be adjusted. Supply may be less elastic in the short run.
Define long run
a period during which all factors of production can be adjusted. Firms can expand or contract production capacity. Supply can be more elastic in the long run.
Why is the short run significant for elasticity of supply
In the short run, supply may be less responsive to price changes due to limited flexibility in adjusting production levels.
Why is the long run significant for elasticity of supply
In the long run, firms have more options to adjust production capacity, making supply more responsive to price changes.
Define market clearing price
Where Demand = Supply ie. The equilibrium point all goods supplied to the market have been cleared (bought).
Draw an excess demand graph and explain it
Suppliers are willing to supply QS but consumers demand QD, which results in excess demand as shown by shaded area.
What happens as a result of a shortage in the market due to the mechanism of excess demand
Firms know they can charge a higher price for their goods, so this will cause an extension in supply and contraction in demand back to the point of equilibrium
Draw an excess supply diagram and explain it
At P2 firms are willing to supply at QS but consumers demand QD, meaning excess supply and a fall in price as firms have unsold goods so will put on sales
What is the price mechanism
In a free market economy the price mechanism allocates resources
How is price determined in the price mechanism
Price is determined by the interactions of demand and supply, which also determines how much is bought and sold.
What is the invisible hand
The idea that people pursuing their own self-interest actually benefit the public at large
Individuals and firms acting in their own self interest guided by the invisible hand of the market will produce and consume goods and services in the most economically efficient way possible leading to the optimal allocation of scarce resources and greatest overall prosperity
What is the rationing function in the price mechanism
When a good is scarce, its price rises.
This rations the good — meaning only those willing and able to pay the higher price can buy it.
As a result, limited resources are spread out to those who value them most.
What is the signalling function in the price mechanism
PM acts as a signal where resources should be used
When p rises producers move resources into manufacturing that good, ie. change in price indicates that market conditions have changed.
What is the incentive function in the price mechanism
Incentive to work hard, buyers realise more money means they can buy more products.
Suppliers realise that if they produce more of a good they will make more money.
Name 3 functions within the price mechanism
Signalling
Incentive
Rationing
Give an example of the rationing function
Covid disrupted supply chains, less imports means fewer goods in supermarkets, demand for food is high but supply is low, price of food rises to ration off excess demand so people who value food the highest get it
Give an example of the incentive function
Due to high house prices in London this provides an incentive for firms to keep building more houses
Define consumer surplus
The difference between the price the consumer is willing to pay and the price they actually pay
What is consumer surplus set by
Price mechanism
How do you show consumer surplus on a graph
Difference between demand curve and price curve
Define producer surplus
The difference between the price the supplier is willing to produce their product at and the price they actually produce at, set by the price mechanism
How do you show producer surplus on a graph
Difference between supply curve and price
What does consumer surplus show
Welfare gained by consumers for buying a good
What does producer surplus show
The economic gain for producers by selling the good
how does demand and supply impact consumer and producer surplus
decrease in demand leads to a fall in producer and consumer surplus
Increase in demand leads to an increase in consumer and producer surplus
supply is the same
how do elasticities impact consumer suprlus
perfectly elastic demand means there is no consumer surplus
perfectly inelastic demand means that consumer surplus is infinite
what is an indirect tax
tax on spending
what are the 2 types of indirect tax
AD valorem (tax increases in proportion to the value of the good. VAT)
specific tax (an amount is added to the price, increases with quantity. Petrol tax 10p a litre)
what is the incidence of tax
The tax burden on the taxpayer