AP Art History Unit 3 Greco Roman - Greek Art
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
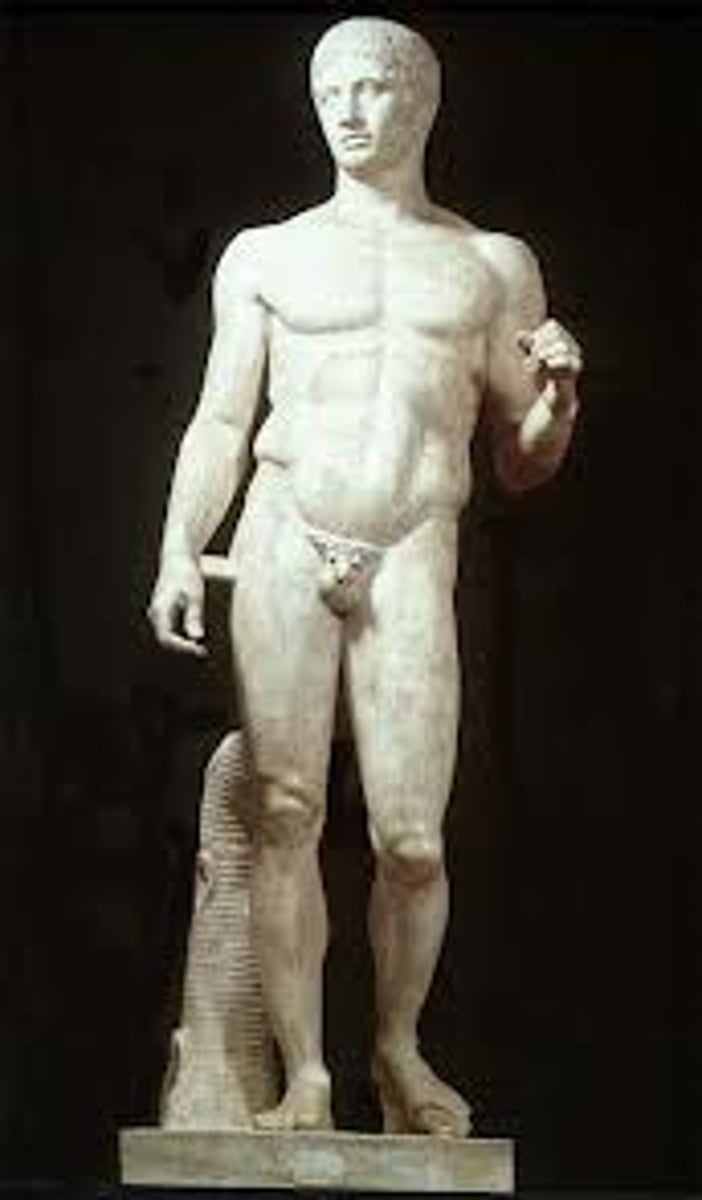
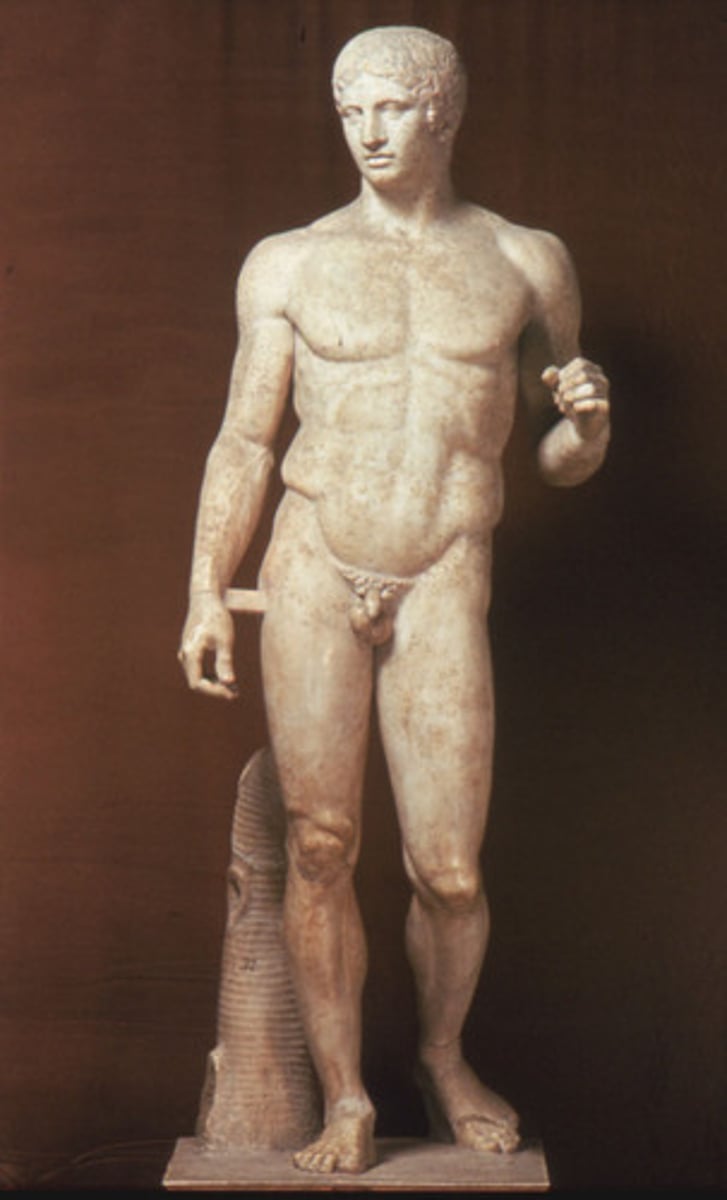
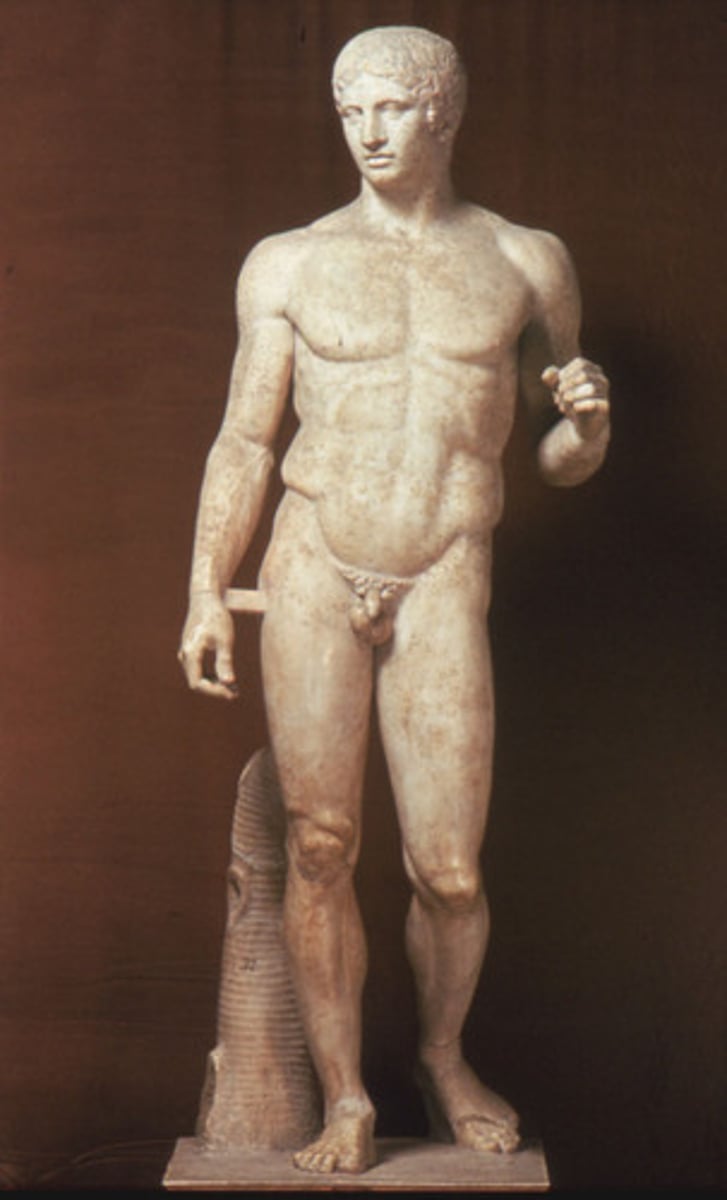
Doryphoros (Spear Bearer)
450-440 BCE

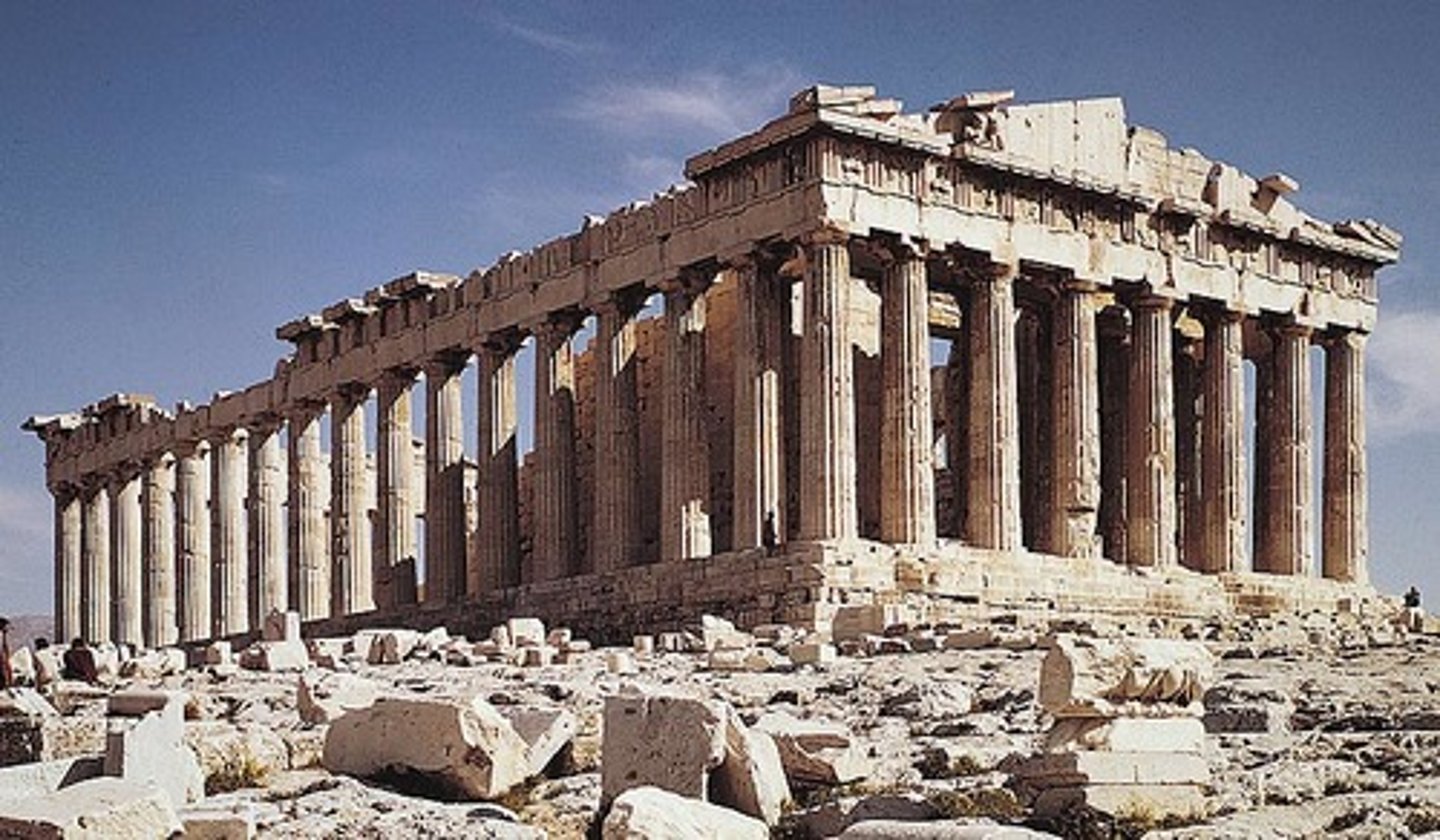
The Parthenon
447-410 BCE

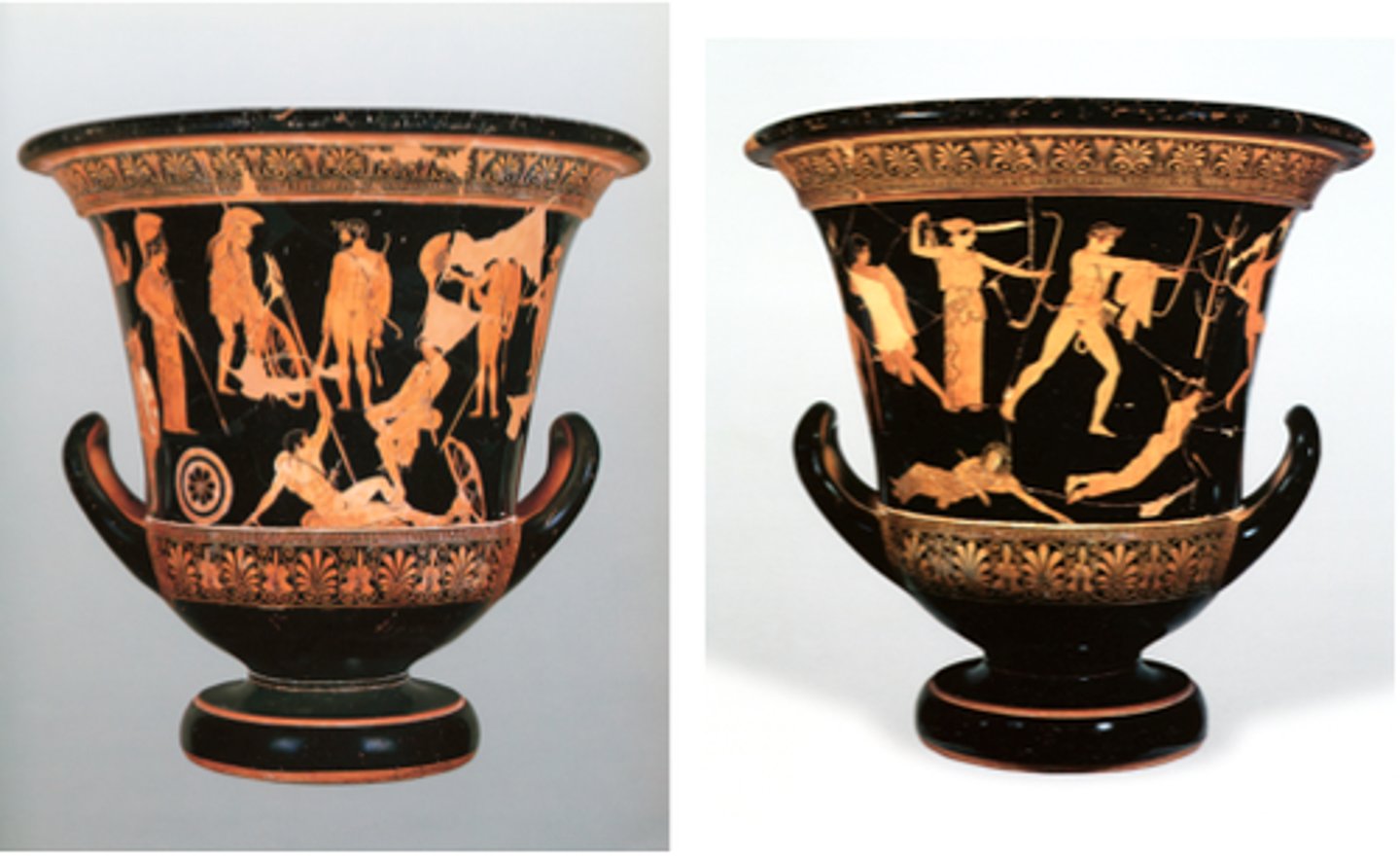
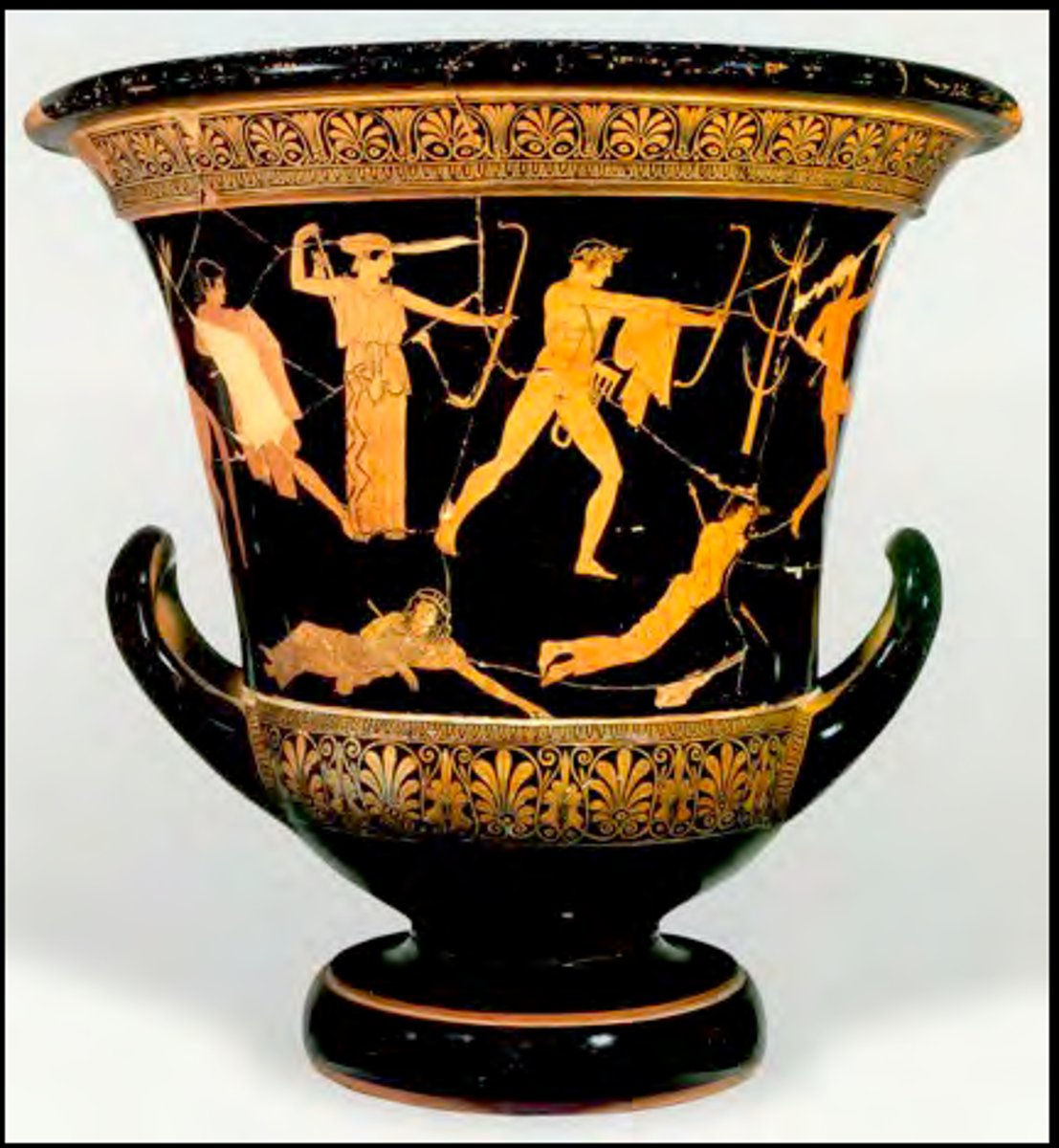
Niobides Krater
460-450 BCE

Ancient Mediterranean, 3500 BCE - 300 CE
Content Area
480-323 BCE
Greek Classical Art
323-30 BCE
Greek Hellenistic Art
Niobe
the model of a grieving mother; after boasting of her fourteen children, jealous gods killed them

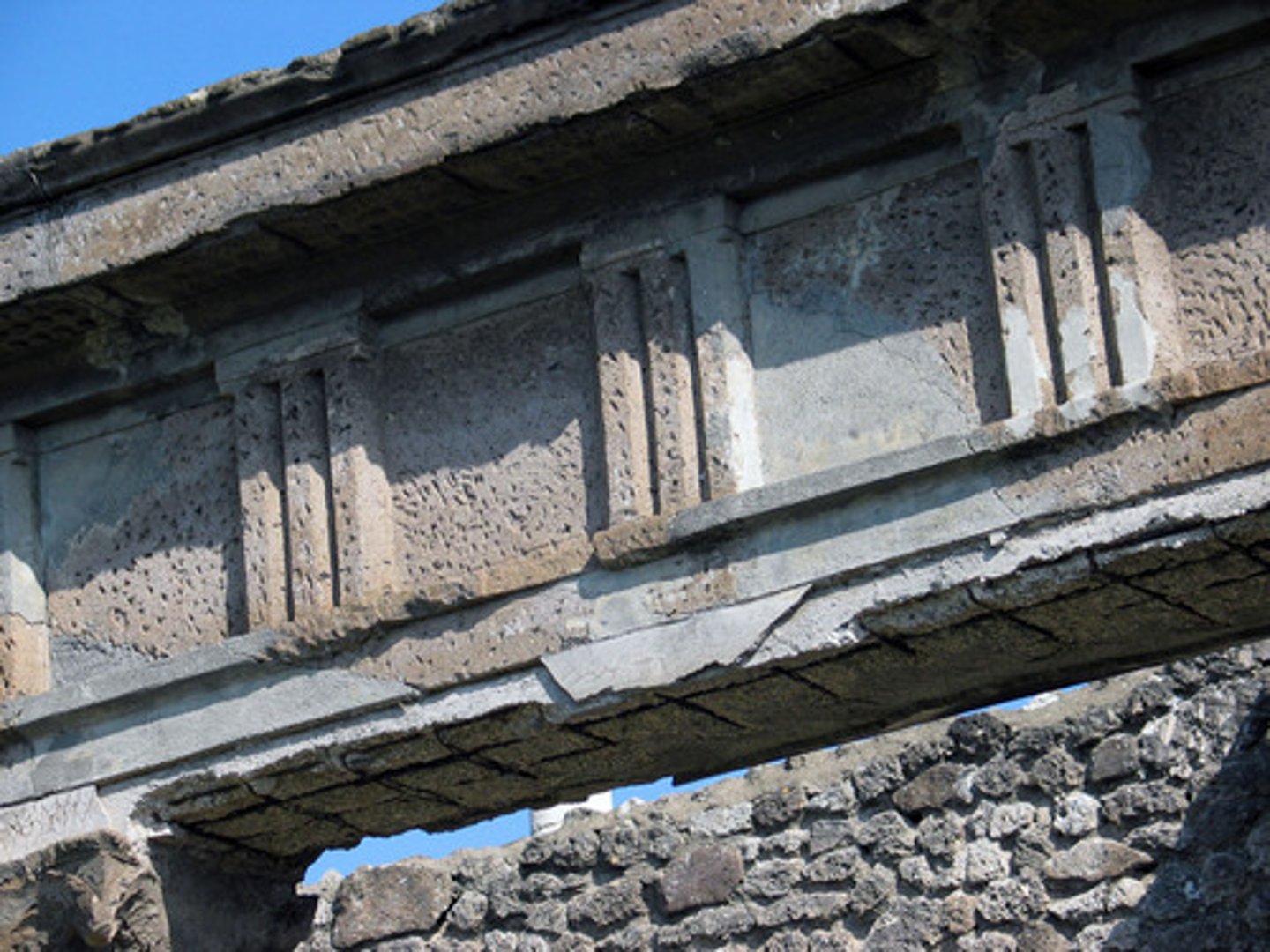
Triglyph
a projecting grooved element alternating with a metope on a Greek temple

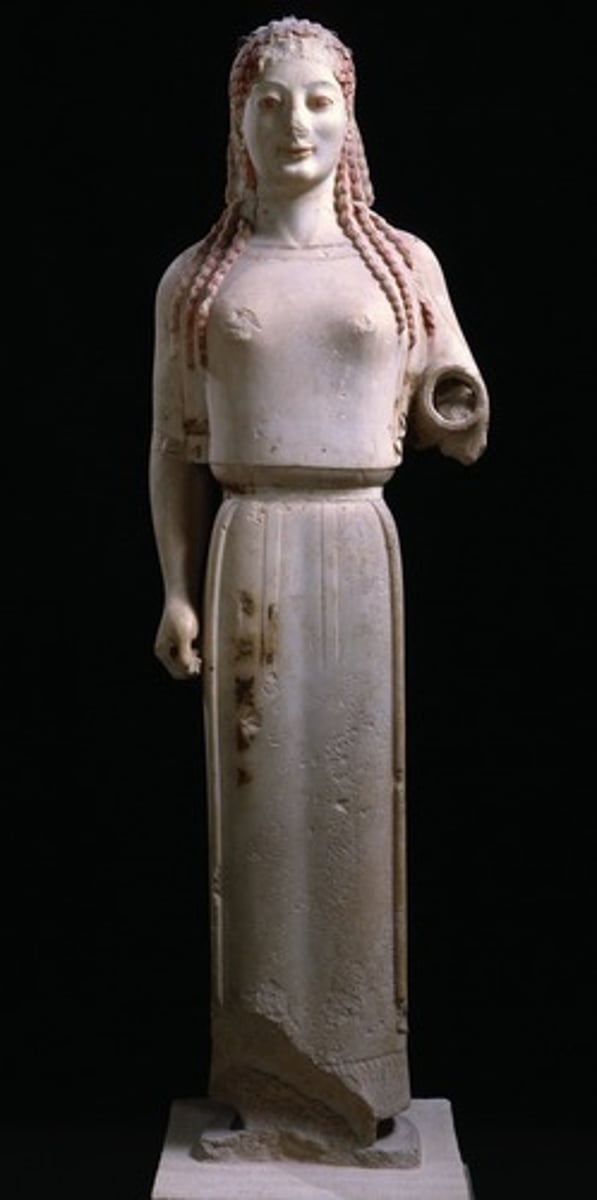
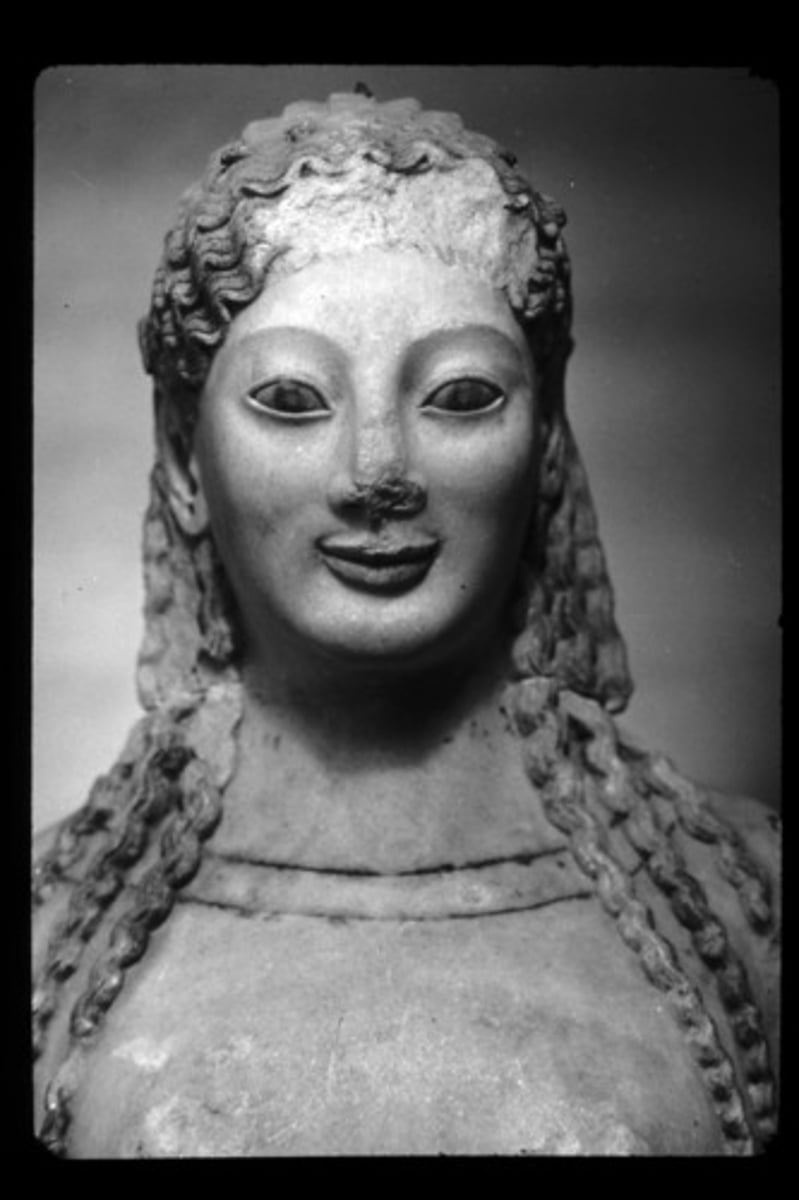
Peplos Kore
530 BCE

Classical Sculpture
Characterized by more fluid, relaxed stances and idealized forms ("heroic" bodies); canon of proportions dictated the head to be 1/7 the body

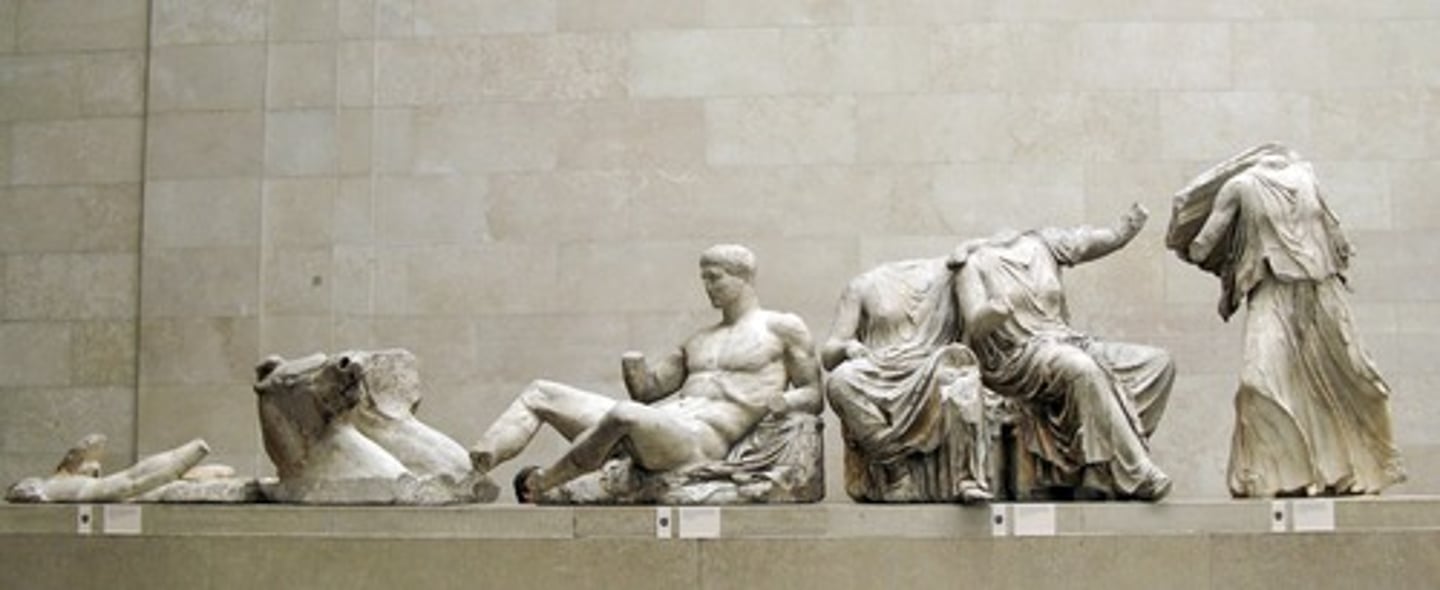
Helios, horses, and Dionysos/Heracles
438-432

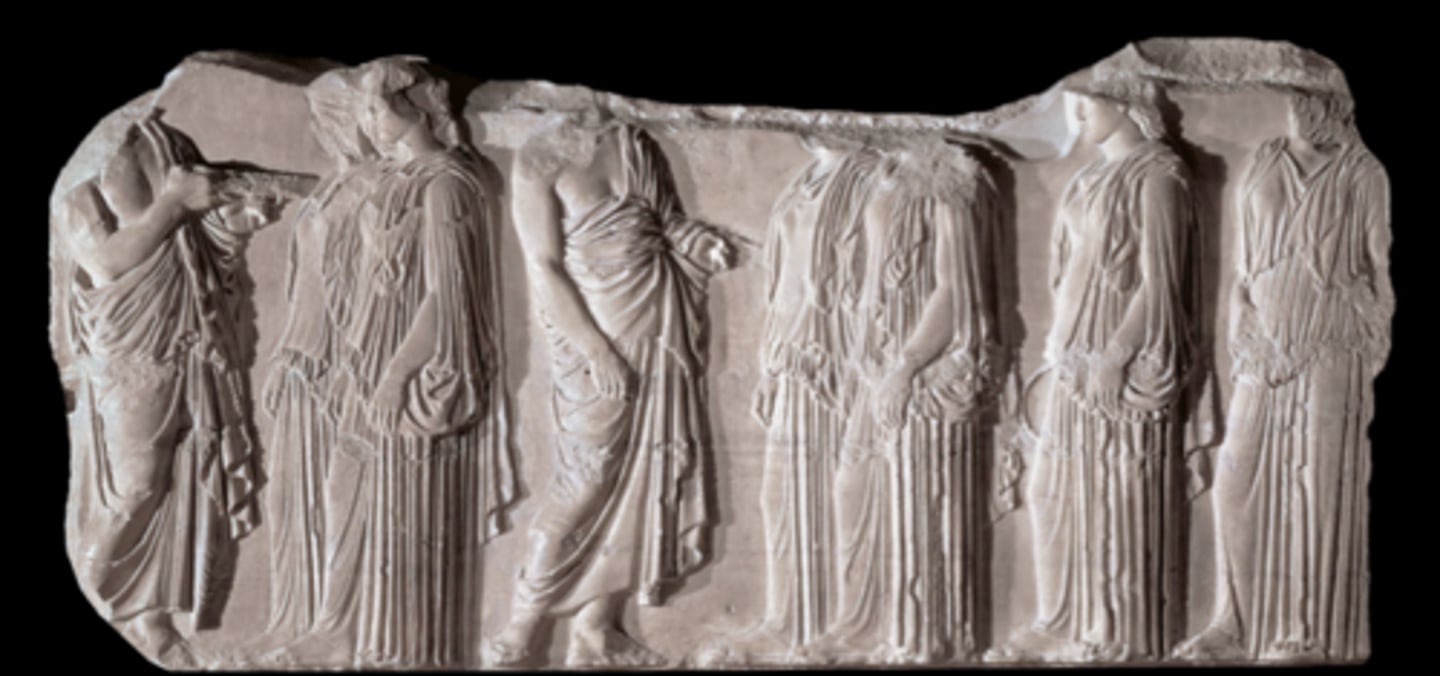
Plaque of the Ergastines
447-438

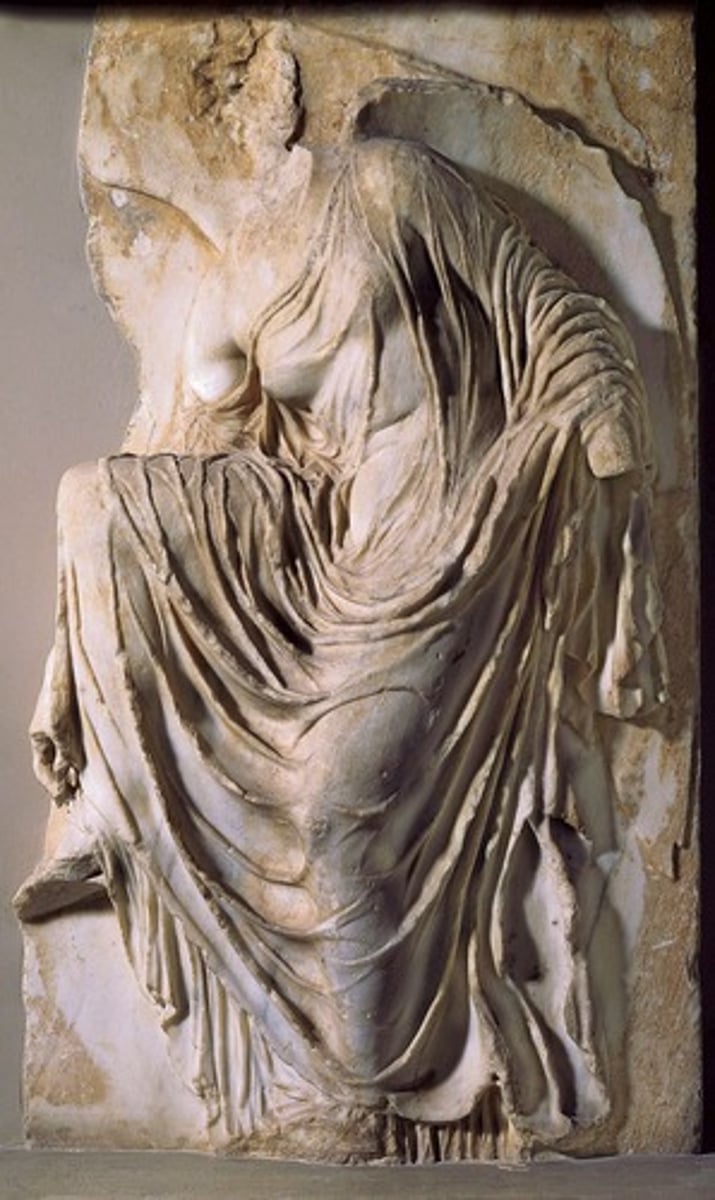
Victory adjusting her sandal
410 BCE

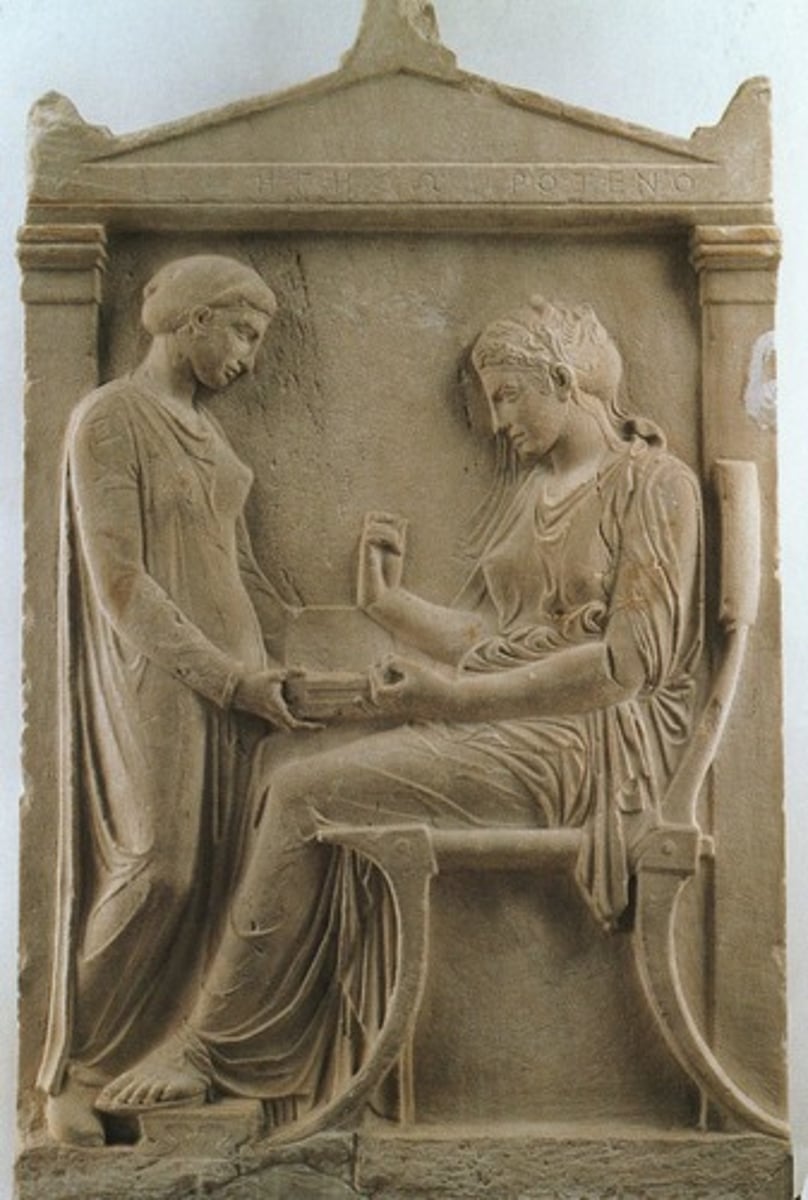
Grave Stele of Hegeso
410 BCE
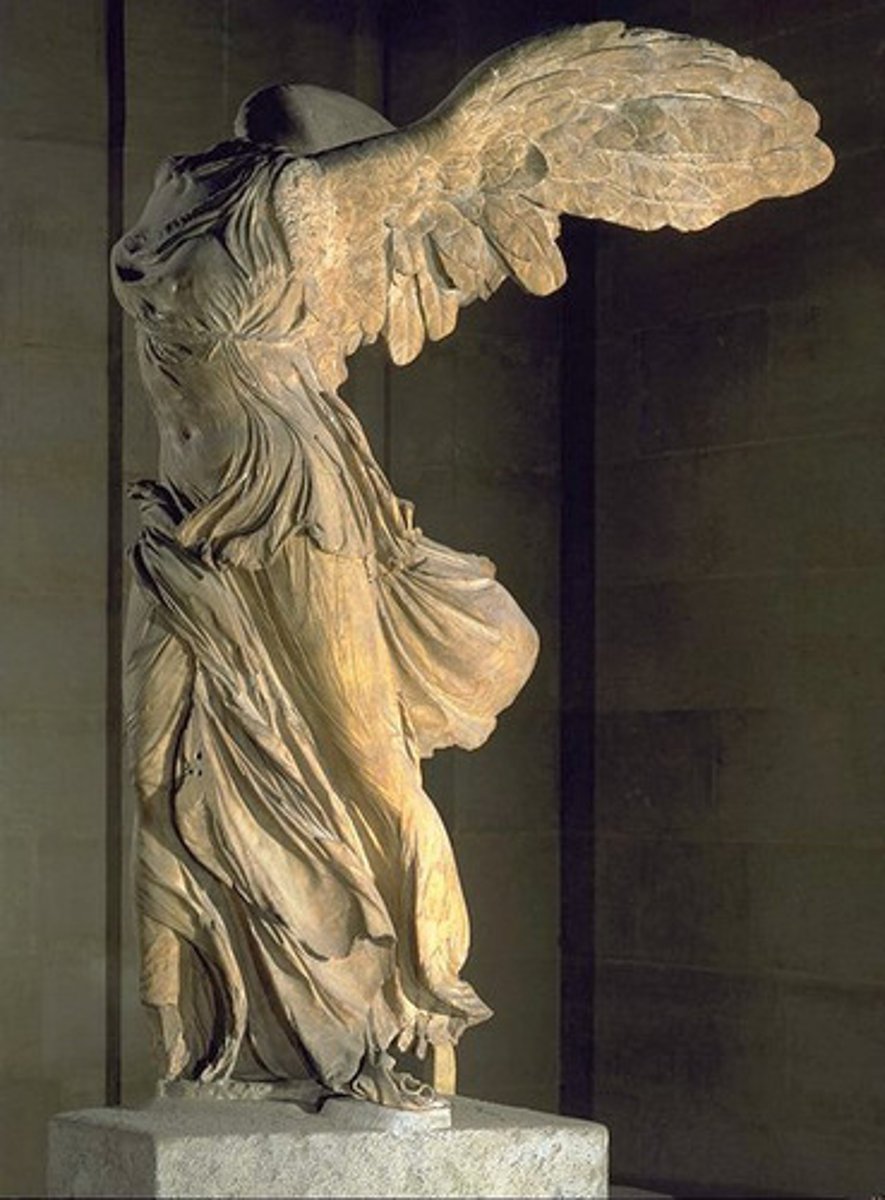
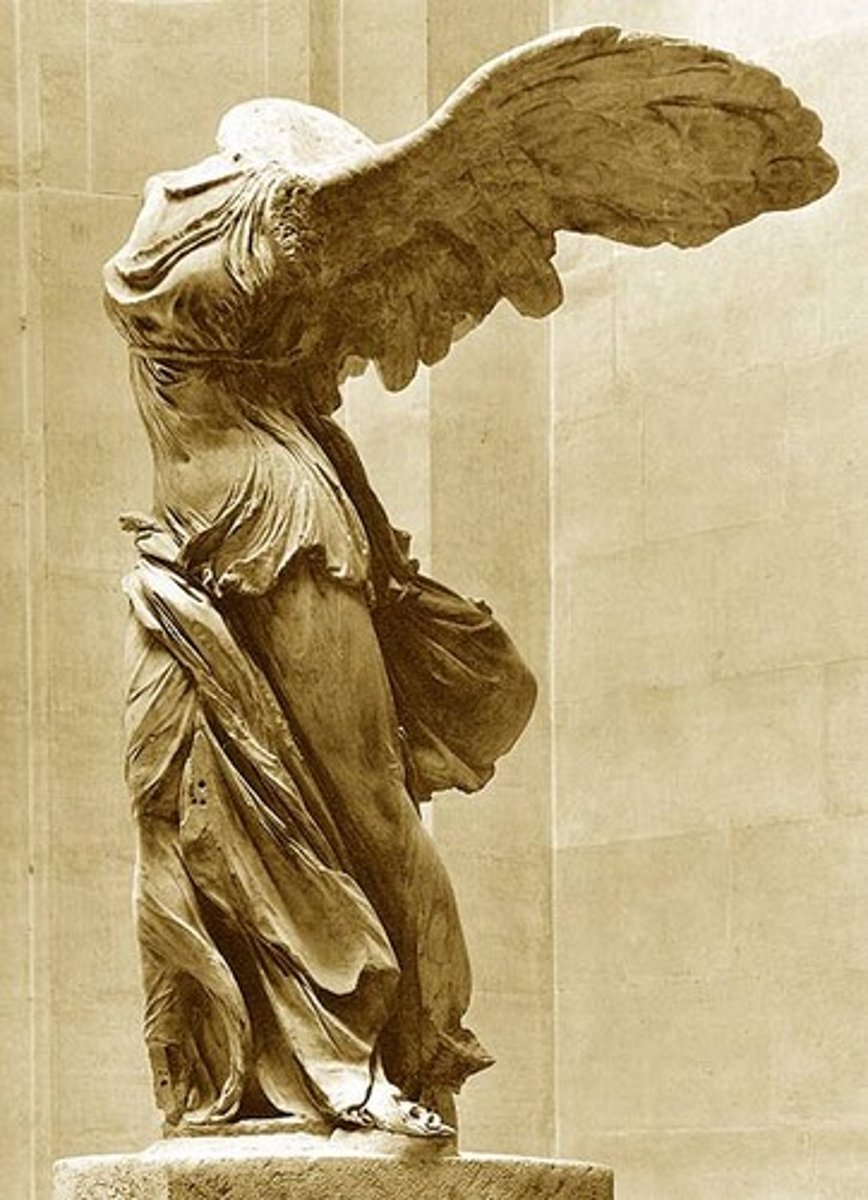
Winged Victory of Samothrace
190 BCE

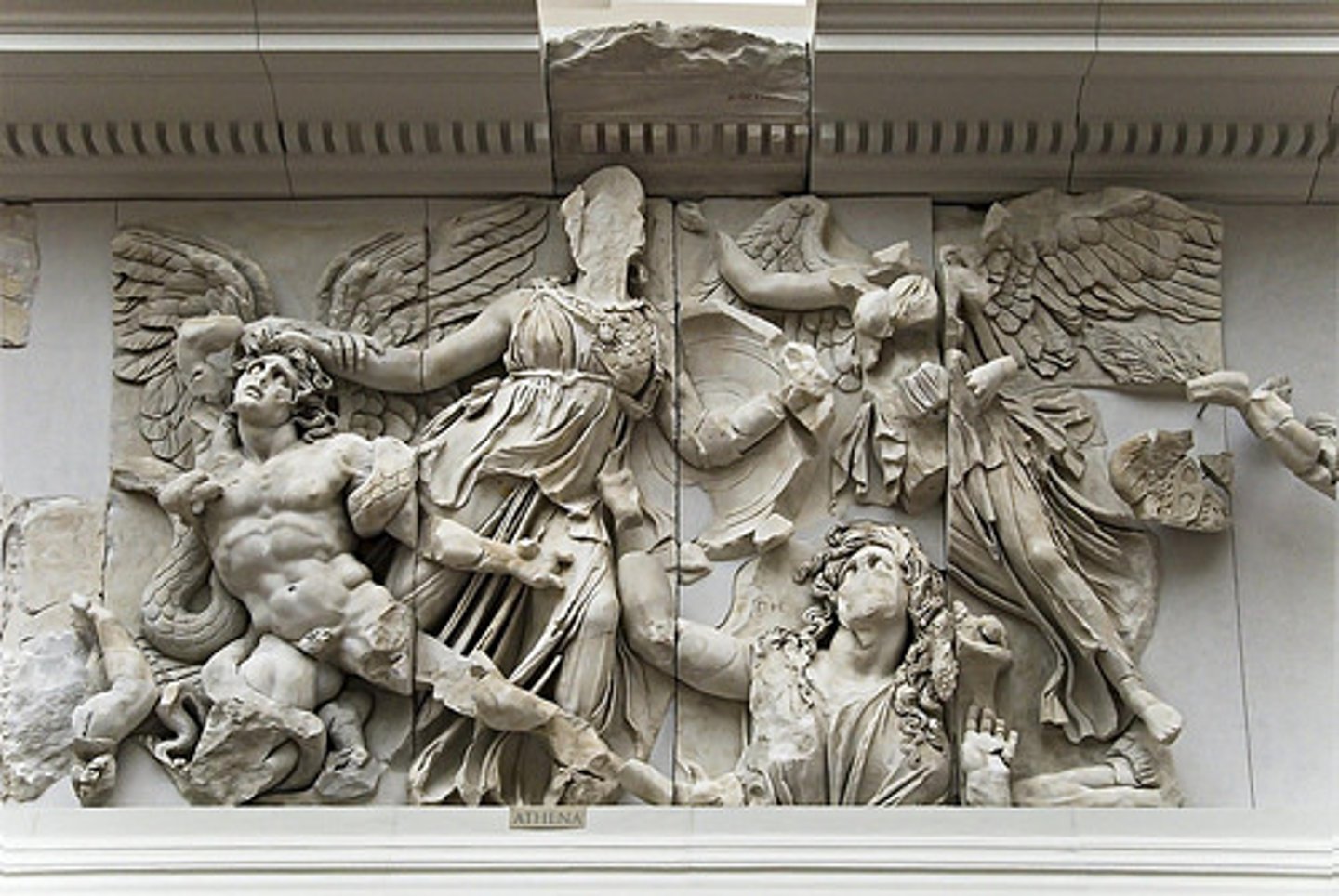
Athena, from Great Altar of Zeus and Athena
175 BCE

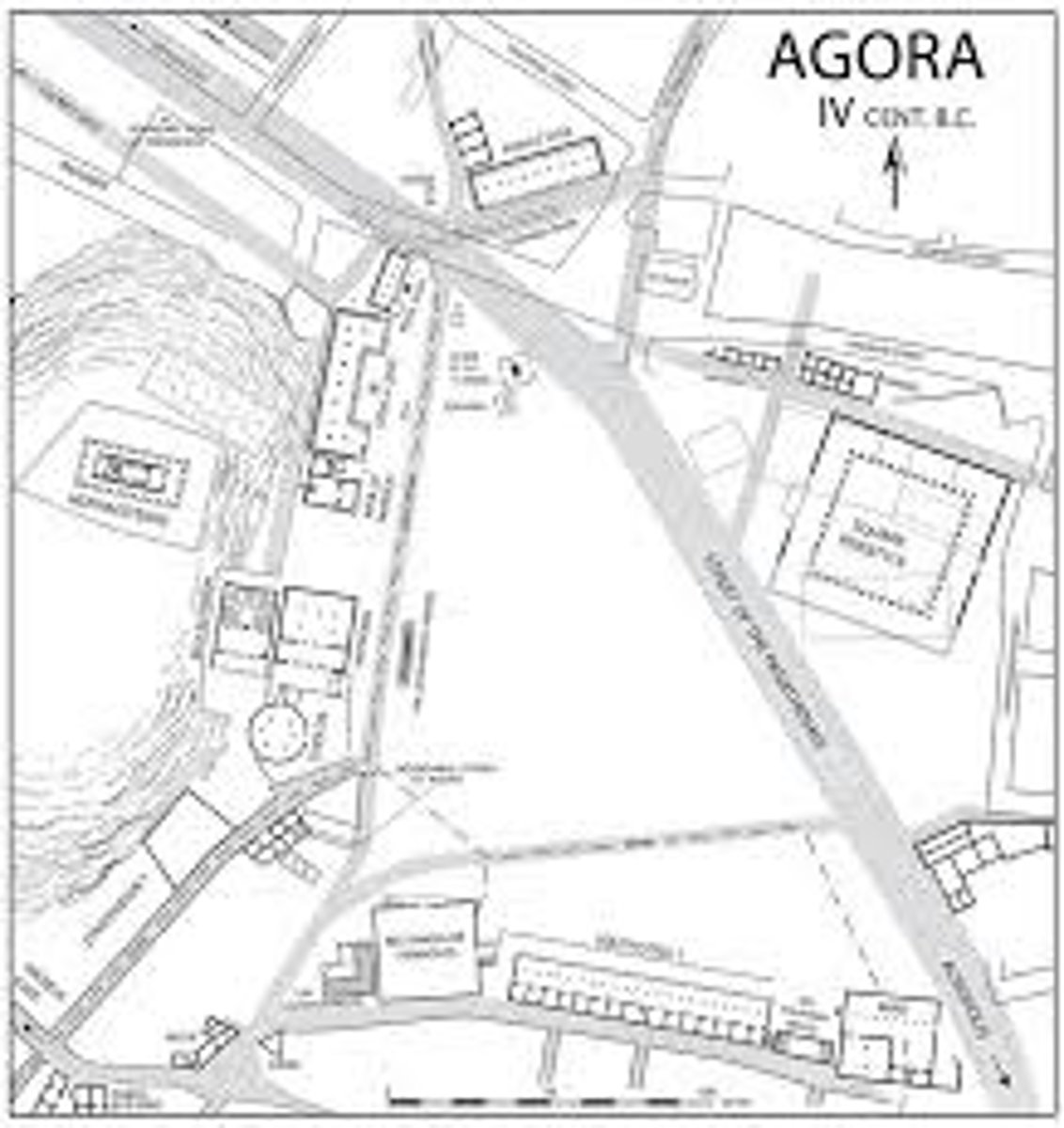
Athenian Agora
600-150 BCE
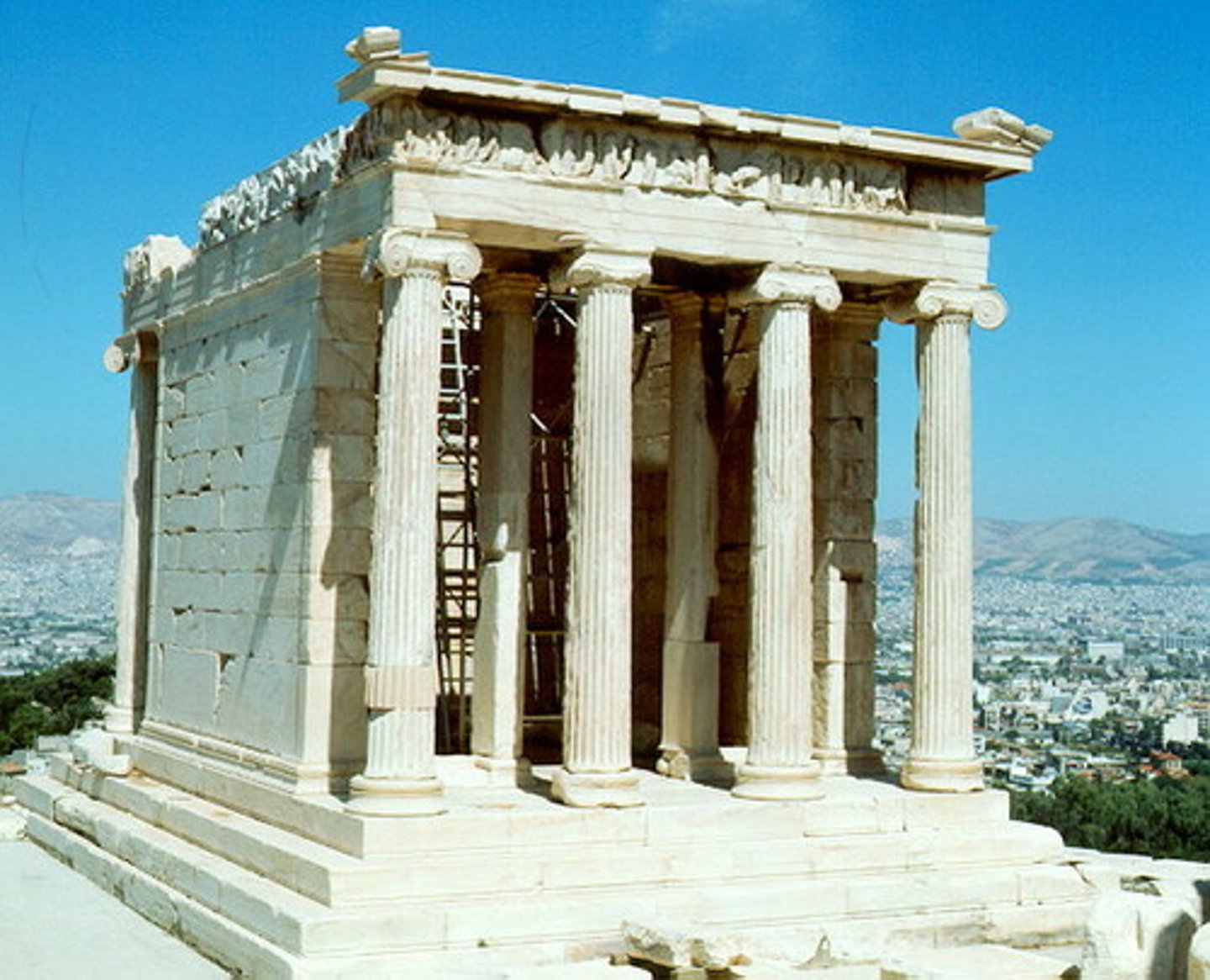
Temple of Athena Nike
427-424 BCE

Great Altar of Zeus and Athena
175 BCE

600-480 BCE
Greek Archaic Art
Acropolis
literally, a "high city," a Greek temple complex built on a hill over a city

Agora
a public plaza in a Greek city where commercial, religious, and societal activities are conducted
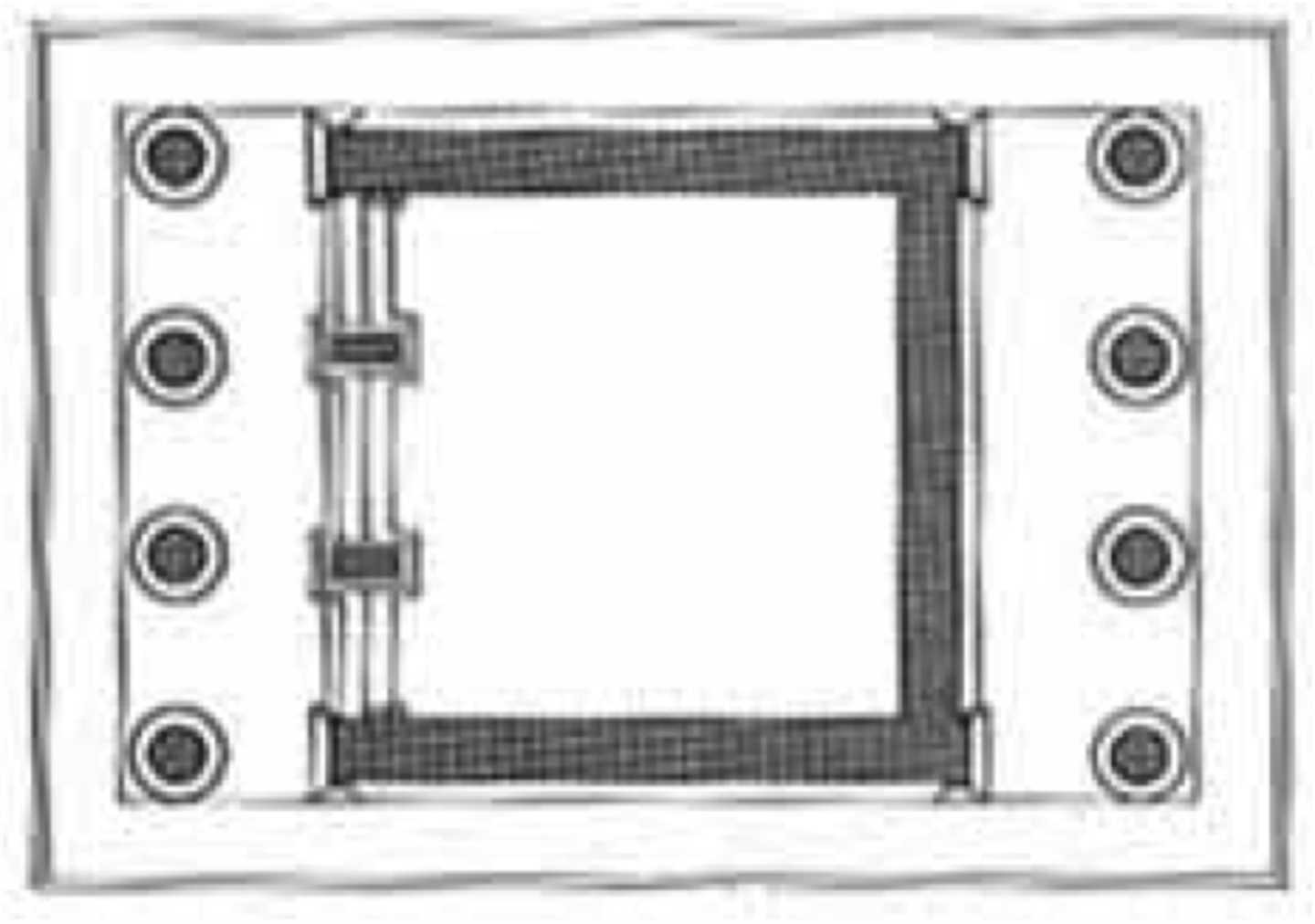
Amphiprostyle
having four columns in the front and rear of a temple
Amphora
a two-handled Greek storage jar

Architrave
a plain, unornamented lintel on the entablature
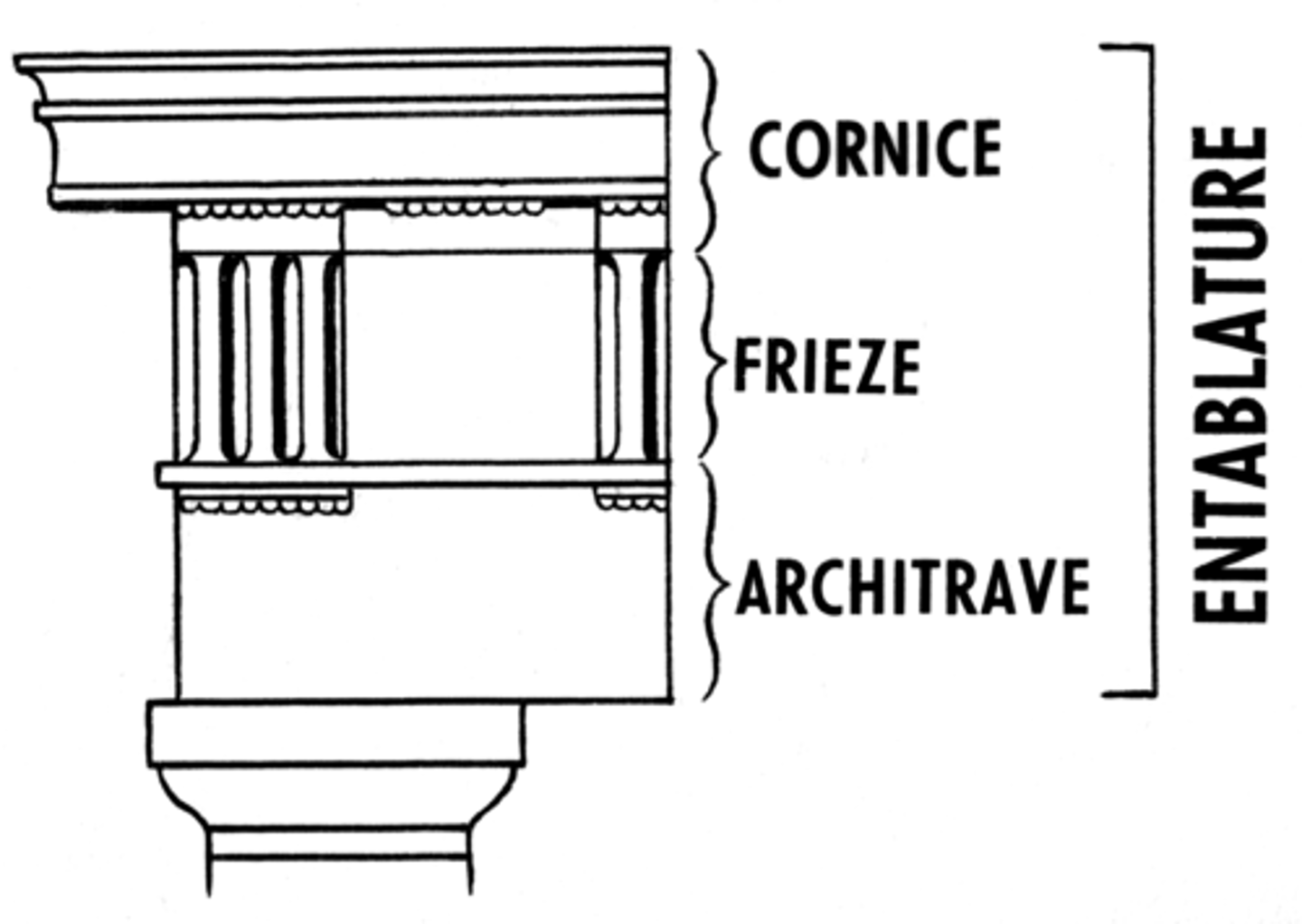
Athena
Greek goddess of war and wisdom; patron of Athens

Canon
a body of rules or laws; in Greek art, the ideal mathematical proportion of a figure

Caryatid (male: atlantid)
a building column that is shaped like a female figure
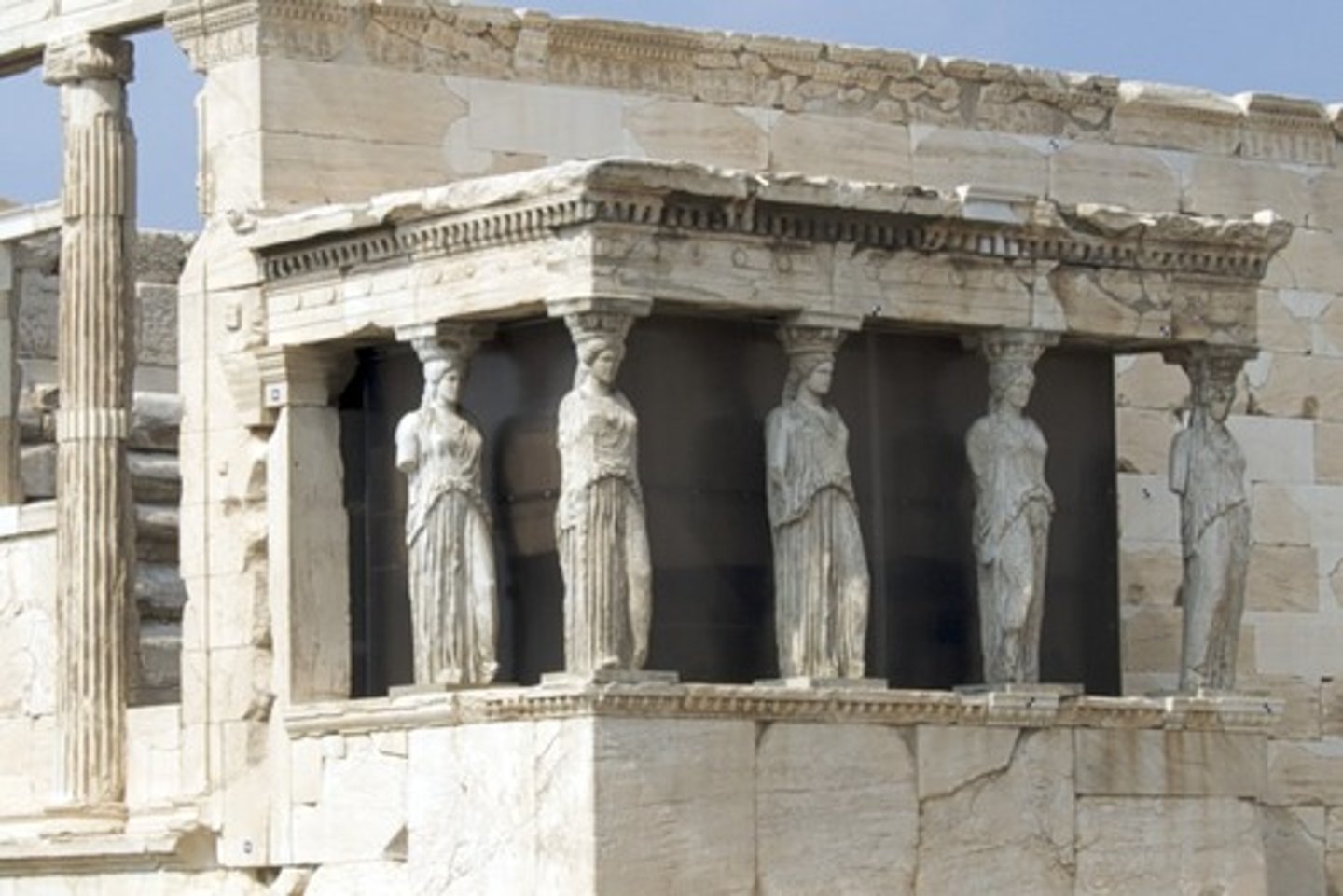

Cella
the main room of a temple where the god is housed
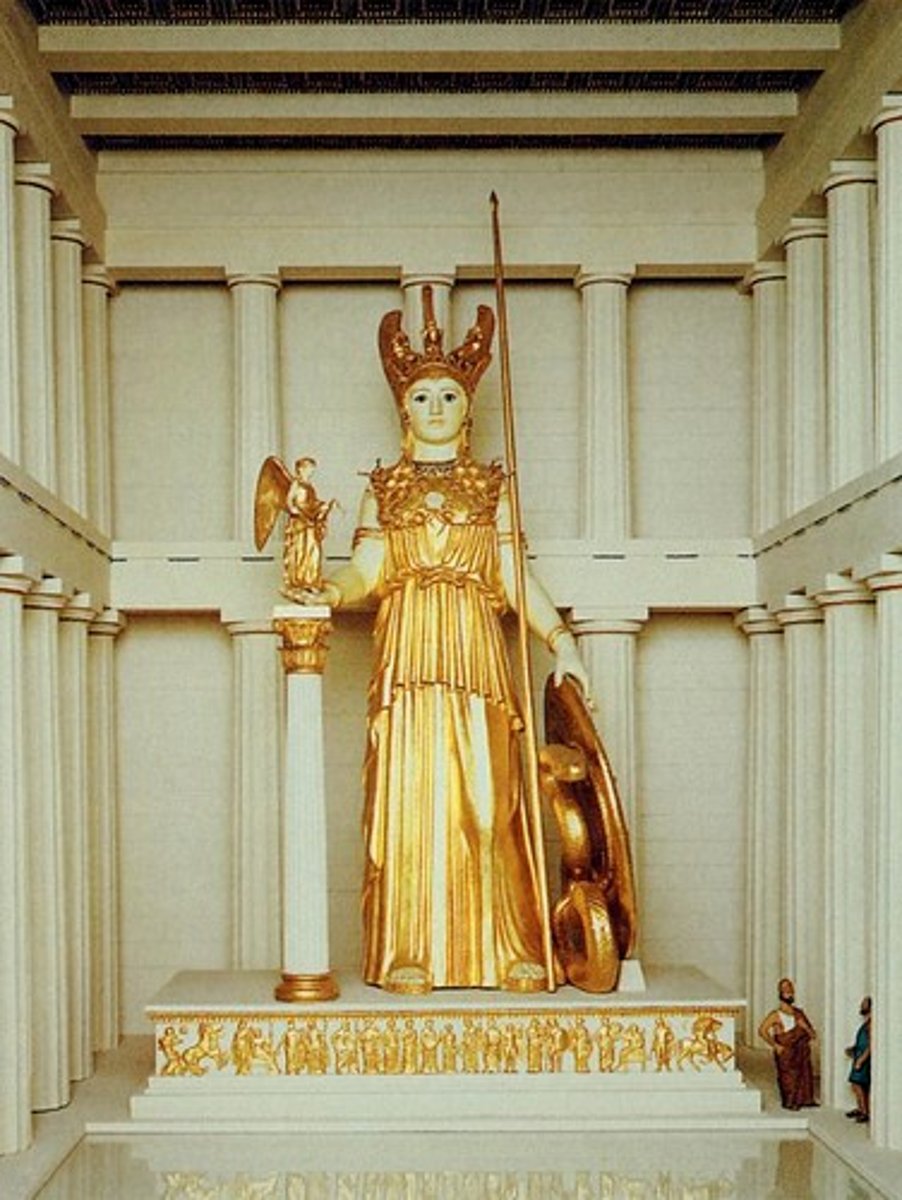

Contrapposto
a graceful arrangement of the body based on tilted shoulders and hips and bent knees

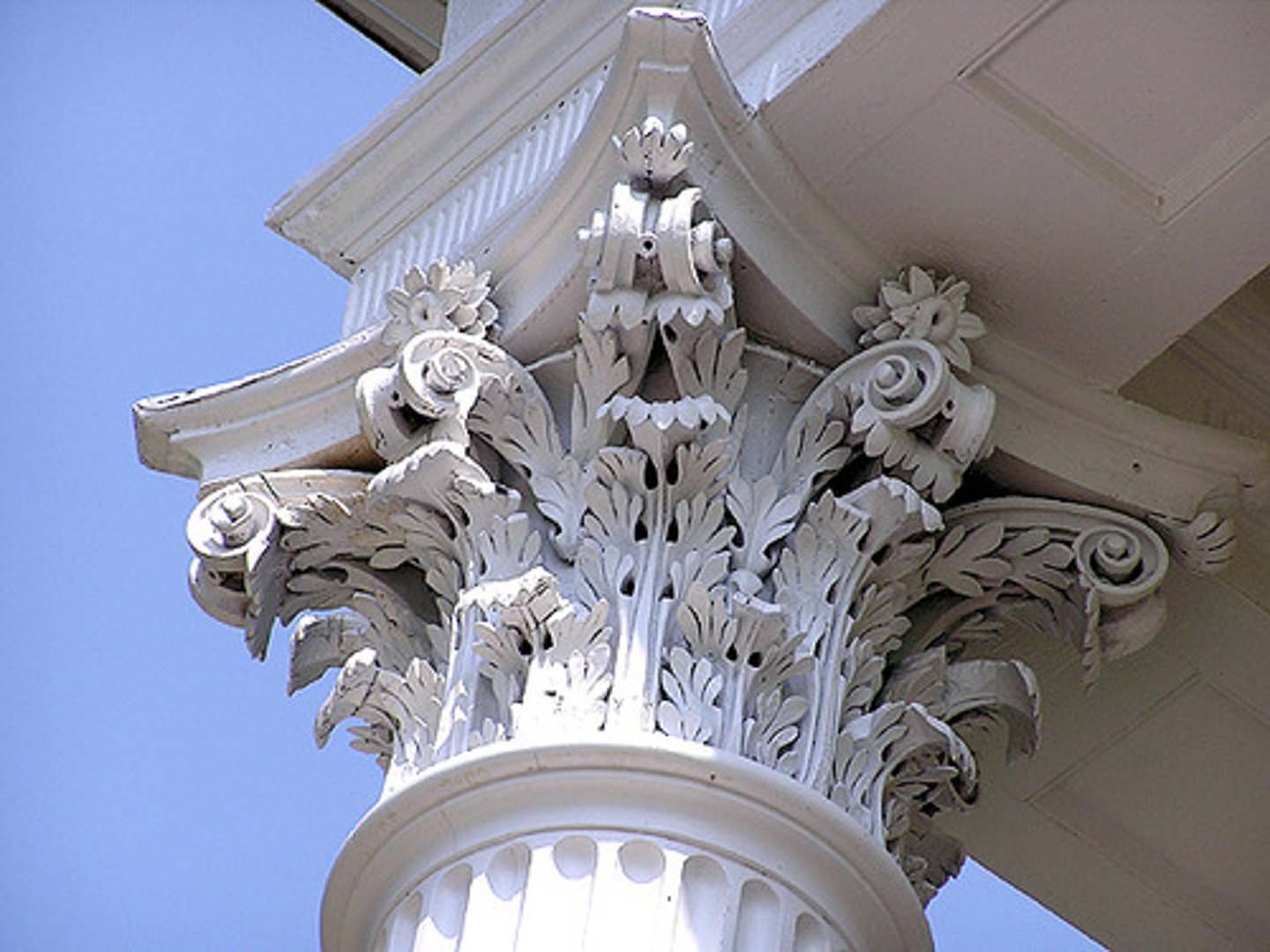
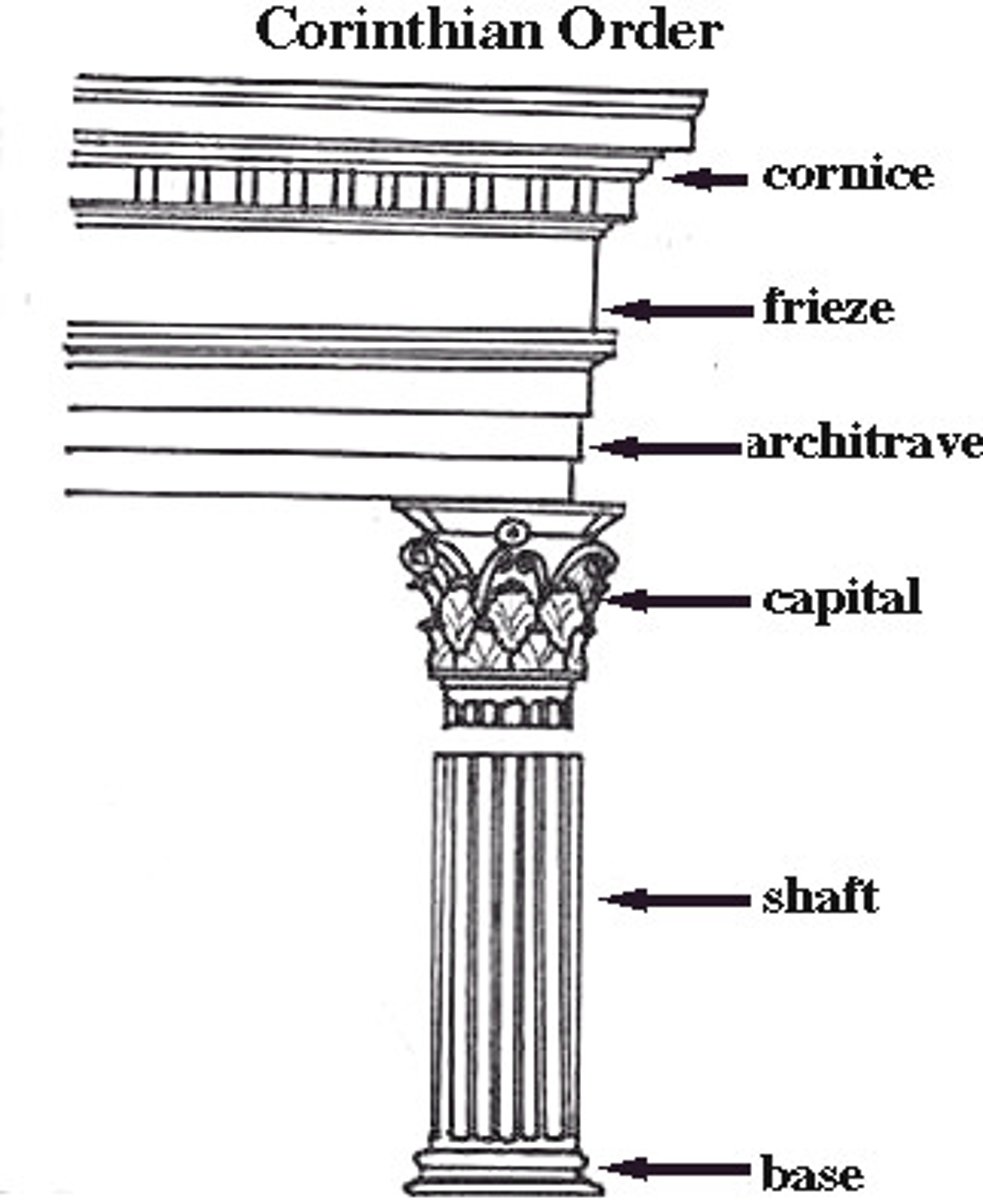
Corinthian
an order of ancient Greek architecture similar to the Ionic, except that the capitals are carved in tiers of leaves; this type of temple pillar was developed last

Cornice
a projecting ledge over a wall
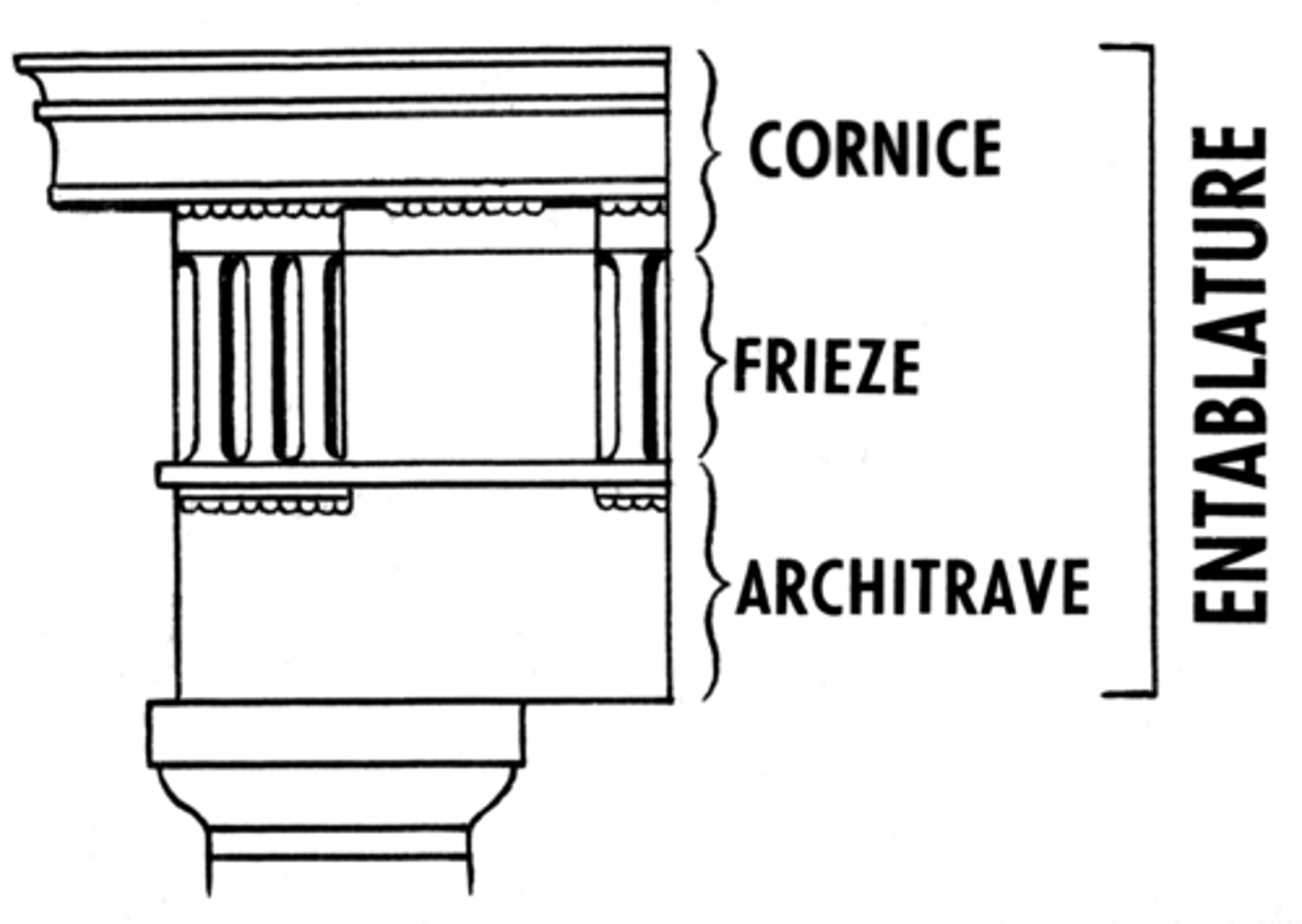
Doric
an order of ancient Greek architecture that features grooved columns with no grooved bases and an upper story with square sculpture called metopes; resonates with mainland Greece and its settlements

Encaustic
a type of painting in which colors are added to hot wax to affix to a surface

Entablature
the upper story of a Greek temple
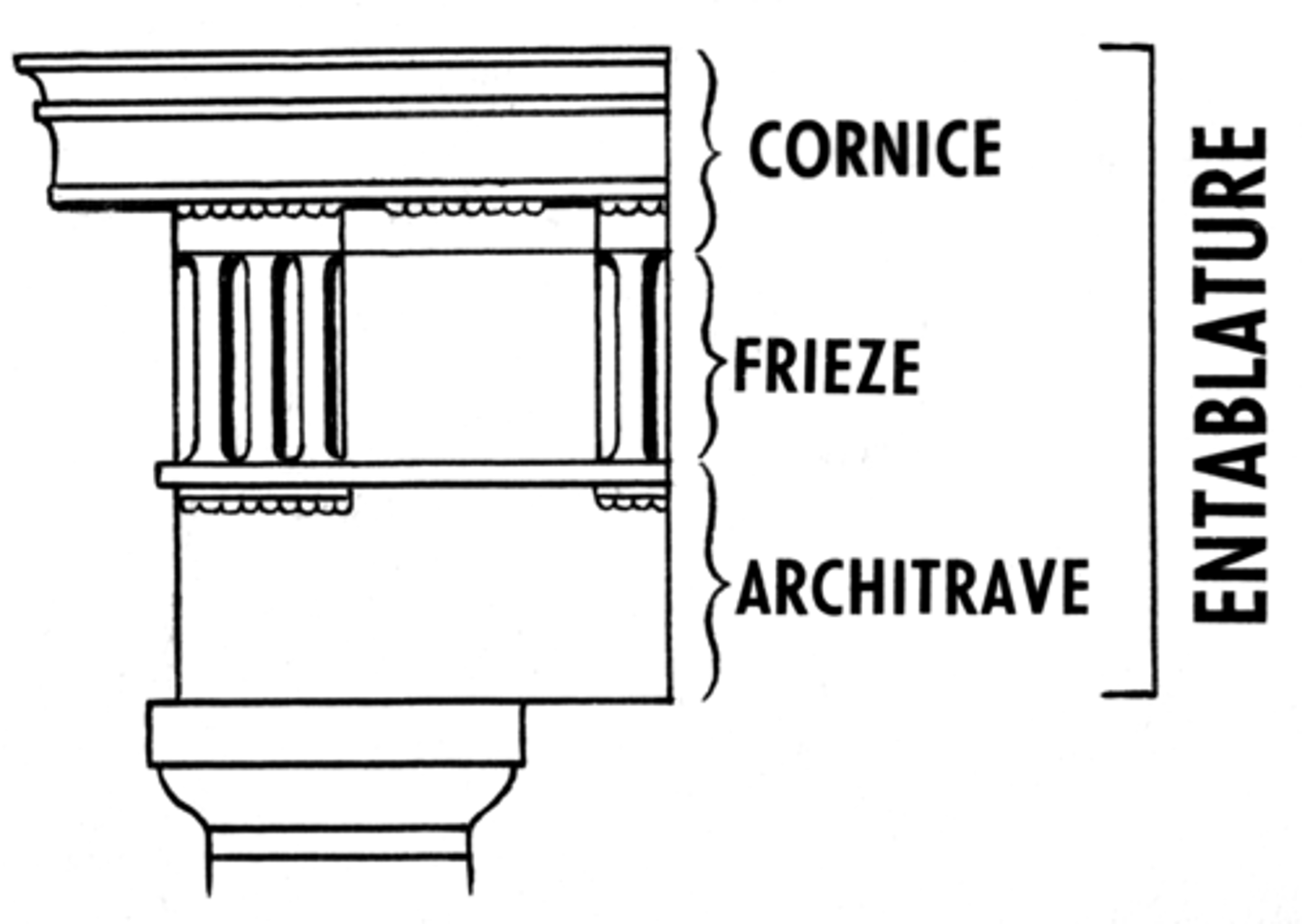
Frieze
a horizontal band of sculpture
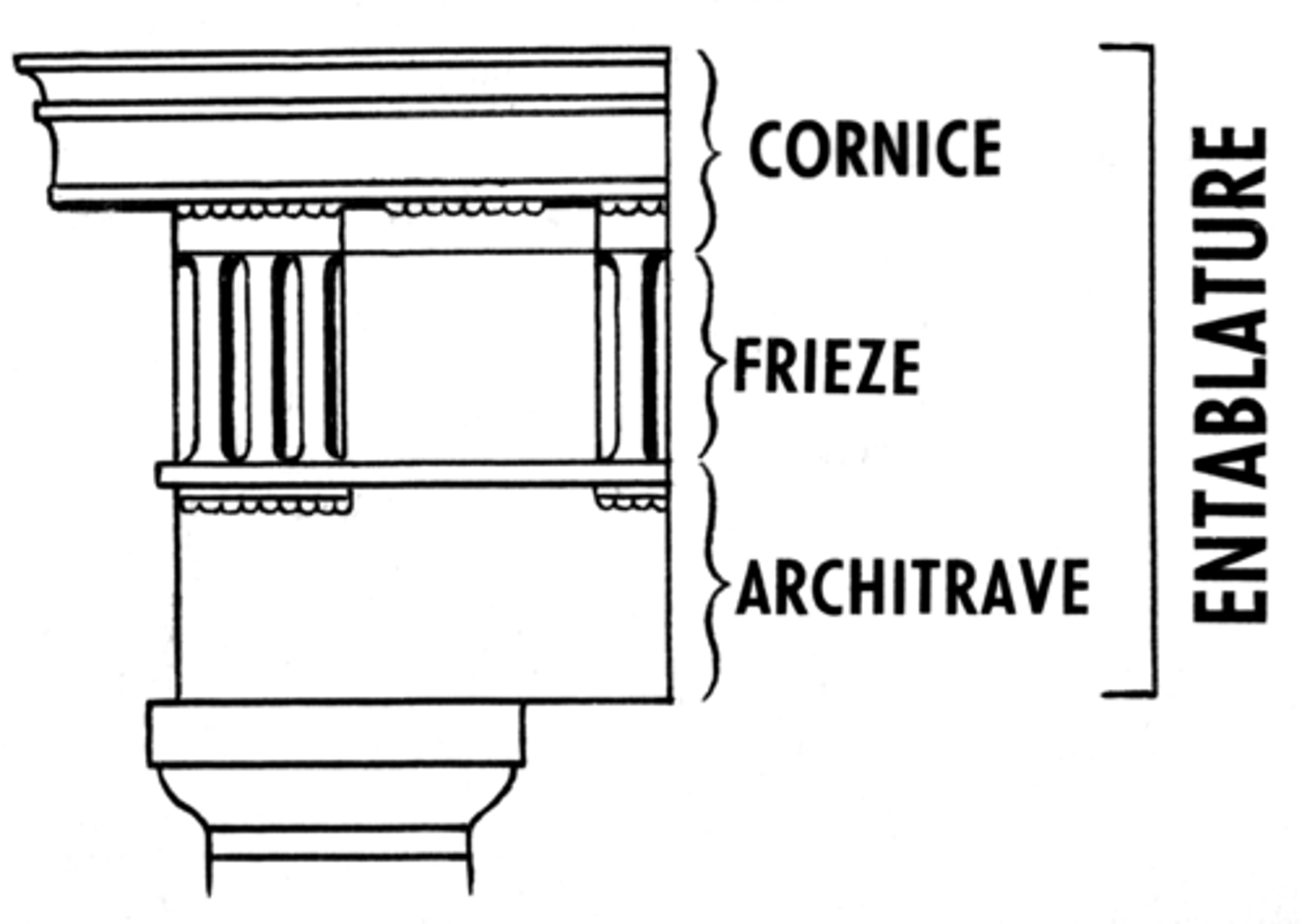
Gigantomachy
a mythical ancient Greek war between the giants and the Olympian gods

In situ
a Latin expression that means that something is in its original location

Ionic
an order of Greek architecture that features columns with scrolled capitals and an upper story with sculptures that are in friezes; preferred by Greek island architects

Isocephalism
the tradition of depicting heads of figures on the same level

Kiln
an oven used for making pottery
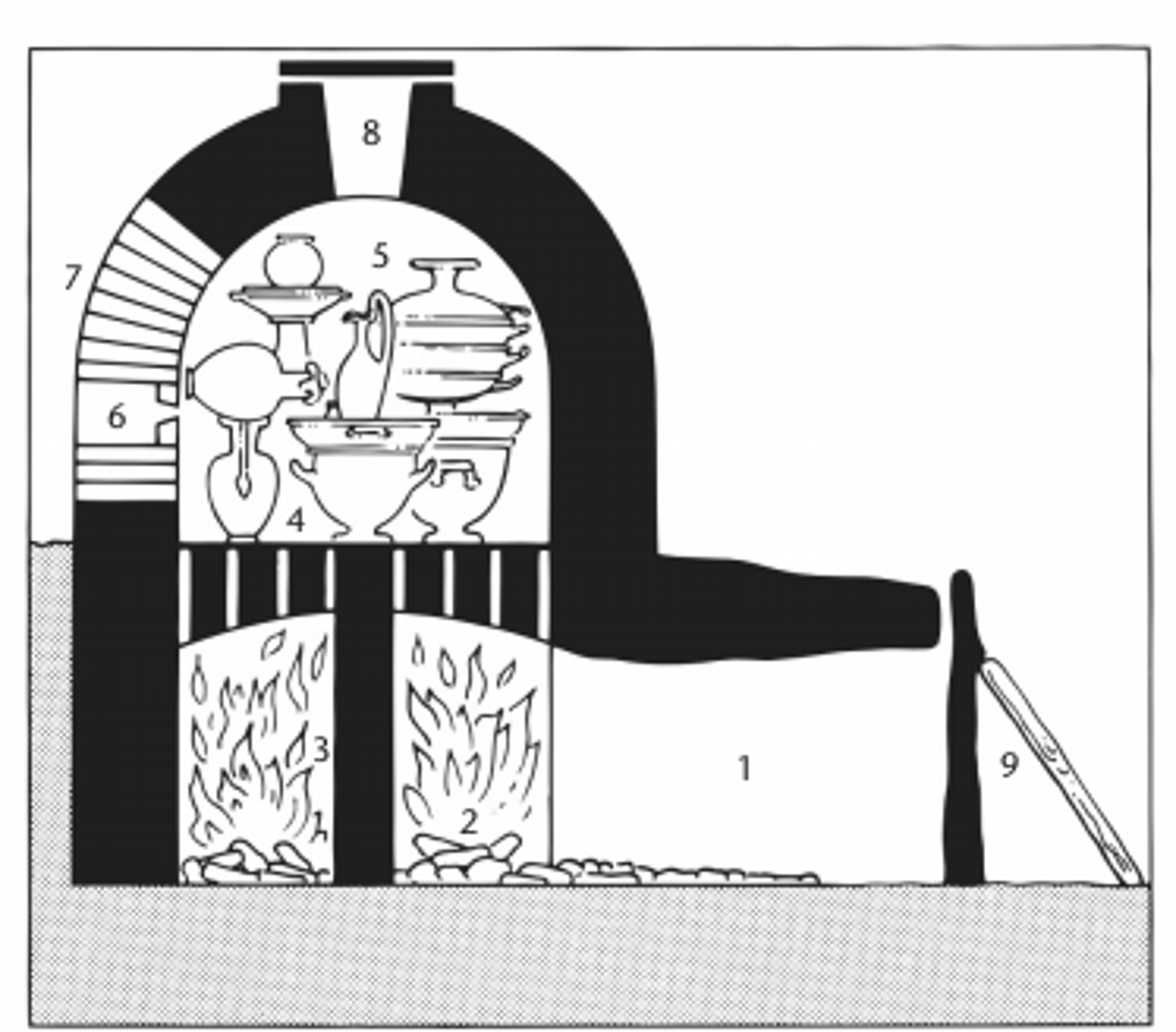
Kouros (female: kore)
an archaic Greek sculpture of a (frontal) standing youth

Krater
a large ancient Greek bowl used for mixing water and wine

Metope
a small relief sculpture on the facade of a Greek temple

Mosaic
a decoration using pieces of stone, marble, or colored glass, called tesserae, that are cemented to a wall or a floor

Nike
ancient Greek goddess of victory

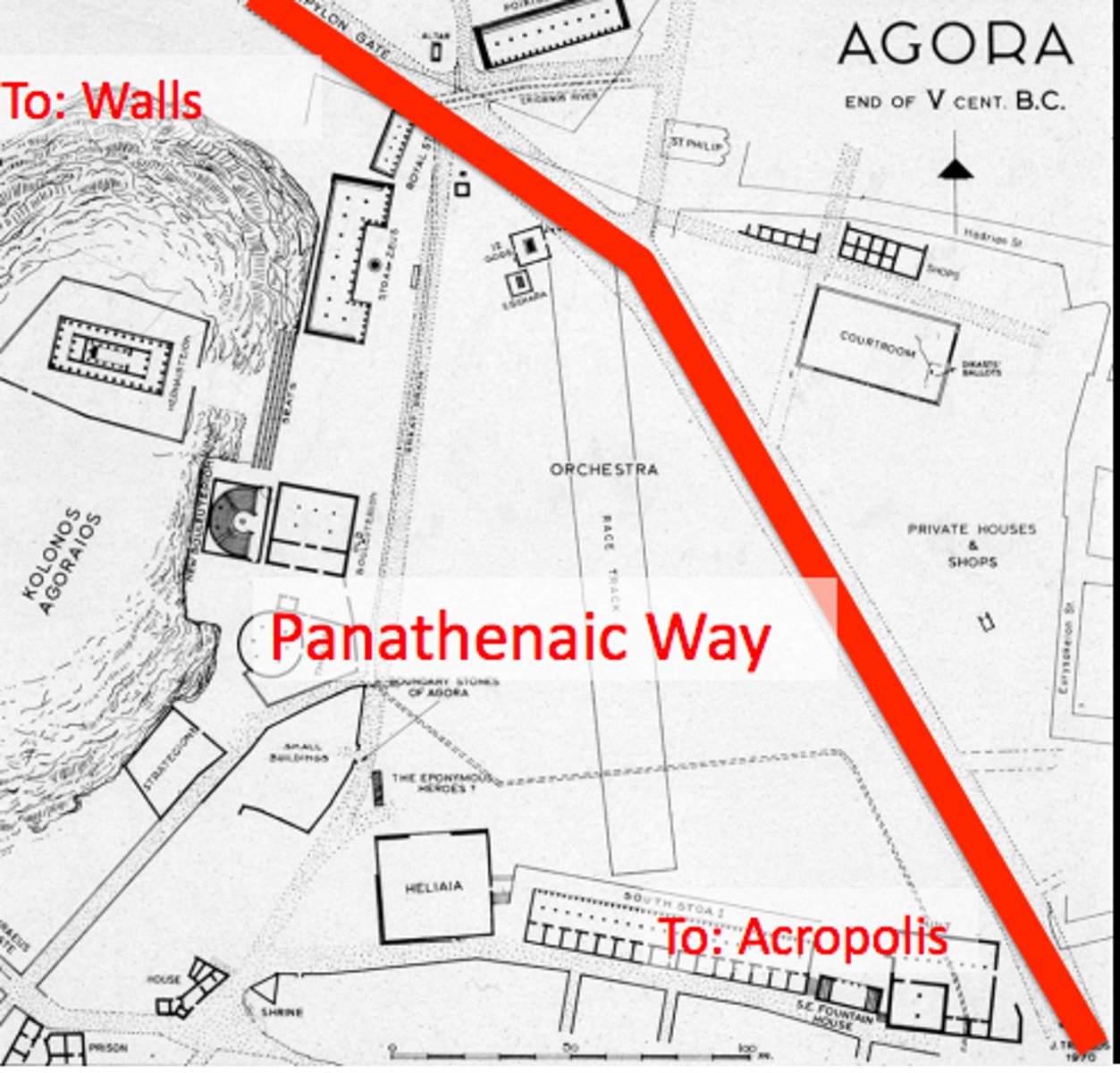
Panathenaic Way
a ceremonial road for a procession built to honor Athena during a festival
Pediment
the triangular top of a temple that contains sculpture

Peplos
a garment worn by women in ancient Greece, usually full length and tied at the waist
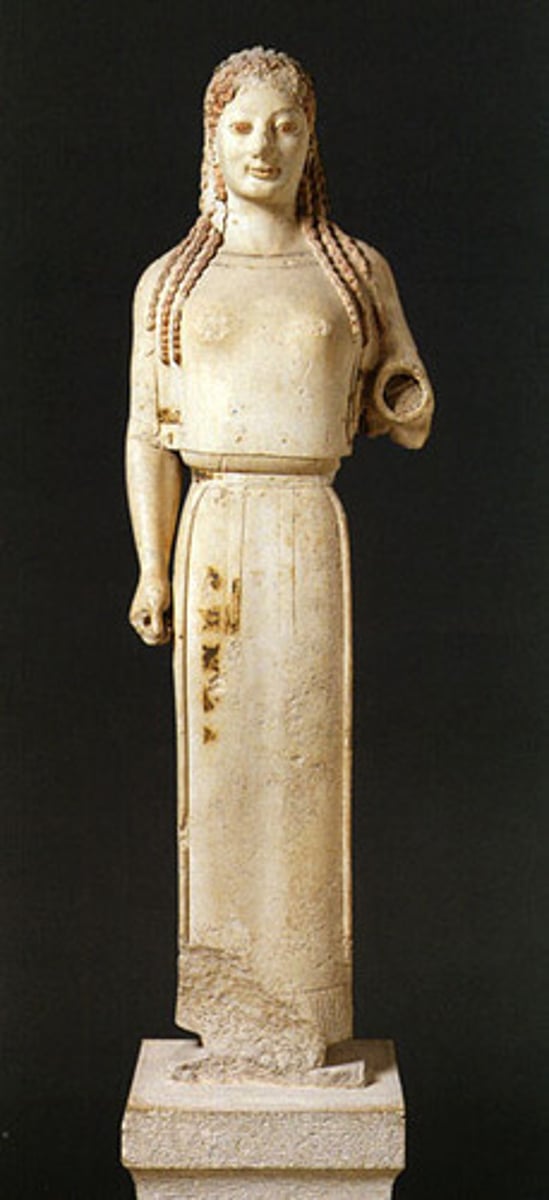

Peristyle
a colonnade surrounding a building or enclosing a courtyard
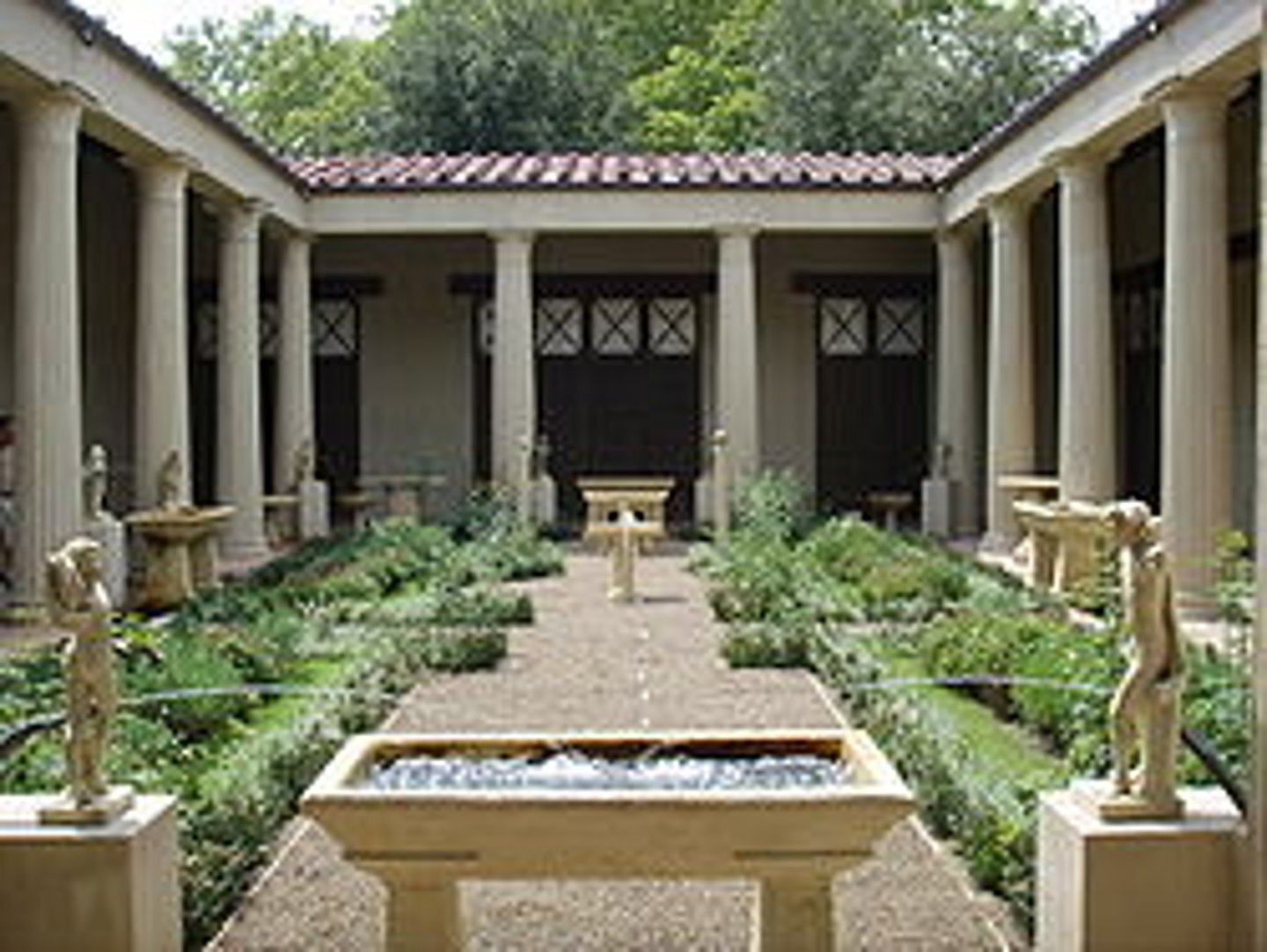

Propylaeum (plural: propylaea)
a gateway leading to a Greek temple
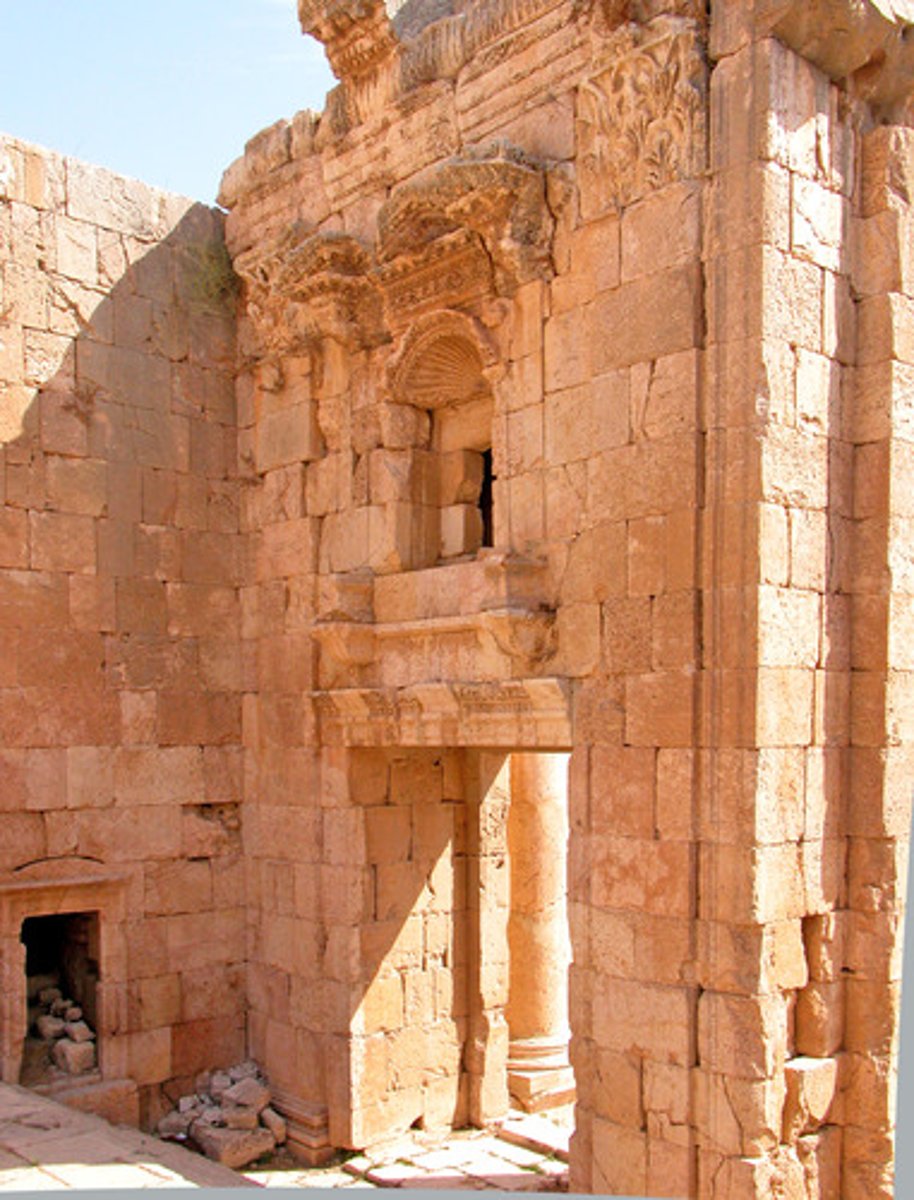

Relief sculpture
sculpture that projects from a flat background. A very shallow relief sculpture is called a bas-relief
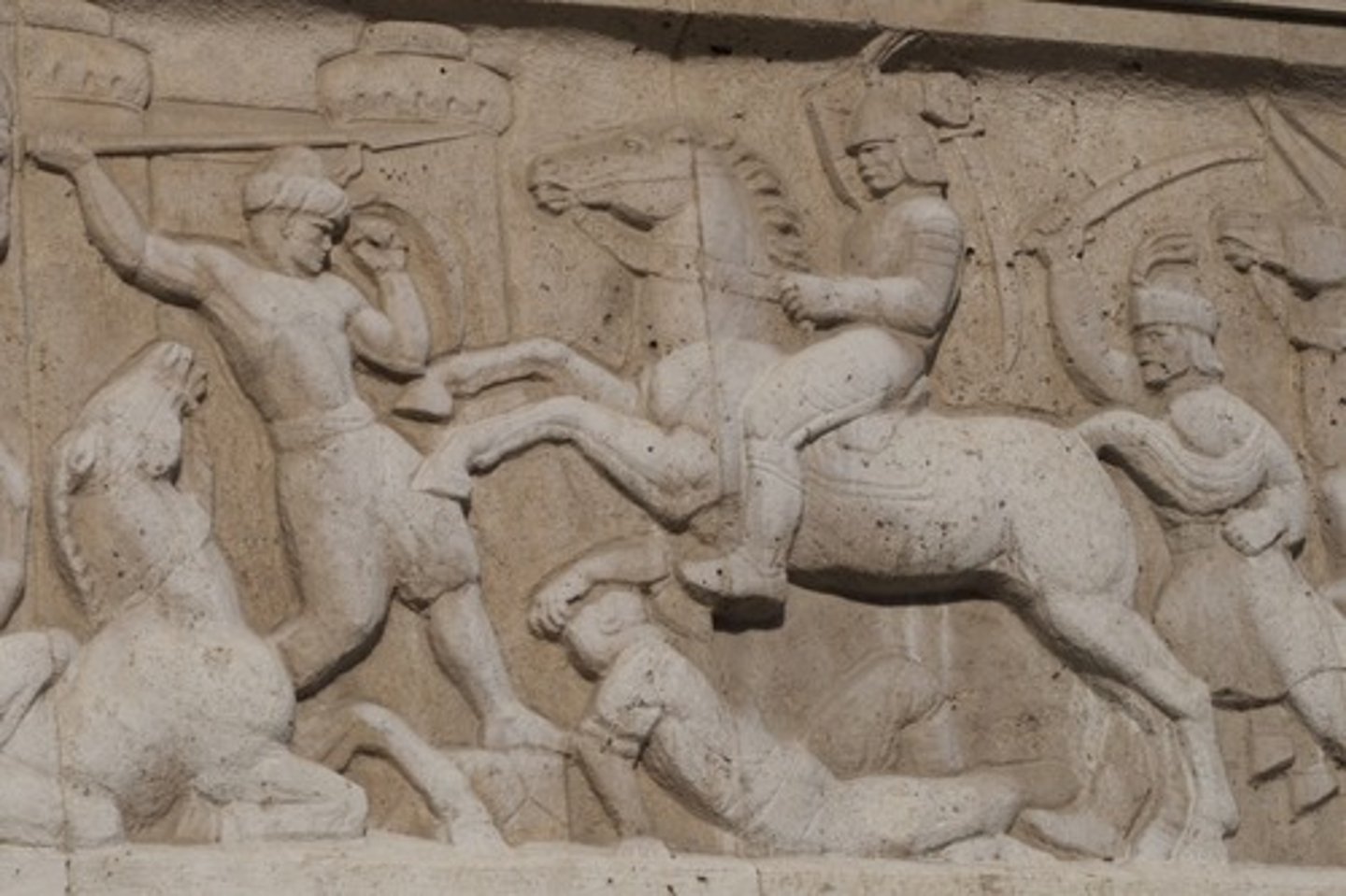

Shaft
the body of a column
Stele (plural: stelae)
an upright stone slab used to mark a grave or a site

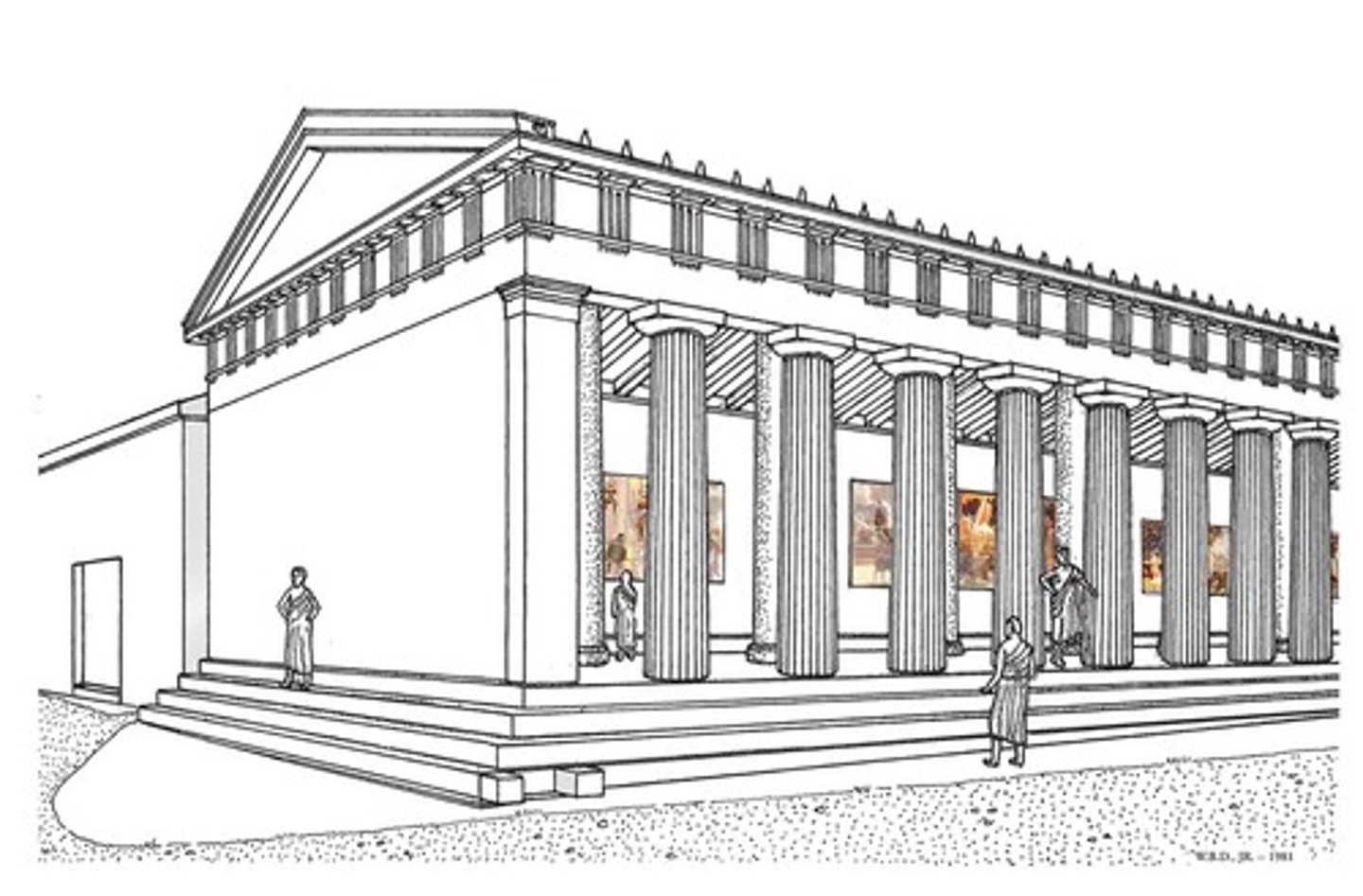
Stoa
an ancient Greek covered walkway having columns on one side and a wall on the other
Tholos
an ancient Greek circular building

Zeus
king of the ancient Gods; known as Jupiter to the Romans; god of the sky and weather

cire perdue
the lost wax process. A bronze casting method in which a figure is modeled in clay and covered with wax and then recovered with clay. When fired in a kiln, the wax melts away, leaving a hollow channel between the two layers of clay which can be used as a mold for liquid metal

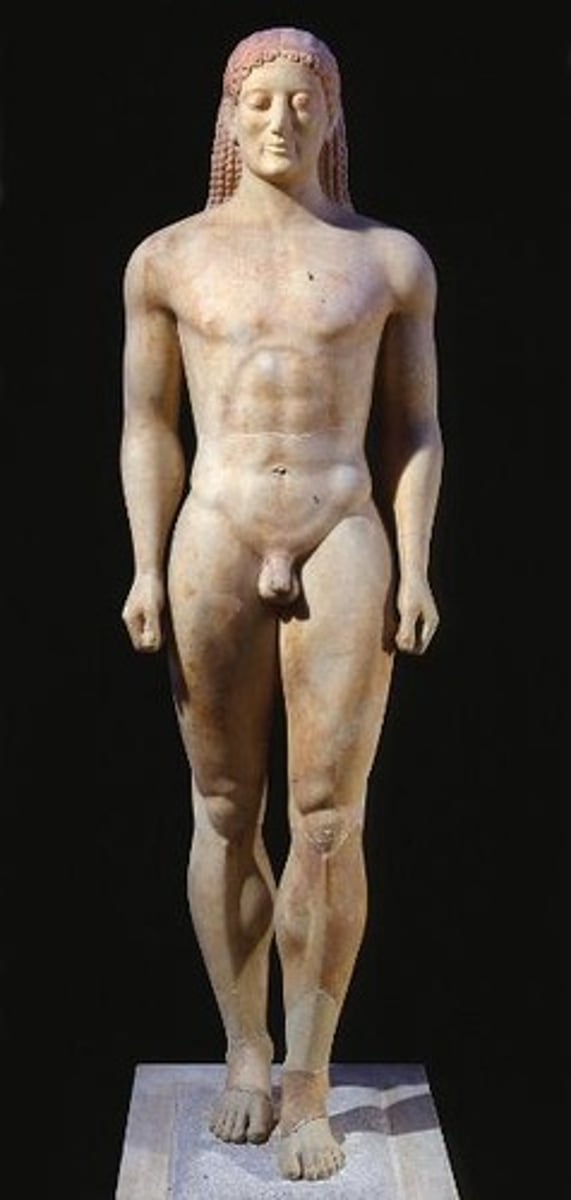
Archaic Sculpture
Characterized by grave monuments such as kouros and kore figures made of primarily marble decorated with metallic accessories; one foot in front of the other and typically incorporates negative space; naturalistic expressions

Anavysos Kouros
530 BCE

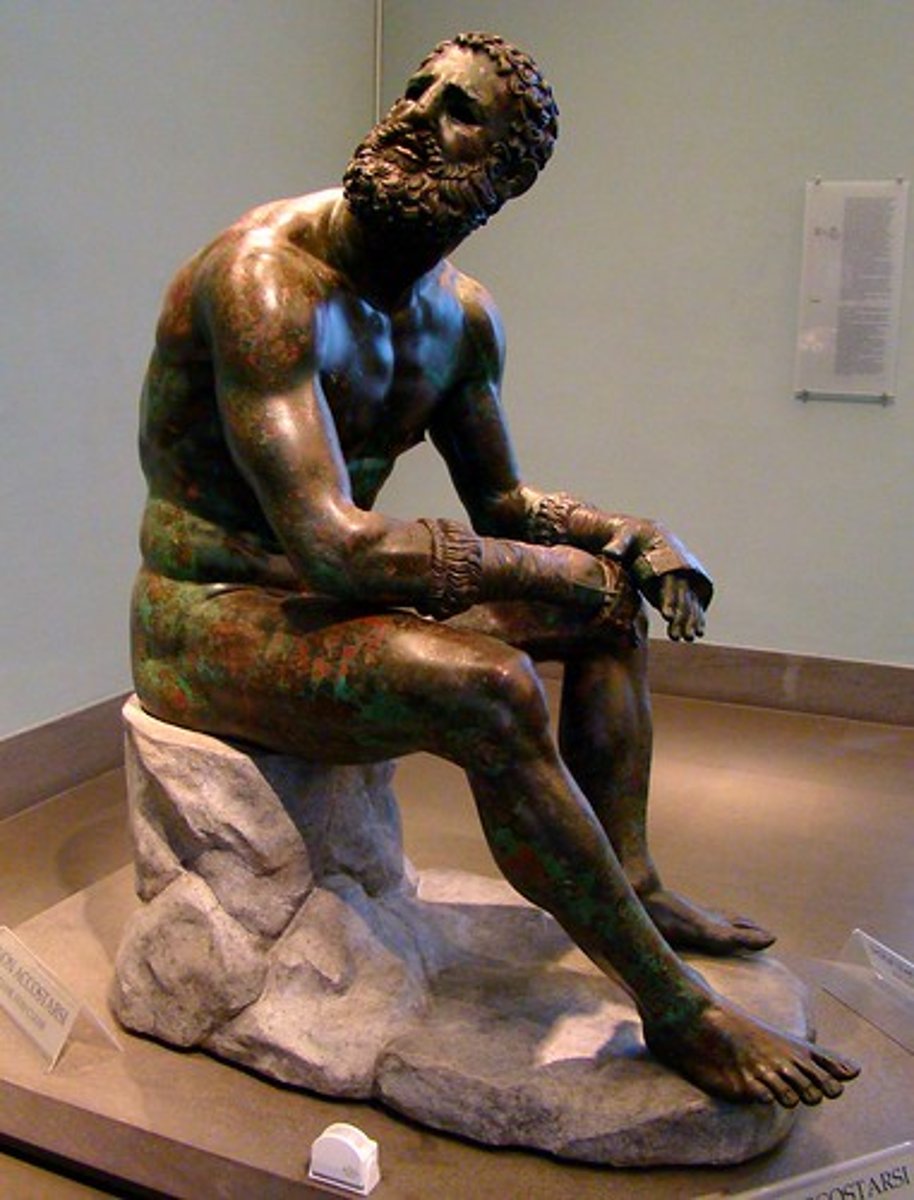
Hellenistic Sculpture
Explores themes untouched in prior eras, offering a wider range of realistic modeling and movement; not meant to be placed near a wall (all angles visible), and emotional themes such as childhood, old age, despair, anger, and drunkenness are common

Seated boxer
100 BCE

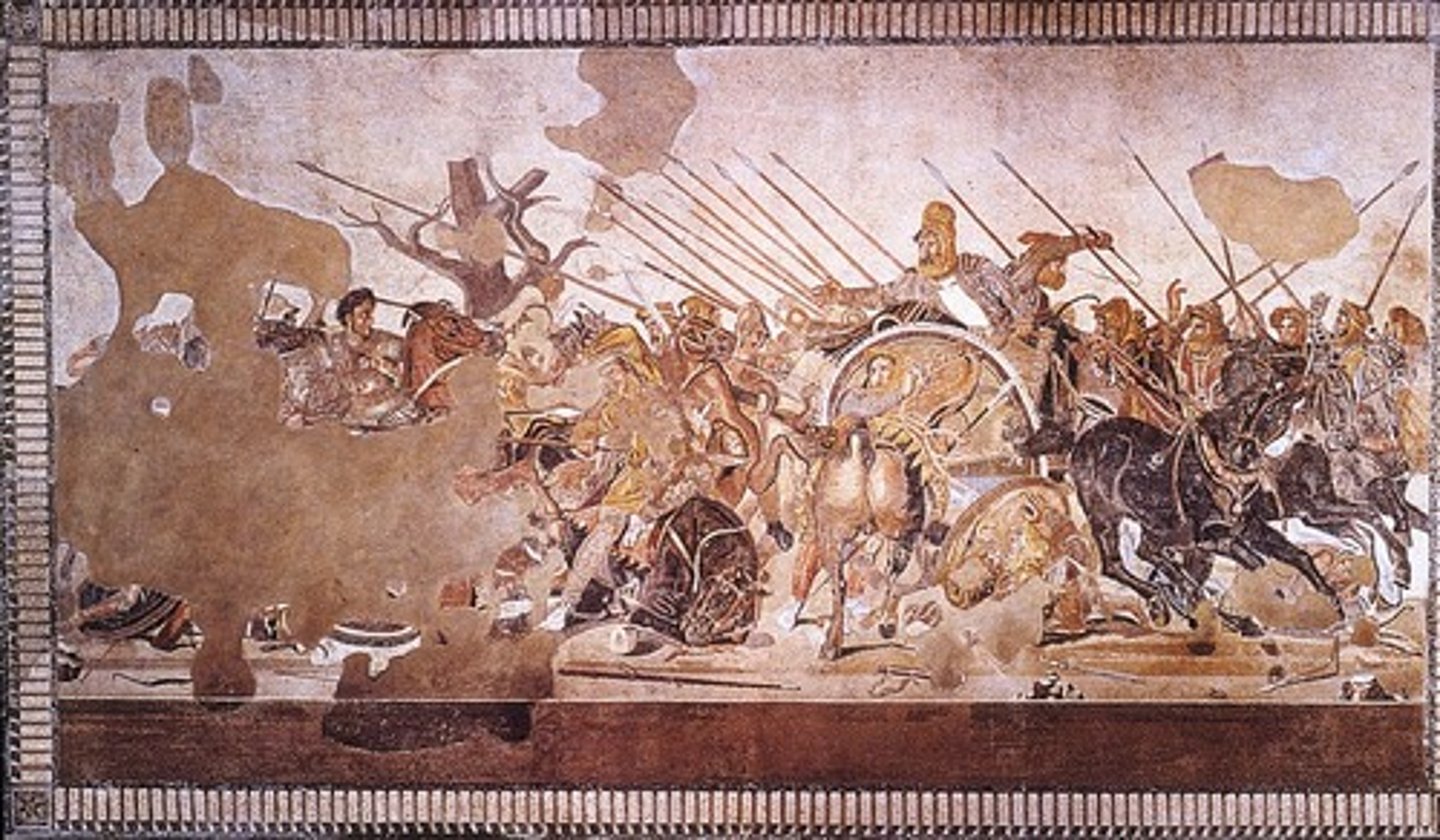
Alexander Mosaic from the House of Faun
100 BCE
