Test objects and Phantoms
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is the requirements for quality assurance?
multiple evaluations of system's components
repairs
preventative maintenance
record keeping
What is the goals for quality assurance?
proper equipment operation
detect gradual changes
minimize downtime
reduce number of repeat scans
What are the quality assurance methods?
test under known, defined conditions
constant instrument settings
use phantom with measurable characteristics
image in identical environment
A phantom is an ____ standard
objective (factual, real)
What are the test objects and phantoms divided into?
those that measure the acoustic output of the instrument and those that test the operation of the instrument
What does tissue equivalent phantoms assess?
detail resolution (lateral and axial)
contrast resolution (gray scale)
penetration (depth) and dynamic range
time gain compensation
accuracy of depth and distance measurement
Tissue equivalent phantoms has ____ of the material similar to that of soft tissue
attenuation
What are tissue equivalent phantoms made of?
graphite-filled aqueous or urethane rubber
What are the echo producers in tissue equivalent phantoms?
graphite particles
What measures detail resolution and distance accuracy in tissue equivalent phantoms?
thin nylon lines
What do some tissue equivalent phantoms contain for various scattering strengths?
cones or cylinders
What do test objects contain?
nylon lines and scattering layers
What do test objects evaluate?
detail resolution and beam profiles
Do test objects stimulate tissue characteristics?What do they provide?
no; instrument performance
What do the beam-profile slice thickness test objects contain?
thin, scattering layer in an echo-free material
What do the beam-profile slice thickness test objects used to show?
beam width in scan plane or perpendicular to it
3rd dimension
What does multi-purpose tissue-cyst phantom test?
dead zone, detail resolution (lateral and axial), depth accuracy, measurement accuracy, contrast resolution, penetration
What is the AIUM 100mm test object made of?
water-filled with pins
Are IUM 100mm test objects used still?
no
What is an ATS multipurpose phantom used for?
dead zone, vertical and horizontal measurement accuracy, sensitivity/penetration, focal zone, axial and lateral resolution, image uniformity, gray scale and displayed dynamic range
What is the CIRS model 040 phantom used for?
image uniformity, axial and lateral resolution, depth calibration, dead zone
What is the CIRS model 040 phantom most importantly used for?
registration within two different backgrounds of attenuation coefficients (attenuation per cm of wave travel) 0.5 and 0.7 dB/cm/MHz
What is the needle biopsy breast phantom used for?
practice aspirating and biopsying (multiple times)
What is CIRS fetal phantom used for?
assessment of composite measurement techniques and biometric analysis programs
3D reconstructions and surface renderings
What is the CIRS fetal phantom anatomy based on?
published biometric data at normal fetal growth rates of 21 weeks
What is the multipurpose ultrasound phantom Kyoto Kagaku N-365 designed for?
assessment and calibration
What is the multipurpose ultrasound phantom Kyoto Kagaku N-365 made of?
urethane elastomer, acrylic, nylon
What is the speed of sound in a multipurpose ultrasound phantom Kyoto Kagaku N-365?
1440 m/s (25 degrees C)
What is the attenuation rate in a multipurpose ultrasound phantom Kyoto Kagaku N-365?
0.57 dB/cm/MHz
What is a hydrophone?
device used to measure the acoustic output of ultrasound instruments
What is another name for a hydrophone?
microprobe
Who is a hydrophone used by?
engineers and physicists
What is the first form of a hydrophone?
small transducer mounted on the end of a hollow needle (1mm or less)
What is the second form of a hydrophone?
large piezoelectric membrane with small metallic electrodes centered on both sides
What is the membrane of a hydrophone made out of and why?
PVDF (polyvilnylidene fluoride) because of its wide bandwidth
hydrophone
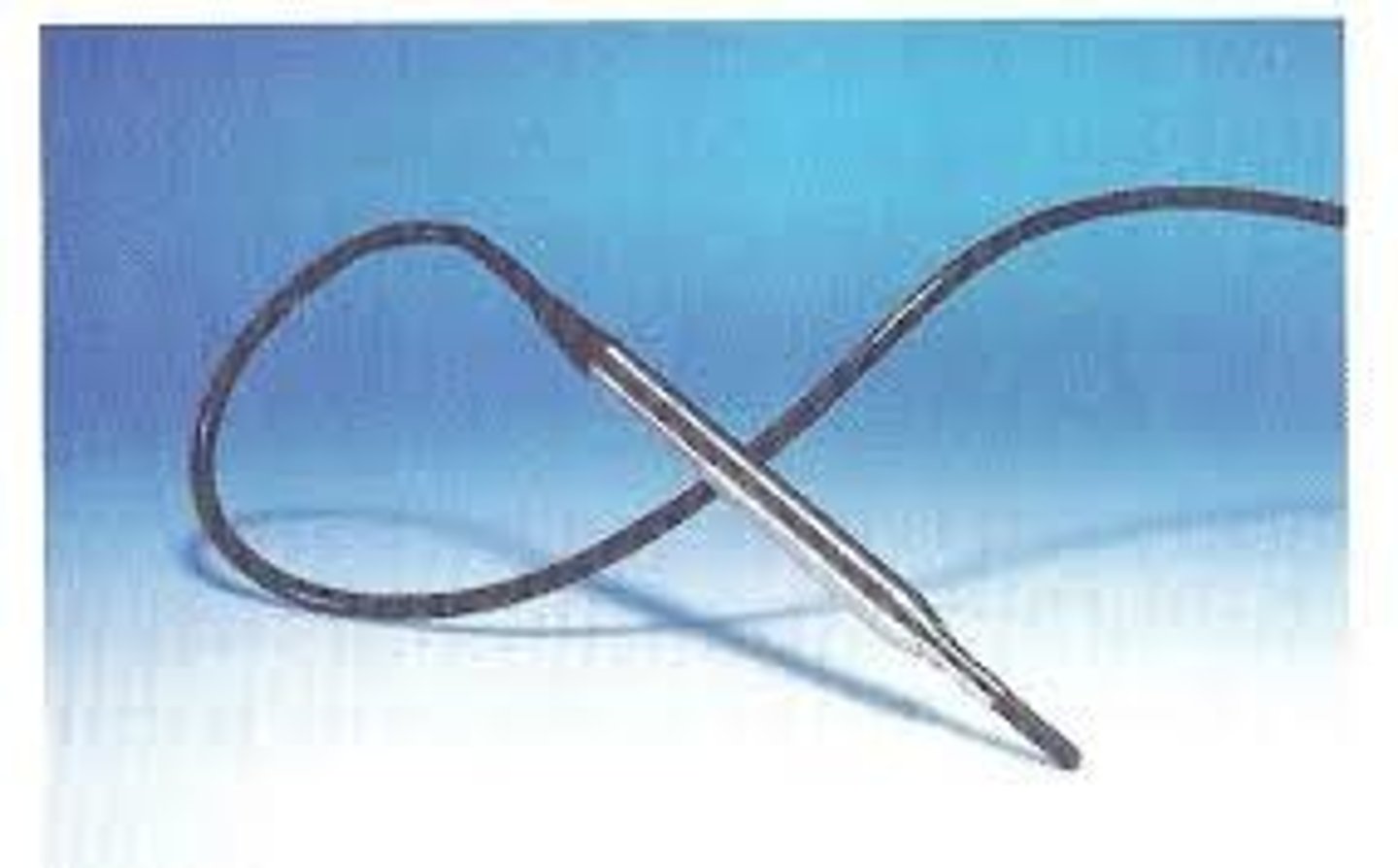

membrane hydrophone
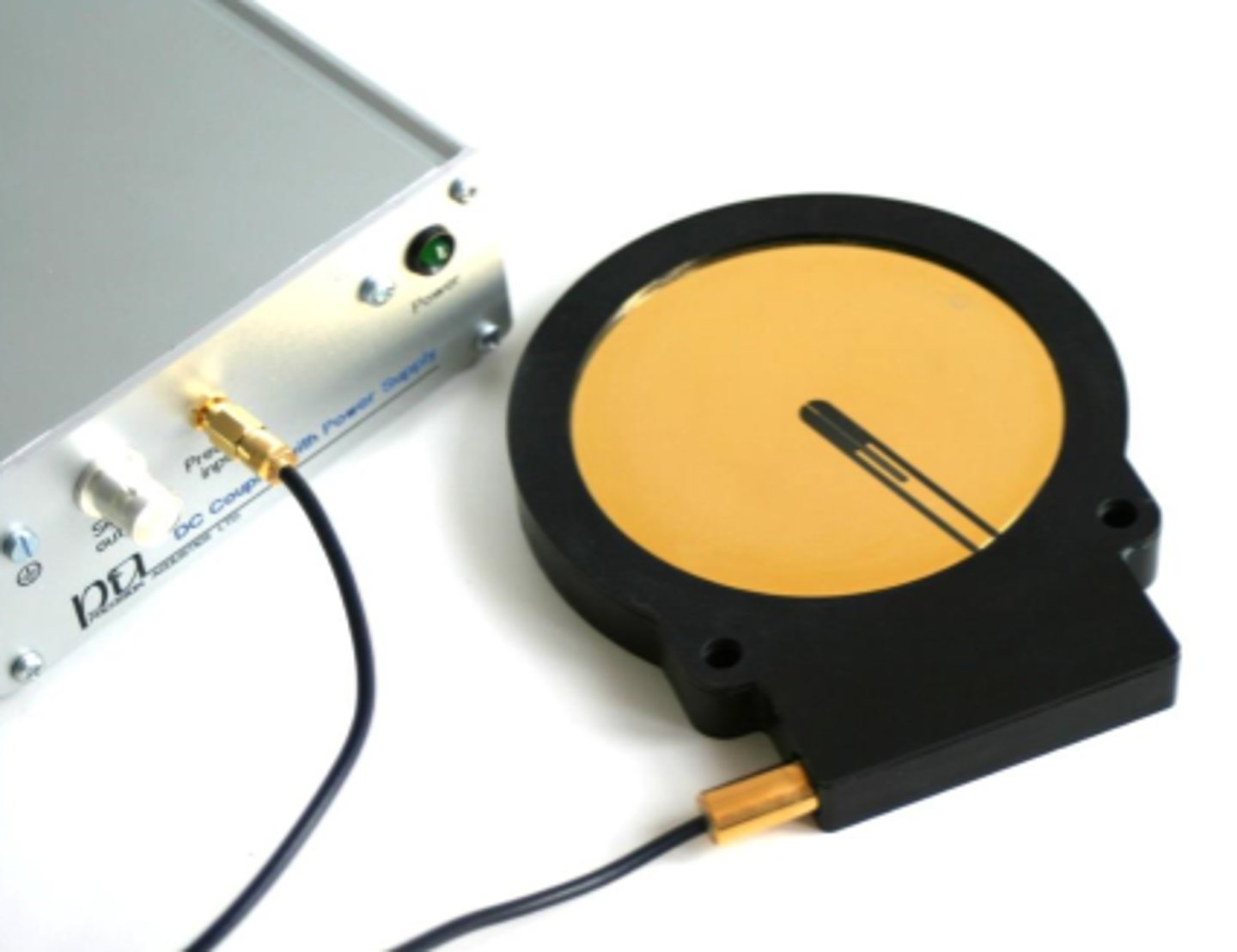

Hydrophones receive sound reasonably well from:
all directions without altering the sound by their presence
A hydrophone measures what?
the pressure in a sound beam
What does a hydrophone produce?
a voltage that can be displayed on an oscilloscope and produces a picture
What can be calculated from the oscilloscope picture?
period, PRP, pulse duration and several other acoustic pulse parameters
Acoustic-optics deal with interaction between:
light and sound waves
Who is acoustic-optics used by?
physicists
What do acoustic-optics study?
characteristics and shape of sound beam
What does acoustic-optics contain?
shadowing system called Schlieren
What does acoustic-optics produce?
2D cross section of beam produced
Are acoustic-optics commercially available?
no, difficult to use
Who is a calorimeter used by?
physicists
What is a calorimeter?
a transducer that turns acoustic energy into heat
What does a calorimeter measure?
temperature increases in absorbing liquid along with time required to obtain the heat (energy to heat)
In a calorimeter, if intensity is known, what can be calculated?
beam area
Is a calorimeter commercially available?
no
calorimeter
What does a thermocouple do?
UIs absorbed, turned into heat
ULS intensity can be measured at specific points
What is a thermocouple?
small device embedded in absorbing material
What does a thermocouple measure?
temperature change
A thermocouple is __ sensitive than a hydrophone.
less
What are crystals?
cholesteric liquid crystals or starch iodine blue
What will crystals do?
turn different colors when hit by different intensities
In crystals what determines the shape and strength of the beam?
shape and color of the crystal
What is the lowest sonographic imaging output?
gray-scale
What is the highest sonographic imaging output?
pulse-spectral doppler
What is the sonographic imaging output in the middle?
M mode and color doppler