Chapter 33B: Flatworms and Annelids
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Characteristics of Lophotrochozoans
Bilateria
Triploblastic
Digestive tract with two openings
Ex: flatworms, rotifers, ectoprocts, brachiopods, mollusks, annelids
Lophophore
naming of Lophotrochozoans
meaning: crown of tentacles that function in feeding
Trochophore
naming of Lophotrochozoans
meaning: distinct larval stage
Phylum Platyhelminthes — Flatworms
Lophotrochozoan;
Habitats: marine, freshwater, damp terrestrial
Free living = Planarians
Parasitic = Tapeworms and Flukes
Size: microscopic → 20 meters
Acoelomates
~Platy
~flat
~helminth
~worm
Protonephridia
flatworms;
maintain water balance
How do flatworms move?
via cilia and muscles
Four classes of flatworms
Turbellaria (free-living)
Monogenea (monogeneans)
Trematoda (trematodes, flukes)
Cestoda (tapeworms)
Turbellaria
four classes of flatworms;
free-living flatworms
ventral nerve cords that run the length of the body
incomplete digestion system via pharynx
ganglia at the anterior end of the worm
Ex: Planarians

First true cephalization
flatworms;
cephalis = head
Light sensitive eyespots
flatworms;
first eyes
Cephalic ganglion
flatworms;
first nervous system
Hermaphrodites
flatworms;
sexual or asexual
Monogenea
four classes of flatworms;
parasitic flatworm
parasites of fish
Trematodes
four classes of flatworms;
flukes
parasites of humans
part of life cycle in snail hosts
Ex: liver flukes, blood flukes
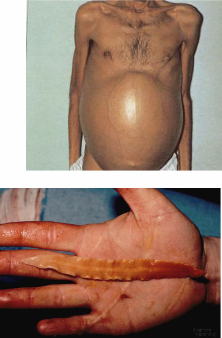
Liver flukes
trematodes;
obtained by eating raw fish
causes Cirrhosis
Blood flukes
trematodes;
causes Schistosoma/schistosomiasis
second most devastating parasitic disease (first is Malaria)
oral and ventral suckers for attachment to host
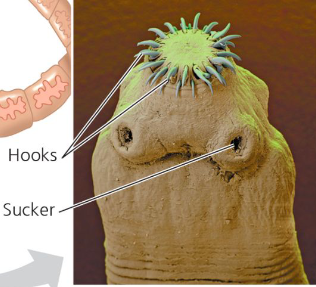
Cestoda — Tapeworms
four classes of flatworms;
parasites of vertebrates
no mouth/digestive system
Scolox “Holdfast”
Proglottids: reproductive segments
obtained by eating beef/pork tapeworms → blocks intestines
Phylum Annelida — Annelids
Lophotrochozoan;
two clades: Errantia and Sendentaria

Clade Errantia
Annelids;
most are mobile/marine
predators and grazers (algae)
segmented body
Trochophore: Ciliated Larva

Features of a segmented body in Clade Errantia
Parapodia: paddle-like, located beside feet; locomotion, protection, gas-exchange
Cirri: long, sensory organs
Clade Sedentaria
Annelids;
less mobile
Sedere ~to sit
Ex: Christmas Tree Worm, leeches, earthworms

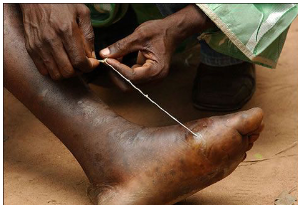
Leeches
Clade Sedentaria;
mostly freshwater
some suck blood from animals
predators that feed on other invertebrates
Hirudin
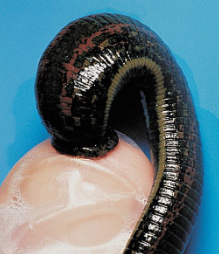
Hirudin
leeches;
chemical secreted to keep blood from coagulating
bloodletting, surgical use
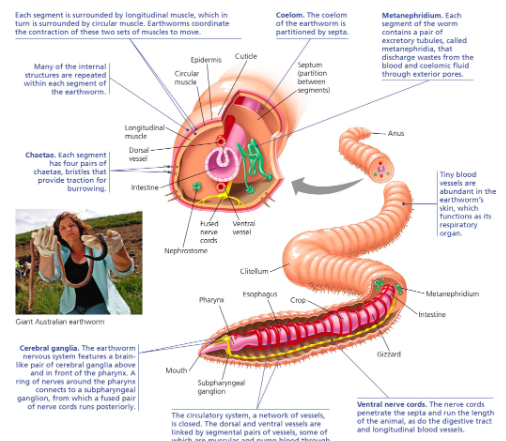
Earthworms
Clade Sedentaria;
soil habitat
eat organic matter
100-175 segments
Hermaphrodites but can cross fertilize