DNA Translation and Transcription
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are the differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA: double stranded, has deoxyribose sugar, bases: A, T, G, C
RNA: single stranded, has ribose sugar, bases: A, U, G, C
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome (joins amino acids together by peptide bonds to make proteins).
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis
How many tRNAs are there per amino acid?
ONE
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome (translated by ribosomes to make proteins).
Transcription steps
1. DNA unwinds --> RNA polymerase binds to a promoter near the start of a gene.
2. RNA is synthesized by complementary base pairing of free nucleotides with the nucleotide bases on the template strand of DNA.
3. The site of synthesis moves along DNA --> DNA that has been transcribed rewinds.
4. transcription reaches the terminator
5. RNA and RNA polymerase are released and the DNA helix reforms.
rifamycin
Inhibits mRNA synthesis and penetrates tissues (can cause red urine, saliva, sweat, and tears).
What is an example of a rifamycin?
Rifampin
Genetic code
a set of rules that determines how a nucleotide sequence is converted to an amino acid sequence of a protein.
What determines the amino acid?
Arrangement of nucleotides (Codon)
degenerate code
multiple codons encode a single amino acid
stop codons
Codons that signify the stop of an amino acid chain: UAA, UAG, UGA
codons
The three-base sequence of nucleotides in mRNA
start codon
AUG (formethionine)
anticodons
Three-base sequence in a transfer RNA molecule base that pairs with a complementary codon in mRNA that decides which amino acid is brought into the ribosome.
What do mRNA codons determine?
Which tRNA "docks" into the ribosome
A site
attachment site on a ribosome for a tRNA
P site
polymerization site where the peptide bonds are formed between amino acids
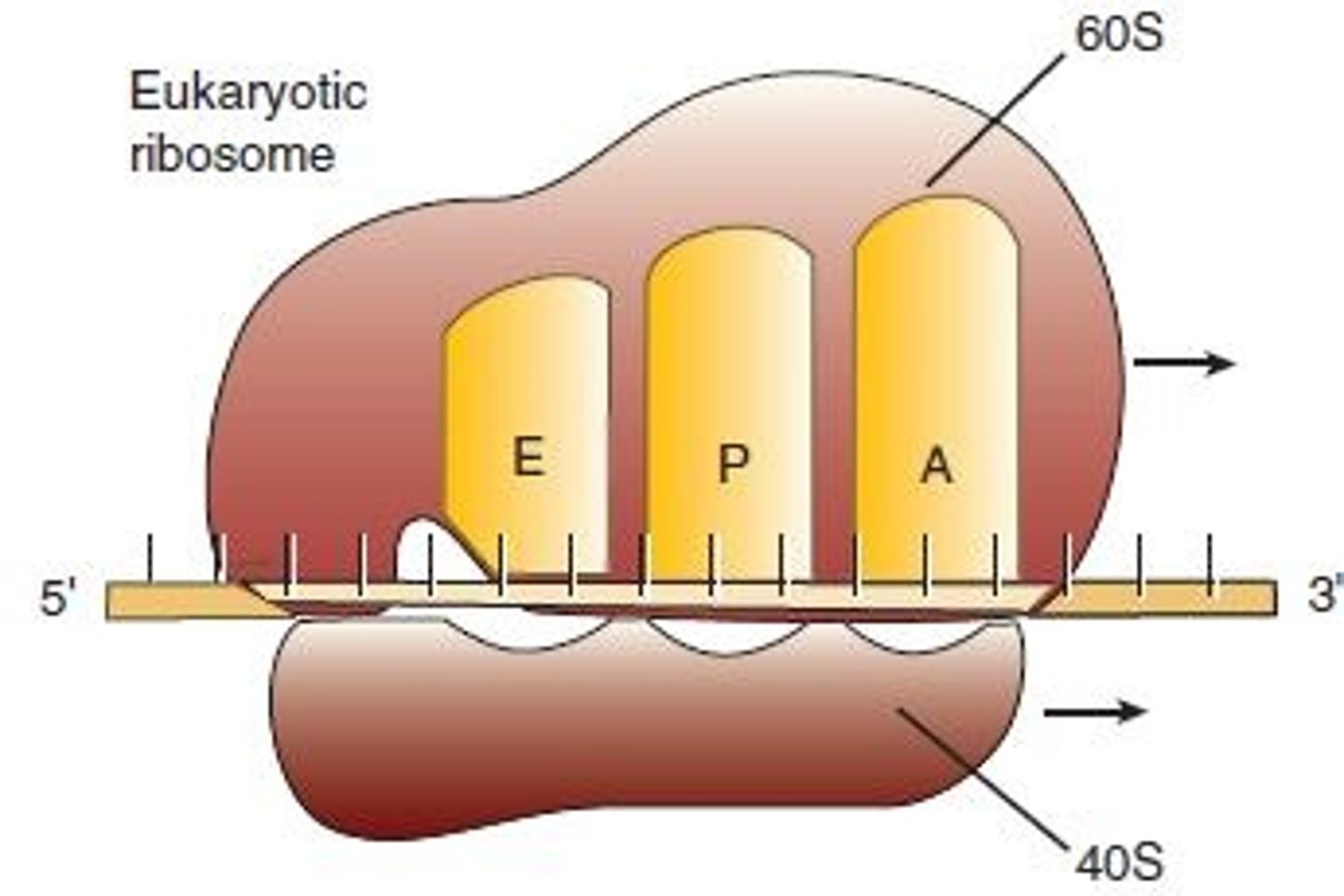
E site
the exit site, where discharged tRNAs leave the ribosome
Following protein synthesis what do the secondary and tertiary structures of a protein form in a bacteria?
the cytosol
True or false? Ribosomes can immediately begin the process of protein translation as mRNA in bacteria.
True
polyribosomes
multiple ribosomes can bind mRNAs and translate them simultaneously.
Is DNA replication, translation, and transcription most active when bacteria are actively growing or dormant?
Actively growing
When are antibiotics most effective?
When bacteria are actively growing
Aminoglycosides
*Works by causing the mRNA to be misread
1. effective against gram negative bacteria
2. can cause damage to the auditory nerve and kidneys
What are some examples of aminoglycosides?
Streptomycin and Gentamycin
tetracyclines
*tRNA is blocked, so no protein is synthesized
1. broad spectrum (gram positive and gram negative)
2. long retention in body and penetration
3. used in animal feed- which is a cause for concern
4. discolor teeth in children and not given to pregnant women (liver damage)
chloraphenicol- simple structure
*formation of peptide bonds is blocked
1. broad spectrum but toxicity problems
2. inexpensive
3. readily diffuses into tissues
4. can cause aplastic anemia
macrolides
*the ribosome is prevented from translocating
1. effective against gram positive bacteria
2. oral antibiotic for children
What is an example of a macrolides?
Erythromycin
coding strand
the strand of DNA that is not used for transcription and is identical in sequence to mRNA, except it contains uracil instead of thymine
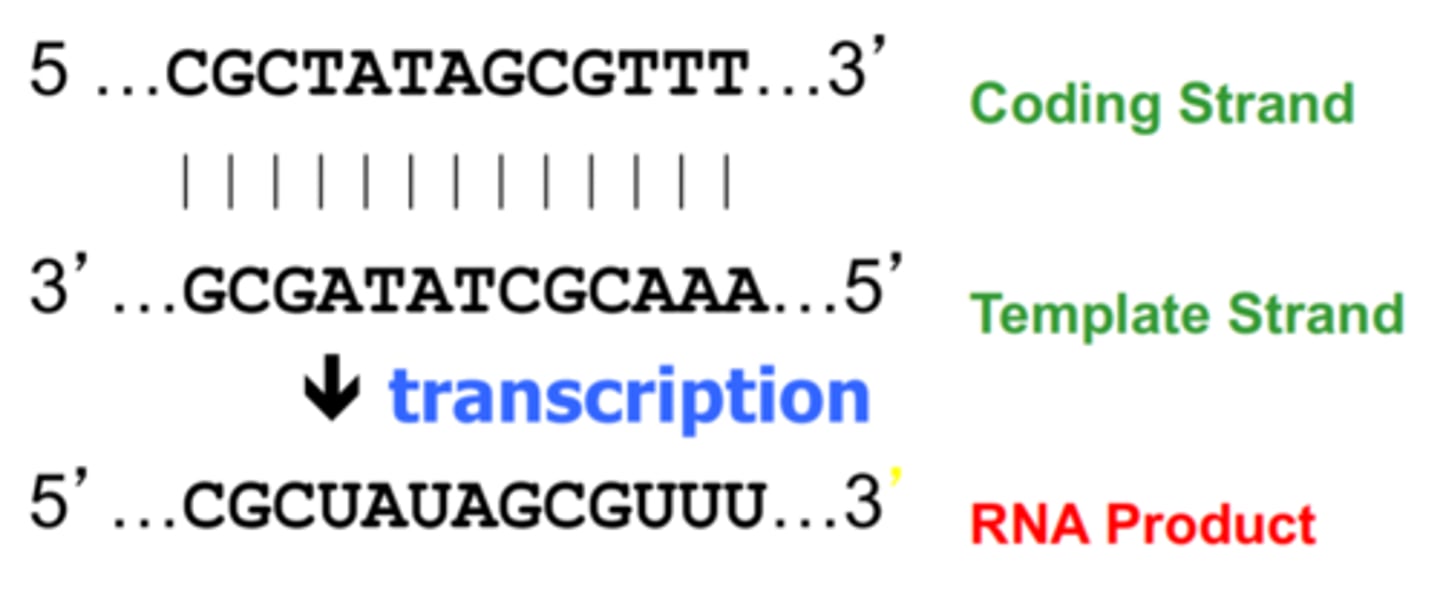
template strand
The DNA strand that provides the template for ordering the sequence of nucleotides in an mRNA transcript.