C5 the reactivity series
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Students should understand the use of the multipliers in equations in normal script before a formula and in subscript within a formula. Students should be able to calculate the percentage by mass in a compound given the relative formula mass and the relative atomic masses. Students should be able to explain any observed changes in mass in non-enclosed systems during a chemical reaction given the balanced symbol equation for the reaction and explain these changes in terms of the particle model. Students should be able to use the relative formula mass of a substance to calculate the number of moles in a given mass of that substance and vice versa.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
the reactivity series
potassium
sodium
lithium
calcium
aluminium
carbon
zinc
iron
tin
lead
hydrogen
gold
platinum
Conservation of mass and balanced chemical equations
The law of conservation of mass states that no atoms are lost or made during a chemical reaction so the mass of the products equals the mass of the reactants. This means that chemical reactions can be represented by symbol equations which are balanced in terms of the numbers of atoms of each element involved on both sides of the equation.
2 Relative formula mass
The relative formula mass (Mr ) of a compound is the sum of the relative atomic masses of the atoms in the numbers shown in the formula. In a balanced chemical equation, the sum of the relative formula masses of the reactants in the quantities shown equals the sum of the relative formula masses of the products in the quantities shown.
Mass changes when a reactant or product is a gas
Some reactions may appear to involve a change in mass but this can usually be explained because a reactant or product is a gas and its mass has not been taken into account. For example: when a metal reacts with oxygen the mass of the oxide produced is greater than the mass of the metal or in thermal decompositions of metal carbonates carbon dioxide is produced and escapes into the atmosphere leaving the metal oxide as the only solid product.
4 Chemical measurements
Whenever a measurement is made there is always some uncertainty about the result obtained.
i should be able to:
• represent the distribution of results and make estimations of uncertainty
• use the range of a set of measurements about the mean as a measure of uncertainty.
moles
Chemical amounts are measured in moles. The symbol for the unit mole is mol. The mass of one mole of a substance in grams is numerically equal to its relative formula mass. One mole of a substance contains the same number of the stated particles, atoms, molecules or ions as one mole of any other substance. The number of atoms, molecules or ions in a mole of a given substance is the Avogadro constant. The value of the Avogadro constant is 6.02 x 1023 per mole. Students should understand that the measurement of amounts in moles can apply to atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, formulae and equations, for example that in one mole of carbon (C) the number of atoms is the same as the number of molecules in one mole of carbon dioxide (CO2).
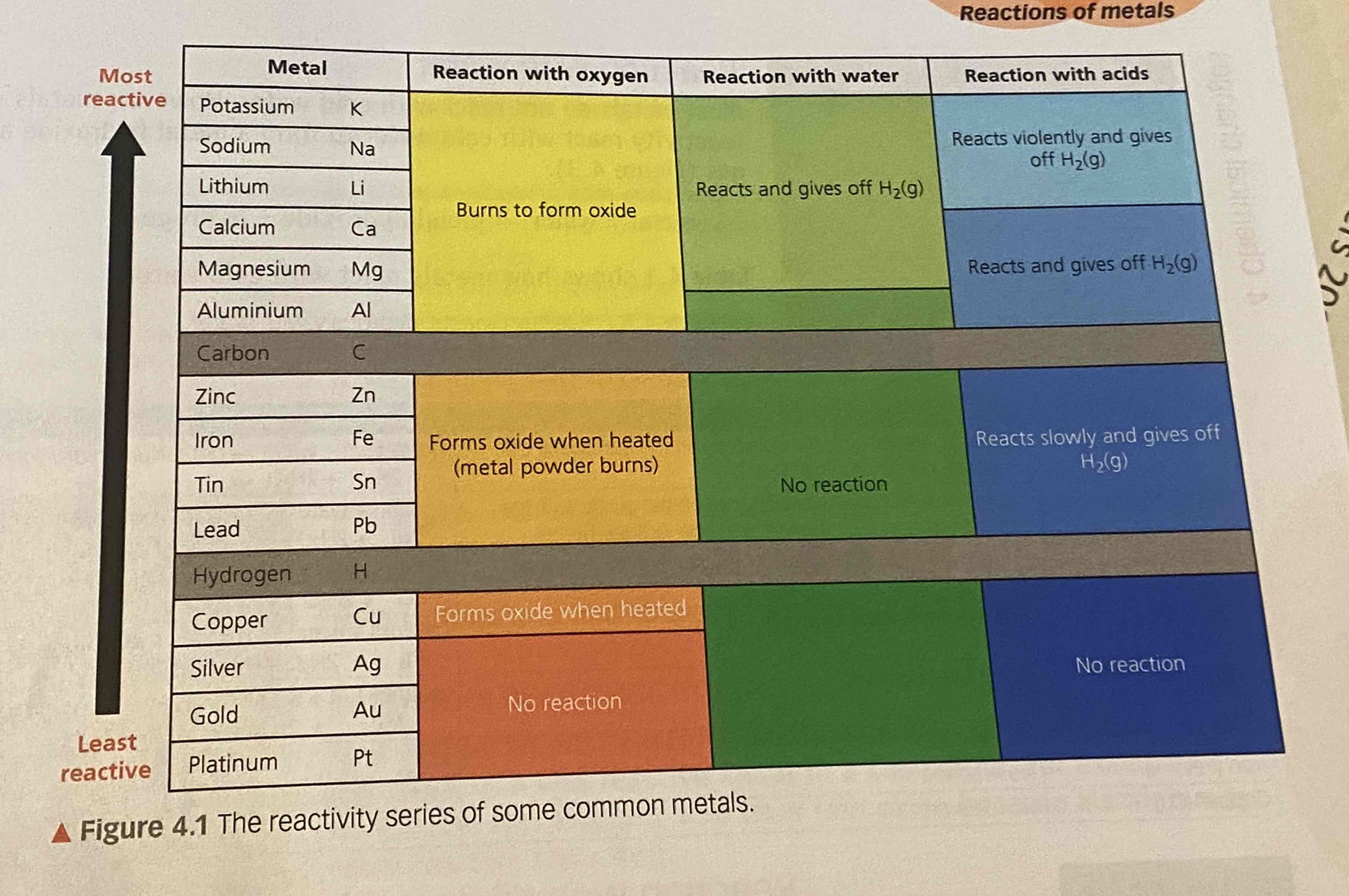
metals + oxygen
reactive metals burn when heated because they react with oxygen
e.g copper is normed forming an oxiden layer on it which is black
unreactive metals dont react with oxygen
metal + oxygen → metal oxide
oxidation reaction
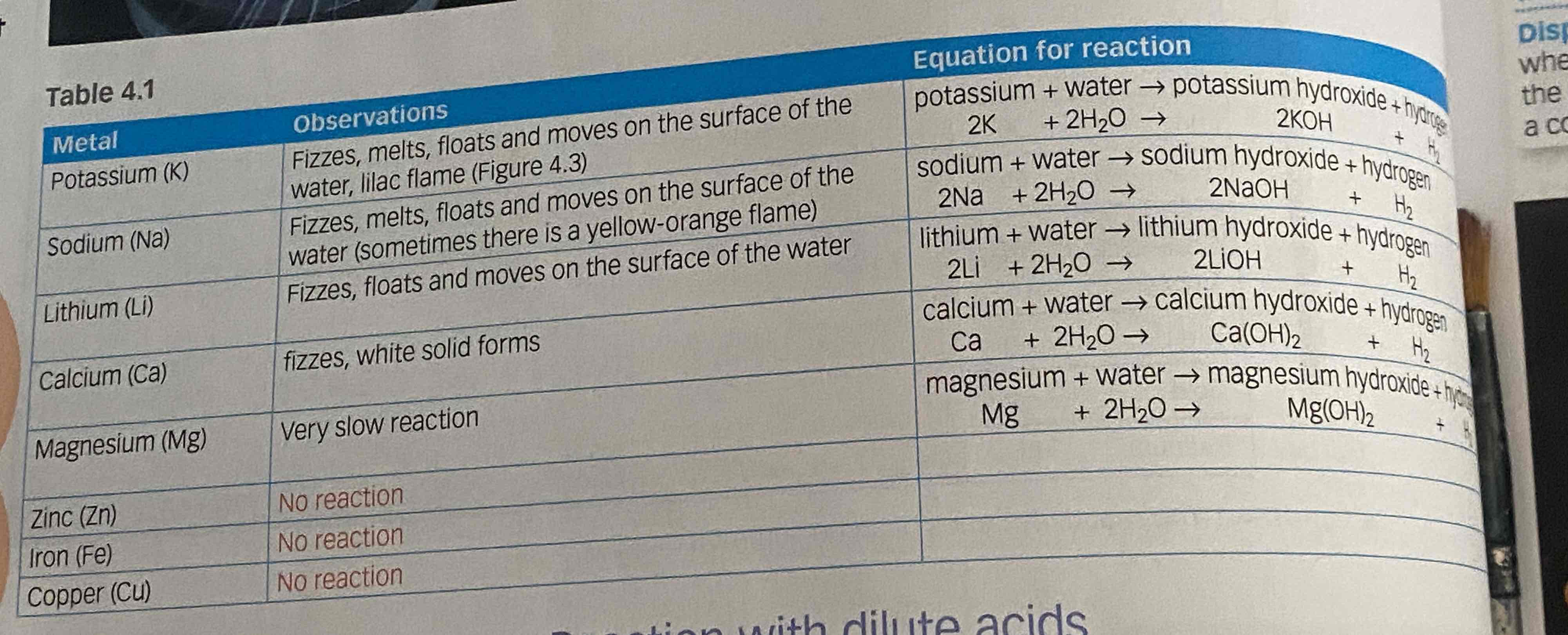
reaction of metals with water
most metals don’t react with cold water because there is not enough energy to start the reaction
very reactive metals react with cold water tho
metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
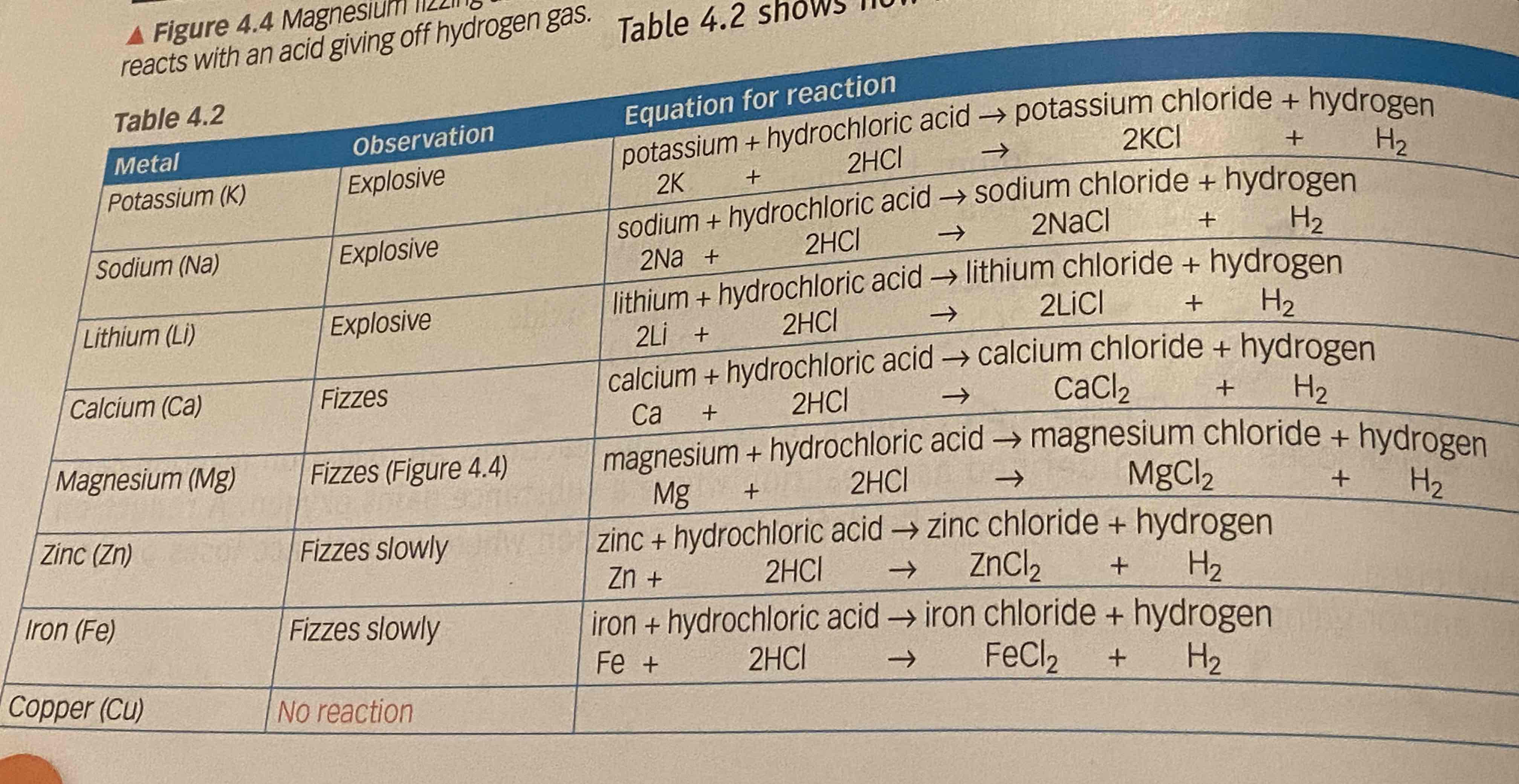
reaction of metals with dilute acids
metal + acid → metal salt + hydrogen
hydrochoric→ chloride salt
sulfuric → sulfate salt
nitric → nitrate
can be explosive if the metal is very reactive
when metals react
lose electrons and become positive
greater tendency to lose electrons= greater reactivity
displacement
more reactive element displaces less reactive element
when one more reactice metals takes the place of a less rective 1
aluminium + iron oxide→ aluminium oxide + iron
OIL RIG is always involved
OIL RIG
oxidation:
gain of oxygen
lose of electrons
loss of hydrogen
reduction
lose of oxygen
gain of electrons
gain of hydrogen
extraction of metals
metals are found on earth as ores
to be extracted a chemical reaction needs to occur
methods to extract metals with
displacement
heating with carbon
electrolysis
acids and alkalis
acid:
produces h+ ions in an aqueous solution
ph is less than 7
alkali:
produces OH- in n aqueous solution
ph is more than 7
PH
from 1-14
measured using universal indicator or PH probe
higher concentration of h+ = lower ph
ph unit decreases by 1 the concentration of h+ iincreases by a factor of 10
strong vs weak acids
strong:
ions fully dissociate/ ionise into h+ or oh- ions
weak:
molecules partially dissociate/ionise in water into oh- or h+
acid + metal
aciid + metal →metal salt +water
redox reaction occurs
neutralisation reaction
metal carbonate
metal carbonate + acid → metal salt + water + carbon dioxide
making salt required practical
Use the pipette and pipette filler and place exactly 25 cm3 sodium hydroxide solution into the conical flask
Place the conical flask on a white tile so the tip of the burette is inside the flask
Add a few drops of a suitable indicator to the solution in the conical flask
Perform a rough titration by taking the burette reading and running in the solution in 1 – 3 cm3 portions, while swirling the flask vigorously
Quickly close the tap when the end-point is reached (sharp colour change) and record the volume, placing your eye level with the meniscus
Now repeat the titration with a fresh batch of sodium hydroxide
As the rough end-point volume is approached, add the solution from the burette one drop at a time until the indicator just changes colour
Record the volume to the nearest 0.05cm3
Repeat until you achieve two concordant results (two results that are within 0.1cm3 of each other) to increase accuracy
Identify 3 other factors, besides atom economy, that should be considered when choosing between two different methods of producing a useful product.
percentage yield
cost of raw materials
position of equilibrium
rate of reaction
cost of maintaining the right conditions
environmental impact of waste products
Suggest 3 reasons why the percentage yield of a chemical reaction may be less than 100%.
The reactants may not all react (e.g. because the reaction is very slow or reaches equilibrium
There may be side reactions, meaning that other products are produced instead
Some of the products may be lost (e.g. gases may float off, or some solids may be left on the filter paper)