AP Psychology Unit 2: Cognition
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Bottom-up processing
The process of sensory input starting at the entry level and building up.
Top-down processing
The process of perception driven by cognition, using prior knowledge.
Perceptual set
A predisposition to perceive things a certain way.
Gestalt psychology
A theory emphasizing that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.
Closure
The tendency to fill in gaps in visual information.
Figure and ground
The organization of the visual field into objects that stand out from their surroundings.
Proximity
Objects that are close together are perceived as a group.
Similarity
Objects that are similar are perceived as a group.
Attention
Focusing awareness on a specific stimulus.
Selective attention
the ability to focus on only one stimulus from among all sensory input
Cocktail party effect
The ability toattendto themention one's name orspecifictopicsinloudor distracting environments.
Inattentional blindness
Failure to notice a visible stimulus because attention is elsewhere.
Change blindness
Failure to notice changes in the environment due to inattention.
Binocular depth cures
Depth cues that depend on the use of both eyes.
Retinal disparity
a binocular cue for perceiving depth by comparing images from the retinas in the two eyes, the brain computes distance—the greater the disparity (difference) between the two images, the closer the object.
Convergence
A binocular cue for perceiving depth; the extent to which the eyes converge inward when looking at an object
Monocular depth cues
Depth cues available to either eye alone.
Relative clarity
Objects that appear clearer are perceived as closer.
Relative size
Objects that appear smaller are perceived as farther away.
Texture gradient
A gradual change from coarse to fine texture signals increasing distance.
Linear perspective
Parallel lines appear to converge with distance.
Interposition
If one object partially blocks another, it is perceived as closer.
Perceptual constancy
perceiving objects as unchanging (having consistent lightness, color, shape, and size) even as illumination and retinal images change
Apparent movement
Perception of movement in a stationary object.
Concept
a mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
Prototype
A typical example of a concept.
Schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
Assimilation
Incorporating new information into existing schemas.
Accommodation
Adjusting schemas to fit new information.
Algorithms
Step-by-step procedures that guarantee a solution.
Heuristic
a simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently; usually speedier but also more error-prone than algorithms
Representativeness heuristic
Judging the probability of an event based on how similar it is to a prototype.
Availability heuristic
Estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory.
Mental set
A tendency to approach problems in a particular way.
Priming
The activation of certain associations in memory.
Framing
The way an issue is posed can affect decisions and judgments.
Gambler's fallacy
Belief that past random events affect the probability of future ones.
Sunk-cost fallacy
Continuing an endeavor because of previously invested resources.
Executive functions
higher order thinking processes that include planning, organizing, inhibition, and decision-making
Creativity
The ability to produce novel and valuable ideas.
Divergent thinking
Thinking that generates multiple possible solutions.
Convergent thinking
Thinking that narrows options to find a single best solution.
Functional fixedness
Inability to see new uses for familiar objects.
Explicit memory
Memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know.
Episodic memory
Memory of personal experiences and events.
Semantic memory
Memory of general knowledge and facts.
Implicit memory
Memories we don't deliberately remember or reflect on consciously.
Procedural memory
Memory of skills and how to perform them.
Prospective memory
Remembering to perform a planned action in the future.
Long-term potentiation
The long-lasting strengthening of synapses between neurons.
Working memory model
A model describing different components of working memory.
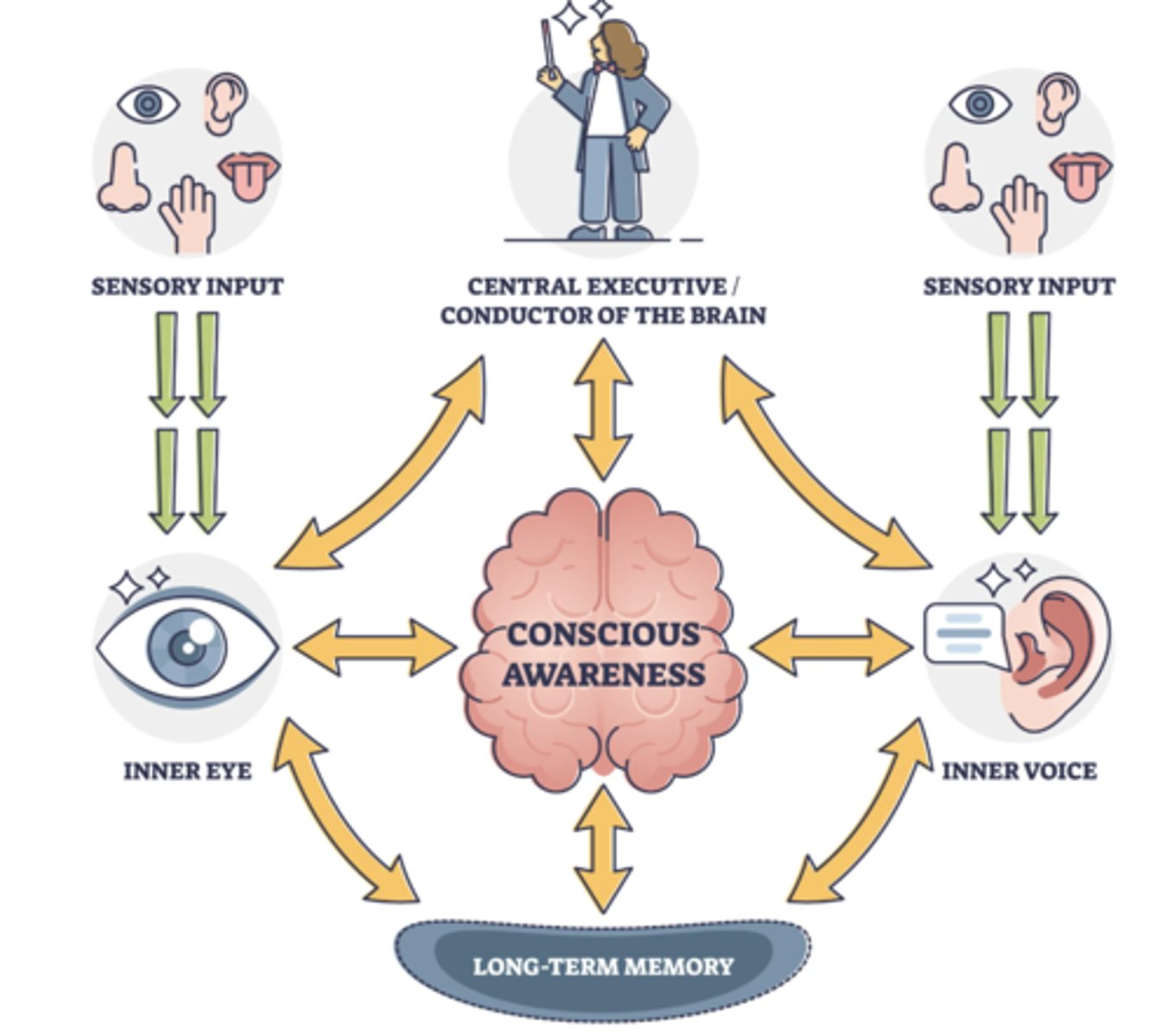
Primary memory system (working memory)
The memory system involved in the temporary storage and management of information necessary for cognitive tasks, often associated with short-term memory.
Central executive
The part of working memory that directs attention and processing.
Phonological loop
The part of working memory that deals with verbal information.
Visuospatial sketchpad
The part of working memory that deals with visual and spatial information.
Long-term memory
The relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of memory.
Multi-store model
A model of memory with three stages: sensory, short-term, and long-term.
Sensory memory
The brief storage of sensory information.
Iconic memory
A momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli.
Echoic memory
A momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli.
Short term memory
activated memory that holds a few items briefly, such as the seven digits of a phone number while dialing, before the information is stored or forgotten
Long term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system. Includes knowledge, skills, and experiences.
Automatic processing
Unconscious encoding of incidental information.
Effortful processing
Encoding that requires attention and conscious effort.
Encoding
The process of getting information into memory.
Storage
The retention of encoded information over time.
Retrieval
The process of getting information out of memory.
Levels of processing model
A model suggesting deeper processing leads to better retention.
Shallow encoding
Encoding based on the structure or appearance of words.
Deep encoding
Encoding based on the meaning of words.
Structural encoding
Encoding based on the structure or appearance of words.
Phonemic encoding
Encoding based on the sound of words.
Semantic encoding
Encoding based on the meaning of words.
Mnemonic devices
Memory aids that use vivid imagery and organizational devices.
Method of loci
A mnemonic technique involving associating items with specific locations.
Chunking
Organizing information into manageable units.
Categories (as they pertain to grouping)
Grouping information into categories to aid memory.
Hierarchies (as they pertain to grouping)
Organizing information into levels of importance.
Spacing effect
The tendency to retain information more effectively when practice is spread out.
Massed practice
Cramming information in a short period.
Distributed practice
Spacing out study sessions over time.
Serial position effect
The tendency to recall the first and last items in a list best.
Primacy effect
The tendency to recall the first items in a list better.
Recency effect
The tendency to recall the last items in a list better.
Short-term memory
The active maintenance of information in short-term storage.
Maintenance rehearsal
Repeating information to keep it in short-term memory.
Elaborative rehearsal
Connecting new information to existing knowledge.
Memory retention
The ability to retain information over time.
Autobiographical memory
A memory system for storing information about one's life events.
Retrograde amnesia
Loss of memory for events before a trauma.
Anterograde amnesia
Inability to form new memories after a trauma.
Alzheimer's disease
A progressive disease that destroys memory and other mental functions.
Infantile amnesia
The inability to recall memories from early childhood.
Recall
Retrieving information learned earlier.
Recognition
Identifying previously learned information.
Retrieval cues
Stimuli that help retrieve information from long-term memory.
Context-dependent memory
Memory that is improved when the context present at encoding and retrieval are the same.
Mood-congruent memory
The tendency to recall experiences consistent with one's current mood.
State-dependent memory
Memory that is aided or impeded by a person's internal state.
Testing effect
The enhanced memory after retrieving information.