Multi-store Model Key study: Murdock (1962)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Aim
to show that memory has more than one store (STM and LTM)
to find support for the serial position effect
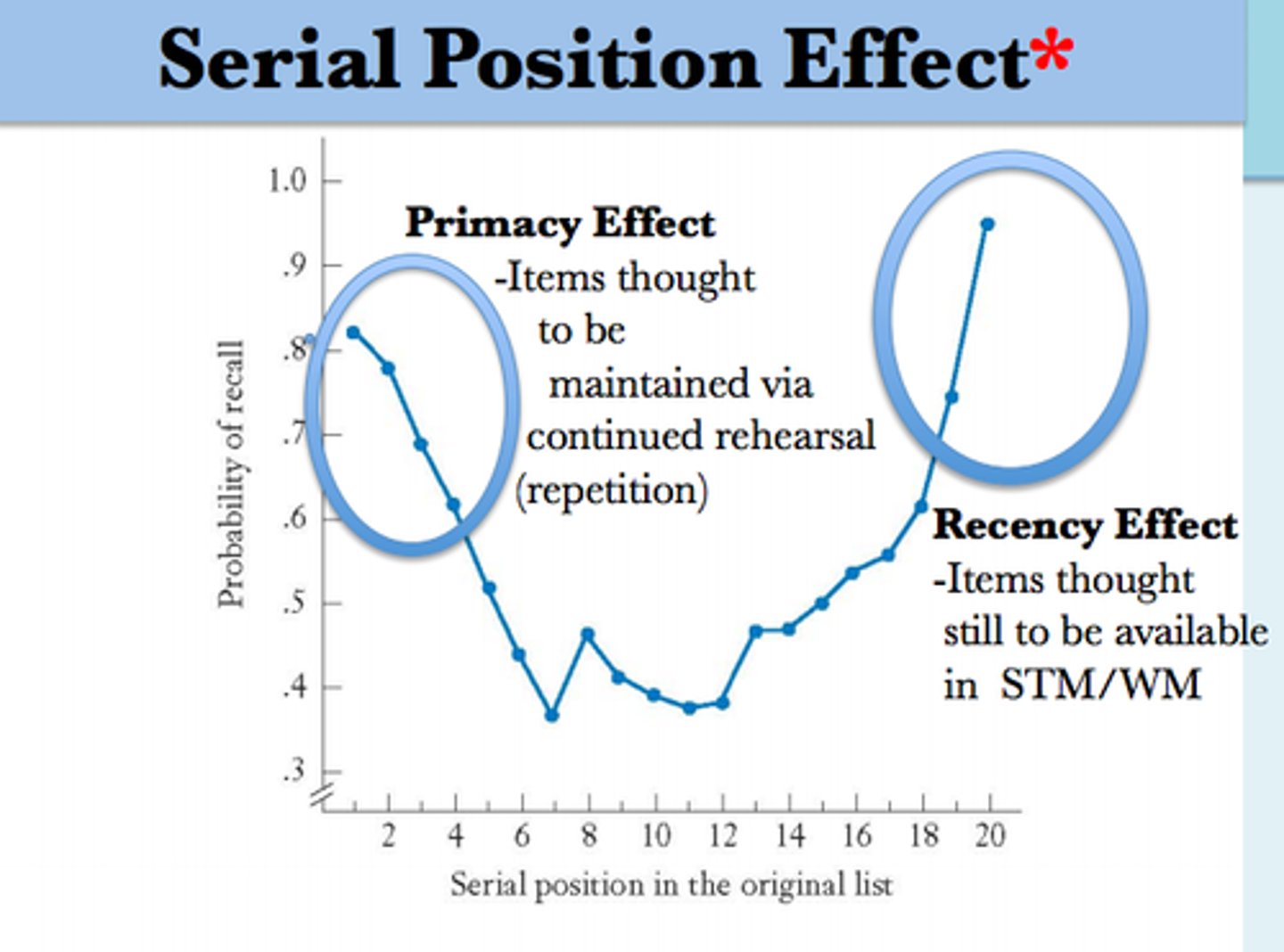
serial position effect
our tendency to recall best the last (a recency effect) and first items (a primacy effect) in a list
Method
asked to recall lists of random words.
shortest list was 10 items long and the longest was 40 items long.
then they compared each word the participants remembered/recalled to where it was in the list originally (i.e. its position in the list) to see if the words remembered were among the first or last items in the list
Results
the words at the start and the end of the list were remembered better than the words in the middle.
the longer the list of words to remember, the more words in the middle were forgotten
found support for the primacy effect (when participants remember the first few words on the list very well) and the recency effect (when words at the end of the list are remembered well
conclusion/implications
When there are too many words for them all to be remembered the primacy effect results in the first words being remembered because it has been rehearsed into LTM and the recency effect results in the last words being remembered as it is still fresh in STM
This shows STM and LTM both exist and are separate stores - i.e. memory is not just made up of a single store
strengths
lab experiment - highly controlled
can be applied to real-life - students could study for exams in small chunks to lessen the amount of information forgotten in the middle of their study sessions
limitations
lab experiment - lacks ecological validity
participants asked to remember random lists of words - doesn't generalise to memory of things on day to day basis - so has low mundane realism
real-life application
students could study for exams in small chunks to lessen the amount of information forgotten in the middle of their study sessions
students should incorporate rehearsal strategies to transfer info into LTM
Film directors should ensure films have an impactful start and ending to the film for the film to be remembered more
What concepts/studies does the study relate to?
STM - recency effect can be explained by this
LTM - primacy effect can be explained by this
Baddeley (1966) - information can also be transferred into LTM if it is semantically encoded; participants who forgot items at the start may have forgotten if they were acoustically similar to other words at the start; participants who forgot items at the end may have forgotten them if they were semantically similar to the other words at the end of the list