Diagram of Cell movement, extracellular matrix and junctions | Quizlet
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
What enables cell motility?
- Energy
- Extracellular components for mechanical interaction
- Guidance
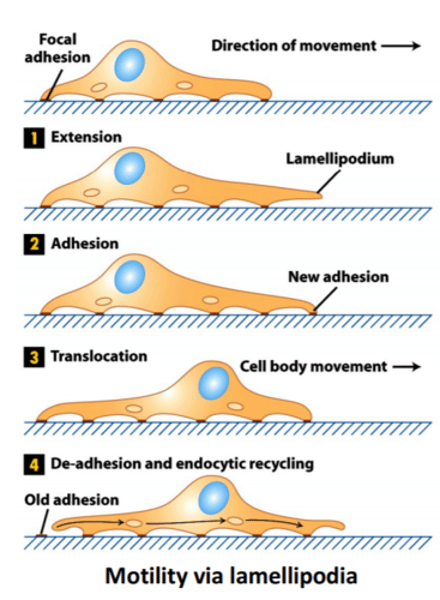
'Crawling' cell motility is enabled by
Actin filaments
'Swimming' cell motility is enabled by
Microtubules
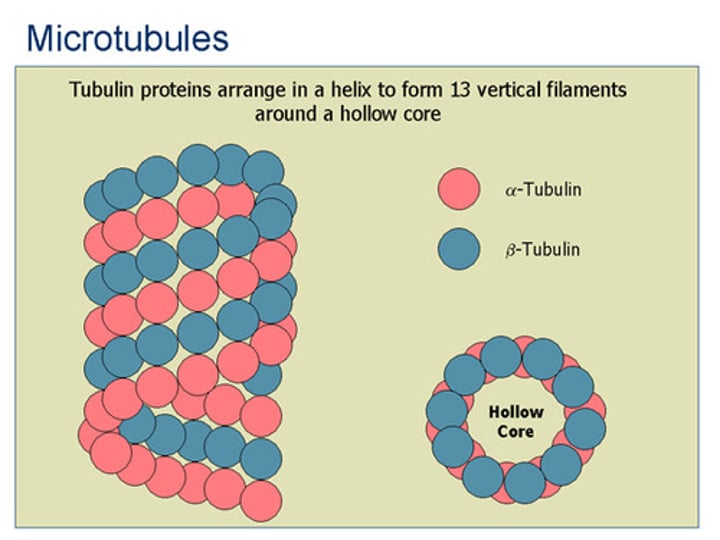
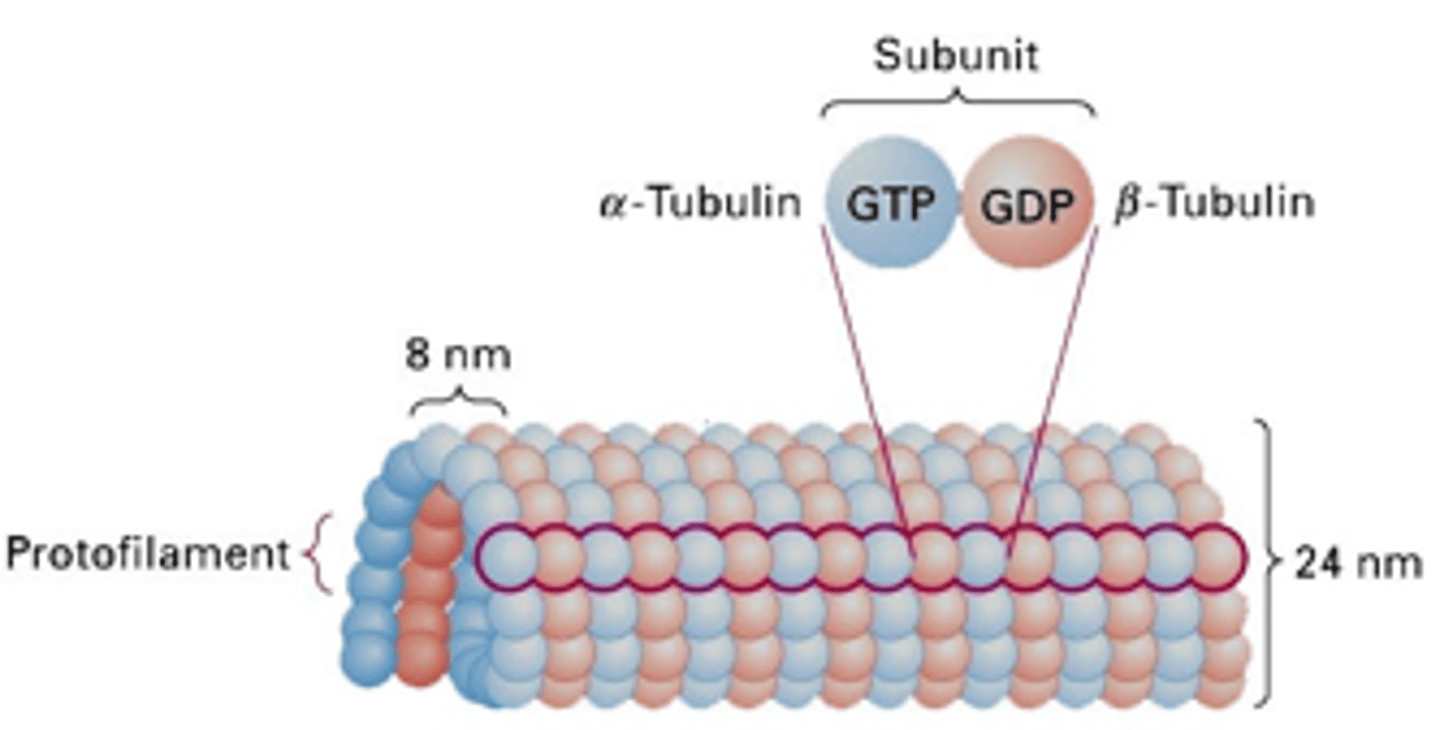
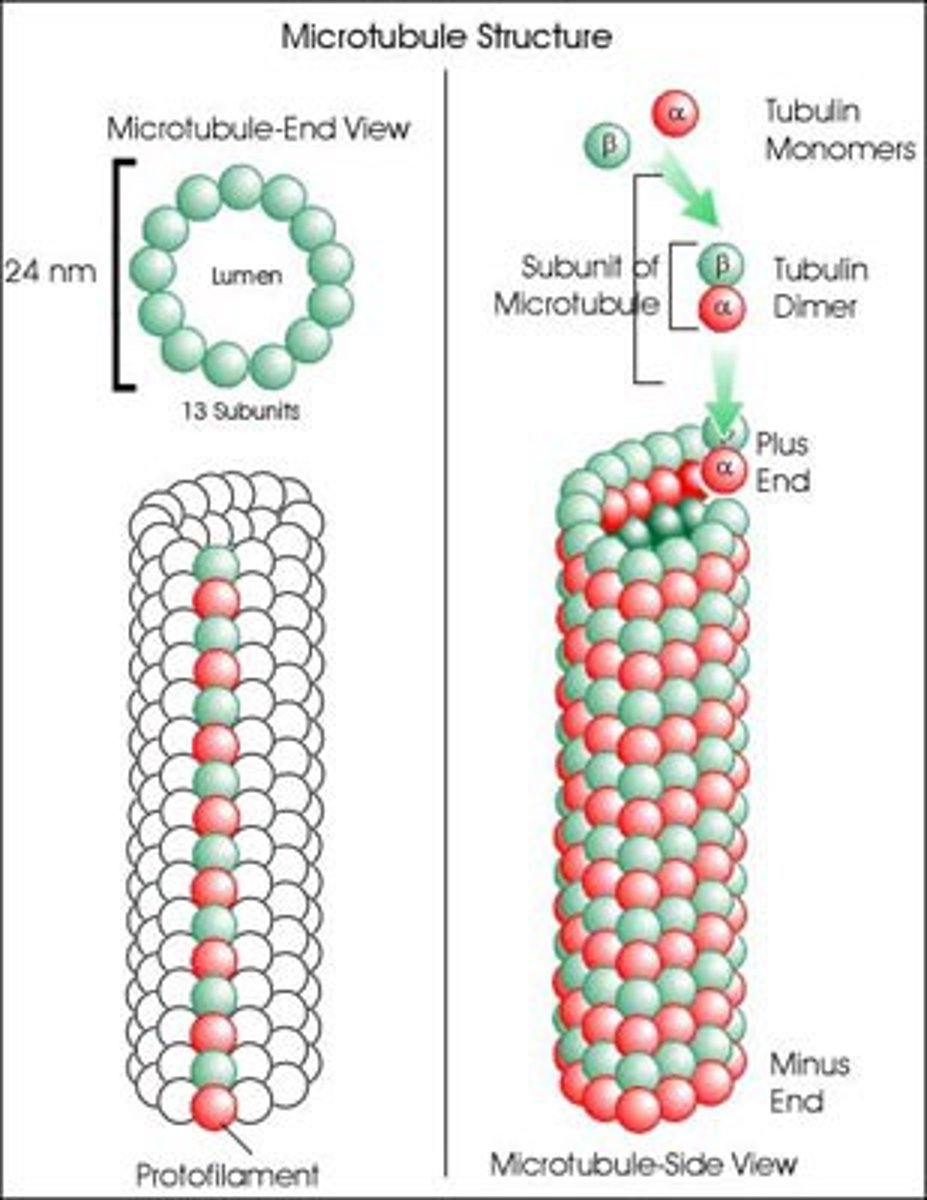
How many protofilaments in a microtubule?
13 protofilaments from a continuous hollow tube, heterodimer (alpha + beta)
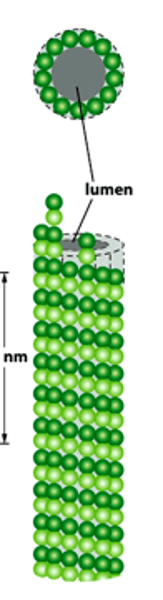
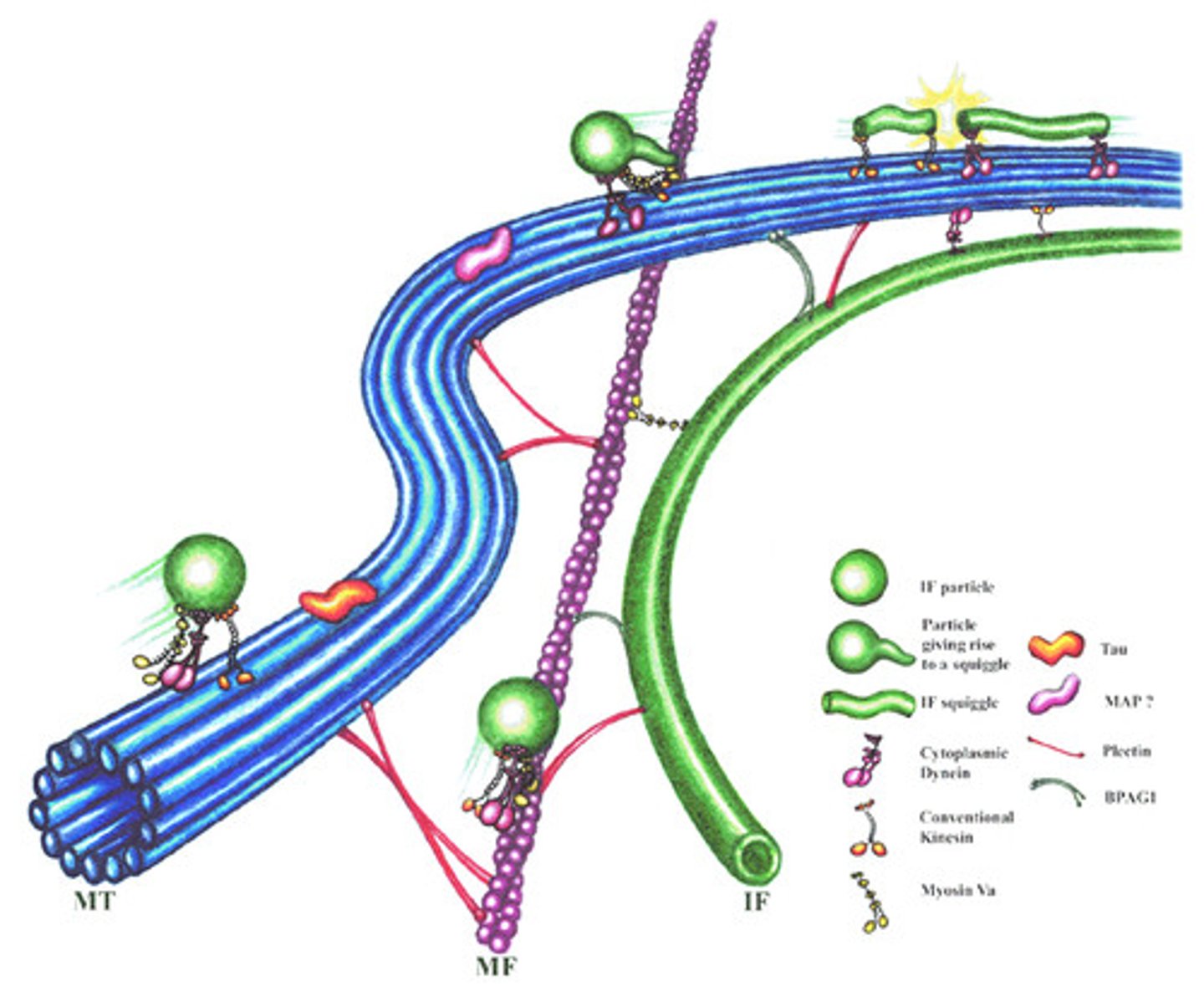
What structures do microtubules form?
Network of unbranched and hollow cylinders...
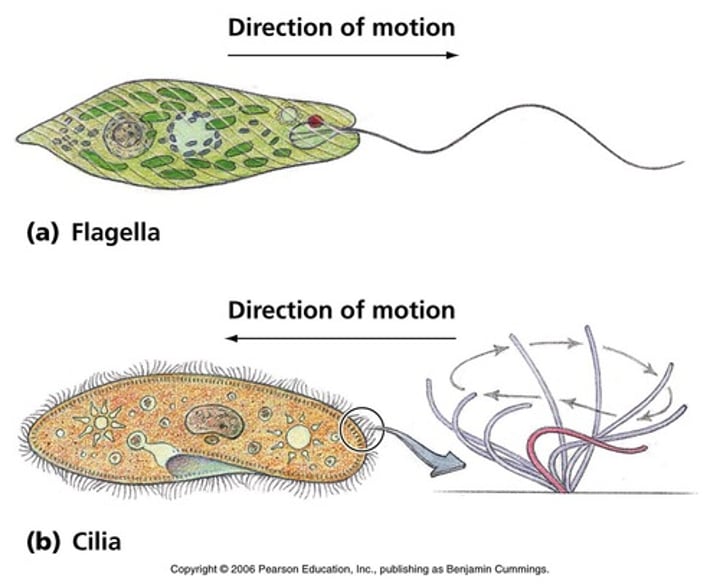
Cilia and Flagella
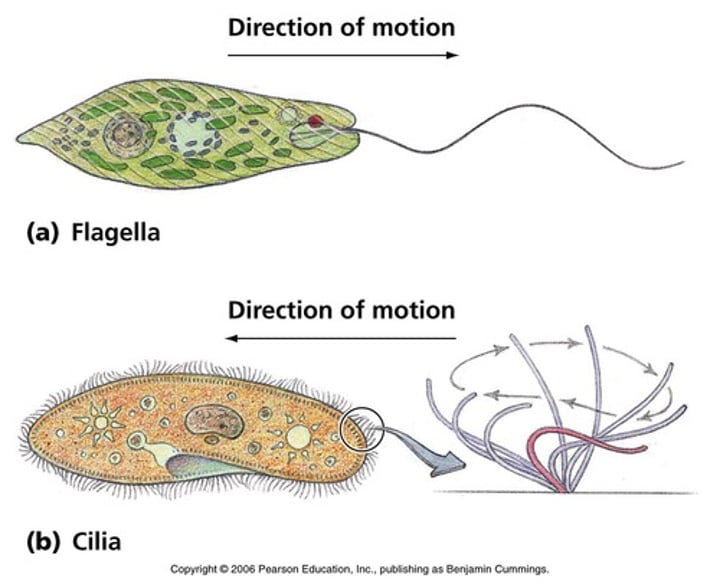
Cilia enable...
The transport of extracellular fluids in the respiratory and reproductive tracts
Flagella enable...
The motility of sperm, protozoa and bacteria
Sizes of the cilia and flagella
Cilia are 2- 10 x 0.25 um
Flagella are much larger, at 100-200 x 0.25um
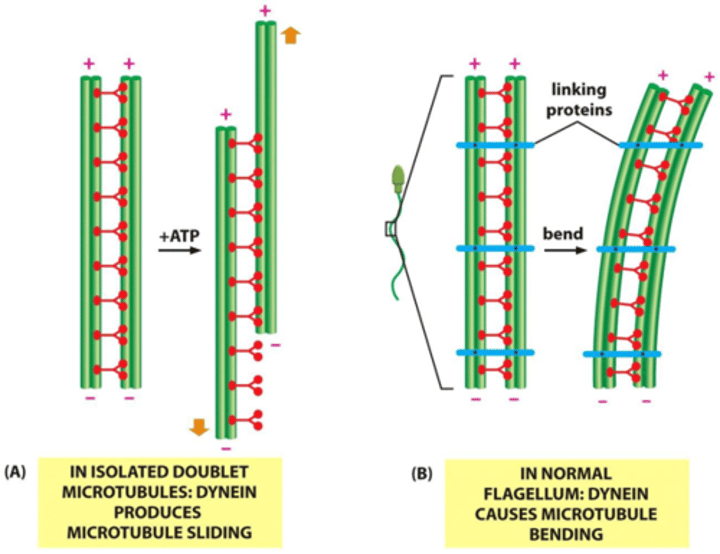
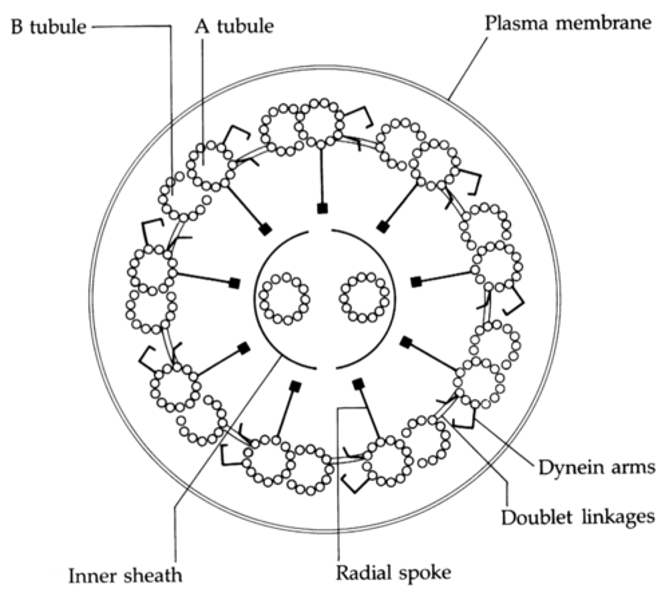
Axoneme
A vital structure found in eukaryotic cilia and flagella and responsible for their motion;
composed of two central microtubules surrounded by nine doublet microtubules
(9 + 2 arrangement)
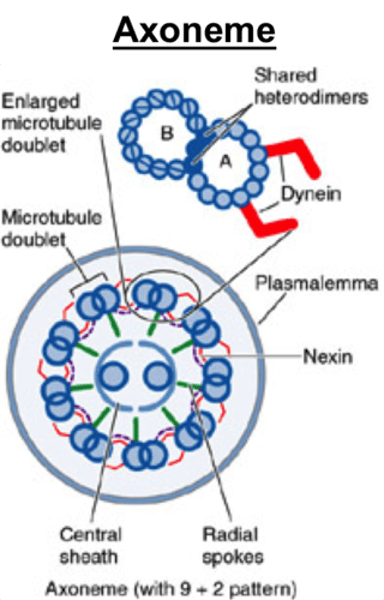
Structure of the axoneme
9 + 2 pair
Radial spokes link outer doublets to inner pairs
Dynein arms
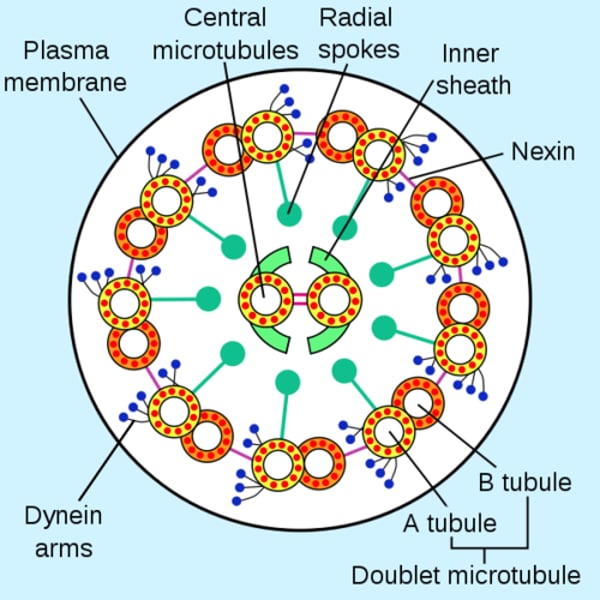
Outer doublets
share protofilaments
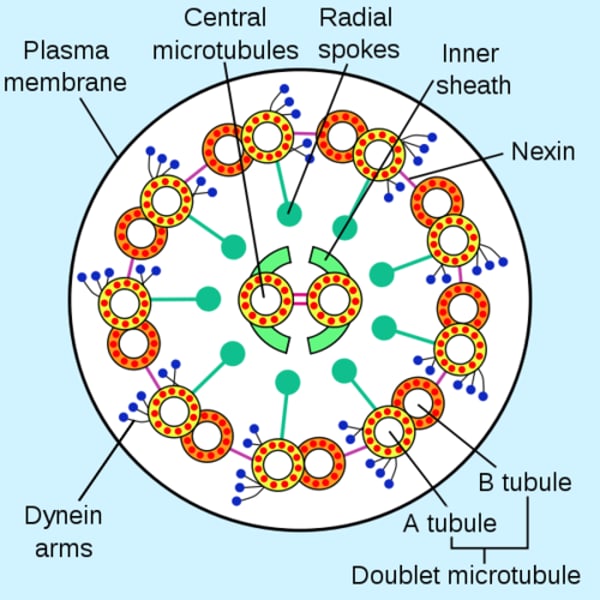
Dynein arms
resides in each pair of peripheral microtubules, makes the cilia move, using GTPto crawl up adjacent microtubules, bending cilia forward.
Nexin crosslinks
Structures which crosslink the dynein arms of the doublets, leading to flexion of the microtubule
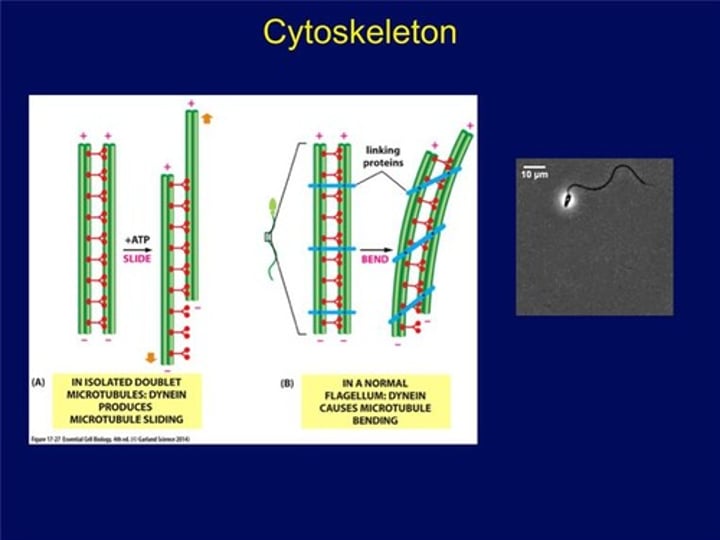
What do nexin crosslinkers enable?
These structures crosslink the dynein arms of the doublets, leads to flexion of the microtubule
What does the inner arm of dynein enable?
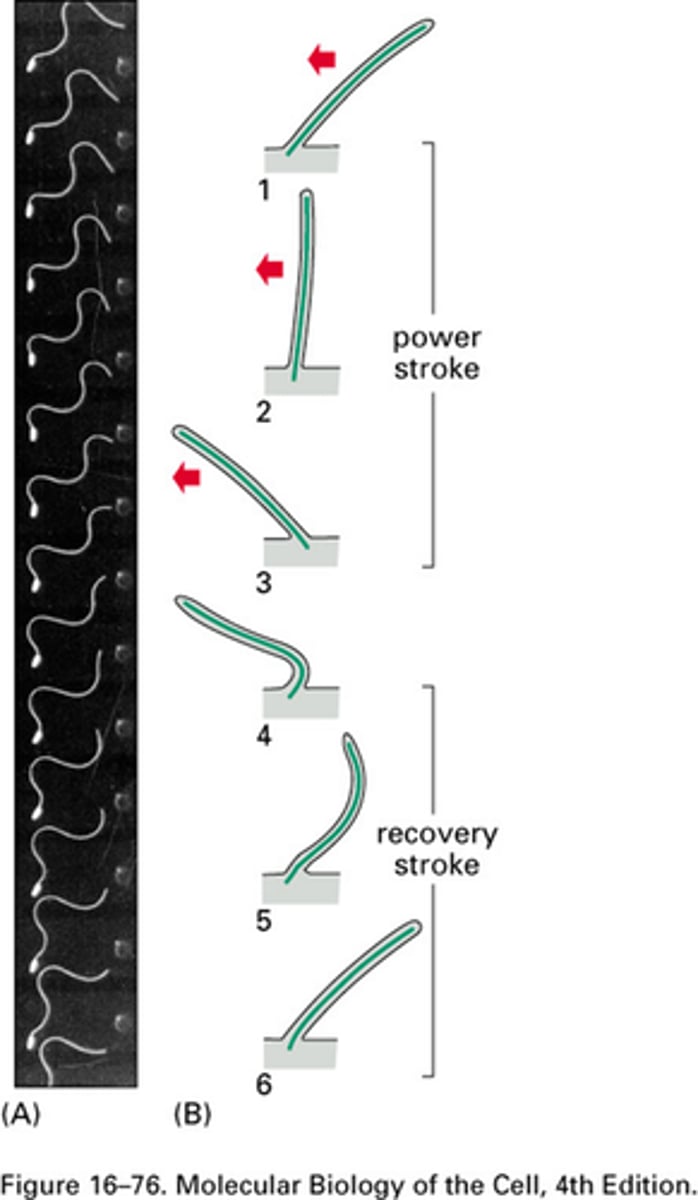
Waveform characterisation of the power stroke
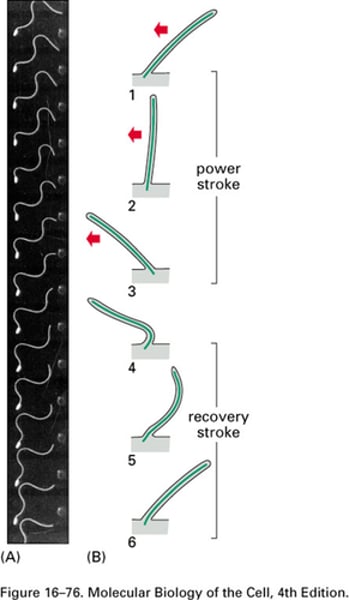
What does the outer arm of the dynein enable?
The power stroke
TERM
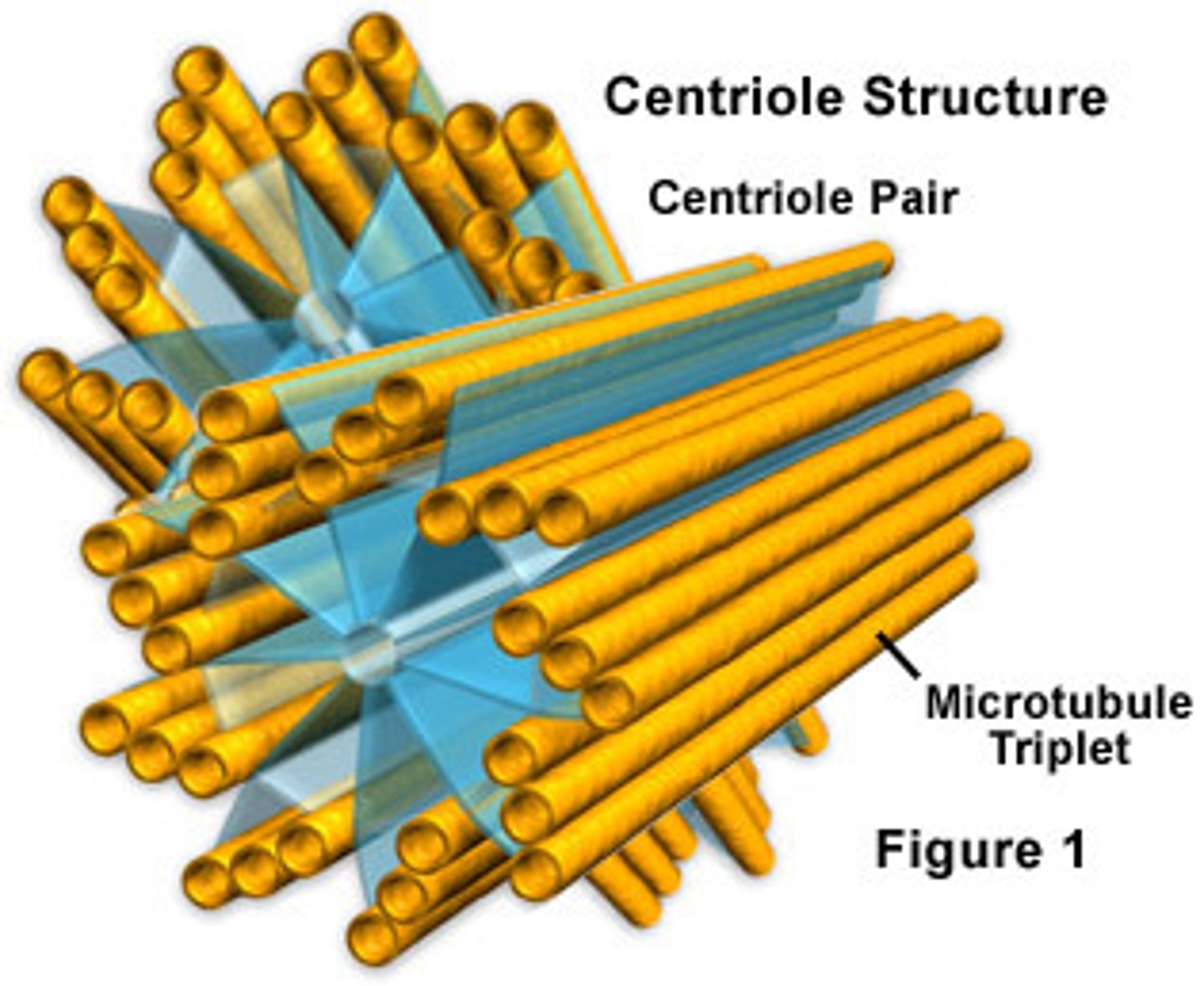
Basal bodies
DEFINITION
Structures which firmly root eukaryotic cilia and flagella at the cell surface
Basal body structure
Centriole structure is identical to basal bodies
They are composed of nine groups of fused triplet microtubules in a cartwheel
Actin based motility
In muscle based organisms, actin is involved in cellular motility
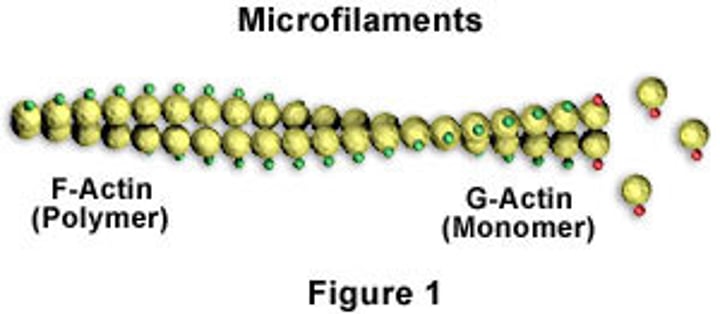
Difference between G and F actin
Globular and Filamentous
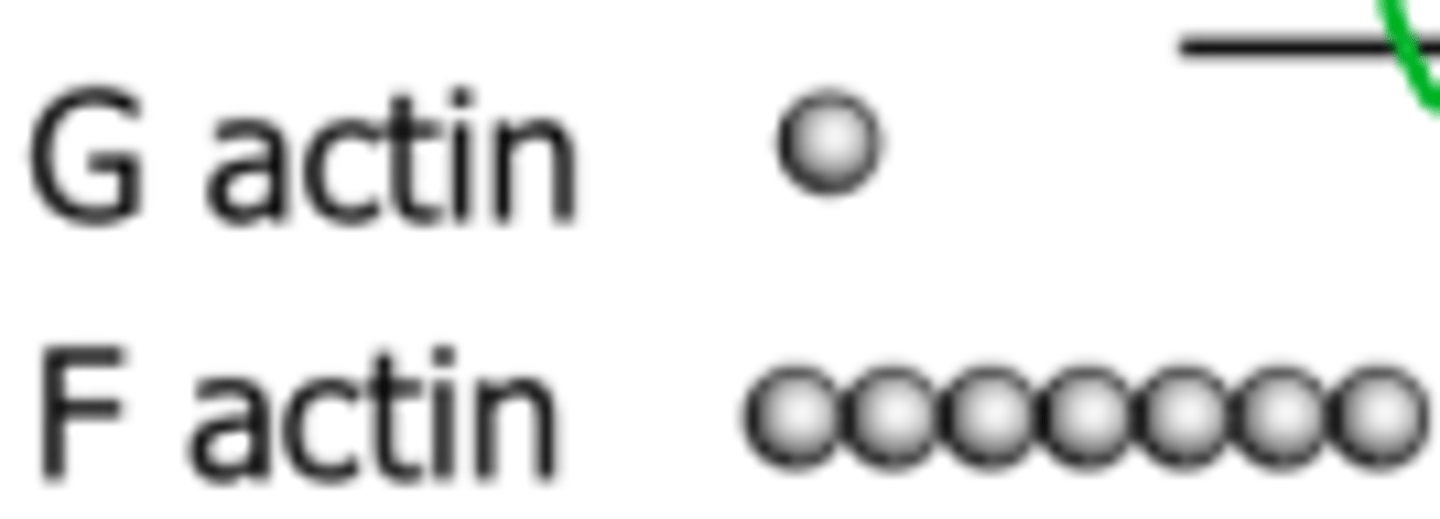
Describe the structure of the microtubule
Helical array of polymerized α- and β-tubulin (13 per circumference)
Polarised structure with a fast growing barbed + end, bound to GTP
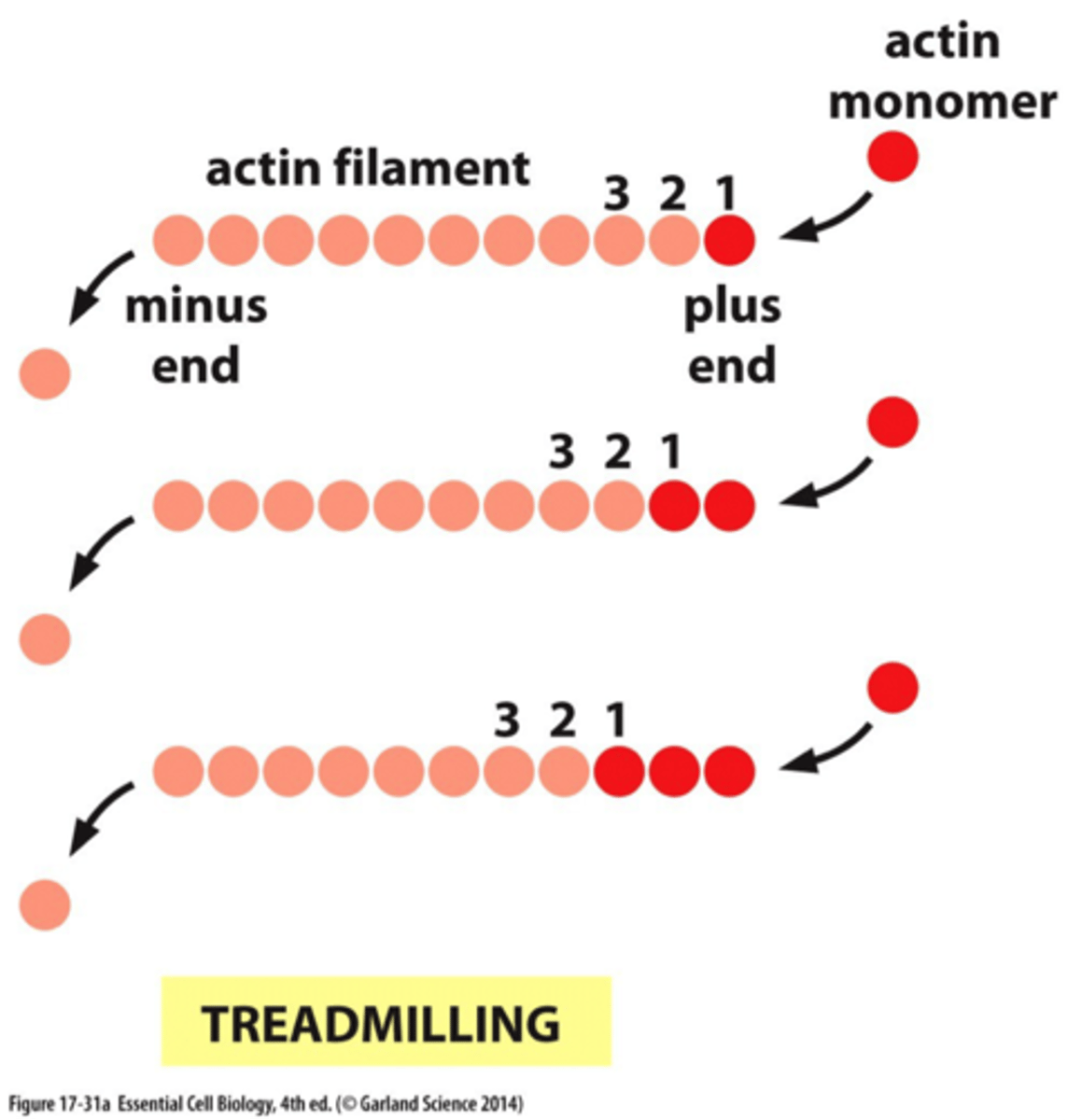
Actin treadmilling
•A G-actin with an ATP bound associates at the PLUS end of an existing F-actin molecule
•ATP is then hydrolyzed to ADP
•A G-actin with an ADP bound tends to dissociate from the minus end of the polymer
Result: a shift in the position of the filament
Contrast actin and microtubules
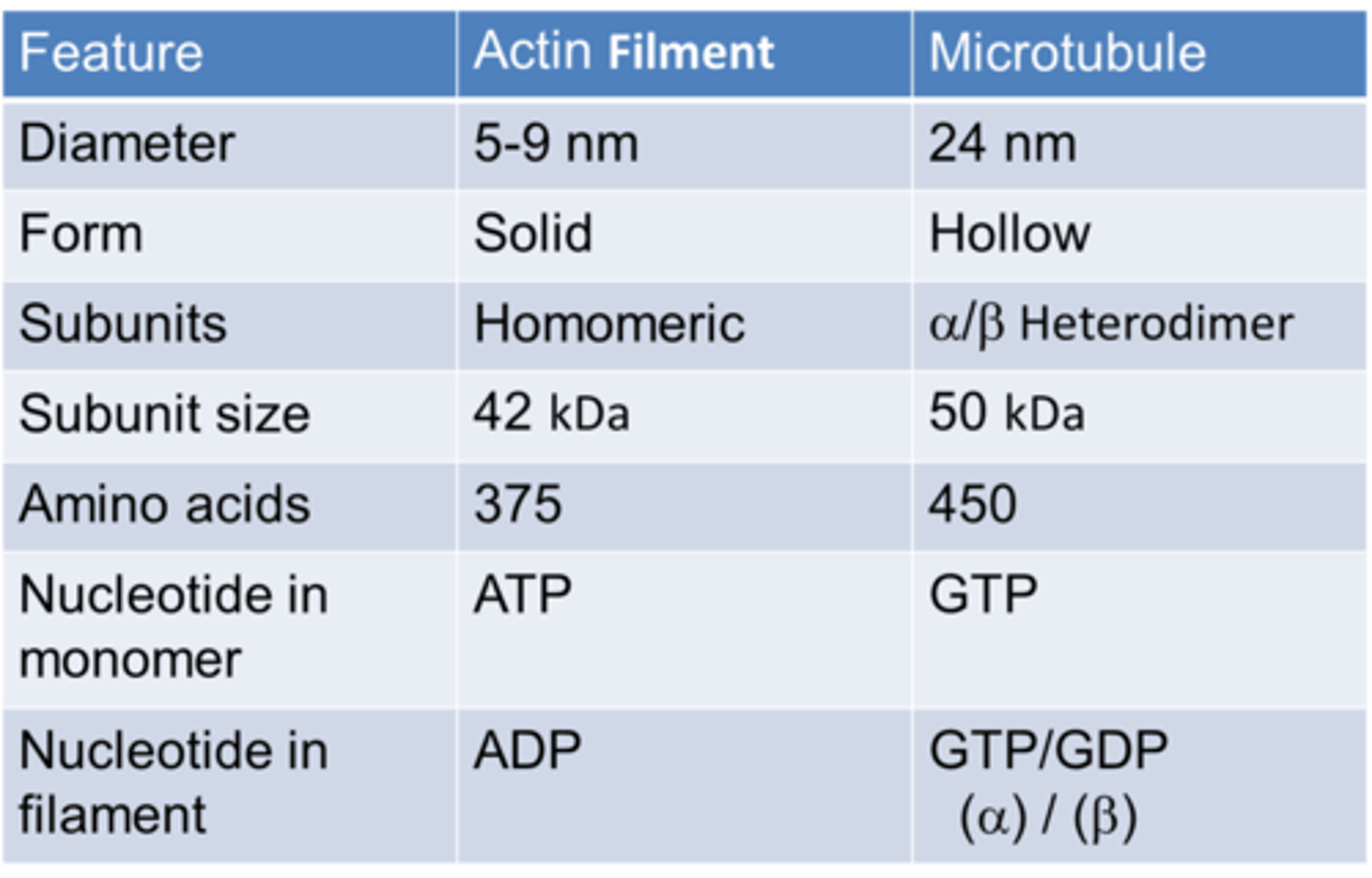
Diameter of actin
5-9nm
Size of actin
42 kDa
Number of amino acids in actin
375

Diameter of microtubule
24nm
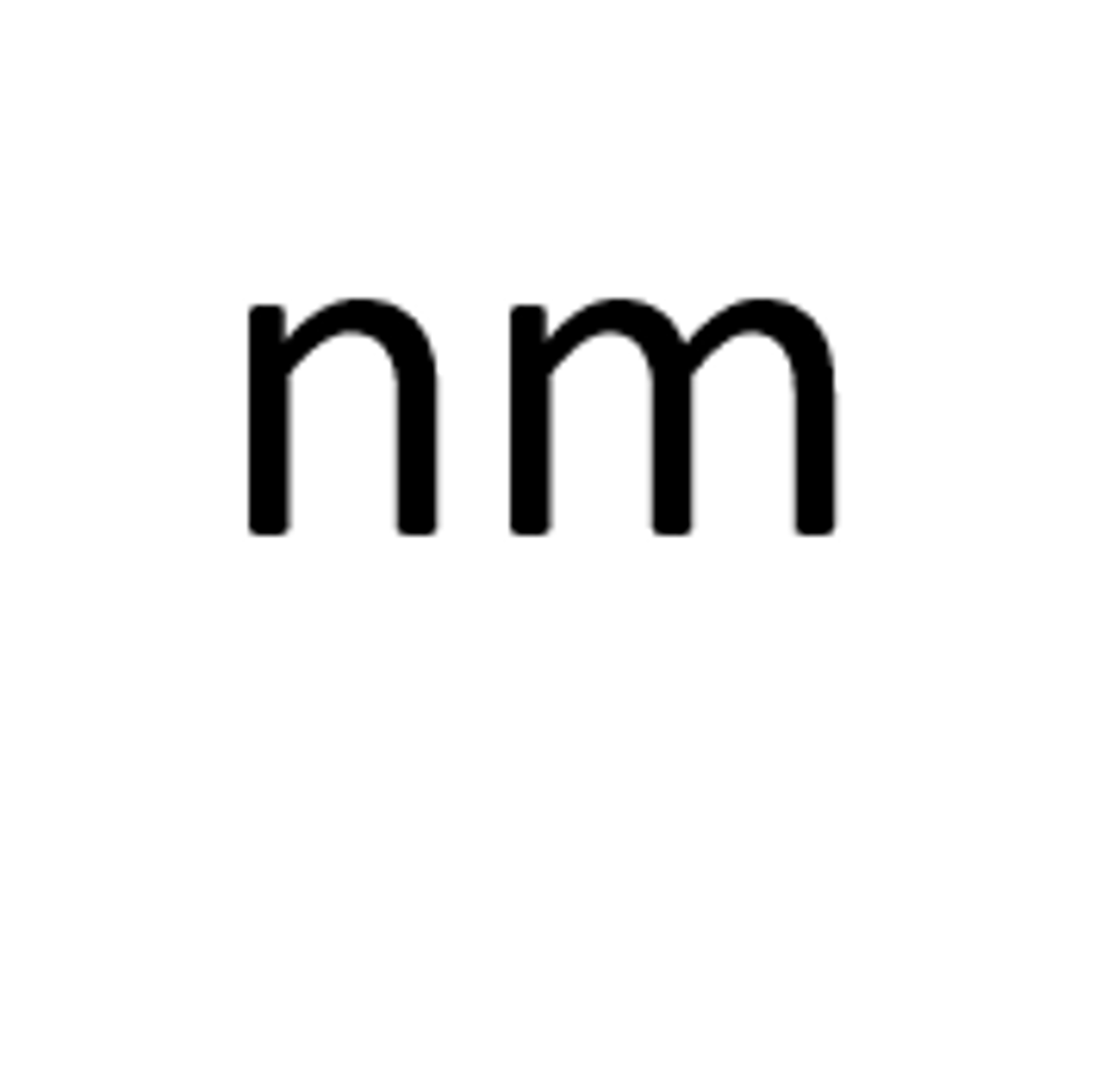
Size of tubulin
50kDa
Number of amino acids in microtubule
450

In which tubulin in GTP retained?
Alpha tubulin
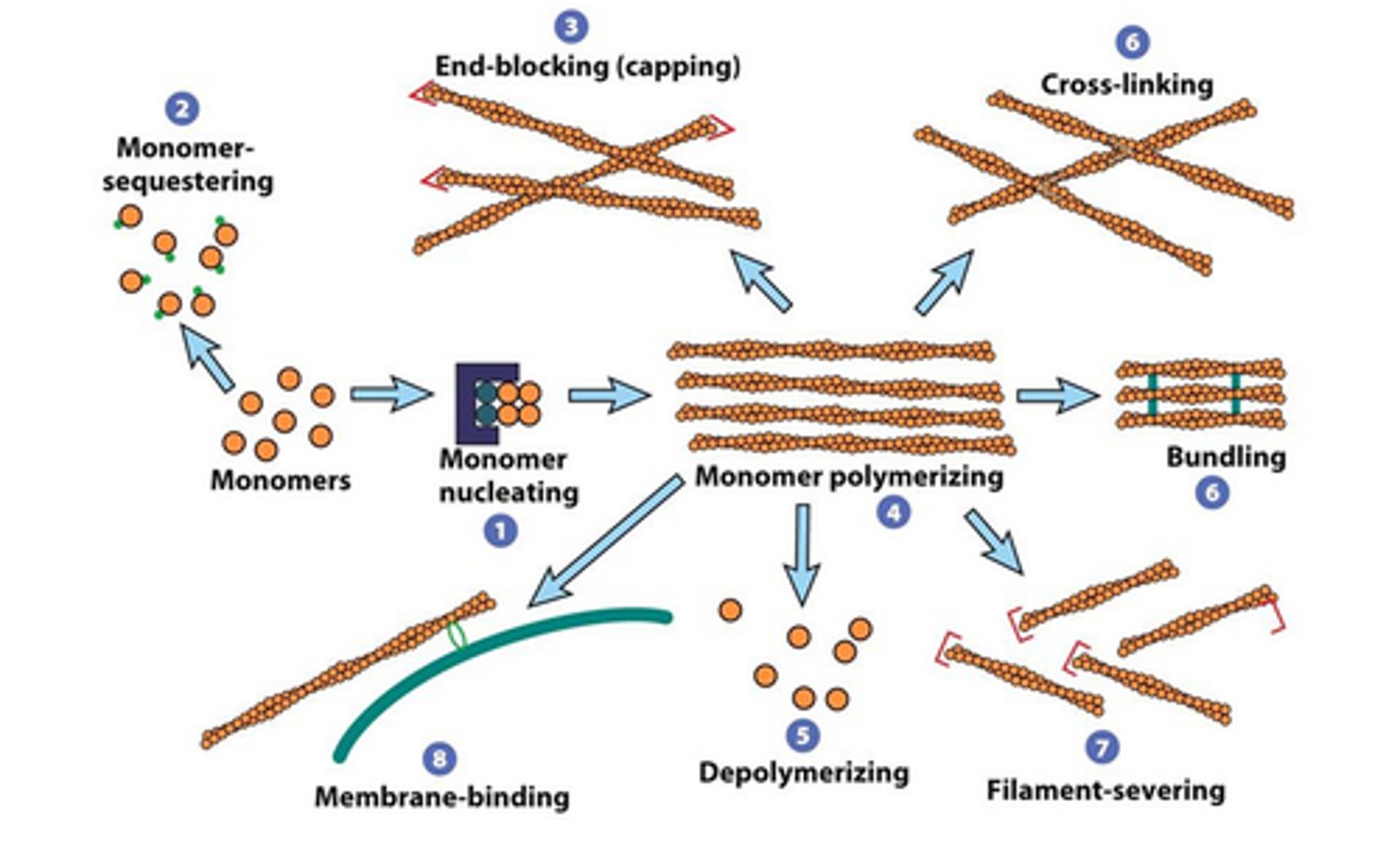
Examples of actin binding proteins
→ Profilin inhibits nucleation
→ Accessory proteins regulate actin dynamics
→ Cofilin leads to filament fracture
Myosin
The contractile protein that makes up the thick filaments of muscle fibres
The motor in cytoskeletal or muscular contraction
What is the filament of a cilia or flagella? The Motor?
Microtubule filament, dynein motor
What is the filament of the cytoskeleton/muscle, and the motor?
Actin filament, myosin motor
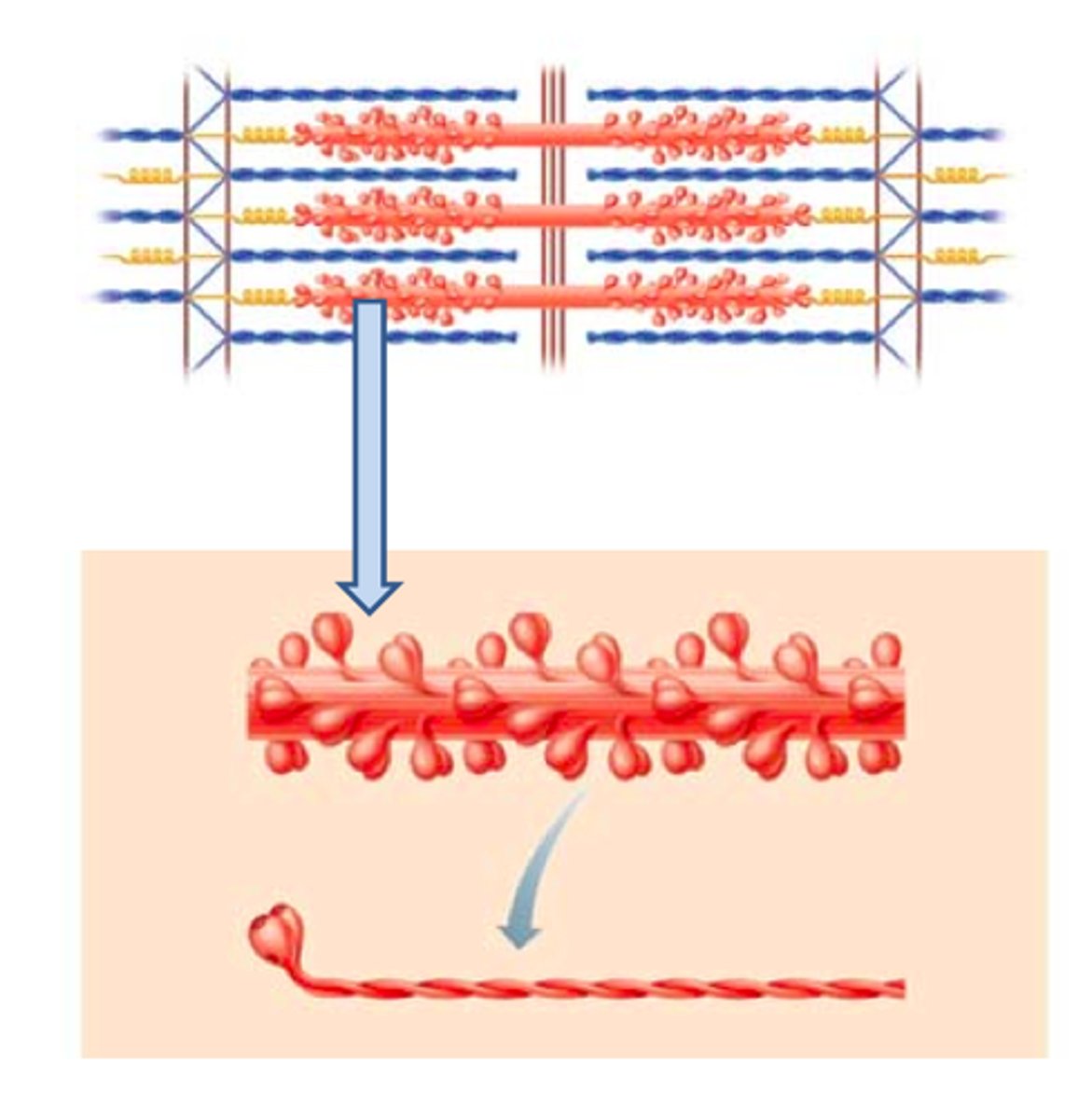
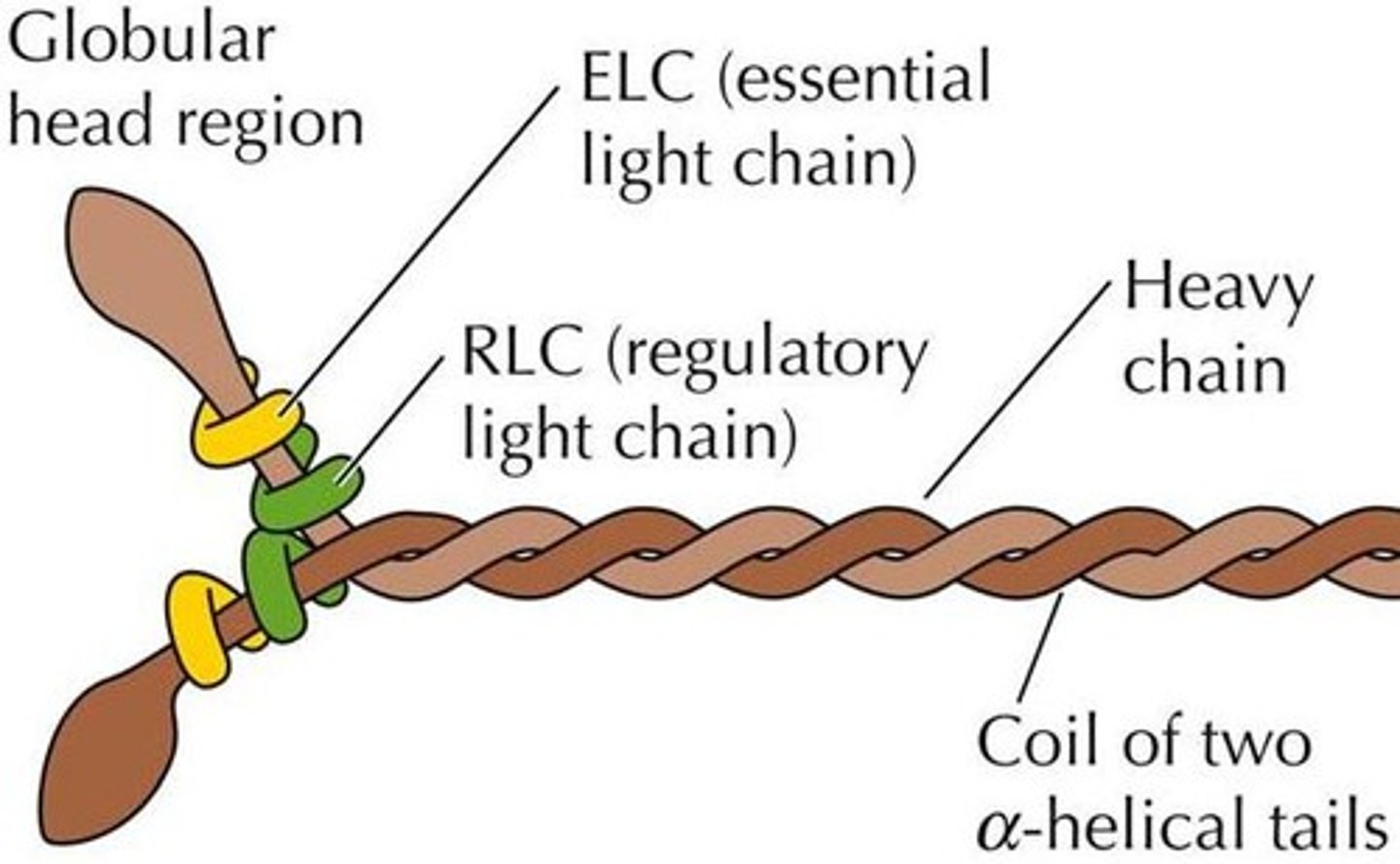
Describe the structure of myosin
Each myosin molecule is shaped like 2 golf club twisted together. About 300 of them make up one thick filament. Myosin heads point away from the M line
Myosin power stroke
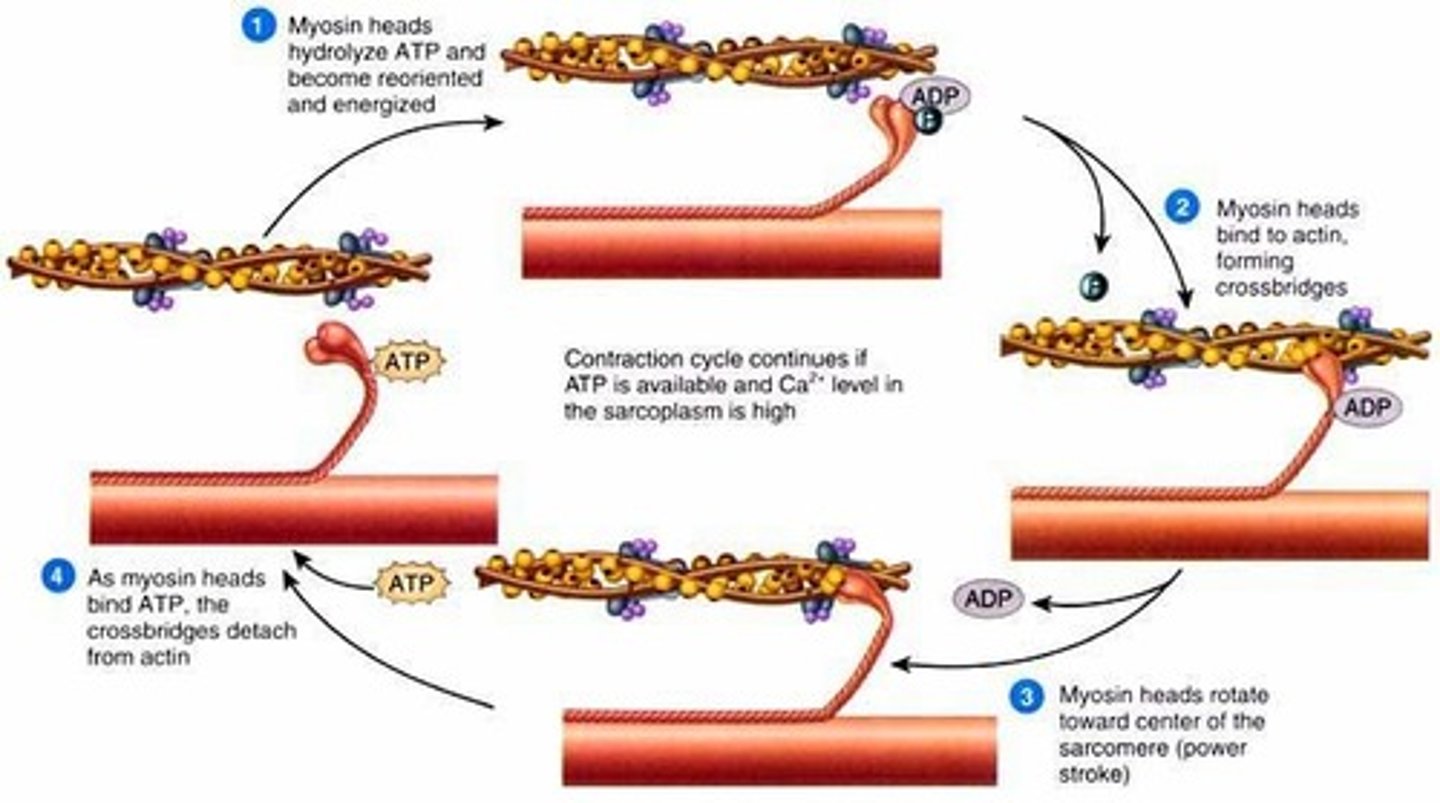
Action potential is transmitted across the neuromuscular junction (via the release of acetylcholine) and depolarises the sarcolemma. Waves of depolarisation spread down the T-tubules to trigger the release of Ca2+ ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+ ions bind to troponin protein attached to tropomyosin and trigger a change in tertiary structure which reveals the actin-myosin binding site upon the actin myofilament
This allows the myosin head (with ADP and Pi attached) to form a myosin-actin crossbridge
An ADP molecule attached to the myosin head means that it is in the correct position to form the cross bridge
The myosin head changes angle and pulls the actin filament along, releasing ADP (and Pi)
This slides the actin myofilament along to shorten the sarcomere (the Z lines become closer together)
An ATP molecule binds to the myosin had, causing it to break crossbridge
Ca2+ ions activate ATPase which catalyses the hydrolysis of ATP to release ADP and Pi and energy required for the myosin head to return to its original position
The myosin head, once more with an attached ADP molecule reattaches further along the actin and the rachet mechanism repeats
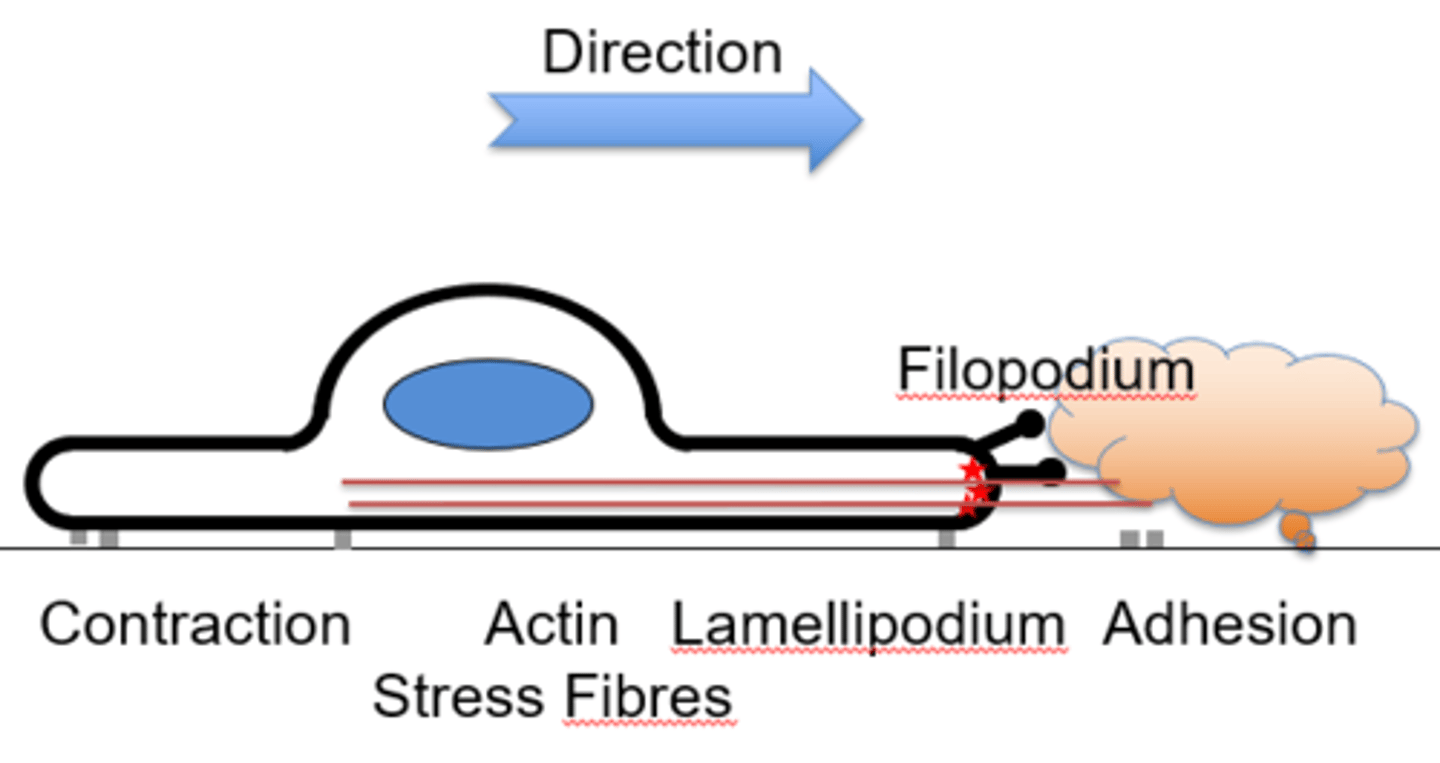
Actin-based motility is enabled by...
Filopodium - finger like projection of actin
Lamellipodium- between the filopodium, crosslinked actin
Stress fibres- Contractile structures
Cortical actin- sheath around cell
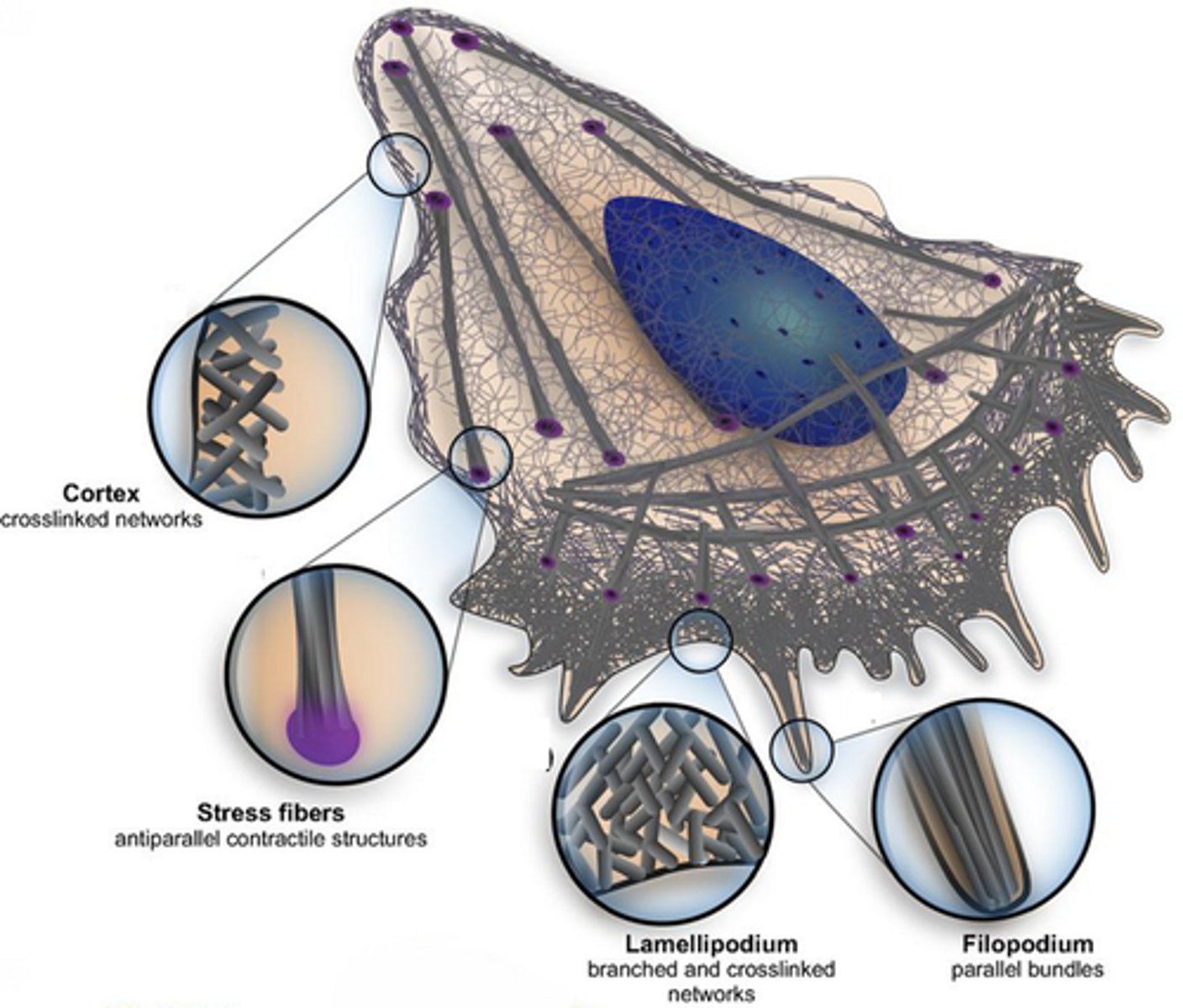
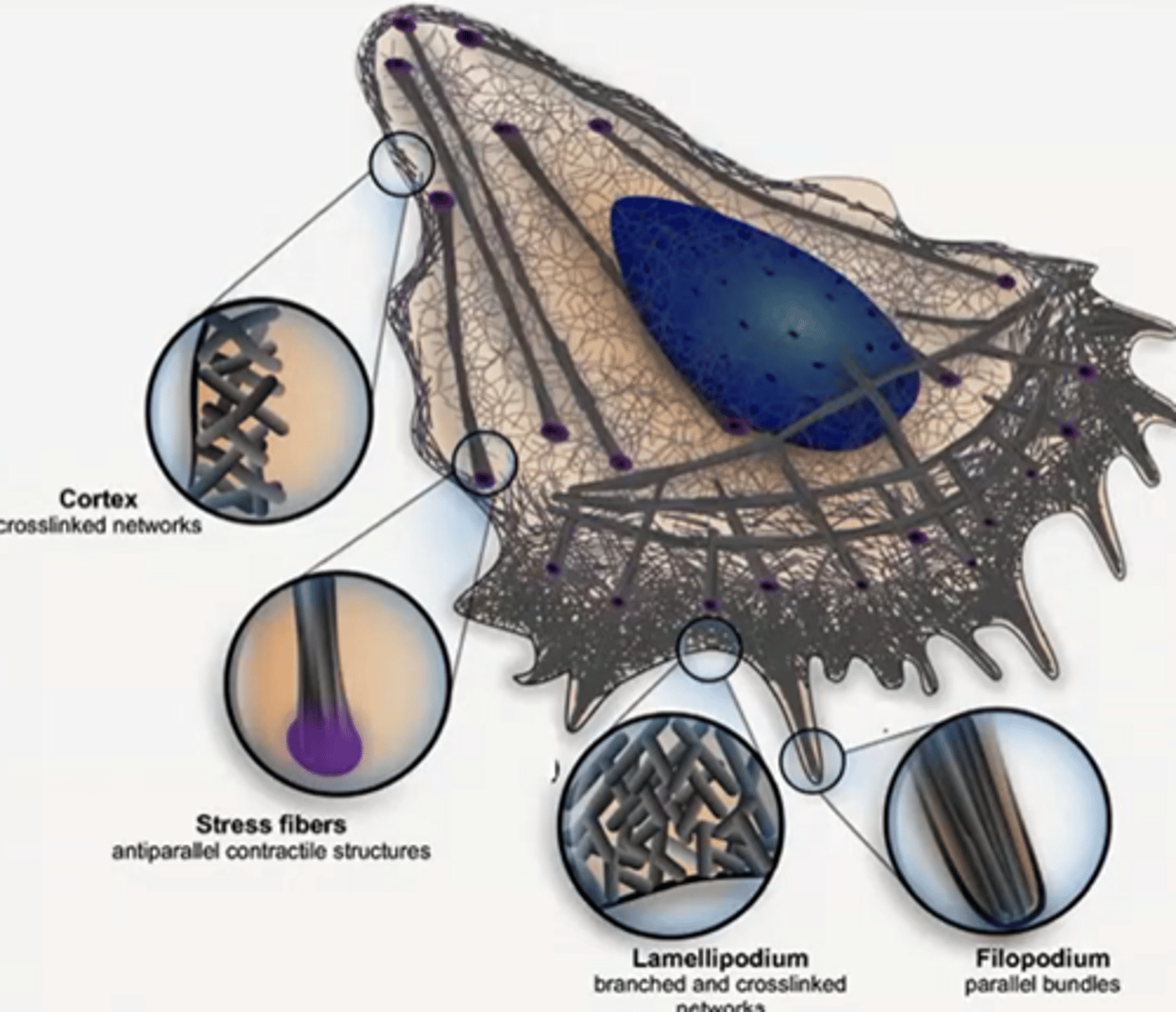
Describe each of the structures which enable Actin-based motility
The filopodium is composed of parallel actin filaments
The lamellipodium is formed by crosslinked actin
Stress fibres are antiparallel contractile features
Cortical actin is a meshed sheath
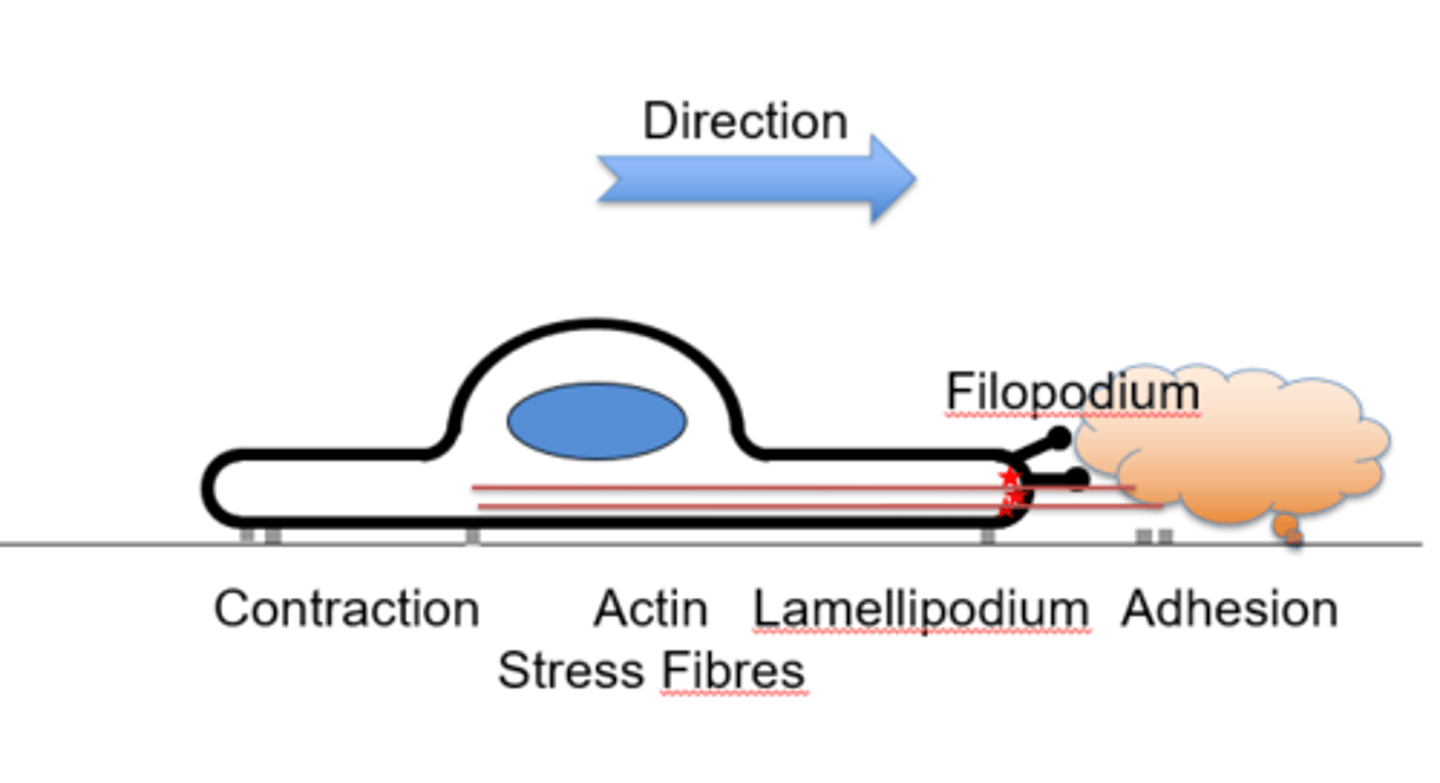
Describe the directional motility of a cell
→ Growth factor or cytokine signals direction for filopodia projection
→ The lamellipodium is formed through signal activation
→ The cell presses forwards, extending, adhering to the factor
→ Contractile force is generated by actin stress fibres
→ Adhesions at back are disassembled and the entire cell contracts
What % of our bodies are cells?
~50%, the rest are various forms of extracellular matrix (ECM)
Features of ECMs
Extracellular matrixes are a meshwork of proteins and hydrated macromolecules
They regulate
...migration of cells, proliferation & specialisation and the shape of cells
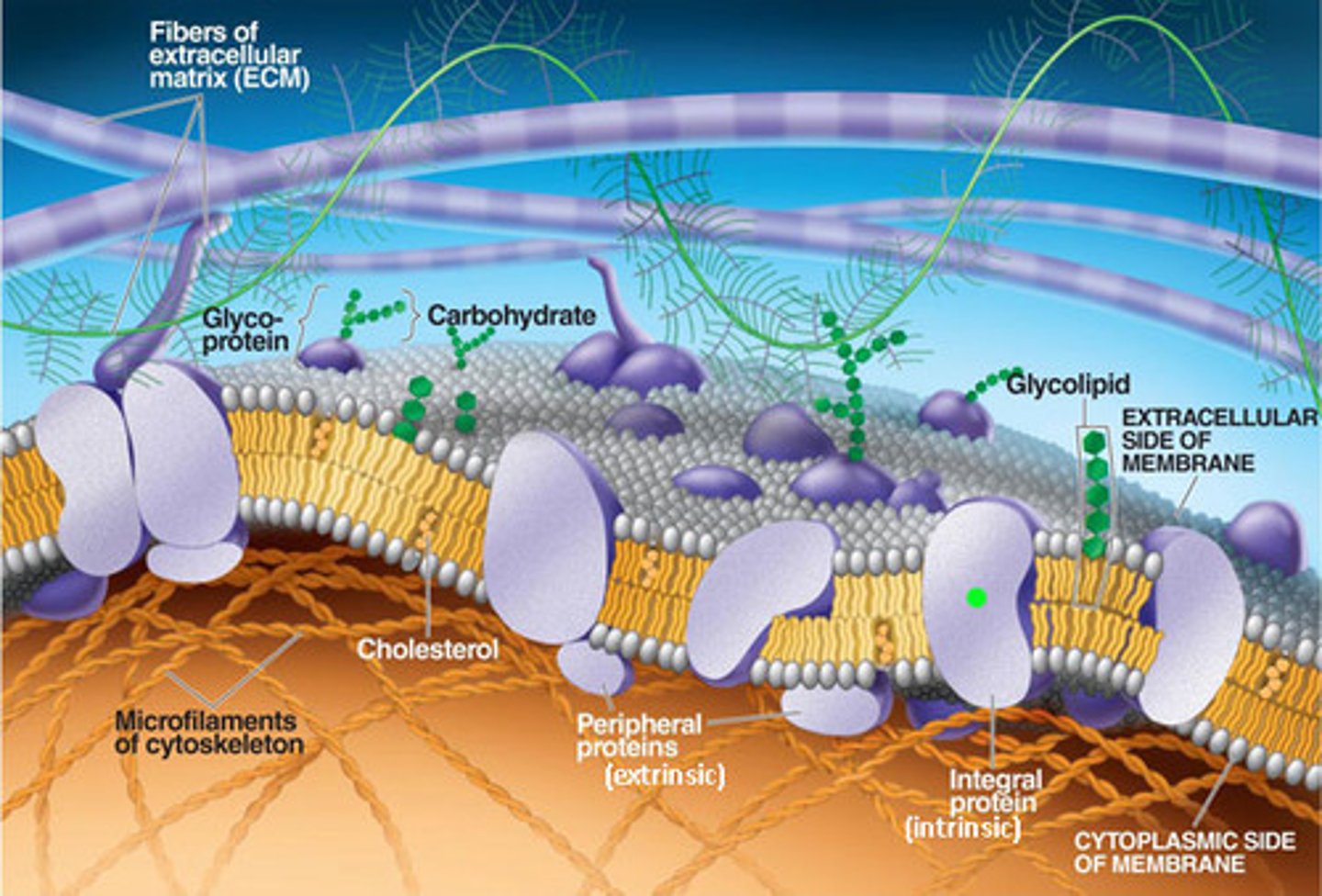
ECM types
Fibrous
Adhesion
Hydrated macromolecules
Fibrous proteins
Collagen and Elastin
Adhesion proteins
fibronectin and laminin
Hydrated macromolecules
These are space filling sugars which hold water
Glycosaminoglycans (Gags)
Proteoglycans (Protein + Gag)
Collagen structure
Triple helices
Glycine-Proline-Hydroxyproline triplet repeats composed of 3 a chains
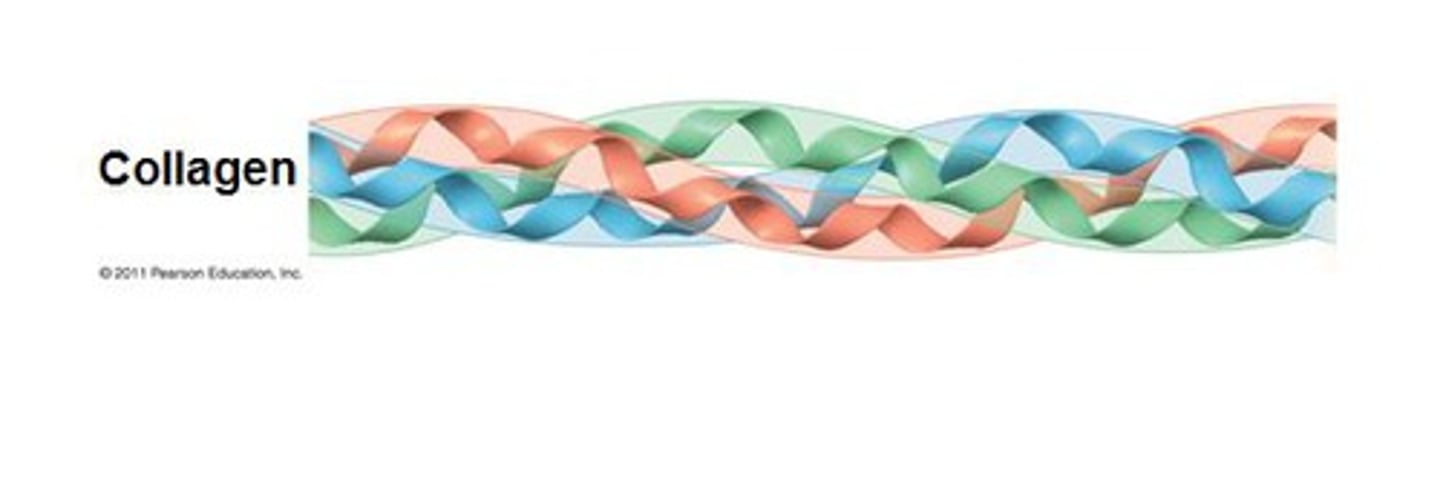
Where is collagen produced?
Fibroblasts and epithelial cells
How many varieties of collagen?
20-40
Collagen defects
Lead to Ehlers-danlos syndrome
Vascular form~
Arterial rupture
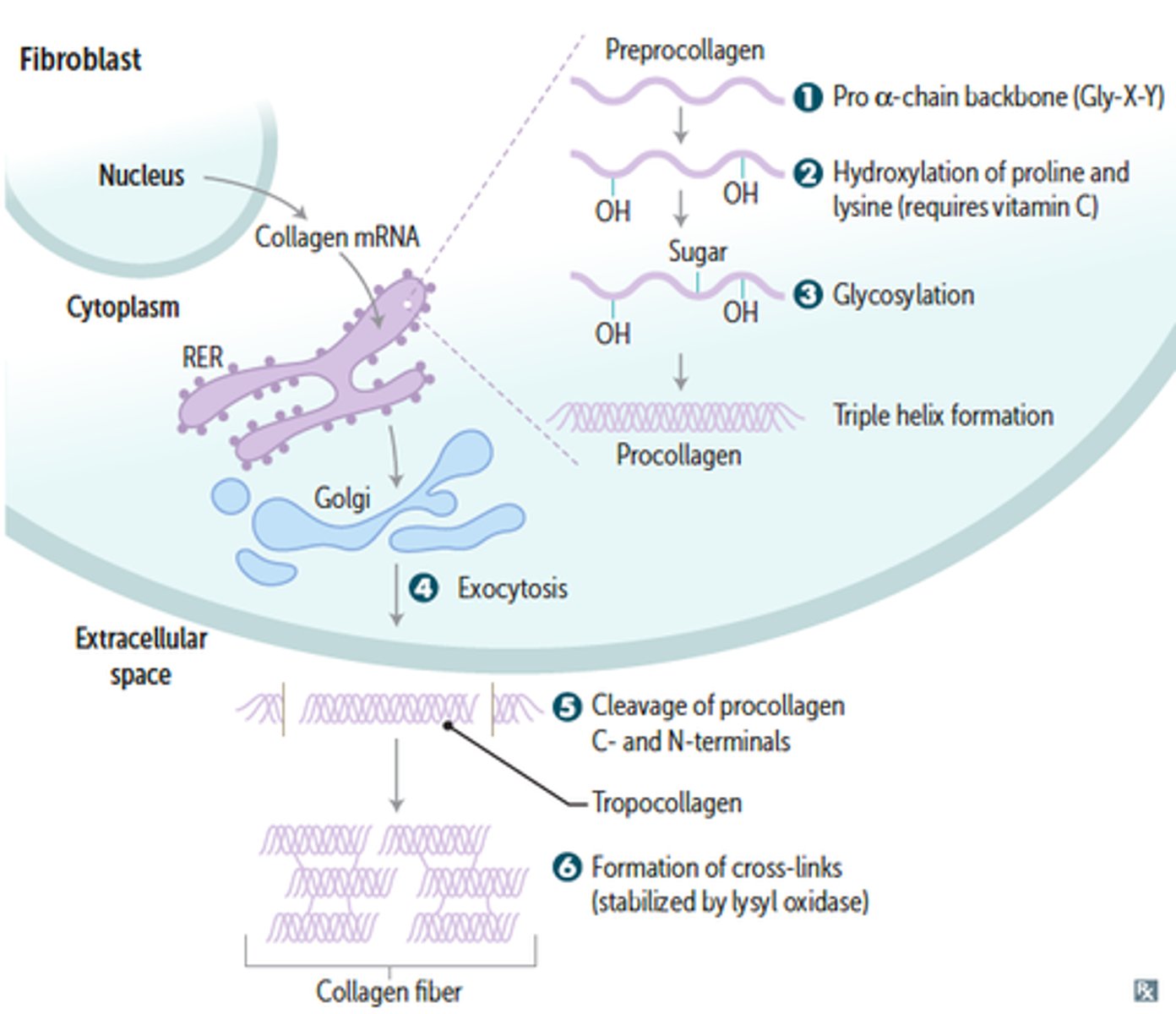
Collagen synthesis
A multistep, self assembly process dependent upon Vitamin C cofactors
Lots of Glycosylation and hydroxylation occurs
TERM
Elastin
DEFINITION
A protein that is similar to collagen and is the chief constituent of elastic fibres.
How does elastin assemble?
Self assembly through the conversion of tropoelastin to elastin by Lysyl oxidase
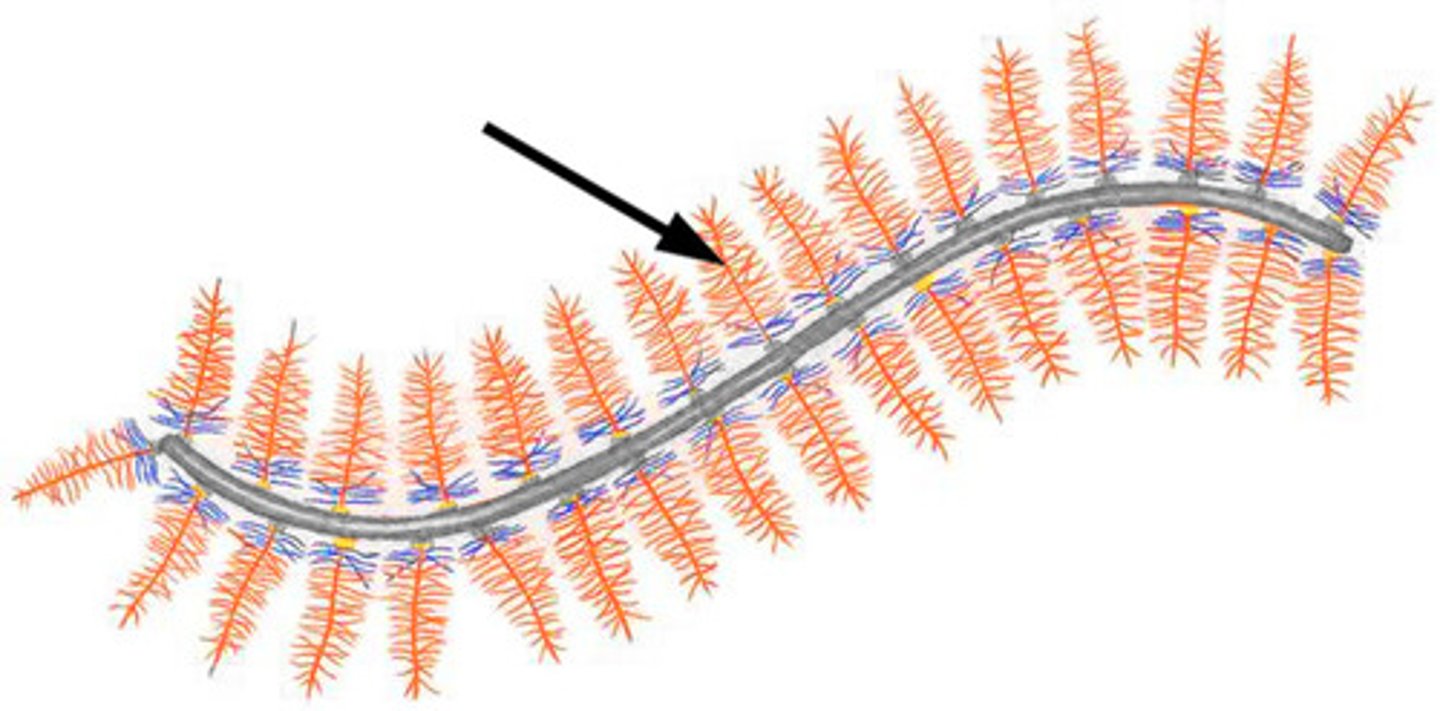
Relationship between elastin and fibrillin
Elastin is laid over a fibrillin scaffold
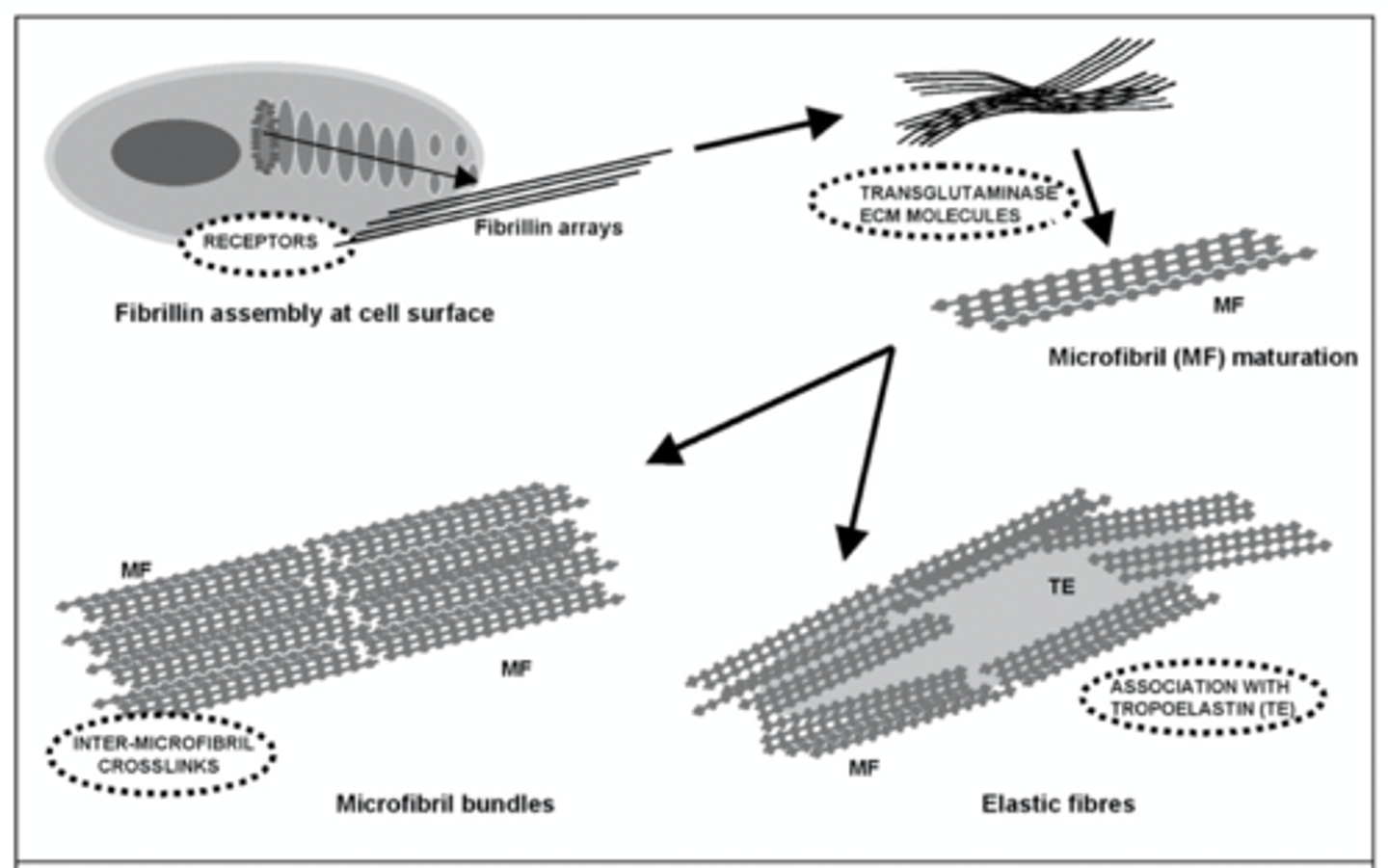
Elastin and Fibrillin are examples of...
Fibrous extracellular proteins
TERM
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
DEFINITION
70-200 unit disaccharide chains which are highly charged and 'sticky'
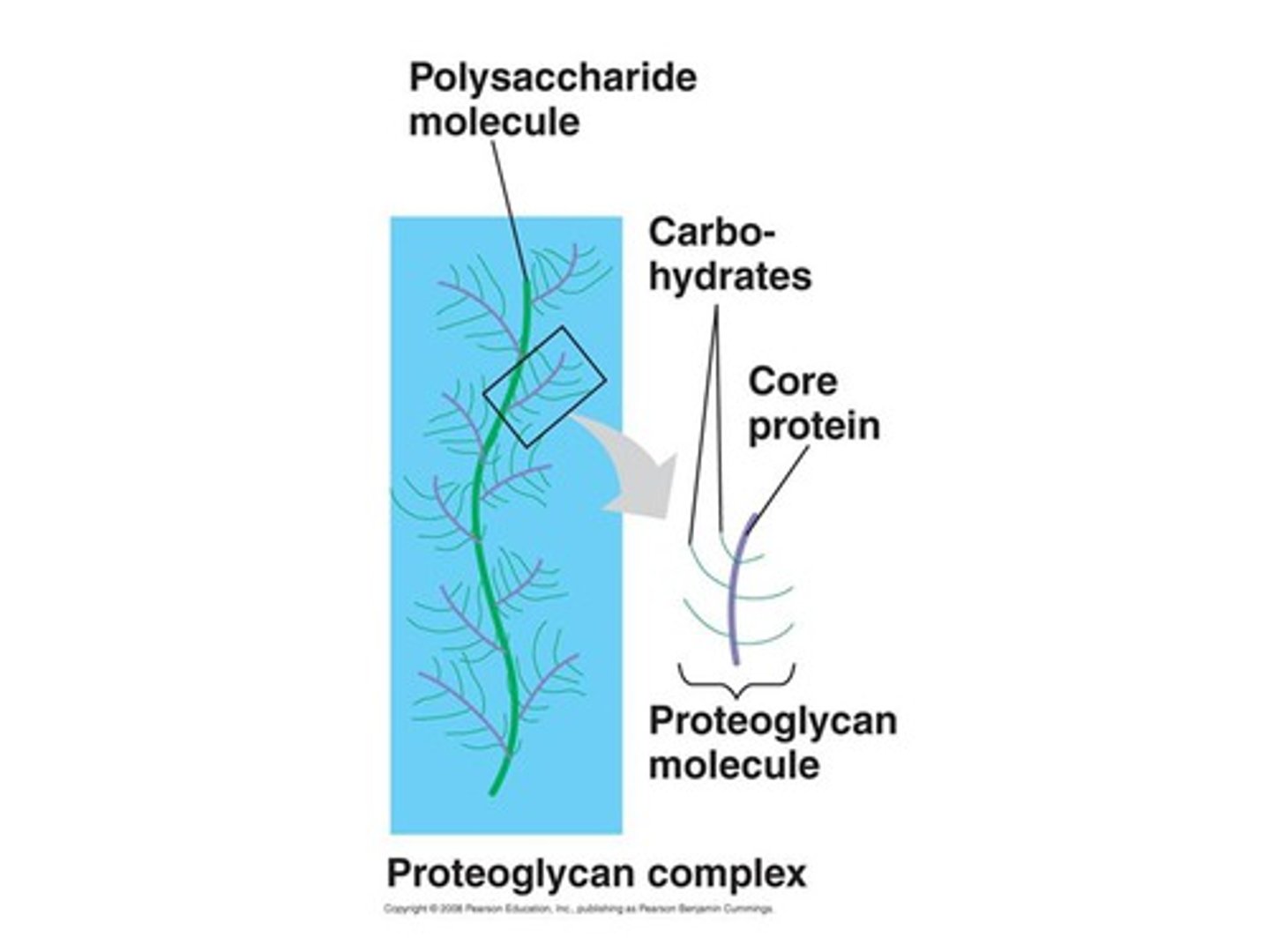
TERM
Proteoglycan
DEFINITION
A glycoprotein containing a protein core with attached long, linear carbohydrate chains.
95% sugar, 80 saccharides
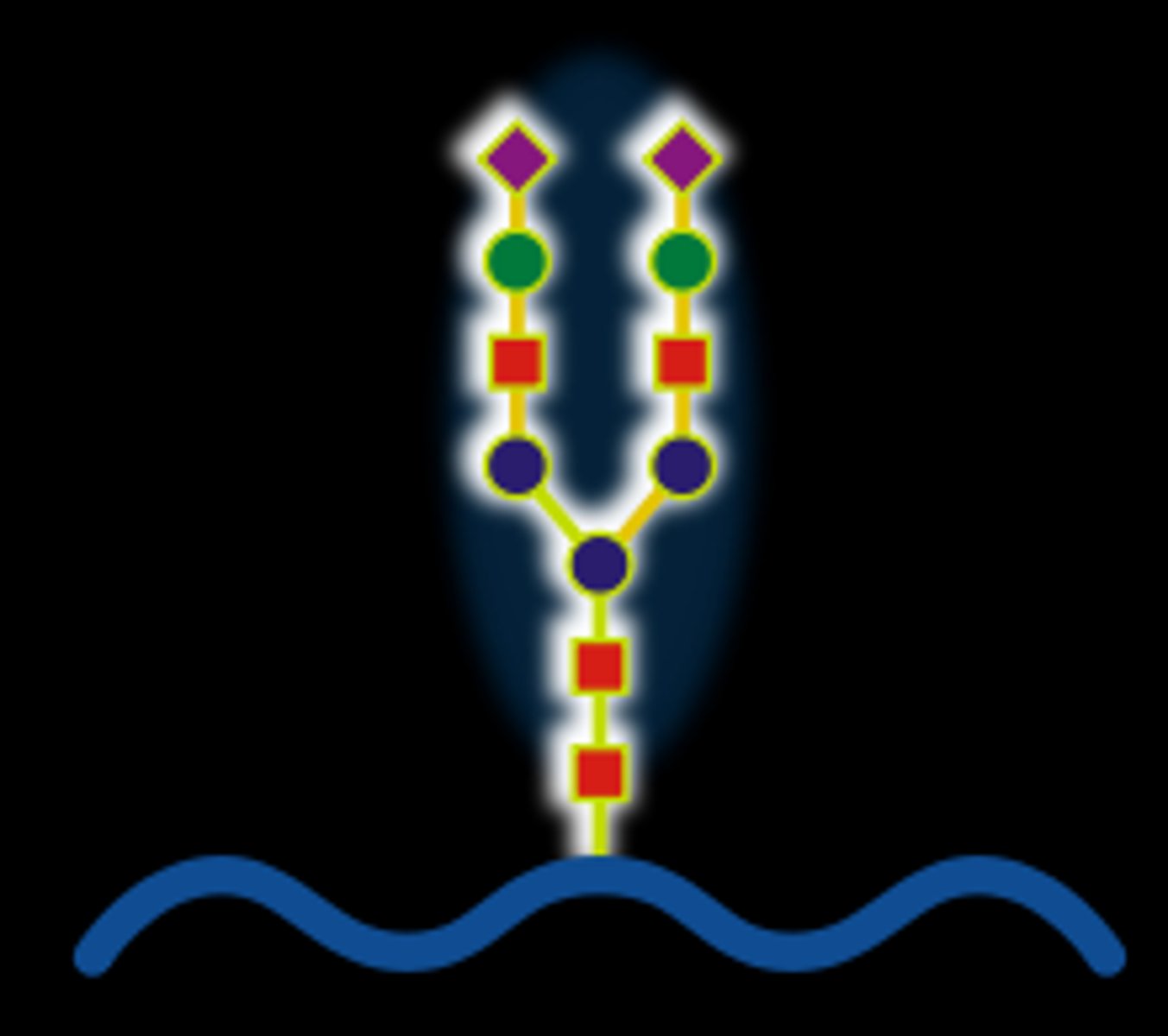
Glycoprotein
60% sugar
15 saccharides
TERM
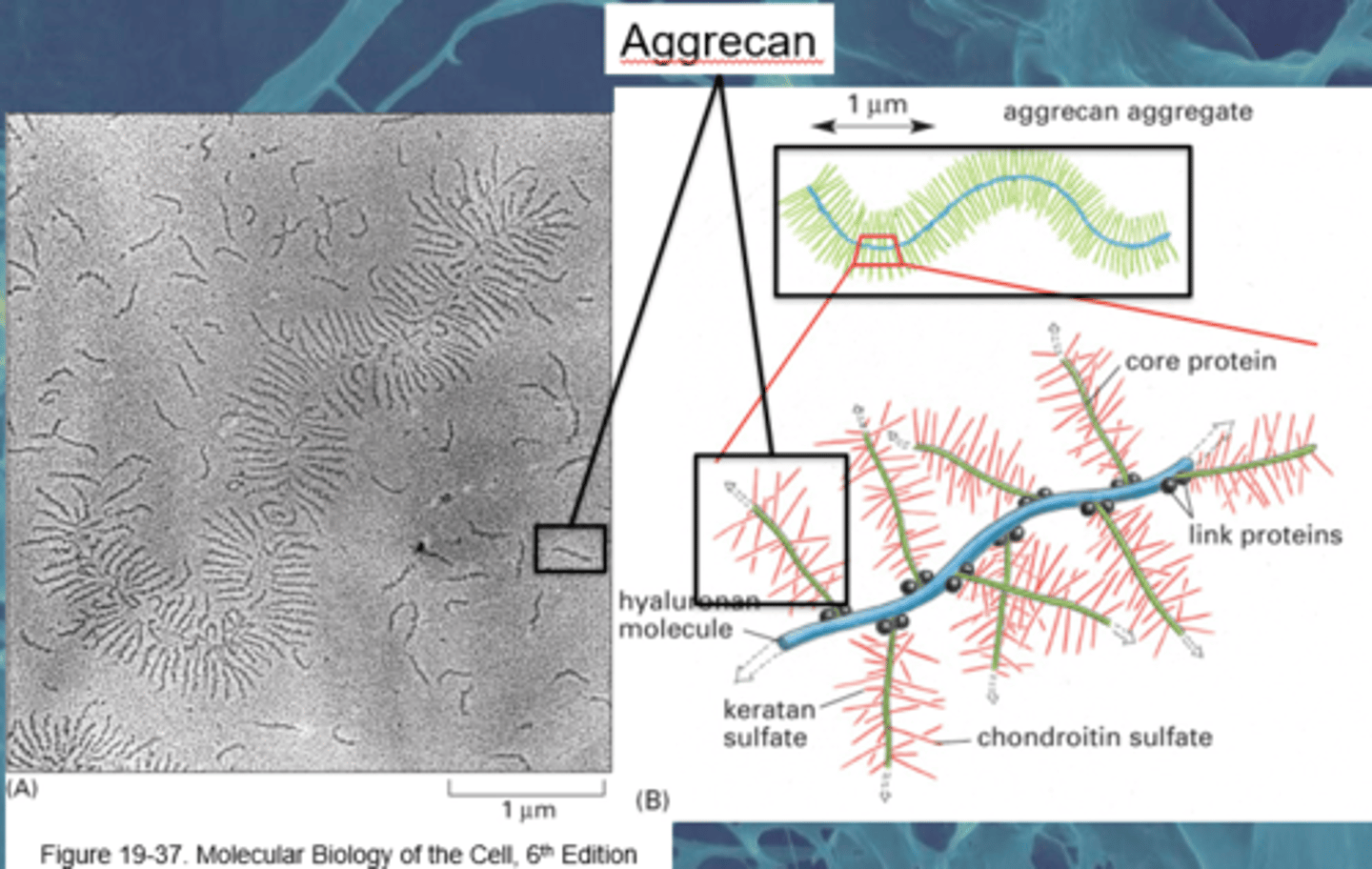
Hyaluronan Complexes
DEFINITION
Hyaluronan is a large space filling molecule with aggrecan branches via. link proteins
Aggrecan is linked with chondroitin sulphate
Adhesion glycoproteins
protein-carbohydrate complexes that bind plasma membrane proteins to collagen and proteoglycans outside the cell wall.
TERM
Laminin
DEFINITION
is the protein found in the basement membrane to which integrins from cells attach
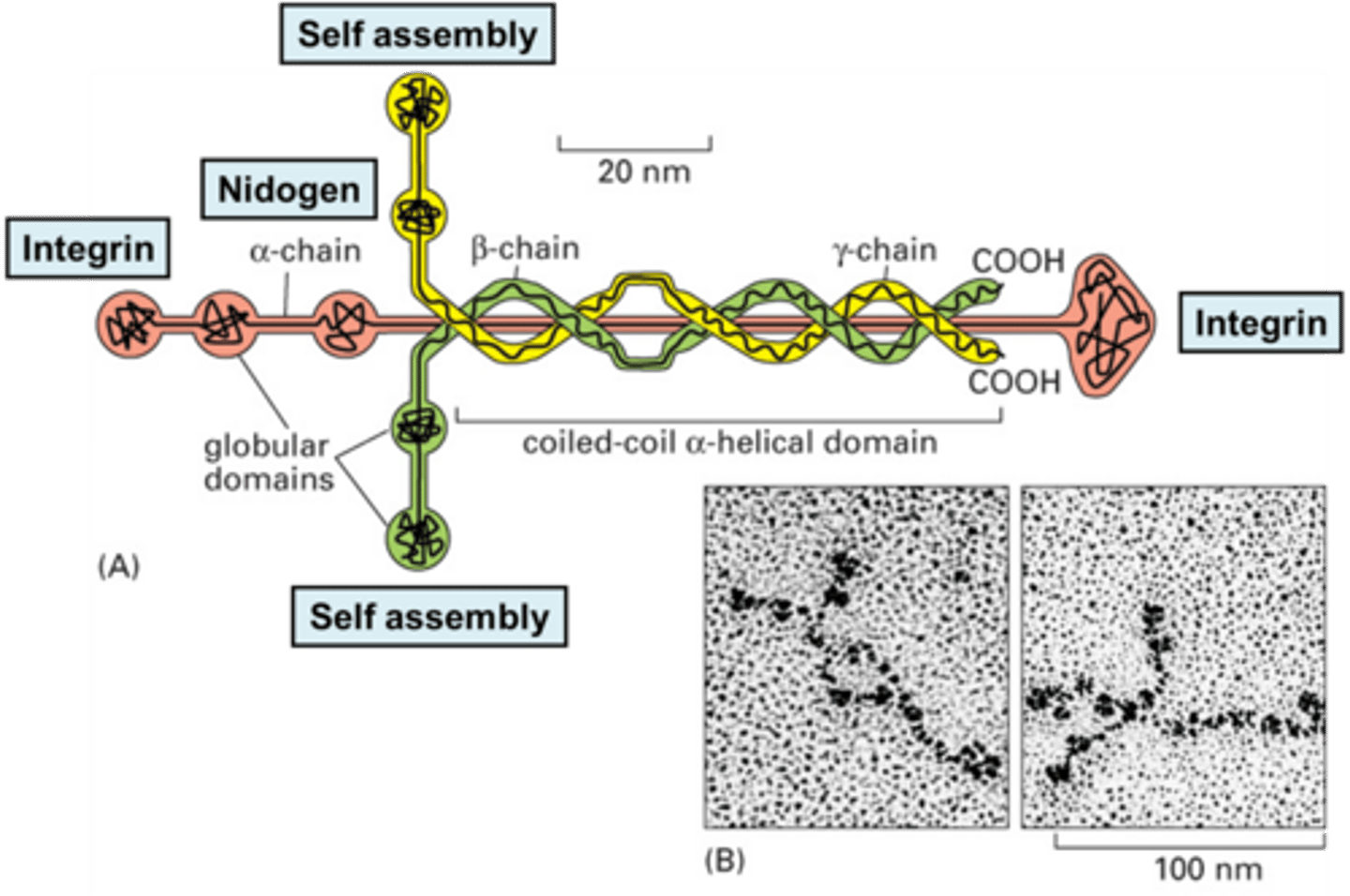
TERM
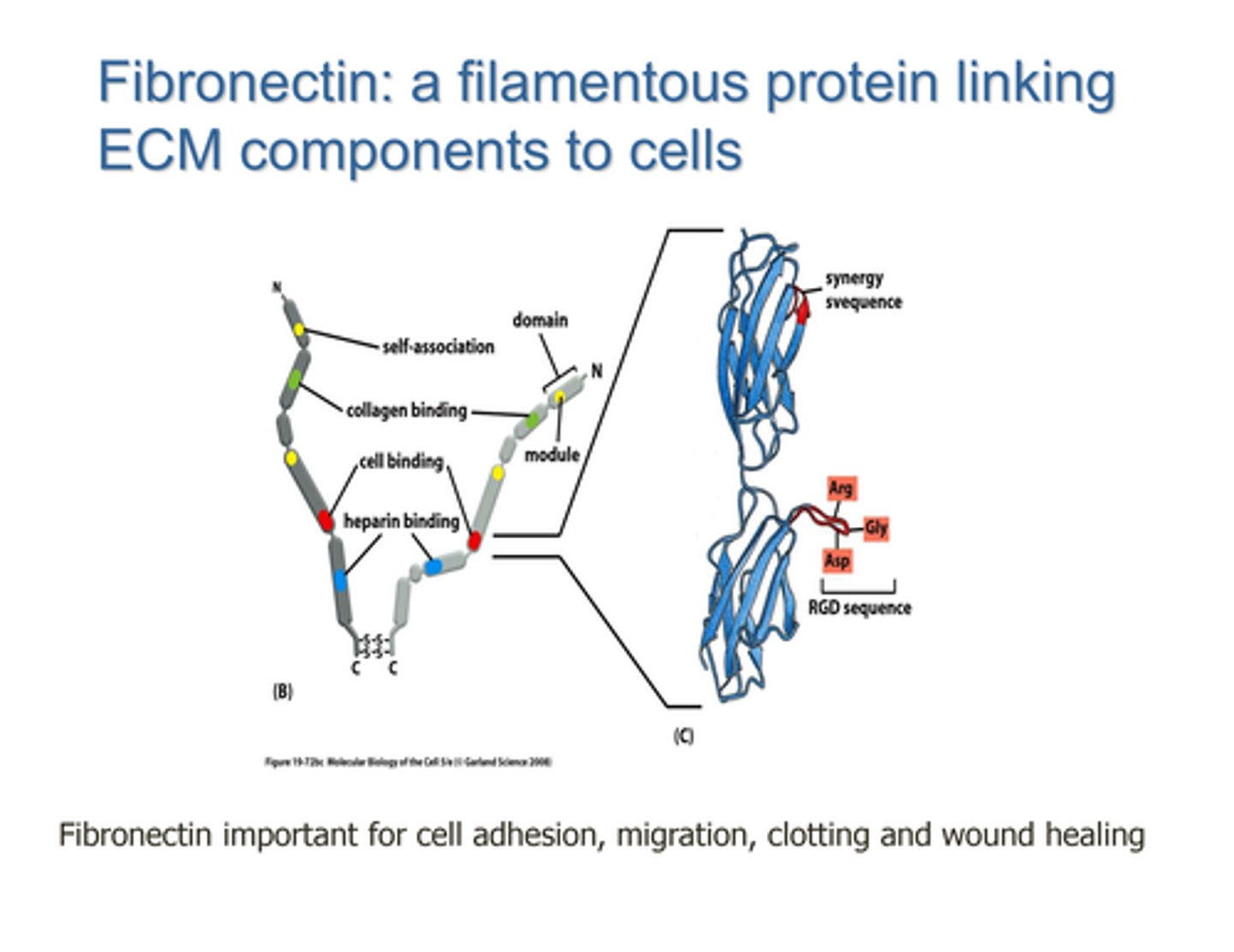
Fibronectin
DEFINITION
An extracellular glycoprotein secreted by animal cells that helps them attach to the extracellular matrix.
Coats a collagen scaffold to allow for cell adhesion and migration
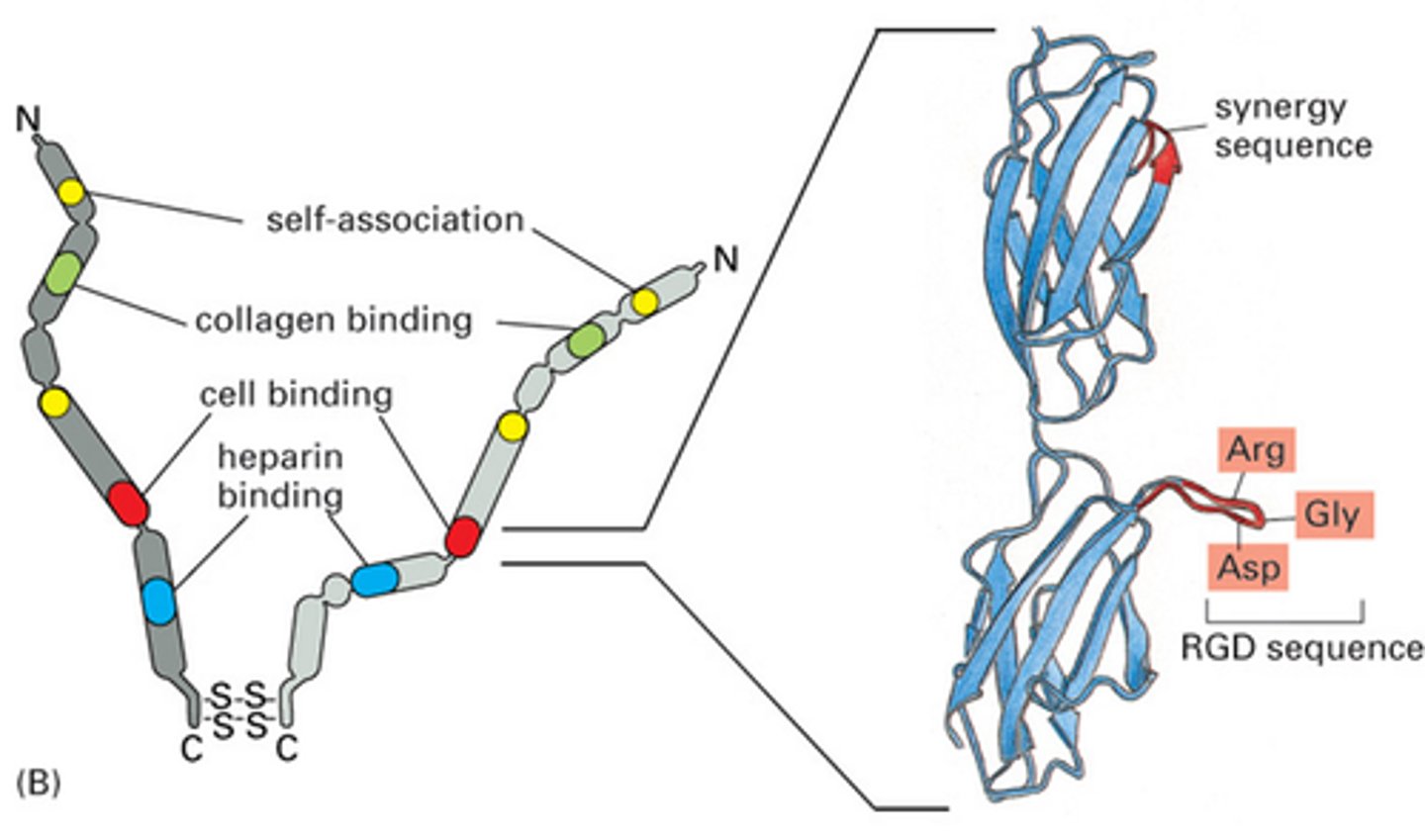
Fibronectin structure
Two dimers linked by disulphide bridges
Cell binding, collagen binding and self-association domains
Cell binding domain has Arg-Gly-Asp RGD sequence
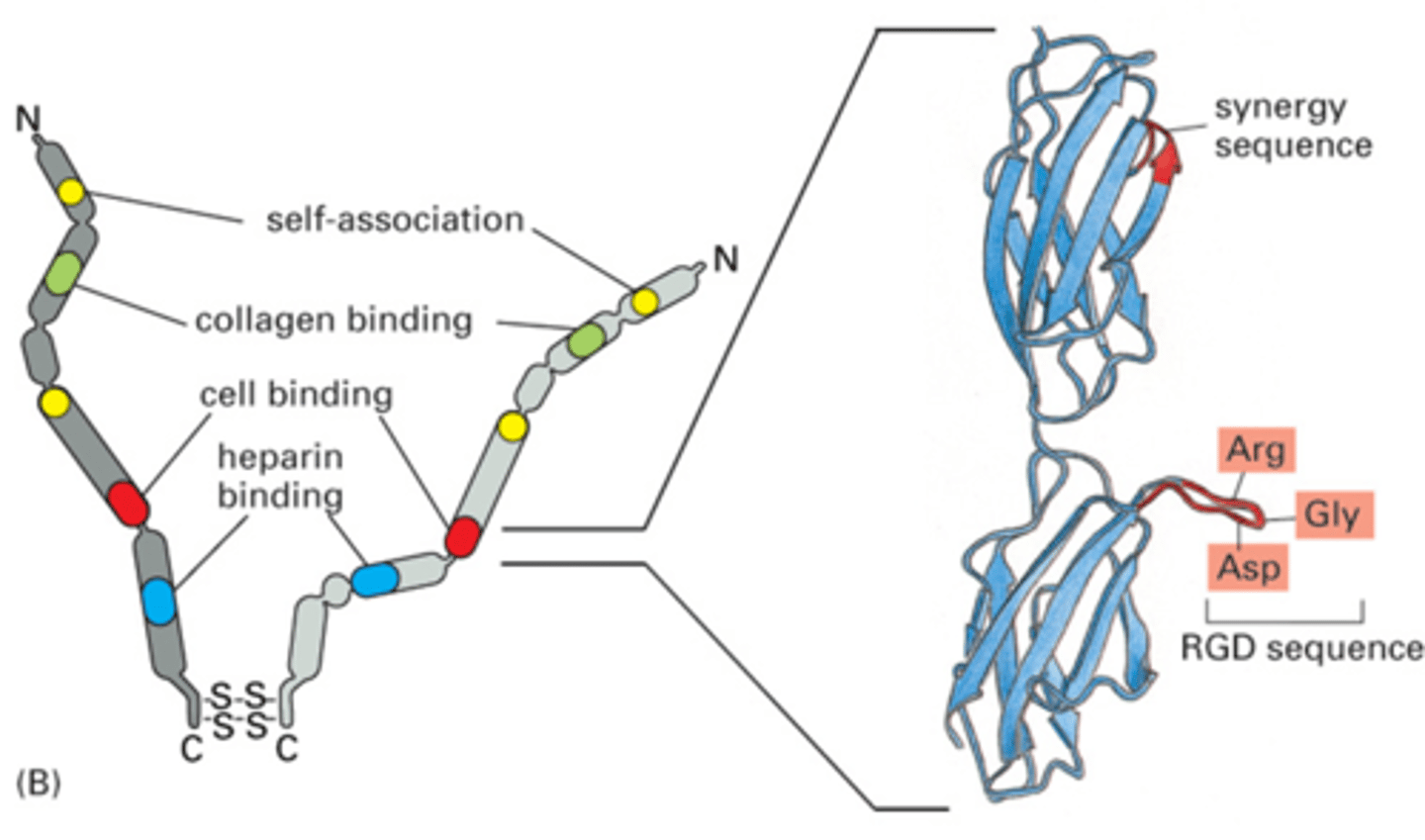
Cell binding site on Fibronectin
RGD sequence allows for polarity and adherence
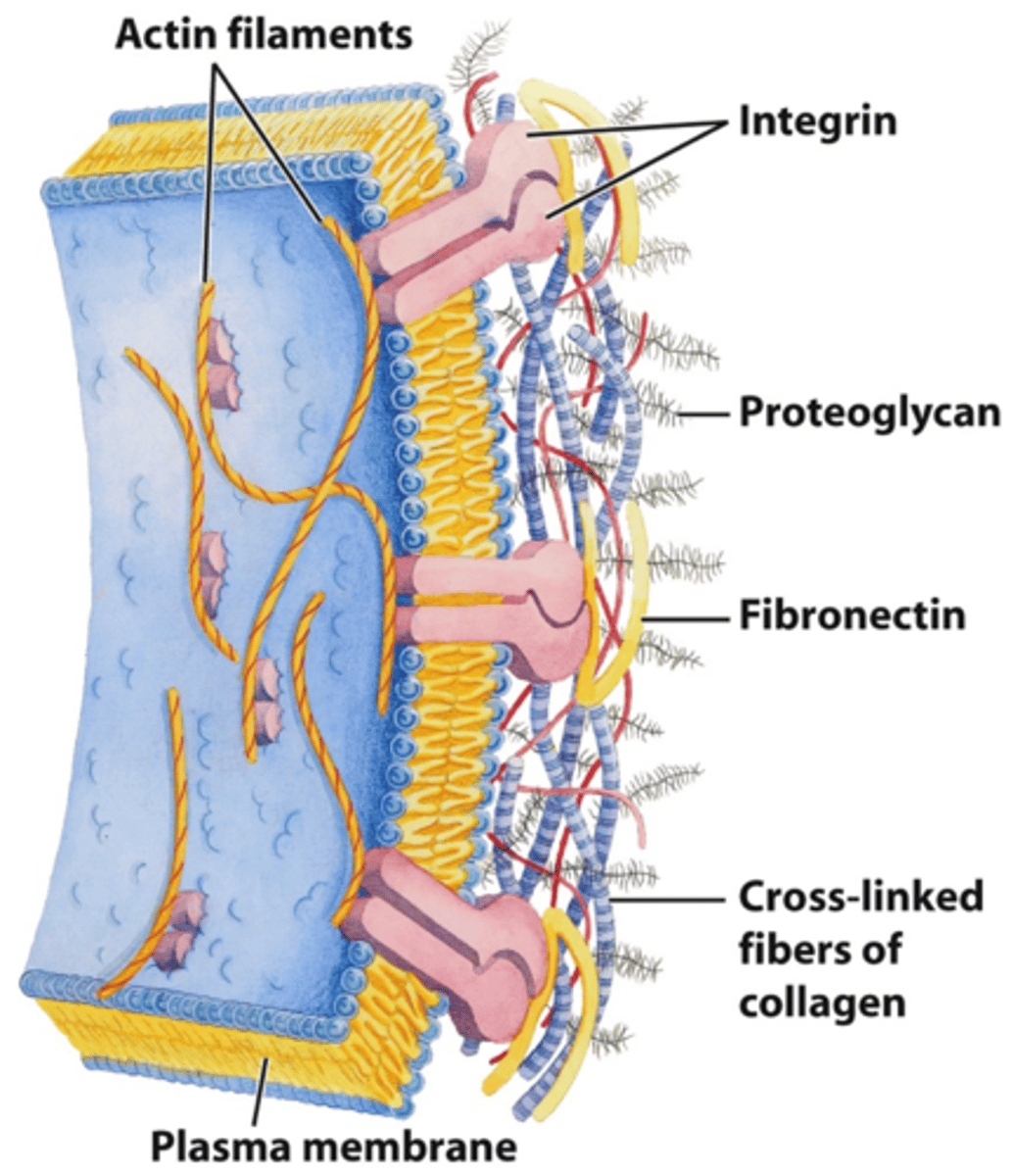
Integrins
membrane proteins; they transmit signals between the ECM and cytoskeleton
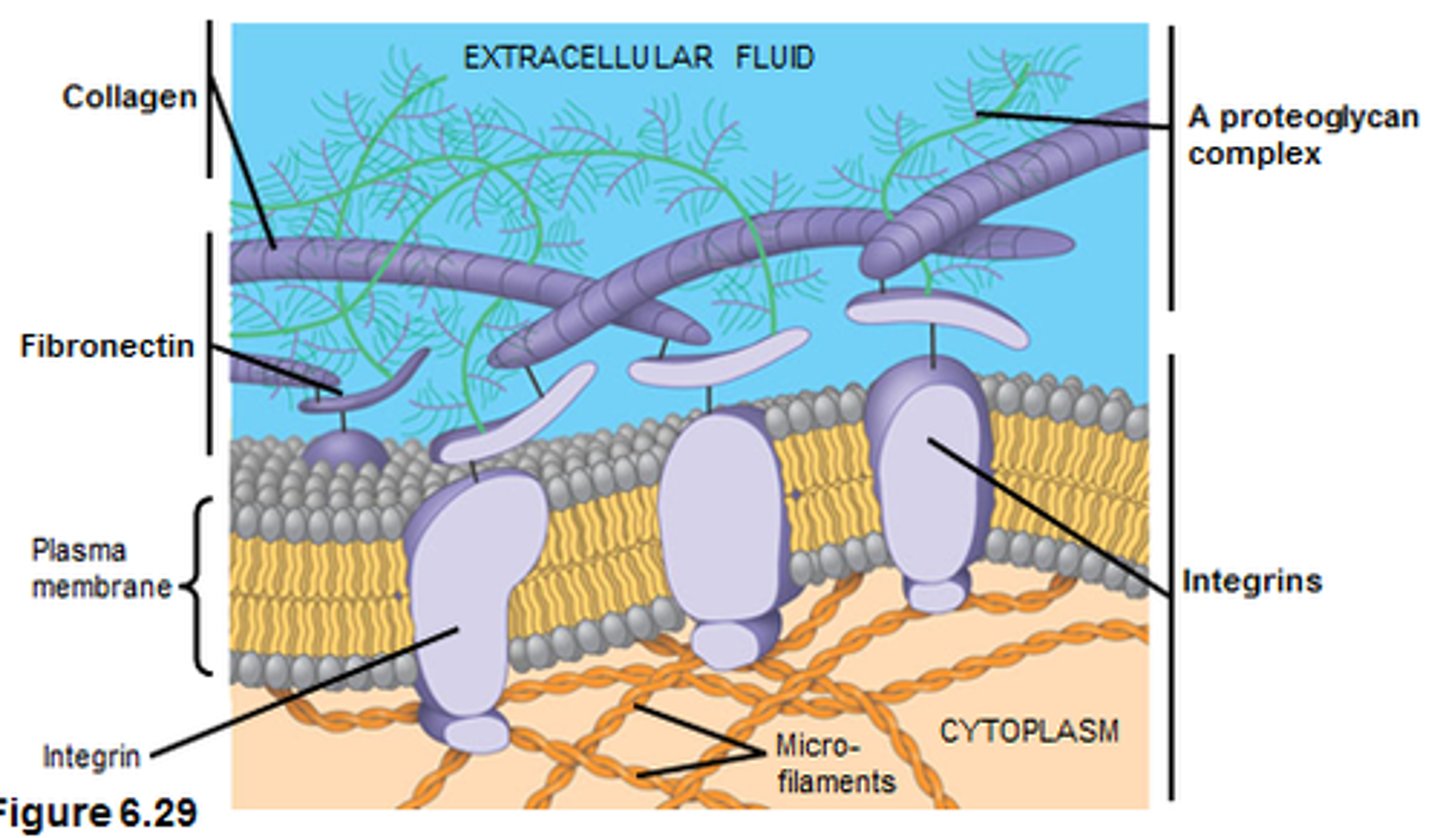
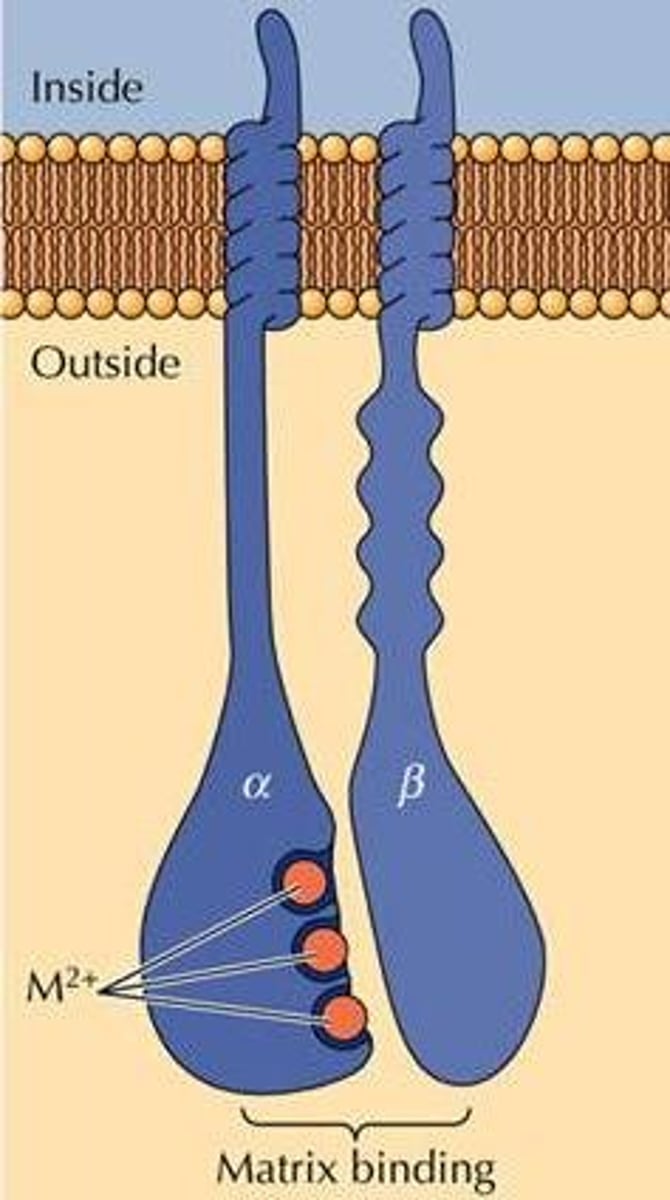
How do integrins bind the ECM?
Divalent cations, removal causes cellular detachment
Focal adhesions
docking sites where cells adhere to their substratum and send signals to the cell interior
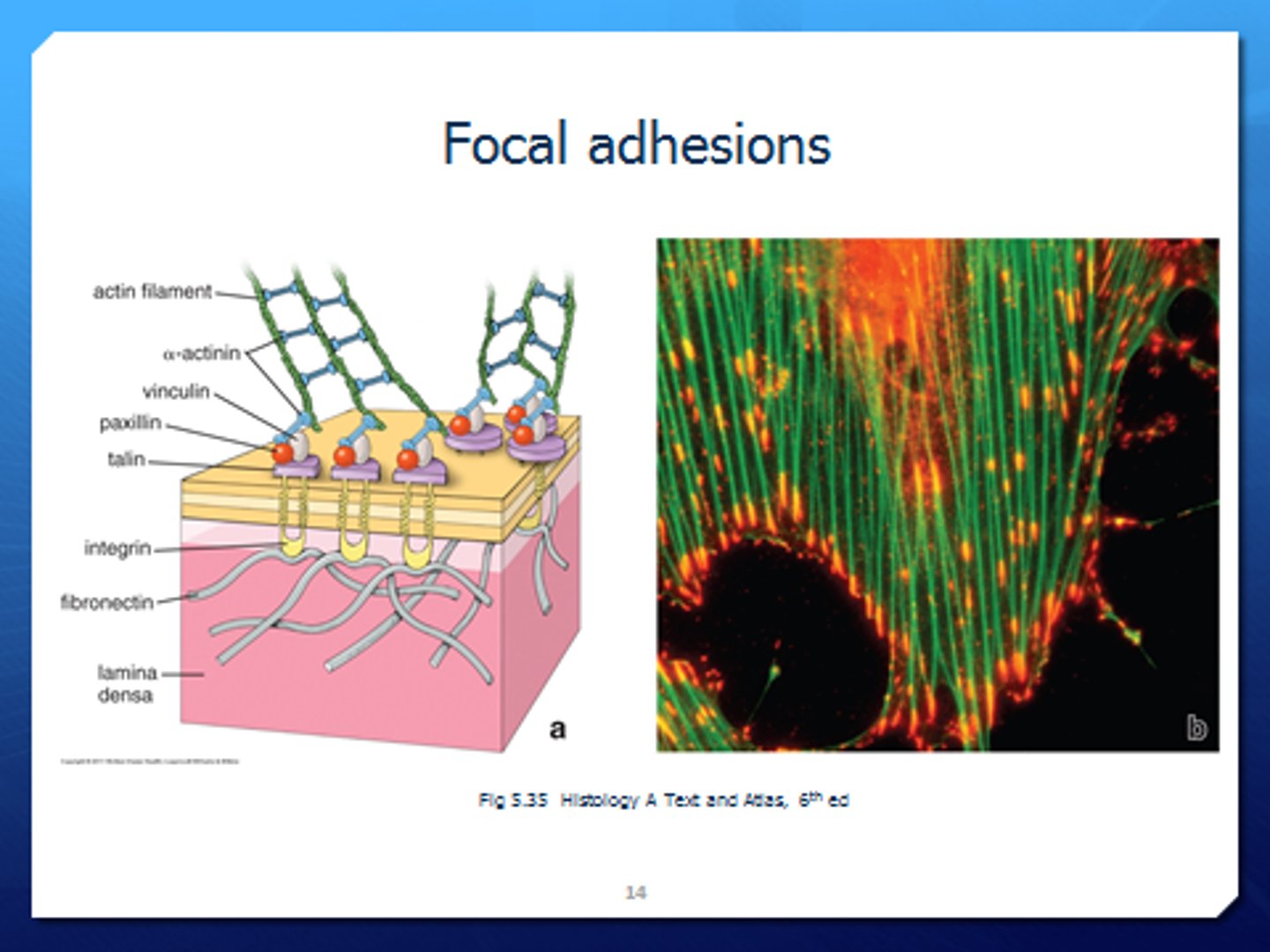
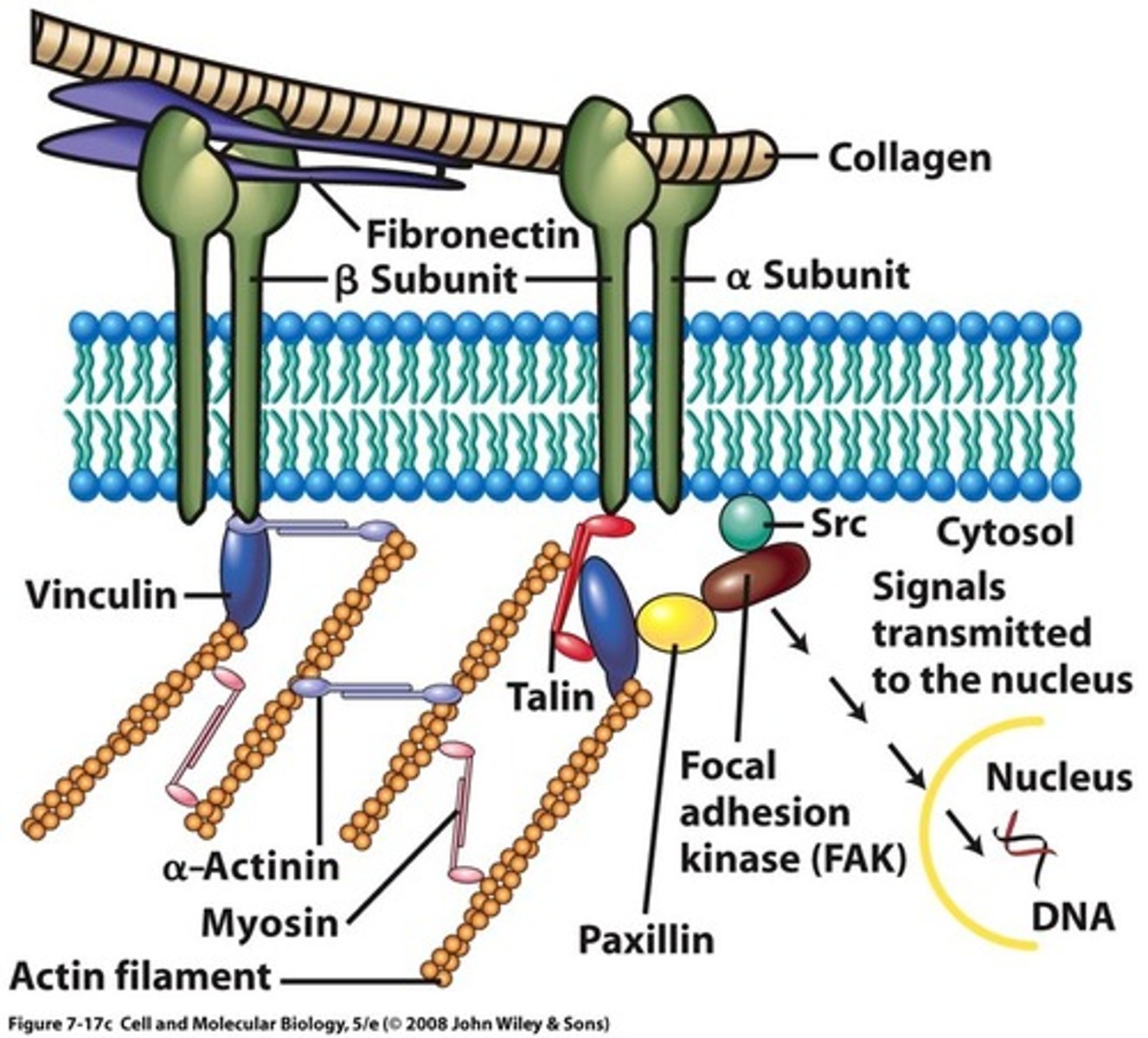
Focal adhesion components
→ Transmembrane receptor
→ Connection to cytoskeleton
→ Signalling
Knockout of focal adhesion proteins
B1 and A5 integrin knockouts are embryonic lethal
Fibronectin is day 9 lethal
Takin is 6-8 lethal
Integrin related defects
Platelet clotting, bleeding gums, LAD syndrome, impaired expression and recurrent bacterial infection
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Defective formation of collagen (risk for aortic dissection)
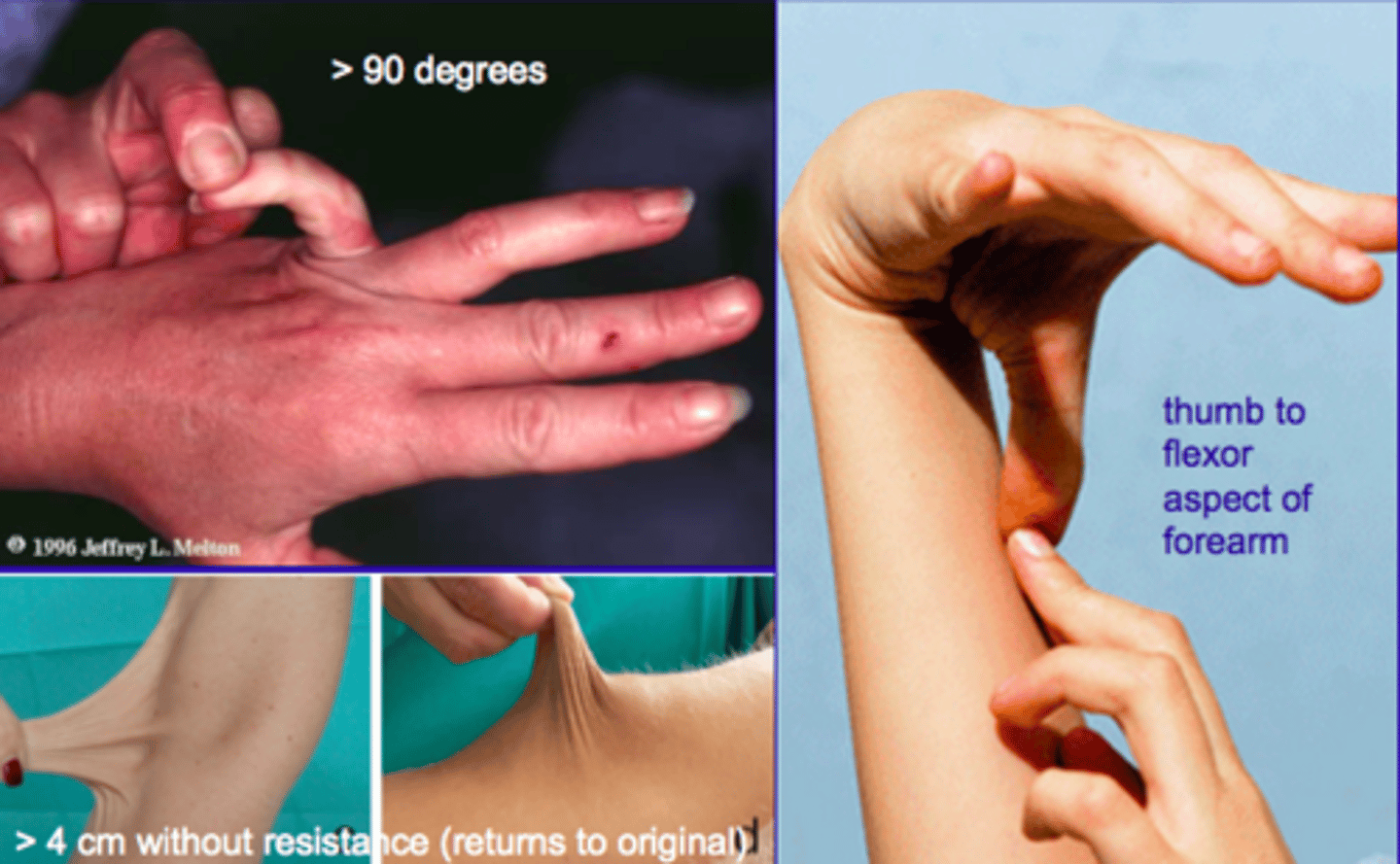
Marfan Syndrome
genetic connective tissue disorder that can cause a ruptured aorta
Related to fibrillin defects (the molecules which scaffold elastin)
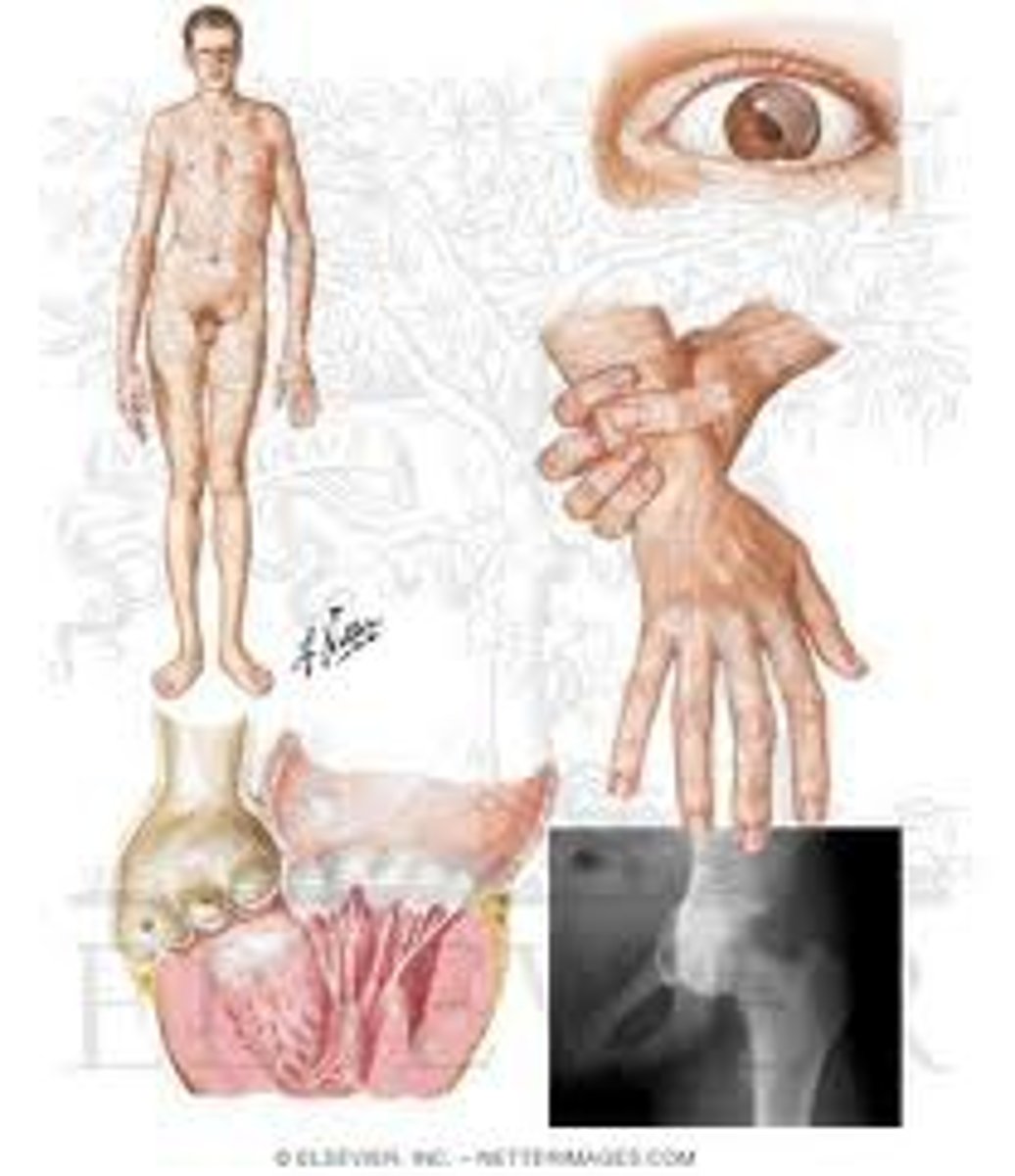
LAD syndrome
Related to defects in B2 integrin
Leads to bleeding gums and vulnerability to recurrent bacterial infections
Cell Junction
structure that connects a cell to another cell or to extracellular matrix
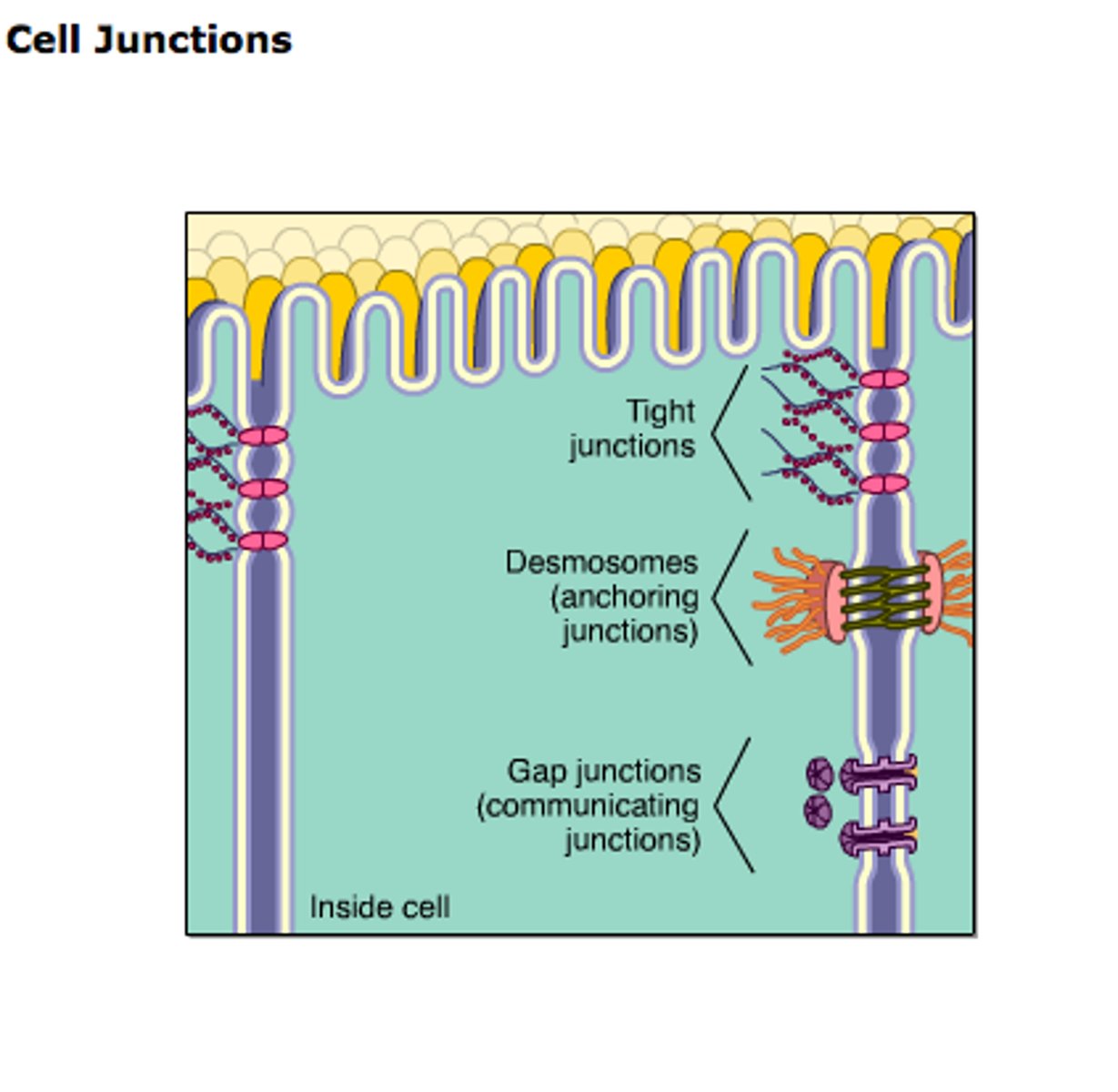
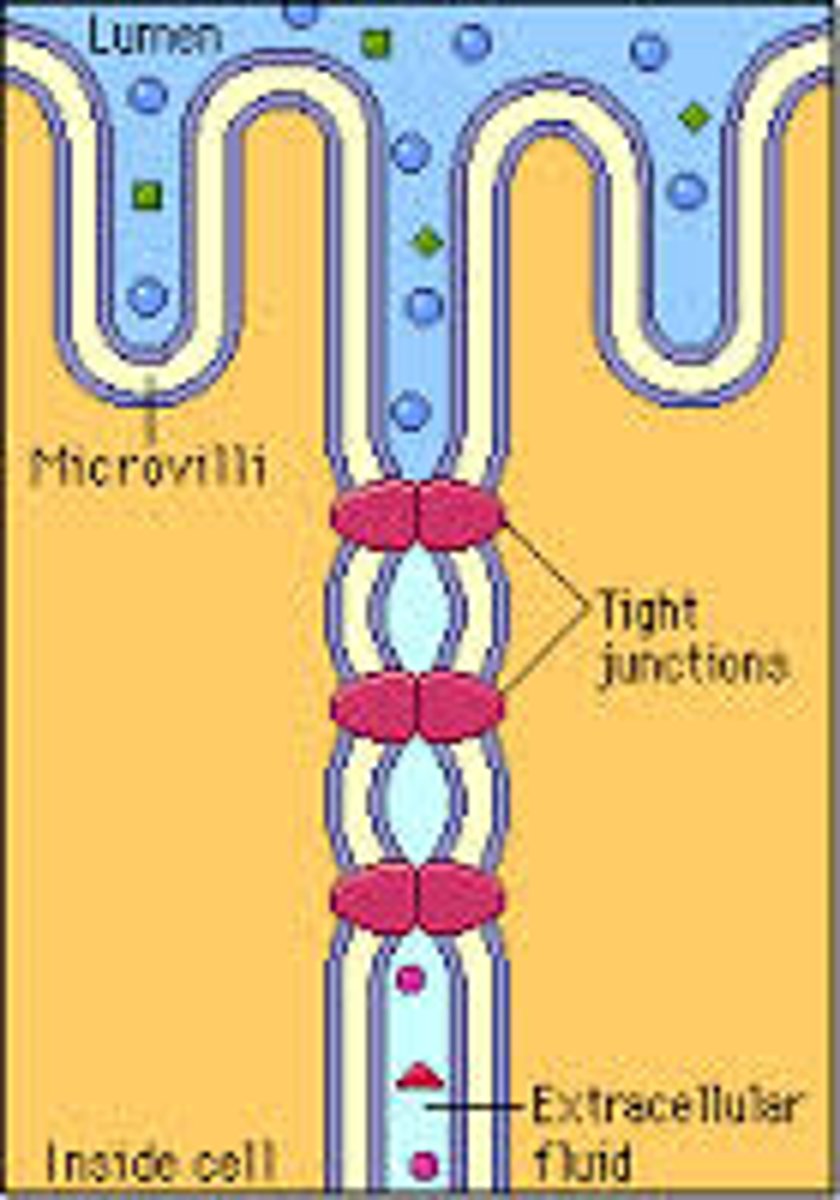
Occluding junction
Type of cell junction that seals cells together in an epithelium, forming a barrier through which even small molecules cannot pass
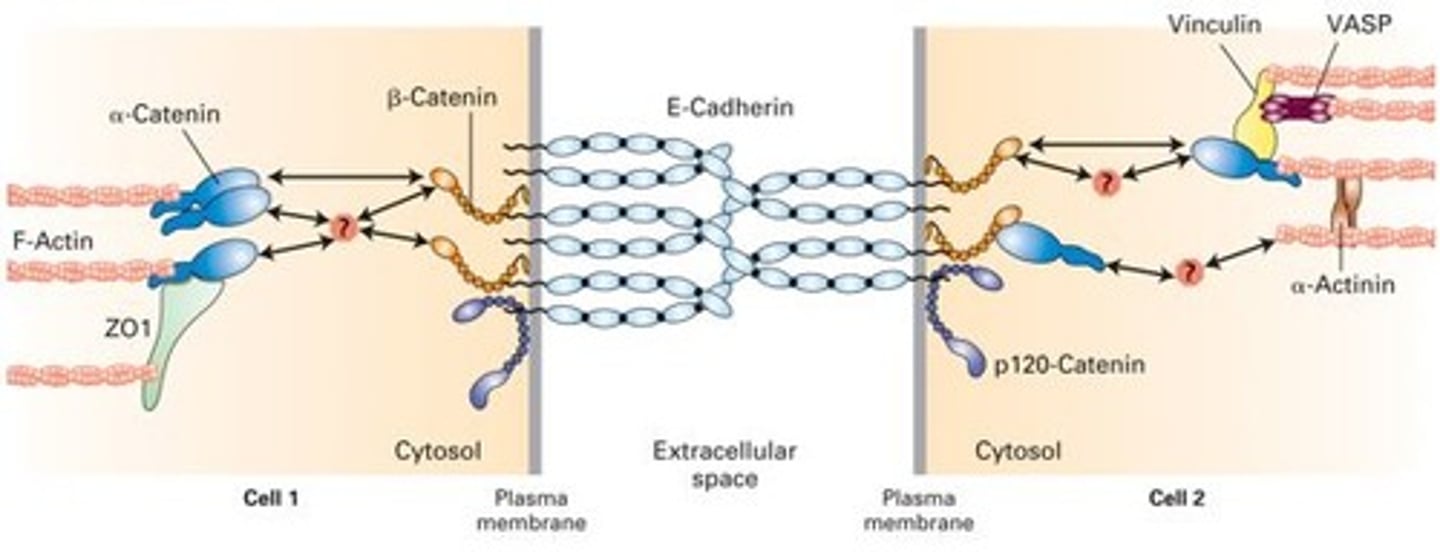
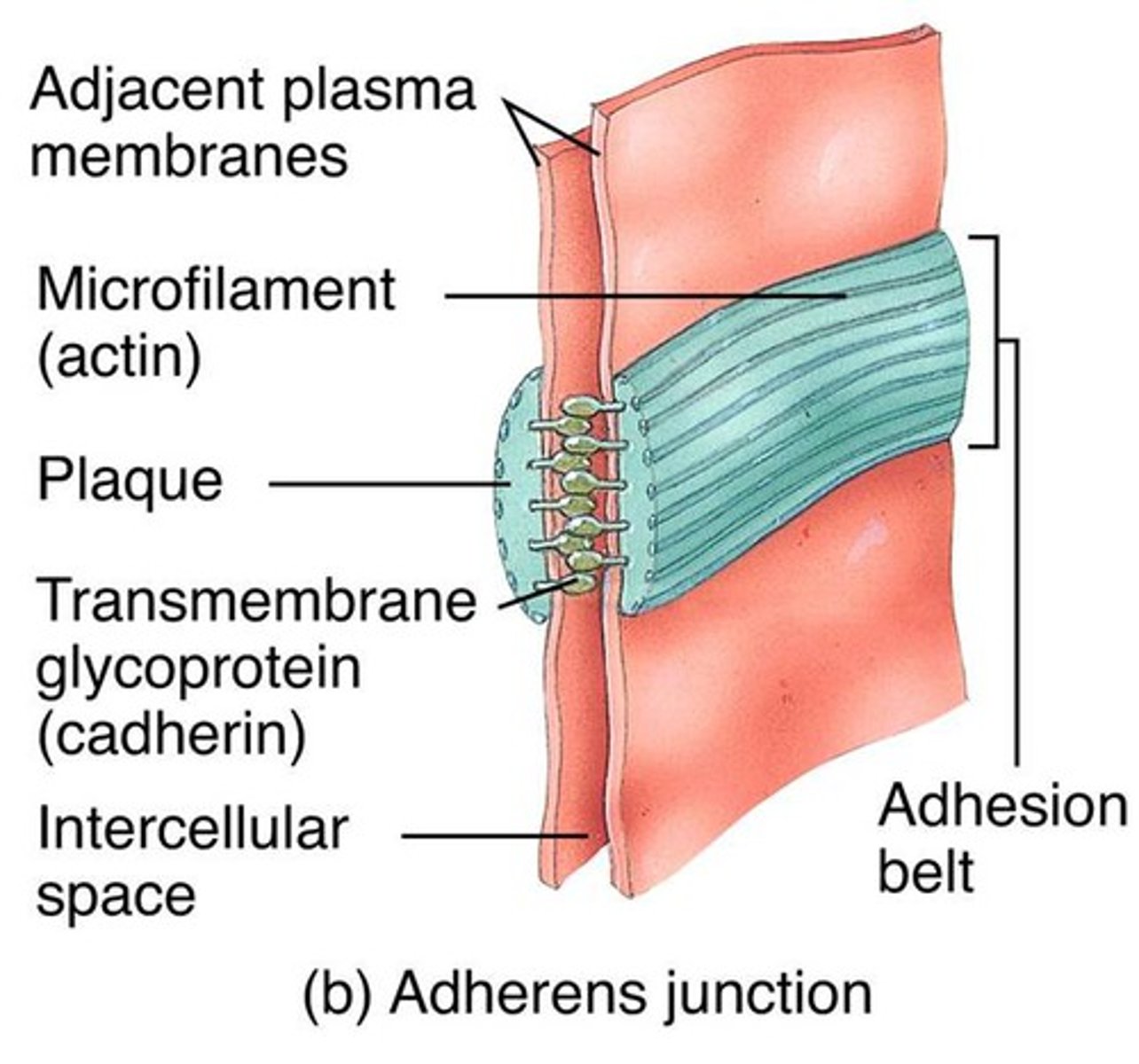
Adherens Junctions
make an adhesion belt that keeps tissues from separating as they stretch and contract
Ca2+ dependent , homophillic interaction, strong intercellular links
Links to actin cytoskeleton
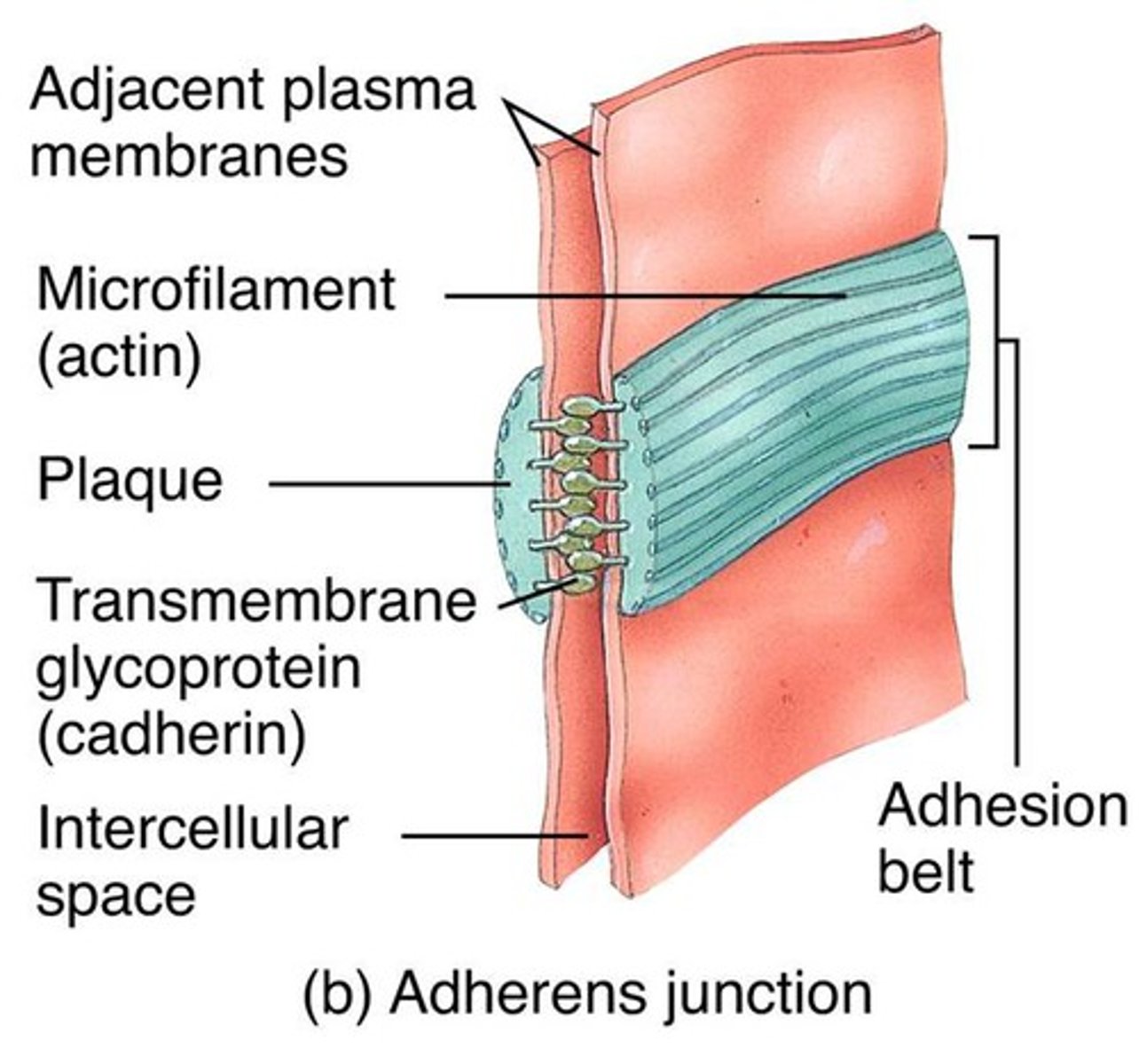
Adhesion belt
Found just below the tight junction, acts as a weak glue that holds cells together
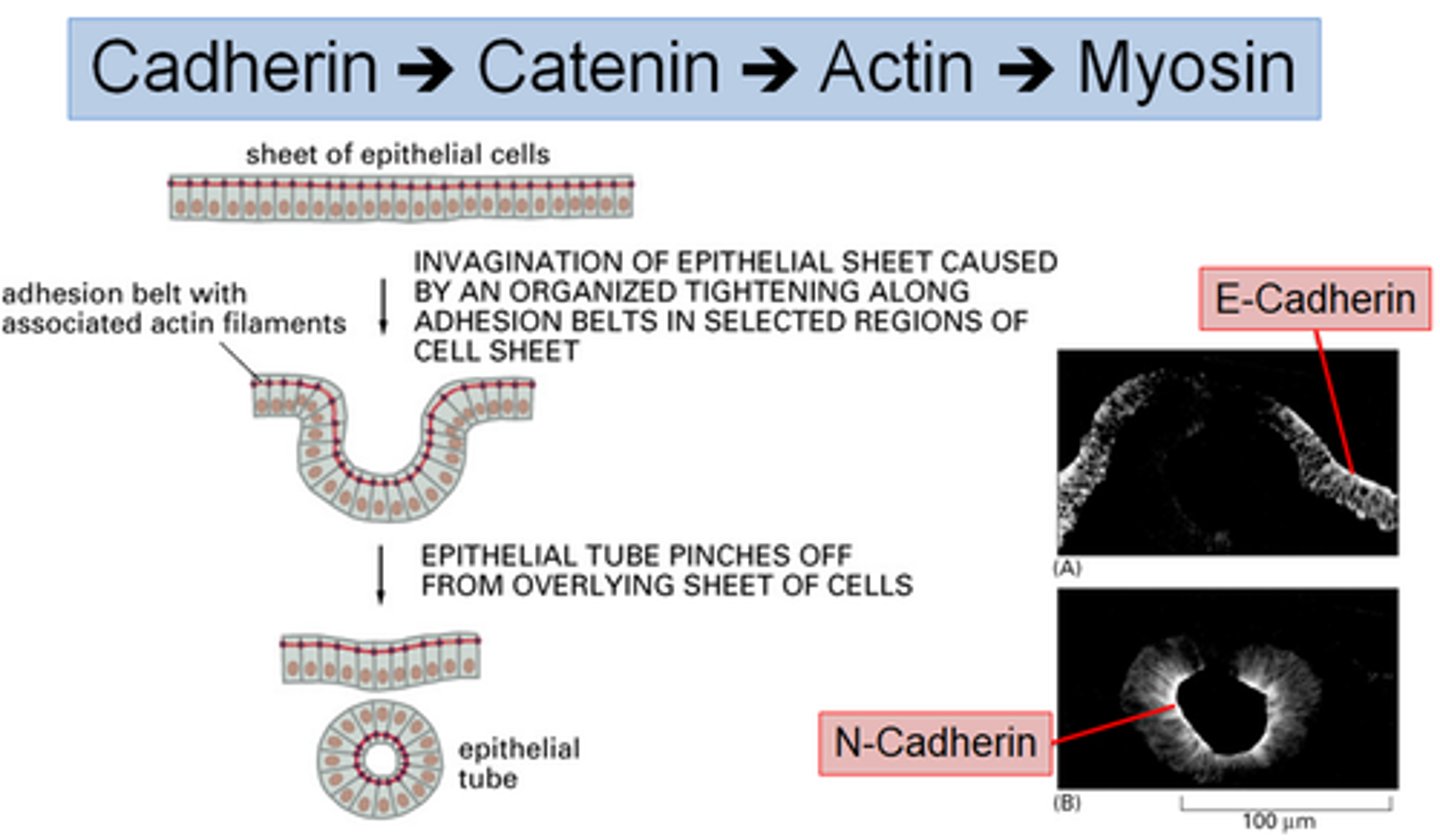
Cadherin -> Catenin -> Actin -> Myosin
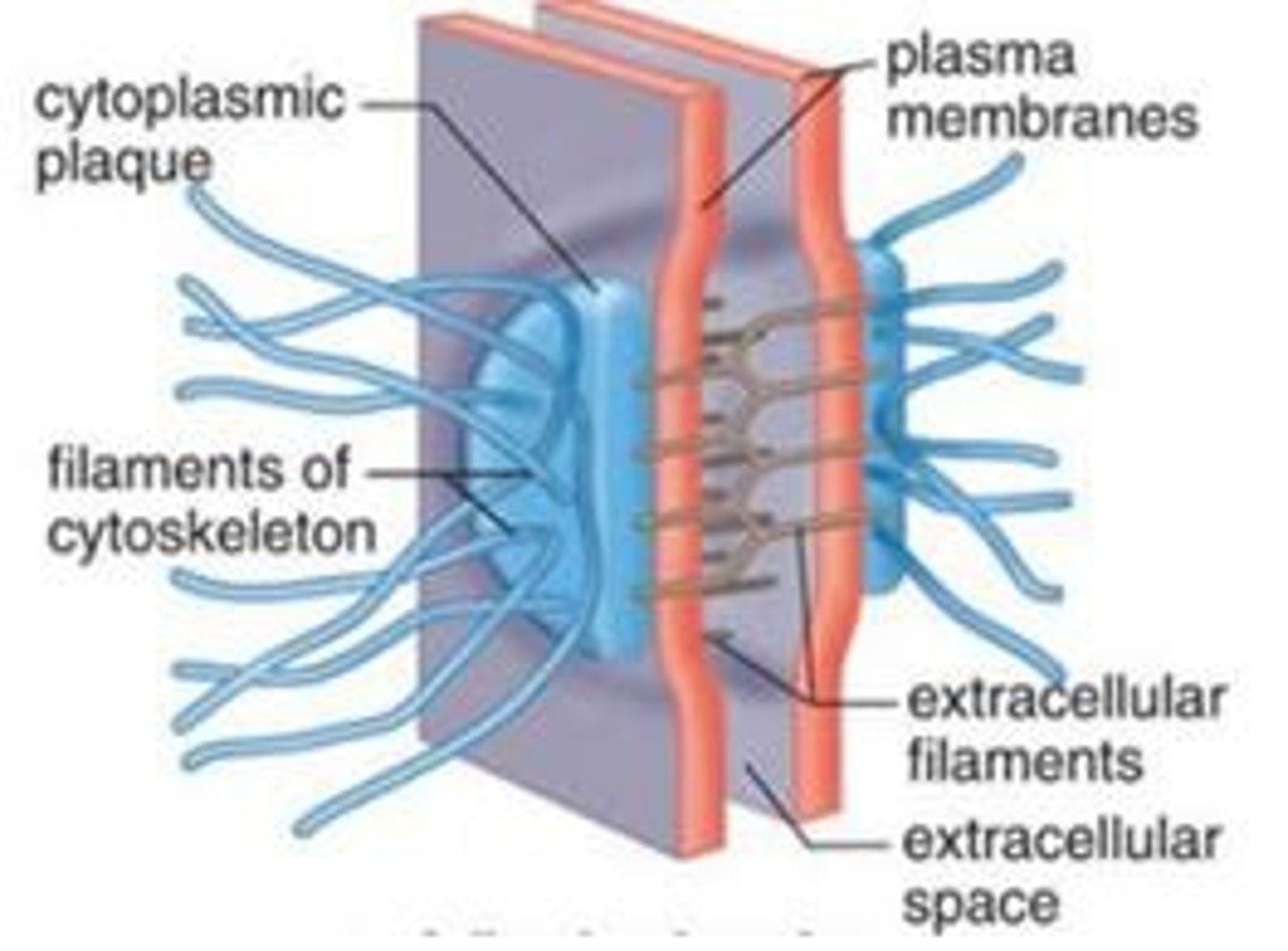
TERM
Desmosome
DEFINITION
a type of intercellular junction in animal cells that functions as a rivet, fastening cells together
Plentiful in heart muscle and epidermis
TERM
Hemidesmosome
DEFINITION
anchors intermediate filaments in a cell to the basal lamina
Via integrins and intermediate filaments
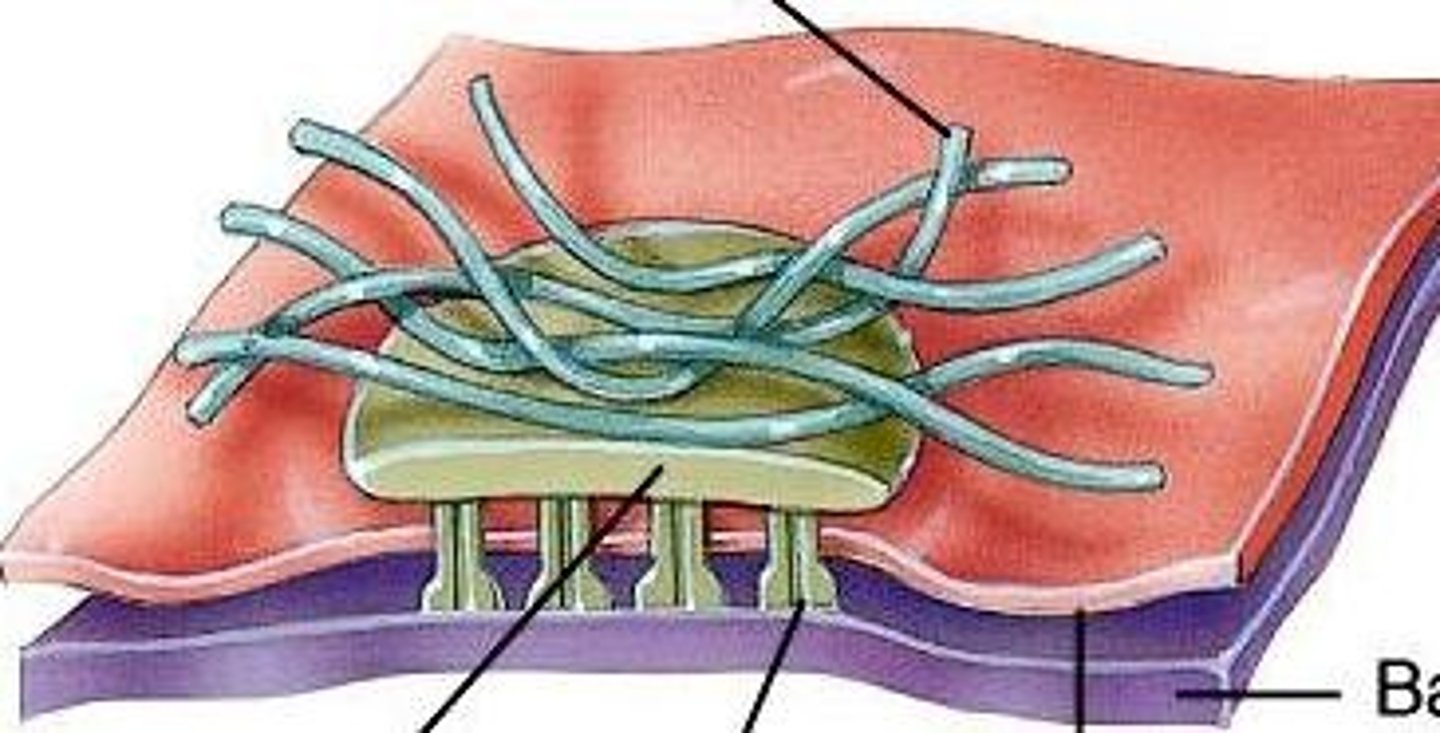
TERM
Integrin
DEFINITION
In animal cells, a transmembrane receptor protein with two subunits that interconnects the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton.
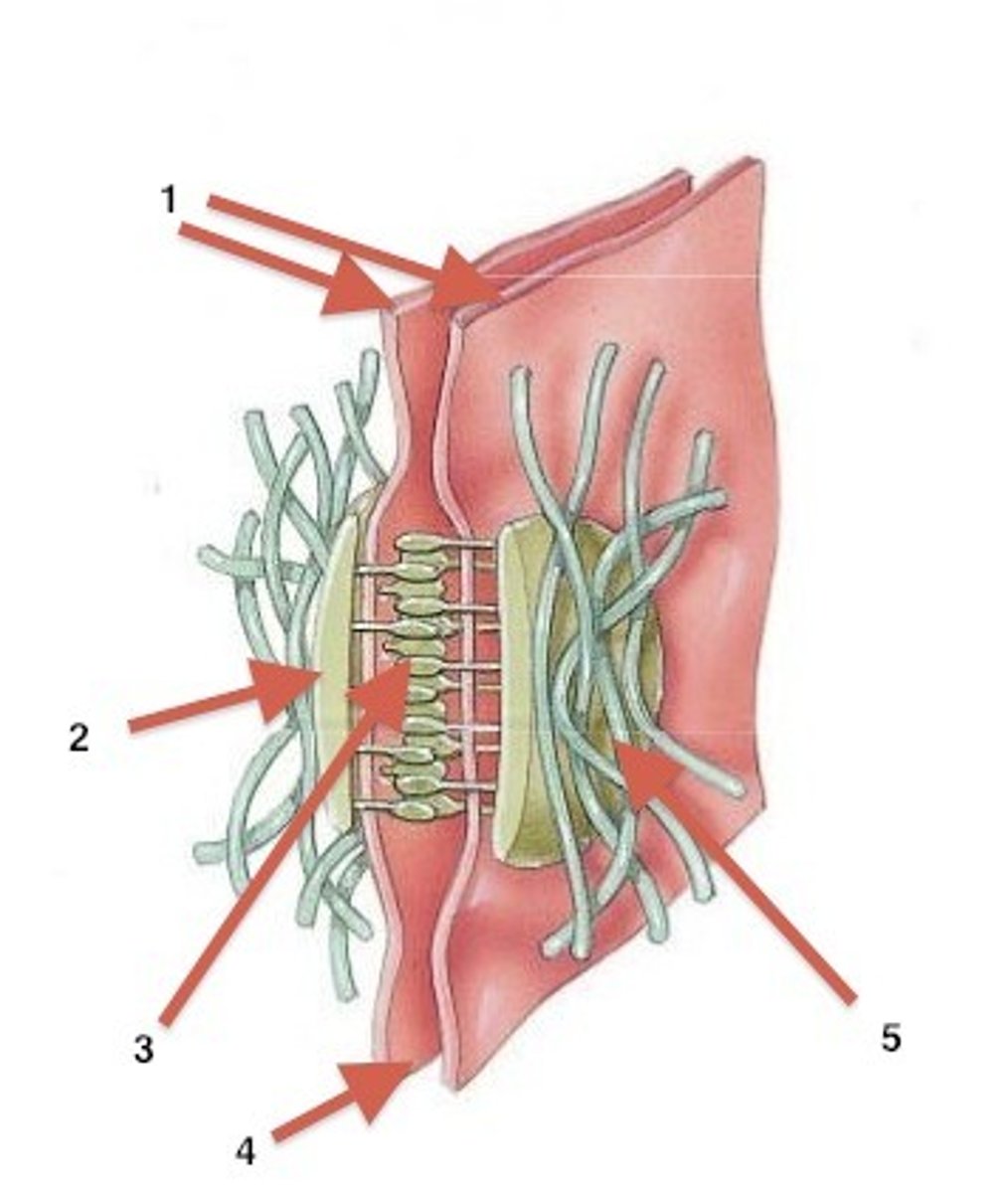
Cadherins
Calcium-dependent glycoproteins that hold similar cells together, extend the actin cytoskeleton to allow for adhesion between cells
Describe how cadherins in adherens junctions allow for the formation of tubular structures
A sheet of epithelial cells are linked by an adhesion belt (comprised of cadherins, catenin, actin and myosin)- these are E cadherins
N cadherins allow for invagination and pinching off to form a tubule
Pemphigus
autoimmune disease that causes skin blistering
Cadherins (desmoglein and desmocollin) which hold together keratinocytes are mutated
TERM
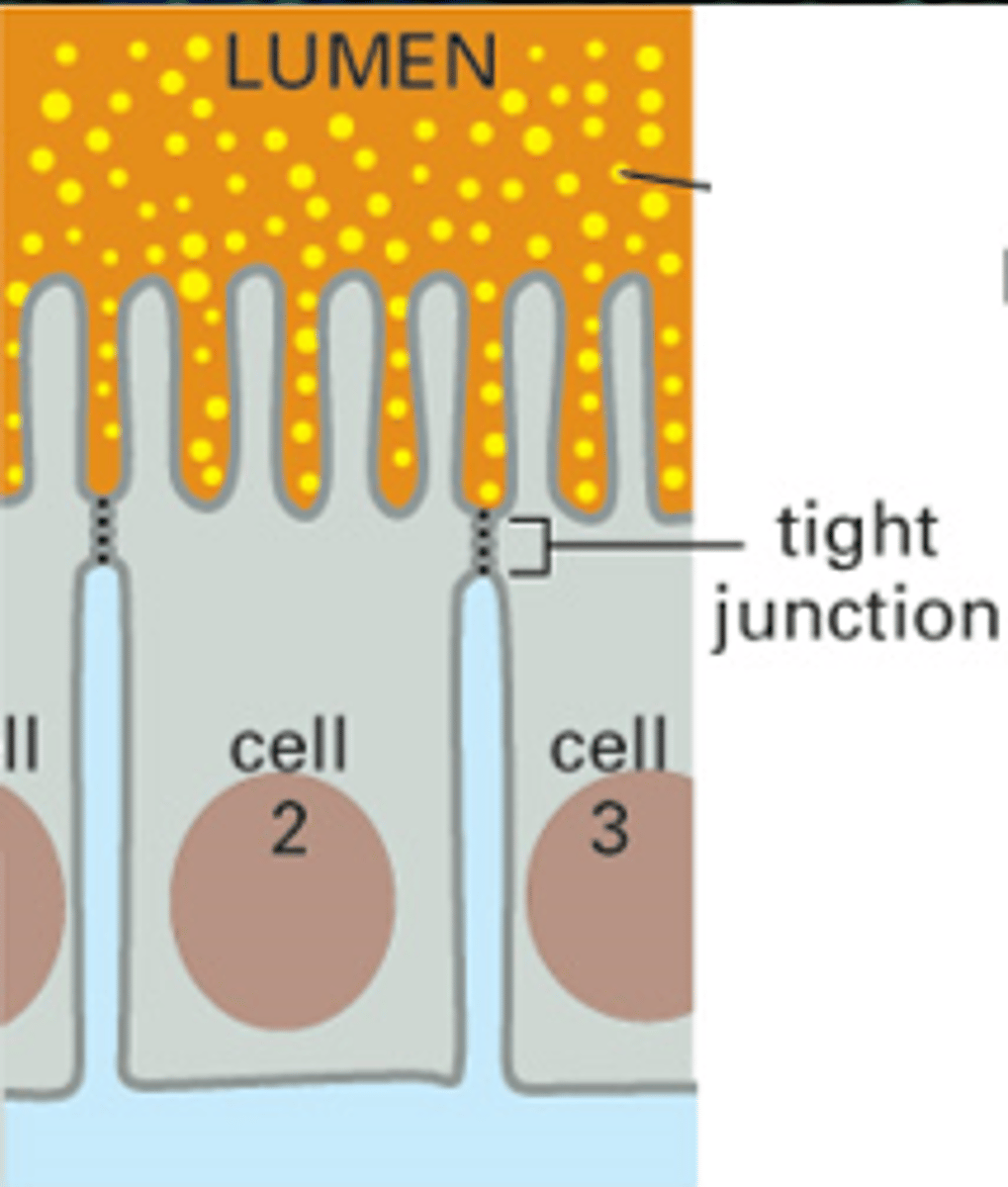
tight junctions
DEFINITION
prevent leakage of extracellular fluid across a layer of epithelial cells
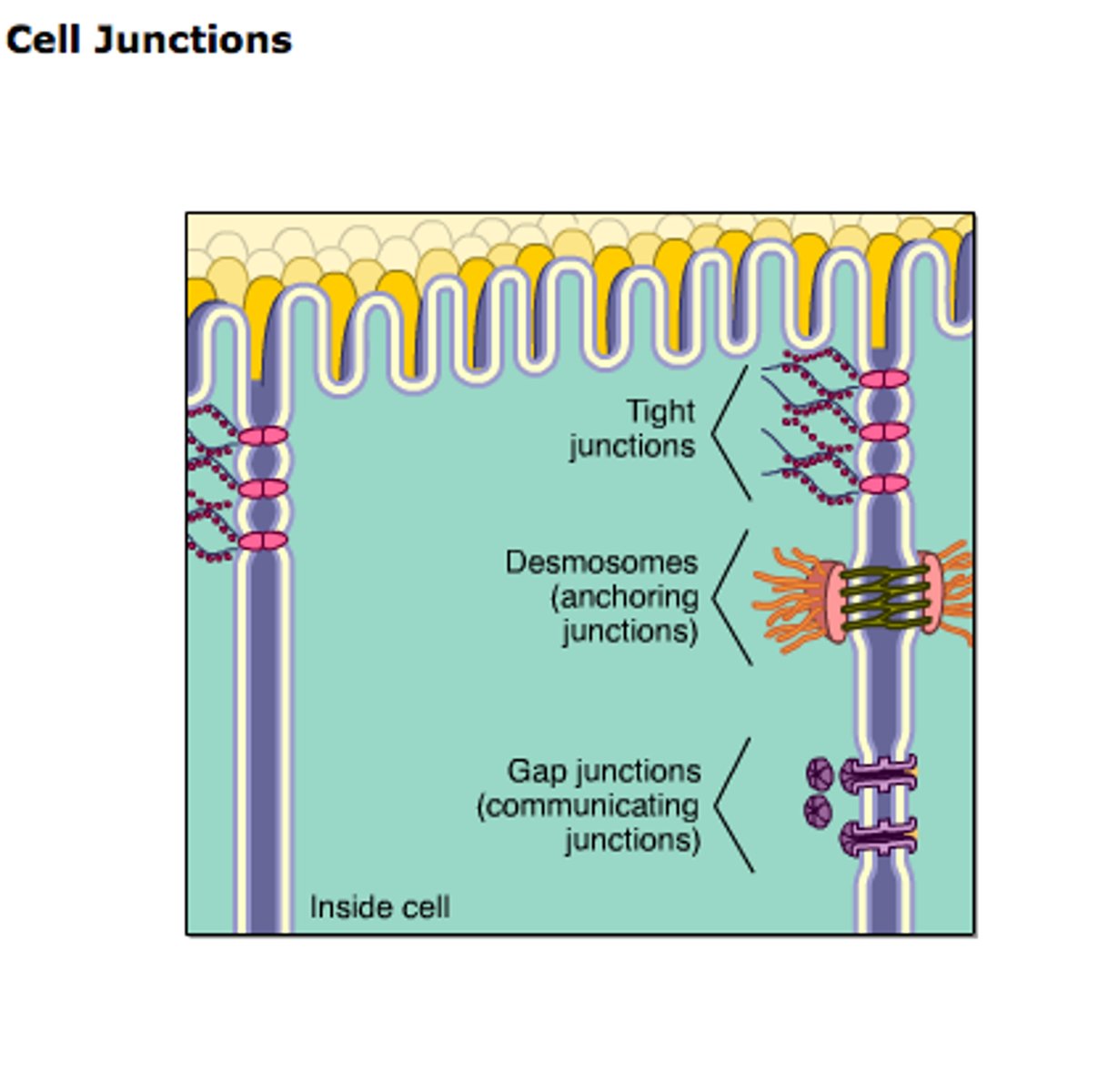
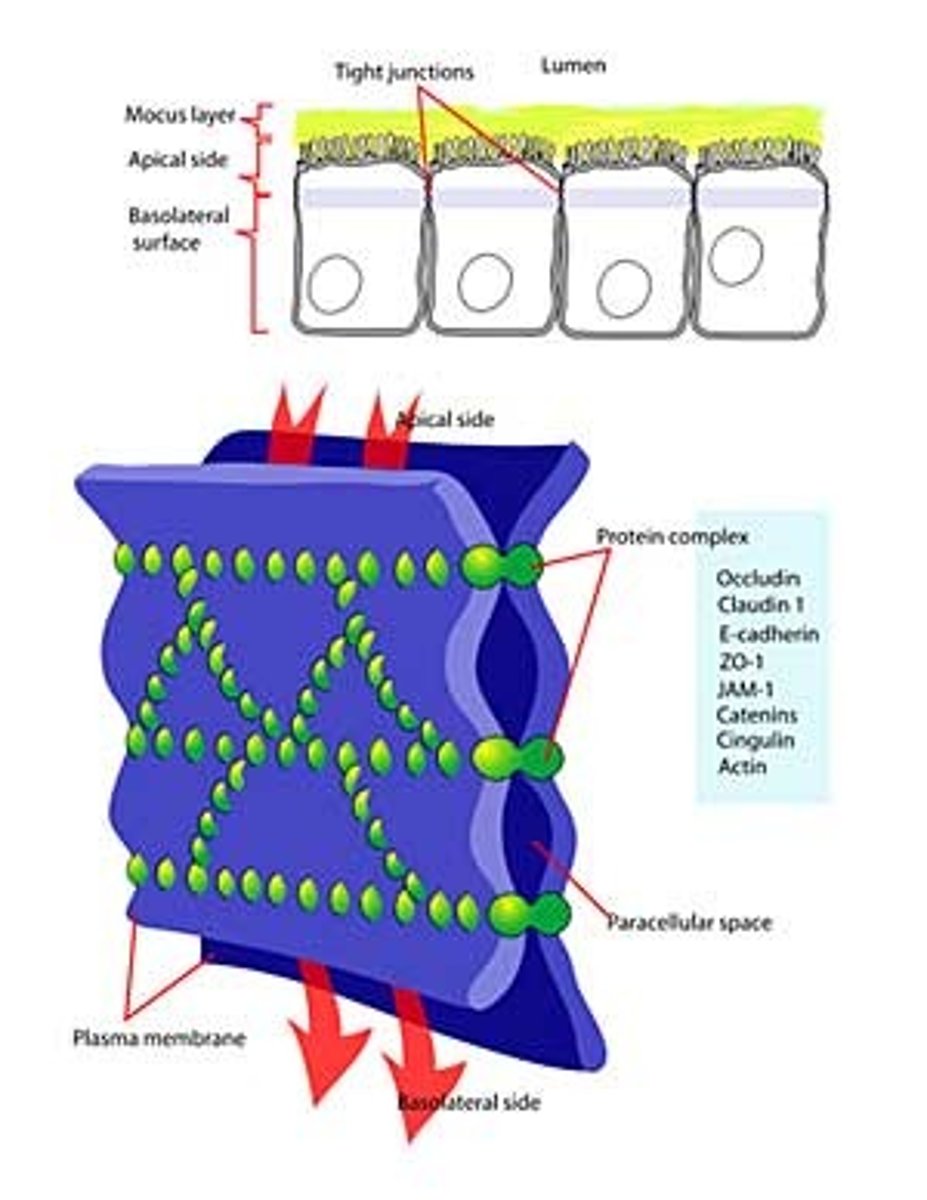
Where are tight junctions found?
At the luminal junction between the cell and the lumen (apical face)
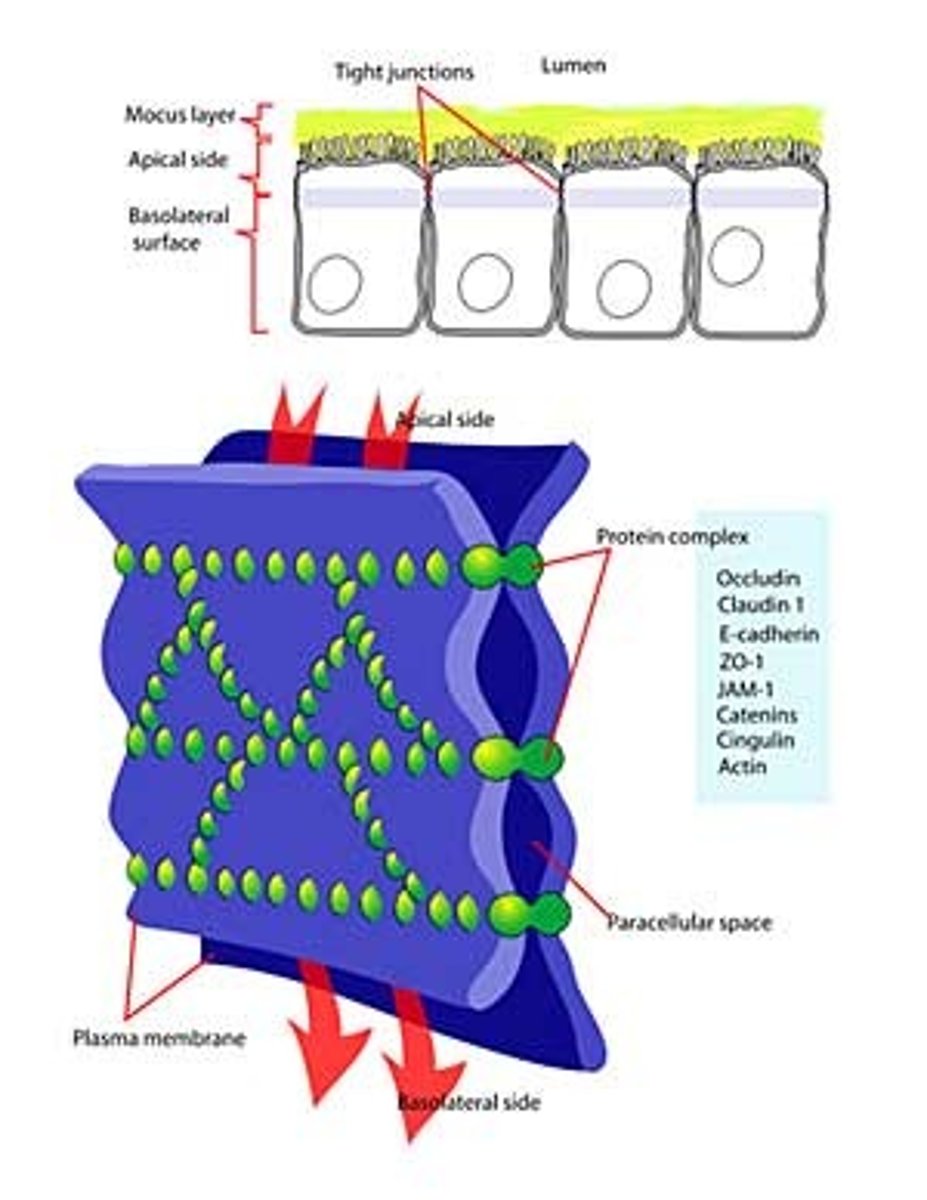
Function of tight junctions?
Prevent fluid, ion and membrane flow
Variable extent
(allow transport of some substances)
Transcellular transport
(transcytosis)
Paracellular transport
(diffusive)
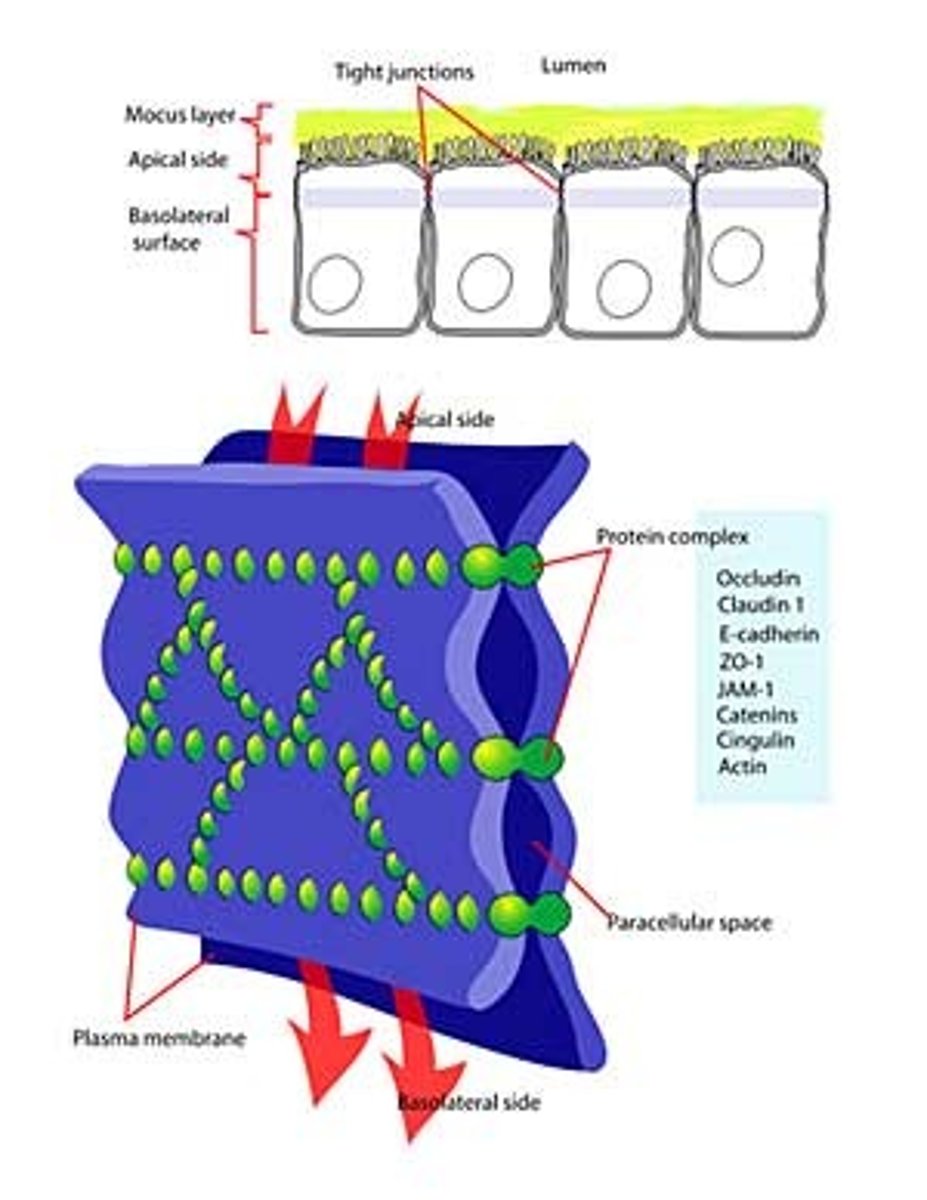
What are tight junctions made of?
Occludin and Claudin
Defining membrane compartments
Specialised membrane regions are lipid and protein segregated
e.g.,
-Apical outer membrane
-Glycolipid
-Cholesterol
-Basolateral
-Phosphatidylcholine
Relates to membrane activity
TERM
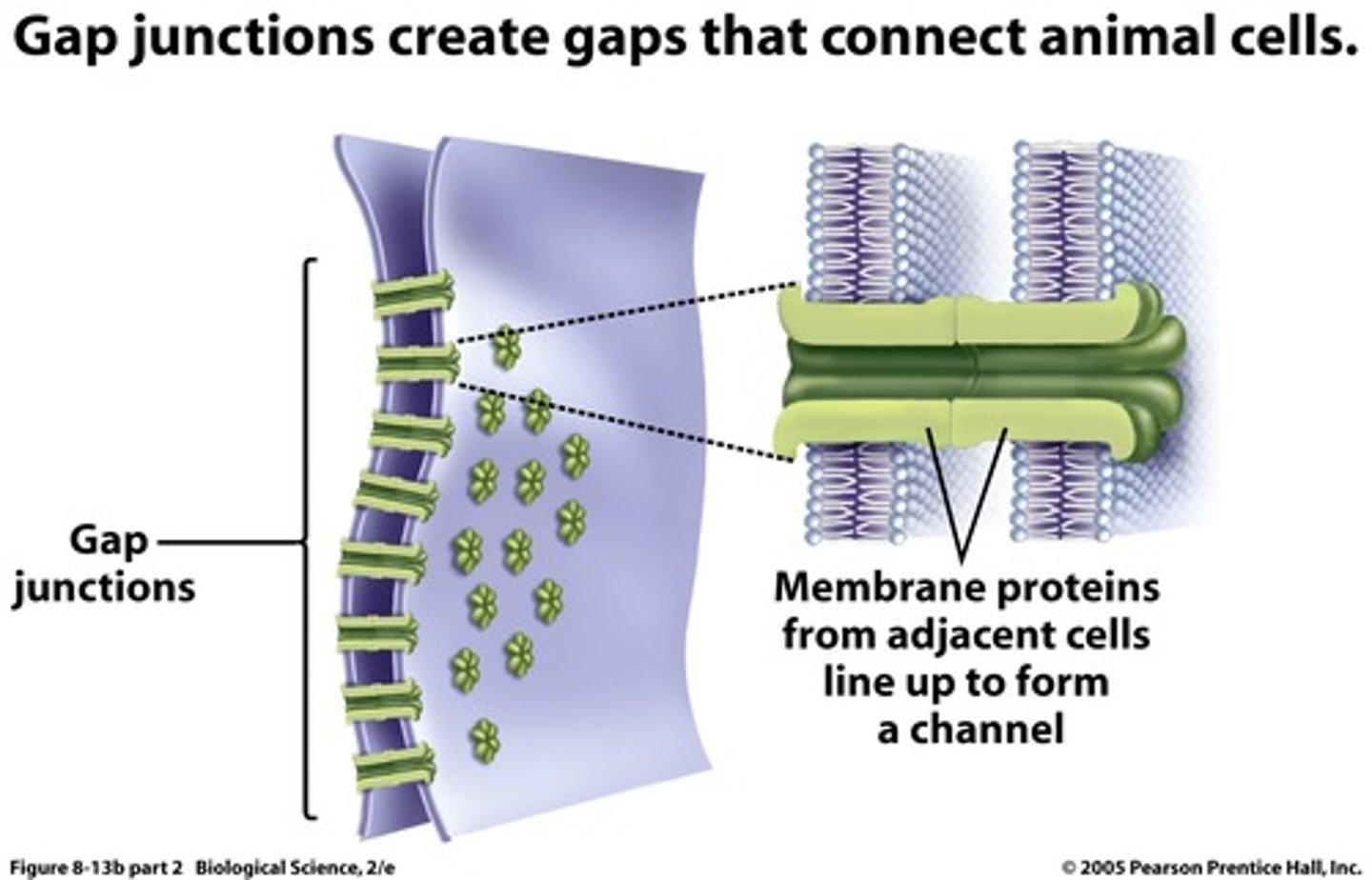
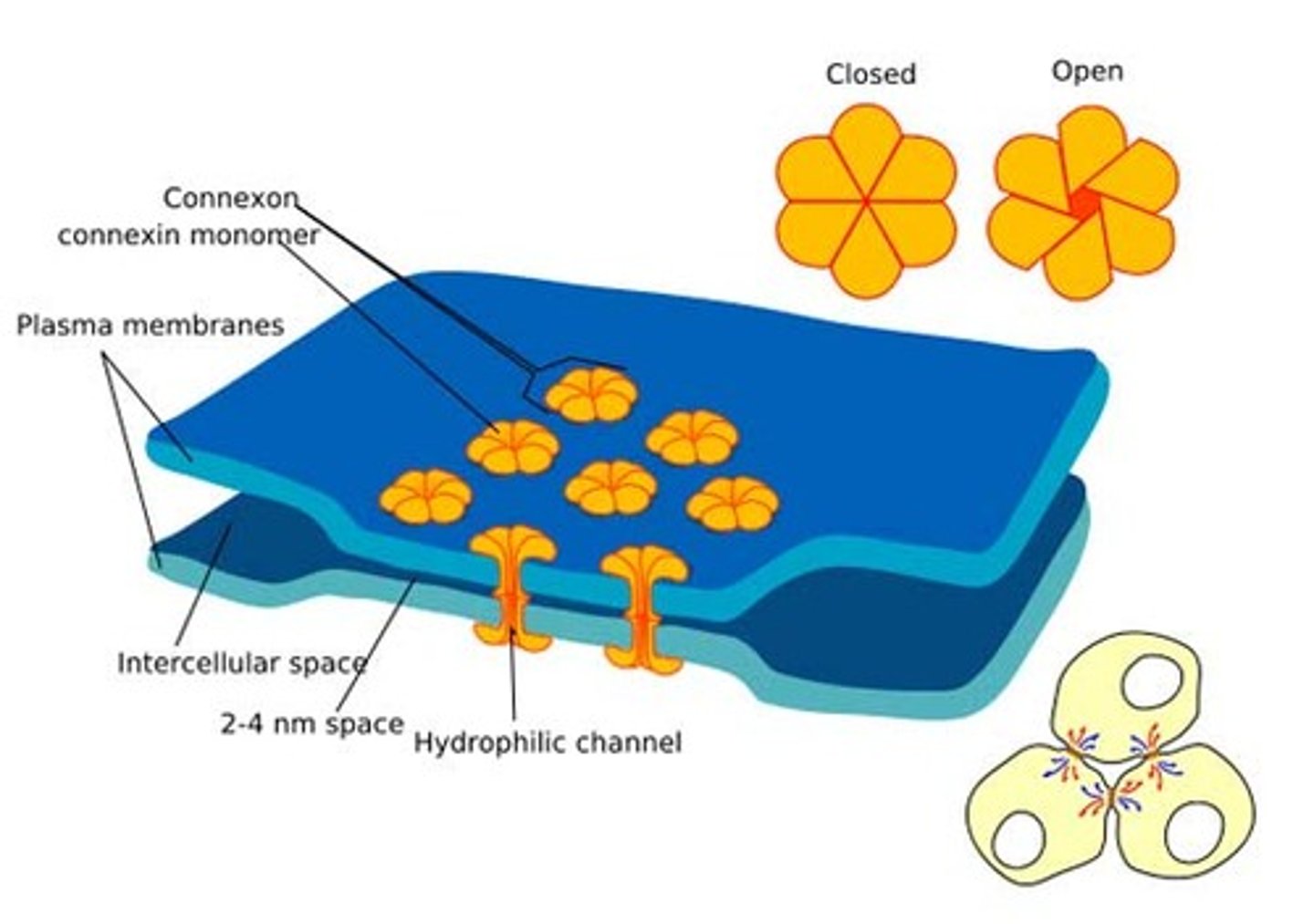
Gap junctions
DEFINITION
provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent animal cells, 100-500nm long and 2-4nm wide
Gap junction opening diameter
1.5nm
Gap of 2-4nm
Distribution of gap junctions
Connective tissue, epithelia, neurones and heart muscles
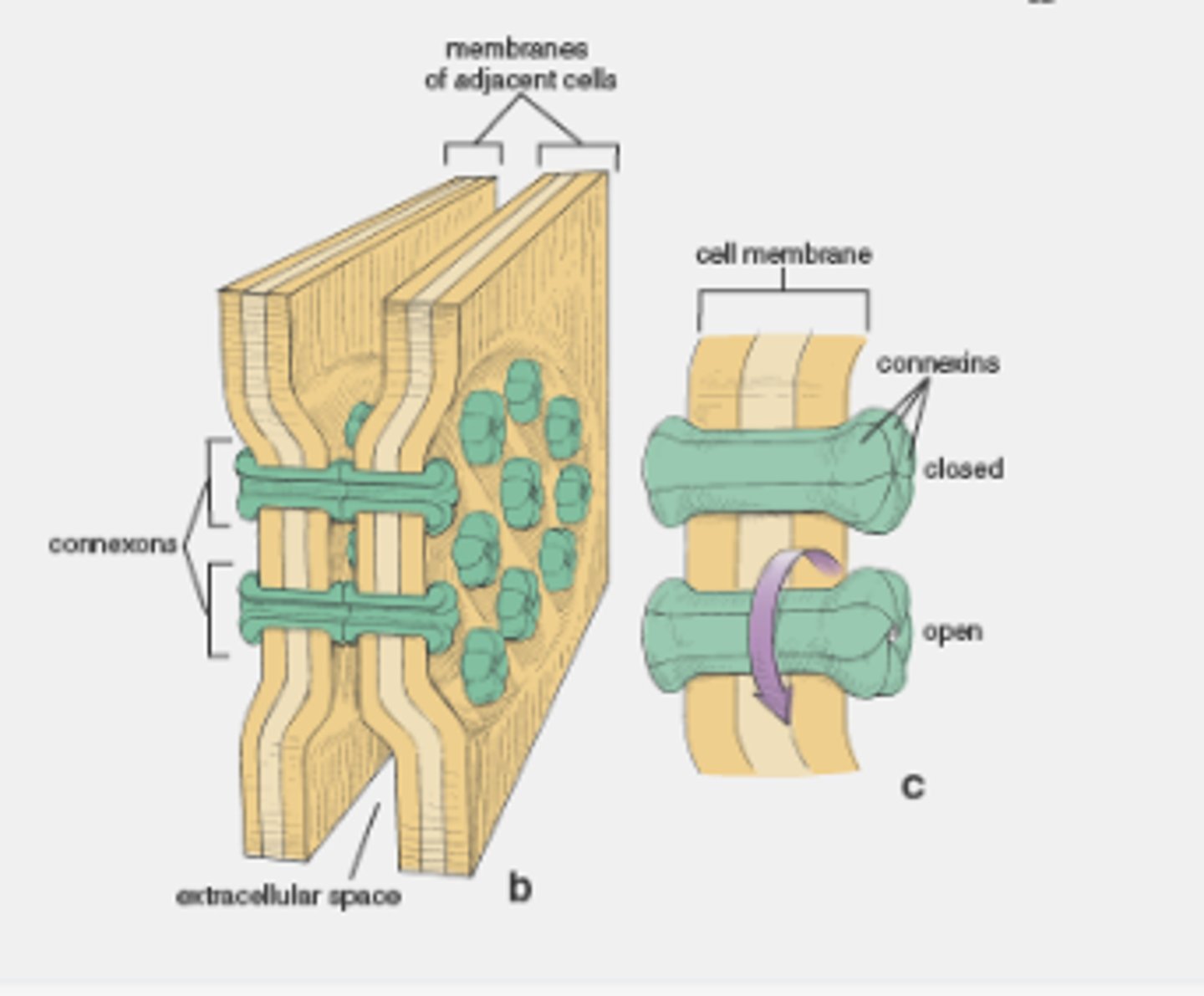
Gap junction structure
6 connexins make a connexon (each connexin has 4 TM parts)
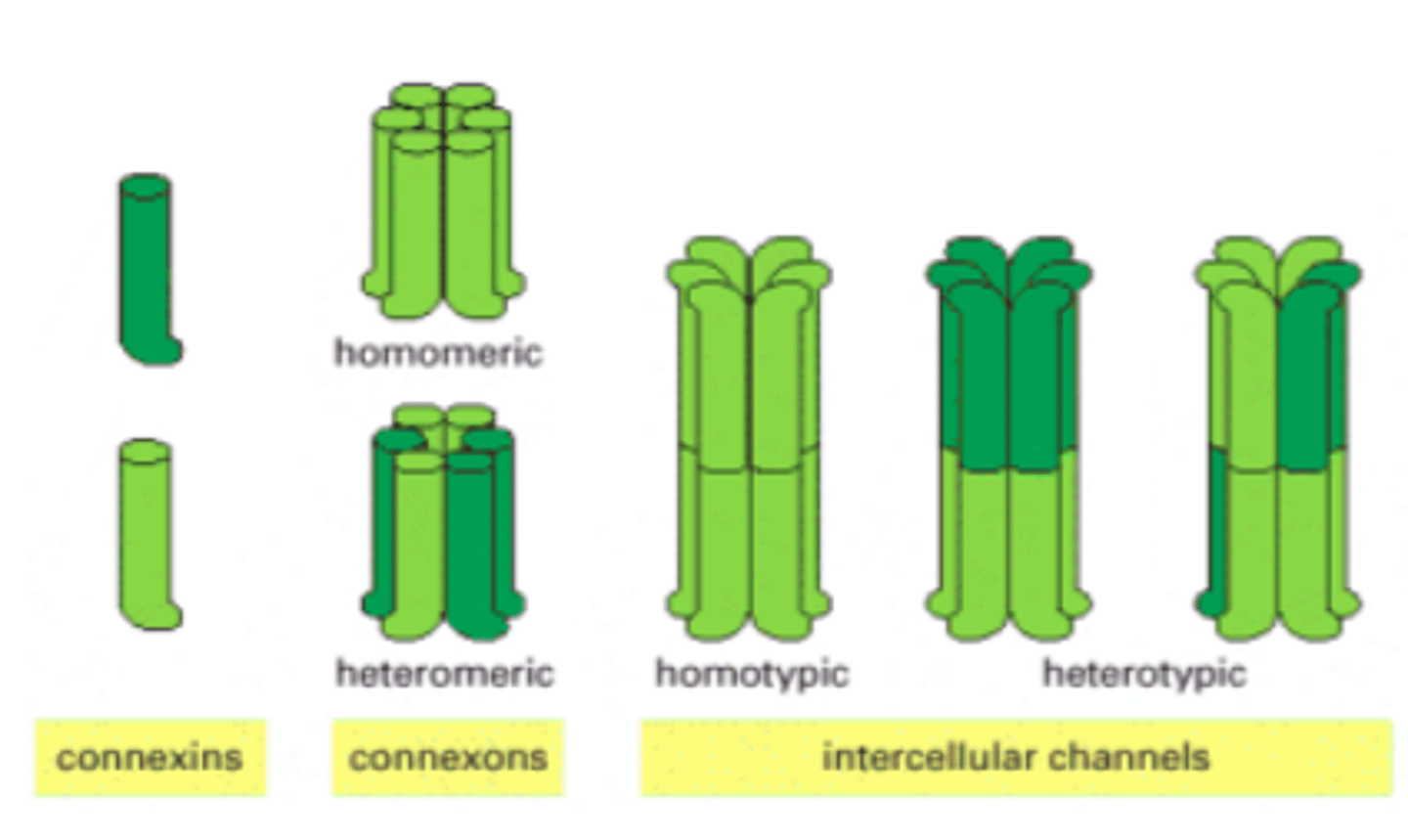
Gap junction regulation
Membrane potential, pH, Ca2+ and cell signals
Gap junctions can be closed by dopamine, preventing the leakage of Ca2+ into adjacent neurones
Limit damage caused by calcium influx
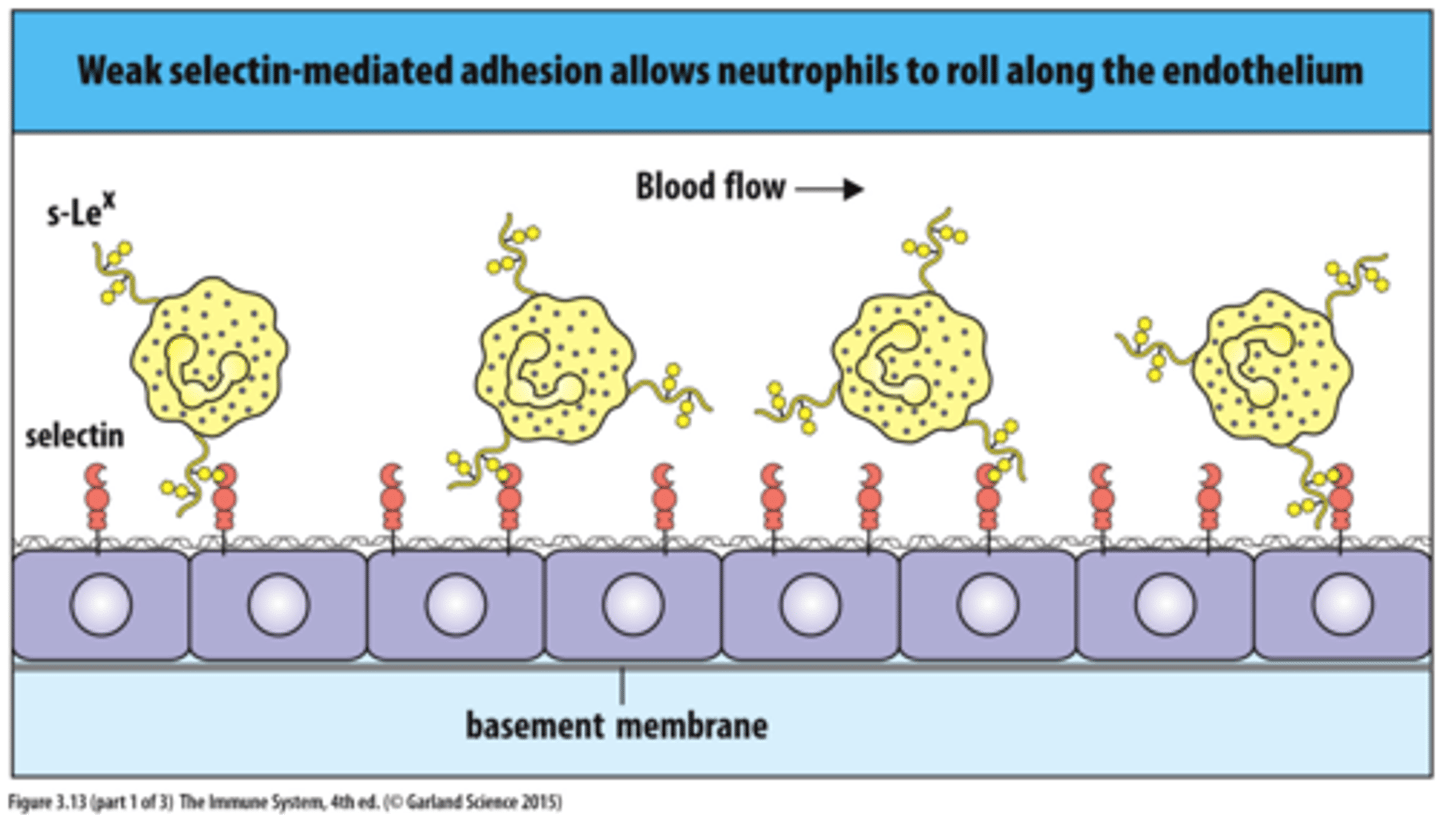
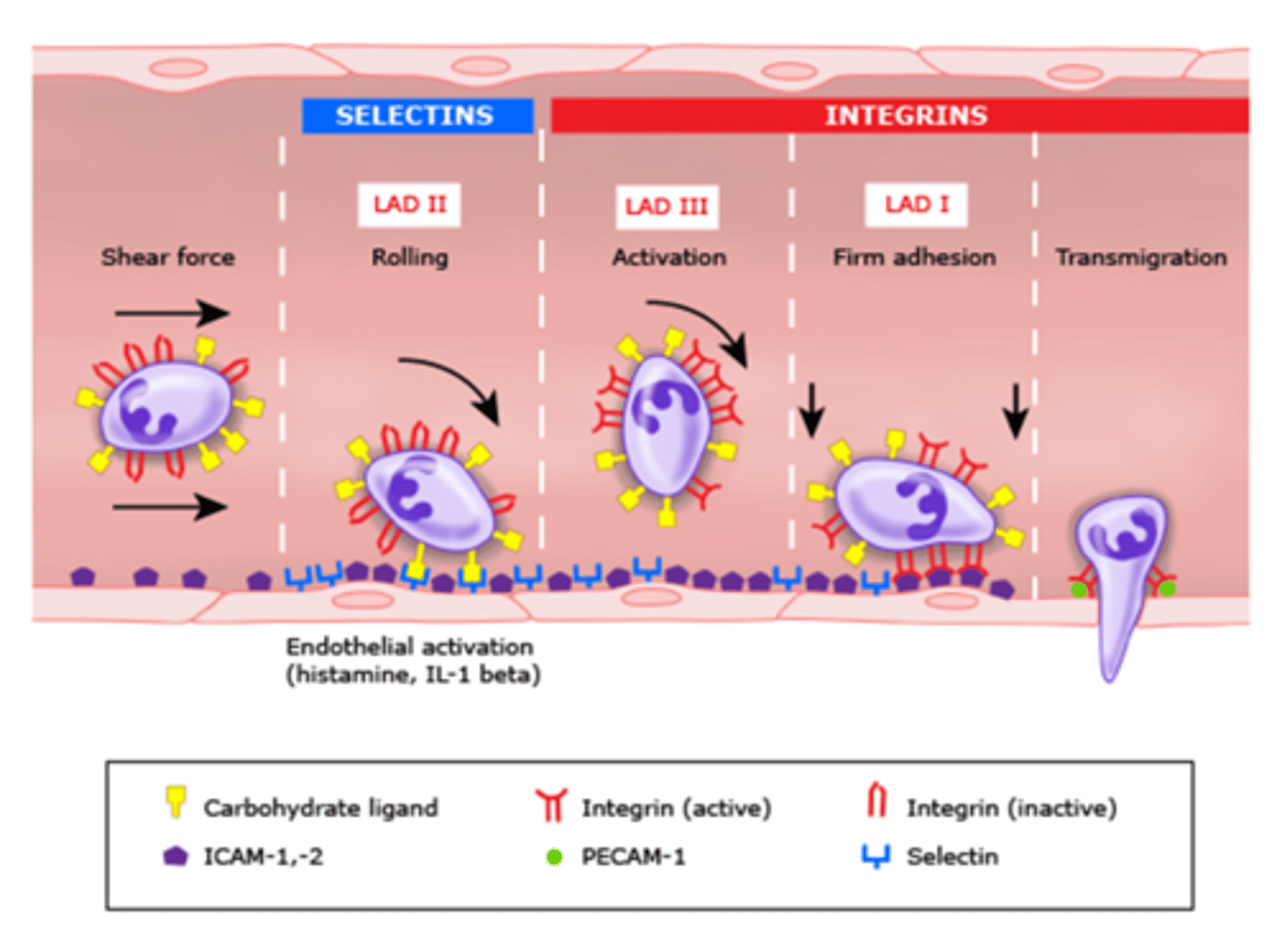
Selectins
allow cells to adhere to carbohydrates on the surfaces of other cells and are most commonly used in the immune system