biomechanics week 3 angular kinematics
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
kinematics
the study of motion
angular kinematics
the study of angular motion
measuring angles
an angle is created between 2 lines
the point at which these 2 lines meet is the centre of a rotation joint
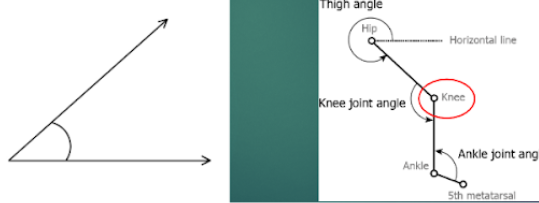
units of measurement ( angular measurement)
degrees
radians (rad) 1 rad = 57.3 degrees
Revolutions (rev) 1 rev = 360 degrees
conversions
converting radians into degrees: multiple by 180 and divide by pi
converting degrees into radians: multiply by pi and divide by 180
concerting degrees into revolutions: divide by 360
determining direction in angular kinematics
clockwise and anti clockwise
an anticlockwise rotation is a positive direction of movement
a clockwise rotation is a negative direction of movement
types of angles
absolute angle, an absolute is measured from an external frame of reference ( this can be a horizontal line measured from the centre of rotation or horizontal line)
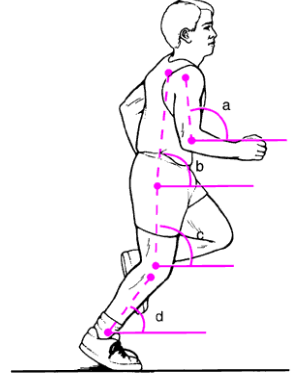
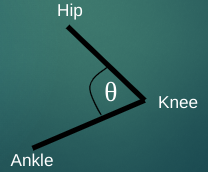
Relative Angles
a relative angle is formed between two limb segments
a relative angle can be defined as degrees of flexion or most commonly as the angle formed at the centre of rotation (joint centre)
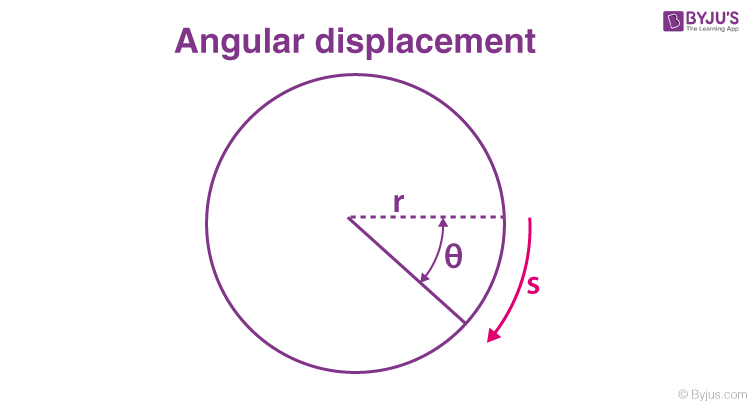
calculating displacement
the angle between the final position and the initial position
angular velocity
angular displacement is the change in angular displacement per unit time:
change in angular position divided by change in time
can be measure in degrees or rads
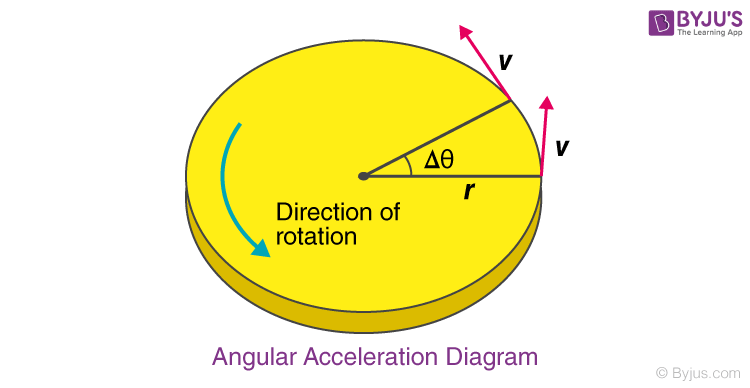
angular acceleration
angular accelaration is the change in angular velocity per unit time.
change in angular velocity divided by time or more simple speed divided by time
angular position and displacement
angular displacement defines the change in angular position
angular displacement is a vector (a vector has magnitude and direction)
angular displacement
= final position - initial position
angular velocity
angular displacement divided by change in time (seconds)
angular acceleration
= change in angular velocity divided by change in time (seconds)