Feline infectious diseases vaccines part 1
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Feline viral Rhinotracheitis responsible for what percent up URI
responsible for 40% of respiratory infections in cats
FVR Etiology and Pathogenesis
what is it caused by
Enveloped or non eveloped
What type of infections
How long is infection
what type of shedding
Caused by feline herpes virus 1
Enveloped
Latent infections
One infected always infected
periodic bouts of recrudescence
periodic or continuous shedding
FVR transmission
Shed in oral and oculonasal secretions
• Very common in shelters!
• Latently infected cats likely to have
reactivation of infection
• Kittens of carrier queens may develop
subclinical infections
FVR clinical signs
Fever
• Sneezing
• Rhinitis
• Inappetence
• Hypersalivation
• Conjunctivitis
• Ocular/nasal discharge
• Dendritic corneal ulcersFever
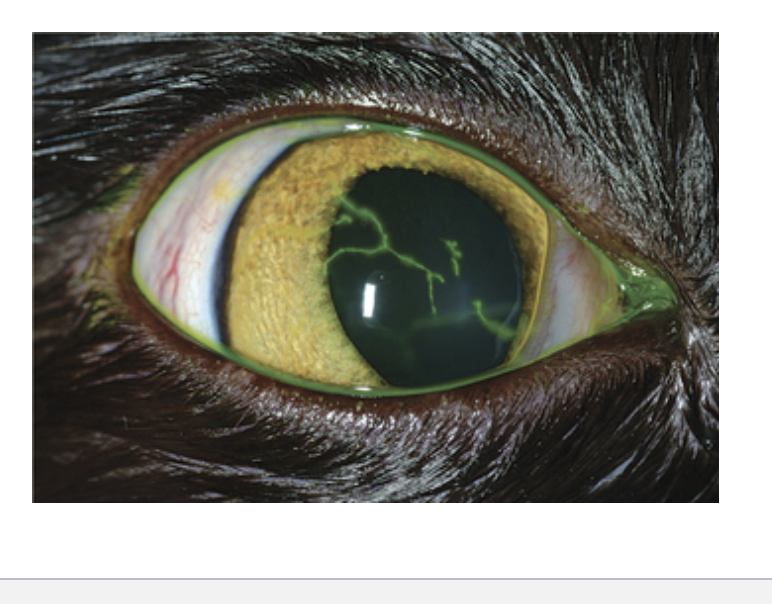
FVR diagnosis
Signalment
History
Clincal signs
FVR treatment
Symptomatic & supportive
Antibiotics, ophthalmic ointment, antivirals
(Dont use steriods on ulcers or it will melt)
FVR control
Vaccination (combo) reduces clinical signs
Proper husbandry techniques
• Disinfection
• Isolation
Feline Calicivirus is responsible for what percent of URI
40%
All feline species are susceptible
High degree of antigenic drift
FCV etiology and pathogenisis
Small, non enveloped virus
Stable in environment
• Resistant to disinfectants
• Replicates in oropharynx
• Travels to conjunctiva & URT
• Typically occurs @ 2-3 months
• Severity related to virulence
FCV transmission
Shed in oculonasal secreations
Some can be lifelong carriers
Common in overcrowded populations
Fomites
FCV clinical signs
Fever, oculonasal discharge conjunctiva
Hallmark signs: oral erosions and ulcerations
High morbidity, low mortality
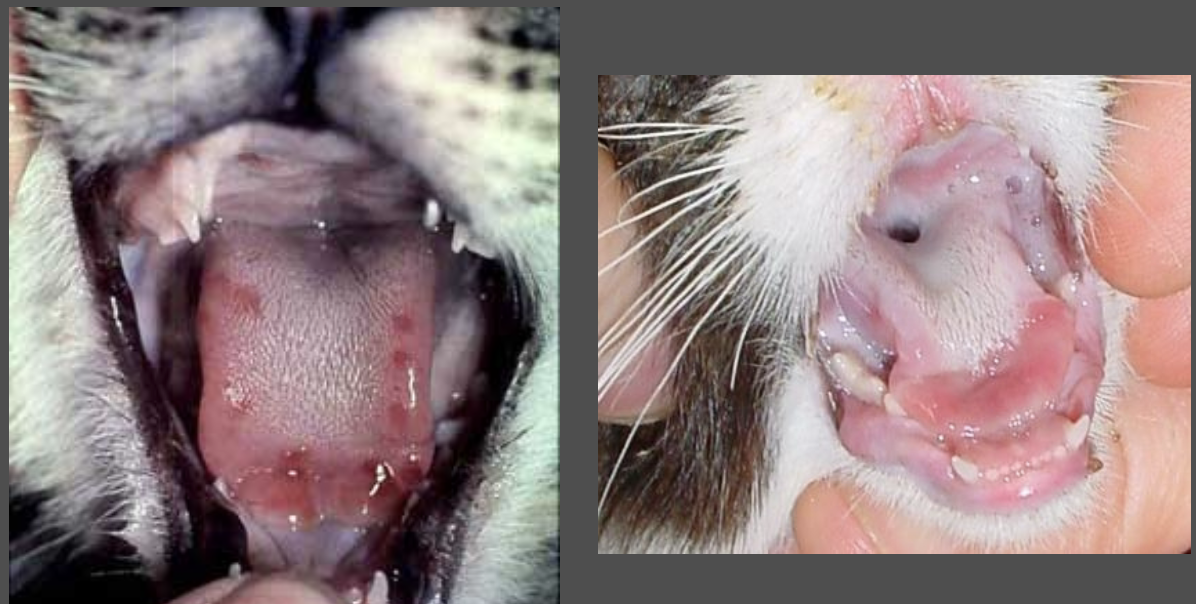
FCV Virulent strain
High mortality in adults
Short-lived outbreaks
URD more severe
Vaccine not protective
FCV Diagnosis and treatment
Signalment, history, and clinical signs
Symptomatic and supportive care
Systemic antibiotics
antivirals
FCV Control
Vaccnination (combo)
Disinfection
Isolation
Feline Panleukopenia (feline distemper but caused by parvo virus)
Aka: Feline infectious enteritis, Feline distemper
• Highly contagious
• Potentially fatal
• Most feline species of any age susceptible
• Rarely diagnosed due to vaccines
Feline panleukopenia etiology
Etiology
• Caused by a Parvo virus (NOT a distemper
virus...)
• Small, non-enveloped viruses
• VERY stable in environment
• Resistant to many disinfectants
• Inactivated by bleach
Feline Panleukopenia Pathogenesis
Affinity for rapidly dividing cells
• Intestinal crypt cells & lymphopoietic
cells of bone marrow
• Intestinal villous atrophy
• Transplacental infection cerebellar
hypoplasia & retinal dysplasia
• Cerebellar Hypoplasia (smaller size)
Video of cat that cannot walk/ unbalanced
Feline Panleukopenia Transmission
Fecal oral and aerosolized droplets
Fecal shedding continues weeks after recovery
Fleas and humans are vectors/ fomites
Feline Panleukopenia Clinical Signs
Mortality rate 25-90%
• Most deaths occur 3-5 days after
onset of illness
4 possible presentations: Know these
1. Subclinical (most infections)
2. Peracute
3. Subacute
4. Acute
What would subclinical infection look like in Feline panleukopenia
mild fever and
leukopenia followed by lifelong
immunity
What would peracute infection look like in feline panleukopenia
The kitten may die with
no symptoms (fading kitten)
What would subacute infection look like in feline panleukopenia
depression, fever, & diarrhea of 1-3 days followed by rapid recovery
What would acute infection look like in feline panleukopenia
Depressed
• Anorexic
• Febrile (104-107°F)
• Vomiting/diarrhea (within two days)
• Severe dehydration
• Hypothermia
• Septic shock
Feline Panleukopenia Diagnosis
Signalment, history, clinical signs
• Leukopenia (particularly neutrophils)
• Canine parvovirus test kits (ELISA test)
can be used
• Many false negatives
• Necropsy
Feline Panleukopenia Treatment
Aggressive IVF
• Whole blood/plasma transfusion
• Broad spectrum parenteral antibiotics
• Nutritional support (parenteral in severe cases)
Feline Panleukopenia control
accination (combo)
• There are inactivated and MLV
• If cat survives natural infection, it will have
antibodies for life
• Isolation
core vaccine schedule
