ESS - Section 1: "Earth Structure and Movement"
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1
New cards
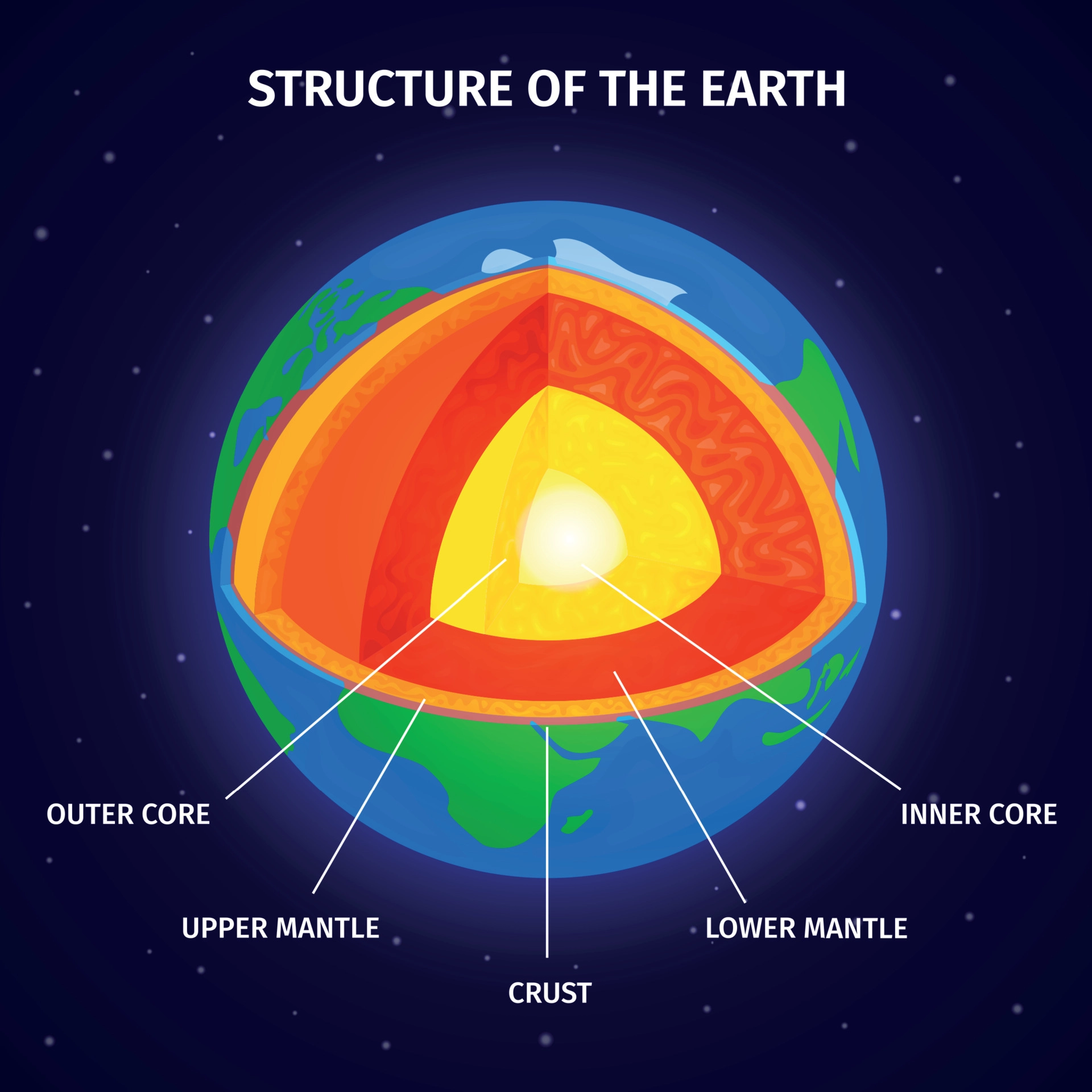
What are the layers of the Earth?
Crust, Lithosphere, Asthenosphere, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core
2
New cards
What is the Asthenosphere?
The asthenosphere is the denser, weaker layer beneath the lithosphere and mantle. It lies between about 100 kilometers and 410 kilometers beneath Earth's surface.
3
New cards
What is the Lithosphere?
A lithosphere is the rigid, outermost rocky shell. It is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more.
4
New cards
What is the average temperature of the crust?
Crust: 14°C (Surface), 200-400°C (Near Moho)
5
New cards
What is the average temperature of the mantle?
Mantle: 1000°C (Near Moho), 3700°C (Near Core)
6
New cards
What is the average temperature of the outer core?
Outer Core: 4500-5500°C
7
New cards
What is the average temperature of the inner core?
Inner Core: 5,200°C
8
New cards
What is the thickness of the Crust?
Crust: 30–70km (continental), 6–12km (oceanic)
9
New cards
What is the tickness of the Mantle?
Mantle: ~2,900km
10
New cards
What is the thickness of the Outer Core?
Outer Core: ~2,200km
11
New cards
What is the thickness of the Inner Core?
Inner Core ~1,200km
12
New cards
What are the three main elements in the Earth's crust?
oxygen
silicon
nitrogen
silicon
nitrogen
13
New cards
What is the composition of the Earth's crust?
Solid Rock
14
New cards
What is the composition of the Mantle?
Solid Rock
15
New cards
What is the composition of the Outer Core?
Liquid Iron-Nickel Mixture
16
New cards
What is the composition of the Inner Core?
Solid Iron-Nickel Mixture
17
New cards
What is the density of the Earth's crust?
Continental: 2.7 g/cm3
Oceanic: 2.9 to 3 g/cm3
Oceanic: 2.9 to 3 g/cm3
18
New cards
What is the density of the Mantle?
4.5 g/cm3
19
New cards
What is the density of the Outer Core?
12.6-13 g/cm3
20
New cards
What is the density of the Inner Core?
9.9-12.2 g/cm3
21
New cards
Why do different layers have different compositions and consistencies?
Denser materials, like iron and nickel, sank to the core. Lighter materials, like aluminum and silicon, stayed closer to the Earth's surface. The crust and mantle are solid as they are not hot enough to be molten. The outer core is molten as it is hot enough, but the inner core is solid, even though there is enough heat for it to be molten, the pressure compresses it into a solid.
22
New cards
What is the theory of plate tectonics?
Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise of a number of large tectonic plates which are slowly moving.
23
New cards
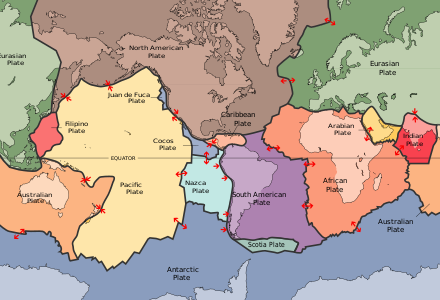
What are the main seven plates?
African, Antarctic, Eurasian, Indo-Australian, North American, Pacific and South American.
24
New cards
What are the minor plates?
Nazcar, Philippine, Arabian, Caribbean, Cocos, Caroline, Scotia, Burma, New-Hebridies
25
New cards
What is the role of convection currents and heat energy in plate tectonics?
Convection currents drive the movement of Earth's rigid tectonic plates in the planet's fluid molten mantle. In places where convection currents rise up towards the crust's surface, tectonic plates move away from each other in a process known as seafloor spreading .
26
New cards
What are faults?
At a small scale level, stress in the crust can cause layers of rock to crack or fracture. A fault is a rock fracture where the two sides have been displaced relative to each other.
27
New cards
What are the three types of faults?
- Normal Fault
- Reverse Fault
- Strike-slip Fault
- Reverse Fault
- Strike-slip Fault
28
New cards
What is a normal fault?
A normal fault is a type of dip-slip fault where the hanging wall moves downwards from the footwall.
29
New cards
What is a reverse fault?
In a reverse fault, the hanging wall has moved up relative to the footwall.
30
New cards
What is a strike-slip fault?
A fault in which rock strata are displaced mainly in a horizontal direction, parallel to the line of the fault.
31
New cards
What is seafloor spreading?
Seafloor spreading is when two oceanic plates at a divergent boundary part and magma rises, cools and solidifies to form new igneous rock.
32
New cards
What is a constructive plate boundary?
At a constructive plate boundary - also known as a divergent plate boundary - the plates are moving apart from one another. When this happens, the magma from the mantle rises up to make (or construct) a new crust. The movement of the plates over the mantle can cause earthquakes.
33
New cards
What is a destructive plate boundary?
At a destructive plate boundary - also known as a convergent plate boundary - when two plates collide. When this happens, one plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. This subduction draws magma up and creates volcanic mountains.