C4 Extracting metals and equilibria
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Displacement reactions
a type of redox reduction (reduction/oxidation)
more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from a compound in terms of electrons
oxidisation
gain of oxygen
loss of electrons
reduction
loss of oxygen
gain of electrons
extraction of metals includes
reduction of ores
extraction of ores in relation to position on the reactivity scale
Metals Below Carbon in the Reactivity Series (e.g., iron) can be extracted by heating with carbon, which is a cost-effective method.
Metals Above Carbon in the Reactivity Series (e.g., aluminium) require electrolysis, which is more expensive due to the high energy demands.
extraction of ores biological methods
Bioleaching uses bacteria to extract metals from low-grade ores, making it cost-effective and environmentally friendly, but slower than traditional methods.
Phytoextraction involves plants absorbing metals from the soil, which is sustainable and good for land restoration, but it’s slow and yields less metal.
Life Cycle Assessment
Raw Materials: Assessing the environmental effects of obtaining and processing the raw materials.
Manufacturing: Evaluating the impact of producing the product, including energy use and waste.
Use: Considering the environmental effects during the product’s usage, such as energy consumption and emissions.
Disposal: Examining the impact of disposing of the product, including recycling, landfill, or incineration.
Reversible reactions
reversible reactions can go both ways ⇌
changing conditions can shift the direction of the reaction
e.g A+B⇌C+D
Dynamic equallibrium
Dynamic equilibrium occurs in a reversible reaction when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal
The reaction appears to stop, but both forward and reverse reactions continue at equal rates.
Formation of ammonia
sources: nitrogen form air, hydrogen from natural gas
dynamic equilibrium: rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal
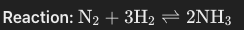
Haber Process
Produces ammonia
use for fertiliser production
Haber process conditions
temp - 450 °C
pressure - 200 atmospheres
catalyst - iron
why is haber process kept at 450°C
compromise between increase the temp for a faster rate of reaction and keeping the temp cool which will push the reaction to the right for higher yield (ammonia side rather than the split apart side)
also heat is expensive
why is the haber process kept at 200 atm (atmospheres/pressure)
increases the pressure for a faster rate of reaction and higher yield
but pressure is expensive and dangerous
Predict how the position of a dynamic equilibrium is affected by changes in
Temperature:
Increase: Shifts equilibrium away from the heat (endothermic direction).
Decrease: Shifts equilibrium toward the heat (exothermic direction).
Pressure:
Increase: Shifts equilibrium toward the side with fewer gas molecules.
Decrease: Shifts equilibrium toward the side with more gas molecules.
Concentration:
Increase Reactant: Shifts equilibrium toward the product side.
Increase Product: Shifts equilibrium toward the reactant side.