H Chem test 2
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The 3 fundemental subatomic particles, Alpha, beta, gamma rays, Atomic structure, and distingushing between atoms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Who was the first to propose the idea of atoms
Democrutus
Who made the atomic theory
John Dalton
Who discovered the electron
J.J. Thomson, a physicist who conducted experiments with cathode rays and identified the electron as a subatomic particle.
Who made the plum pudding model
J.J. Thomson, who proposed that atoms are made up of a positively charged substance with negatively charged electrons embedded within it.
Who made the nuclear model
Ernest Rutherford, who conducted the gold foil experiment that led to the discovery of the atomic nucleus and proposed a model where electrons orbit a dense, positively charged nucleus.
Who figured out that the atom is mostly space and has a dense nucleus
Ernest Rutherford, who demonstrated through his gold foil experiment that most of an atom's volume is empty space surrounding a small, dense nucleus.
Who provided evidence of the proton
Goldstein discovered the proton using a cathode ray tube experiment, showing that atoms contained positively charged particles.
What year was the proton discovered
1886
Who provided evidence of the neutron
Chadwick
What year was the neutron discovered
1932
The symbol for gamma rays

The symbol for Beta particles
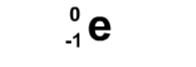
The symbol for Alpha particles

Hetrogenus
Not uniform throughout
Homogenus
Uniform composition, called a solution
How do compounds turn back into their original elements
They chemically decompose
All the chemical change signs
Change in smell, Temp, Color, Gas, and forming of perciptate
Thing to remember about physical changes
If something new is created it is not a physical change
Gas
Has a indefinite shape and volume
Solids
Have a definite shape and volume
Liquids
Don’t have a definite shape but a definite volume
Physical traits
Texture, color, Temp it melts at, and WEIGHT
What does AMU stand for
Atomic mass unit
Isotopes
Same protons, diff mass number and diff neutrons
Atomic number equals?
The amount of protons
What are radio isotopes
Unstable Isotopes that cause radiation
All isotopes with an atomic number greater than 83 are…
all isotopes with atomic number greater than 83 are radioactive
What particle occurs in heavier atoms
Alpha particles (Heavy answer)
Positron
the same as an electron
Fission
Bombarding of neutrons to split the nucleus
Fusion
Two light atomic nuclei combining
Mass of a alpha particle
4
Mass of Beta particle
1/1837
Mass of a Gamma ray
0
Charge of a alpha particale
+2
Charge of a Beta particle
-1
Charge of a gamma ray
0
Proton symbol
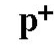
Electron symbol
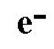
Neutron symbol
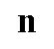
Proton charge
1+
Neutron charge
0
Electron charge
-1
Mass of a proton
1.007
Mass of neutron
1.009
Mass of electron
5.486×10
What can stop alpha particles
paper
What can block beta particles
Metal foil
What can stop Gamma rays
Nothing, but thick lead or concrete can slow them down and contain them a bit.
What is a half life
The time required for ½ of nuclei of radistopes to decay
Does fusion or fission make energy
Both do