Art of the Ancient Near East: Art History Unit 1 Quiz
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Cuneiform
a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East; in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-shaped impressions which form its signs
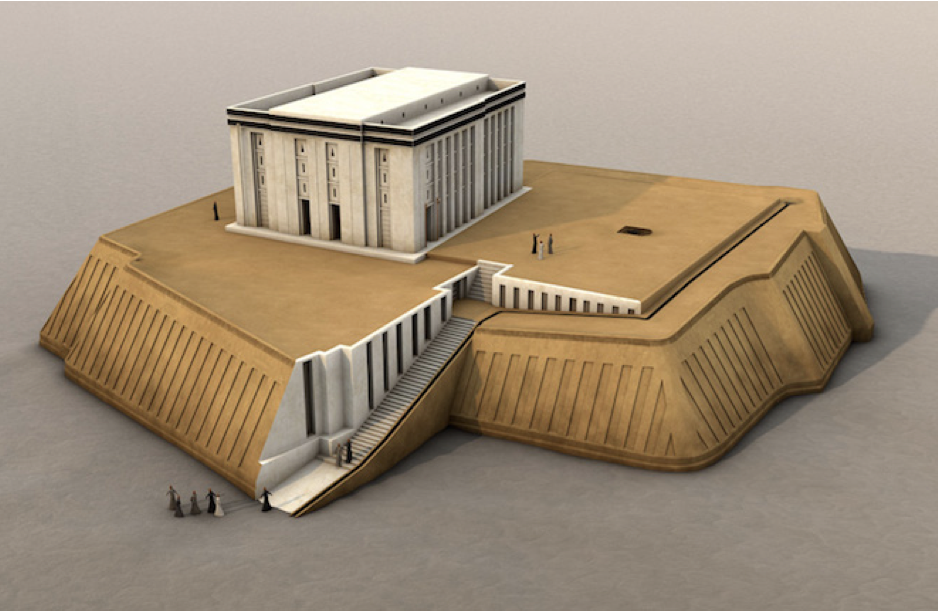
Ziggurat
a type of massive structure built in ancient Mesopotamia. It has the form of a terraced compound of successively receding stories or levels.
Stele
standing stone slab used in the ancient world primarily as a grave marker but also for dedication, commemoration, and demarcation.
Hieratic scale
a technique used in art, mostly in sculpture and painting, in which the artist uses unnatural proportion or scale to depict the relative importance of the figures in the artwork
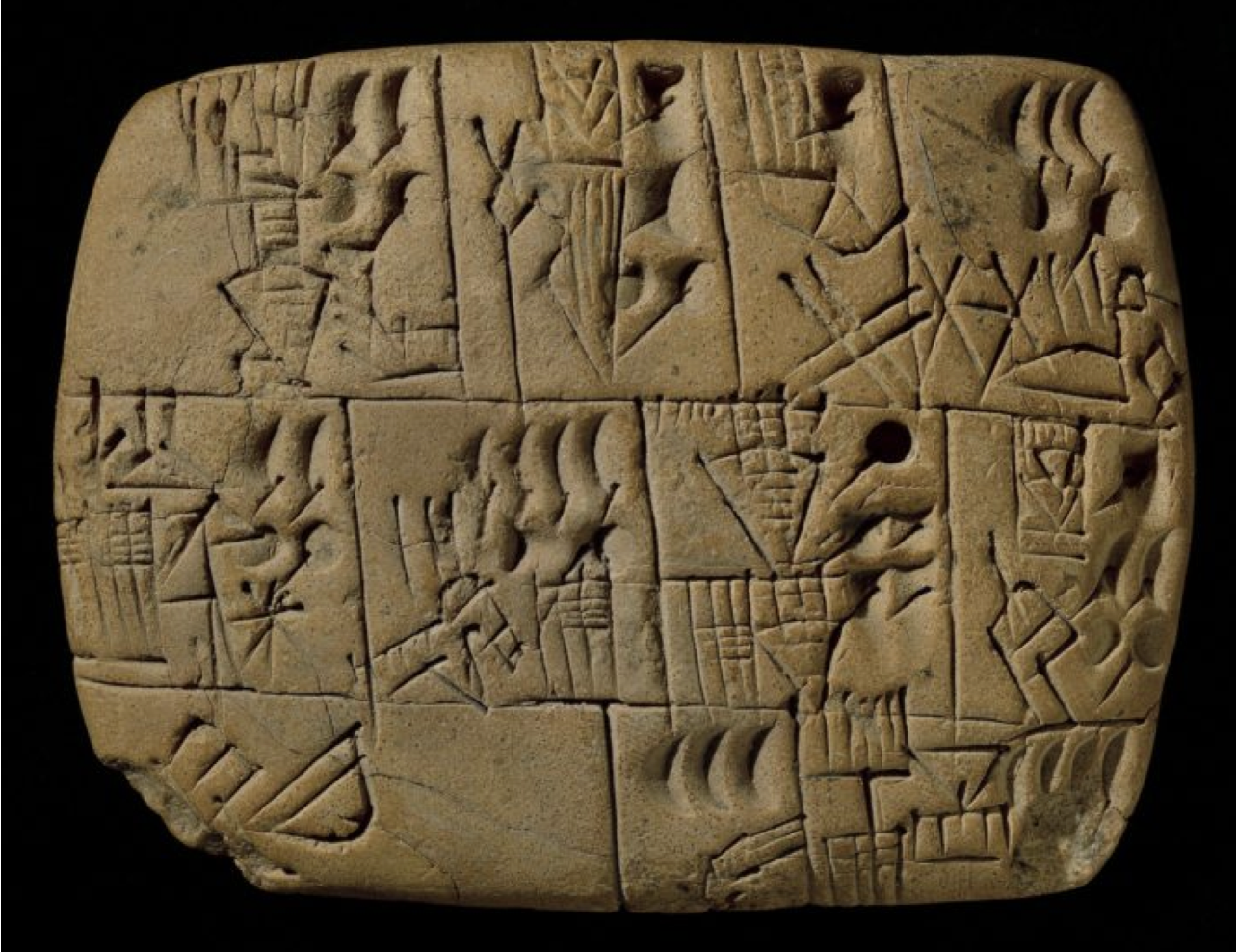
Early writing tablet recording the allocation of beer, 3100–3000 B.C.E, Late Prehistoric period, clay, probably from southern Iraq.

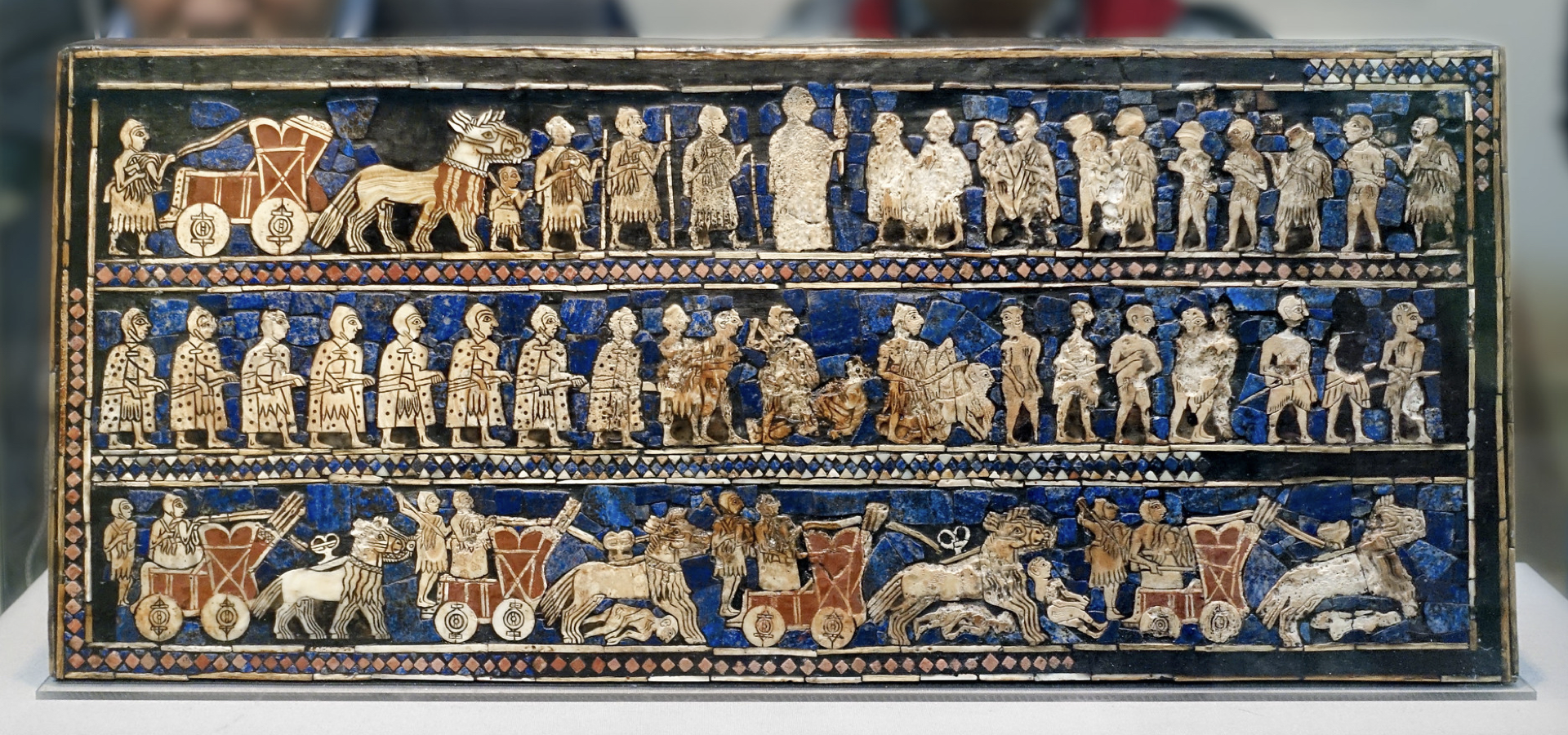
The Standard of Ur, 2600–2400 B.C.E.

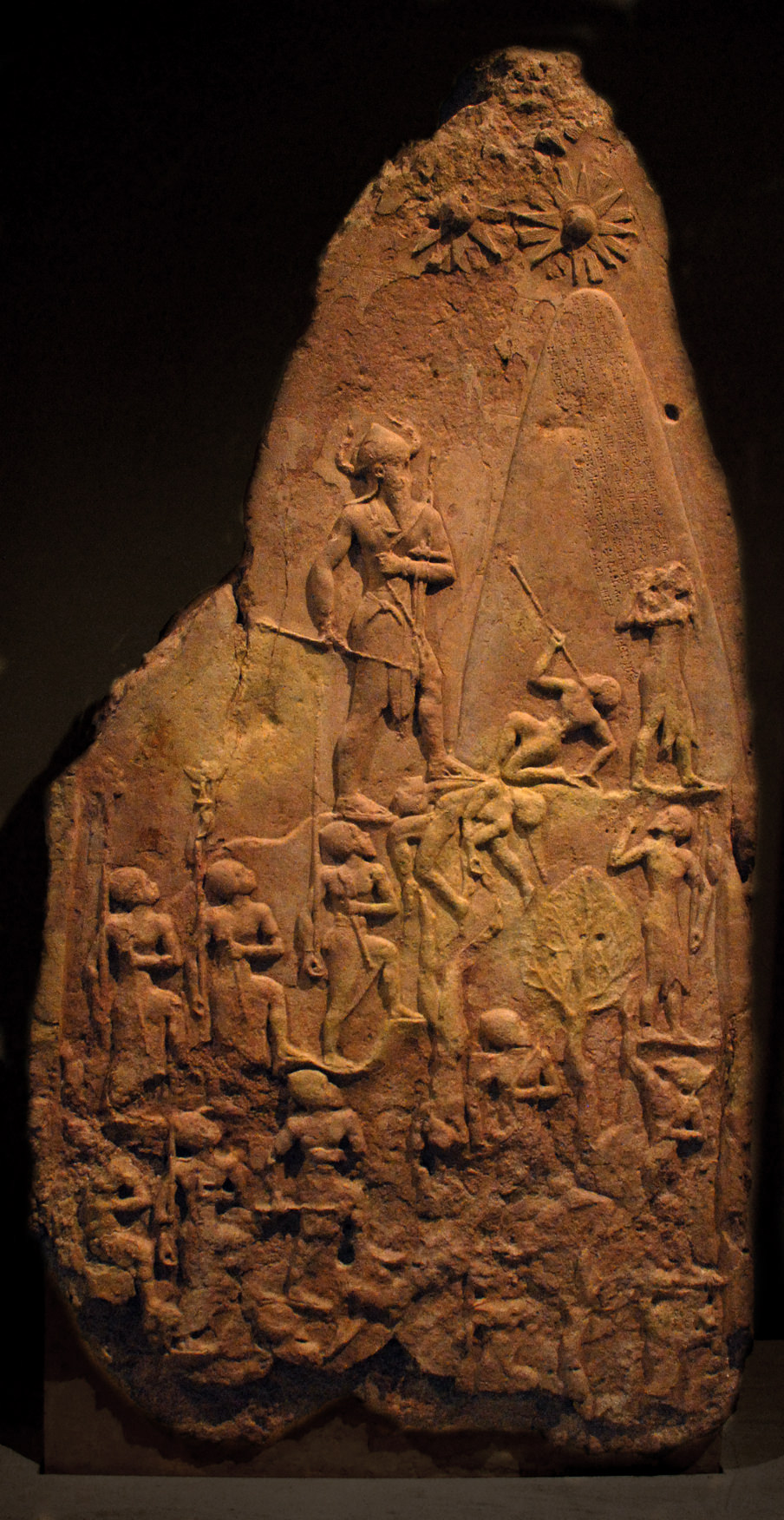
Victory Stele of Naram-Sin, 2254-2218 B.C.E., pink limestone, Akkadian (Musée du Louvre, Paris)

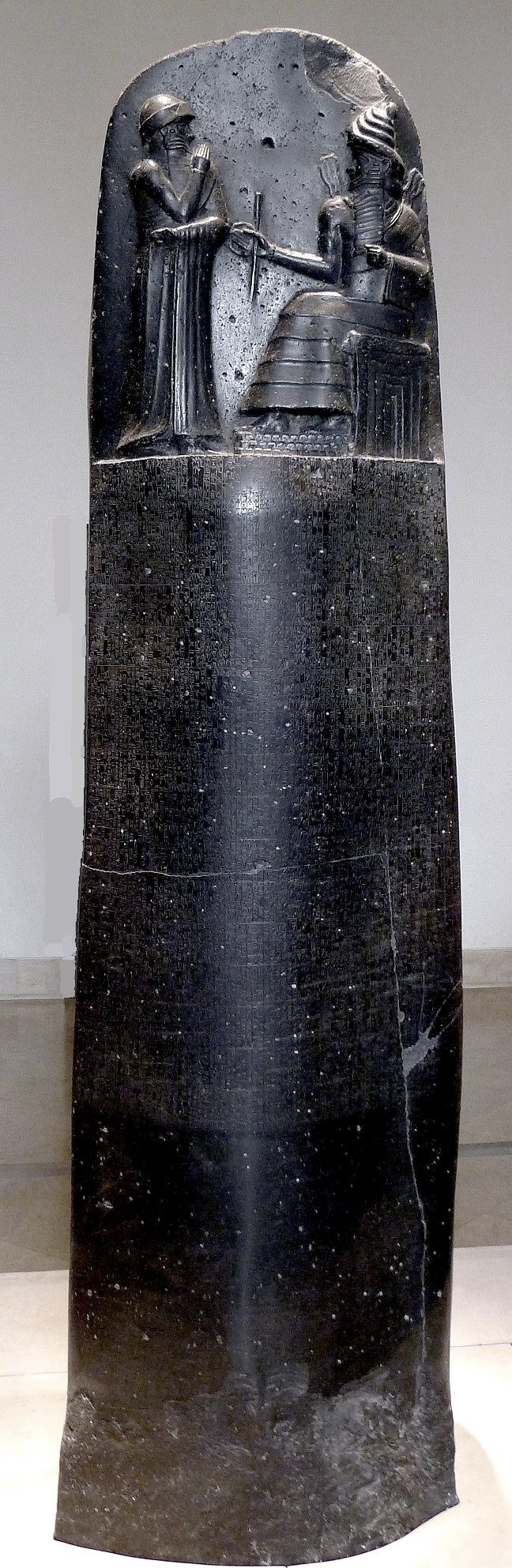
Law Code Stele of King Hammurabi, basalt, Babylonian, 1792–50 B.C.E. (Musée du Louvre, Paris)

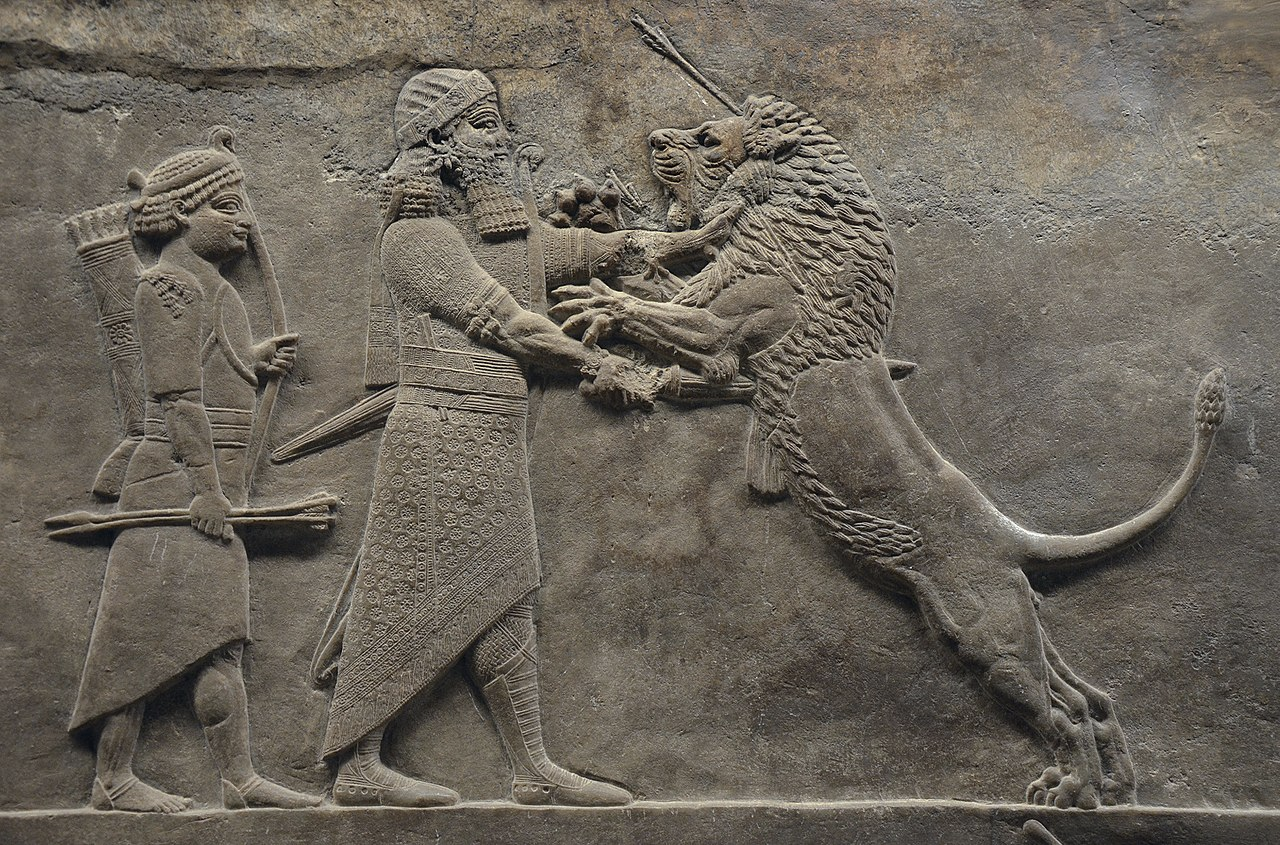
Relief with Ashurbanipal killing a lion, c. 645–635 BC

Capital
the uppermost portion of a column, which often features distinctive architectural elements that cap the building's overall design
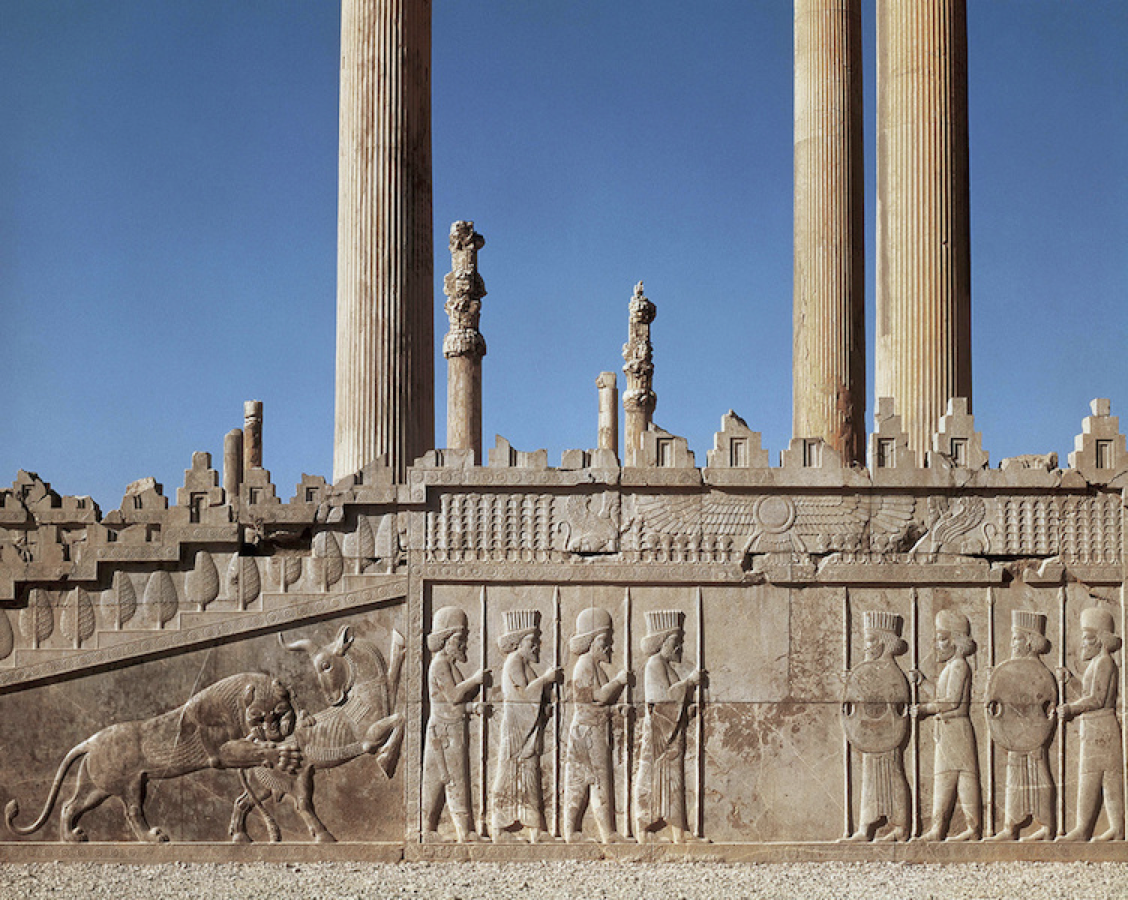
Relief (east stairs), Apādana, Persepolis (Fars, Iran), c. 520–465 B.C.E.
