Aerobic Respiration
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
cellular respiration
cells convert glucose into energy (ATP) using oxygen (or without it during glycolysis)
metabolism
the chemical reactions in a living thing that convert food (glucose) into energy (ATP).
aerobic
involving oxygen
anaerobic
without oxygen
glycolysis inputs
glucose, 2 ATP, 4 ADP, and 2 NAD+
glycolysis outputs
2 pyruvate, 2 ADP + 2 ATP, and 2 NADH
transition reaction inputs
2 pyruvate, 2 NAD+, and 2 CoA
transition reaction outputs
2 acetyl-CoA, 2 NADH, and 2 CO2
krebs cycle inputs
2 acetyl-CoA, 6 NAD+, 2 FAD, and 2 ADP + 2P
krebs cycle outputs
2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2, and 4 CO2
electron transfer cycle inputs
10 NADH, 2 FADH2, 6 oxygen, 32 or 34 ADP
electron transfer cycle outputs
32 or 34 ATP, 6 H2O, NAD, FAD, H+
how much ATP is generated in the electron transfer cycle?
30-32 molecules
what is the only anaerobic process of cellular respiration?
glycolysis
where does glycolysis occur
in the cytoplasm
where does the transition reaction & krebs cycle occur
in the mitochondrial matrix
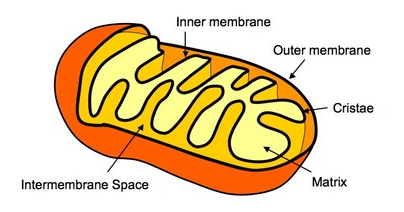
what is the mitochondria’s cristae
folds of the membrane jutting into the matrix
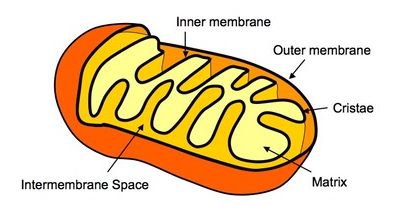
what is the mitochondria’s matrix
innermost compartment filled with gel-like fluid

where does the electron transfer cycle occur
in the inner mitochondrial membrane
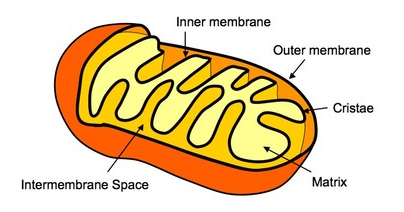
final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration
oxygen
how many times does the krebs cycle occur? (per glucose molecule)
2
what forms when hydrogen ions travel the electrochemical gradient in the cristae of mitochondria?
ATP
what is chemiosmosis
process of an H+ gradient storing energy to drive ATP synthesis
what is ATP synthase
enzyme that makes ATP from ADP
purpose of glycolysis
breaks glucose into 2 pyruvate
purpose of link reaction
reduces 2 pyruvate into acetyl coa
purpose of krebs cycle
after acetyl-coa enters, glucose is fully broken down to carbon dioxide
purpose of electron transport chain
electron transport is coupled with ATP synthesis
purpose of oxygen during the krebs cycle
oxygen accepts H from NADH to turn into NAD, so if no O, there is no NAD for krebs cycle or electron
oxidative phosphorylation
inorganic phosphate added to ADP, powered by redox reactions of ETC
substrate-level phosphorylation
enzyme transfers phosphate group from substrate molecule to ADP, occurs during glycolysis and krebs cycle
cytochromes
protein electron carriers: the final passes electrons to oxygen
what is the direct energy source that drives ATP synthesis during respiratory oxidative phosphorylation in eukaryotic cells
the proton-motive force (H+ gradient) across the inner mitochondrial membrane