Unit 1: Anatomy of the Lungs, the Bronchial Tree, Major Vessels, Nerves of the Thorax
1/193
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
194 Terms
-surrounded by pleura
-separated from each other via mediastinum
-superior to diaphragm
How are the lungs positioned in the thorax in relation to the pleurae, mediastinum, and diaphragm?
-bronchi
-pulmonary arteries, veins, and nerves
How are the lungs anchored to the mediastinum?
-Mesothelium: single layer of cells
-Supportive connective tissue
What are pleural cavities lined with?
-pleura
The pleural cavities form the ____.
-serous membrane
-it is double layered
The pleura is a ______. What does this mean?
-parietal pleura
-visceral pleura
What are the two types of pleura?
-superficial layer
-closer to thoracic wall
The parietal layer is the ___.
-Costal part = near ribs and intercostal spaces
-Diaphragmatic part = near diaphragm
-Mediastinal part = near mediastinum
What are the different portions of the parietal pleura?
-Deeper layer
-Closer attached to lung tissue
The visceral layer is the ___.
pleural cavity
The two pleura are separated by the ____.
parietal pleura
2
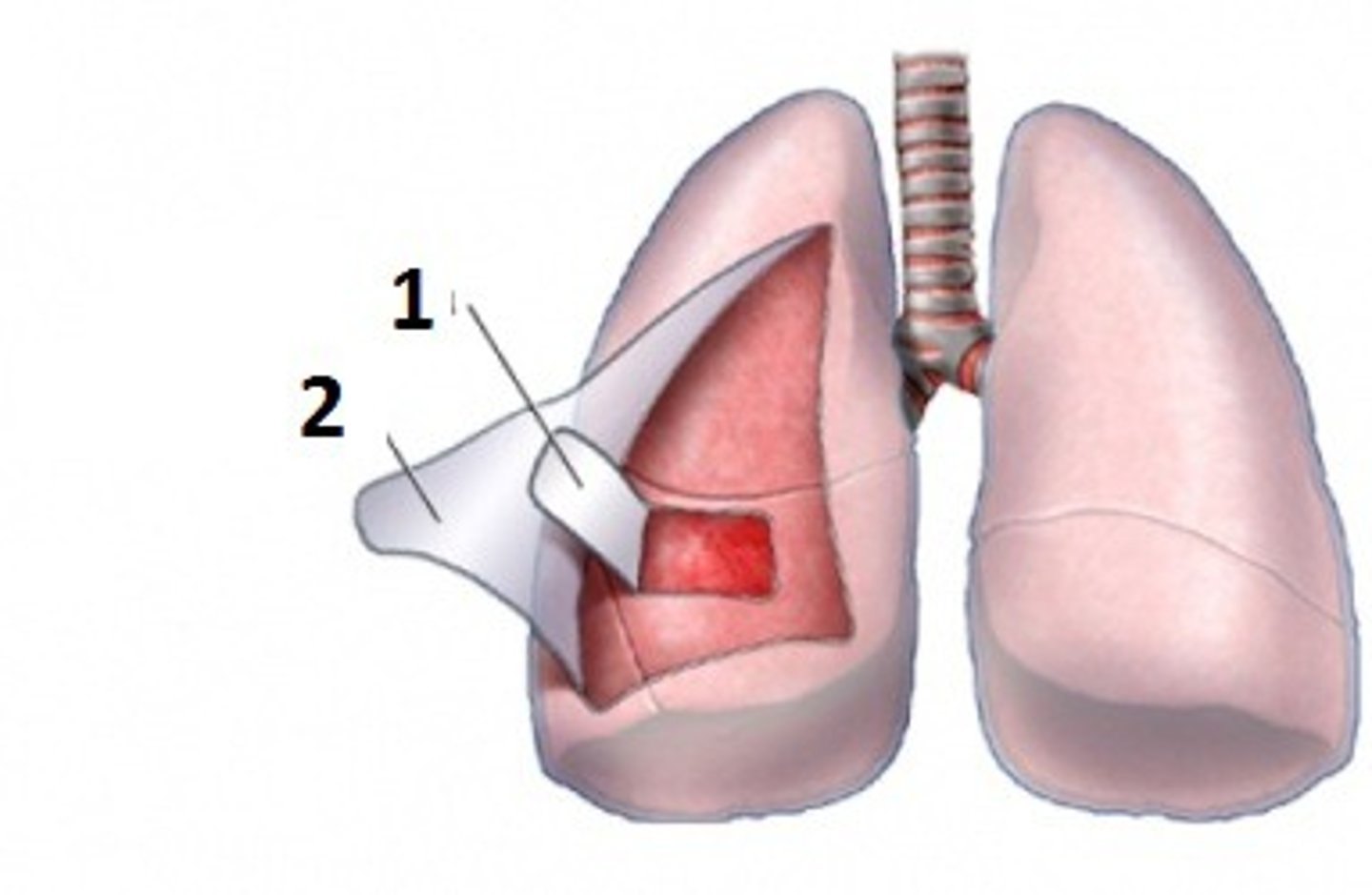
visceral pleura
1
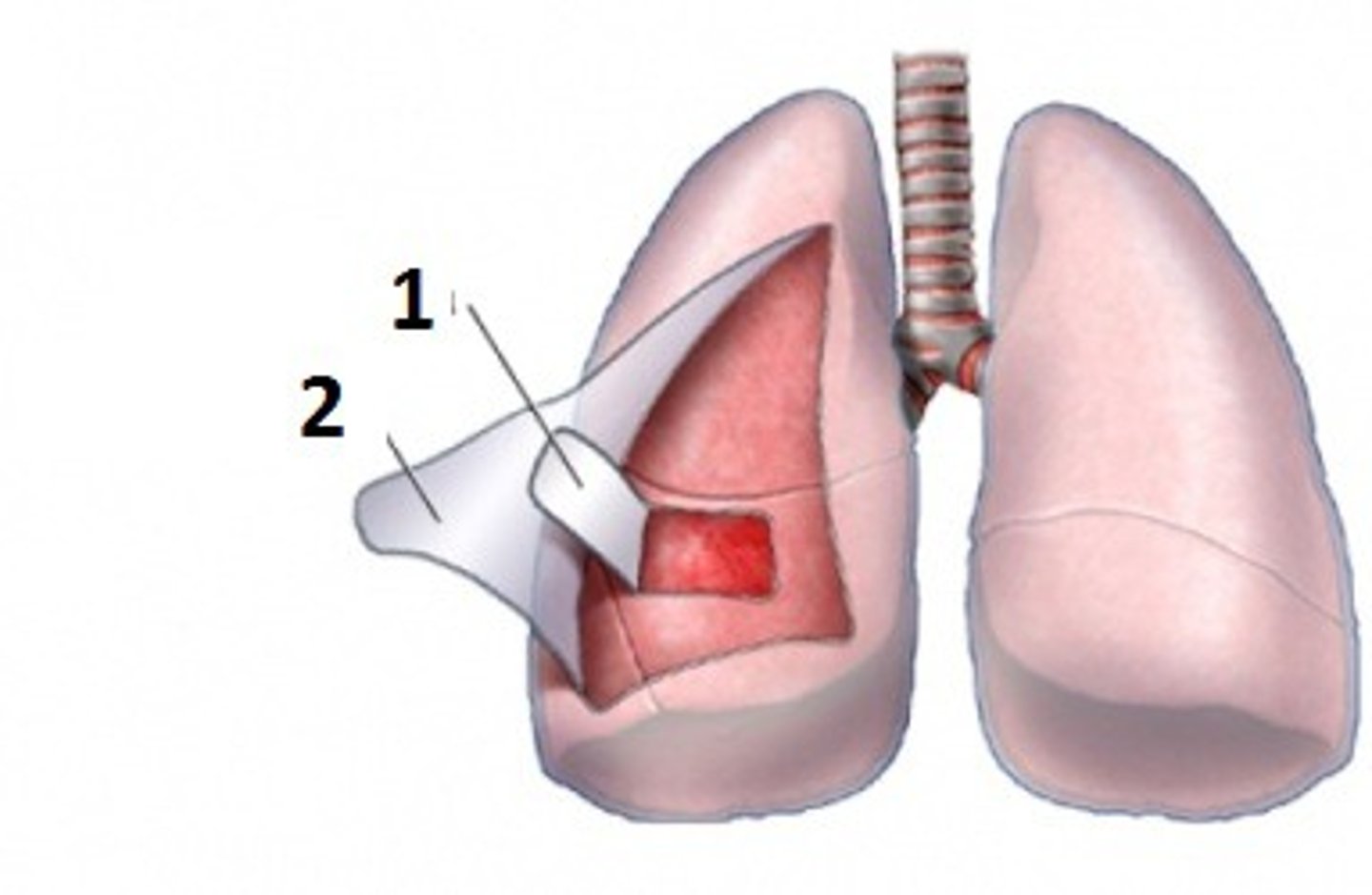
pleural cavity
Serous fluids
What is between the parietal and visceral layers?
-Allows for sliding movement
-does not allow for pulling movement
Describe the purpose of the serous fluids.
-Surface of lung & visceral layer directly opposes and slides freely over parietal pleura attached to wall
Why do serous movements allow for sliding movement?
visceral pleura gets pulled with it
Since the parietal pleura attaches to the thoracic wall, what happens when the thorcic wall moves or when the parietal pleura is pulled?
-fill with air, fluid, blood
What can happened to the pleural cavity?
-Air fills pleural cavity
-lung collapsing
Describe a pneumothorax.
-Fluid fills pleural cavity
Describe a pleural effusion.
Blood fills pleural cavity
Describe a hemopneumothorax.
-spaces formed by pleura that are not filled with lungs
-Where two layers of the parietal pleura oppose each other
What are pleural recesses?
lungs do not expand into the recesses
When normally breathing, what happens to pleural recesses?
lungs do expand into the recesses
When forced inspiration, what happens to pleural recesses?
-Fluid can collect here
-May need to aspirate the fluid
Why are recesses clinically important?
-anterior
-where copstal pleura are opposed to mediastinal pleura
Describe costomediastinal recess.
-On left and right lungs
-Larger on left side overlying the heart
The costomediatsinal recess is located _____.
-largest recess
-between costal pleura and diaphragmatic pleura
-between inferior margin of lungs and inferior margin of pleural cavities
Describe costodiaphrgamatic recess.
-Smaller during inspiration
-Larger during expiration
The costodiaphrgamatic recess is smaller ___ and larger ___.
Fluid will tend to collect here because of gravity
Why is the costodiaphrgamatic recess clinically important?
Costomediastinal Recess
A
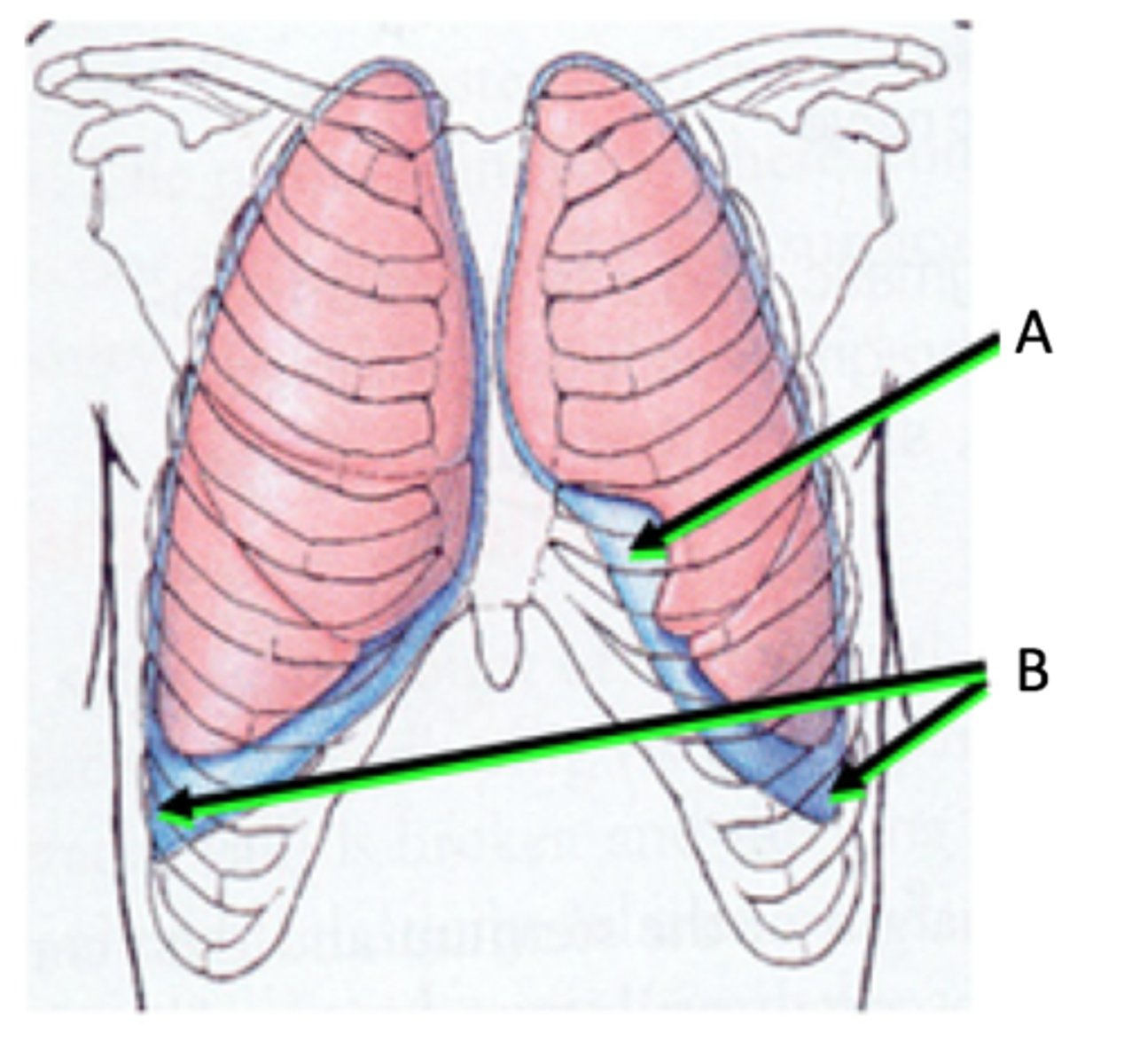
Costodiaphragmatic Recess
B
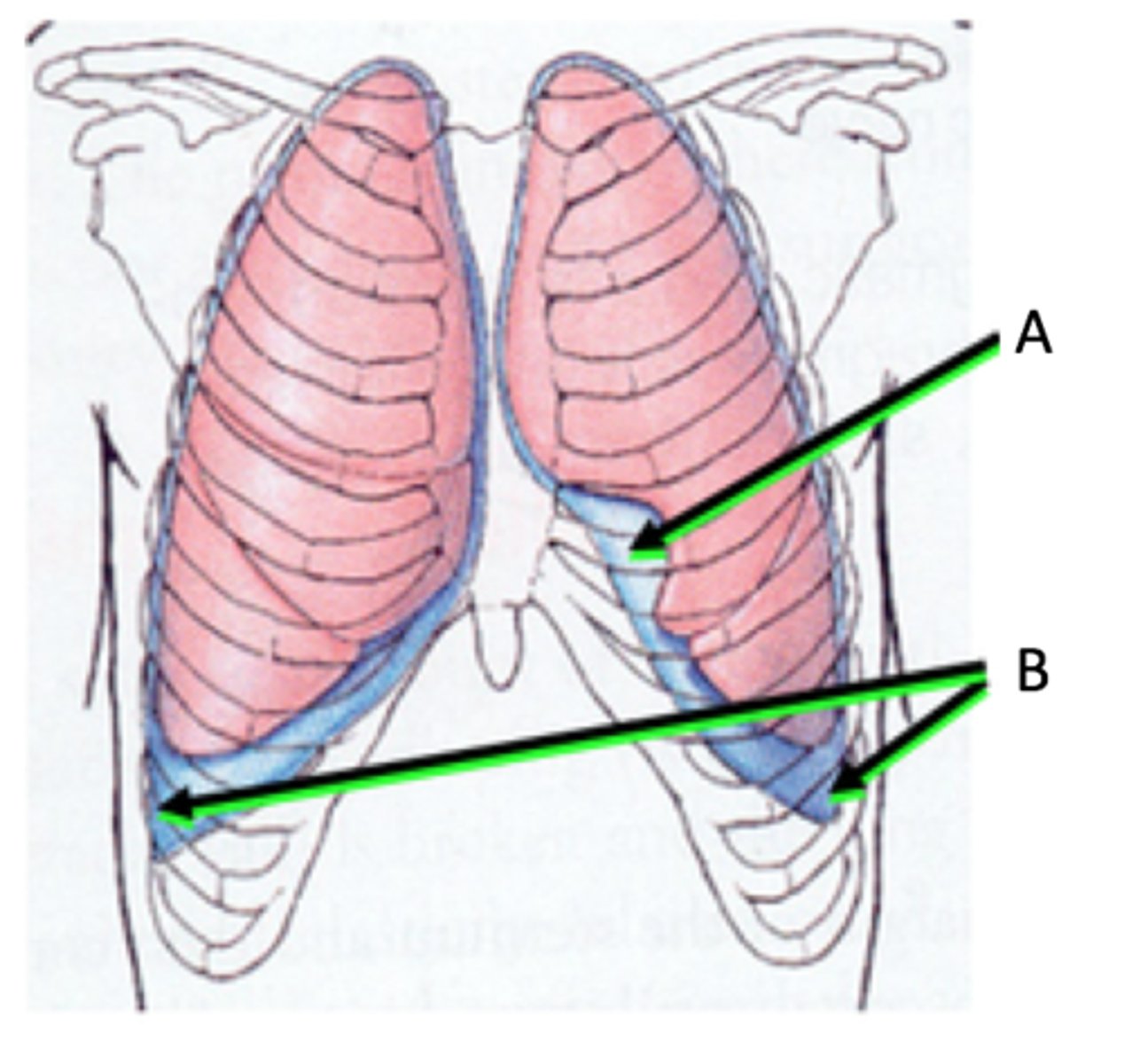
Inferior margins of lungs rest on top
Where is the respiratory diaphragm?
Pulmonary ventilation
What is the process of respiration?
gas flows into lungs
Describe inspiration.
gas flows out of lungs
Describe expiration.
-changes in volume of thoracic cavity
-changes in volume leads to changes in pressure
What does respiration depend on?
-Inverse relationship
-increase volume → decrease pressure
-decrease volume → increase pressure
Describe the relationship between volume and pressure.
-Respiratory diaphragm (domed to flat)
-Intercostal muscles
What are volume changes dependent on?
Relaxed = expiration
When does the diaphragm become domed?
Contracts = inspiration
When does the diaphragm become flat?
-External intercostal muscles = elevate the ribs
-Internal intercostal muscles = depress the ribs
Describe the intercostal muscles and their movement.
-Sternum = moves anteriorly when taking a deep breath
-Ribs = move laterally when taking a deep breath
Describe the movement of the rib cage.
-attached to the walls of the rib cage and lungs
-serous fluid between the pleura
Pleura are firmly _____. What causes this?
pleura to pull apart
The serous fluids does not allow ___.
Pressure decreases
When the volume of the lungs increases during inhalation?
Pressure increases
When the volume of the lungs decreases during exhalation?
-Diaphragm contracts → flat
-External intercostal muscles = elevate the ribs
During inhalation, describe the muscles.
-Increase volume
-Decrease pressure
-Air moves in
During inhalation, describe the volume and pressure.
-Diaphragm relaxes → domed shape
-Internal intercostal muscles = depress the ribs
During exhalation, describe the muscles.
-Decrease volume
-Increase pressure
air moves out
During exhalation, describe the volume and pressure.
passive = muscles relaxed
Quiet respiration is _____.
-active
-Requires contraction of other muscles
Forced respiration is _____.
-Internal and innermost intercostals
-Abdominal muscles
What muscles are used in forced respiration?
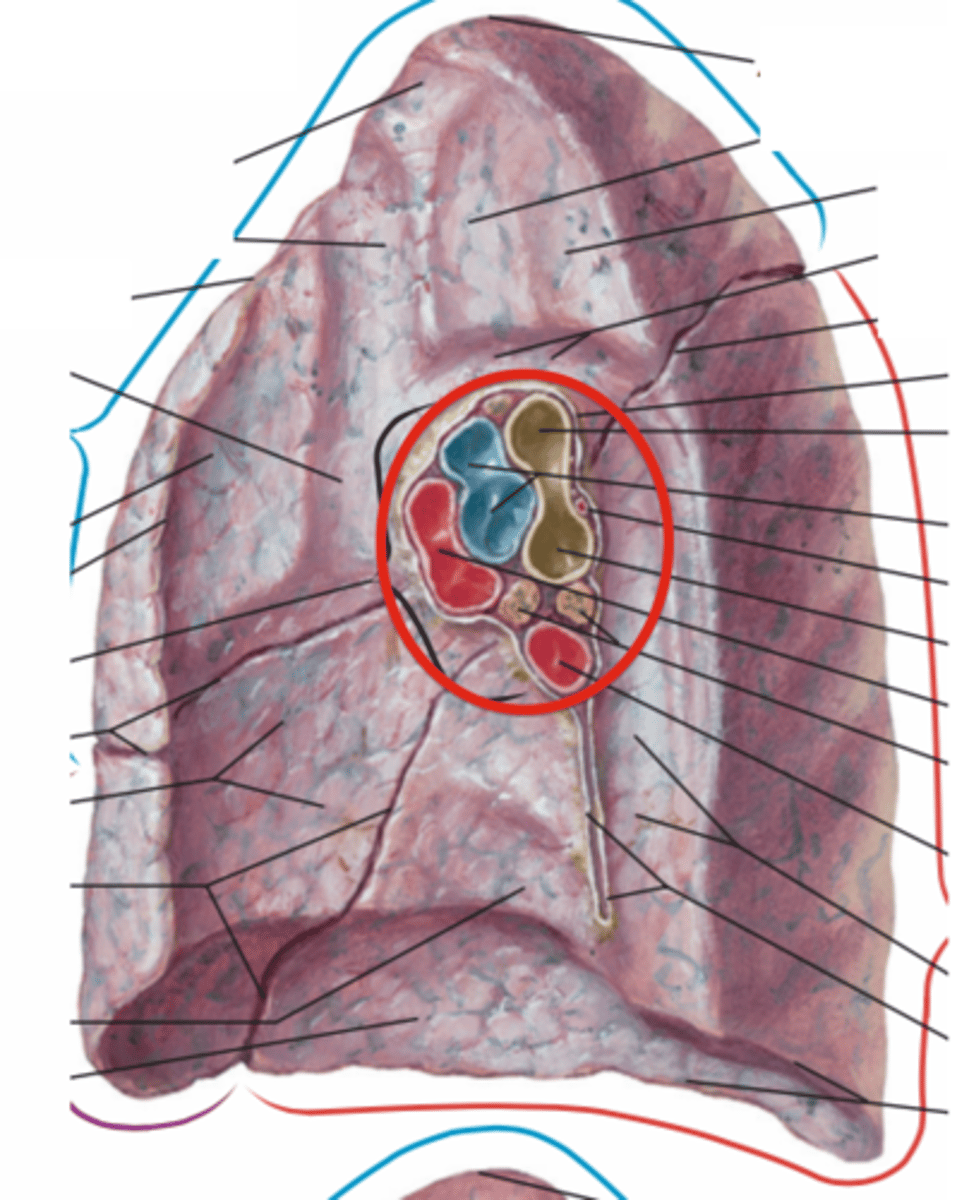
Apex
Diaphragmatic surface
Superior Lobe
Inferior Lobe
Oblique Fissure
Both right and left lungs have _____.
-left lung = 2 (superior, inferior)
-right lung = 3 (superior, middle, inferior)
How many lobes does each lung have?
-left lung = oblique fissure
-right lung = horizontal fissure & oblique fissure
How many fissures does each lung have?
separates superior and inferior lobes
What does the oblique fissure separate?
separates superior and middle lobes
What does the horizontal fissure separate in the right lung?
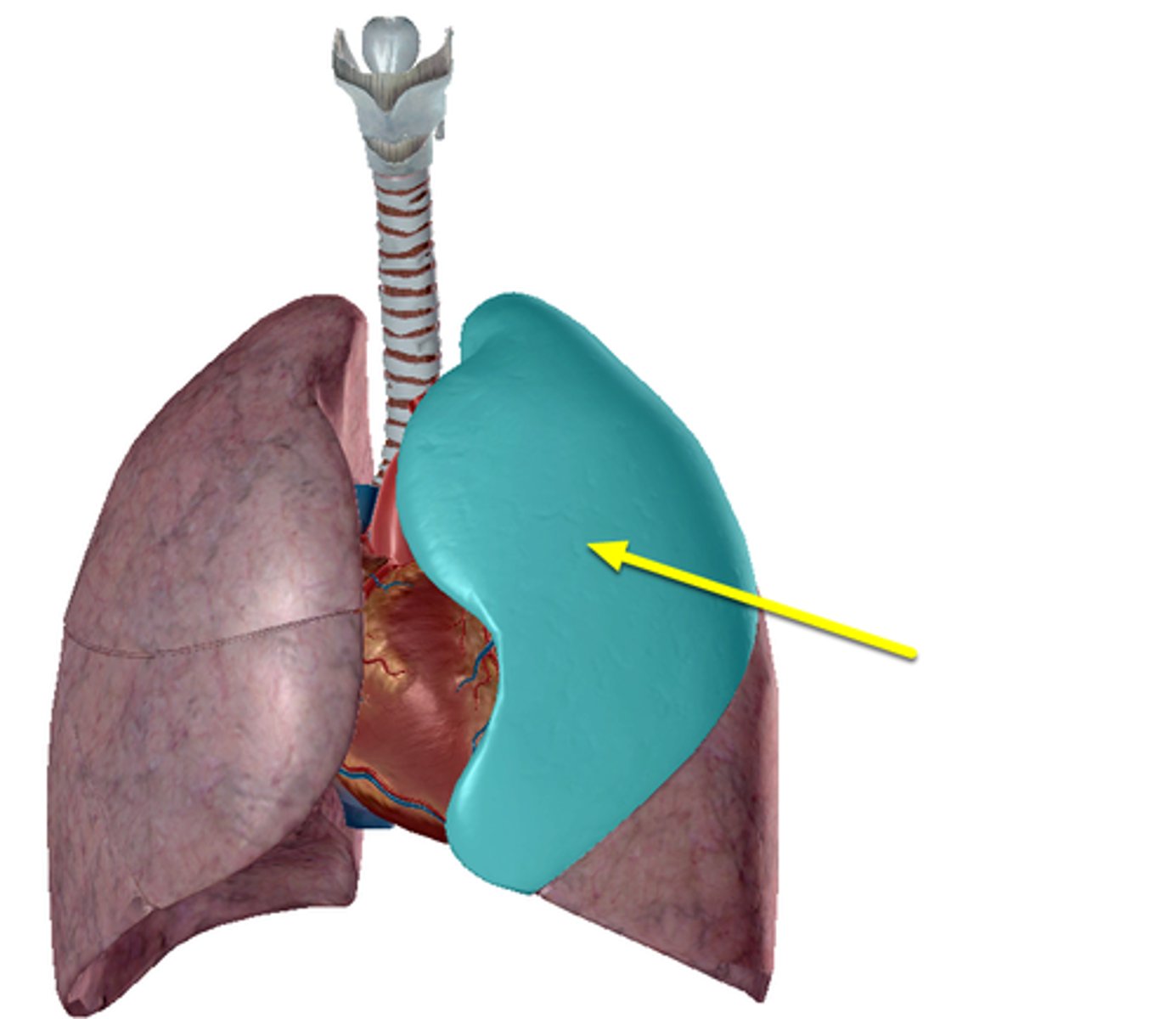
-cardiac notch
-lingula
The left lung has _____.
-Heart bulges more to left than right
Describe the cardiac notch.
Tongue-like extension over bulge of heart
Describe the lingula.
Heart
aortic arch
thoracic aorta
esophagus
The medial surface of the left lung lies adjacent to _____.
Heart
inferior vena cava V
superior vena cava V
azygos V
esophagus
The medial surface of the right lung lies adjacent to _____.
apex of lung
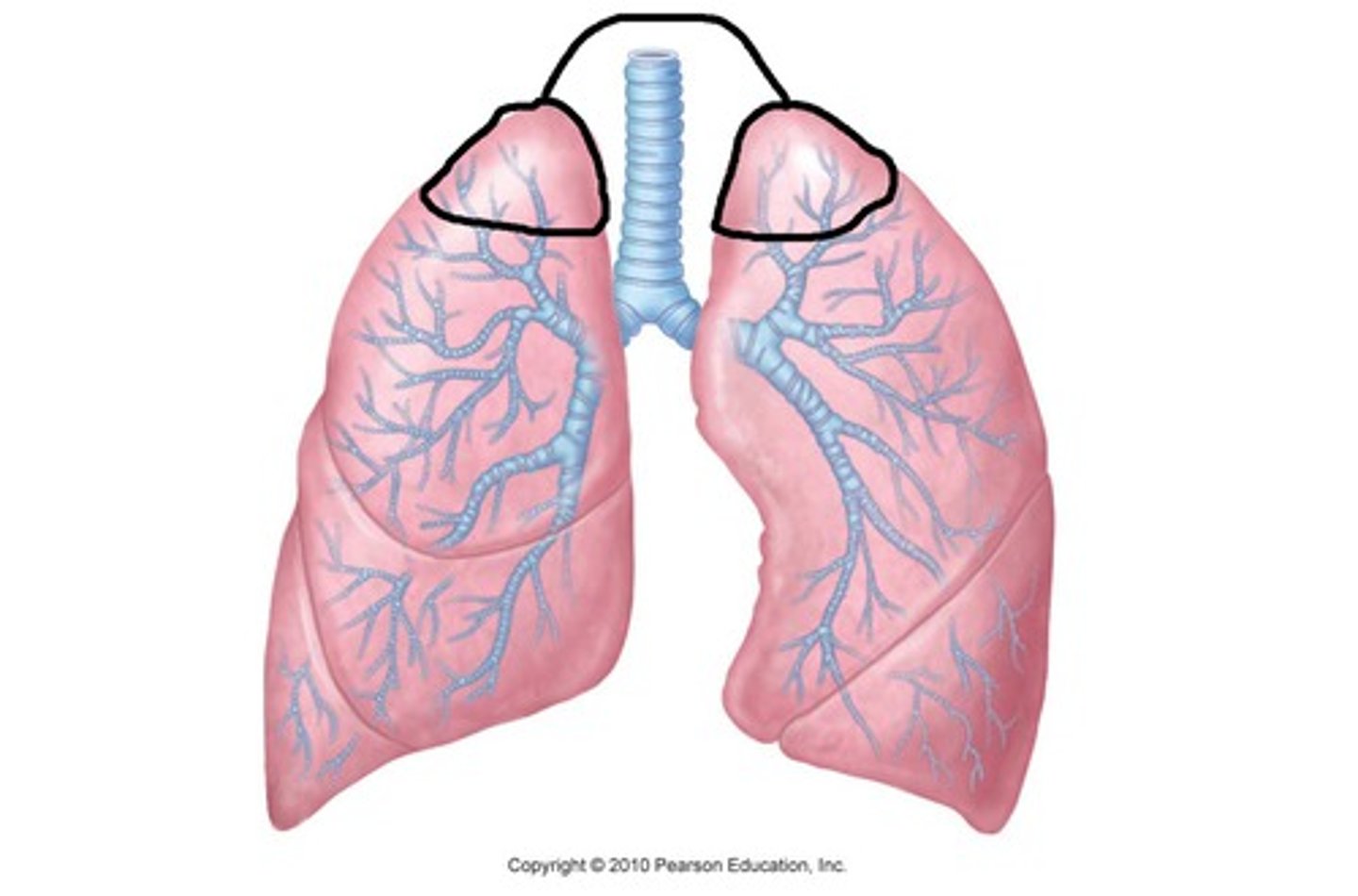
diaphragmatic surface of lung
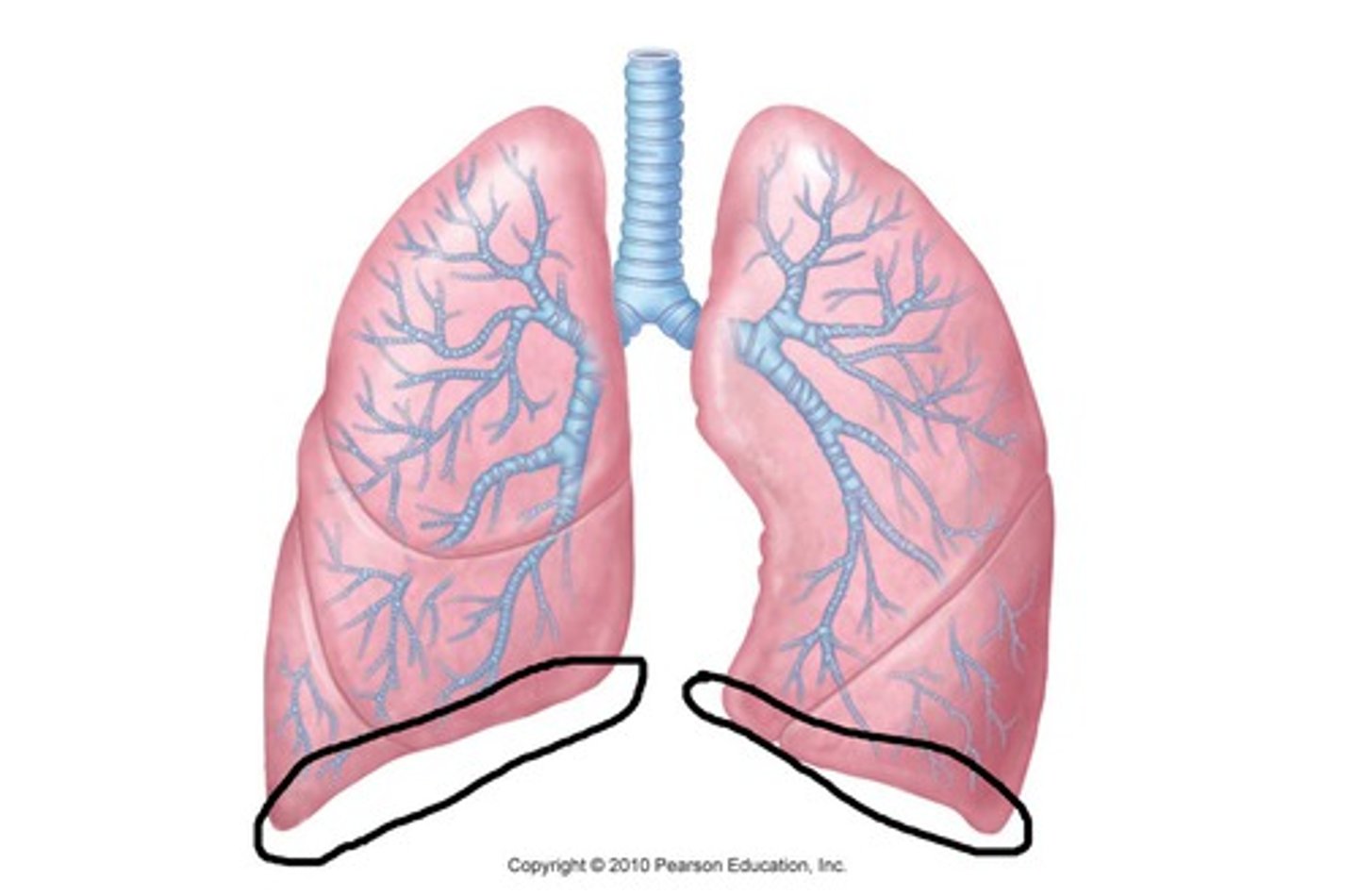
superior lobe of left lung
inferior lobe of left lung
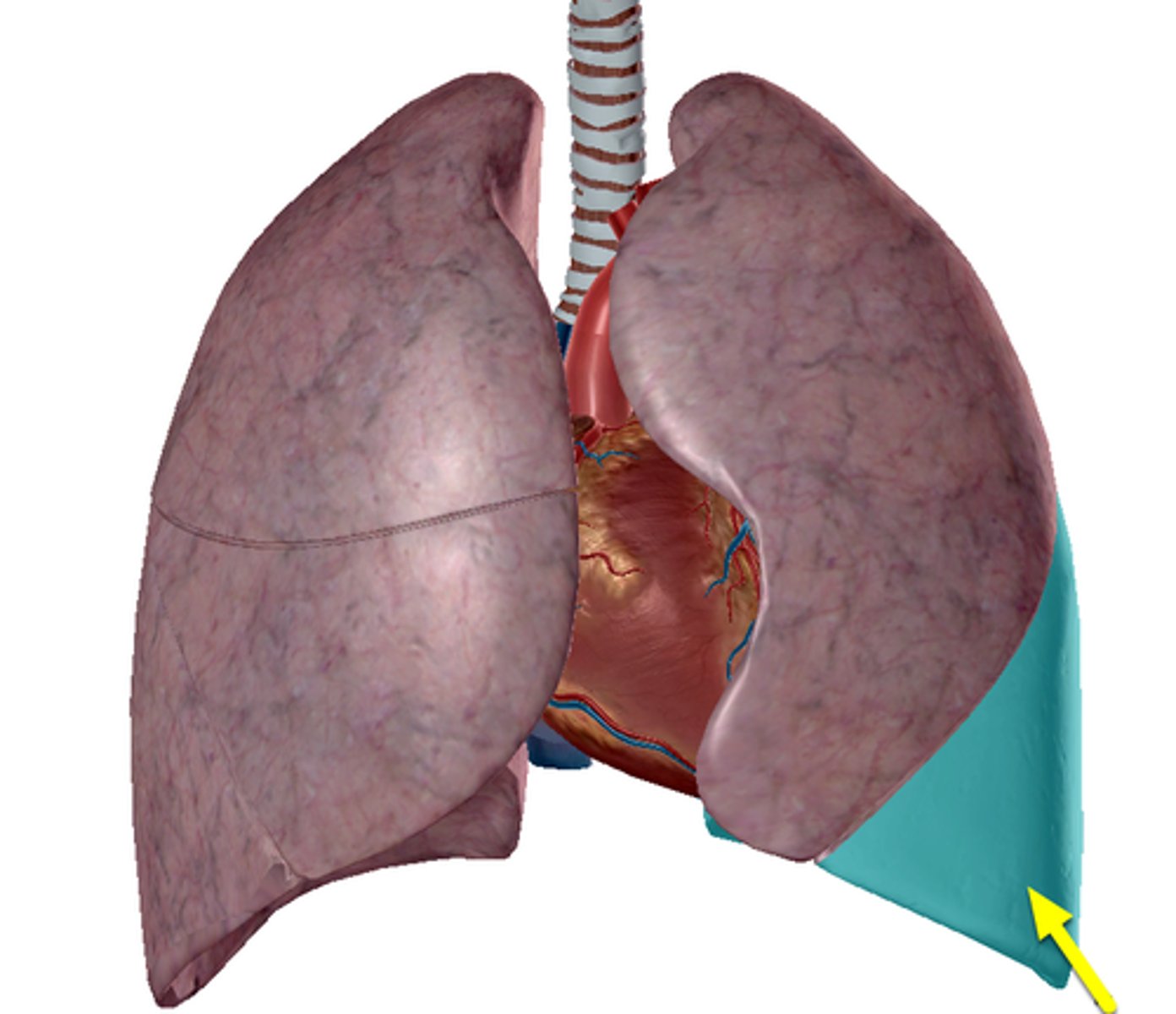
superior lobe of right lung
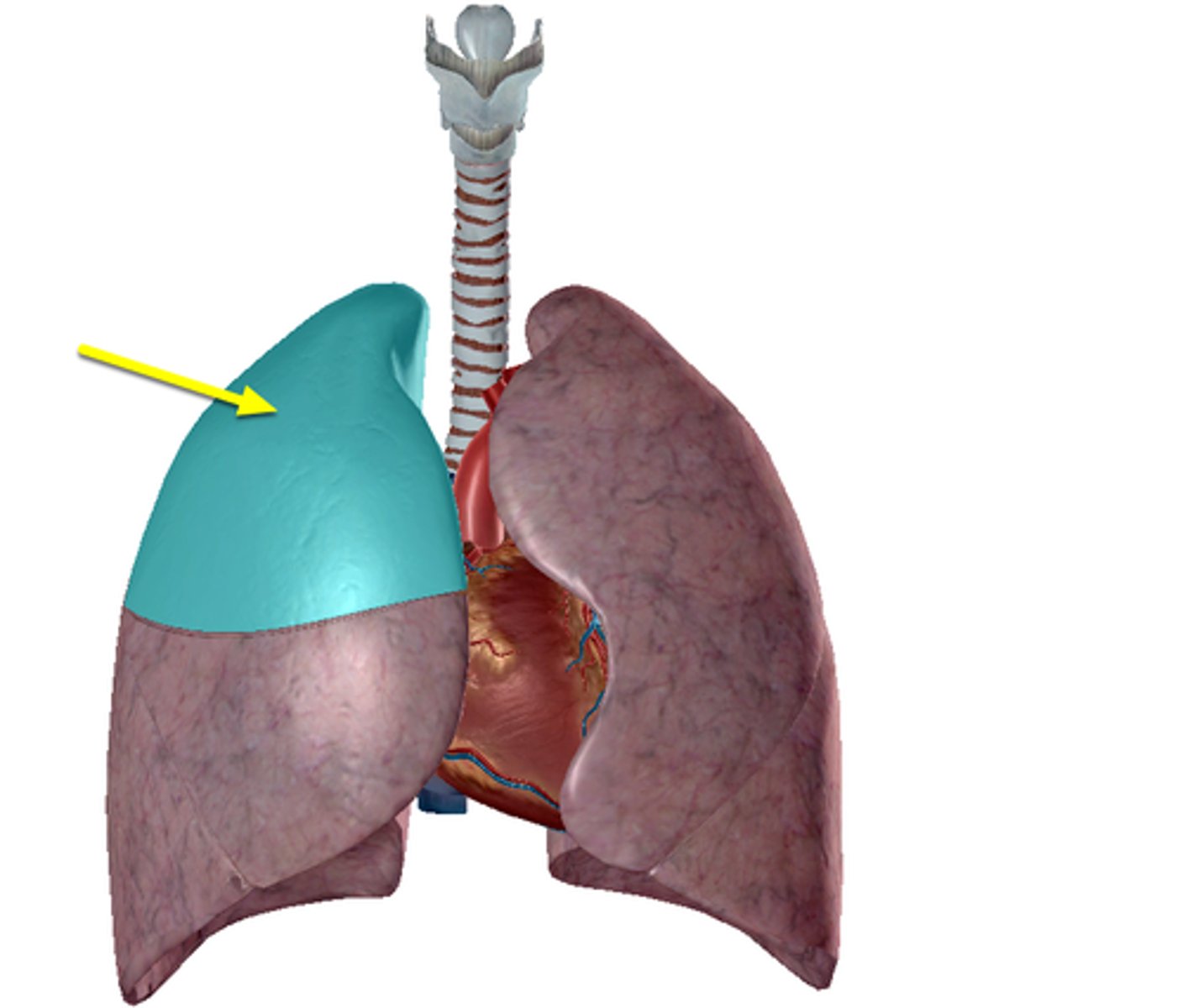
middle lobe of right lung
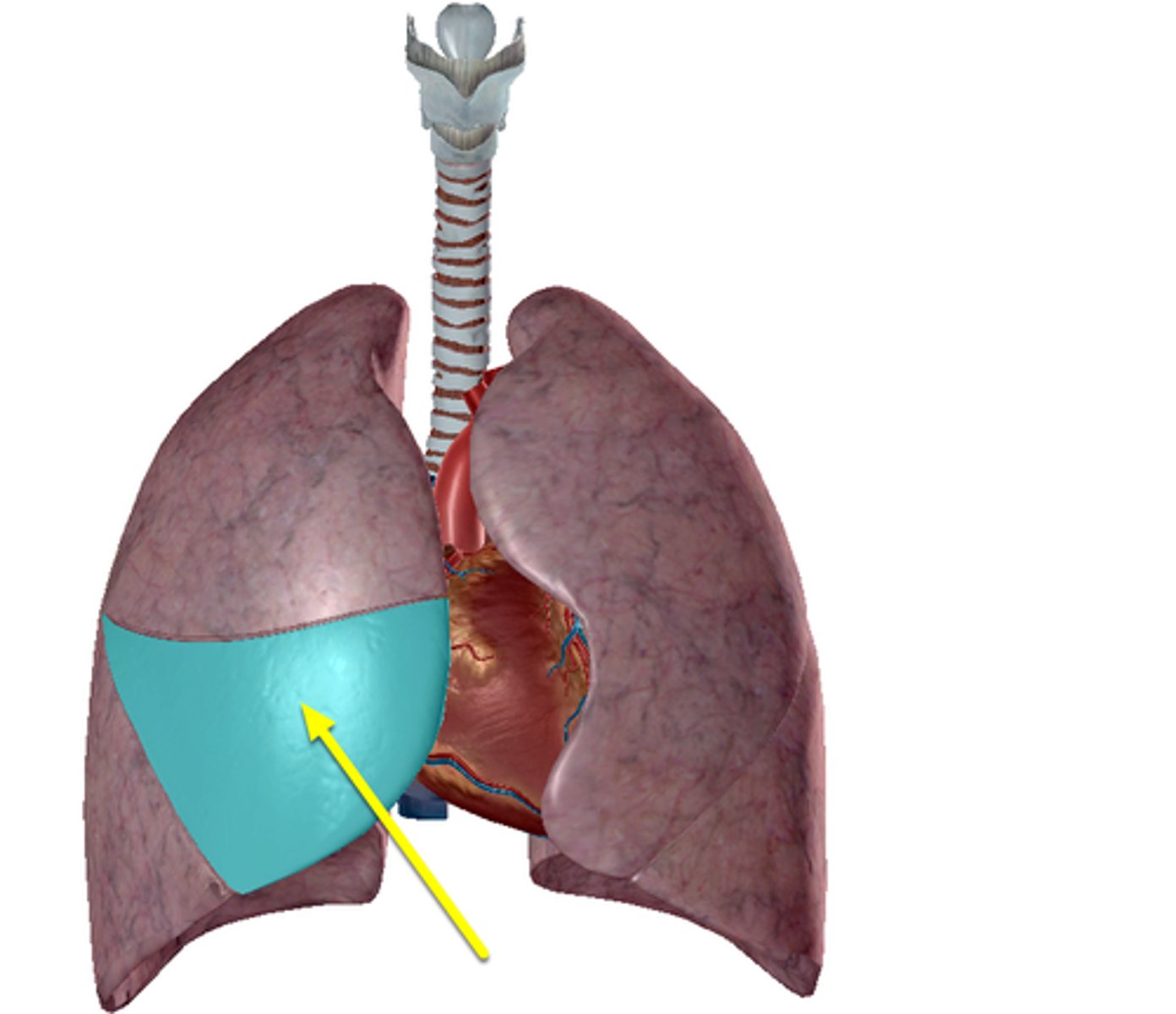
inferior lobe of right lung
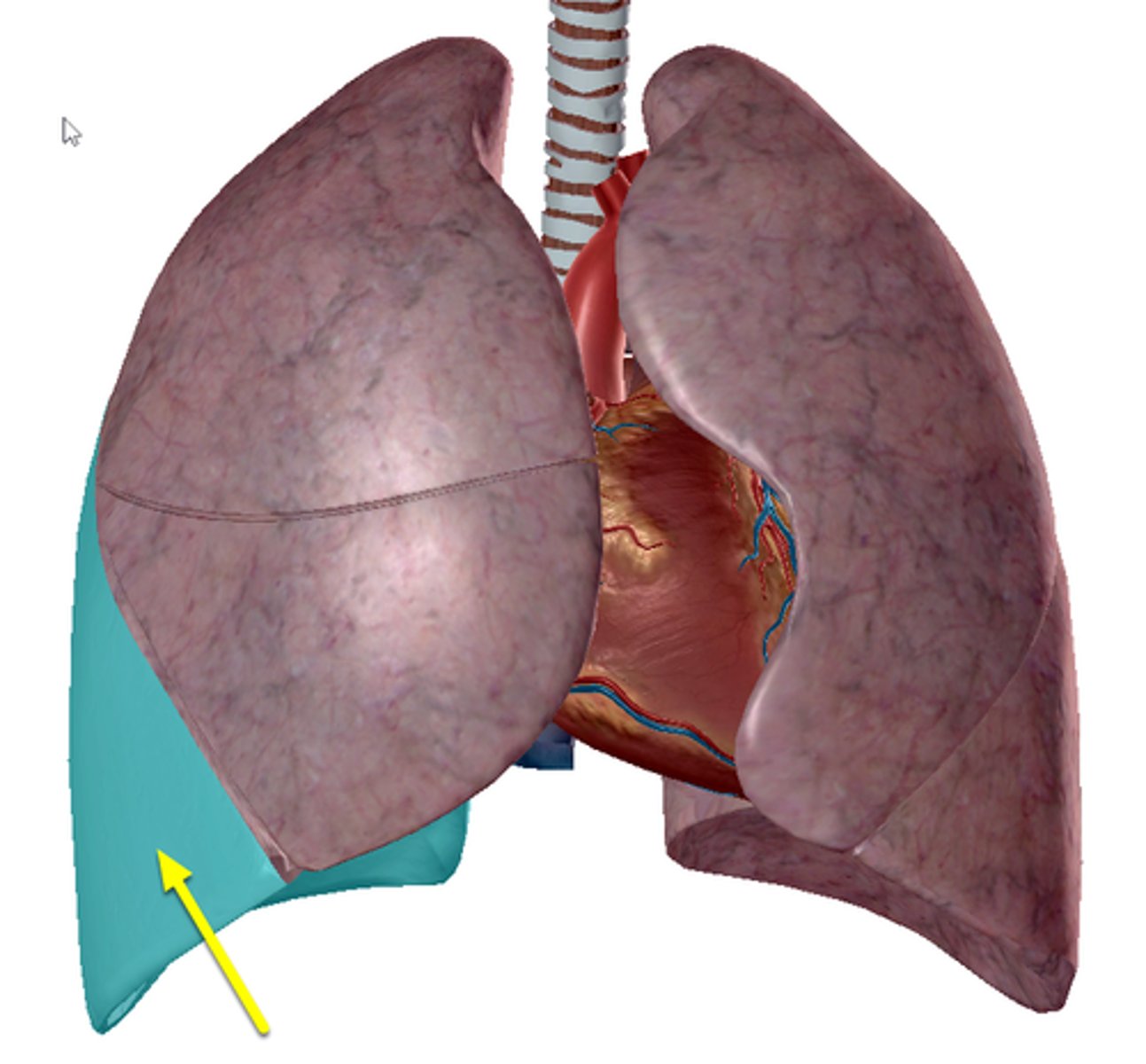
Oblique Fissure of right lung
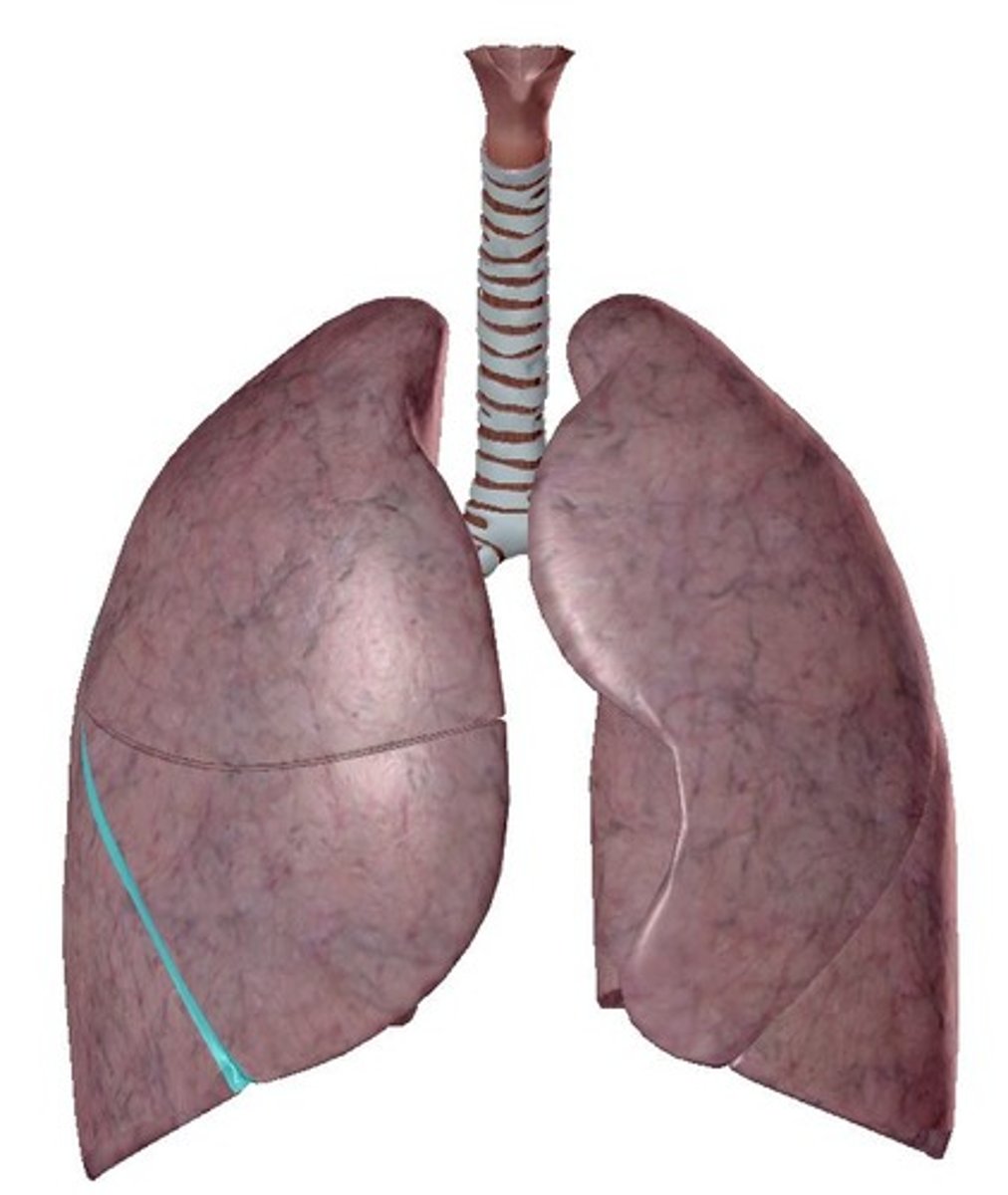
Oblique Fissure of left lung
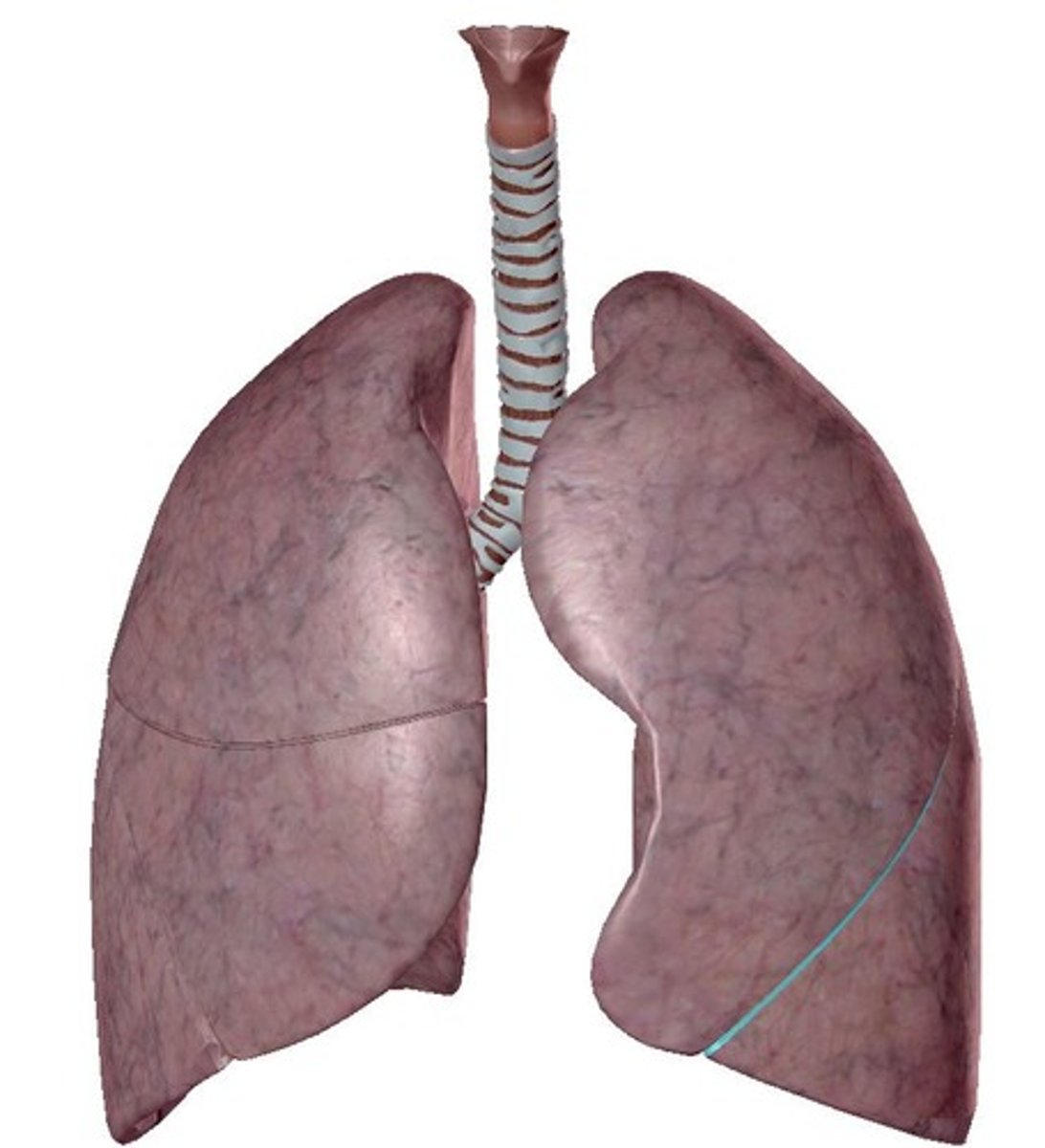
horizontal Fissure of right lung
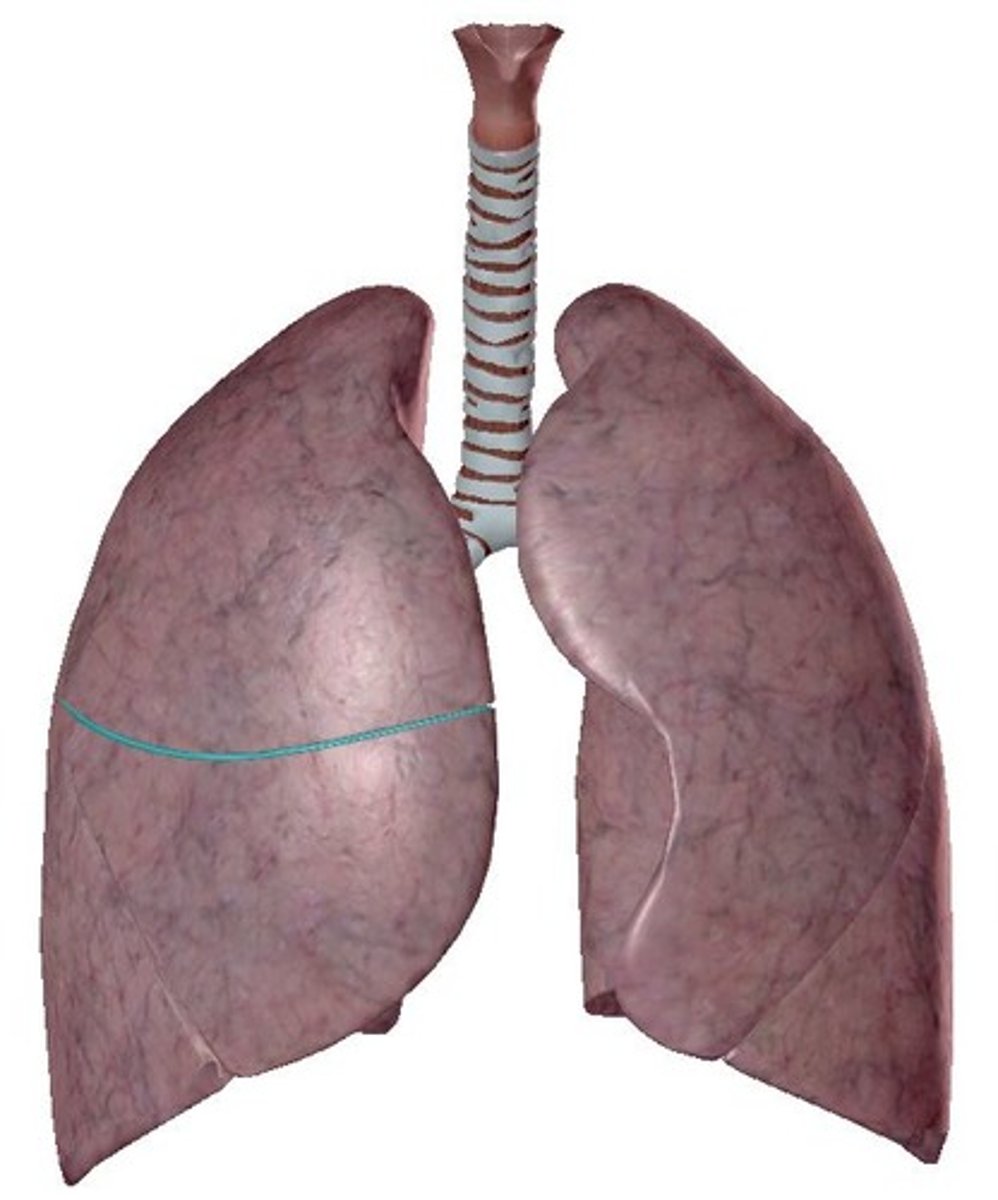
cardiac notch
lingula
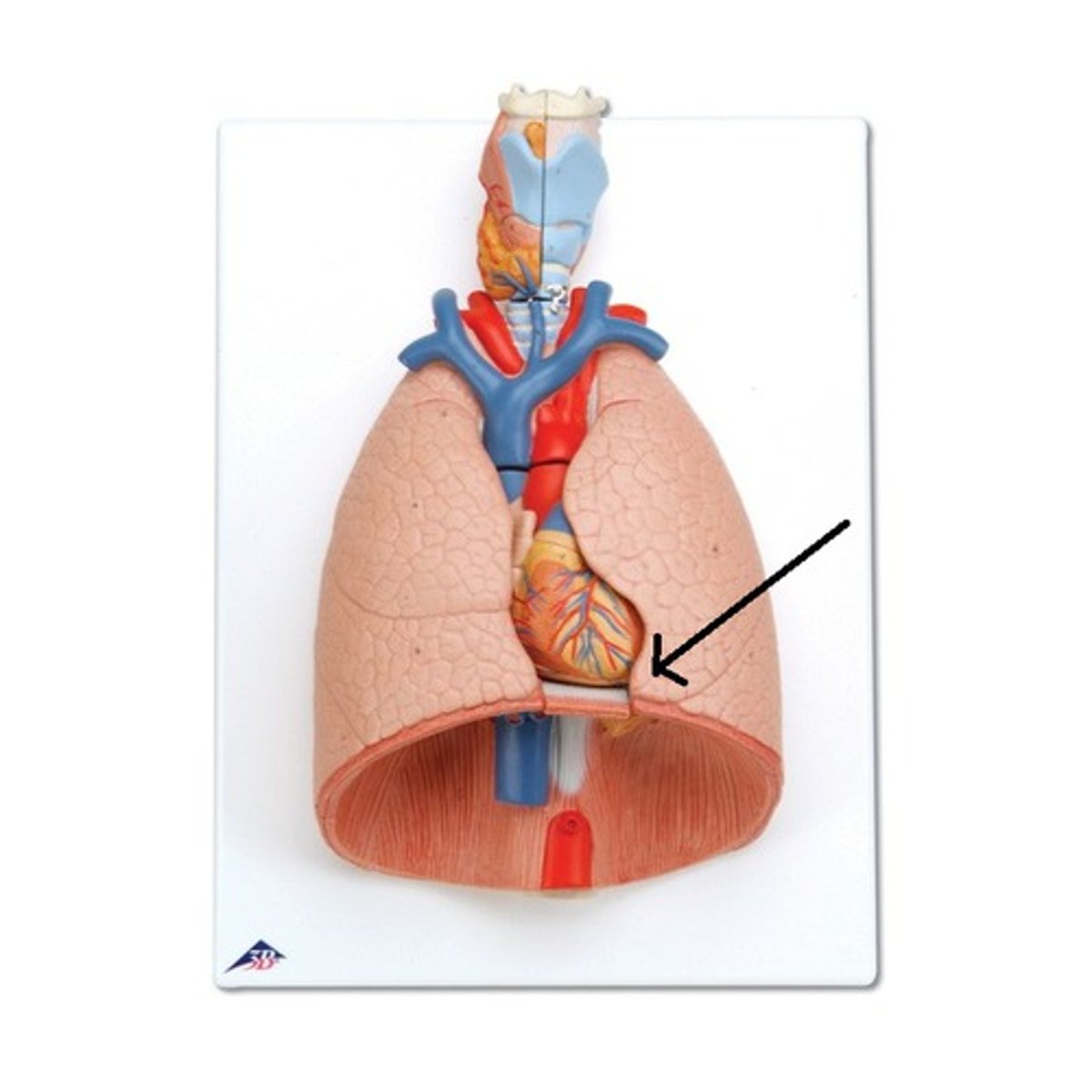
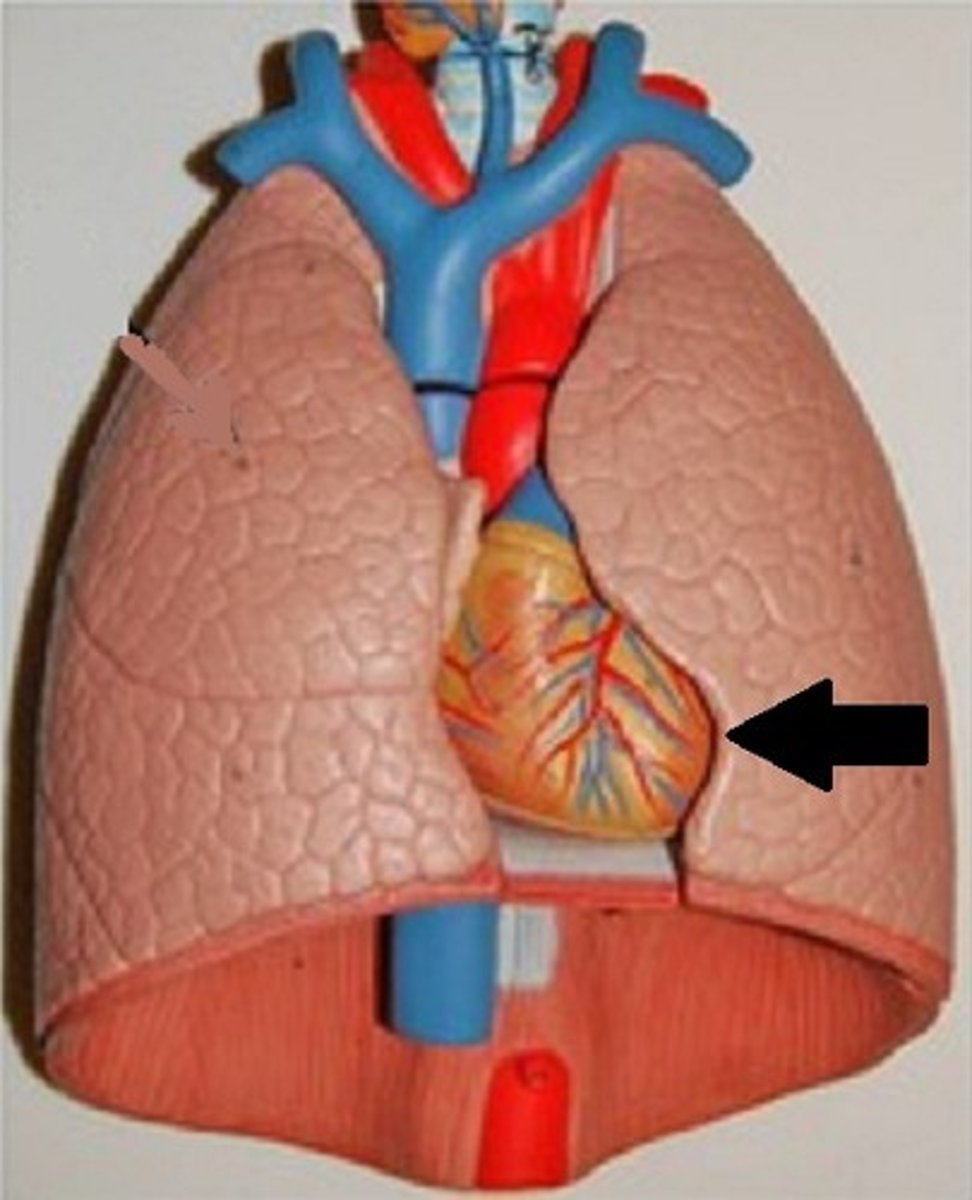
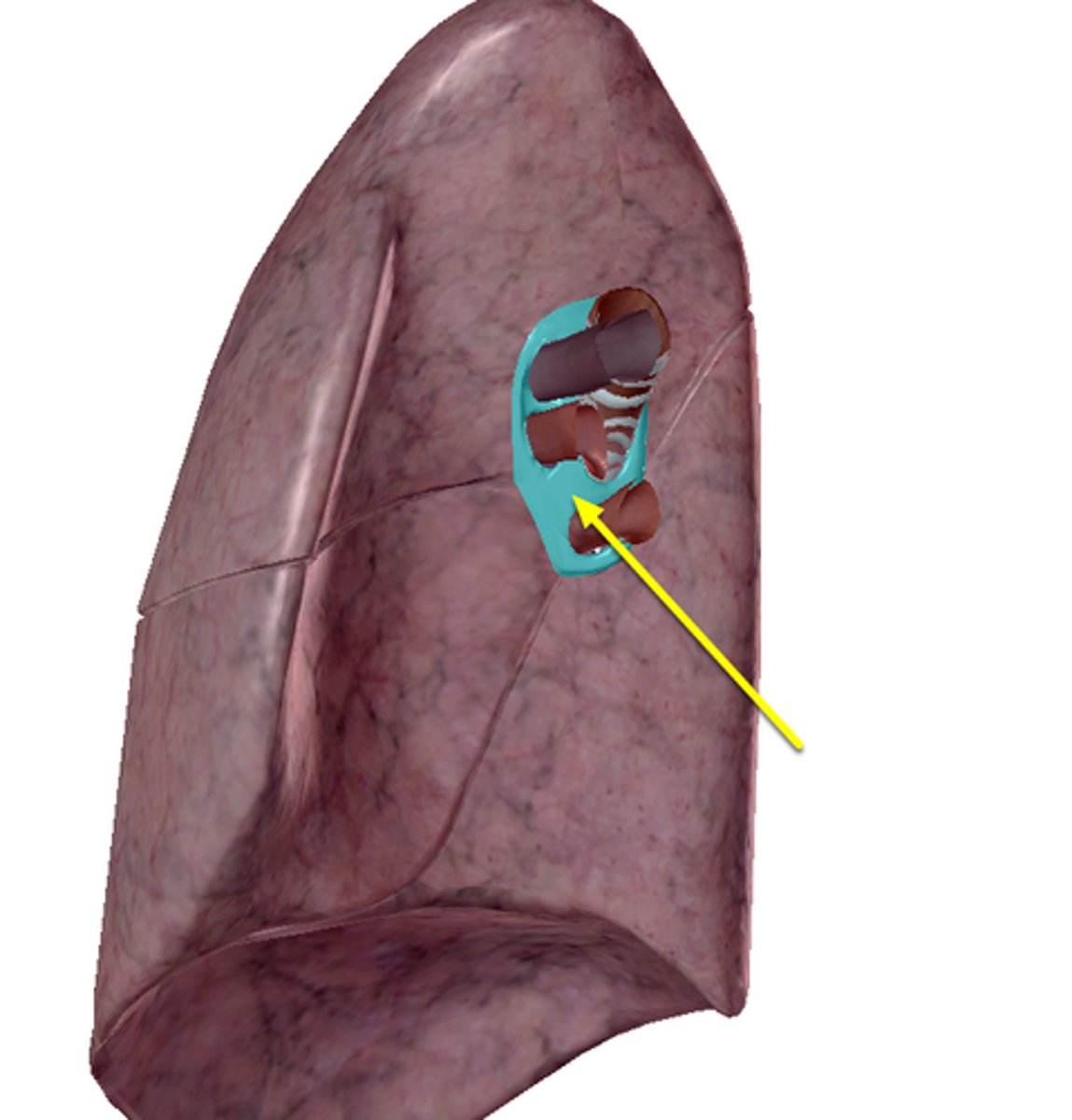
collection of structures that attach the lung to the mediastinum
Define the root.
bronchus, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein
What does the root consist of?
posterior to root of lung
Where is the vagus nerve located?
anterior to root of lung
Where is the phrenic nerve located?
area of entrance and exit of main vessels of lung
Define the hilum.
bronchus, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein
What does the hilum contain?
hilum
root
pulmonary trunk artery
Where emerges off the right ventricle?
L and R Pulmonary Arteries
What arises from the pulmonary trunk artery?
deoxygenated blood from heart to lungs
The left and right pulmonary arteries carry ____.
superiorly placed in the hilum
Left and right pulmonary arteries are located ____.
-right pulmonary artery = longer
-left pulmonary artery = shorter
Describe the difference between right and left pulmonary artery.
-passes horizontally across mediastinum
-passes anteroinferior to bifurcation of trachea
-anterior to right main bronchus
-posterior to ascending aorta, superior vena cava, most superior right pulmonary vein
Describe the location of the right pulmonary artery.
-into 2 at the root
-Divides again within lung so branch goes to each lobe
The right pulmonary artery branches ____.
-Anterior to ascending aorta
-Posterior to superior to upper most pulmonary vein
Describe the location of the left pulmonary artery.
within the lung
The left pulmonary artery branches ____.
oxygenated blood from lungs back to left atrium of heart
The left and right pulmonary veins carry ____.
-2 veins per lung
--Superior pulmonary vein
--Inferior pulmonary vein
How many pulmonary veins are there?
-trachea
-main bronchi
-lobar bronchi
-segmental bronchi
-bronchioles
-alveoli
What are parts of the bronchial tree?
Vertebral level C6-T4/5
Where is the trachea located?
-Flexible tube
-C-shaped cartilaginous rings to strengthen
Describe the trachea.
esophagus its behind the trachea
Why is the trachea C-shaped?
Enters lungs via hilum
Where are the two main bronchi located?