PSYC 304: Midterm 1
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
neuroscience
study of relationship between brain and behaviour
common neuroscience metaphors
explain what is not possible to observe/know yet
Galen’s humours
brain/heart as source of intelligence
hydraulics
dualism vs. materialism
electricity
Bell and Magendie - direction of charge
biological machine vs. spirit
computers
two initial schools of thought for the brain
doctor: brain is source of intelligence
philosophers: heart is source of intelligence
evidence for interest in the brain in prehistory
trepanation in ancient skulls (holes drilled in the brain, likely to treat mental health concerns)
ancient Egypt’s brain interest
didn’t ascribe too much value to it, instead preserved the heart during mummification
ancient Greece’s interest in the brain
Hippocrates: brain injuries are from emotional/intelligence problems
Aristotle: heart is source of intelligence
ancient Rome’s interest in the brain
Galen: humans and animals are the same - animal dissections
identified cerebellum (as motor control) and cerebrum (as memories)
ventricles and nerves
the 4 humours
knowledge lost until the Renaissance
materialism in science
assuming that everything in the universe can be physically observed, correspond to physical laws - everything in brain can be observed/measured
brain understanding from Renaissance to the 18th century
hydraulics
Descartes
White/grey matter mapping
ventricles
gyri and sulci
the brain in the 19th century
Benjamin Franklin and electricity - brain functions through electricity? (Galvani and du Bois-Reymond)
Bell and Magendie found that the “wires” are nerves
localization of function (Fluorens, Gall, Broca)
Darwin’s natural selection
Schwann’s cellular theory
Golgi’s stain
mixed silver and nitrate to stain neurons, able to see them individually
reticular theory
2 theories of neuron function
Golgi: neurons are connected and continuous, signals travel from inside a neuron to another, like mesh
Cajal: drew neurons in detail and noticed a variety of cell types - neuron doctrine: base unit of nervous system is the neuron (was the more right one)
Ramon y Cajal’s neuron drawings
drew neurons in detail and noticed a variety of cell types
neuron doctrine: base unit of nervous system is the neuron
discovered some neurons input info and some output
discovered synapse
20th century brain
when modern neuroscience was born
the brain as a computer
modern metaphor - binary was chosen because of neurons, neuroscience uses computer-like terms (wiring, coding, processing)
computers represent info, brains construct info
levels of analysis
molecular neuroscience
cellular neuroscience
systems neuroscience
behavioural neuroscience
cognitive neuroscience
human brain size
2-3% of body weight, ~3 lbs - consumes 20% of your energy/oxygen
slightly larger in men, huge individual variation
make-up of the human brain
neurons (<100 billion, more than half in cerebellum), glia (support cells), stem cells, blood vessels
consistency of soft tofu
convolutions = wrinkles on brain
cells are not replaced
adult neurogenesis?
cell regeneration
identified in fish and birds
found some neurogenesis in the hippocampus until 13 years old - not significant enough
locust brain
nervous system clusters - loosely built
a lot of sensory organs
structures ensure speed and reflexes
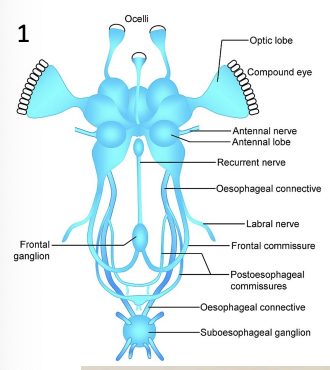
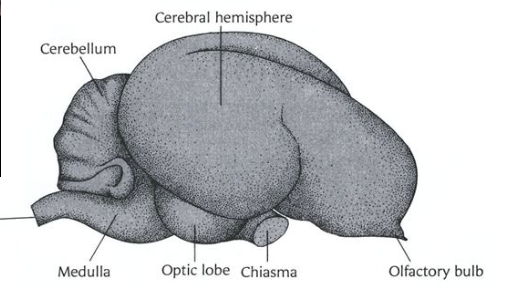
fish brain
same regions as us, with small cerebral cortex
midbrain proportionally aligns with ours
tectum responds intensely to stimuli, cerebrum is small so not good at pulling away
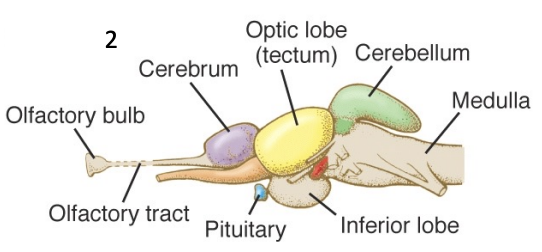
rat brain
cerebellum and cerebrum are larger and cover midbrain (not wrinkled)
olfactory bulb at the end
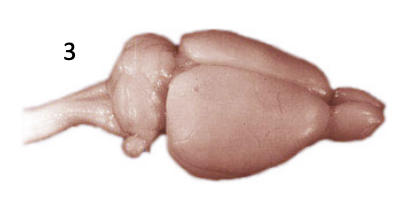
dog brain
cerebrum is getting larger (wrinkles), olfactory bulb is at the front (strong smell), strong interaction/direction skills, empathetic
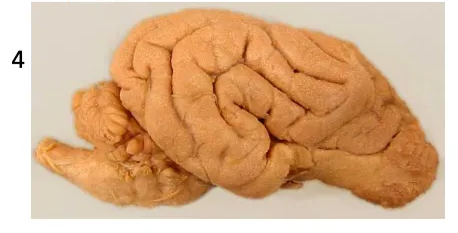
monkey brain
spinal cord goes out below animal’s head like animals
convolutions
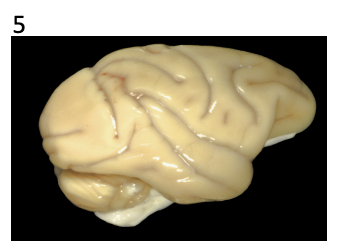
chimpanzee brain
similar to humans - big cerebrum, convolutions
smaller frontal lobe
understand tool use, theory of mind, sense of self
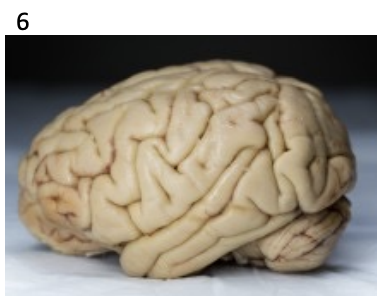
developments as the brain gets more human
more convolutions
more system layering
frontal lobe and forebrain getting bigger
human brain vs. dolphin brain
dolphin brain is huge, with more convolutions - have vocab, play, interact with humans, don’t have limbs/dexterity
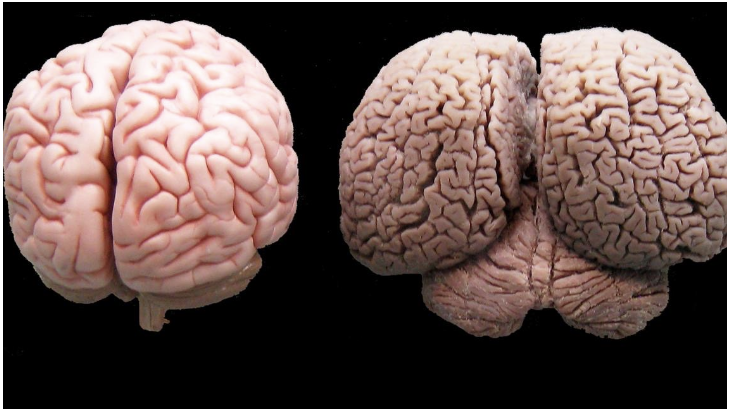
human brain vs. parrot brain
can count, talk, answer spoken questions, but have small and smooth brains
brain size significance
doesn’t carry the most weight, but humans do have the disproportionally largest brain for body size
doesn’t give us function
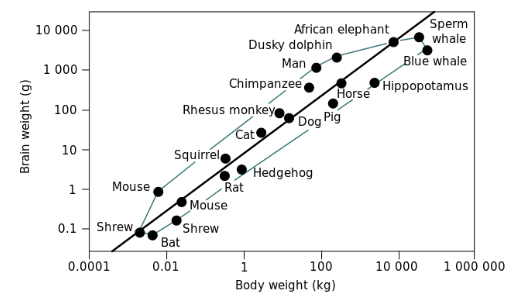
measuring brain cell density
counting neurons per unit of mass/volume - intelligence correlated with sophistication of cellular connections
grey matter
cell bodies, unmyelinated neuorns
white matter
fatty substane, myelin, makes it white (axons moving info to different parts of the brain)
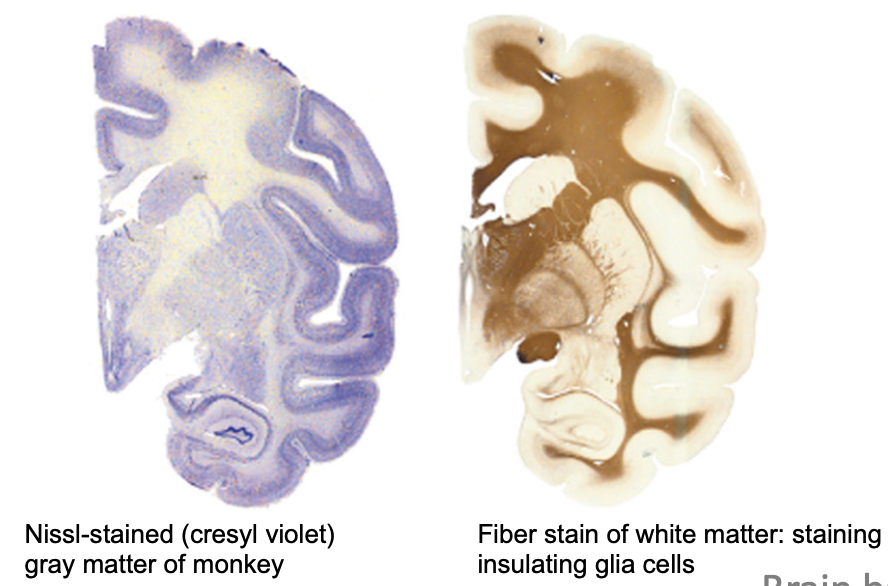
brain matter staining
nissel: darker stains = grey matter, nucleic acids in rough ER, cell bodies
Best for seeing cell bodies, neuro-degeneration, neuron density
fibre: darker stains = white matter, binds to myelin, won’t show whole cells
Best for seeing white matter and nerve fibres
golgi: darker stains = neurons and dendrites
Best for seeing the entire neuron
neurons
communicating cells, specifically through axon (carry info very fast through action potential)
specific commands are for specific areas
many types, but similar design
dendrite → soma → axon → terminals
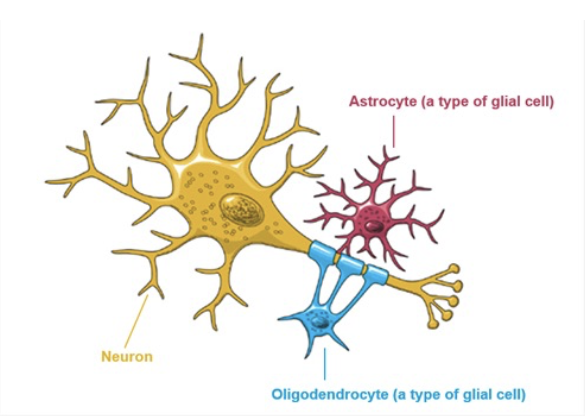
glia
communicating cells, support cells - build brain foundation
build glia
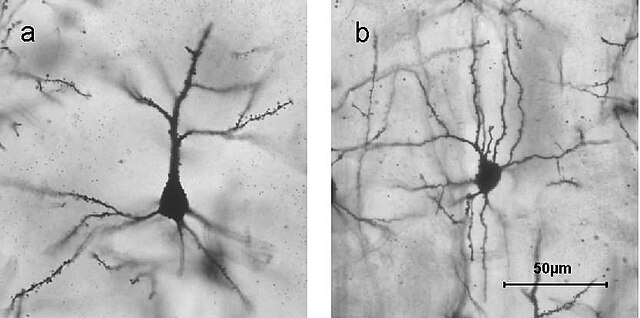
pyramidal neuron
in the cortex, travels deep into brain
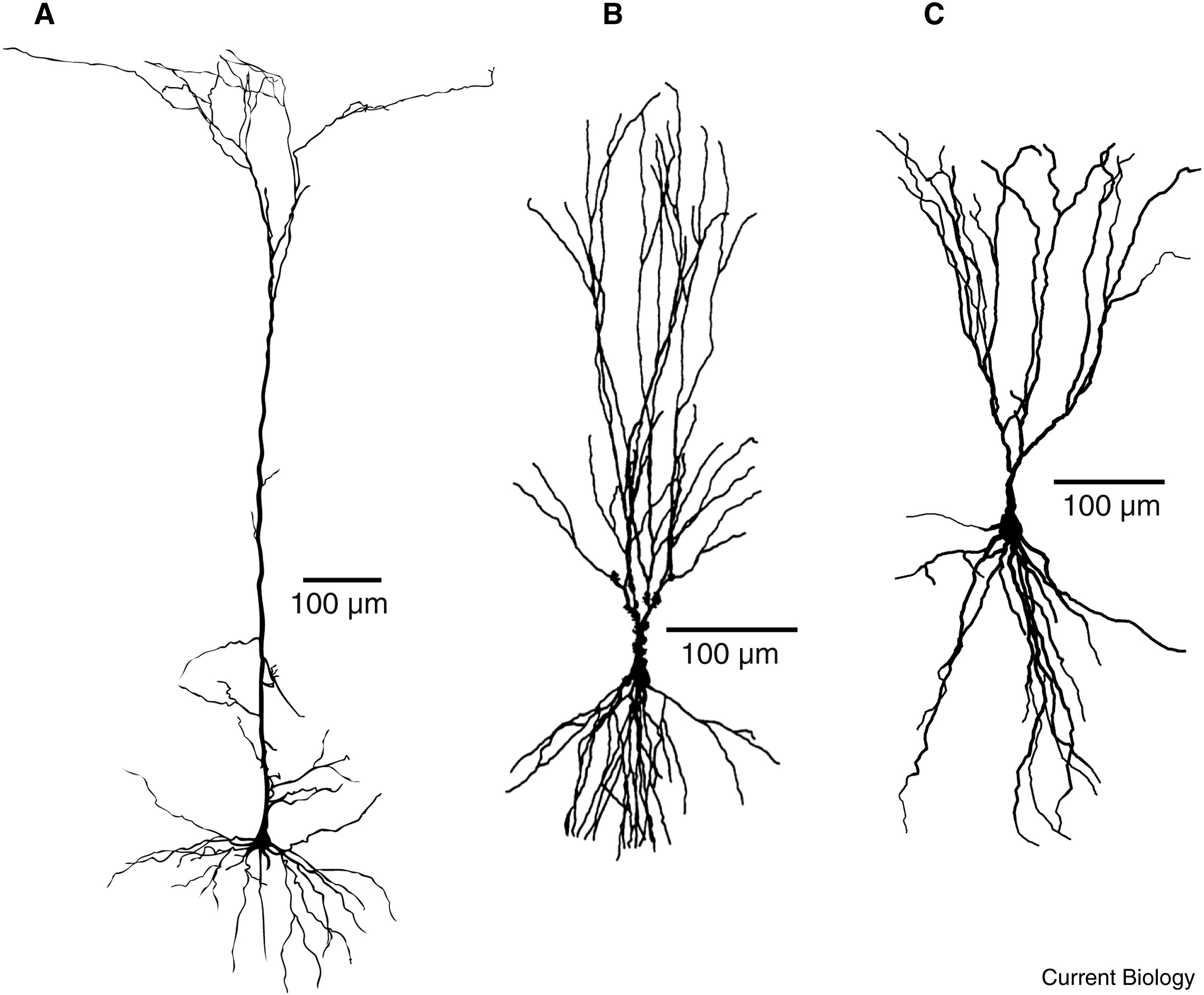
stellate neurons
in cells in central nervous system
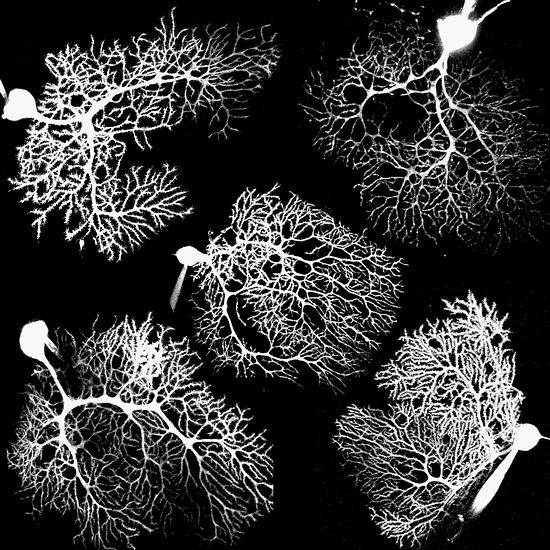
purkinje neurons
cells in the cerebellum
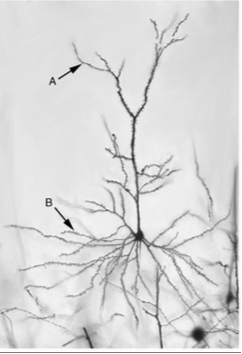
projection neurons
often modifying, have long axons that project to different brain areas
long axon
pyramidal and purkinje
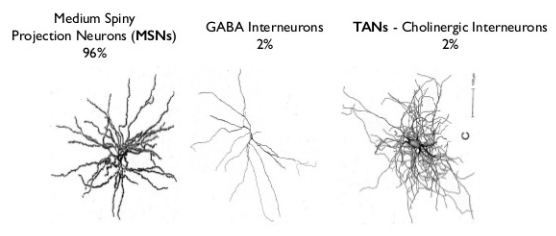
interneurons
star shaped, projected locally - inhibiting and synchronizing, generate patterns of brain activity
short axon
macroglia
regulate retinal metabolism, modulate neuron function and blood vessels
astrocyte, schawan cell, oligodendrocyte
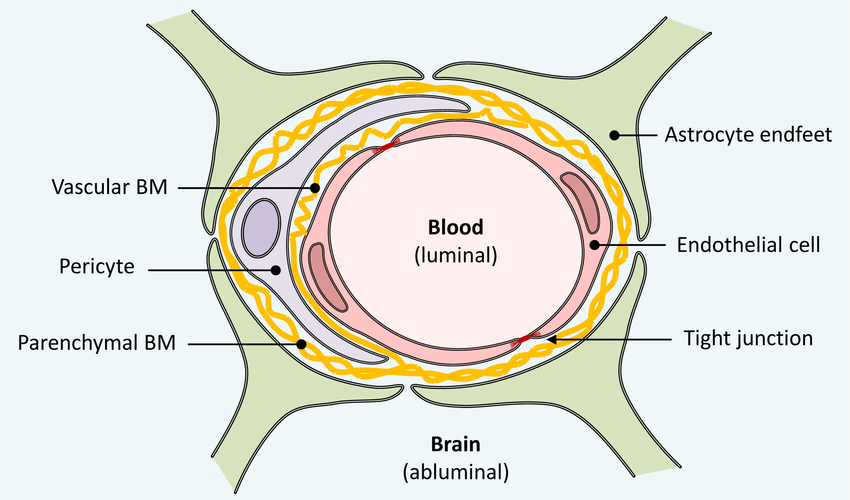
blood-brain barrier
membrane between blood and brain that keeps brain healthy from viruses, brain is often blocked from immune system
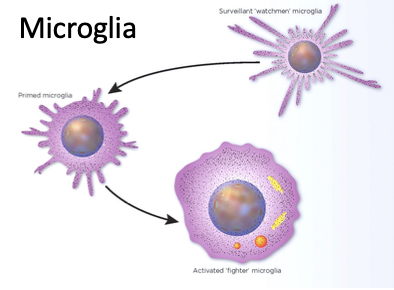
microglia
immune system for the brain - protect from foreign pathogens
covered in receptors
absorb foreign objects and dissect them
Schwan Cell and Oligodendrocytes
myelinating glia (myelinate axons)
Schwan: only myelinate single axons for peripheral nervous system
Oligodendrocytes: myelinate several axons, speed up signals
astrocytes
glial networks - half of the blood-brain barrier, mediate nutrition for the brain (oxygen, glucose)
maintains brain environment (synapse)
repair scarring
gap junctions that create pathways to neighbouring ones that also form reticular nets
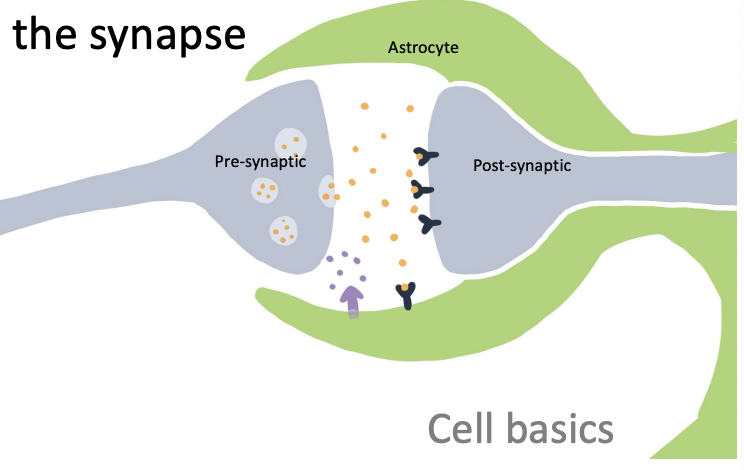
synapse
space between neurons - neurotransmitters released at pre-synaptic, bind at post-synaptic receptors after floating through synapse
pre-synaptic (axon terminal), synapse, post-synaptic (dendrites), astrocyte signals
astrocytes control environment and release chemical messages
glia shape conditions
communication = voltage
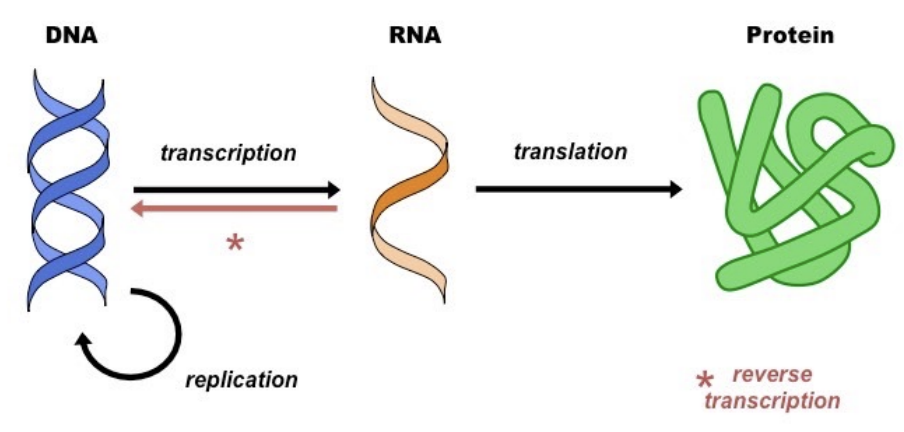
central dogma of molecular biology
DNA → mRNA → Protein
proteins
main character of brain activity, do everything including being the basis for neuronal function
coded by RNA
many of them combine to create genes to create traits
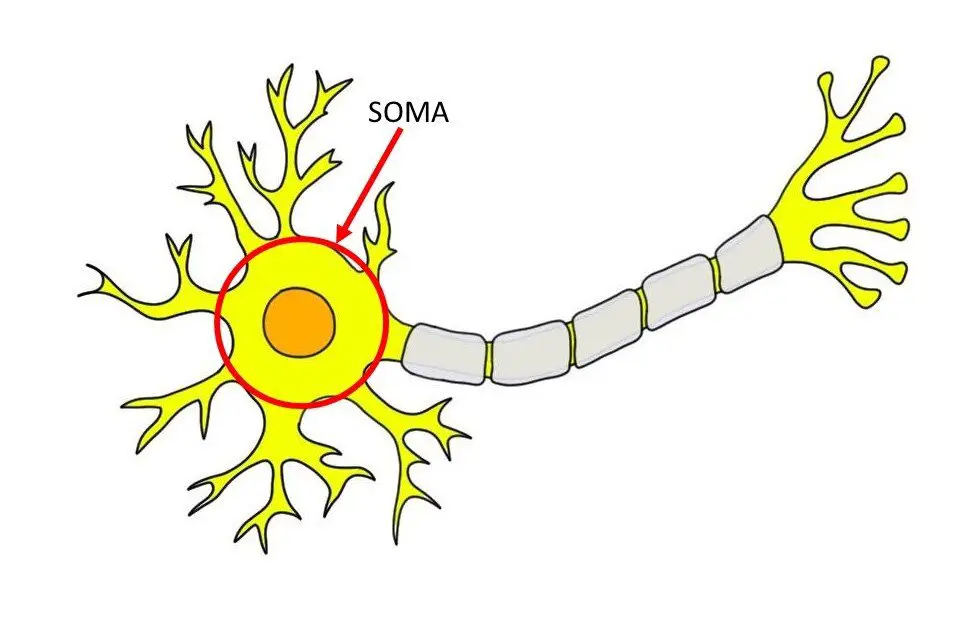
soma
the nucleus in the neuron - tell when and where to code genes, makes RNA
transcription
process by which info in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA)
occurs if activators are present and the repressor is absent
little/no transcription occurs if only one activator is present
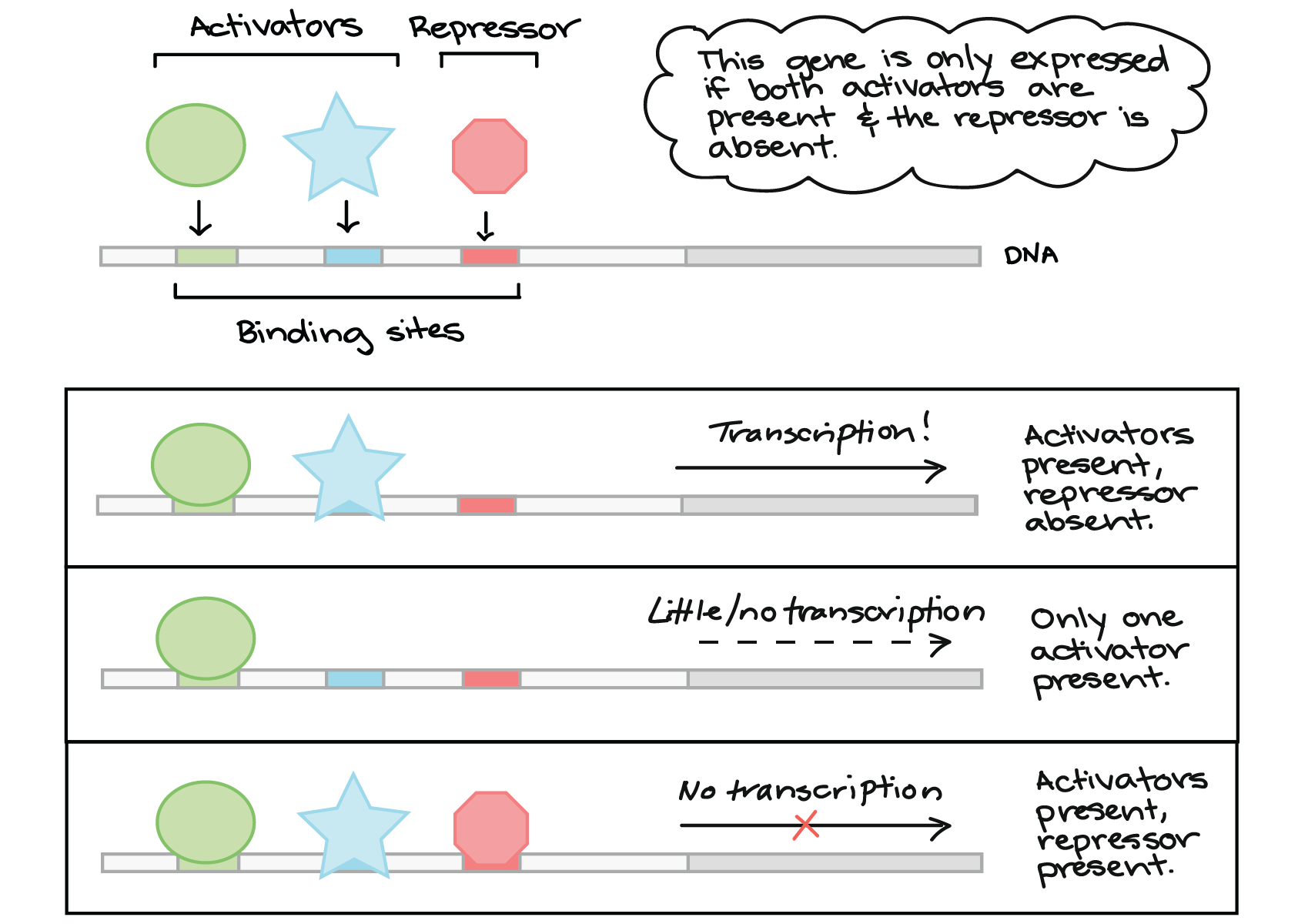
transcription factors
signalling mechanisms that will determine likelihood of gene being transcribed into RNA
Epigenetics (changes gene expression) - depends on tightness of histones around a gene (methylation)
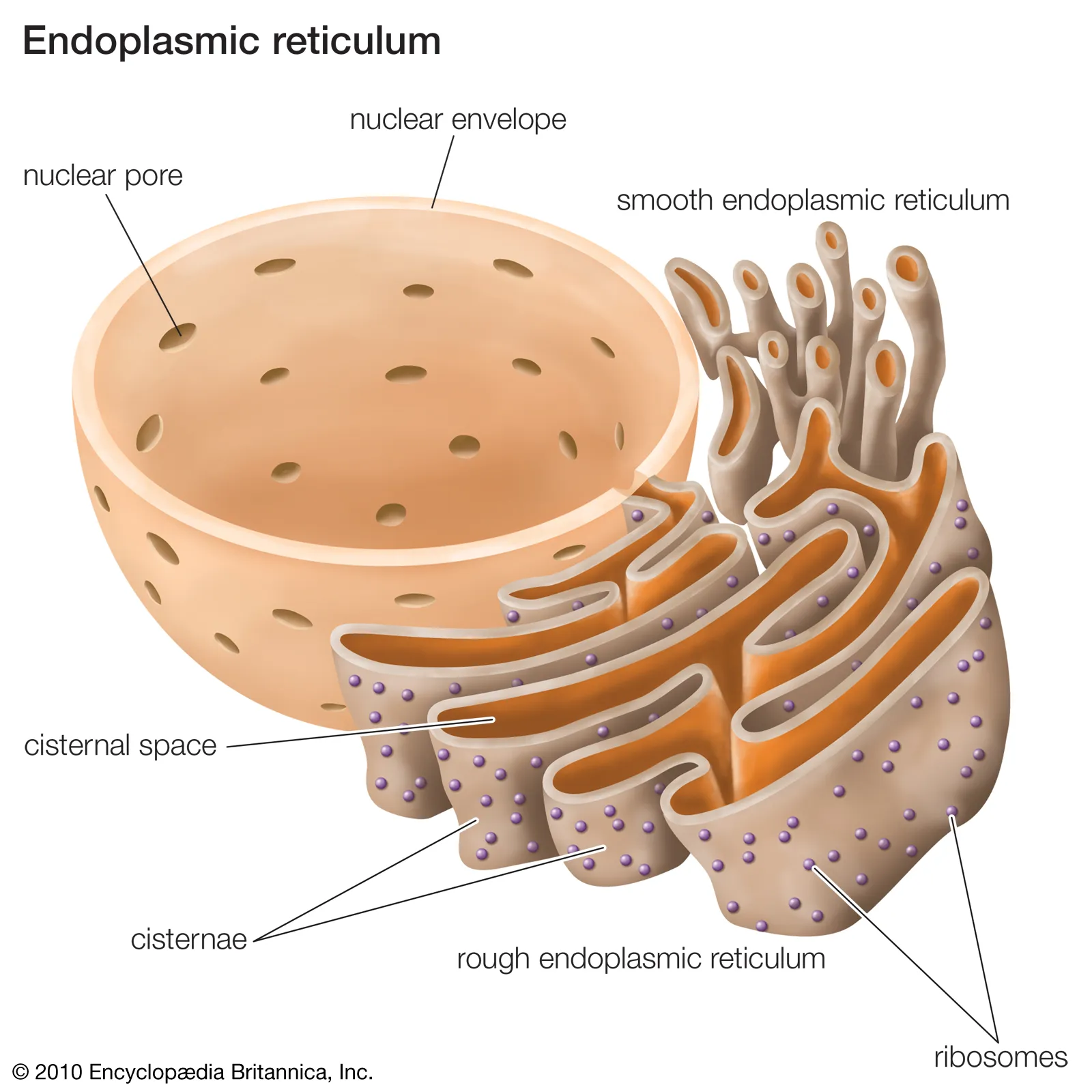
ribosomes
in endoplasmic reticulum - produce proteins
endoplasmic reticulum
membrane pieces that can be transported through out the cell by the golgi apparatus (rough or smooth)
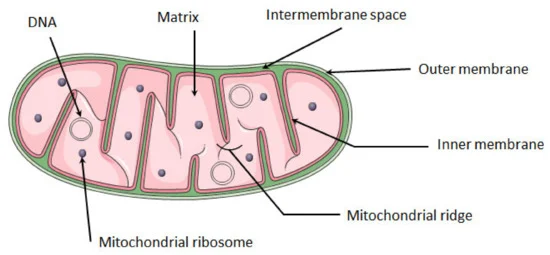
mitochondria
powerhouse of the cell - produce ATP (main energy source)
cell membrane
barrier for any foreign threats trying to enter the cell - has pores for things that should be going in and out
cytoskeleton
structural integrity of the cell, transportation path to and from axon (kinesin = anterograde, dynein = retrograde)
consume ATP to continue transportation
axon
conducts axon potentials in neurons, myelin sheath
dendrites
arms of neurons that receive neural communications
Dendritic spines = spiny neuron (almost all are glutamate receptors)
No dendritic spines = non-spiny neuron (GABA receptors)
glutamate receptors
bind to the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain
GABA receptors
bind to the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
damage: anything from issues with hormone regulation/memory categorization to death
peripheral nervous system
outside of brain and spinal cord - somatic and autonomic nervous system
damage = sensory system impairments, affects brain’s ability to communicate with muscles/organs
somatic nervous system (SNS)
external environment, mostly conscious - bringing info to the brain, acting in outside world
afferent signal: sensory receptors to brain
efferent signal: motor signals from brain to body
damage = cramps/spasms/loss of control (motor nerve damage), loss of touch sensation/numbness (sensory nerve damage)
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
internal environment, mostly non-conscious sensory info (ex. stomach acid)
signals to internal signals - sense some like heart rate, stomach ache, headache
efferent: sympathetic and parasympathetic NS
damage: nerve damage - high blood pressure, sexual difficulties, difficulty digesting food
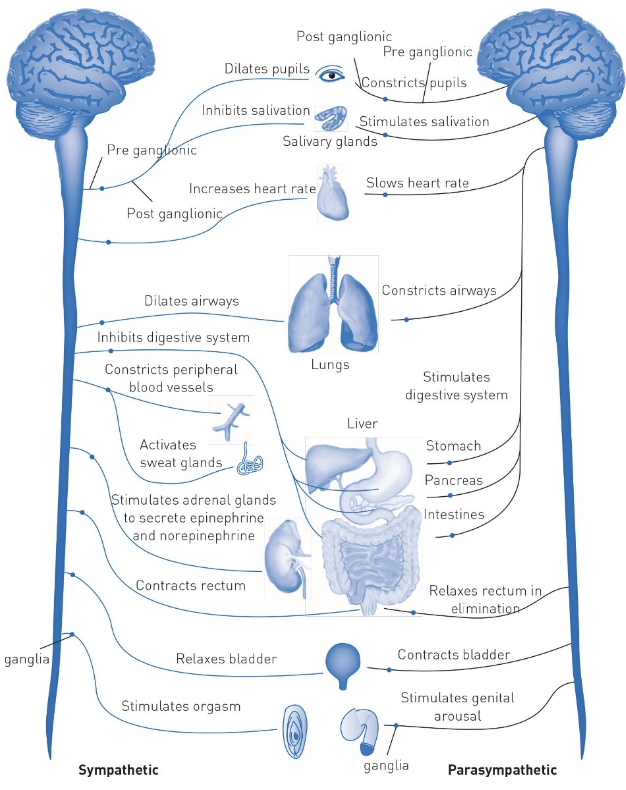
sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system
SNS: mobilizes energy, fight of flight
damage = metabolism problems, heart rate issues, dizziness, sexual dysfunction
PNS: conserves energy
damage = constipation, heart rate problems, sexual dysfunction
not always mutually exclusive or in opposition to one another (like sexual activity)
effects aren’t always generalized across body
cell clusters
CNS: grey matter region - nuclei (different from cell nucleus)
PNS: ganglia
bundle of axons
white matter
CNS: tracts
PNS: nerves
Both: fibres
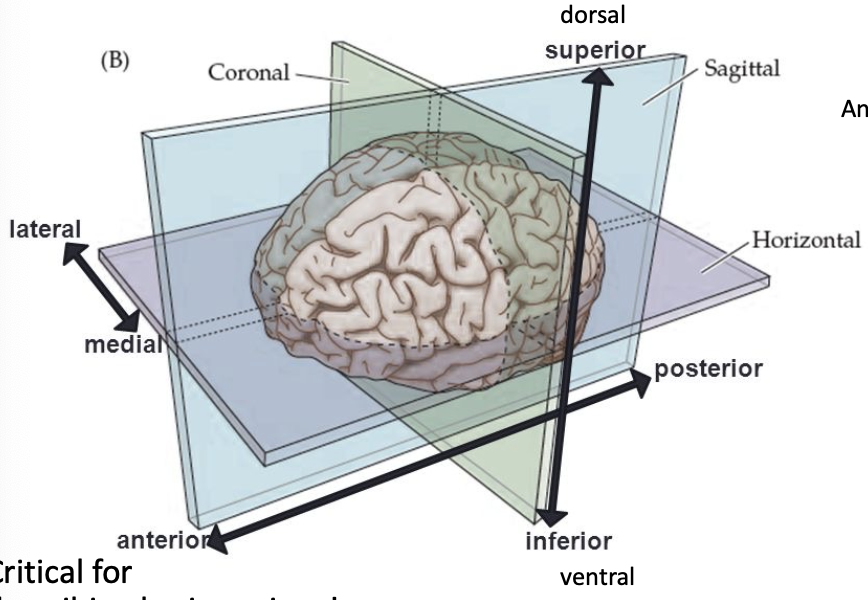
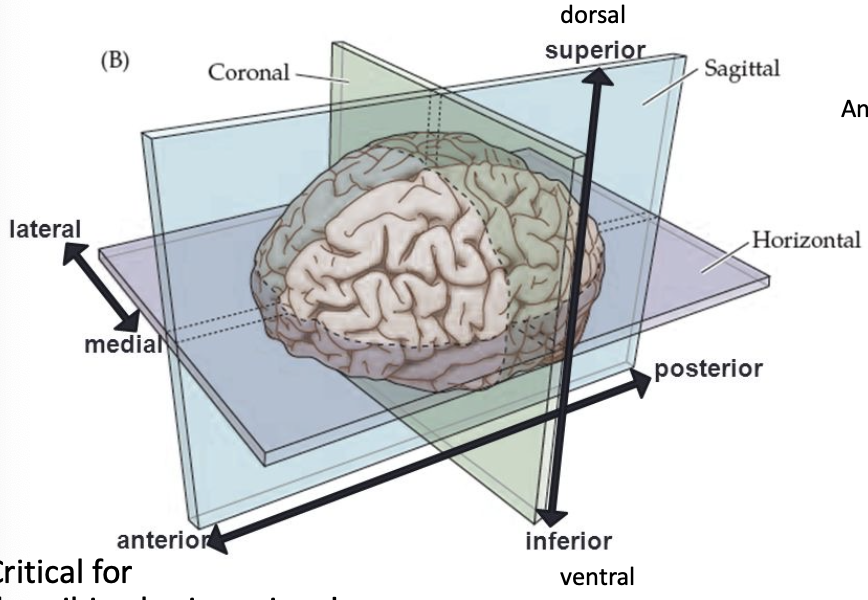
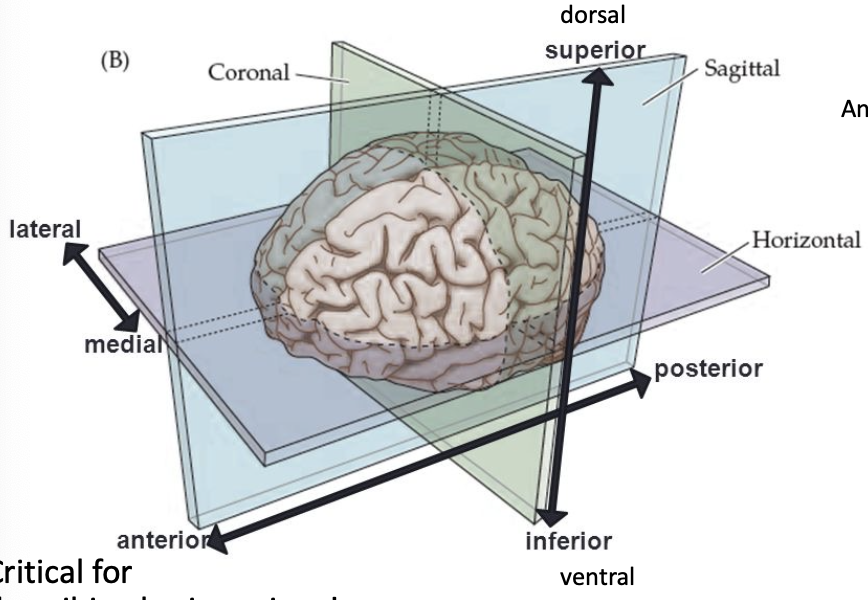
anterior
in front of, toward the face
posterior
behind, toward the back
superior
above, toward the head
inferior
below, toward the feet
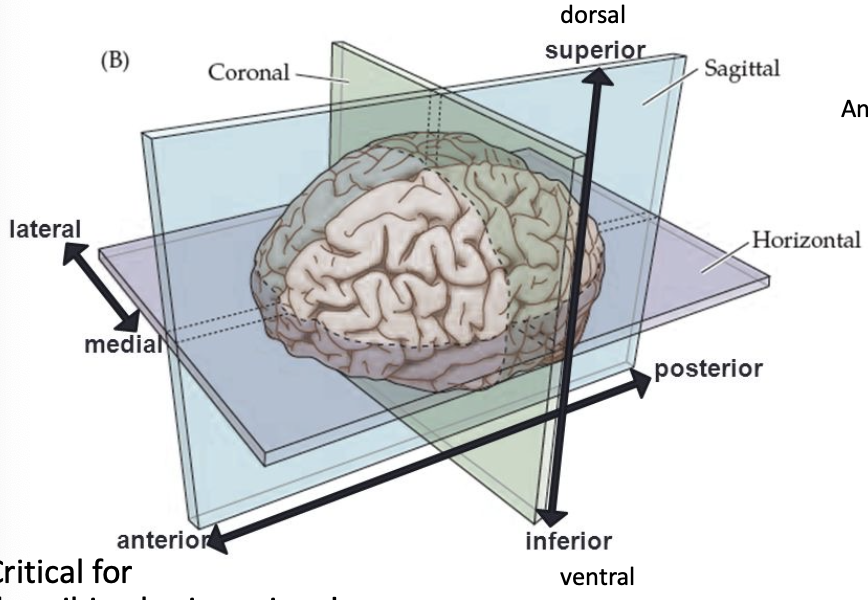
medial
toward the middle
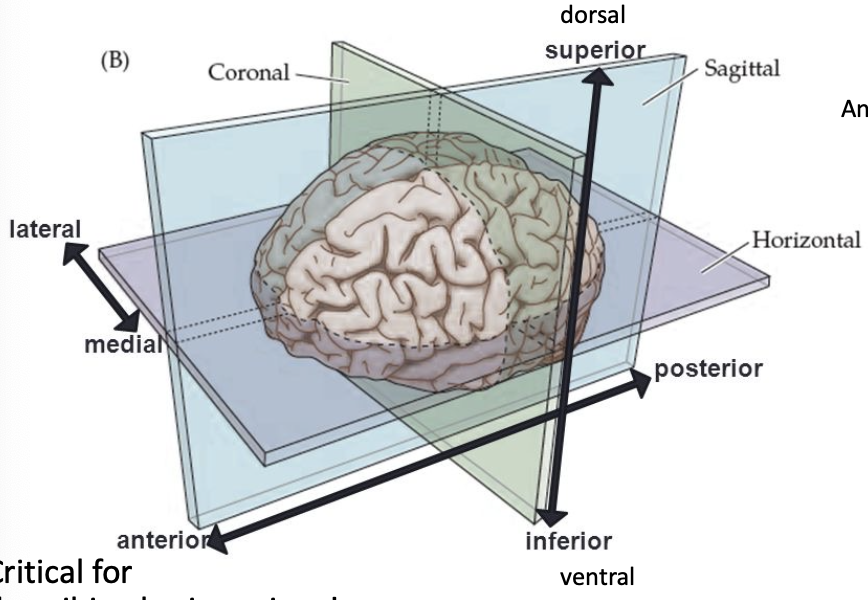
lateral
toward the edge
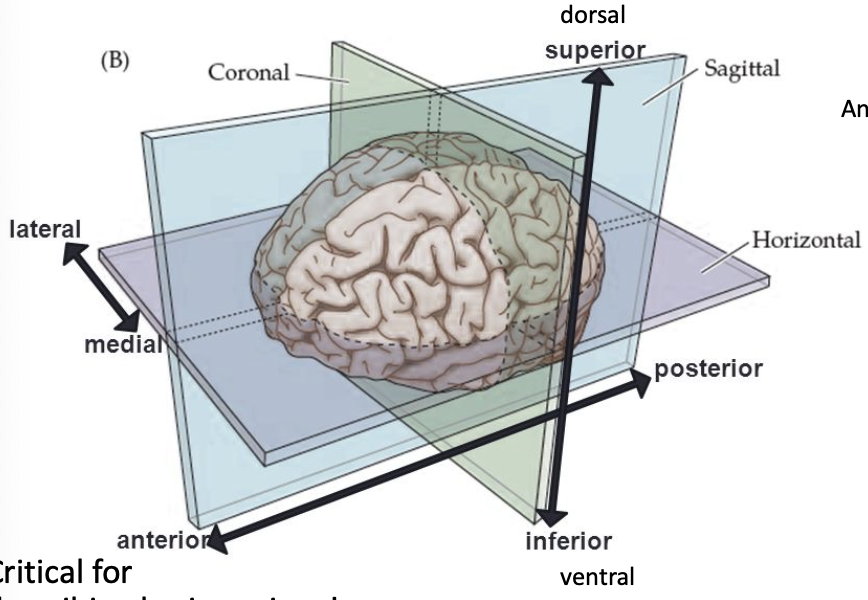
dorsal
toward the top of the brain/back of the spinal cord
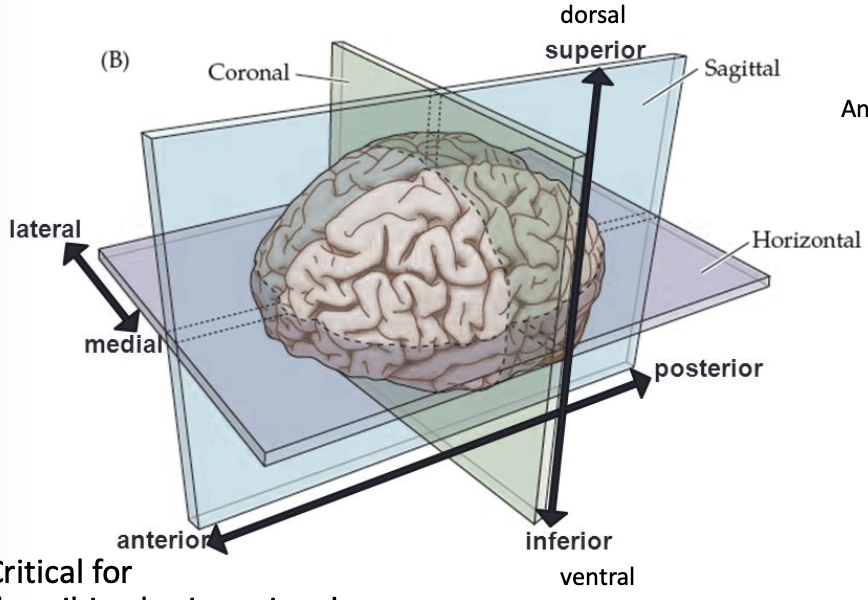
ventral
toward the bottom of the brain/front of the spinal cord
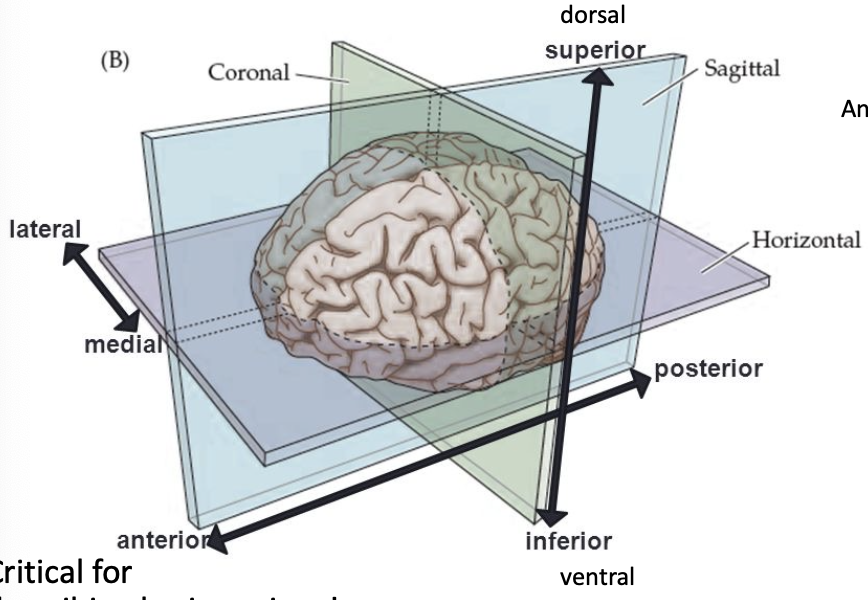
anterior vs. posterior in animals
2-legged: posterior is feet, move vertically to anterior frontal lobe
4-legged: posterior is tail, move laterally to nose
brain sections/cuts
coronal (frontal) section
horizontal section
mid-sagittal (medial) section
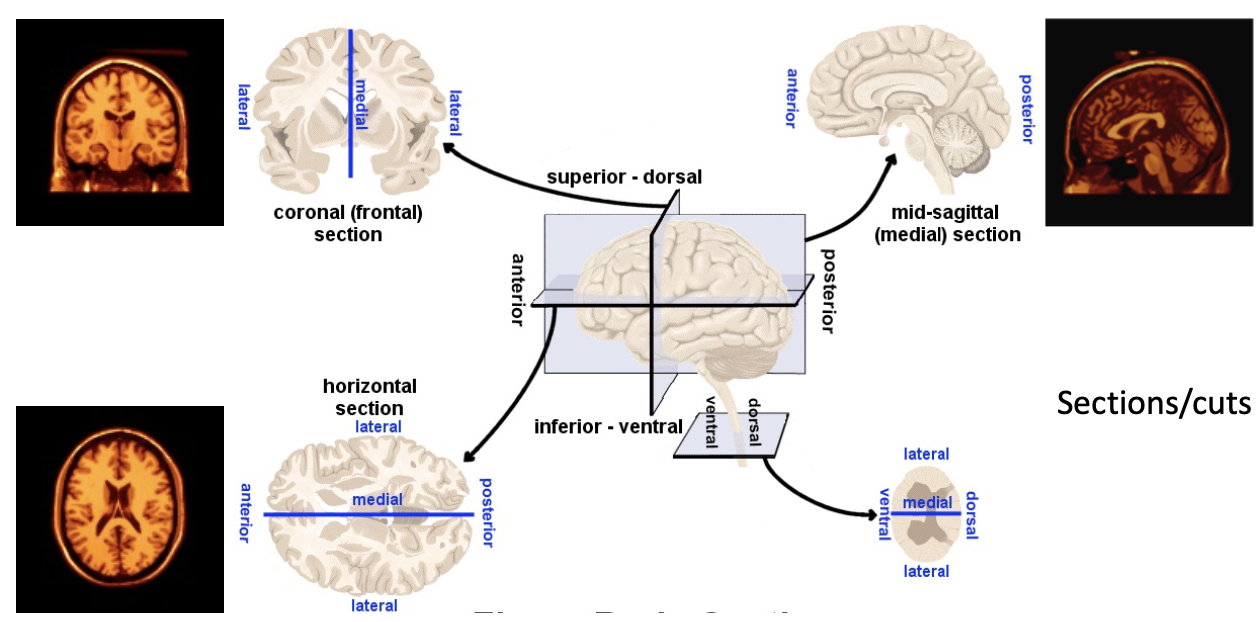
line of symmetry
down the middle of humans (medial to lateral)
indicate direction from patient/participant’s point of view
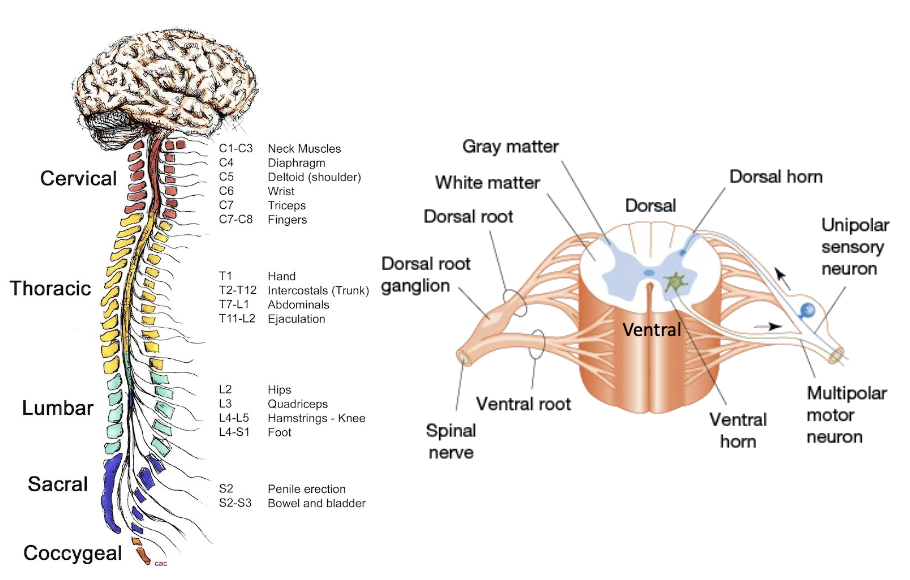
intermittent projections from spinal cord
protected by bone, so axons can only go through this area
cervical nerves
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
sacral
coccygeal
narrow as the move down the spinal cord because axons travel up spinal cord, so there are barely any axons at the end
grey/white matter divisions
dorsal/ventral side organization
spinal cord damage to a spot will also affect everything below it
development of human brain
starts as a neural tube - 3 swellings (forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain)
forebrain
largest part of the brain, responsible for higher cognitive functions.
includes structures
cerebrum: sensory processing, reasoning
Thalamus: sensory information
Hypothalamus: homeostasis, temperature, hunger, and thirst
Limbic System: emotions and memory
disproportionally large
damage considers so much of the brain so anything from issues with decision making or spatial awareness or vision problems to sensory issues to hunger control to motor issues to memory to processing emotion problems
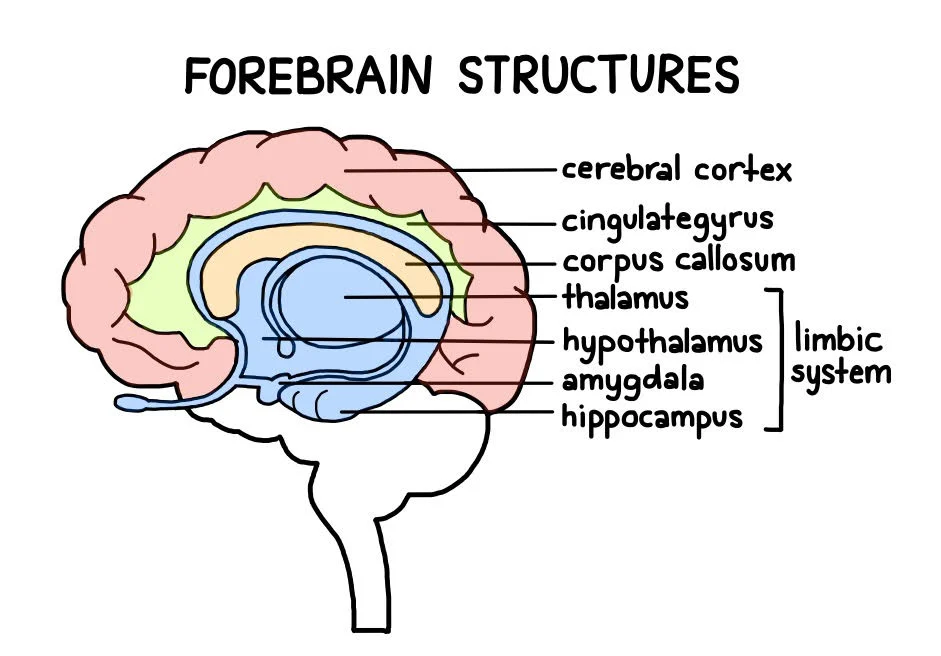
cerebrum
largest/most developed part of the brain (85% of brain’s total weight) - functions include cognition, sensory perception, voluntary motor actions, higher order thinking
left and right hemisphere
cerebral cortex
white matter
lobes (frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital)
basal ganglia
limbic system
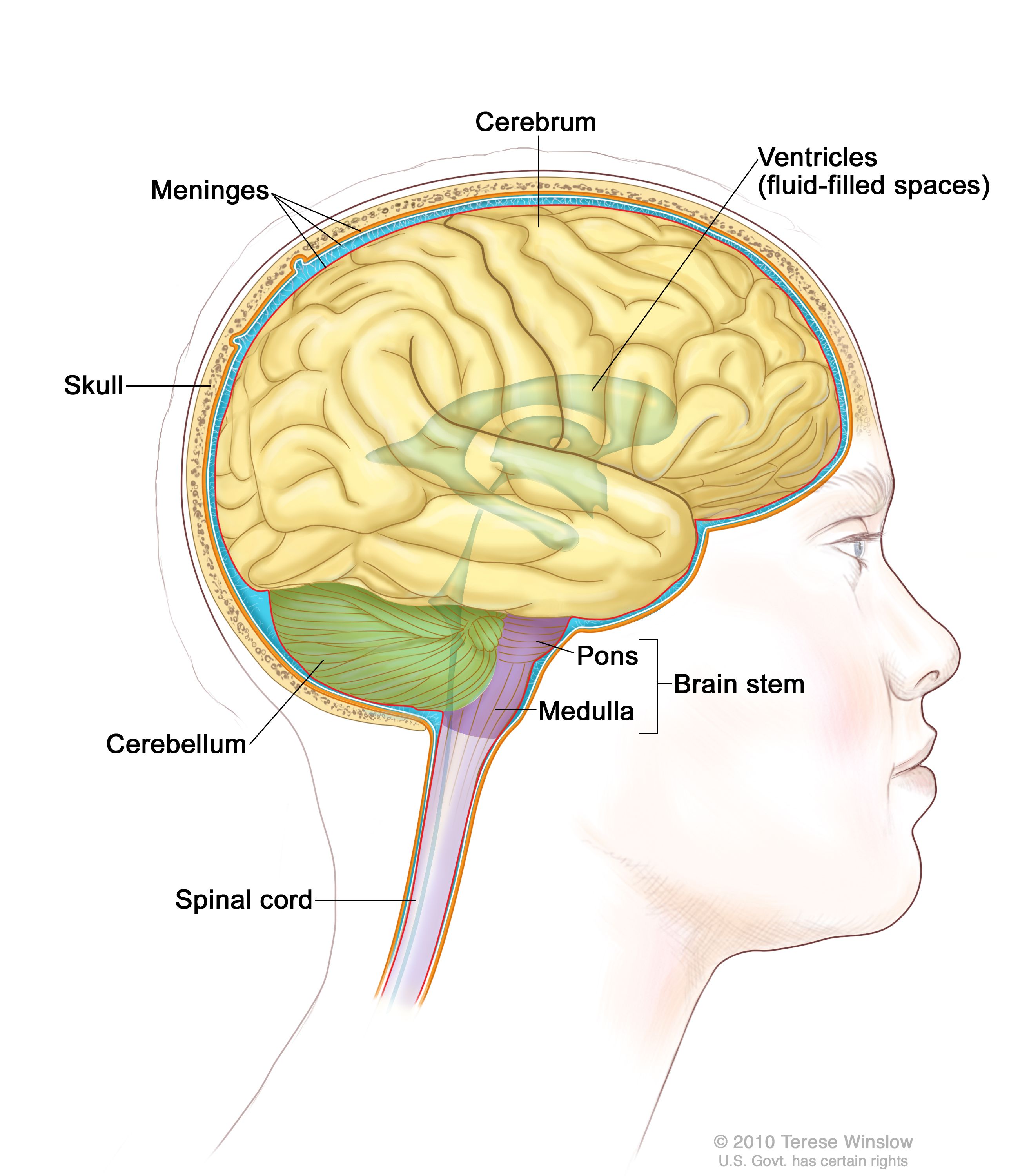
midbrain
vital for
Vision and Hearing: superior and inferior colliculi
Motor Control: regulates movement
Arousal and Alertness: sleep-wake cycle and attention - processing sensory information and coordinating responses
tegmentum
tectum
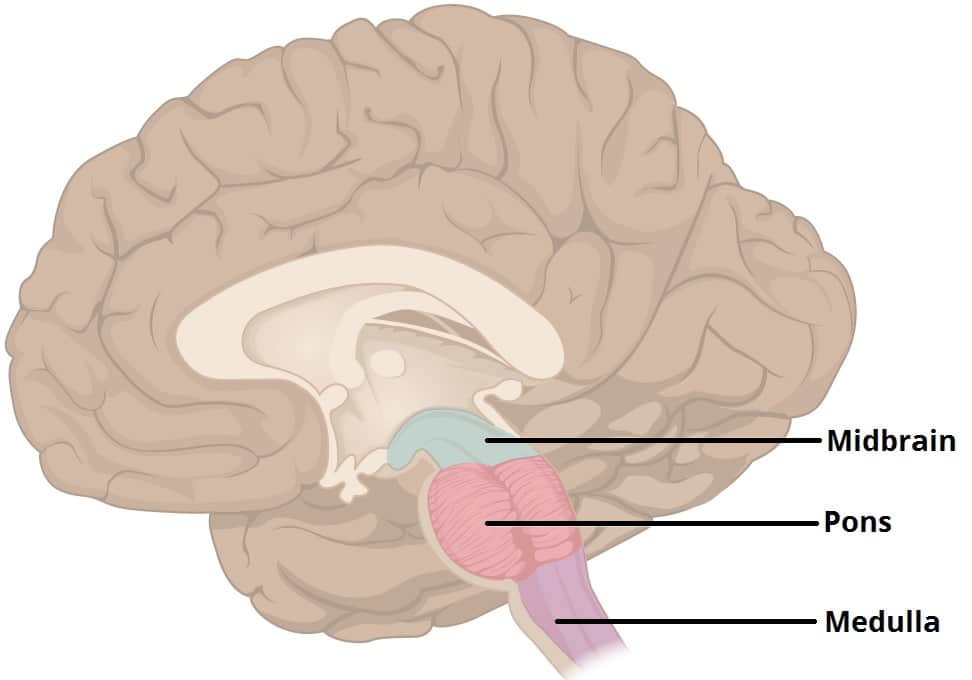
hindbrain
located at the lower back of the skull, consists of three main structures:
Medulla Oblongata
Pons
Cerebellum
medulla oblongata
autonomic functions like breathing and heart rate
pons
connects brain parts, regulates sleep and arousal, holds a lot of myelin (sensory and motor loss when damaged)
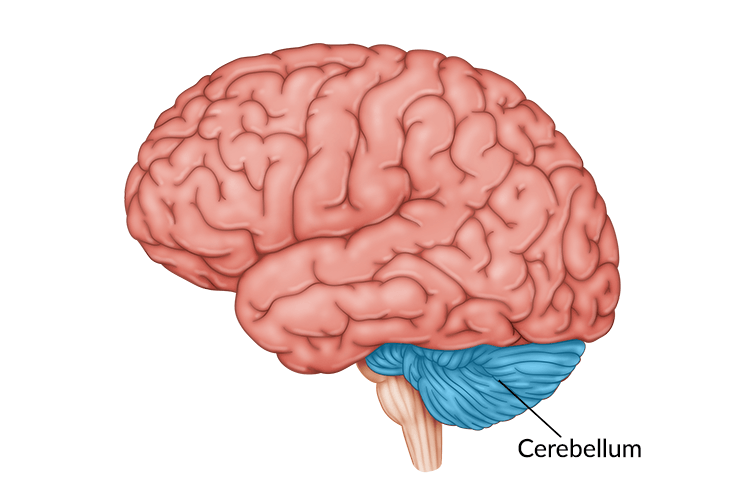
cerebellum
coordination, balance, correcting what you did with what you meant to do - essential for vital bodily functions and motor control.
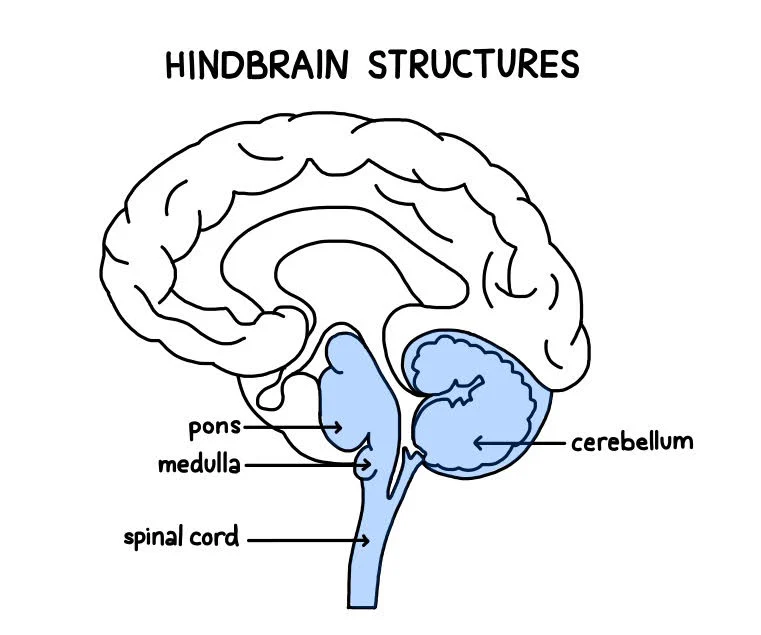
myelencephalon
most posterior region of the brain - medulla oblongata
adjacent to spinal cord
lots of tracts (afferent signals going in, efferent going out)
damage here is often fatal
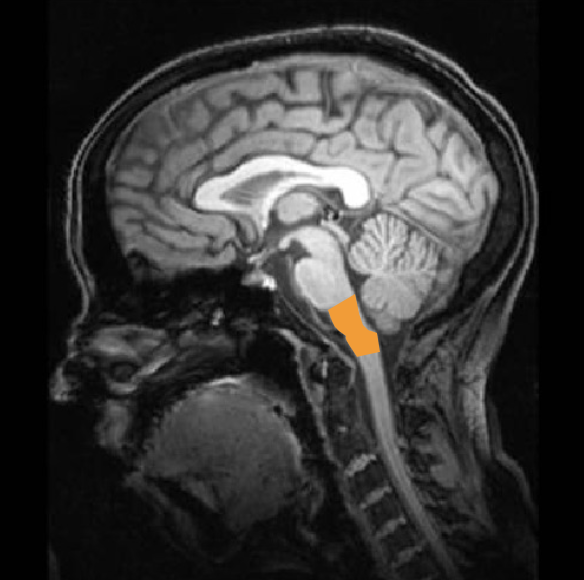
reticular formation
brain stem - runs from myelencephalon to mesencephalon
critical for arousal, wakefulness, attention, sleep
damage to this region can be critical/fatal
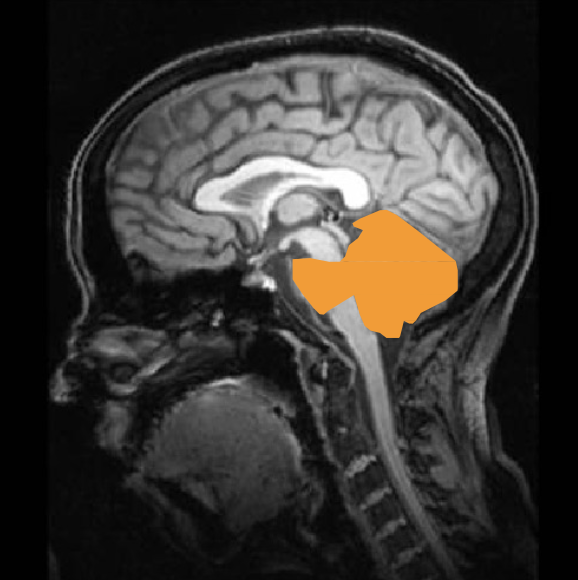
metencephalon
ventral side: pons - lots of tracts, strokes can cause sensory/motor impairments, difficulties with wakefulness
dorsal side: cerebellum - critical for motor coordination, but being born without is manageable (damaging it later on is difficult)
alcohol affects cerebellum and balance when drunk
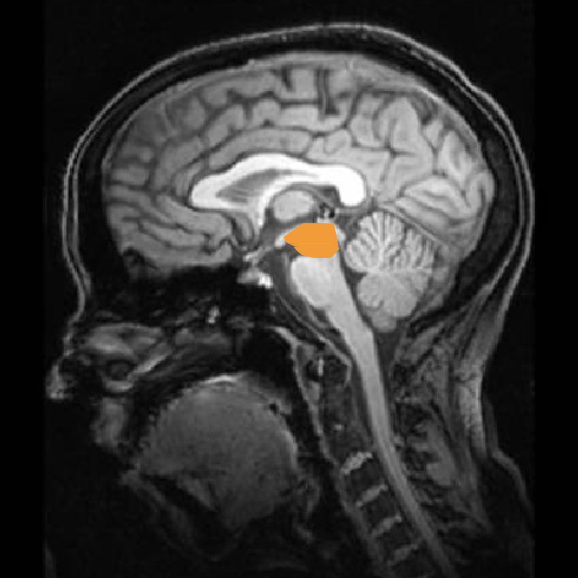
mesencephalon
midbrain - roof (tectum, dorsal side), floor (tegmentum, ventral side)
damage = vision/hearing problems, ataxia, lack of pain inhibition, tremors, motor deficits
tegmentum
reticular formation, fibres, periacqueductal grey (amygdala connection) (dopamine producing regions, linked to movement, motivation; red nucleus)
tectum
colliculi (vision with respect to eye movement, audition with respect to orientation)
diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
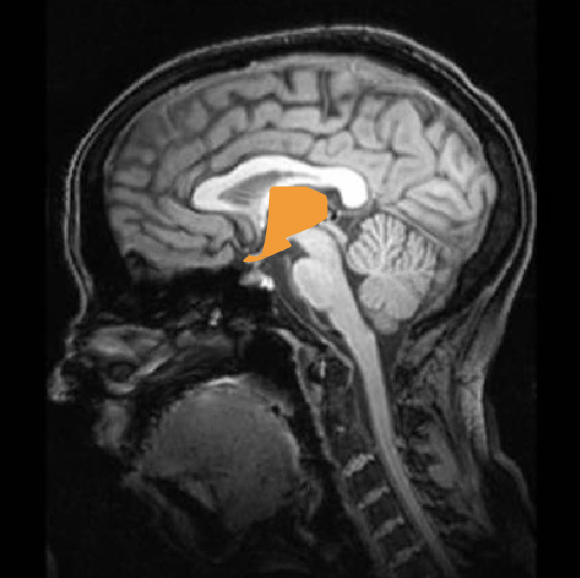
thalamus
“relay” centre for sensory information, receives almost as much from cortex as it sends to cortex
another site of modification, reverberate connection
damage = sleep disorders, sensory problems
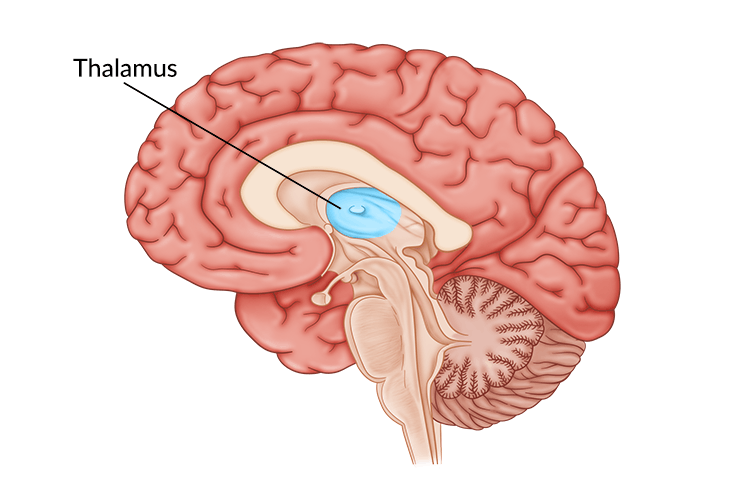
hypothalamus
interacts with with endocrine system via pituitary gland to influence hormonal release - affects sex, aggression, feeding, sleep, wake
damage = uncontrollable behaviours like eating compulsively or halting these behaviours, narcolepsy, sex aggression
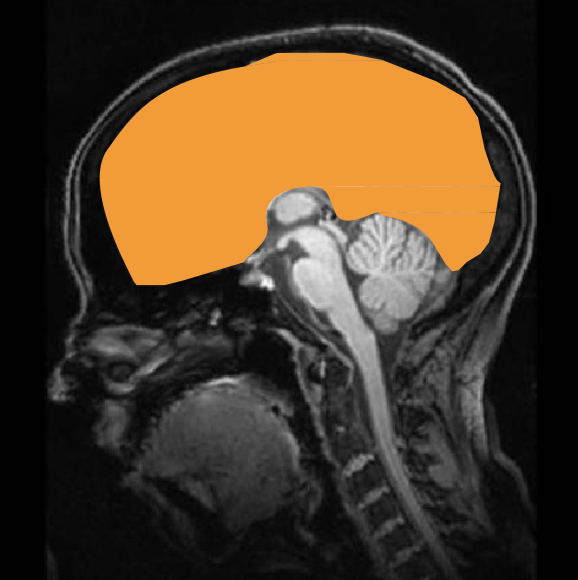
telencephalon
largest and most sophisticated division of brain - cortex and underlying structures
cerebral cortex
convolutions
cerebrum hemispheres
commissures
limbic system
basal ganglia
cerebral cortex
outermost layer of brain - sulci grooves and raised gyri
layered
convolutions (continuous)
commissures
connect the two hemispheres
largest = corpus callosum