Chapter 19 - Lab
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Carries sensory information to the brain, motor commands from the brain, processes information, and executes reflexes.
What is the function of the spinal cord?
Spinal nerves
Carry information directly to and from the spinal cord; there are 31 pairs.

Neurons
Responds to a stimulus by generating an electrical impulse that will signal another cell and effectors
Sensory neurons
Send signals from sensory receptors to the central nervous system.
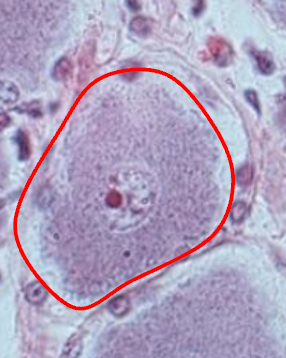
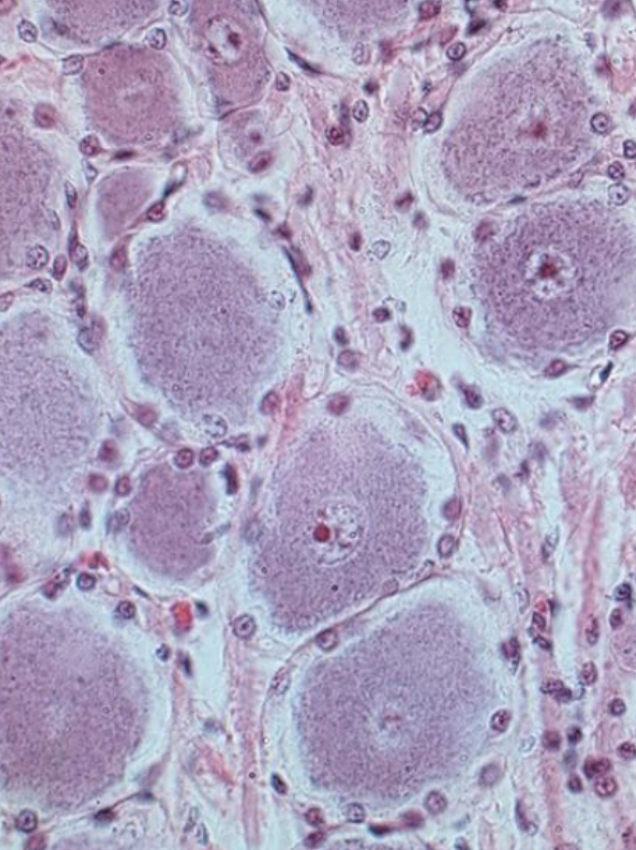
Interneurons
Send signals from sensory receptors to the central nervous system.
Motor neurons
Send signals from the central nervous system to effectors.
Visceral motor neurons
Send signals to glands, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle cells.
Somatic motor neurons
Send signals to skeletal muscle cells.
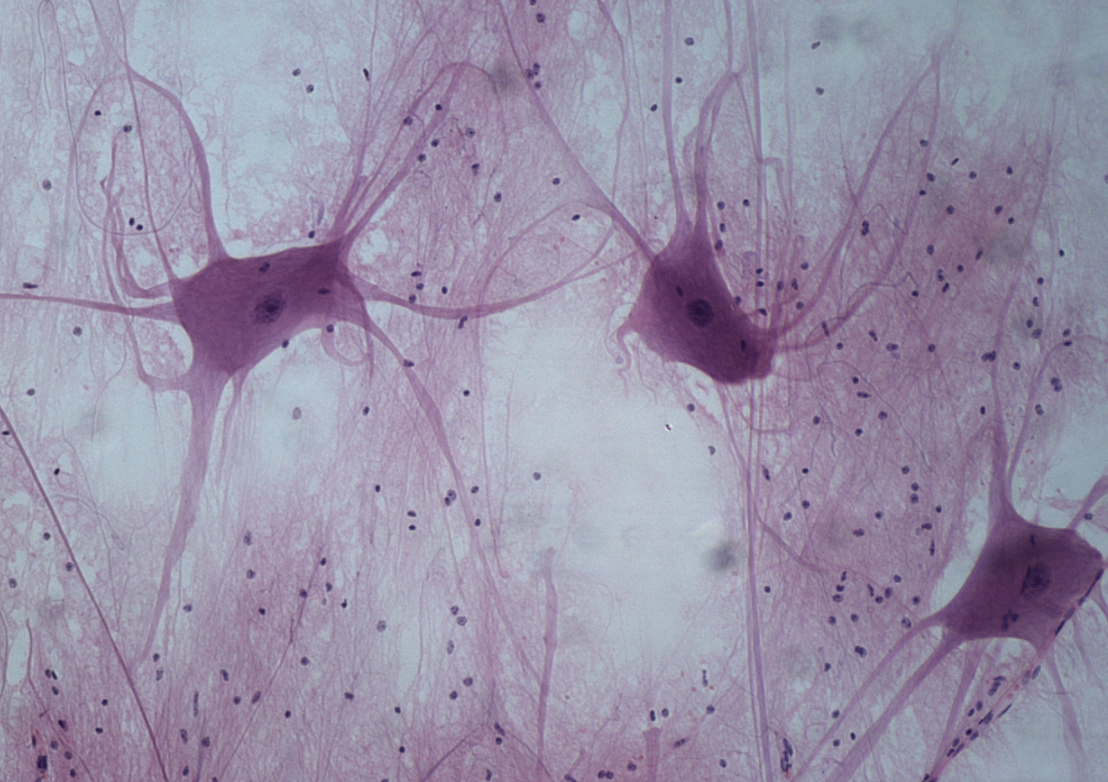
Neuron structure
Composed of dendrites, soma (cell body), and an axon.
Dendrites
Receive stimuli from the environment.
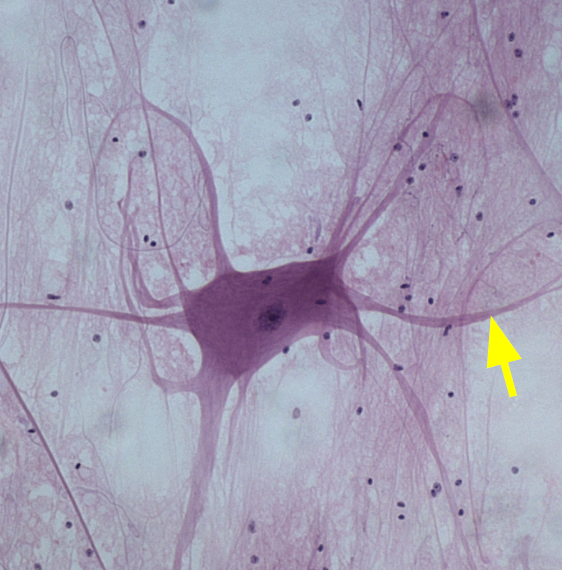
Soma
The cell body of the neuron.
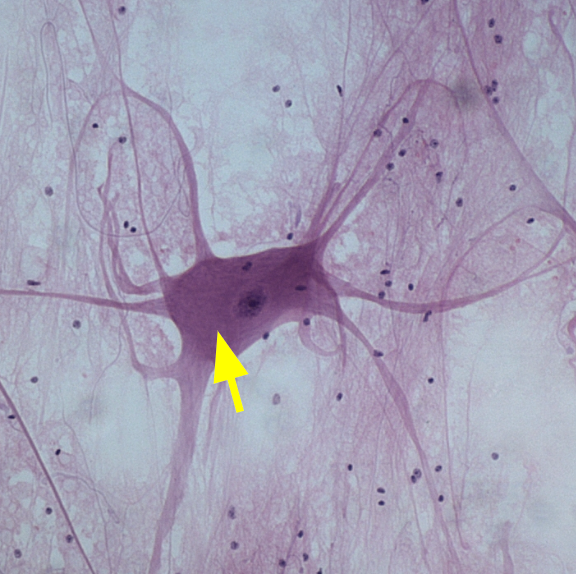
Axon
Sends an electrical impulse to other cells.
Multipolar neurons
Have numerous dendrites and one axon extending from the soma.
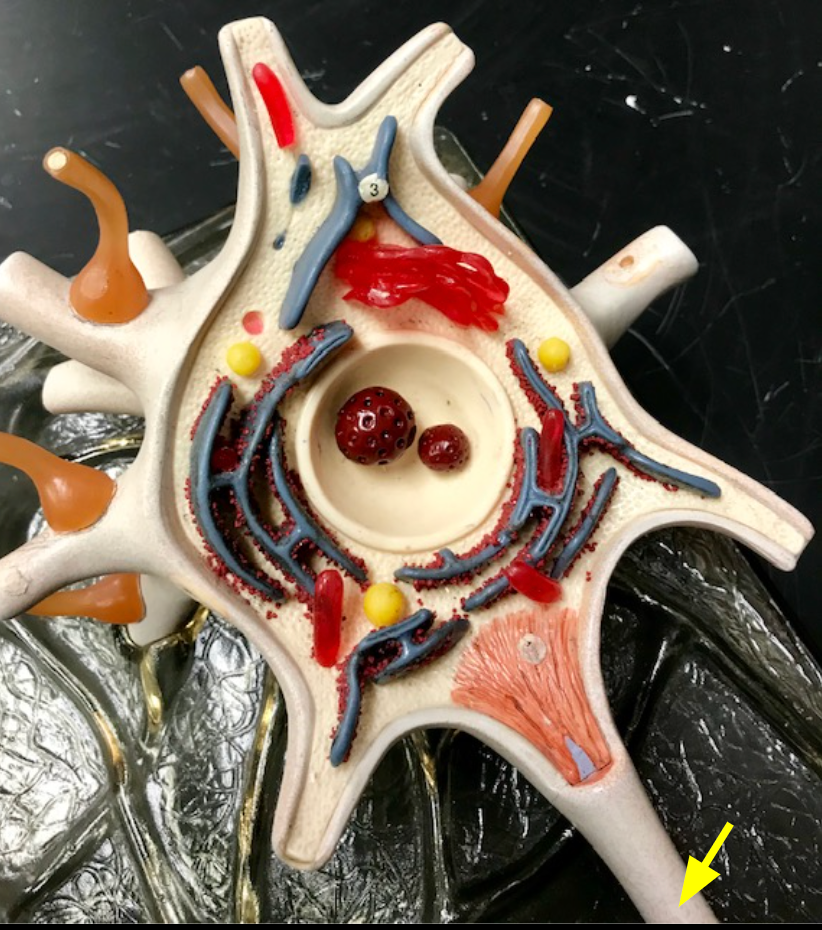
Axolemma
The plasma membrane surrounding the axon.
Axon hillock
The beginning of the axon where action potentials are initiated.
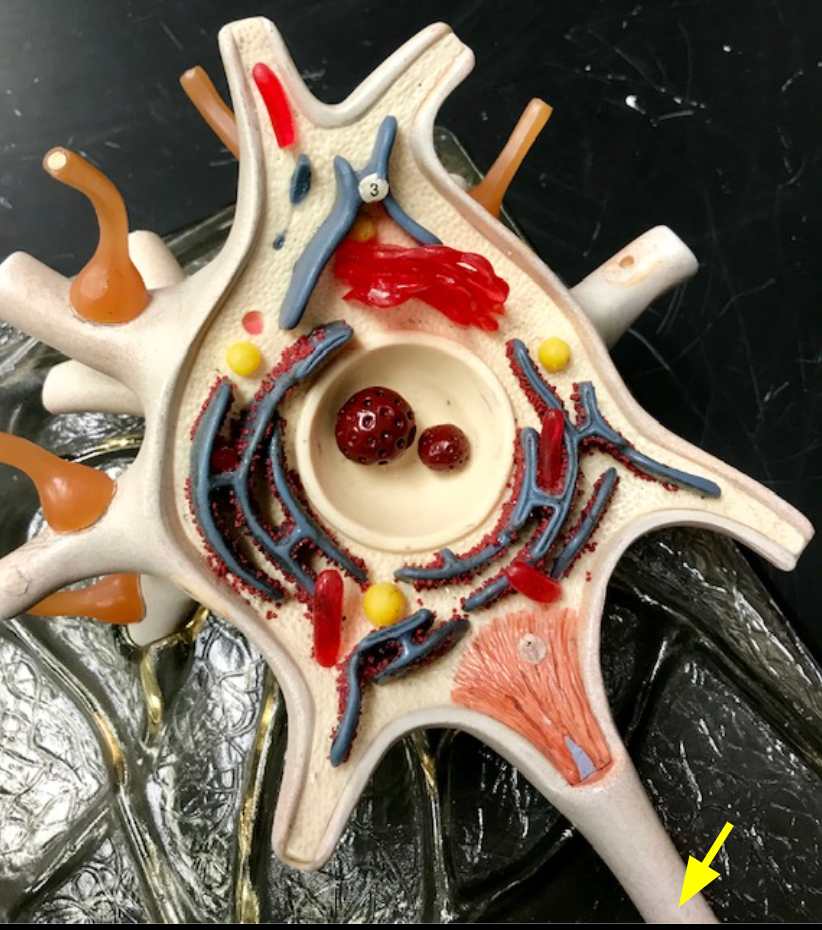
Neurolemmocytes
Cells that wrap the axolemma and form the myelin sheath.

Myelin sheath
Wraps around the axon, protecting, insulating, and increasing the speed of action potentials.

Neurofibril nodes
Gaps between neurolemmocytes, also known as nodes of Ranvier.

Endoneurium
Layer of connective tissue that wraps the axon and myelin sheath.
Telodendria
Branched extensions of axons that synapse with other neurons.
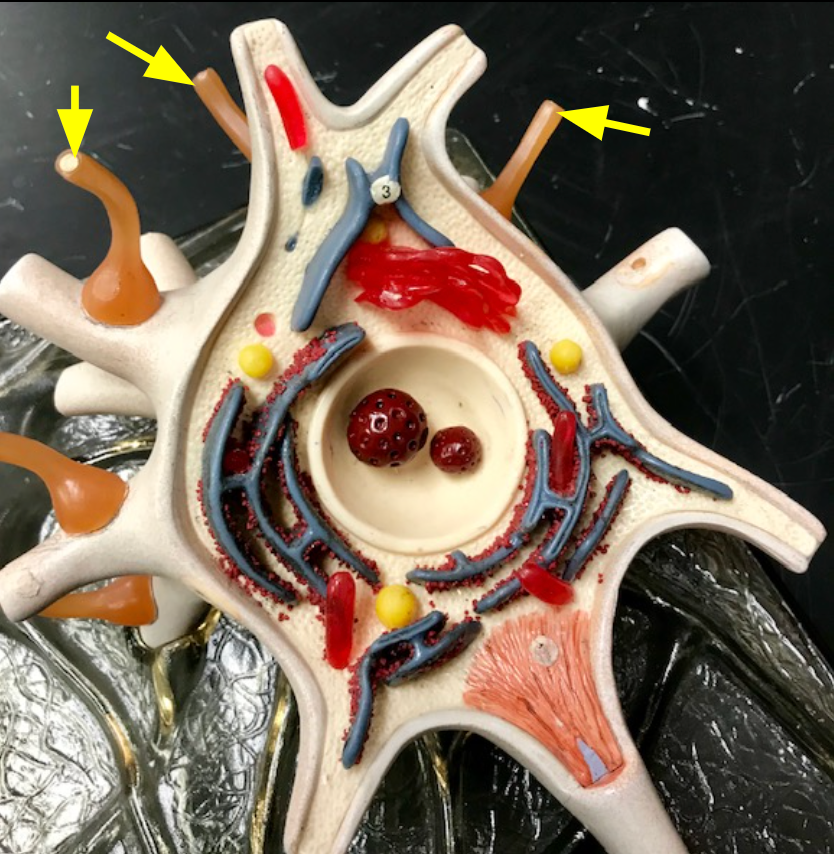
Axon terminals
Ends of telodendria, releasing neurotransmitters at synapses.
Synaptic knobs
Rounded structures at the ends of axon terminals that store and release neurotransmitters.
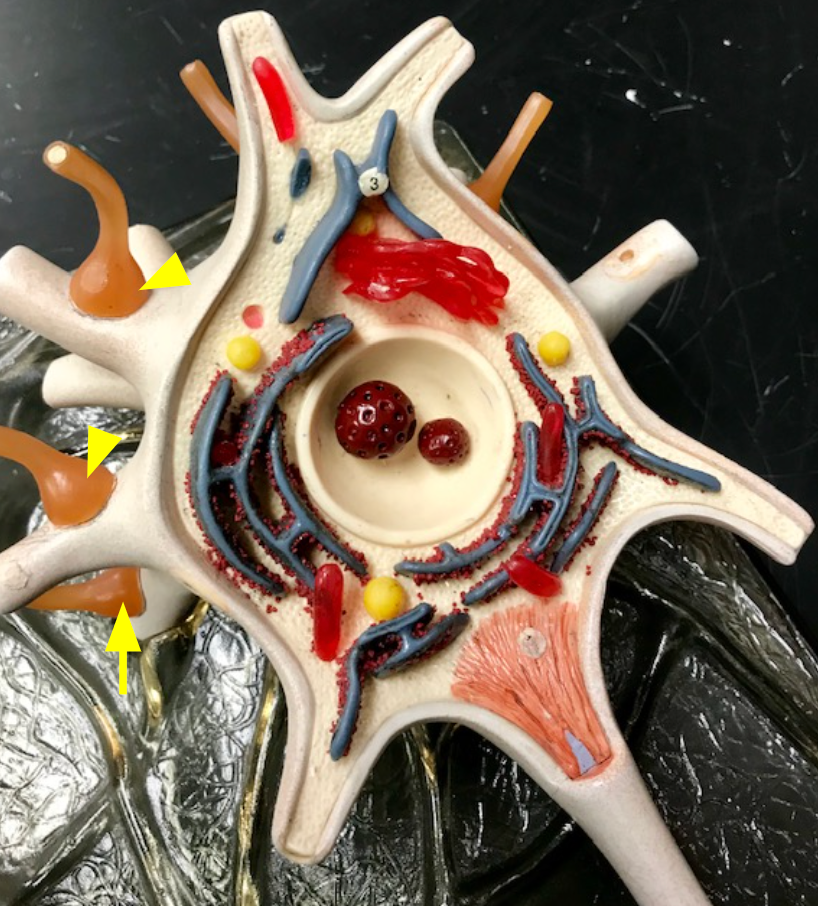
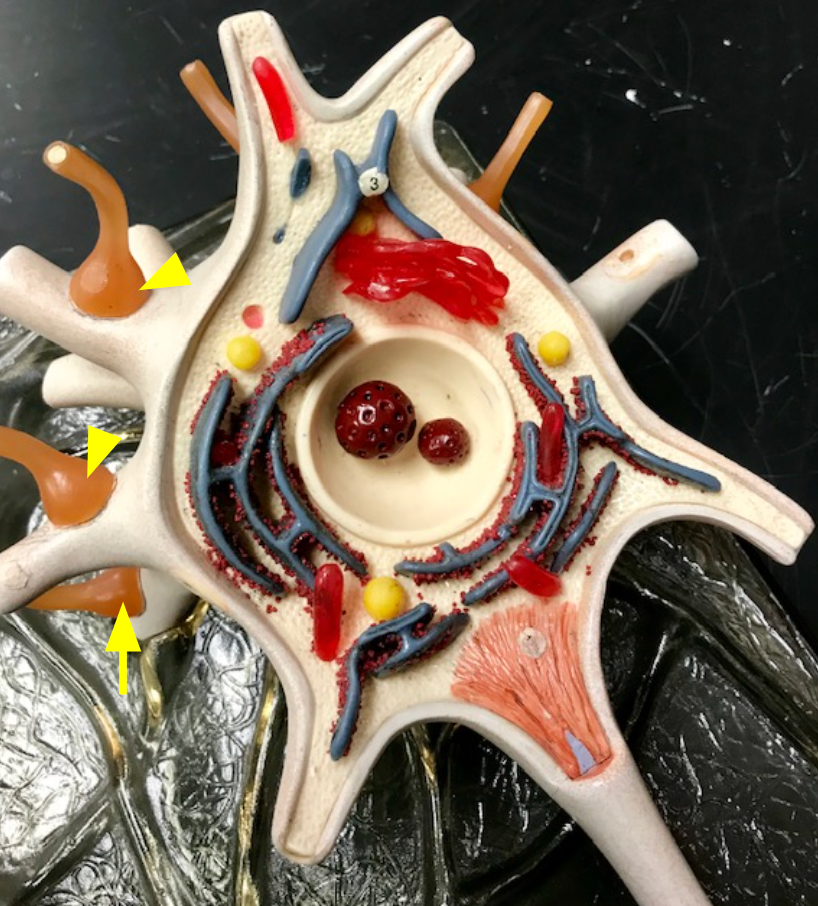
Schwann cells
cells that wrap their plasma membrane around the axon

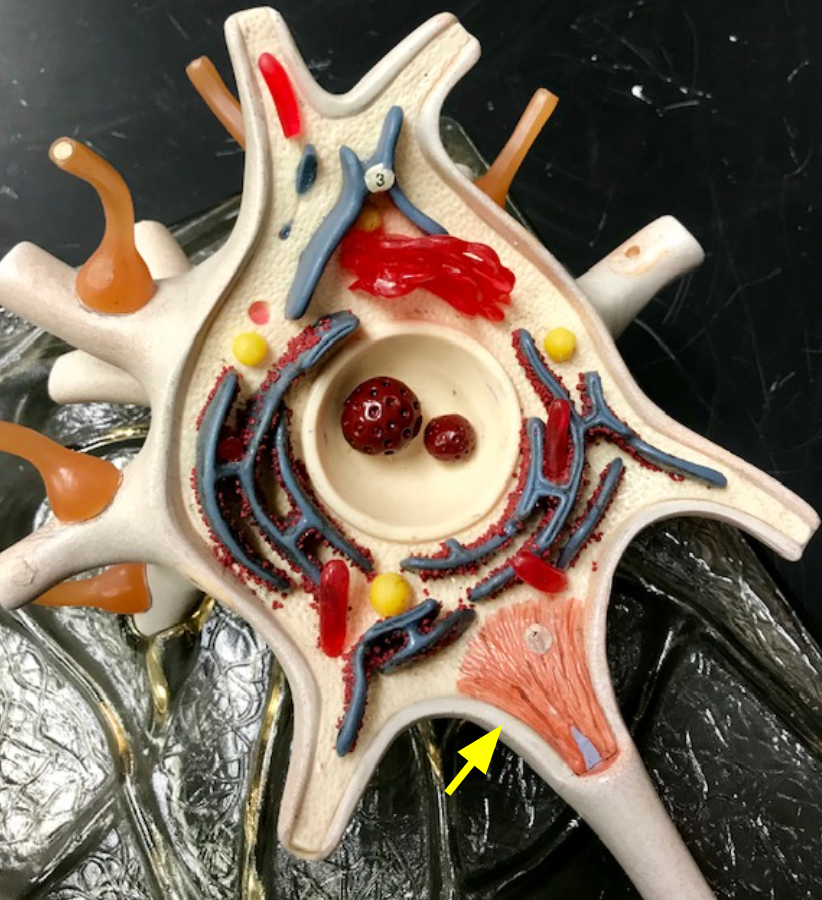
Skeletal muscle
Where is the end of a somatic motor neuron axon, along with its telodendria and synaptic knobs, located?
Junction between two neuron or a neuron and effector cell
What is a Synapse?
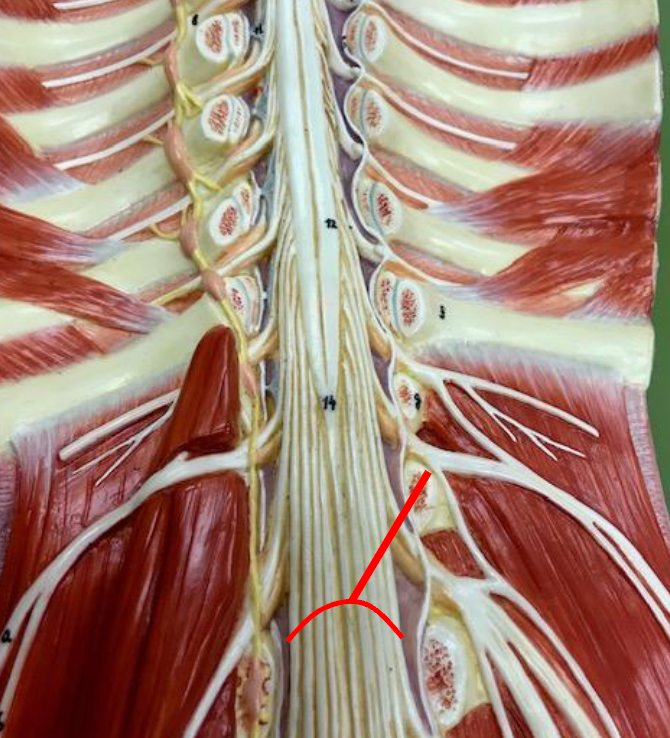
Conus Medullaris
The inferior tip of the spinal cord.
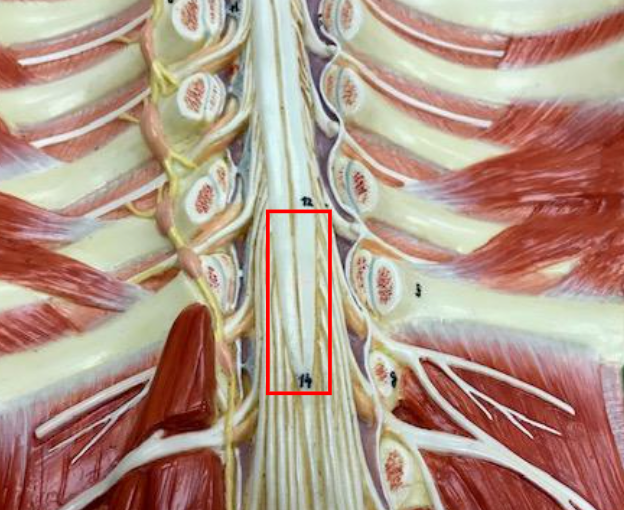
Cauda equina
Structure below the conus medullaris, resembling a horse's tail.
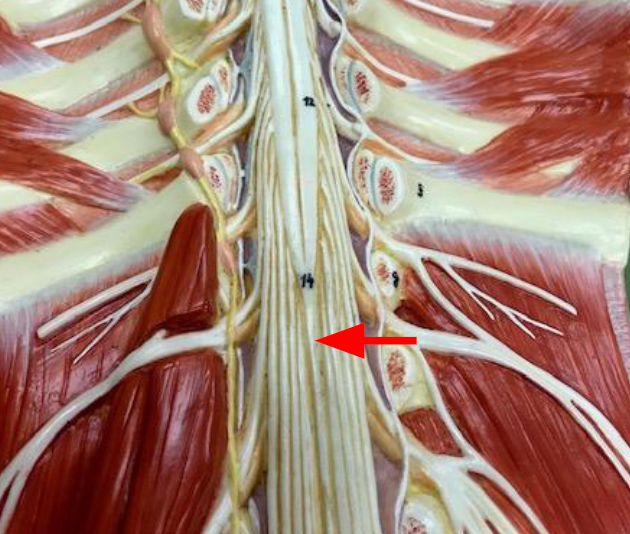
Filum terminale
Extension of pia mater that anchors the conus medullaris to the coccyx.
Cervical enlargement
Region where upper limb nerves connect to the spinal cord.
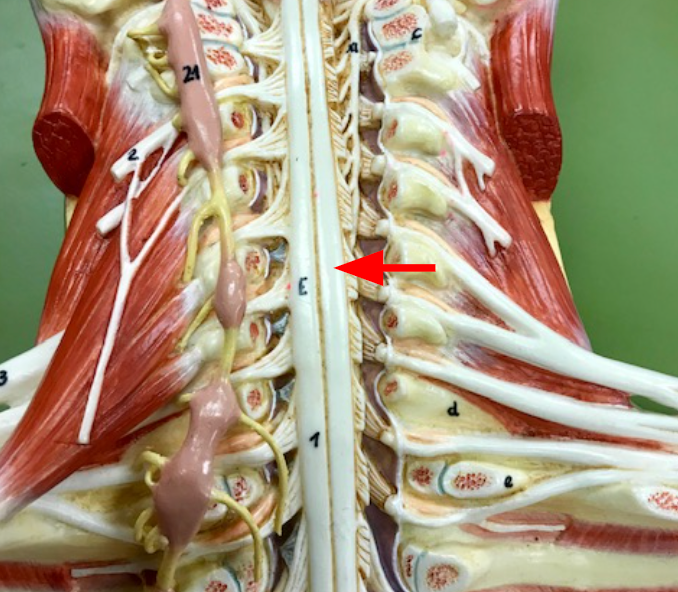
Lumbosacral enlargement
Region where lower limb nerves connect to the spinal cord.
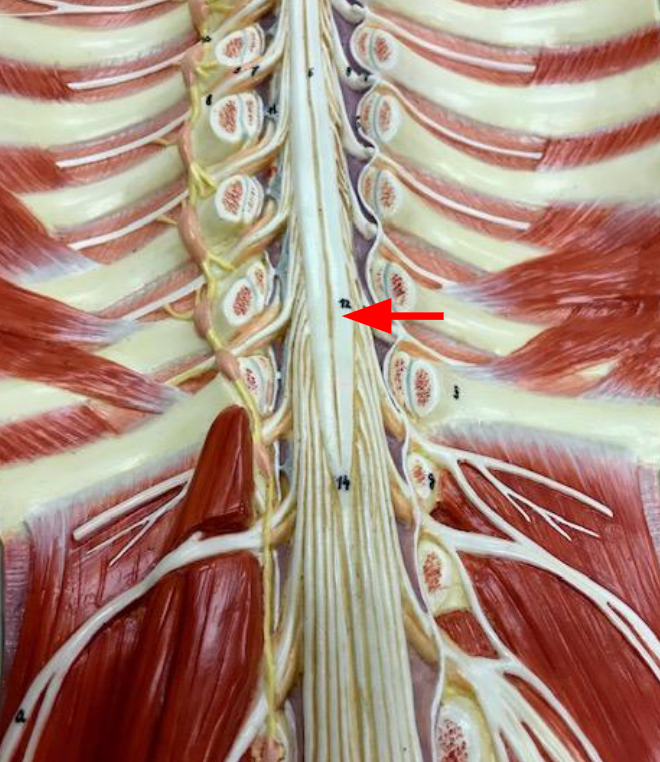
Posterior median sulcus
a thin groove that runs longitudinally down the back of the spinal cord
Anterior median fissure
a somewhat wide groove the runs longitudinally down the front of the cord
Anterior rami
intermingle to form networks called plexuses.
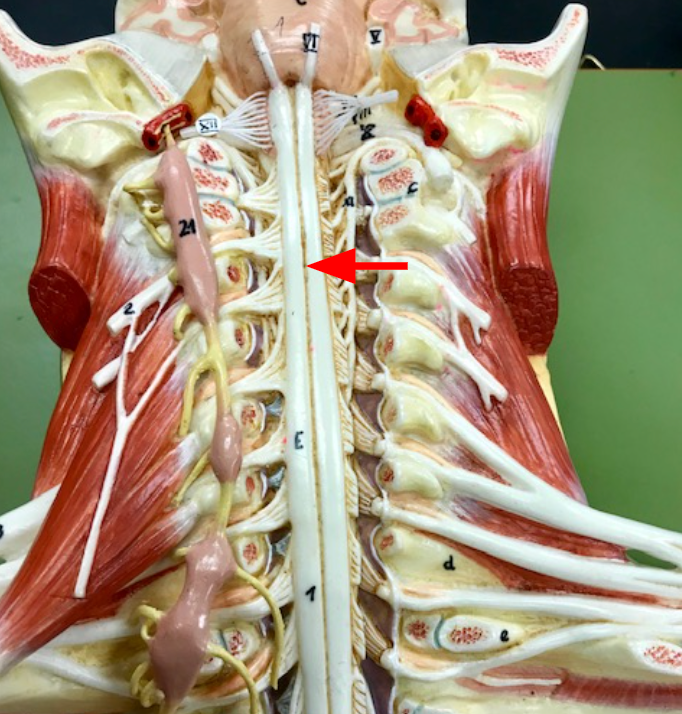
Cervical plexuses
Branches of spinal nerves C1 to C4, innervate certain muscles in the neck along with the skin of the neck and parts of the head and shoulders
Phrenic nerve
nerve that extends from each cervical plexuses innervates the diaphragm and is important for breathing
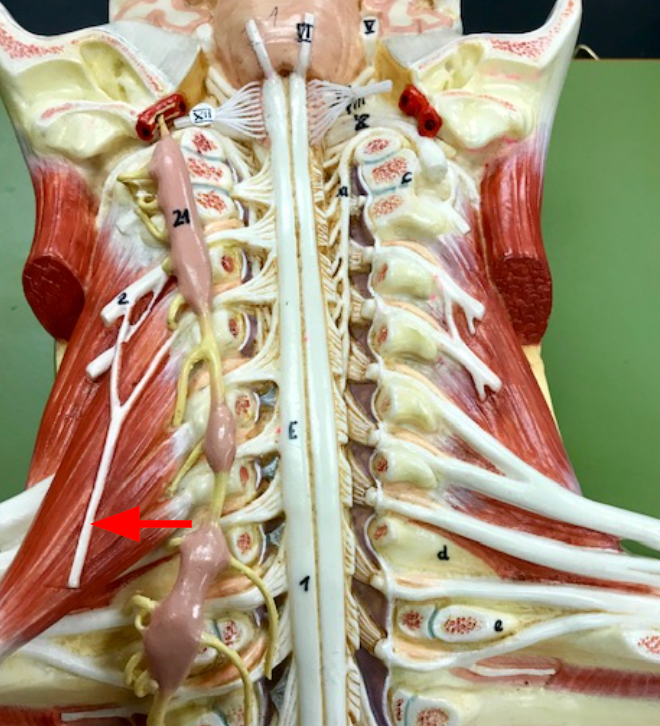
Brachial Plexuses
Branches of spinal nerves C5 to T1, innervate the pectoral girdles and upper limbs
Lumbosacral plexuses
give rise to various nerves that innervate the lower limbs
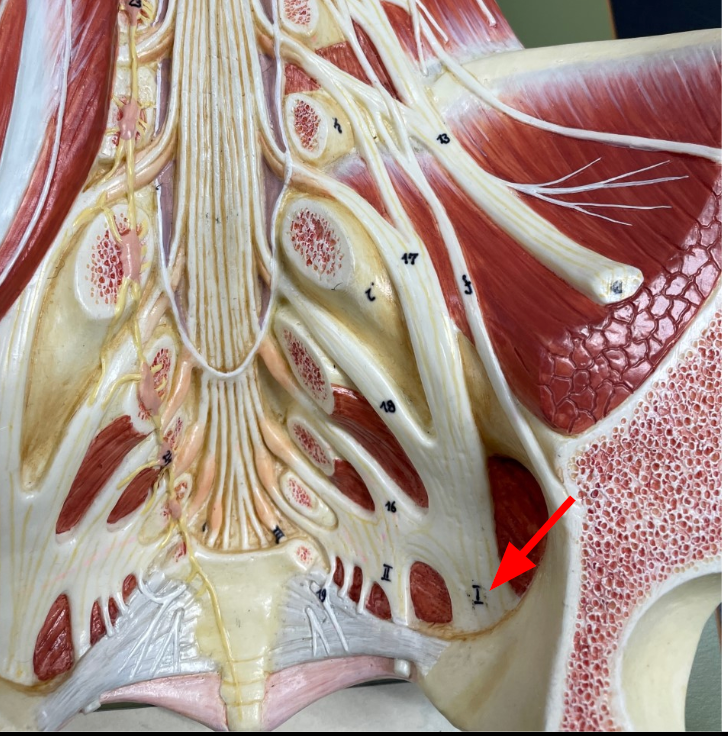
Obturator nerves
passes through an obturator foramen to innervate muscles and skin of the medial thigh
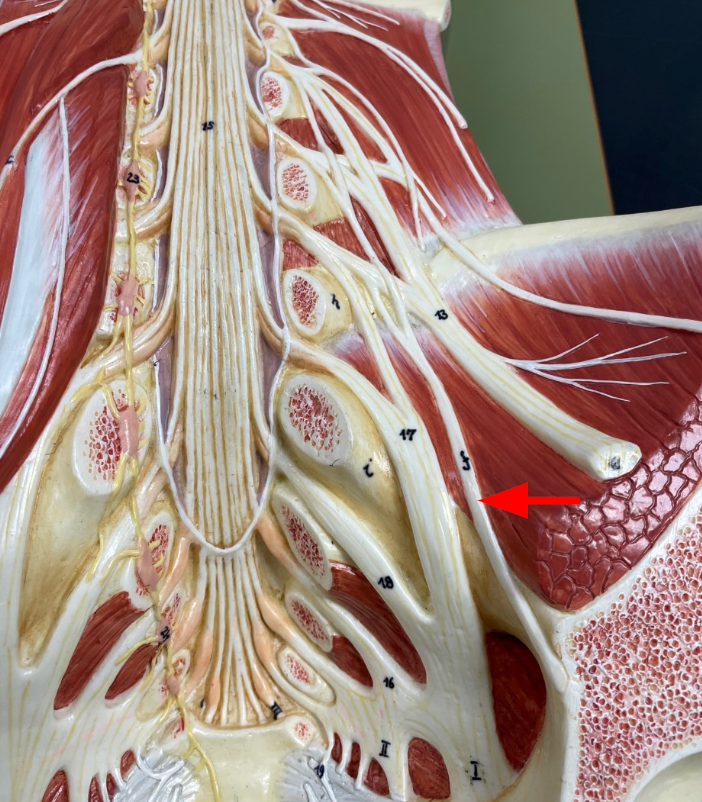
Sciatic nerves
largest nerves in the body, they innervate much of the lower limbs
Intercostal Nerves
Travel parallel to each other, between the ribs, from the back to the chest
The cranial dura mater is made up of two layers, the spinal dura mater is made up of just one layer, the presence of space between the spinal dura mater and the surrounding vertebrae.
WHat is the difference between spinal meninges and cranial meninges
Epidural space
Space between the spinal dura mater and surrounding vertebrae filled with adipose tissue.
They are where spinal nerves that innervate the arms and legs, respectively, join the spinal cord
Why is the spinal cord enlarged in two places?
The nerves exit the vertebral cavity at the lumbar and sacral regions of the spine
The lumbosacral enlargement of the spinal cord is located in the lower thoracic region of the spine. Why is it called the lumbosacral enlargement?
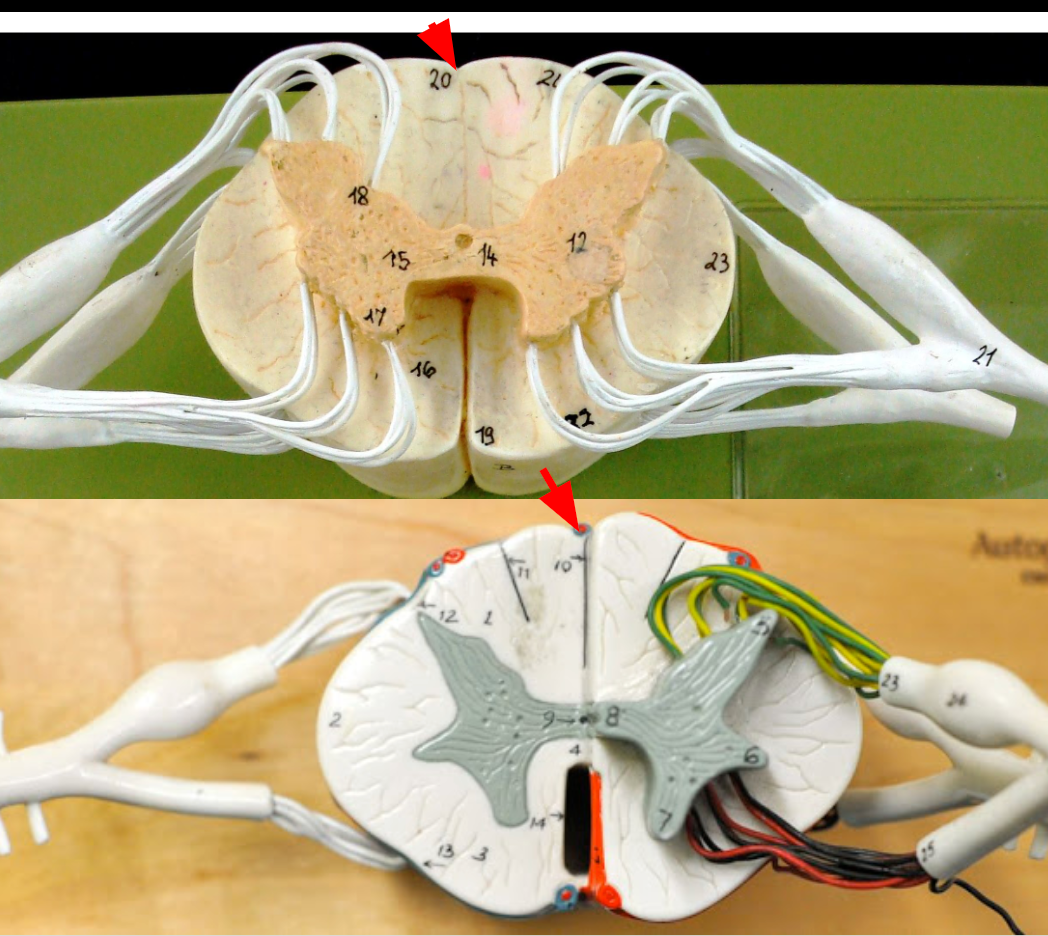
Central Canal
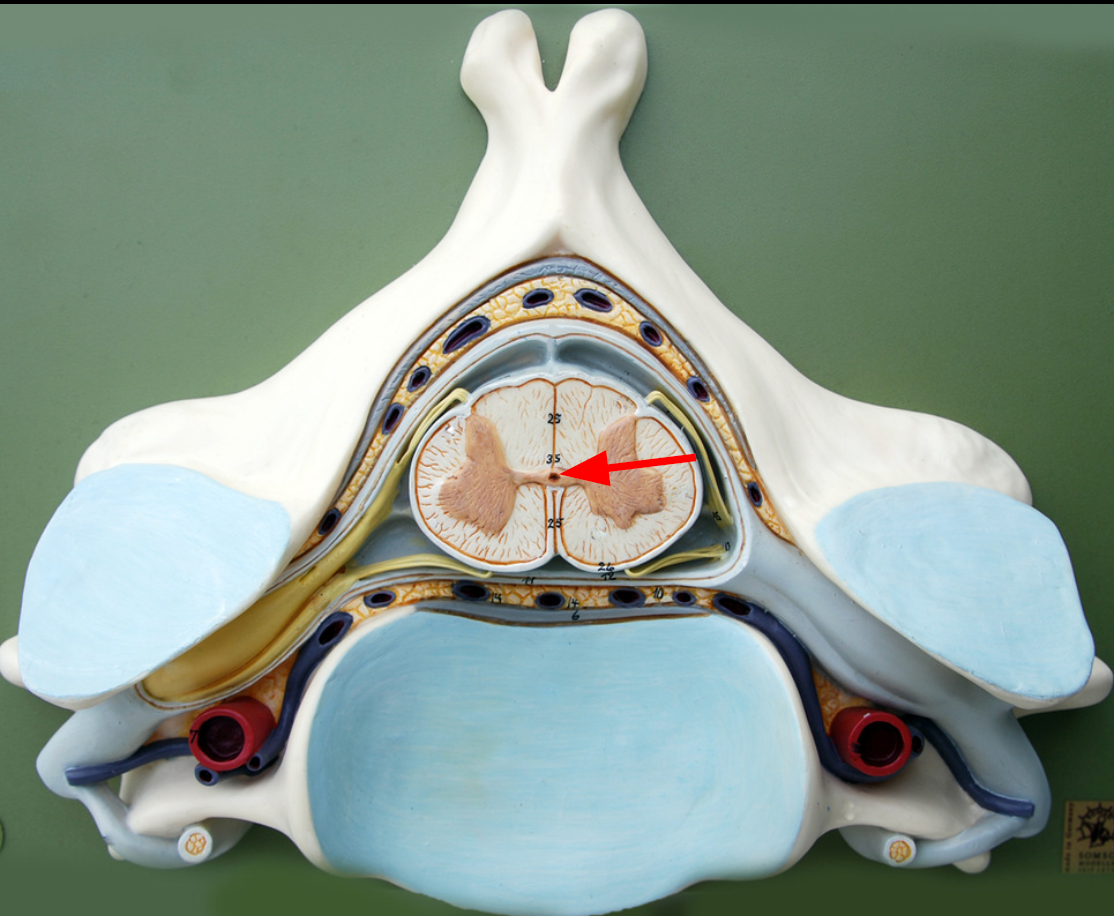
Dorsal horn
Anterior part of butterfly-shaped gray matter containing bodies of somatic motor neurons.
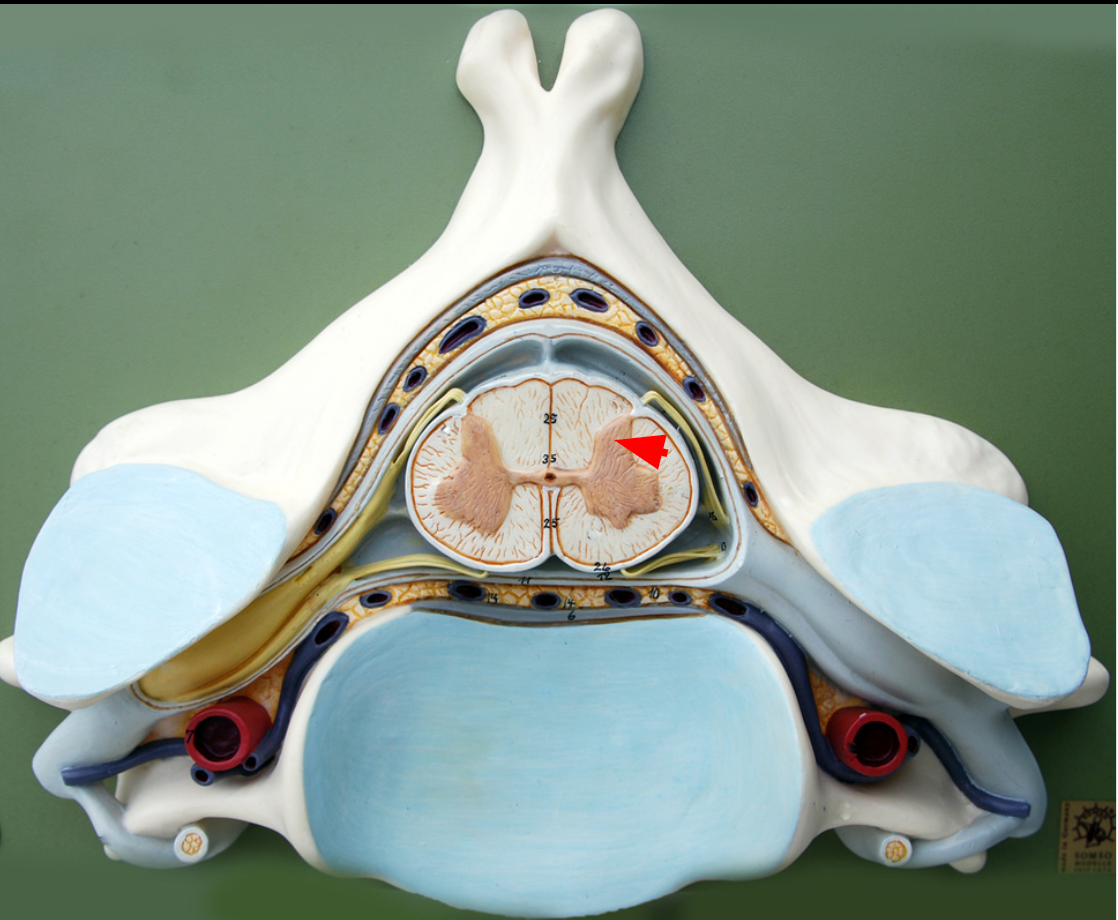
Ventral horn
Anterior part of butterfly-shaped gray matter containing bodies of interneurons.
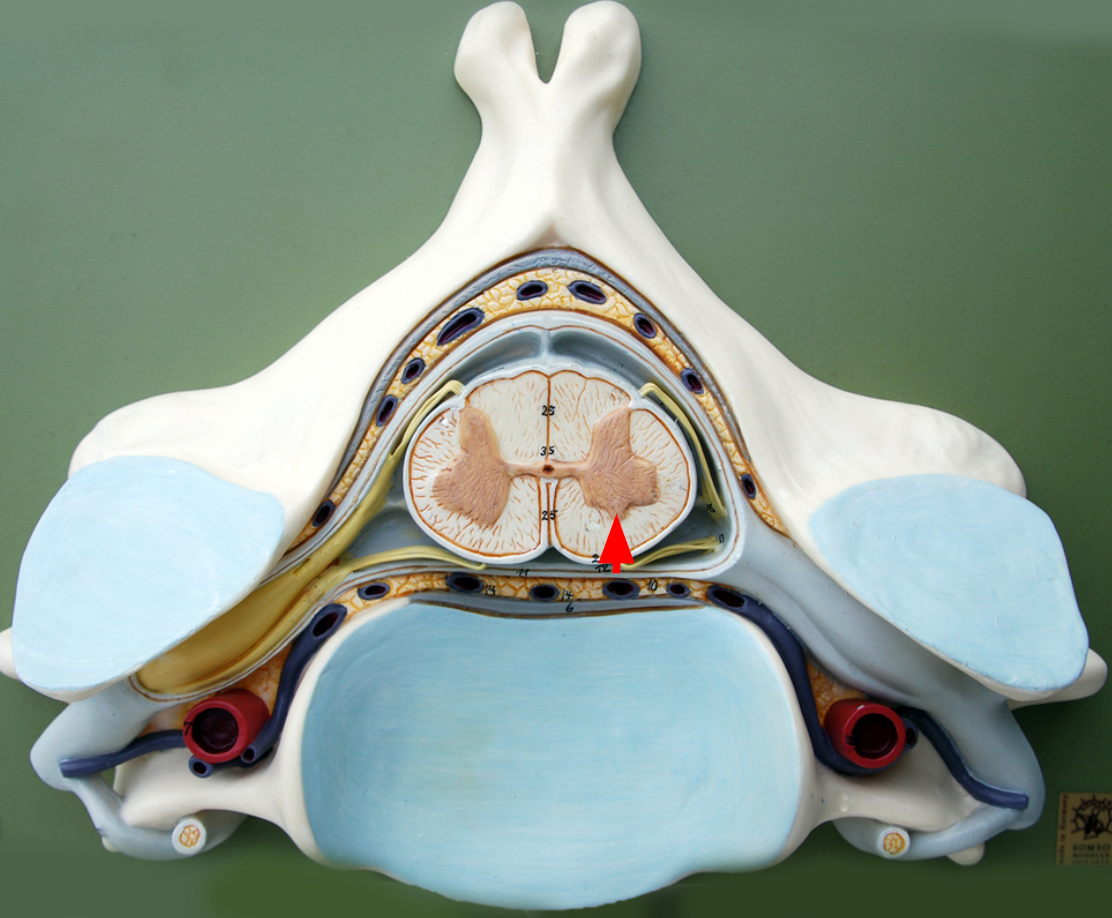
Lateral horn
Contains bodies of visceral motor neurons.
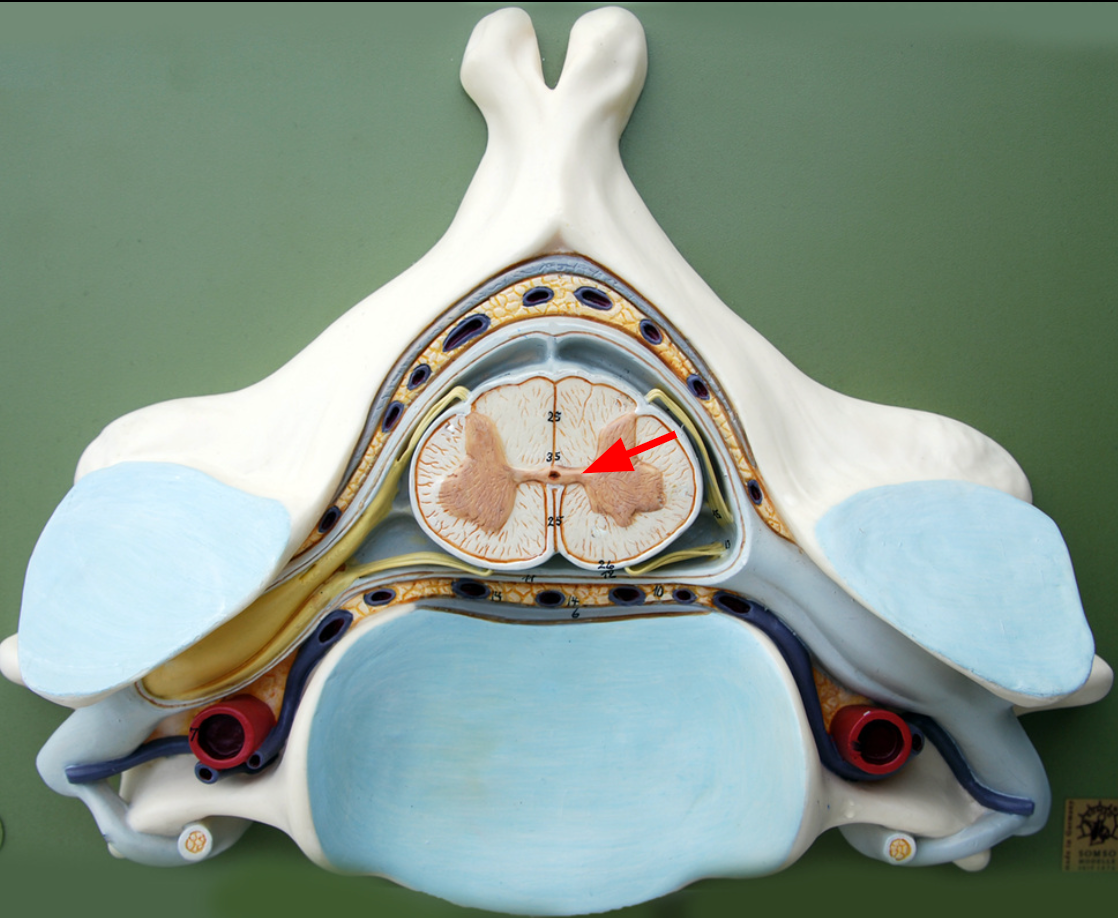
Gray commissure
portion of gray matter that connects the two wings
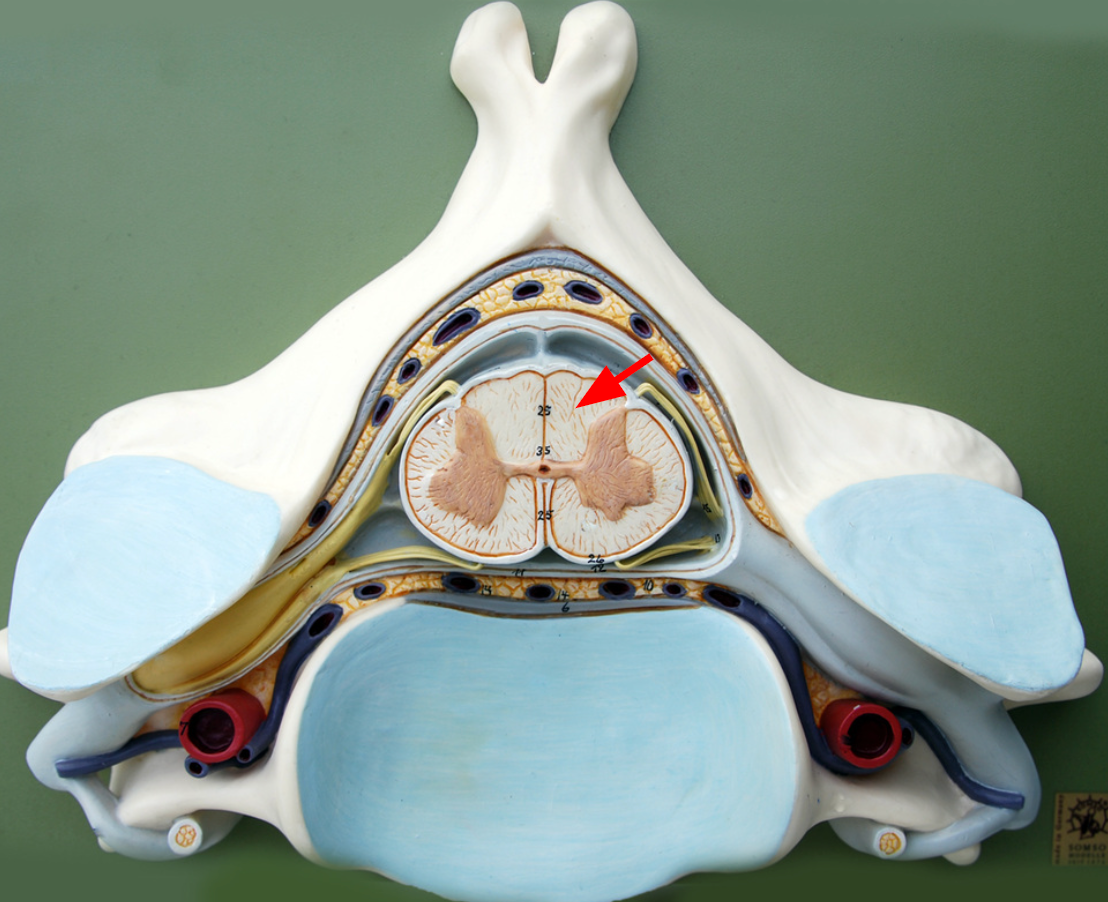
Posterior funiculi
posterior portion of the white matter
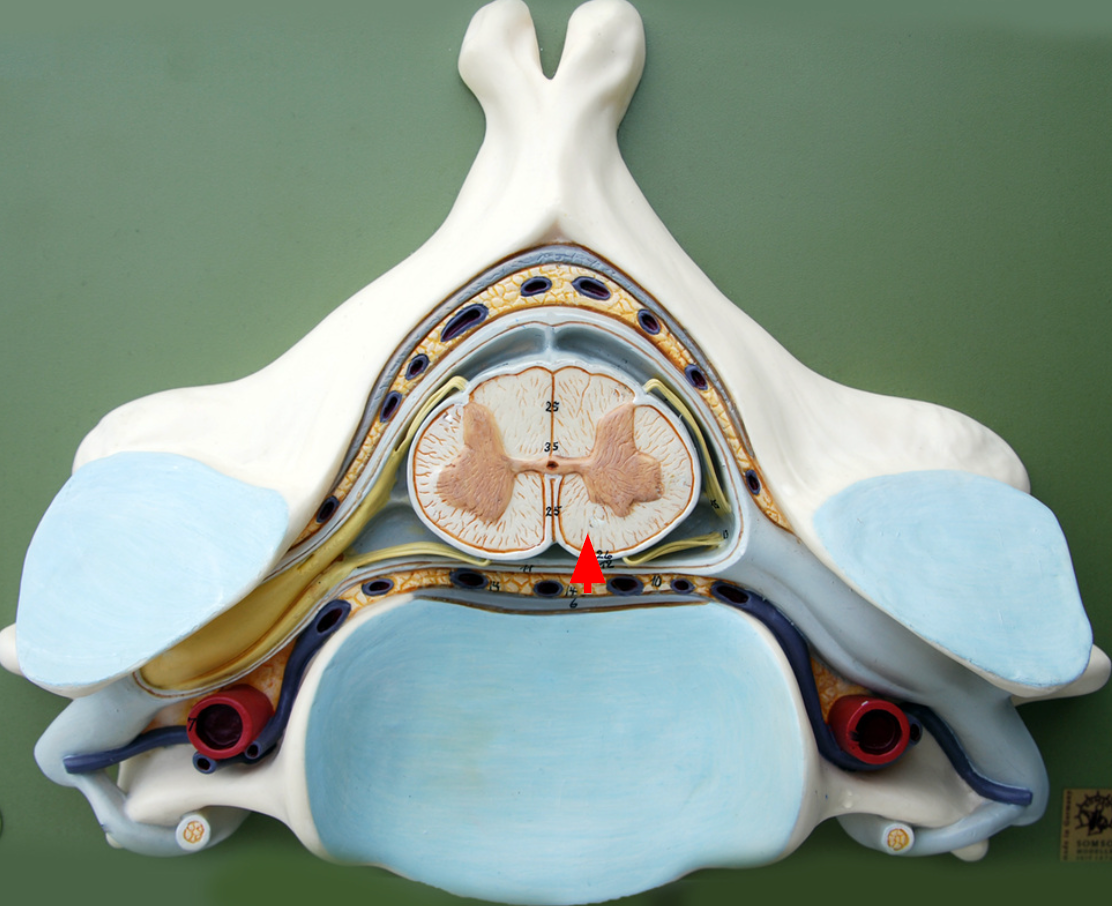
Anterior funiculi
anterior portion of of the white matter
Lateral funiculi
the lateral portion of the white matter
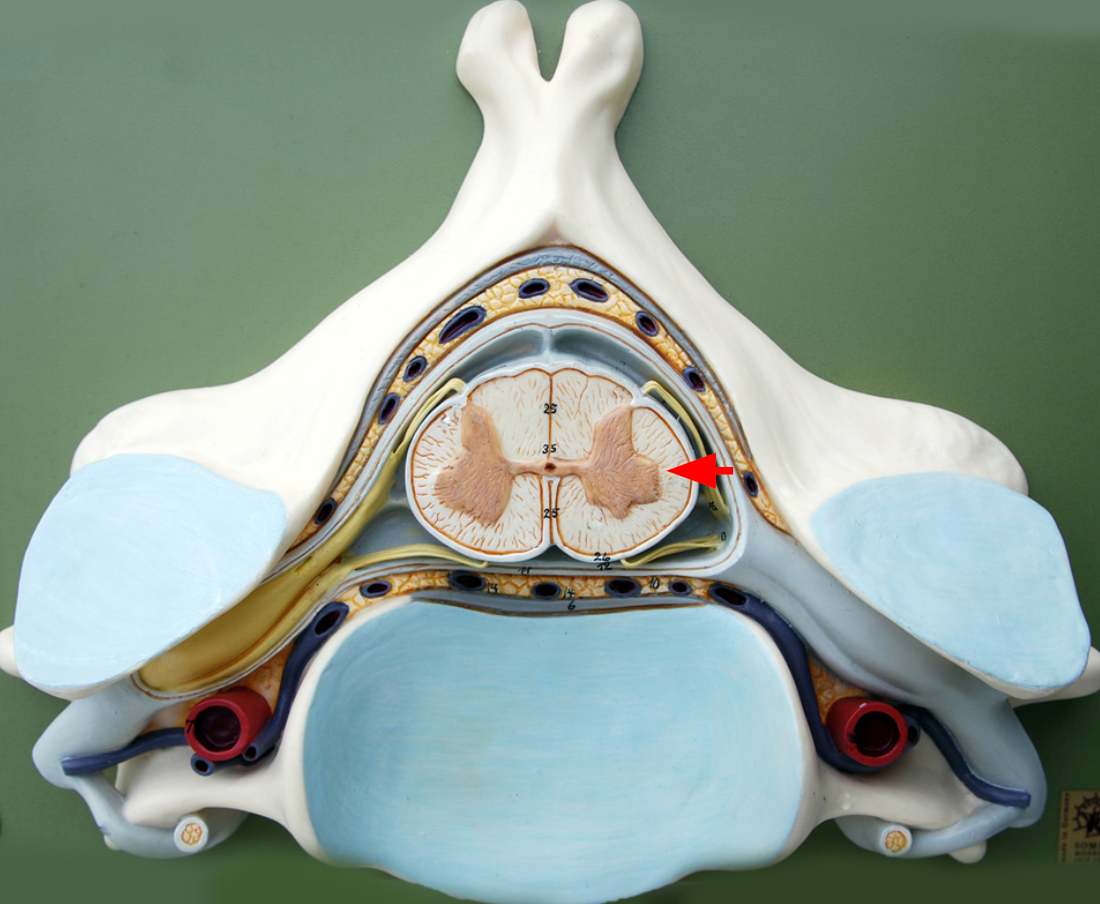
Ventral roots
nerves that allow motor neuron axons to exit the front of the spinal cord
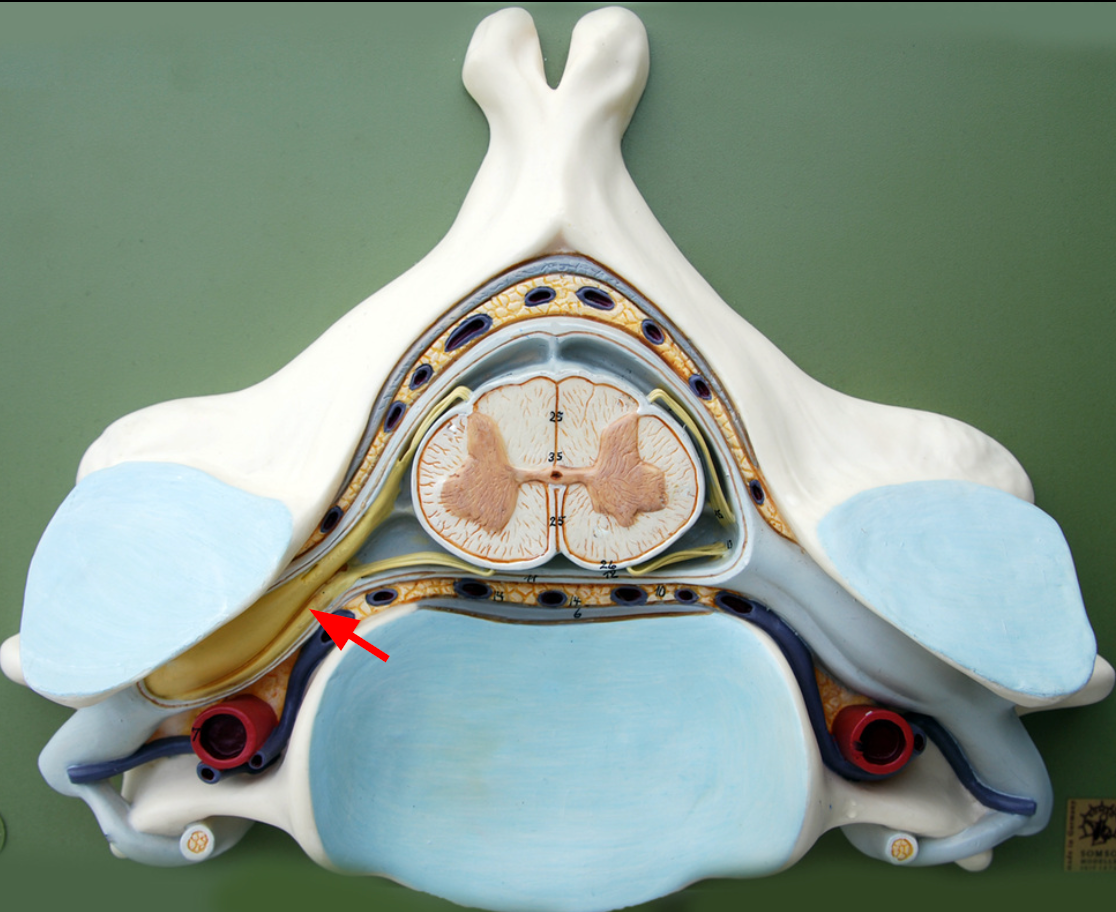
Dorsal root ganglia
Sensory neuron bodies whose axons travel into the back of the spinal cord.
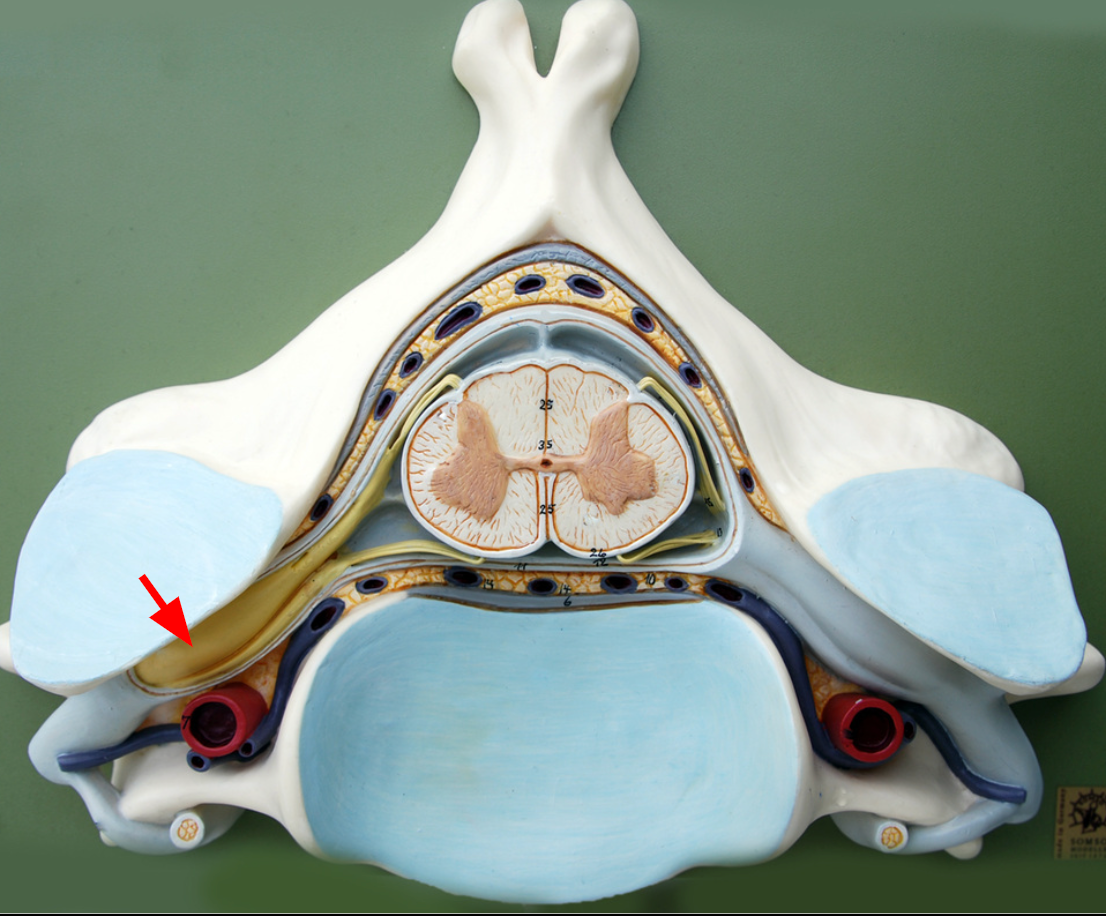
Dorsal roots
nerves
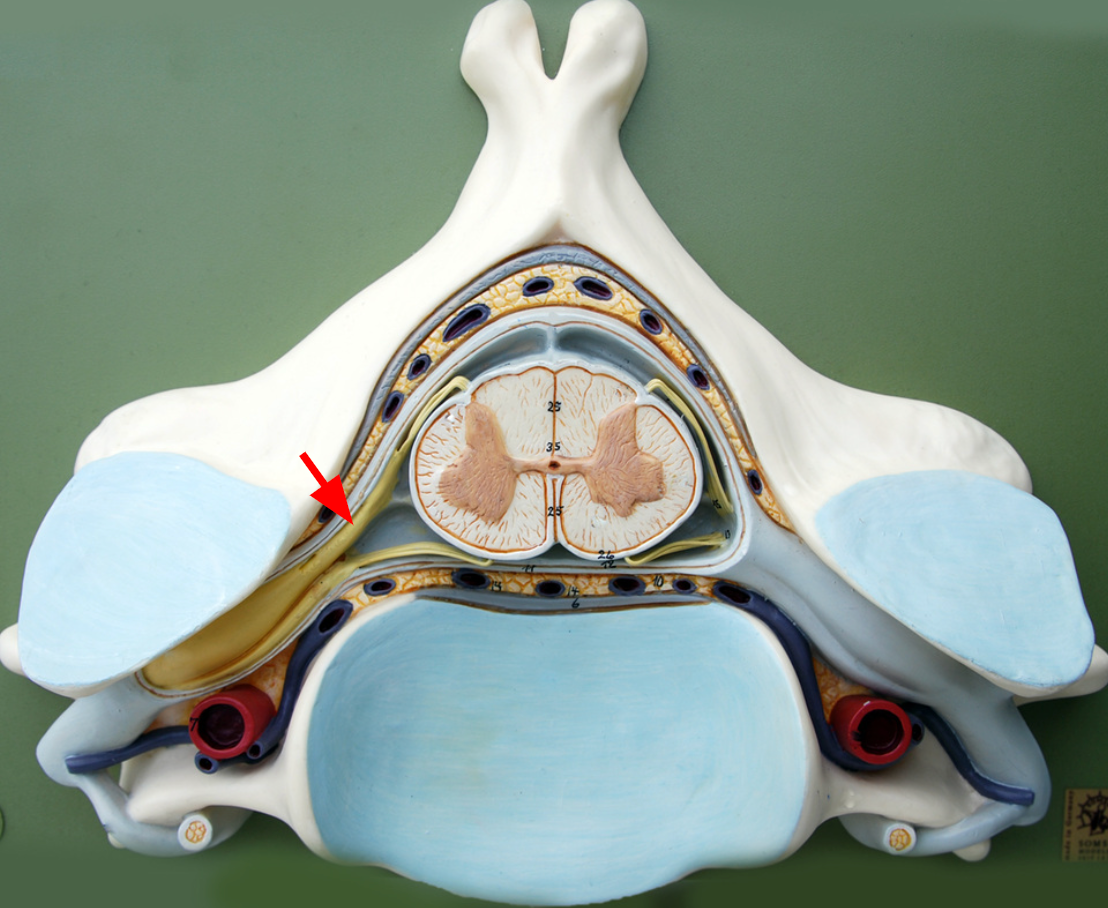
Ganglion
a structure that houses neuron bodies and lies outside the CNS
Ventral horns
In what part of the spinal cord are bodies of somatic motor neurons found?
dorsal root ganglia
In what structures are the bodies of sensory neurons found?
Motor neurons are multipolar with processes; sensory neurons are unipolar with no obvious processes.
Motor neuron vs. sensory neuron
Effect of cutting ventral roots
Effectors would receive no motor commands.
Spinal cord would receive no sensory information.
Effect of cutting dorsal roots
spinal dura mater
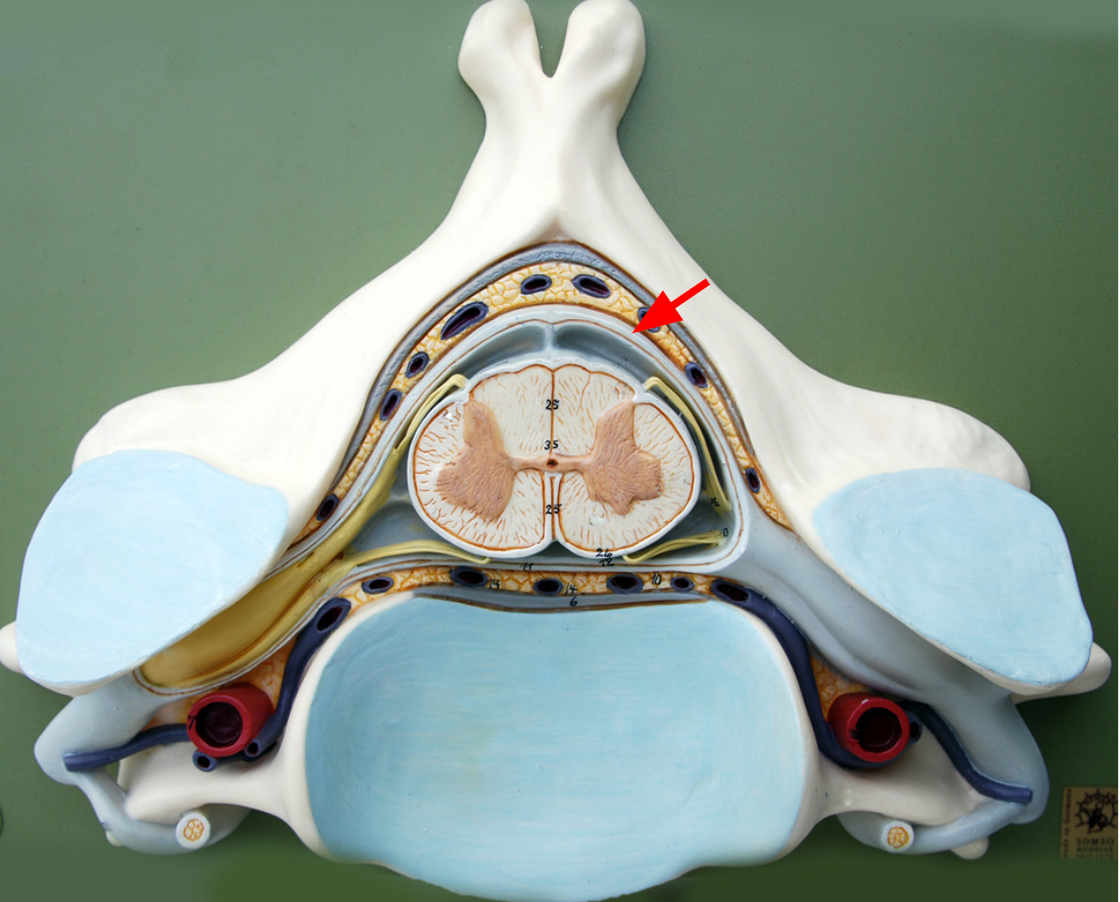
Arachnoid mater
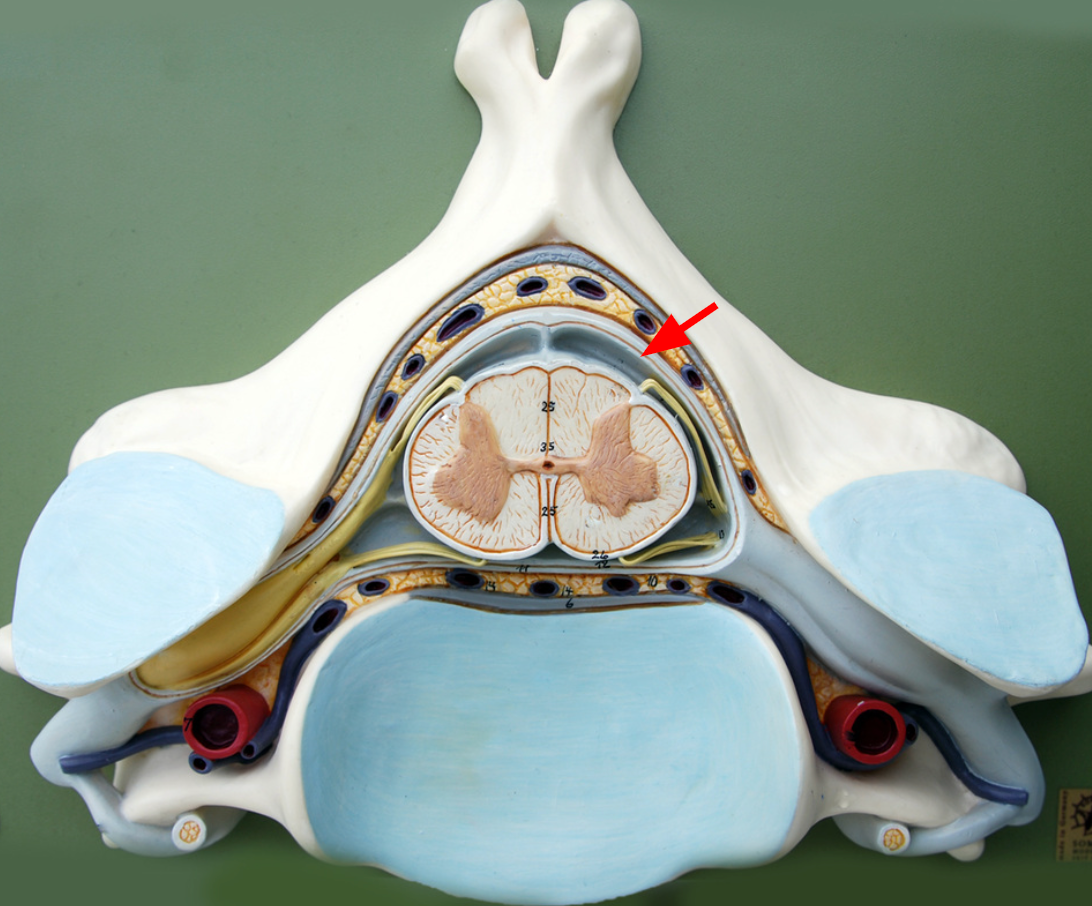
Subarachnoid space
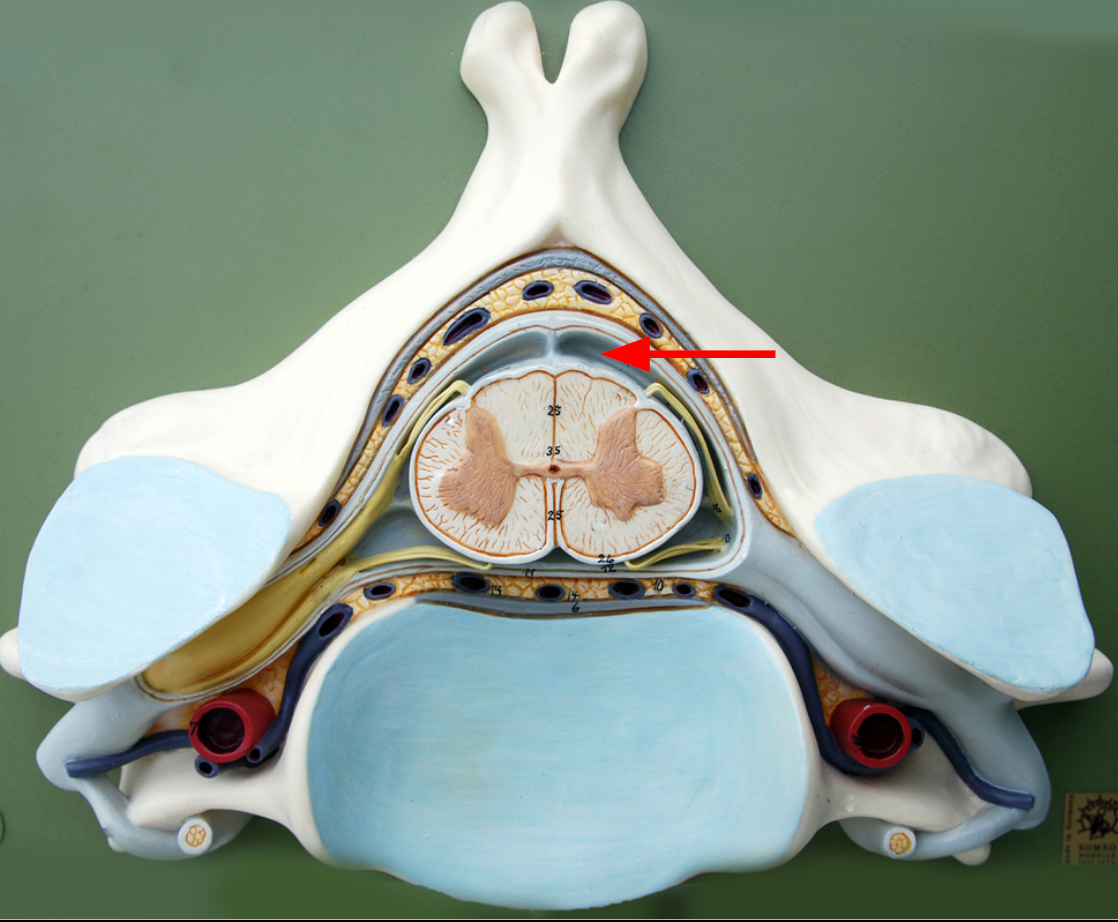
Pia mater
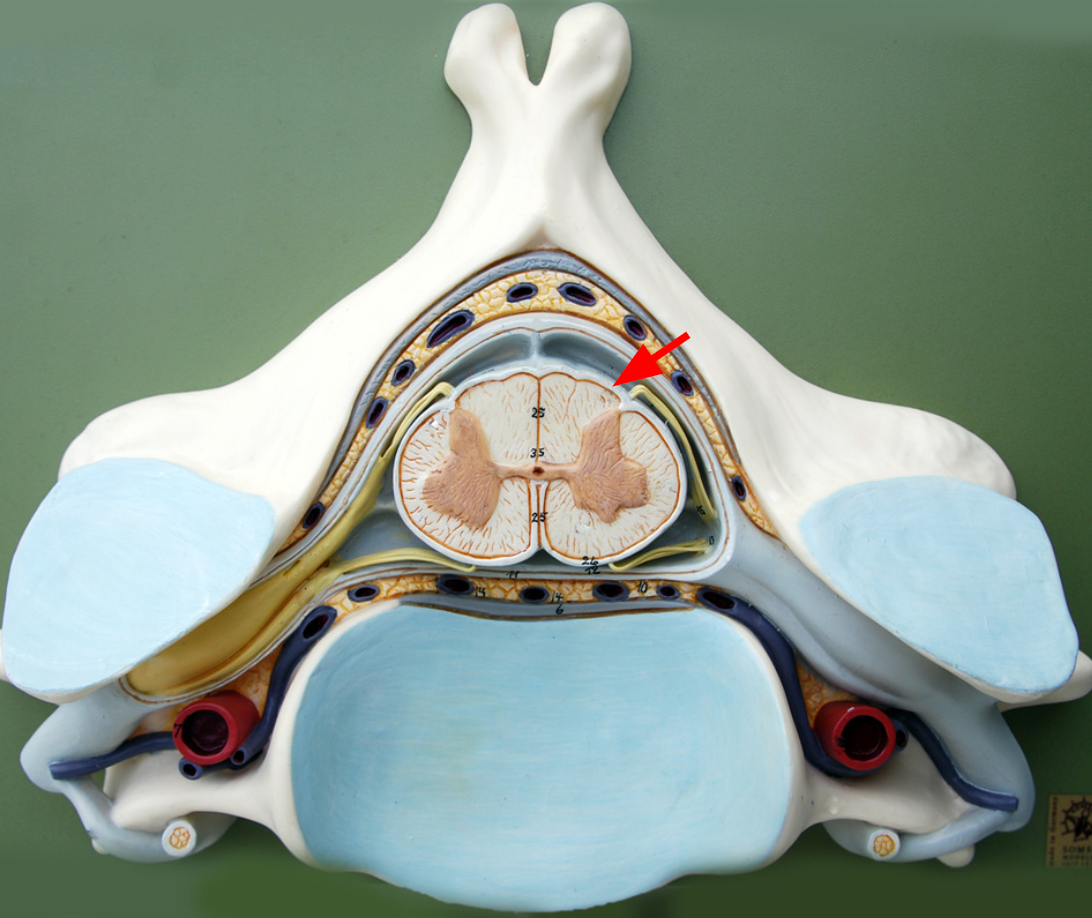
Dorsal root
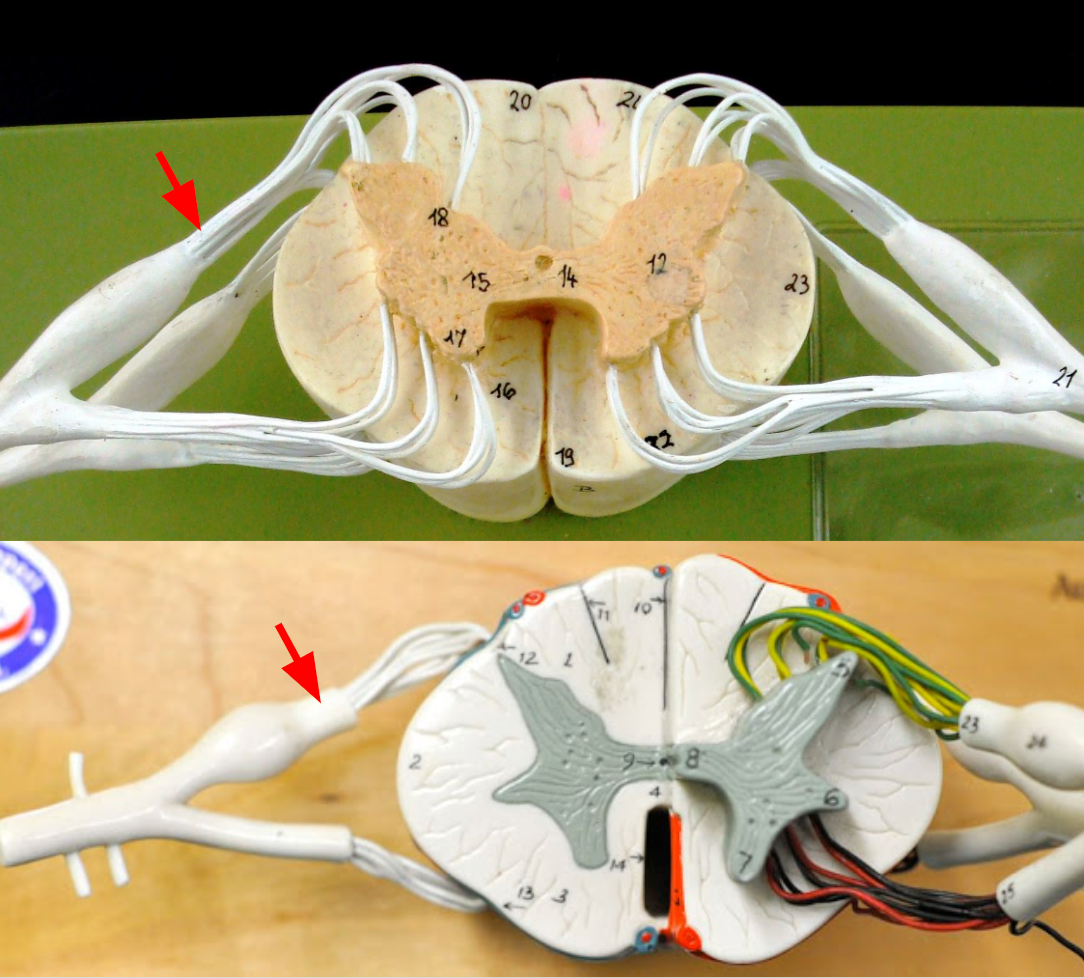
Dorsal root ganglion
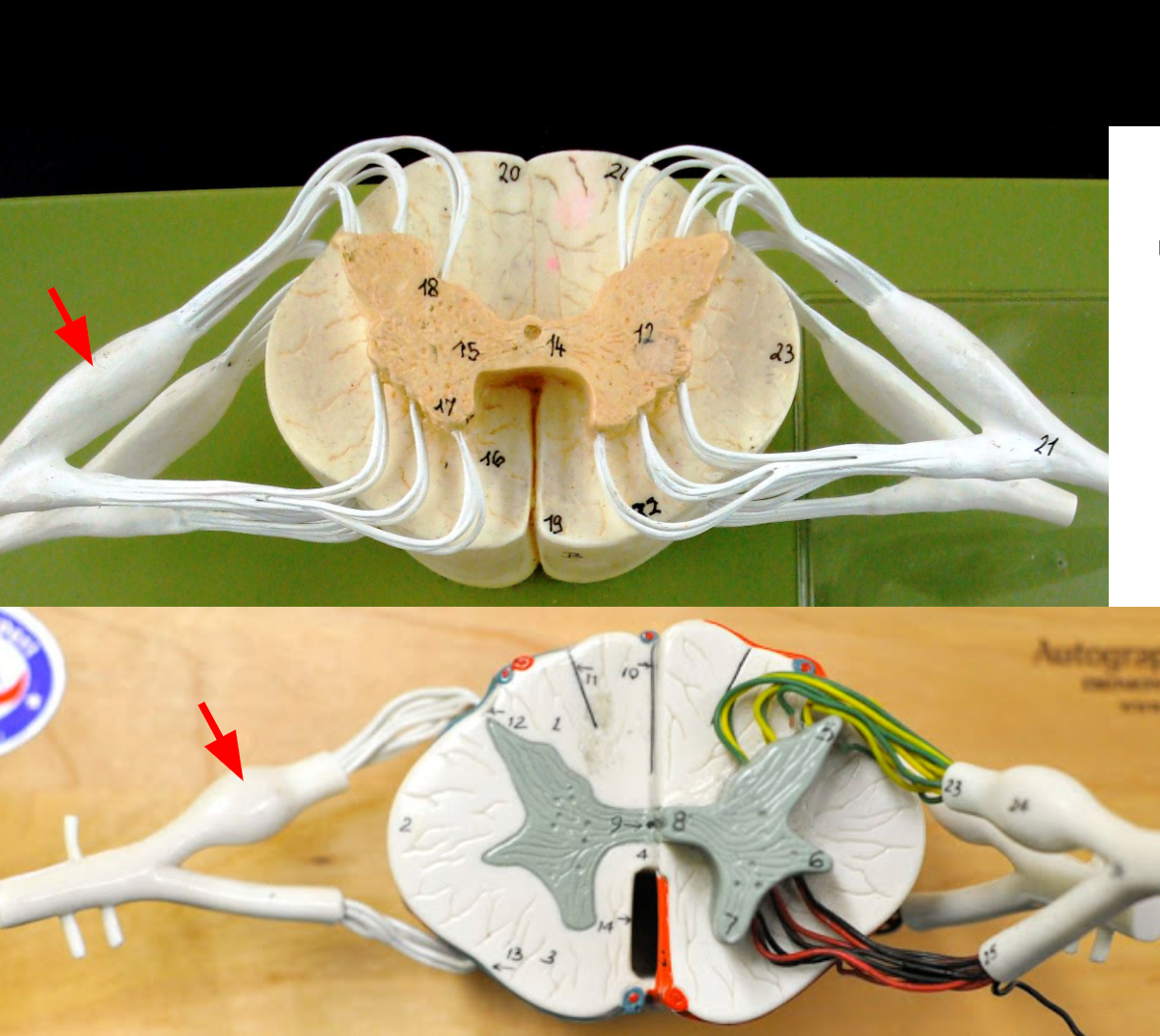
Ventral root
Spinal nerve
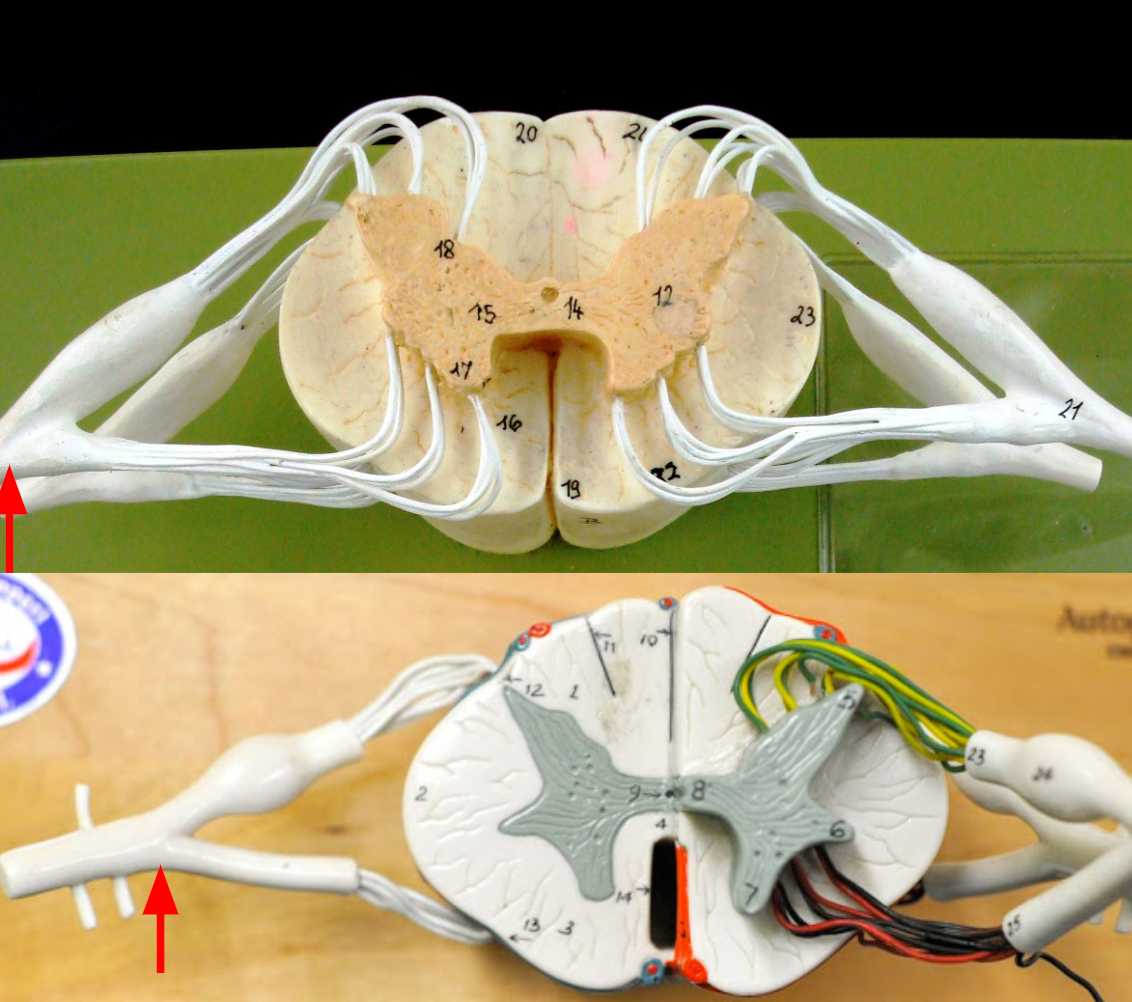
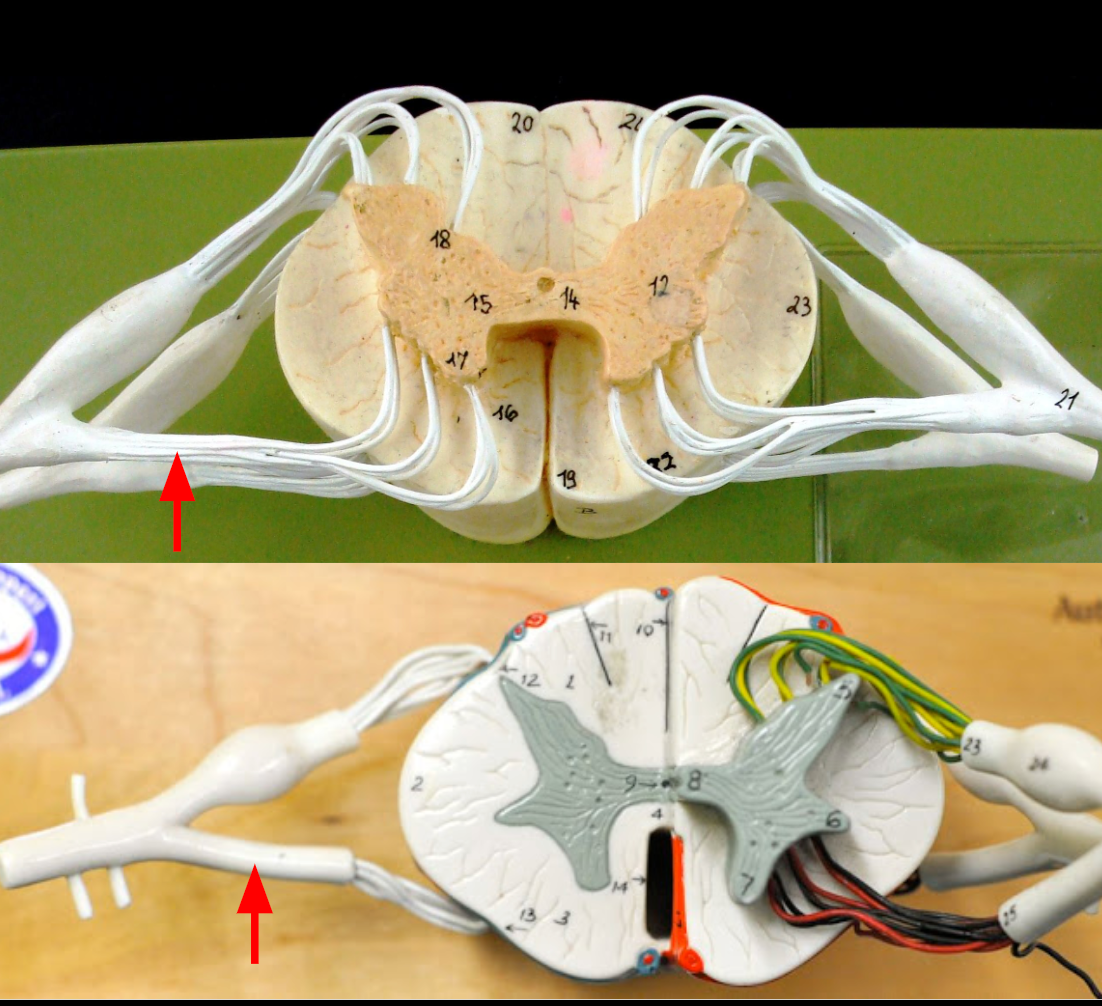
Anterior median fissure
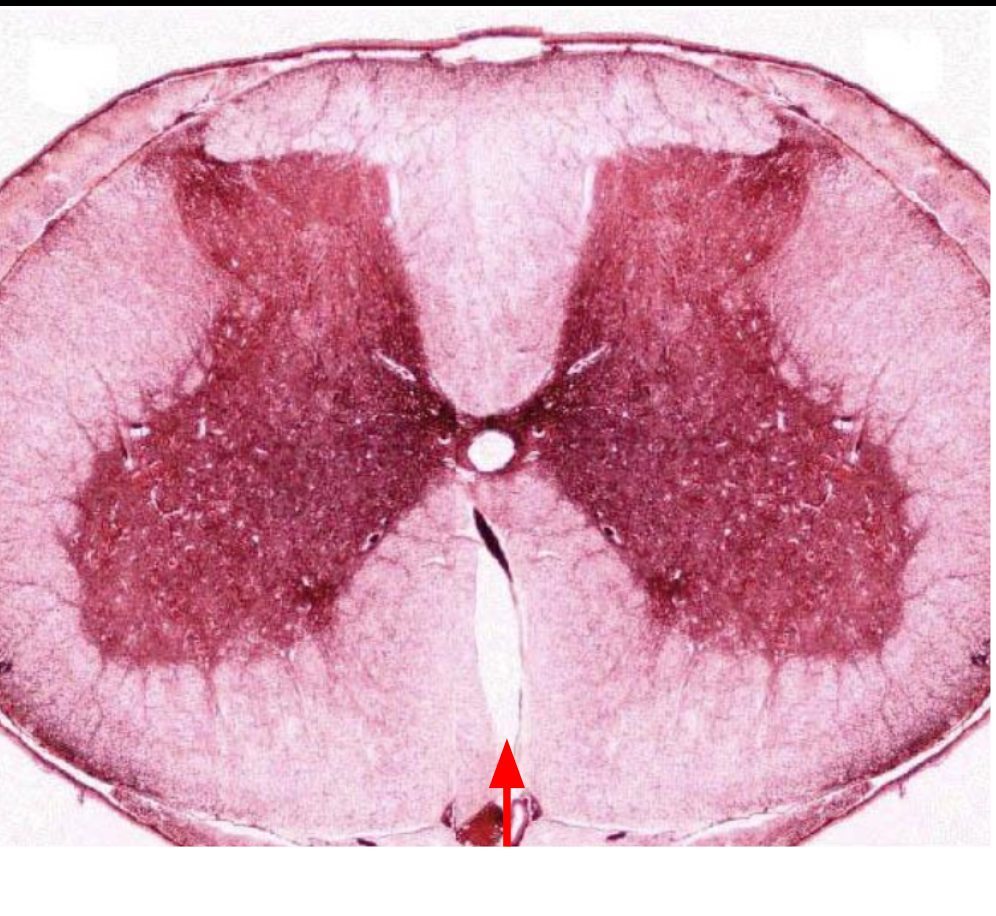
Anterior funiculus
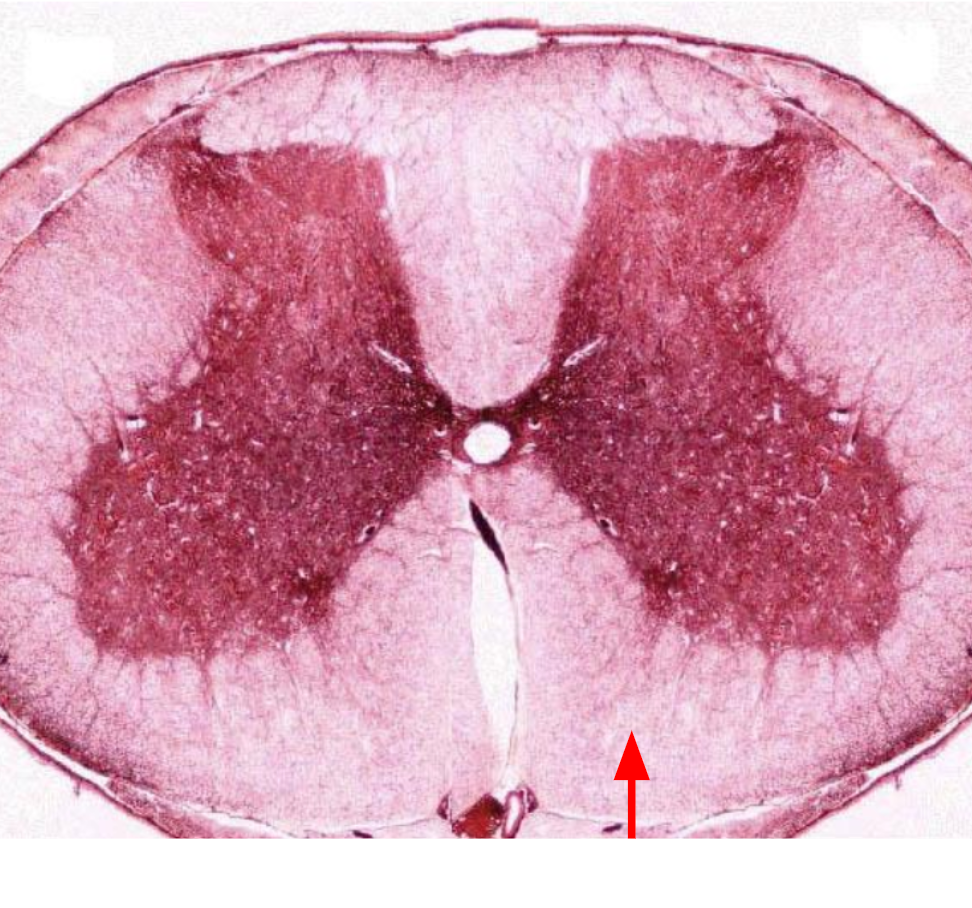
Lateral funiculus
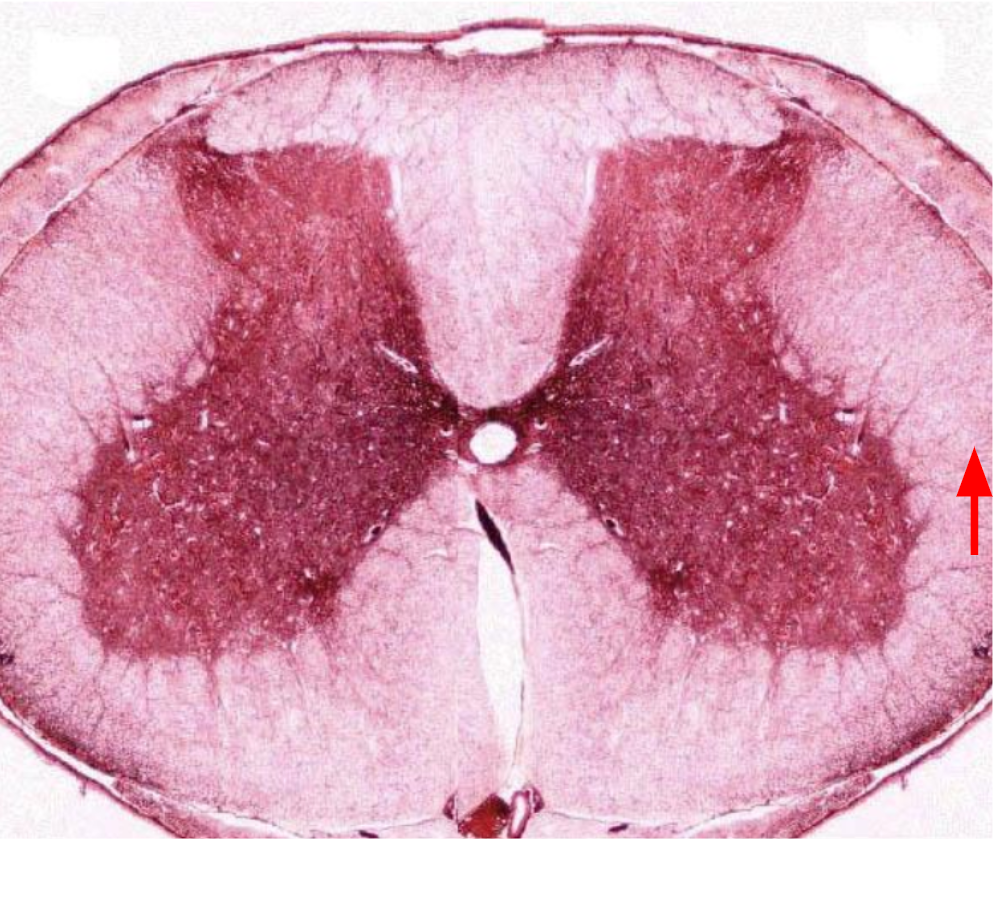
Posterior funiculus
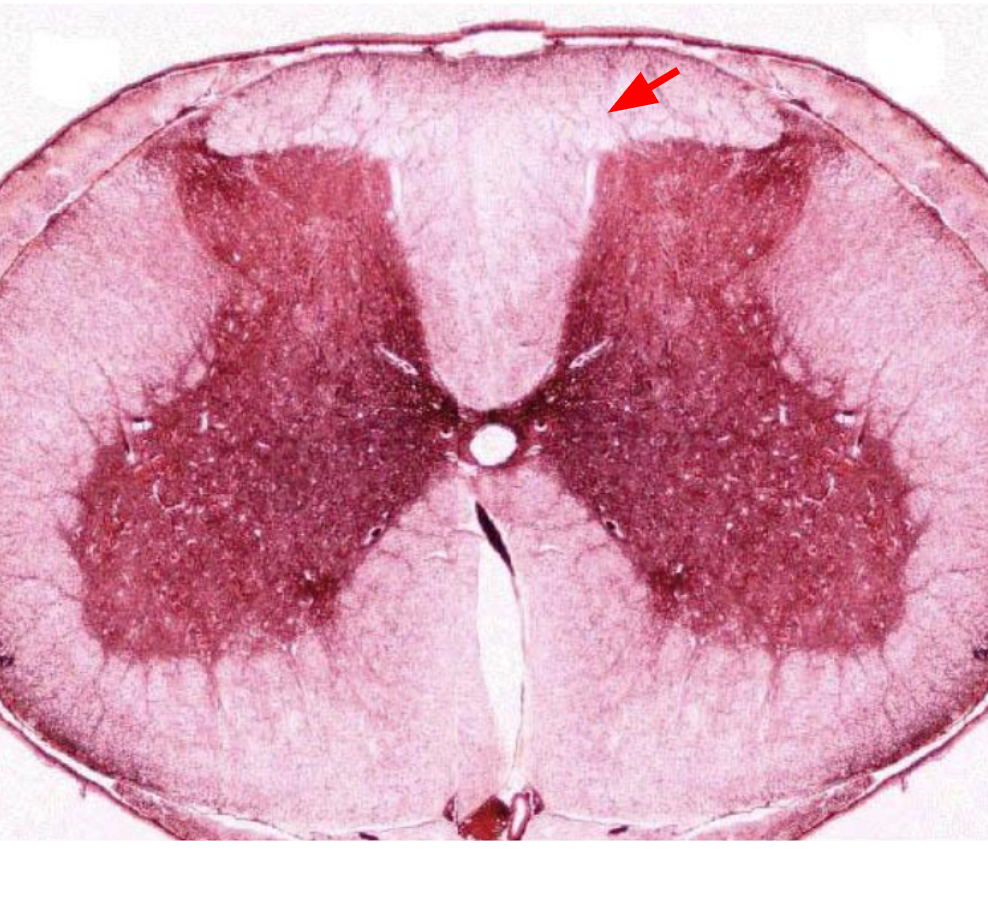
Ventral horn
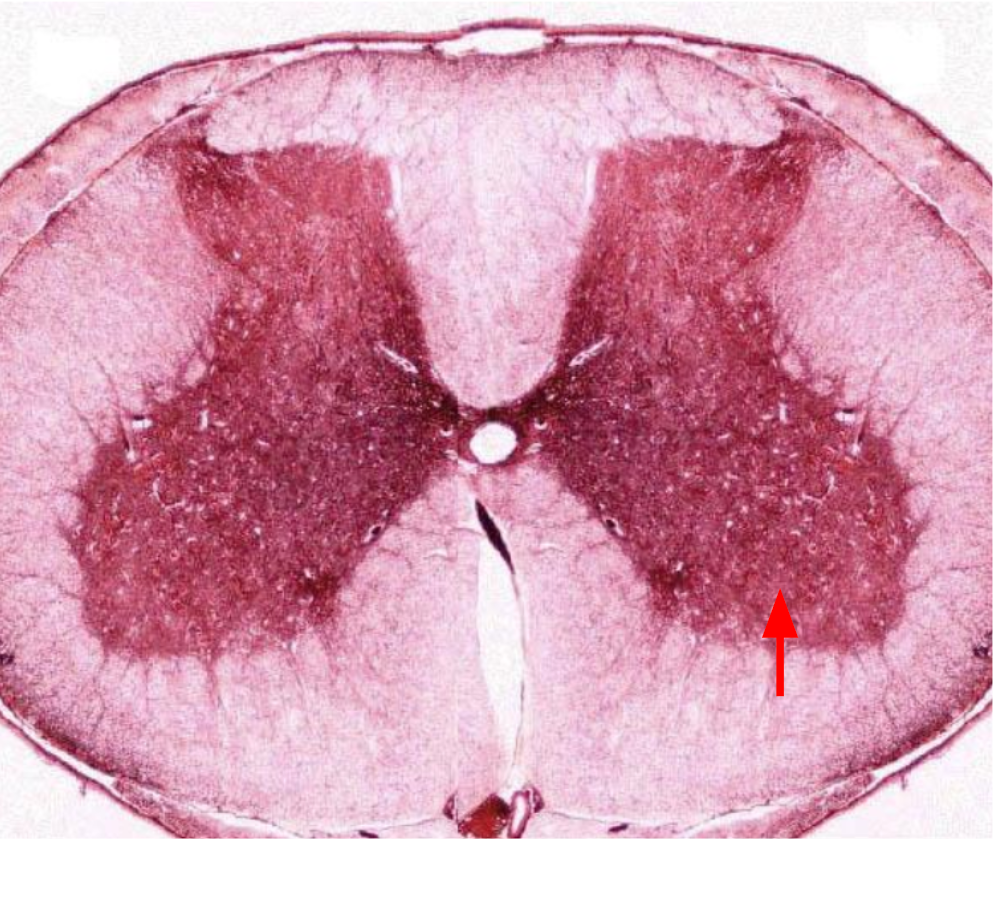
Gray commissure
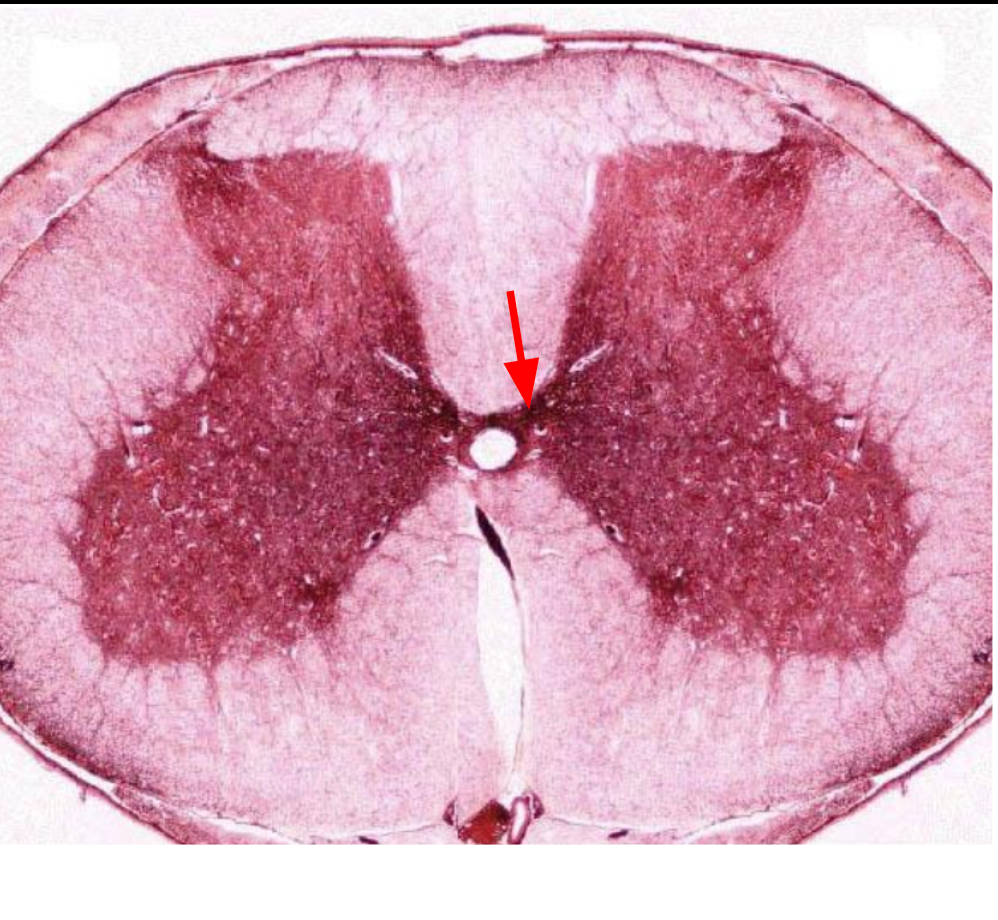
central canal
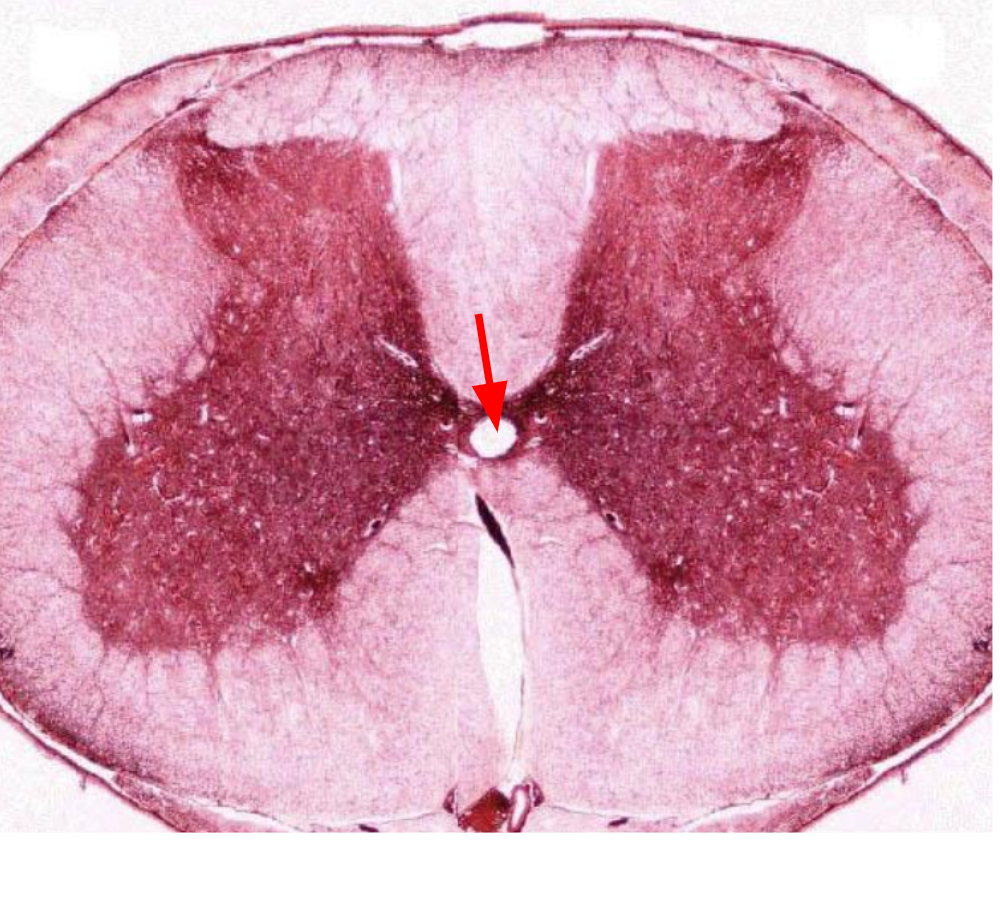
Dorsal root ganglion