Exam 2 Study Quizlet | American History to 1865 | HIST 1512 | Fall 2023 | Kebron Teshome
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Empire of Liberty
Thomas Jefferson's concept of a nation built on landholding farmers and the ideals of freedom and democracy.
Louisiana Purchase
The acquisition of a vast territory from France by the United States in 1803, doubling the size of the country.
War of 1812
A conflict between the United States and Britain, primarily caused by trade disputes and British interference with American shipping.
Proclamation line of 1763
A boundary established by the British government that prohibited American colonists from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains.
Civilization Policy
A policy in the late 18th and early 19th centuries that aimed to transform Native American economies and lifestyles to align with those of white Americans.
Tenskwatawa (Shawnee Prophet)
A Native American leader who preached a return to traditional ways and resistance against American assimilation.
Tecumseh
Tenskwatawa's brother and a prominent Native American leader who organized a pan-Indian military alliance.
Indian Removal
The forced relocation of Native American tribes from their ancestral lands to designated territories in the West, primarily through the Indian Removal Act of 1830.
Trail of Tears
The forced removal of the Cherokee Nation from their lands in the Southeast to present-day Oklahoma, resulting in the death of thousands of Cherokee people.
Cotton Revolution
The rapid expansion of cotton production and the rise of the cotton industry in the southern United States, fueled by the invention of the cotton gin.
Cotton industry
Refers to the production and trade of cotton, which was a major industry in the United States.
Cotton gin
A machine invented by Eli Whitney that mechanized the process of cleaning cotton, leading to increased cotton production.
Plantation
Large agricultural estates in the Southern United States where crops, particularly cotton, were grown using slave labor.
Slaveholding
Refers to the percentage of households in the South that owned slaves.
Appalachian Mountains
A mountain range in the Eastern United States that remained largely unsettled due to geography and native population presences.
Indian Removal Act
A law passed in 1830 that forced Native American tribes to relocate from their ancestral lands to designated areas west of the Mississippi River.
Enslaved population
Refers to the number of enslaved people in different regions of the Southern United States.
Gabriel's Rebellion
A failed slave rebellion that took place in 1800 in Virginia.
Nat Turner's Rebellion
A slave rebellion led by Nat Turner in 1831 in Virginia.
Trickster tales
Folktales that were forms of cultural resistance used by enslaved people to outwit and trick those in power.
Industrial Revolution
A period of rapid industrialization and technological advancements that occurred from the late 18th to the mid-19th century.
Cash crops
Crops, such as tobacco and cotton, that were grown for sale rather than for personal consumption.
Erie Canal
A canal that connected the Great Lakes to the Hudson River, facilitating trade and transportation in the 1820s.
Railroads
A transportation system that used tracks and locomotives to transport goods and people, becoming prominent in the 1840s.
Telegraph
A communication system that used electrical signals to transmit messages quickly, revolutionizing communication in the 1840s.
Pre-Industrial
Refers to a time period before the rise of industrialization, characterized by handcrafted goods and individual labor.
Boston Associates
A group of Boston merchants who traded textiles with English merchants and established the first factory in 1813.
Lowell, Massachusetts
A textile mill town known for its industrial textile factories, considered America's first.
New Immigrants
Refers to immigrants who arrived in the United States during the 1830s-1850s.
Irish Immigrants
Immigrants from Ireland who came to America, particularly as a result of the Irish Potato Famine.
Nativism
A belief that favors the interests of native-born inhabitants over immigrants.
American Party
Also known as the Know-Nothing Party, a political party in the 1840s-1850s that opposed the influence of Catholics and immigrants.
Second Great Awakening
A religious revival movement in the early 19th century that emphasized personal transformation and social reform.
American Bible Society
An organization founded in the 1820s with the goal of distributing Bibles to every household in America.
American Temperance Society
A society founded in 1826 that advocated for temperance and the reduction of alcohol consumption.
Conservative Anti-slavery efforts
Efforts to abolish slavery gradually, compensate former enslavers, and promote colonization.
American Colonization Society
A society founded in 1816 that aimed to send free blacks back to Africa, particularly Liberia.
Radical Abolitionism
A more extreme form of abolitionism that called for immediate emancipation and equal rights for African Americans.
David Walker's "Appeal to the Coloured Citizens of the World"
A radical anti-slavery essay written by David Walker in 1829.
William Lloyd Garrison
An abolitionist who published the newspaper "The Liberator" and played a significant role in the anti-slavery movement.
American Anti-Slavery Society
A society formed in 1833 with the goal of abolishing slavery in the United States.
Frederick Douglass
An escaped slave who became a prominent abolitionist and leader in the anti-slavery and civil rights movements.
Local officials
Officials at the local level who had goals of converting people to anti-slavery ideals and provoking outrage.
Petition campaign
A campaign in 1837 that involved anti-slavery petitions and speeches in Congress against anti-slavery petitions.
Gag rule
A rule passed that stated no anti-slavery petitions would be accepted into Congress.
Women's Rights movement
A movement that grew out of abolitionism and aimed to fight for women's rights.
World Anti-Slavery convention
A convention held in London in 1840 where Lucretia Mott and Elizabeth Cady Stanton were denied seats and could not speak because they were women.
Middle-class society
A society characterized by towns and cities, where women were responsible for the home (domestic sphere) and men were responsible for work (public sphere).
Cult of Domesticity
The idea that middle-class women were the heart of the home and had to adhere to certain characteristics and roles.
Double Standard
A societal expectation that allowed men to engage in certain activities while women would be shunned and ostracized for the same actions.
Manifest Destiny
The belief that it was the nation's destiny to expand and settle the continent.
Free soil
The belief that all territories should be free and not allow slavery.
Pro-Slavery
The belief that slavery should be allowed in all territories, as recognized by the constitution and laws.
Popular sovereignty
The idea that the people living in a territory should decide whether it would be a free or slave state.
Compromise of 1850
A series of legislative measures that aimed to address the issue of slavery in the newly acquired territories, including the admission of California as a free state and the implementation of a tough fugitive slave law.
Fugitive Slave Law
A law that made assisting fugitive slaves a federal crime and required federal officials to assist in capturing and returning escaped slaves.
Sectional Conflicts
Conflicts between different regions of the United States, particularly regarding the issue of slavery.
Southern "Fire-Eaters"
A minority group of southern newspaper editors who called for secession and were unhappy with the Compromise of 1850.
Anthony Burns
An enslaved fugitive who escaped to Boston in 1854 and became the center of riots and demonstrations due to his arrest under the Fugitive Slave Law.
Harriet Beecher Stowe
The author of "Uncle Tom's Cabin," a novel that depicted the harsh realities of slavery and had a significant impact on public opinion.
Kansas-Nebraska Act
An act that led to the creation of the Republican Party and allowed for popular sovereignty in the territories of Kansas and Nebraska.
French and Indian War
Conflict fought between 1754 and 1763 in North America, involving the British and French, as well as Native American tribes. It resulted in the British gaining control of Canada and much of the eastern half of North America, but also led to increased tensions between the British and American colonists.
Creek War
______ was a conflict between the United States and the Creek Native American tribe that took place from 1813 to 1814. It was part of the larger War of 1812. The war resulted in significant losses for the Creek tribe and ultimately led to the cession of millions of acres of their land to the United States.
Battle of New Orleans
A significant battle fought during the War of 1812. It took place on January 8, 1815, and was the final major battle of the war. The American forces, led by General Andrew Jackson, successfully defended the city of New Orleans against the British forces. Made Jackson an national hero
Andrew Jackson
_______ was the seventh president of the United States, serving from 1829 to 1837. He was a prominent figure in American history, known for his role in expanding presidential power and his controversial policies, such as the Indian Removal Act. ______ also played a significant role in the Creek War, which was a conflict between the United States and the Creek Native American tribe in the early 19th century.
Battle of Fallen Timbers
______________ was a decisive conflict that took place on August 20, 1794, in present-day Ohio, United States. It was fought between the Western Confederacy of Native American tribes and the United States Army. The battle marked a turning point in the expansion of the United States into the western frontier.
California Gold Rush
________ was around the 1850s when gold was discovered in California, United States. This discovery led to a massive influx of people from around the world who migrated to California in search of gold. The gold rush had a significant impact on California's population, economy, and development, as it spurred rapid growth and urbanization in the region. It also played a crucial role in shaping the history of the American West. Chinese Immigrants faced intense discrimination.
Stephen Douglas
_______ was an American politician. He was a member of the Democratic Party and served as a U.S. Senator from Illinois. He played a key role in the passage of the Kansas-Nebraska Act, which allowed for the expansion of slavery into new territories. Was morally indifferent to slavery, wanted to be president of US but lost to Lincoln.
Mexican-American War
In early 1830s Mexico reached up to upper California and Texas
Mexican government invited American immigrants to come settle in Texas and become Mexican citizens
Many of the Americans who came and the Mexicans who lived in Texas revolted against Mexican rule - Texas Revolution
Texas wins the revolution and becomes an independent nation.
Texas claimed their borders were along the Rio Grande river, while Mexico said it was further East.
In 1846 America sent troops to patrol the area along the disputed territory, and sparked a war.
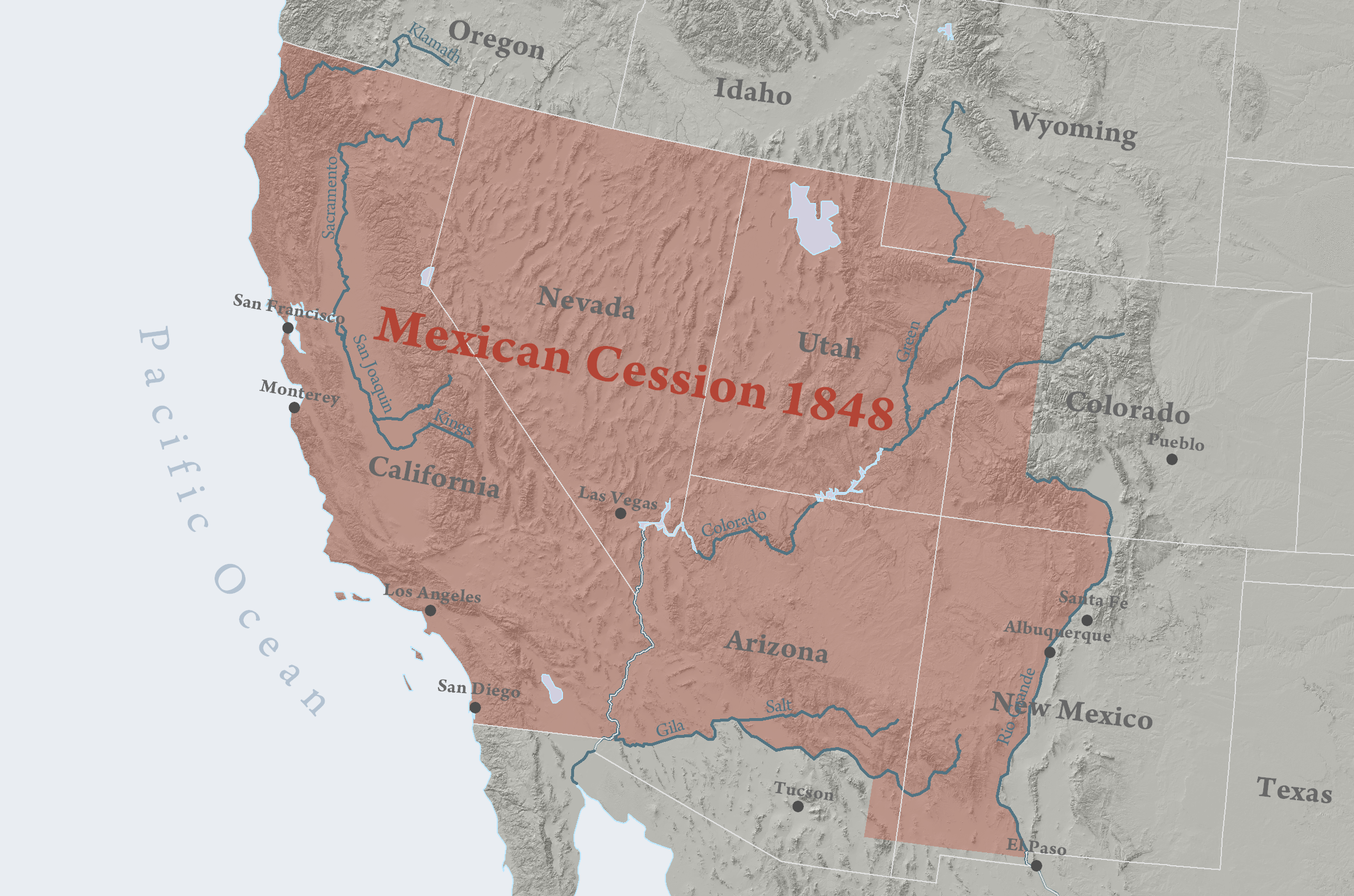
Mexican Cession
America wins the war, gains the modern states of Arizona, California, New Mexico, Nevada, Utah, parts of Colorado, and Texas.
John Brown
A committed abolitionist who came to Kansas
Retaliated against pro-slavery settlers’ attacks with “Massacre at Pottawatomie Creek”
Massacre at Pottawatomie Creek
Violent incident in Kansas, 1856. Pro-slavery settlers attacked by John Brown and his followers. 5 pro-slavery men killed. Increased tensions and violence in the lead up to the American Civil War.
Senator Charles Sumner
influential American politician who served in the U.S. Senate from 1851 to 1874. He was known for his advocacy of civil rights and opposition to slavery. Said The Crime Against Kansas speech.
The Crime Against Kansas
May, 1856 speech given by Sumner
In the speech he discusses the horrible things Southerners were doing in Kansas
Referred to slavery as the mistress of a senator he called out
The term was very intentional, as there was much discussion amongst abolitionists about the sexual assault, offended much Southerns
This extremely offended many southerners
Representative Preston Brooks
A 19th-century U.S. politician who infamously attacked Senator Charles Sumner with a cane on the Senate floor in 1856, in response to Sumner's anti-slavery speech. The incident highlighted the growing tensions between pro-slavery and anti-slavery factions in the United States, leading to further division and conflict.
Northwest Confederacy
The Native American alliance led by Chief Little Turtle and Blue Jacket, fought against the United States in the Battle of Fallen Timbers in 1794.
Treaty of Greenville (1796)
Ended the Northwest Indian War. Native American tribes ceded land in the Northwest Territory to the United States.
Missouri Compromise Line
Boundary line established in 1820 to address slavery in the United States. It divided the Louisiana Purchase into two regions: the North, where slavery was prohibited, and the South, where it was allowed. The line ran along the southern border of Missouri, marking a temporary solution to maintain a balance between free and slave states.
David Walker
American abolitionist and writer who published "Walker's Appeal," a powerful pamphlet advocating for the end of slavery and the empowerment of African Americans. Born to enslaved father and free mother, so was free.