2. THE SELF-CONCEPT
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Which of the following examples best illustrates the "I" in the William James' concept of self?
A. Ethan identifies himself as a team player when describing his role in a group prokect
B. Chloe considers herself as a kind and empathetic person
C. Maria reflects on a recent conversation and concludes "I felt misunderstood during that discussion"
D. Kerry describes himself as being tall adn having blue eyes
C. Maria reflects on a recent conversation and concludes "I felt misunderstood during that discussion"
What are the two concepts of self by William James
"I" and "Me"
"I"
The self-as-subject; the self that thinks, experiences, perceives, and decides
"Me"
The self-as object; the ways in which one describes oneself, including material possessions, social roles, and personal, inner qualities
Self Concept
a cognitive representation of the knowledge and beliefs we have about ourselves
what are somethings included inside our self-concept
everything a person claims as "me" or "mine".
ex. personality traits, abilities, social roles, values, goals and desiresm, and physical characteristics
Why is a self-concept important
it shapes how we think about the world, feel, and behave
Which part of William James' self relates to self-concept
"me"
How do social psychologists think of the self concept as?
Associative Network
Associative Network
all memory and knowledge is organized as a metaphorical network of cognitive concepts interconnected by links
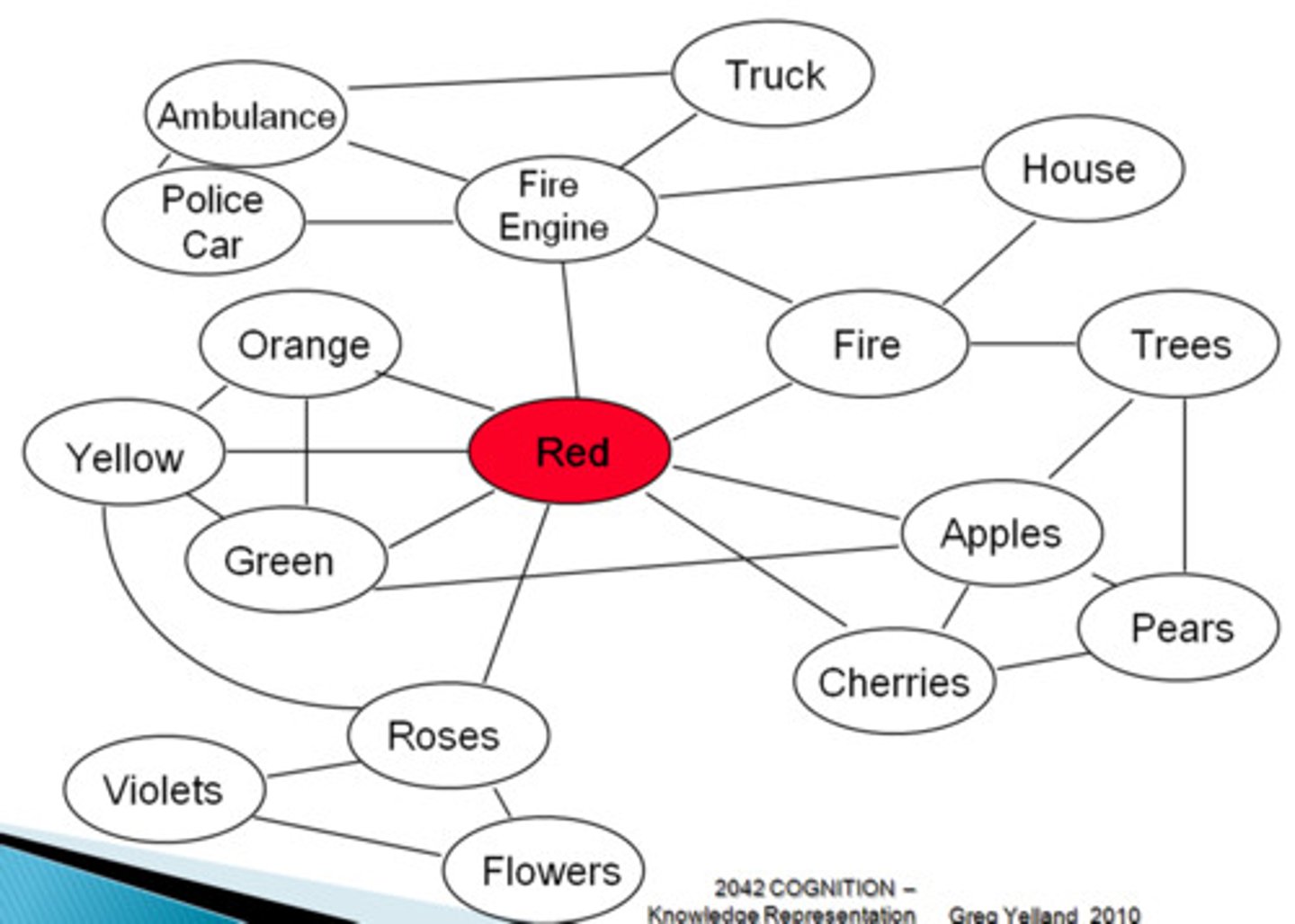
Unitary self concept
Self-concept implies a unitary, fixed, and integrated idea about the self
What is a "But" in unitary self concept
But, people have lots of ideas about themselves, sometimes in contradiction with each other
Working Self-concept
the subset of self-knowledge that is the current focus of awareness ex. spotlight
self-concept
the entirety of our self-knowledge
how is the working self concept created
moment to moment
situational activation
different situations can activate different pieces of self-knowledge thus creating different working self-concepts
Spreading activation
when specific self-aspects is activated, other self-aspects that are linked with it are also activated
What determines what's in the working self-concept (the contents of the self-working self-concept)
the situation we are in based on what is most accessible or salient in that moment)
accessibility of self-knowledge is determined by (what's gonna be most accessible and salient to us)
distinctive, relevance, frequency to the situation
Distinctiveness theory / Distinctive to the situation (accessibility of self-knowledge is determined by)
A person's unique, distinctive characteristics are more salient to them than characteristics that they have in common with others
Reason for Distinctiveness theory
When we think of ourselves in a distinctive way, it becomes more valuable in distinguishing yourself from others (vs. stuff that we have in common)
What makes distinctiveness theory being automatic interesting
we are not strategically thinking about what makes me unique, rather automatically what comes to mind about who we are a person is what's distinctive about us in this situation
Study result for: 6th graders completed "Who am I?" exercise
students with distinctive features were more likely to include those distinctive features in the activity compared to similar aspects to other kids
what does the <6th graders completed "Who am I?" exercise> study show about accessibility of self-knowledge and distinctiveness theory
how much these distinctive aspects of ourselves automatically come to mind depending on the context
Relevance to the situation (accessibility of self-knowledge is determined by)
ex. at a job interview vs. party
Situational Activation
distinctive and relevance to the situation, immediately coming to mind based on the situation
Frequency of activation (accessibility of self-knowledge is determined by)
very important self-aspects or self aspects we engage in and demonstrate often
implications of working self-concept
the self-concept is malleable and dependent on context (different versions of our selves)
what does having a malleable, contextual self-concept mean?
non-central self-aspects can enter the working self-concept
How do contradictory self-aspects to simultaneously exist
Contradictory self-aspects simultaneously exist, just not activated in the same situation
What does the working self-concept influnece
how we behave, and explains why we behave differently in different situations
how does the working self-concept influence our behavior
depends on situational activation to influence behavior
A person identifies strongly as an artist and frequently engages in creative activities. Although they don't see their family often, during a family gathering, the person focuses on their role as a sibling. Which factor of the working self-concept most likely explains this shift?
A. Distinctiveness of being a sibling
B. Relevance of being a aibling
C. Frequency of activation of roles as a sibling
D. Lack of importance of artistic identity in this context
B. Relevance of being a aibling
natural endowment (elements common to true self theories)
already born with a true self (often in the form of potential)
ex. Maslow's hierarchy of need with self-actualization on top
feels authentic (elements common to true self theories)
When our behaviours match up with our internal states = this is when we're behaving in line with the true self
People naturally want to be true to themselves (elements common to true self theories)
living accordance with true self leads to satisfying and fulfilling life
competes with external influences (elements common to true self theories)
reason why it is difficult to be in tune with true self and follow it (true self vs. external pressure)
Study result on "do people believe in a true self and use it as a guide to make decisions?"
People believe that following one's true self is an important strategy for making satisfying decisions
Study: thinking about true self (who you really are) or actual self (who you are in everyday life) and rated satisfaction with recent big life decisions
When P had a hard time having access to their true self - reported less satisfaction w life decisions (maybe bcuz them not knowing their true self, can't use as a guide them to feel good ab their decision)
What does the study on true self resulting to satisfaction in life decision imply
idea of a true self resonates with people and people are more satisfied with their decisions when these are in accord with the true self(vs. when they are not)
What is a problem with the idea of a true self, specifically natural endowment
Natural endowment of a true self is not a provable idea. Can't prove cuz how do you assess a baby's potential
What is a problem with the idea of a true self, specifically to self-beliefs being inaccurate
true self require an accurate sense/self knowledge about what they're actually like but self-concepts are full of inaccuracies (ex. better than average effect)
What is a problem with the idea of a true self, specifically true self being what is 'good'
true self seems to be about social desirability, rather than acting in line with one's unique characteristics (feels most authentic when accepting external influence when making personal decisions)
Authenticity and Big Five Study(trait vs state reports), when do people feel most authentic? result
People felt consistently authentic when they were behaving in socially desirable ways, rather than consistent with their personality
What do we assume about others 'true selves' with the idea of true self being what is good
People assume that others are being their "true selves" when they are behaving in a morally good way (ex. when sm is rude - they are in a bad mood ex. when someone is kind - we see that as a indicative of their true self)
What is the conclusion of true self
true self is more of a guide than reality
What is true self when we have seen we tend to be more authentic behaving in line w social desirablity
true self reflects desired reputation
desired reputation
what is valued by society (ideals) + what distinctive role one's own abilities and traits are best suited to (actual self)
according to desired reputation and true self aligning, when do people feel most authentic
when actions are consistent with desired reputation
according to desired reputation and true self aligning, how does this explain about ppl with other people
this desired reputation being a true self explains why we are slightly different with different people (but generally similiar)