2. Tables, Graphs & Charts
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Types of Graphical Displays on the TEAS
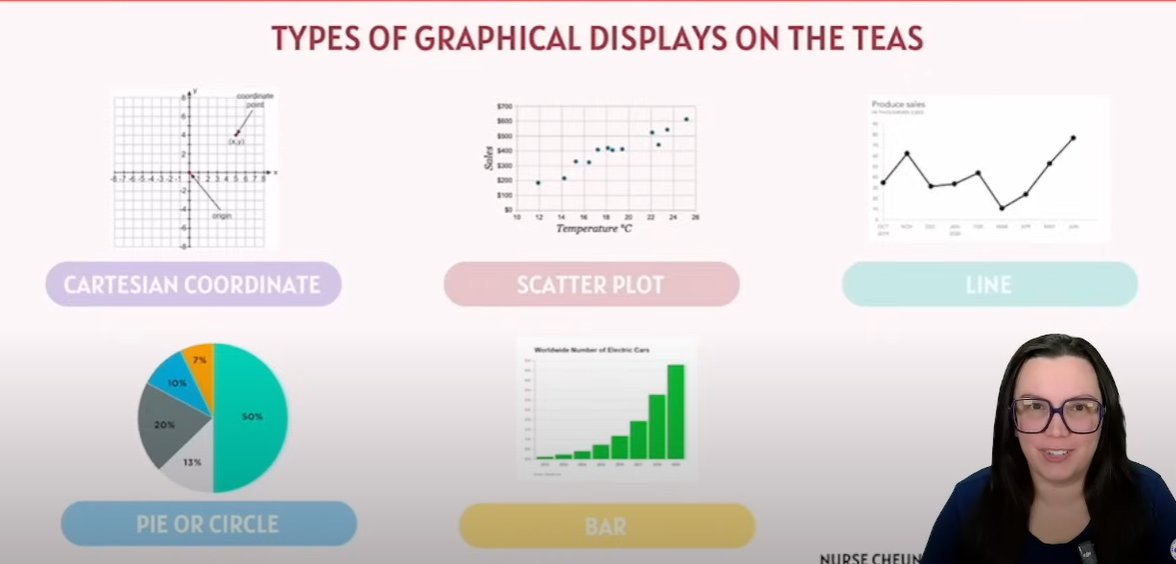
Cartesian Coordinate
When to use ?
How one variable relates another
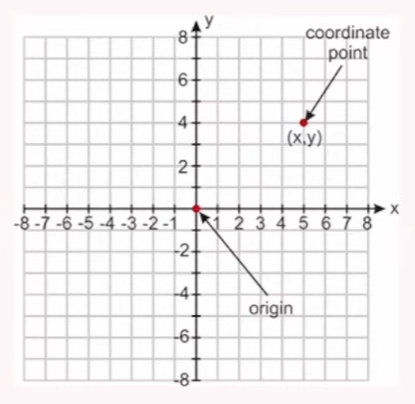
Scatter Plot
When to use ?
Correlation btw variables
Line Graph
When to use ?
Trends over time or continuous data

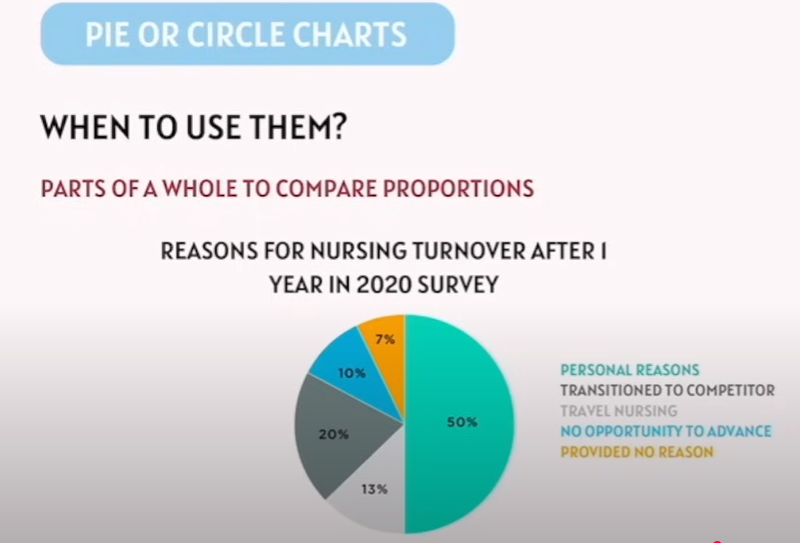
Pie or Circular Charts
When to use ?
Parts of whole to compare promotions
Bar Graphs
When to use ?
Compare btw different groups or categories
Overviews

Graphical Trend
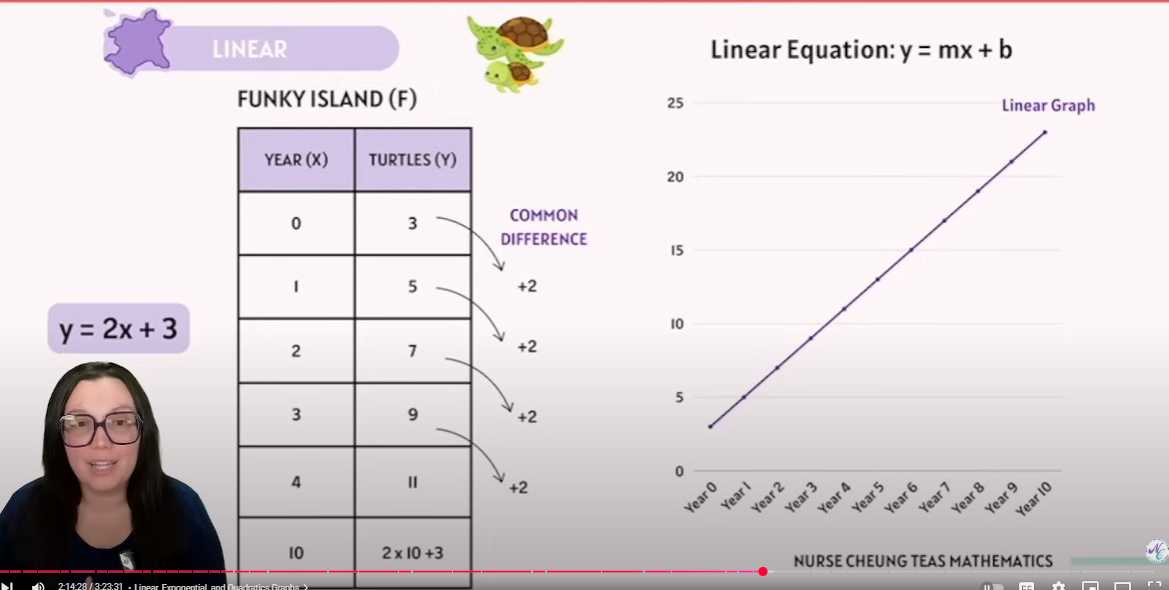
Linear: every equal step in xxx adds the same amount to yyy.
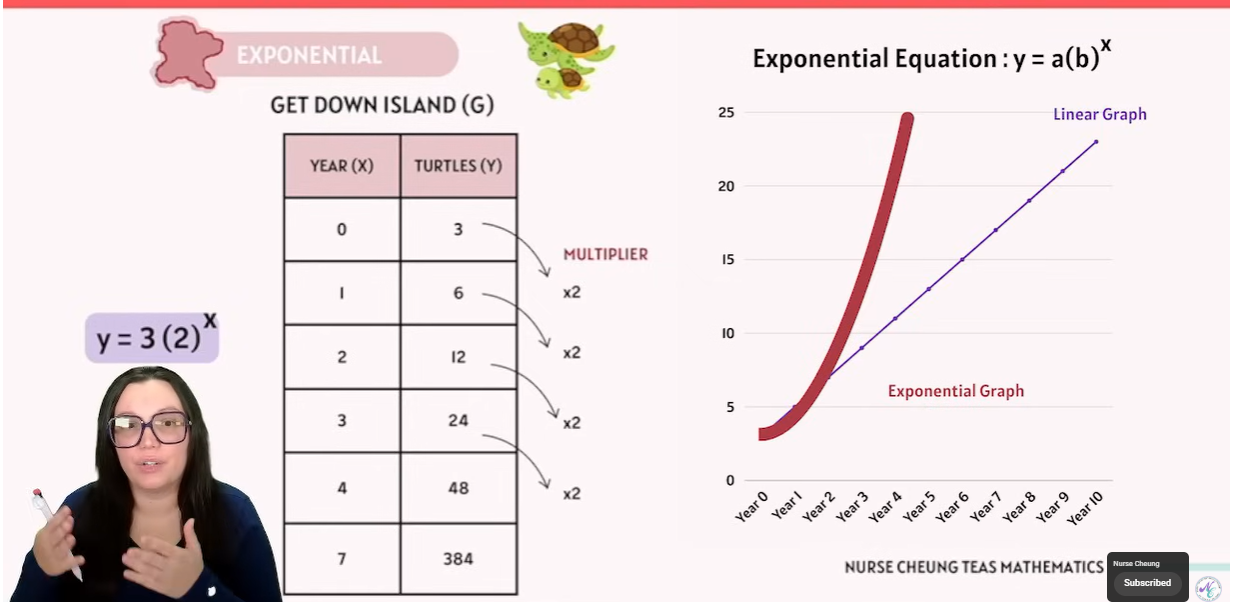
Exponential: each step multiplies yyy by a constant factor.
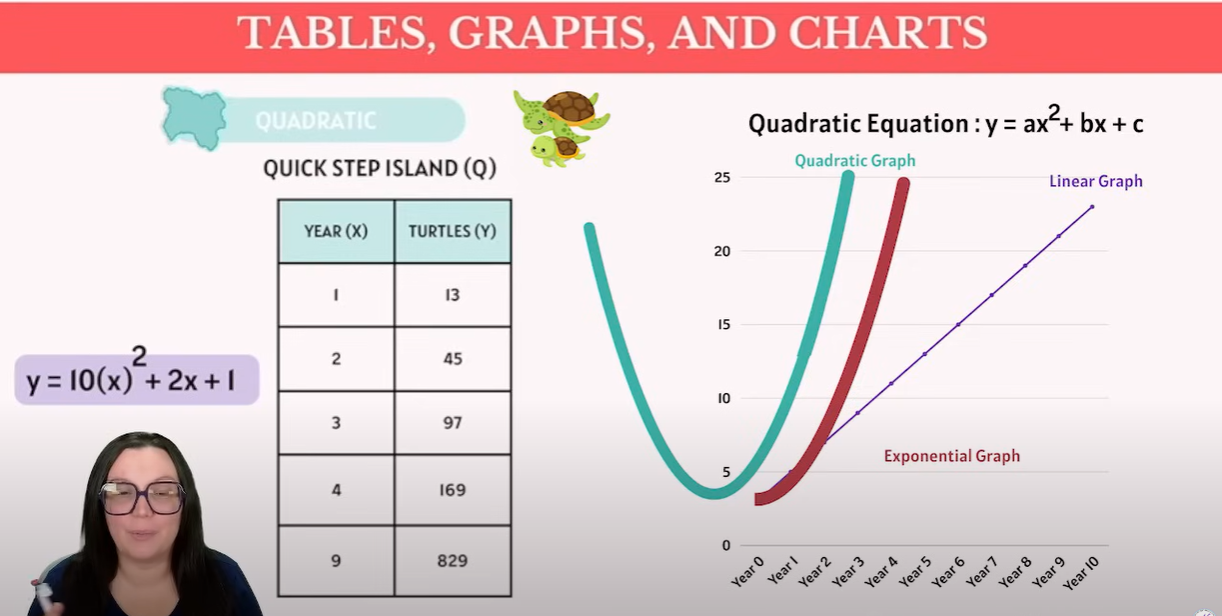
Quadratic: change in yyy accelerates (or decelerates) at a constant rate—producing a “U” or inverted “U.”
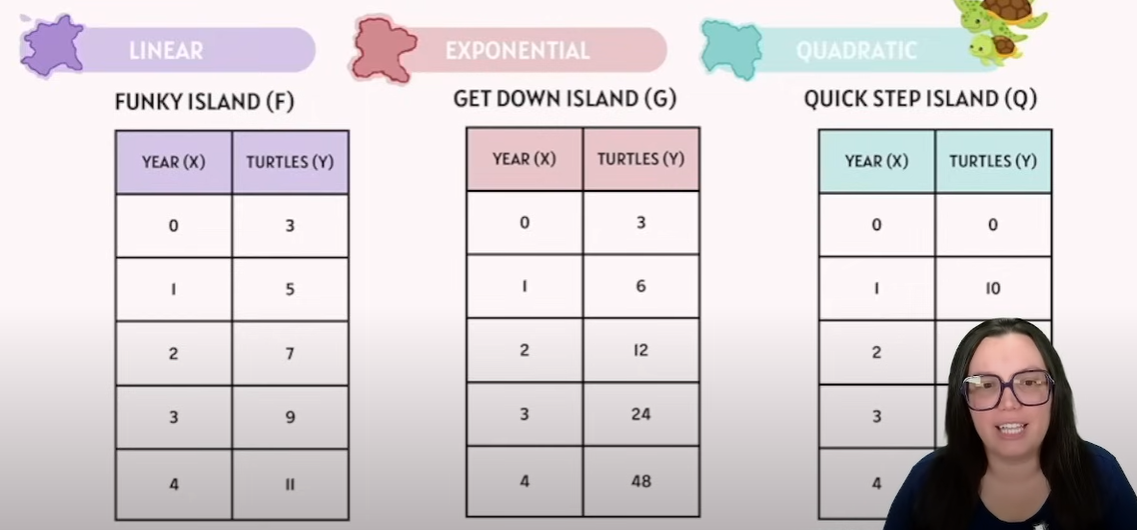
Linear
y =mx +b
Exponential
y = a(b)2
Quadratic
y = ax2+bx+c
Direction of Trends in Graphs
What concave,

DENEPENDT & INDEPENDENT
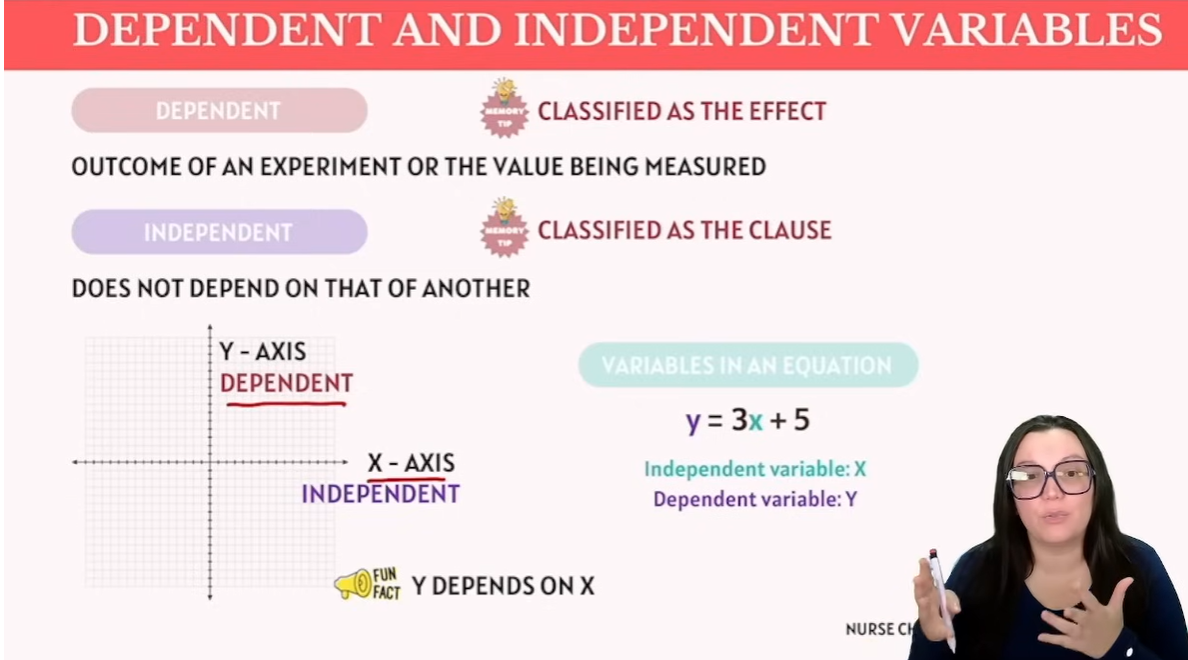
Correlation/Covariance
Type of Correlation | Definition | Graphical Pattern | Direction of Change |
|---|---|---|---|
Positive Correlation | As one variable increases, the other tends to increase. | Points clustered around an upward‐sloping line. | X ↑ → Y ↑ |
Negative Correlation | As one variable increases, the other tends to decrease. | Points clustered around a downward‐sloping line. | X ↑ → Y ↓ |
No Correlation | Changes in one variable do not consistently predict changes in the other. | Points scattered with no clear trend. | No consistent relationship |
Direct & Inverse (Indirect) Relationship
Relationship | Equation | Description | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
Direct | y=kxy = kx | Two variables change proportionally in the same direction. | x↑ ⟹ y↑x\uparrow \implies y\uparrow |
x↓ ⟹ y↓x\downarrow \implies y\downarrow | |||
Inverse (Indirect) | y=kxy = \tfrac{k}{x} | Two variables change proportionally but in opposite directions. | x↑ ⟹ y↓x\uparrow \implies y\downarrow |
x↓ ⟹ y↑x\downarrow \implies y\uparrow |
kkk is the constant of proportionality in both cases.
Direct (also “directly proportional”) describes, for example, distance traveled as speed increases.
Inverse (also “indirectly proportional”) describes, for example, the pressure of a fixed amount of gas as its volume changes.
Circle Circumference & Area Calculation
Concept | Definition | Formula | Memory Tip |
|---|---|---|---|
Circumference | Perimeter of the circle, i.e. the distance around its edge | C=π×d C = \pi \times d | “Cherry pie’s delicious” |
Area | Region covered or enclosed within the circle’s boundary | A=π×r2 A = \pi \times r^2 | “Apple pies are too” |
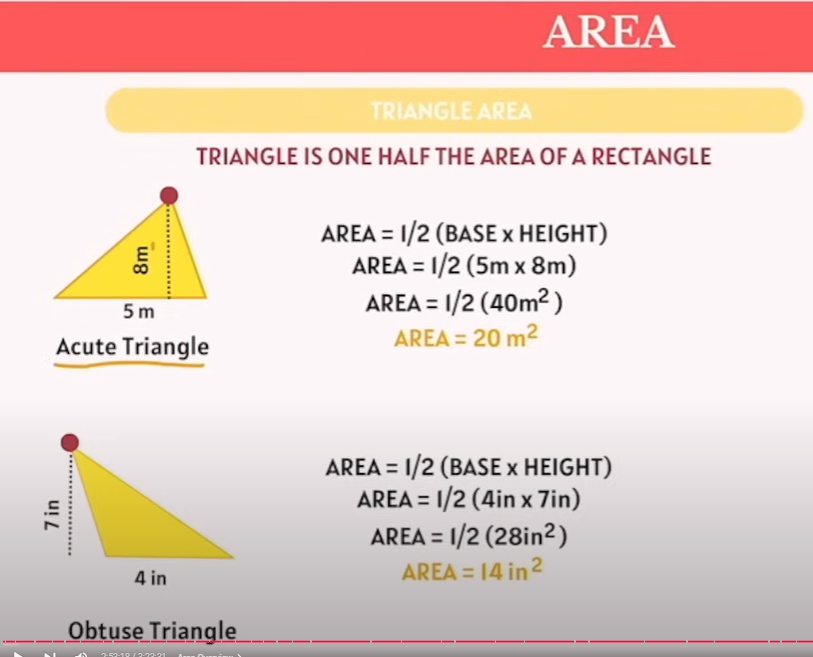
Triangle area calculation

Parallelogram & Trapezoid Area

Special Area

Triangle Prism Volume

3-D Space Volume - Cylinder
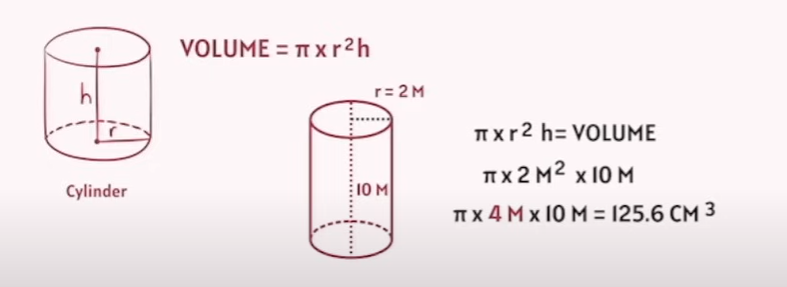
3-D Space Volume - Cone

3-D Space Volume - Rectangular Pyramid

3-D Space Volume - Sphere
Every time we deal with volume with circle, we Cube it
Every time we deal with are with circle, we Square it
