Atoms and bonding
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
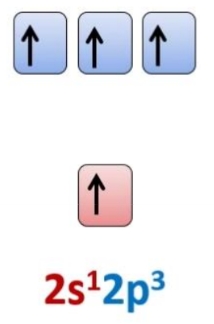
Electronic configuration of carbon

What bond is formed first
sigma bonds
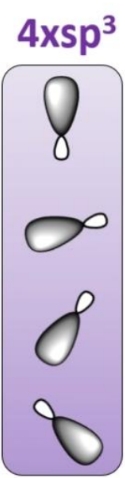
Hybridisation state of carbon with 4 single bonds
Angle between each sp3 orbital
How does Carbon bonds to H
SP3

Y
Hybridisation of carbon with a double bond
Shape and angle
sp2 -each atom in the bond must keep a p orbital free for the pi bond
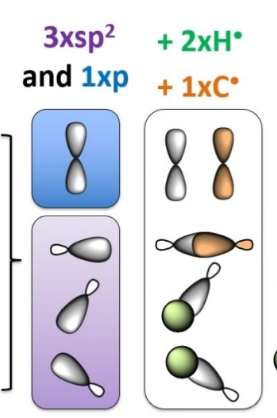
The 3 sigma bonds are trigonal planar (same plane)
The Pi bond is in different plane
120 deg
Hybridisation of carbon ith a triple bond
SP = 2 pi bonds and one sigma bond1
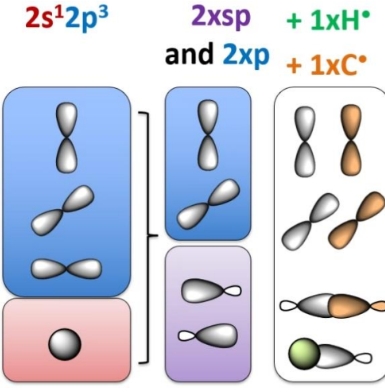
Why are sp orbitals shorter
Less p character (50%)
sp2 has 60%
SP3 has 75%
= they are stronger bonds (3 bonds and atoms are closer to eacho ther) and more acidic due to a more stable conjugate base (negative charge on carbon is held in sp3 orbital)
Electronic configuration of N
How many bonds can N form?

3 covalent bonds, one lone pair left
Hybridisation state of N for single bonds
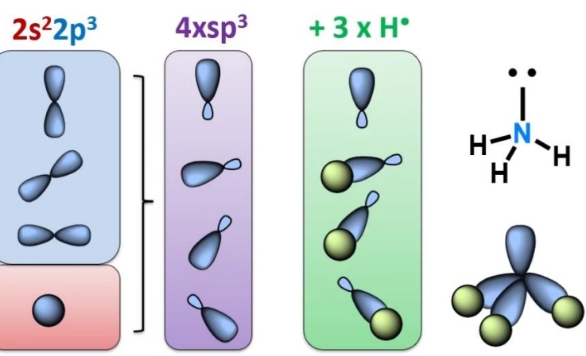


Why is NH3 isoelectric with methane
Lone pair in NH3 can make a sigma bond to H+ forming a molecule with the same electron configuration as methane
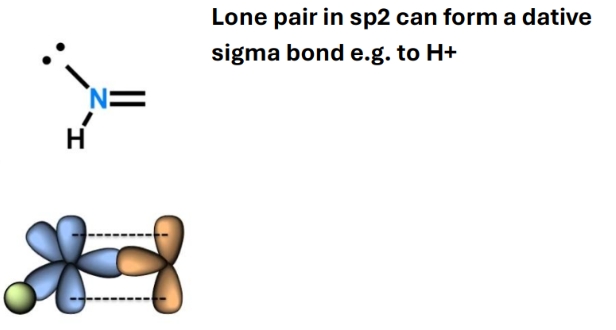
Hybridisation of N with double bond
SP2
Lone pai in SP2
Trigonal planar
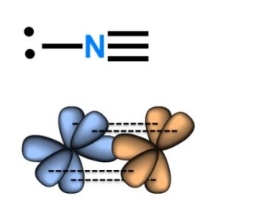
Hybridisation of N in triple bond
sp
Lone pair in sp
Why is N a copycat
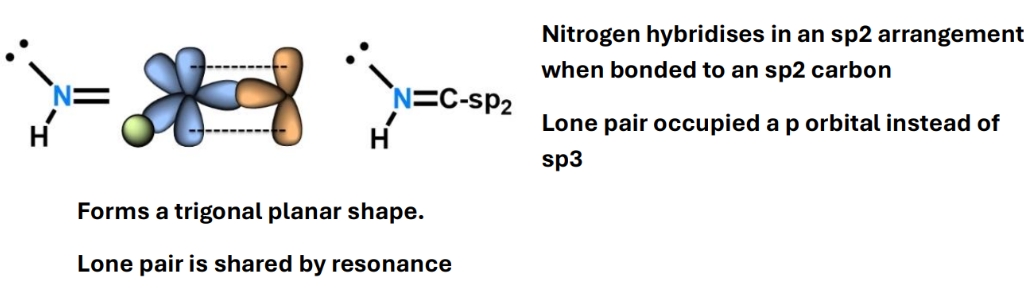
E.g. in an Imine HN=CR2
This also occurs when nitrogen is expected to be sp3 e.g. when bonded to an aromatic ring but it rehybridises into sp2 if the carbon that it is attached to is sp2 hybridised by being doube bonded to another atom in the ring.
Generally occurs whenever its attached to an sp2 carbon by a double or single or triple bond
Electronic configuration of O and what bodns can it form

Hybridisation of O when single bonds
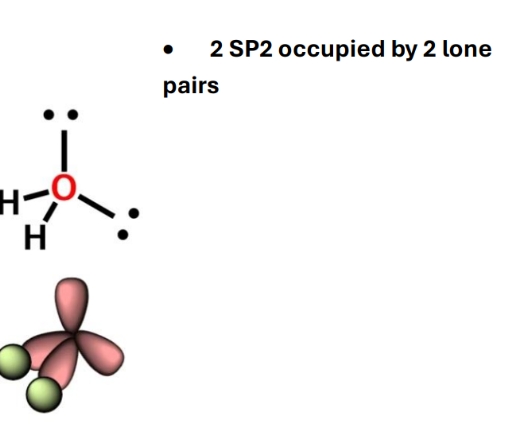
sp3
104.5 due to repulsion
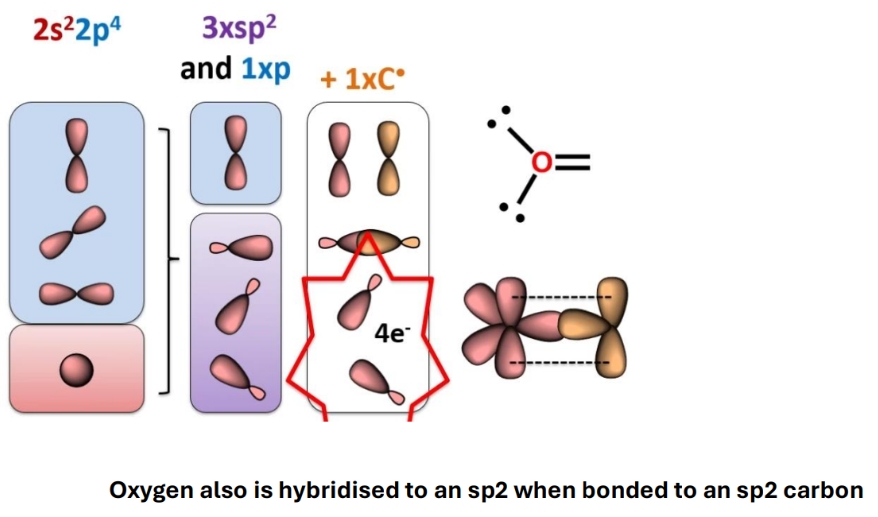
Hybridisation of O when double bonds
When does bond polarisation value increase
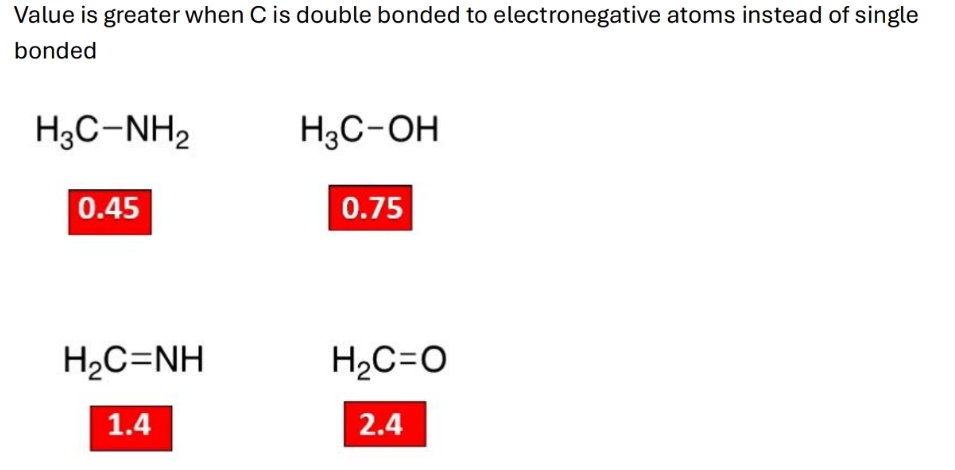
Greater electronegativity difference
Inductive effect
Shorter bonds = stronger dipole interaction
What is the effect of an electronegative group on a molecules pka

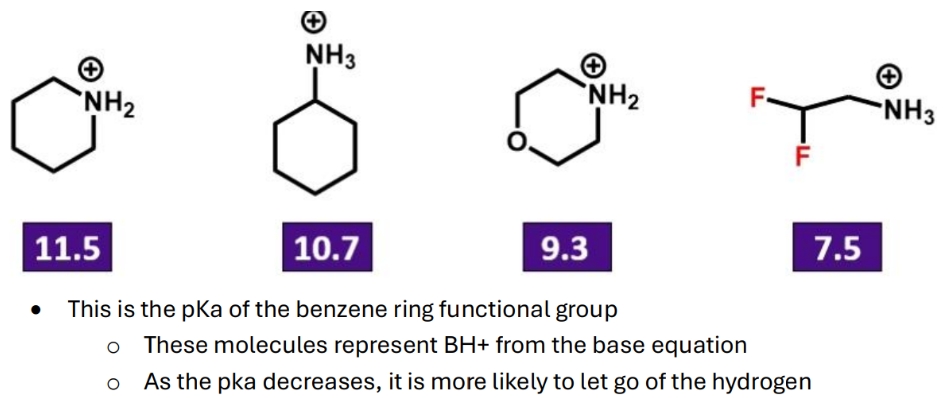
The positive charge can resonate = stability
Why does an amine and an amide have different pkas

Why do sp3 carbons have higher pkas

Why do imines have lower pka than amines

Why the pka of a nitrile so low
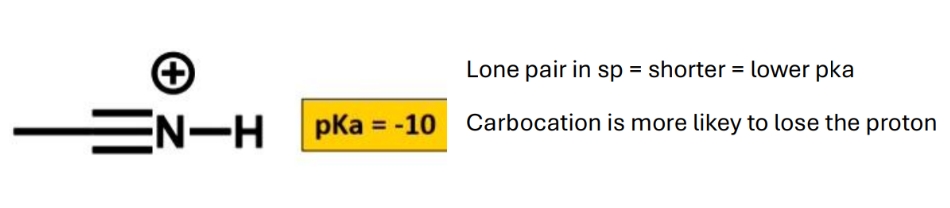
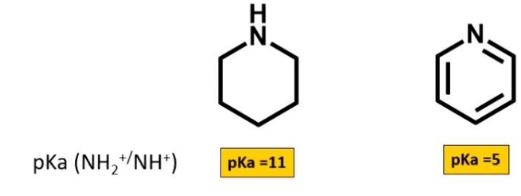
Why is pyridine a weaker base

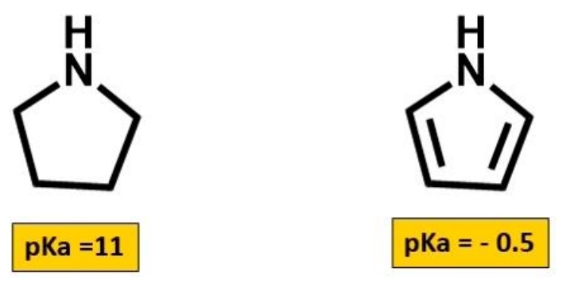
Why is pyrrole a weaker base

Where are the lone pairs in this
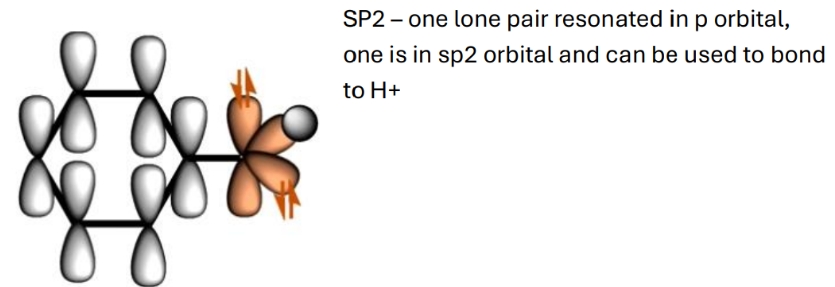
How to increase stability of this with inductive effect of electron withdrawing groups


Pka is dependednt onn
resonance, inductive effect, hybridisation state
What moves in resonance
Lone pairs in p orbitals of sp2 hybridised atooms or the charge of a negatively charged atom (can even be a negatively charged carbon)
Lone pairs in p orbitals jump from p orbital to p orbital on the atoms
How to draw resonance structures
Double headed arrows
brackets
charges must b the same on both sides
How does resonance affect stability

If there is no difference between stability of 2 resonance structures
they exist in a 50:50 proportion in a mixture
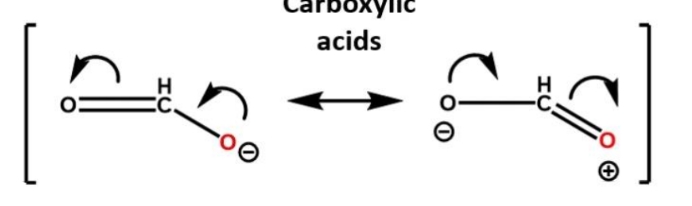
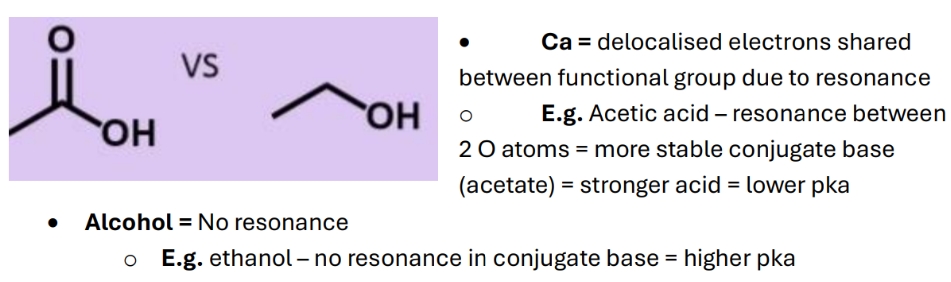
Why do carboxylic acids have lower pka than alcohols
How to draw resonance when theres positive charge

Why is this more stable

Shape of benzene ring

Huckel's rules for aromaticity

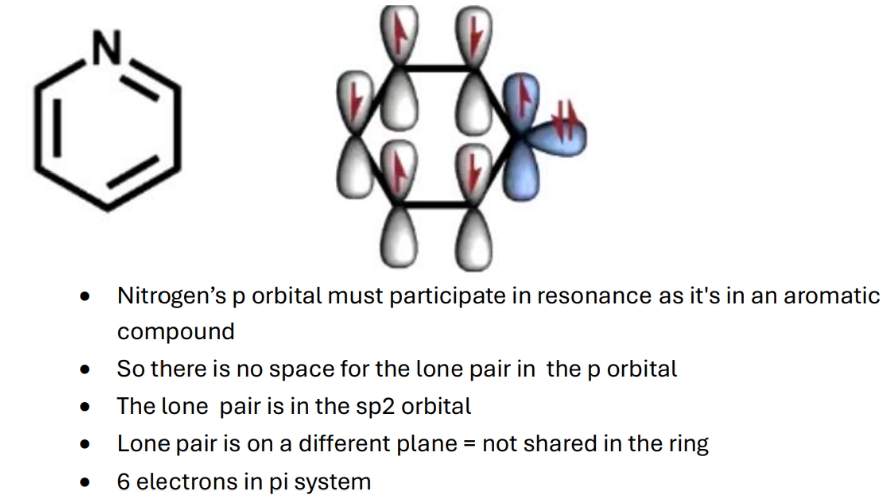
Why are the 6 electrons in pi system in pyridine
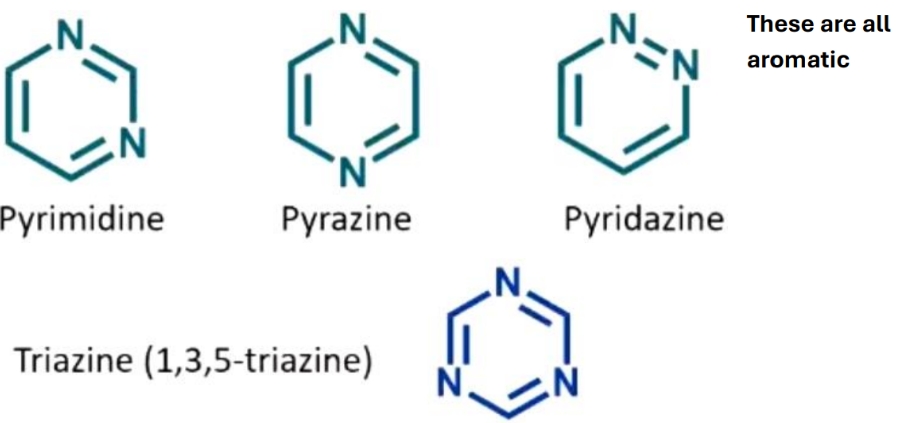
Draw these compounds

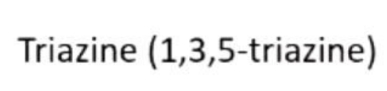
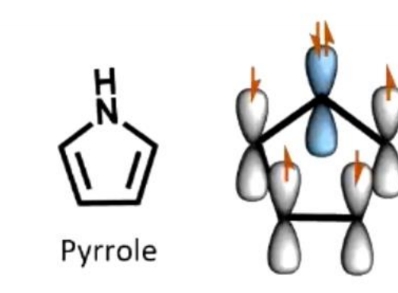
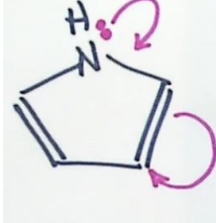
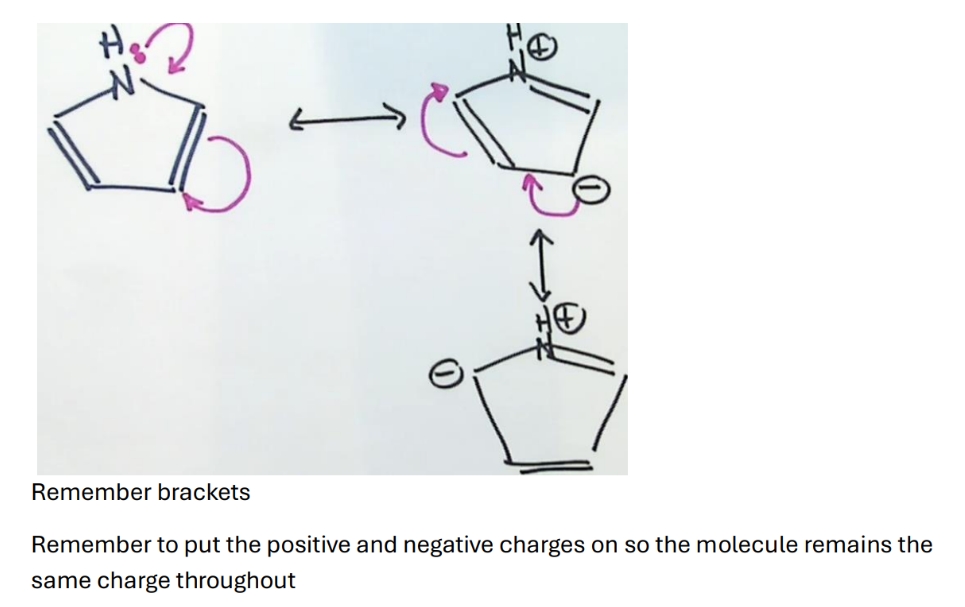
Why is pyrrole aromatic
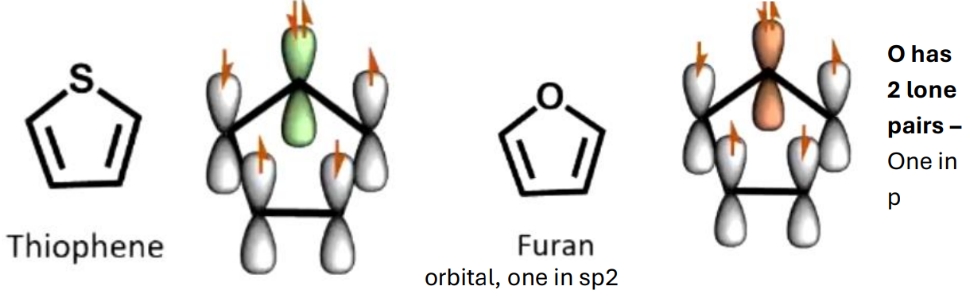

Where ar the electrons in these rings
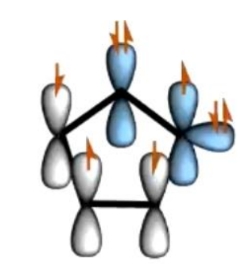
Double bonded nitrogen - sp2 hybridised but it needs to use the p orbital for double bonds to C = can't use it to keep thr lone pair. So lone pair is in sp2
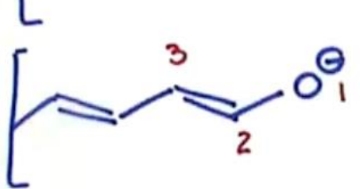
Draw resonance structures
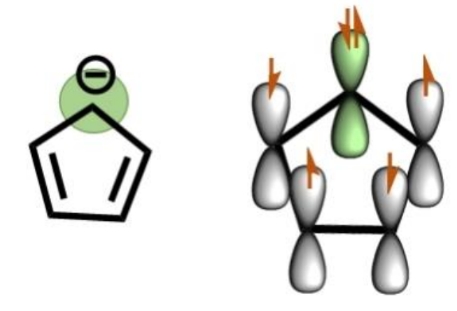
Why are pentene ring anions aromatic

C1 starts off as sp3 and then loses h+, leaving behind a lone pair
Now it has only 3 bonds (C-C, C-C, C-H) and a lone pair. Need 3 sp2 orbitals for the bonds, the lone pair goes in p orbital so it can resonate and stabilise the structure
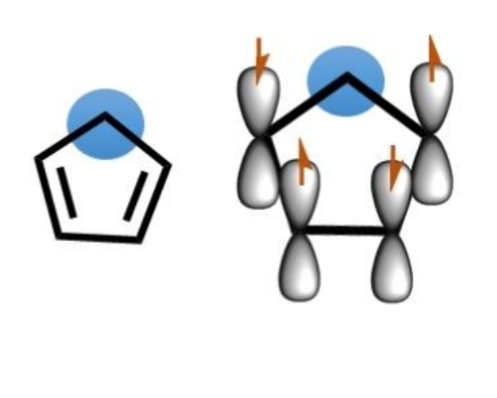
Why are pentene ring cations not aromatic

Why are N-containing 6 membered rings electron deficient
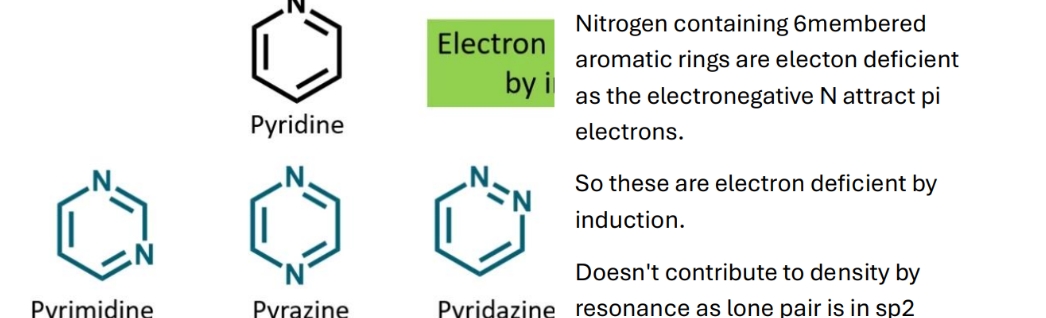
Is this structure electron deficient?
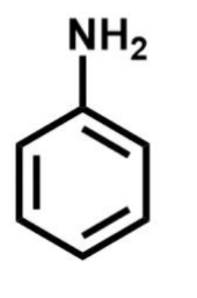

Why do resonance effects have more influence on electron density than inductuve effects

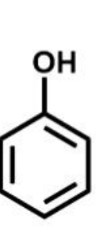
Why is phenol more reactive than benzene (aka poof that resonance always wins over inductive effects)
