Comprehensive Overview of Eating, Schizophrenia, Dissociative, and Substance Use Disorders
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
What are eating disorders?
A category of partially overlapping syndromes marked by eating dysregulation, including anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorder.
What characterizes anorexia nervosa (AN)?
Inability to maintain a normal healthy body weight, distorted body image, and unhealthy weight-loss behaviors.
What are the three diagnostic criteria for anorexia nervosa?
1) Disturbance in body weight or shape experience, 2) Undue influence of body weight on self-evaluation, 3) Lack of recognition of the seriousness of low body weight.
What are the two subtypes of anorexia nervosa?
Restricting subtype and binge-eating/purging subtype.
What defines bulimia nervosa (BN)?
Recurrent binge eating episodes with a sense of loss of control, followed by compensatory behaviors.
What are common compensatory behaviors in bulimia nervosa?
Self-induced vomiting, laxative use, diuretic misuse, fasting, and excessive exercise.
What is the BMI requirement for a diagnosis of bulimia nervosa?
A BMI greater than 18.5 kg/m².
What characterizes binge eating disorder (BED)?
Recurrent binge eating without regular compensatory behaviors, occurring at least weekly for 3 months.
What are some criteria for binge eating disorder?
Eating rapidly, eating until uncomfortably full, eating large amounts when not hungry, eating alone due to embarrassment, feeling disgusted or guilty afterward.
What does OSFED stand for?
Other Specified Feeding/Eating Disorders, applying to presentations that do not meet full criteria for any eating disorder.
What is a culture-bound syndrome?
A collection of signs and symptoms restricted to a limited number of cultures due to psychosocial features.
What is the main finding of Keel & Klump (2003) regarding AN and BN?
Bulimia nervosa is a culture-bound syndrome, while anorexia nervosa is not.
What historical evidence supports the existence of anorexia nervosa?
Self-starvation behaviors have been documented for centuries, predating modern dieting culture.
What is the role of culture in the expression of eating disorders?
Cultural context shapes the expression of disorders, influencing how symptoms manifest and are diagnosed.
Why are eating disorders often underdiagnosed in minorities?
ED criteria were developed using white middle-class women, leading to misdiagnosis in individuals from other backgrounds.
What are the eating disorder rates among African Americans?
Lowest rates of anorexia nervosa; binge eating and bulimia nervosa are present but often linked to stress rather than thin ideals.
What specific risk factors are associated with binge eating disorder in African American women?
Childhood sexual abuse is linked to binge eating disorder.
What treatment works best overall for eating disorders?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT).
What is the significance of cultural adaptations in treatment?
Cultural adaptations, such as family involvement and language considerations, can increase treatment effectiveness.
What are the obesity rates among minority groups in the U.S.?
Hispanic children have the highest childhood obesity rates, followed by Black and White children.
What individual-level contributors affect obesity in minority groups?
Dietary habits, physical activity levels, and biological differences.
How does the community environment contribute to obesity in minority populations?
Food deserts and limited access to healthy food options increase obesity risk.
What is the impact of acculturative stress on eating disorders?
Acculturative stress is a strong predictor of bulimia nervosa and binge eating.
What are the main characteristics of schizophrenia?
Impairments in social functioning, difficulties in maintaining relationships, and problems with self-care.
What is a necessary criterion for diagnosing schizophrenia?
Problems in daily living without significant impairment in intellectual functioning.
What are the three major dimensions of schizophrenia?
Positive symptoms, negative symptoms, and cognitive impairments.
What are positive symptoms of schizophrenia?
Thoughts, sensory experiences, and behaviors that are present in persons with the disorder but absent in those without it, such as hallucinations and delusions.
What are negative symptoms of schizophrenia?
The absence or reduction of normal cognitive functions, feelings, or behaviors, including blunted affect and poverty of speech.
What cognitive impairments are associated with schizophrenia?
Problems with attention, memory, and problem-solving skills.
What is required for a diagnosis of schizophrenia?
Presence of two or more symptoms (delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, grossly disorganized behavior, negative symptoms) for at least a month, with continuous disturbance for at least 6 months.
What is the significance of delusions in schizophrenia diagnosis?
One of the symptoms must be delusions, hallucinations, or disorganized speech.
How does urbanicity affect schizophrenia prevalence?
Schizophrenia is more concentrated in urban areas, suggesting environmental stressors may play a role.
What is the social drift hypothesis?
The idea that the debilitating effects of schizophrenia lead to a decrease in socioeconomic status and increased poverty.
What is the diathesis-stress model in relation to schizophrenia?
It combines genetic vulnerability with environmental stressors to explain the onset of schizophrenia.
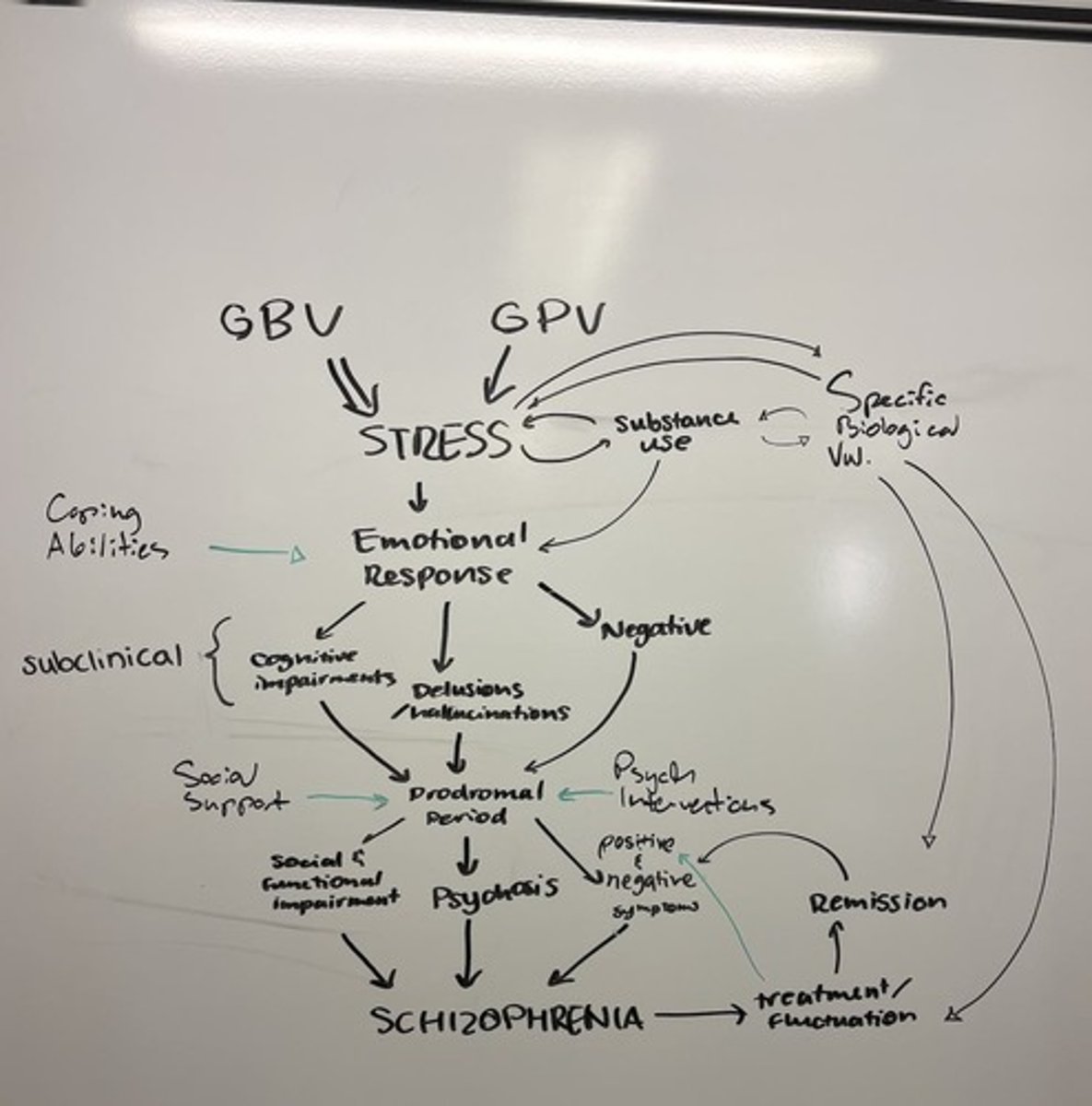
What prenatal factors may contribute to schizophrenia risk?
Oxygen deprivation, malnutrition, or infections during pregnancy.
What are some biological factors linked to schizophrenia?
Alterations in brain structure, dopaminergic complications, and obstetric complications.
What is the dopamine hypothesis in schizophrenia?
It suggests that alterations in dopamine levels are responsible for the symptoms of schizophrenia.
What is the prodromal phase of schizophrenia?
A period characterized by subclinical symptoms such as mild paranoia and social withdrawal before full-blown psychosis.
What are common treatments for schizophrenia?
Antipsychotic medications, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), psychoeducation, and social skills training.
What is the role of antipsychotic medication in treating schizophrenia?
It targets dopamine systems and is effective for positive symptoms but less so for negative symptoms.
What are the outcomes for individuals with schizophrenia receiving treatment?
Many can live independently with proper treatment, while untreated symptoms may worsen.
What are biomarkers in the context of schizophrenia?
Measurable biological indicators that relate to disease presence, risk, or treatment response.
Why is it difficult to identify biomarkers for schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a heterogeneous syndrome with overlapping symptoms and varying biological pathways.
What types of biomarkers are being studied for schizophrenia?
Genetic markers, neuroimaging markers, neurophysiological markers, and inflammatory or hormonal markers.
What are the ethical implications of using biomarkers in schizophrenia diagnosis?
They could lead to premature labeling and discrimination, necessitating careful consideration before clinical use.
What is the impact of trauma and PTSD on schizophrenia?
They can worsen the course of schizophrenia and exacerbate symptoms.
What is the significance of early detection in schizophrenia?
Early treatment can improve outcomes and may prevent the progression of the disorder.
What are the traditional subtypes of schizophrenia?
Paranoid, Disorganized, Catatonic, Undifferentiated, and Residual.
How does schizophrenia manifest in terms of brain development?
It is seen as a neurodevelopmental disorder, with changes occurring long before symptoms appear.
What is the relationship between substance use and schizophrenia?
Substances like cannabis and alcohol can trigger psychosis in individuals with genetic vulnerability.
What is the main takeaway regarding schizophrenia?
It is a multifactorial disorder influenced by genetic, environmental, and developmental factors, and can be managed with early detection and integrated treatment.
What are dissociative disorders characterized by?
A disruption of and/or discontinuity in the normal integration of consciousness, memory, identity, emotion, perception, body representation, motor control, and behavior.
What common feature do dissociative disorders share?
They are frequently manifested in the wake of trauma and are influenced by their proximity to trauma.
What is the estimated genetic influence on dissociative disorders?
Approximately 50%.
What is Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) formerly known as?
Multiple Personality Disorder.
What characterizes Dissociative Identity Disorder?
A disruption of identity characterized by two or more distinct personality states and recurrent gaps in the recall of everyday events, personal information, and/or traumatic events.
What are the two distinct forms of dissociation proposed?
Detachment (including depersonalization and derealization) and Compartmentalization (including dissociative amnesia).
What is dissociative fugue defined as in DSM-5?
Apparently purposeful travel or bewildered wandering associated with amnesia for identity or other important autobiographical information.
What is the post-traumatic model of DID?
It posits that DID arises primarily from a history of severe physical and/or sexual abuse in childhood.
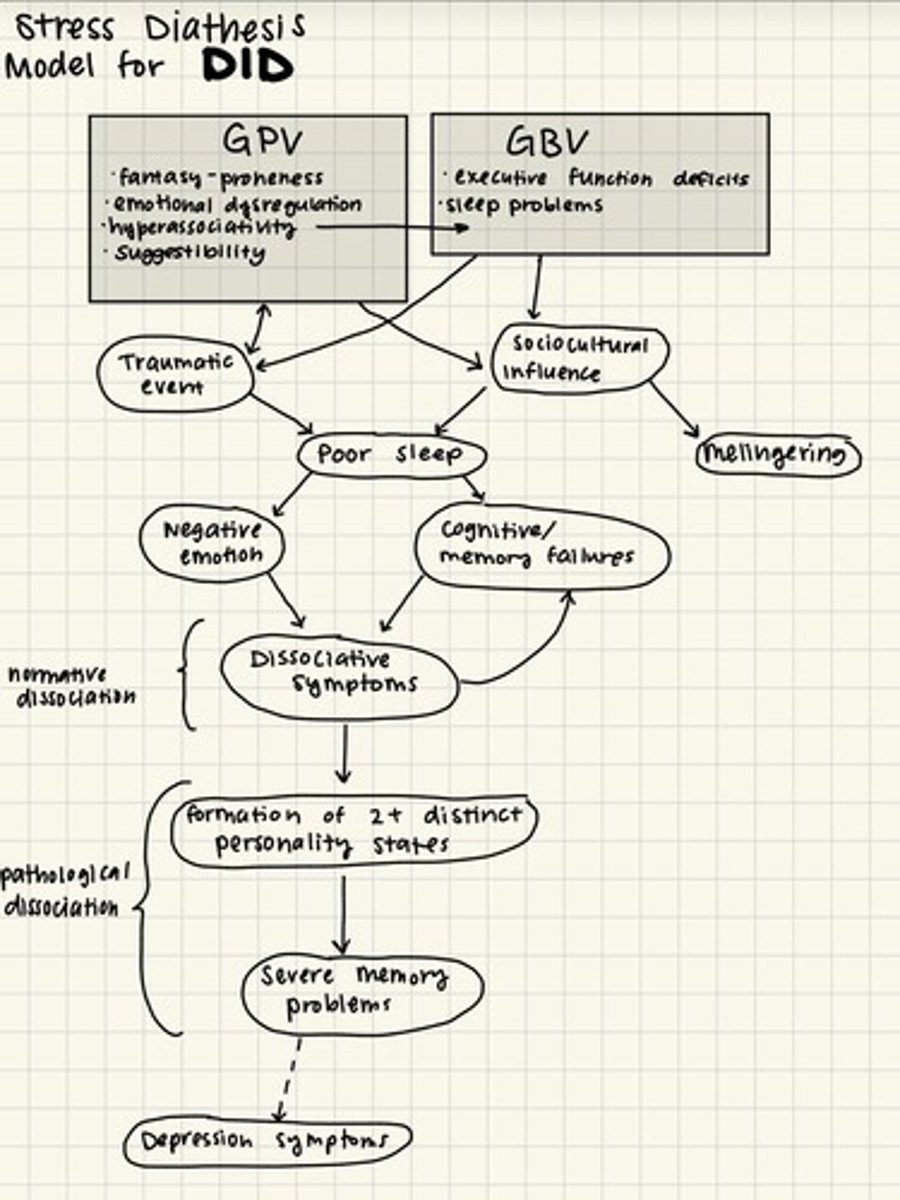
What does the sociocognitive model argue regarding dissociative disorders?
It suggests that fantasy-proneness, media influences, suggestibility, and cognitive failures contribute to self-reports and diagnosis of dissociative disorders.
What is the criticism of the trauma model (TM) of dissociation?
Correlations between highly aversive events and dissociation are highly variable, and many dissociative patients report no aversive events.
What is the definition of Alcohol Use Disorder?
A problematic pattern of alcohol use leading to significant impairment or distress as manifested by at least two specific criteria.
What are some criteria for diagnosing Alcohol Use Disorder?
Using alcohol in larger amounts than intended, persistent desire to cut back, significant time spent on alcohol-related activities, cravings, and failure to fulfill obligations.
What does the disease concept of alcohol addiction suggest?
It views alcohol addiction as a medical disorder, which became dominant in the US in the mid-1900s.
What is ambivalence in the context of alcohol use disorder?
A focus point of the clinical picture where individuals are not very compelled to change their drinking habits, often leading to denial.
What is the continuum conceptualization of alcohol use problems?
It ranges from risky drinkers or 'misusers' to moderate or severely dependent individuals.
What is a common outcome of highly aversive events and negative emotions?
They can disrupt the sleep-wake cycle and predispose individuals to dissociative symptoms.
What role does hyperassociativity play in dissociative disorders?
It fuels 'set-switching' particularly in the presence of low levels of meta-consciousness and high levels of negative affect.
What is the significance of the case of Sybil in the context of DID?
It is a controversial case that raised questions about the validity of multiple personalities and the influence of suggestive therapy.
What is the relationship between dissociation and sleep?
Poor sleep can trigger negative emotions and thoughts of aversive events, leading to dissociation.
What is the impact of emotional dysregulation on dissociative symptoms?
Emotional dysregulation predicts dissociative symptoms.
What are the two types of dissociation mentioned?
Depersonalization and derealization, which are part of the detachment form.
What is the role of suggestibility in the diagnosis of dissociative disorders?
It can contribute to self-reports and the diagnosis of dissociative disorders.
What is the criticism of the sociocognitive model (SCM)?
It may overlook the role of trauma in dissociation, despite suggesting that media and cognitive factors influence self-reports.
What is the significance of the overlap between BPD, schizophrenia spectrum disorders, and dissociative disorders?
It suggests common variables that contribute to these disorders.
What organization proclaimed alcoholism as a disease?
The American Medical Association
What was the intended effect of embracing the disease concept of alcoholism?
To shift responsibility from the criminal justice system to the health care system and destigmatize alcohol addiction.
How does Alcoholics Anonymous view alcoholism?
As a biological aberration (an allergy to alcohol) and a progressive disorder.
What percentage of risk for alcoholism is attributed to genetics?
About 50%.
What does current research suggest about alcoholism as a progressive disorder?
It is not progressive; it includes periods of varying severity of alcohol problems.
What factors are associated with continued drinking behavior?
Conditioned cues and positive consequences rather than physical dependence.
What does the DSM-5 say about alcohol use disorders?
It eliminates the distinction between alcohol dependence and alcohol abuse, viewing them as varying in severity.
What are the two key determinations in diagnosing alcohol use disorders?
(a) Severity of the problem and (b) likelihood of withdrawal symptoms when drinking is reduced.
What is the global burden of disease attributed to alcohol?
Around 5%.
Which demographic has higher rates of alcohol use disorders?
Men, Native Americans, and Whites.
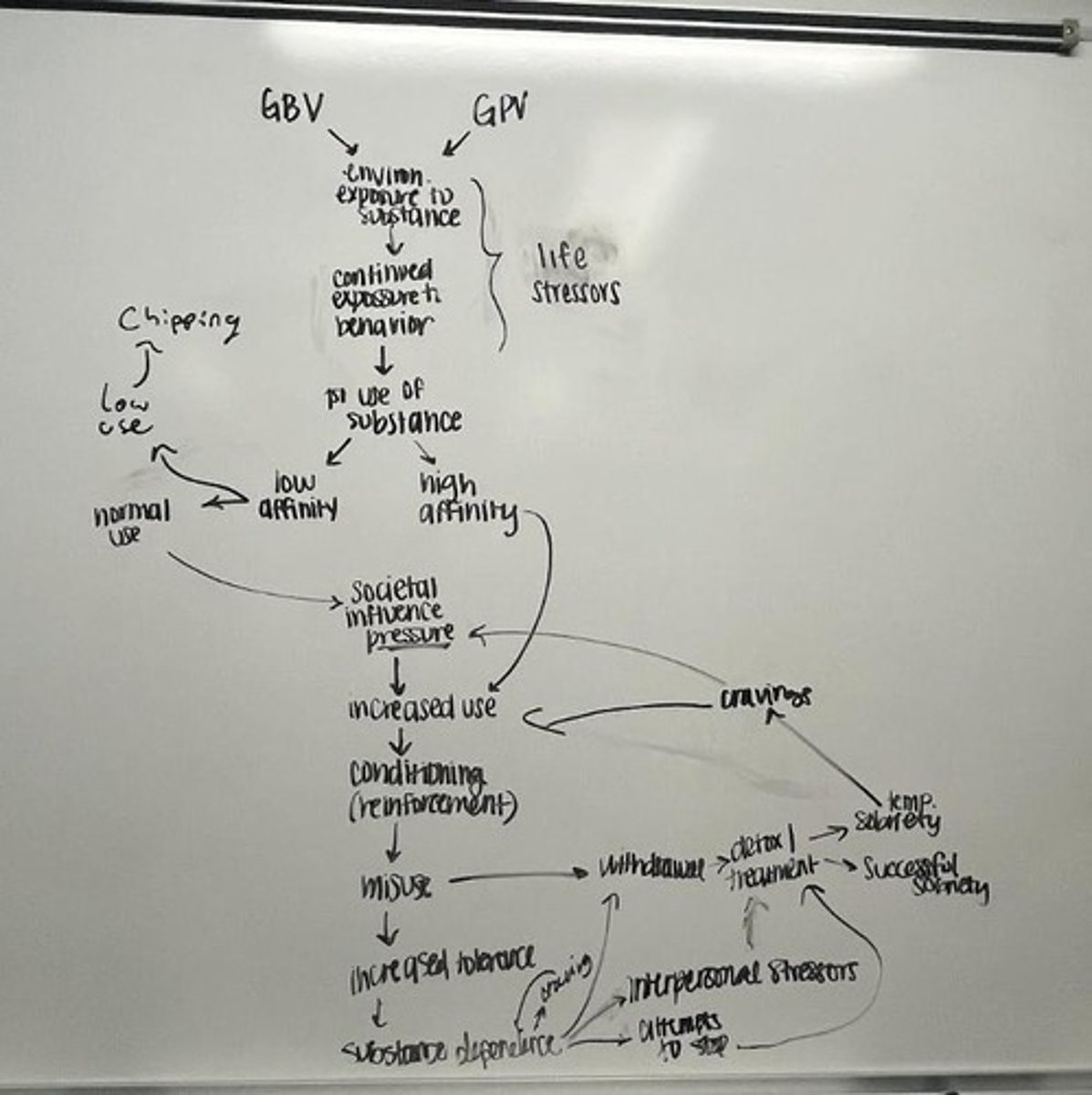
What are the two main genetic factors contributing to substance use disorders?
(1) Level of response to alcohol and (2) neurophysiology markers.
What role does learning theory play in drinking behavior?
Drinking is largely learned through classical and operant conditioning.
What is the essence of the DSM classification system for substance use disorders?
It includes 10 drug classes, each defined as a separate substance use disorder.
What is the essential feature of substance use disorders?
Continued substance use despite clinically and functionally significant impairment or distress.
What are the four categories of maladaptive behaviors related to substance use?
Impaired control, social impairment, risky use, and pharmacological criteria.
What is the classification of substance use disorders based on symptom severity?
Mild (2-3 symptoms), moderate (4-5 symptoms), or severe (6+ symptoms).
What is the impact of chronic substance use on neurological circuitry?
It may lead to persistent changes that increase vulnerability for relapse.
What is the role of the HPA axis in addiction?
Stress and adversity are risk factors for substance use disorders.
What is the 'hijacking view' of addiction?
Modern substances bypass adaptive systems, directly affecting emotion and motivation circuits.
What does the harmful dysfunction perspective suggest about addiction?
Addiction is a motivational dysfunction with compulsive behavior affinities.
What is the false 'pathology versus choice' paradigm in addiction?
It assumes addictive behavior is either caused by pathology (involuntary) or by choice (voluntary).
What is equifinality in the context of addiction?
A disorder can derive from multiple different pathways.
What does 'chipping' refer to in substance use?
The ability to use an addictive substance in low levels without developing problematic use.
What is the significance of the P300 wave component of ERPs in addiction?
Low amplitude is associated with an increased risk of drinking problems.
How does the behavioral economics perspective explain substance use disorders?
Individuals discount delayed reinforcers compared to immediate reinforcers.