Chapter 11- Cranium, Facial Bones, and Paranasal Sinuses
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
how many cranial and facial bones are there?
8 cranial, 14 facial
the 8 bones of the cranium are divided into the _______ and the _______
calvarium, floor
what are the 4 bones of the calvarium?
frontal, right and left parietal, occipital
what are the 4 bones of the floor?
right and left temporal, sphenoid, ethmoid
the frontal bone is comprised of the _____________ (vertical portion) and the ____________ (horizontal portion)
squamous, orbital
what is the smooth raised prominence between the eyebrows?
the glabella
what are the slight depressions above each eyebrows?
the supraorbital grooves (SOG)
the SOG correspond to the floor of the ____________ _________ of the cranial vault
anterior fossa
what is the superior rim of each oribt?
the supraorbital margins (SOM)
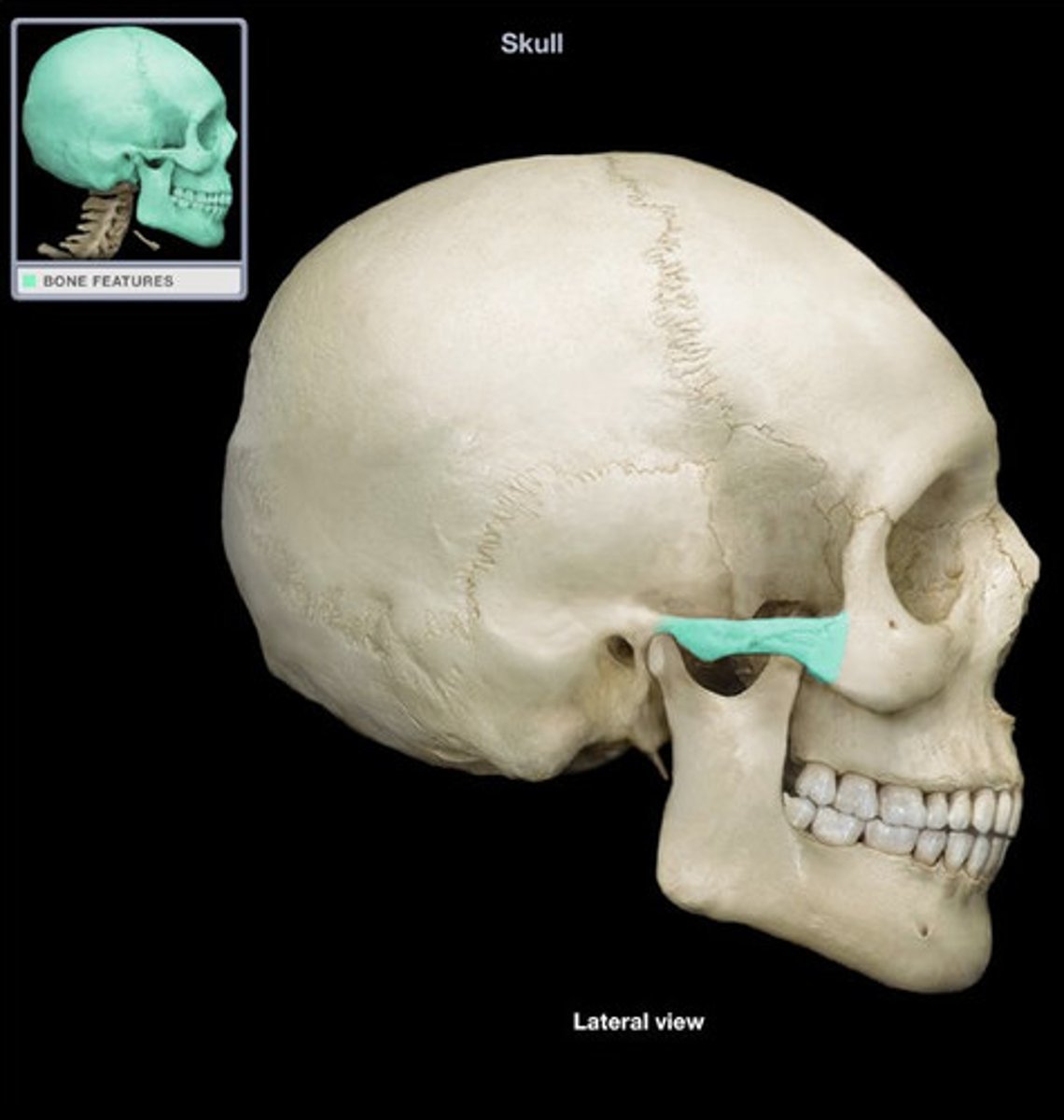
what separates the orbital plates?
ethmoid notch
what 4 cranial bones does the frontal bone articulate with?
right and left parietals, sphenoid, ethmoid
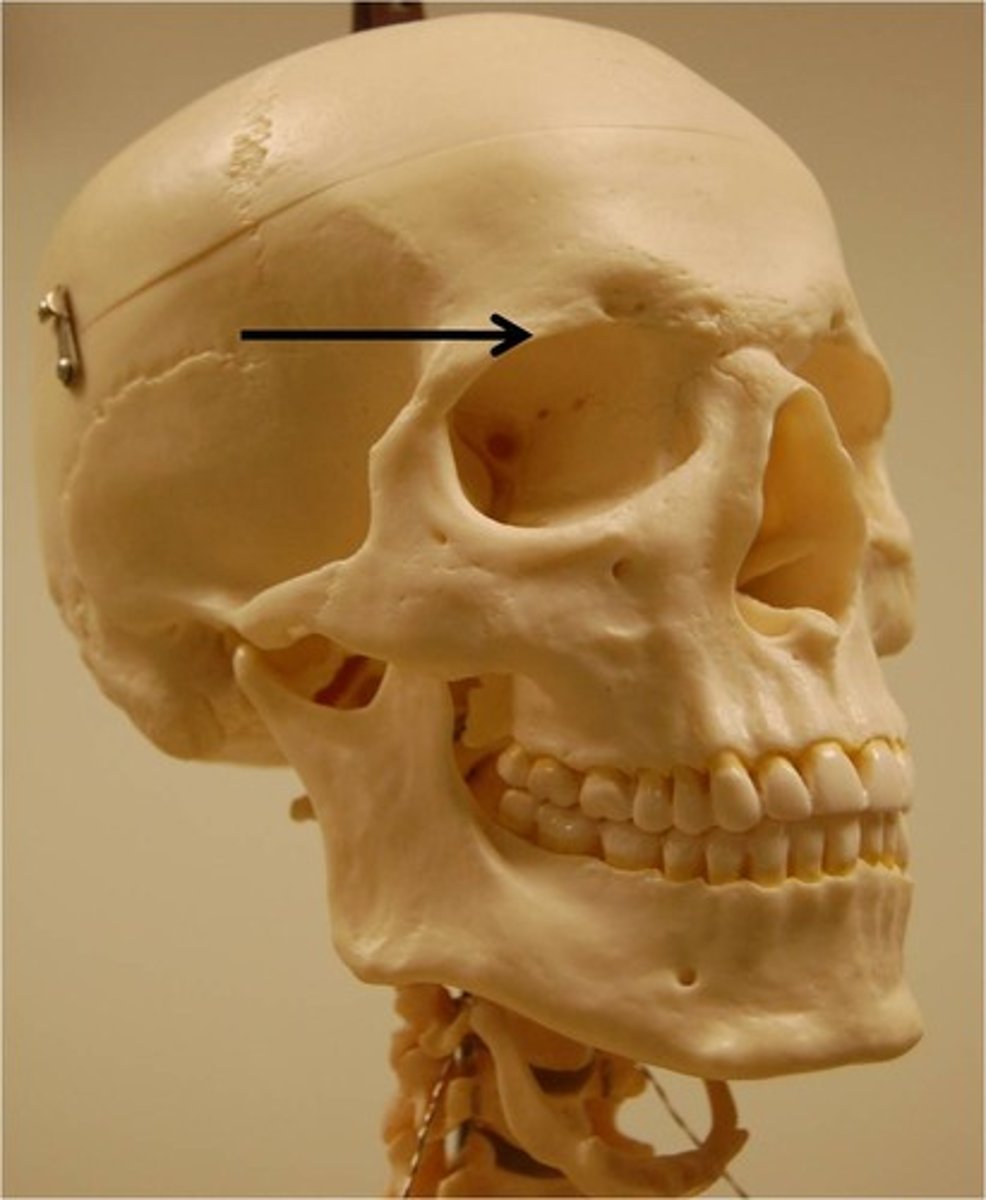
the lateral walls of the cranium and part of the roof are formed by the two _____________ bones
parietal
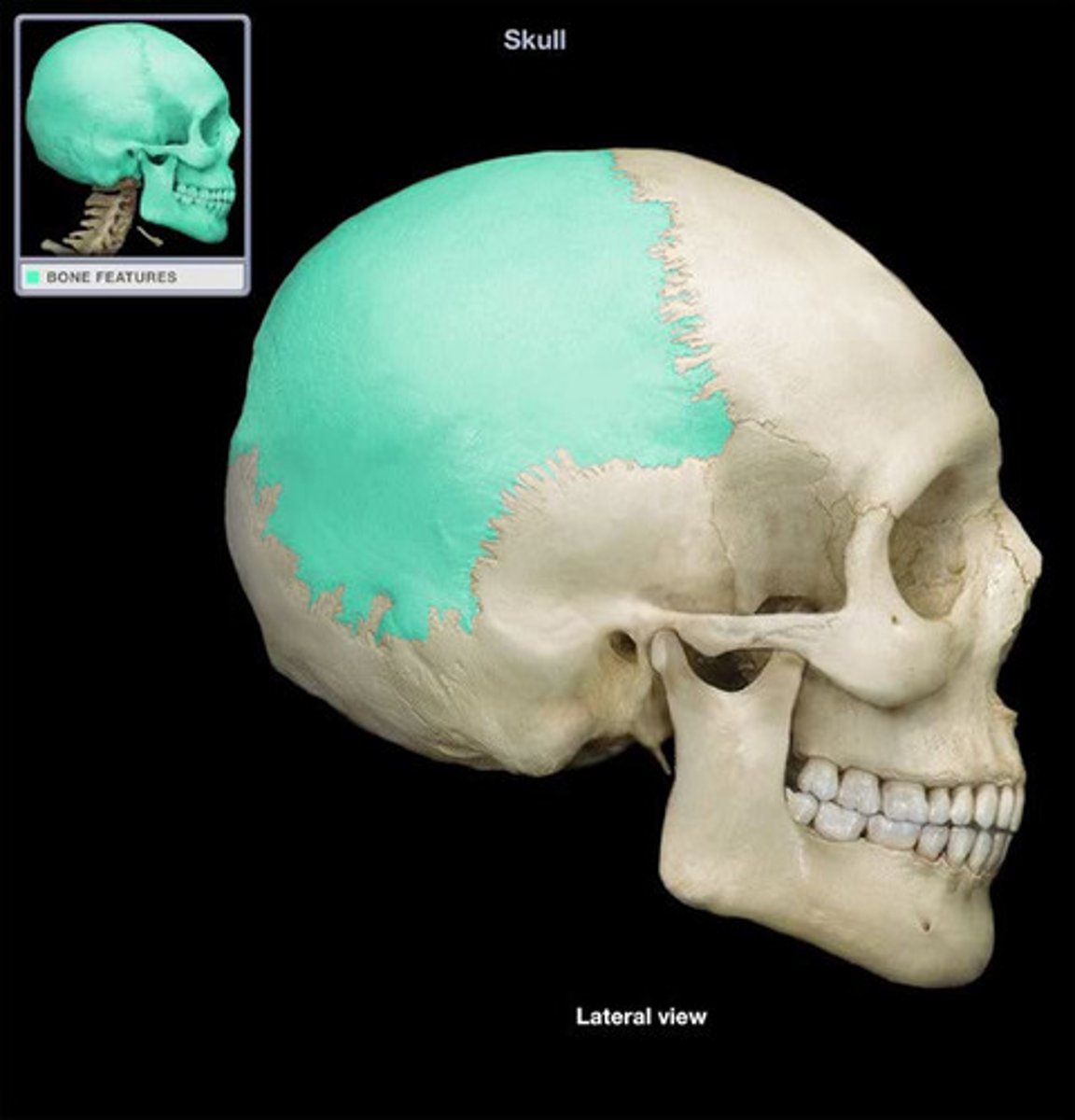
the widest portion of the skull is between the ___________ ___________ of the 2 parietal bones
parietal tubercles (eminences)
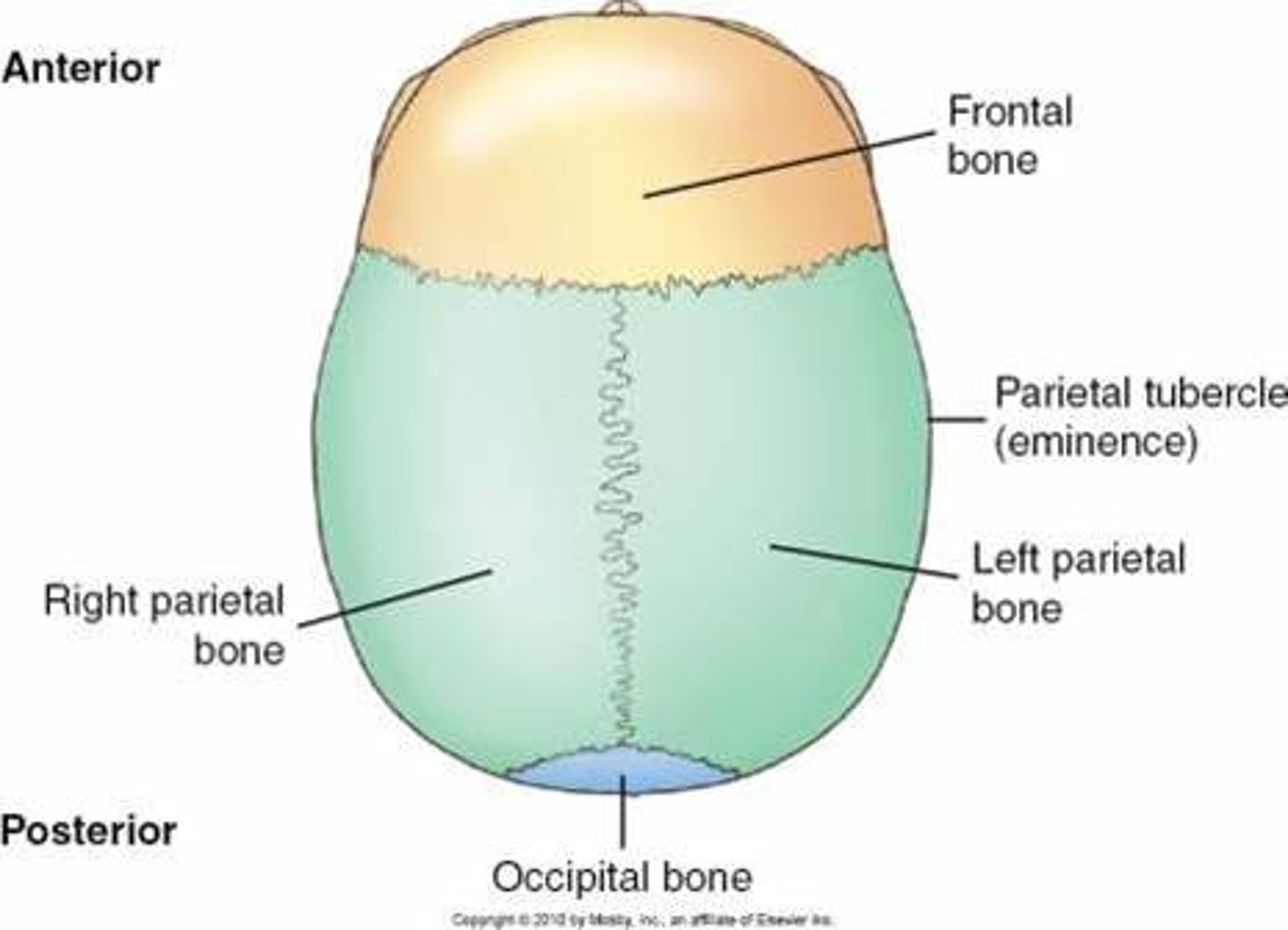
each parietal bone articulates with which 5 cranial bones?
frontal, occipital, temporal, sphenoid, and the opposite parietal bone
what bone forms the inferoposterior portion of the calvarium?
the occipital bone
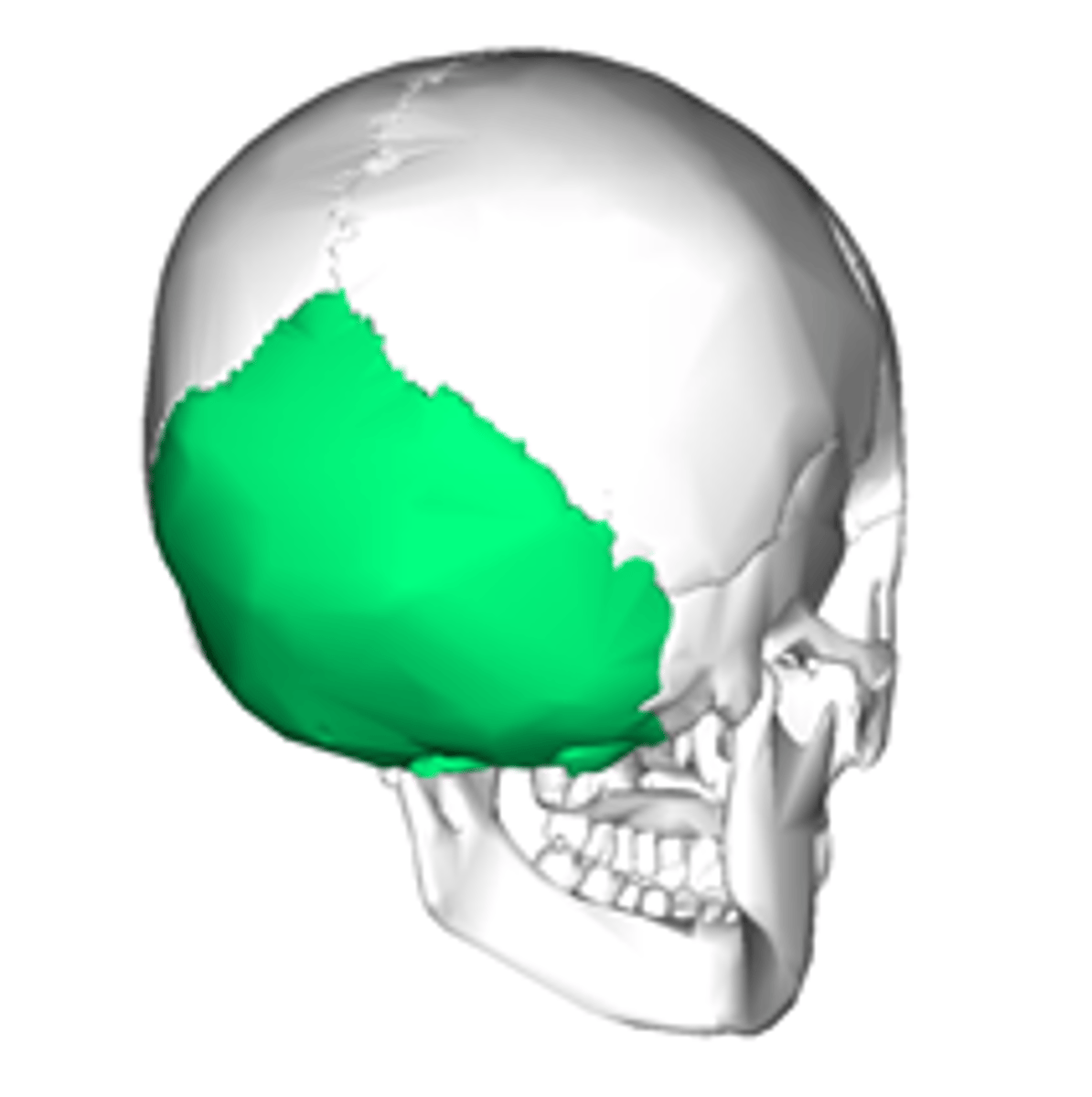
which portion of the occipital bone forms most of the back of the head and is superior to the external occipital protuberance?
the squamous portion
what is the prominent bump at the inferoposterior portion of the skull?
the external occipital protuberance (or inion)
what is the large opening at the base of the occipital bone? what passes through here?
foramen magnum, the spine
what do the 2 occipital condyles articulate with and what is that joint formed?
depressions on the first cervical vertebra, the atlantoccipital joint
what bones does the occipital bone articulate with?
the 2 parietals, 2 temporals, sphenoid, and atlas
what do the temporal bones house?
the delicate organs of hearing and balance
the _______________ _____ meets the _____________ ____________ of the zygomatic bone to form the zygomatic arch
zygomatic process, temporal process
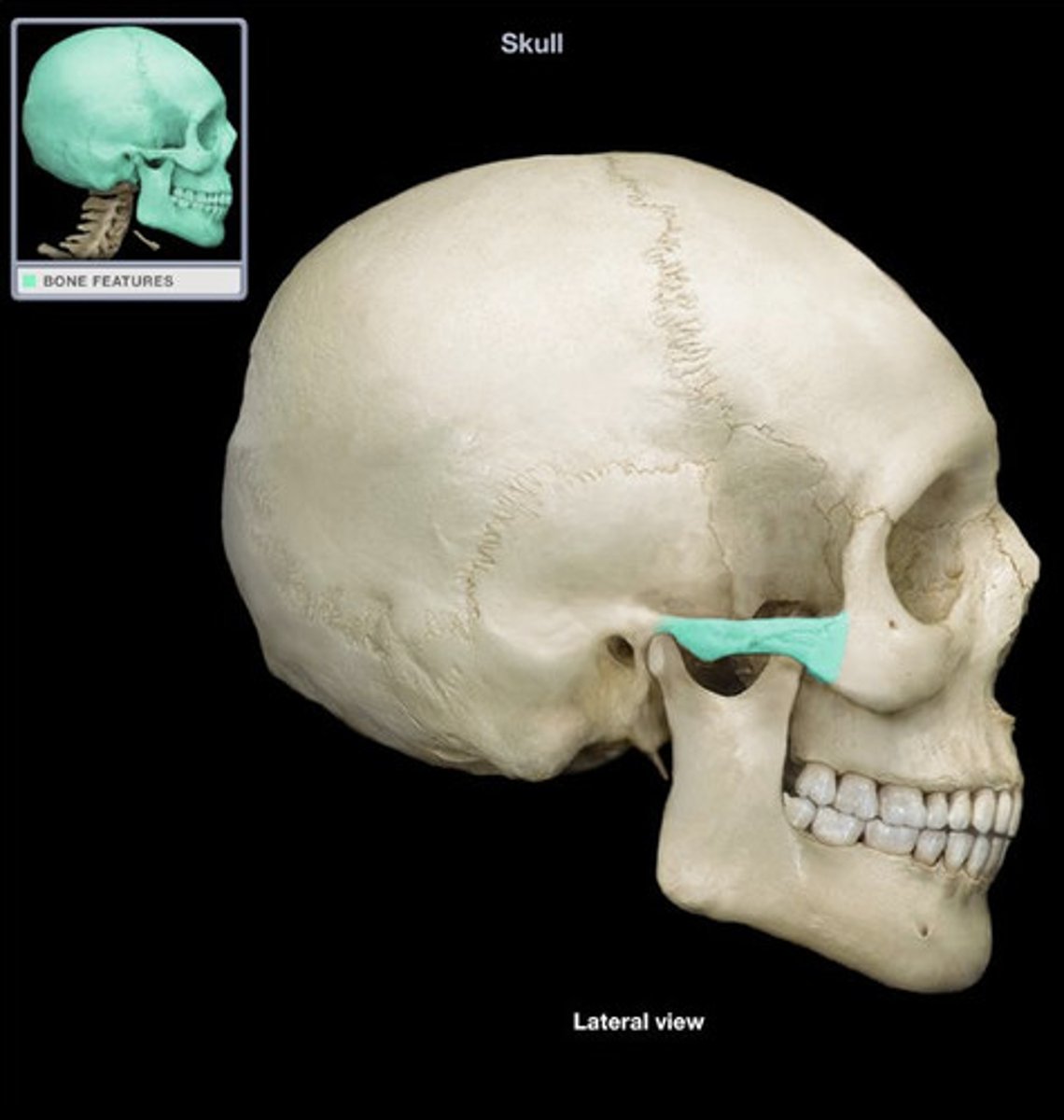
the temporomandibular (TM) fossa is _______ to the zygomatic process and ___________ to the EAM
inferior, anterior
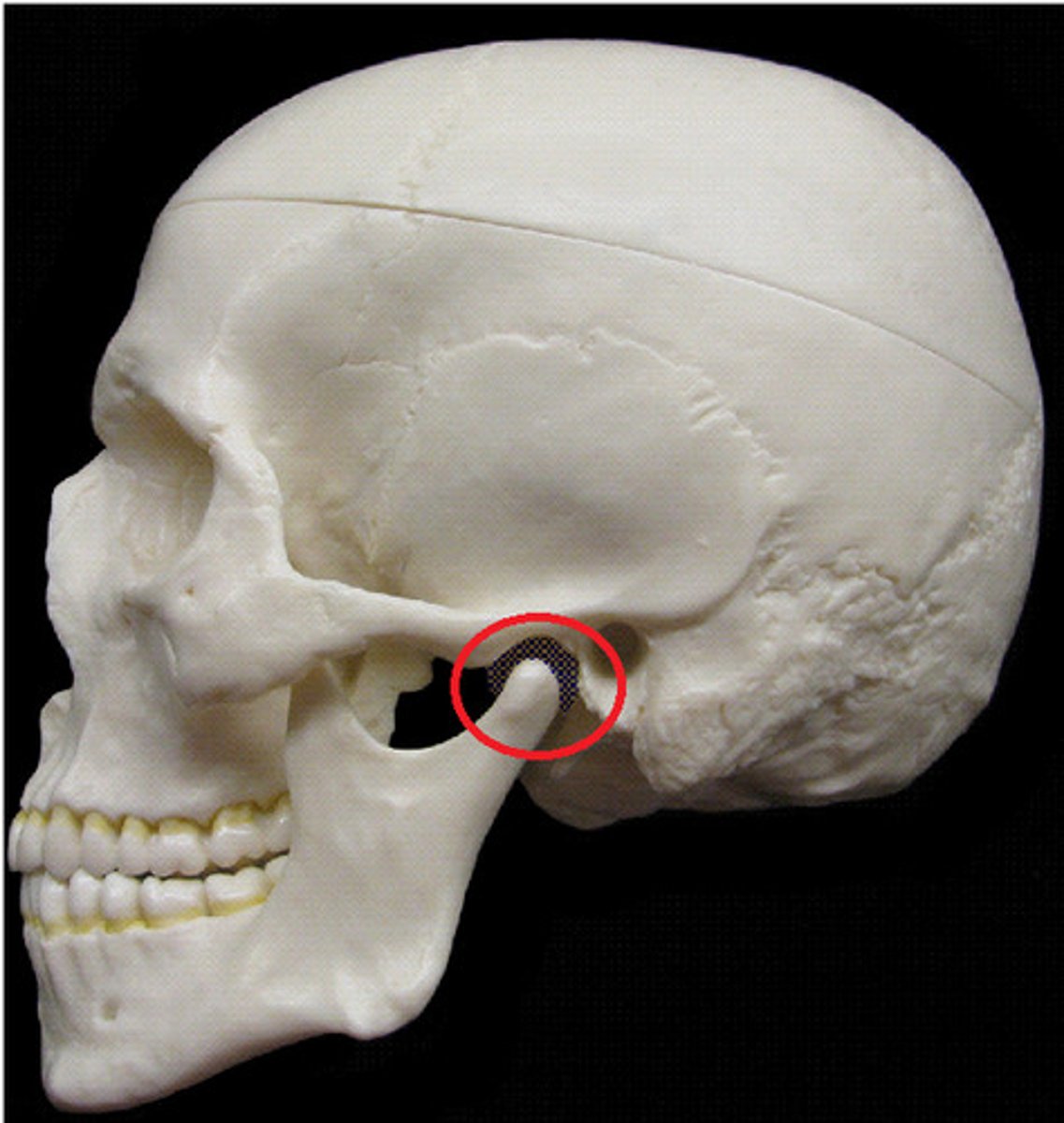
the styloid process is __________ to the mandible and ____________to the EAM
inferior, anterior
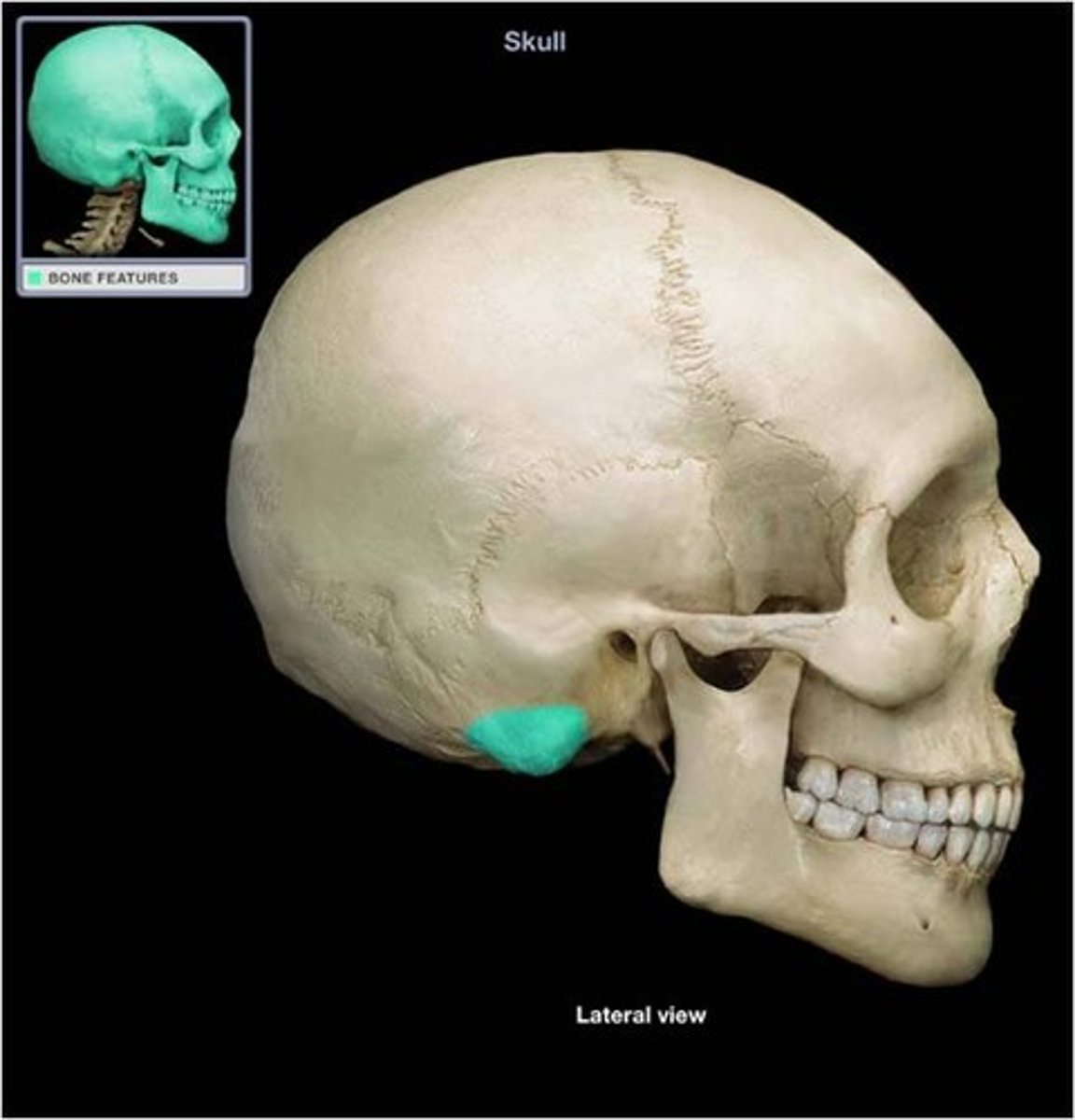
what are the 3 parts of the temporal bones?
squamous portion, mastoid portion, and petrous portion
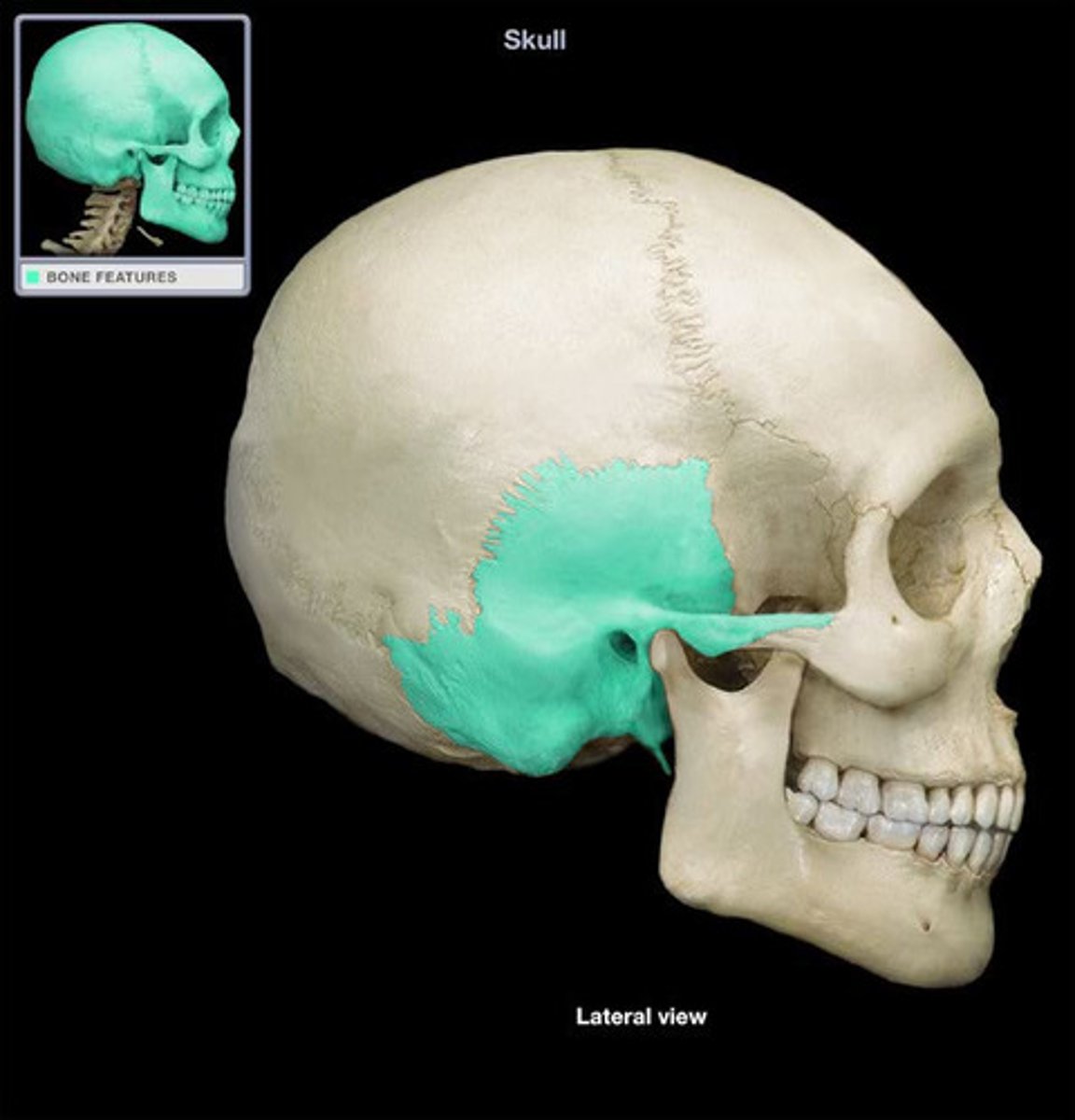
what is the thin and most vulnerable portion of the entire skull to fracture?
the squamous portion of the temporal bone
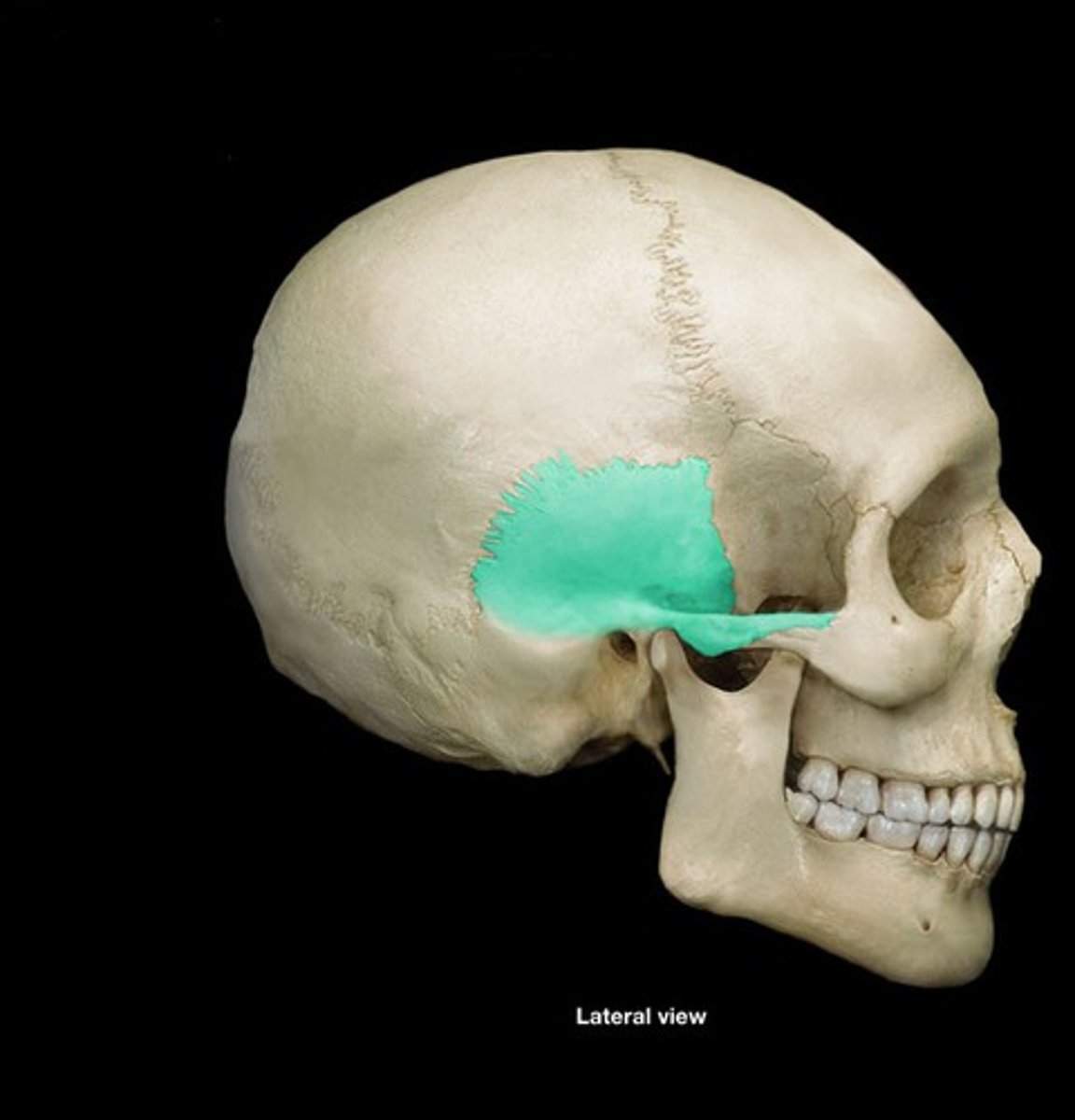
what cranial bone has a mastoid portion? what does it hold?
the temporal bone, air cells
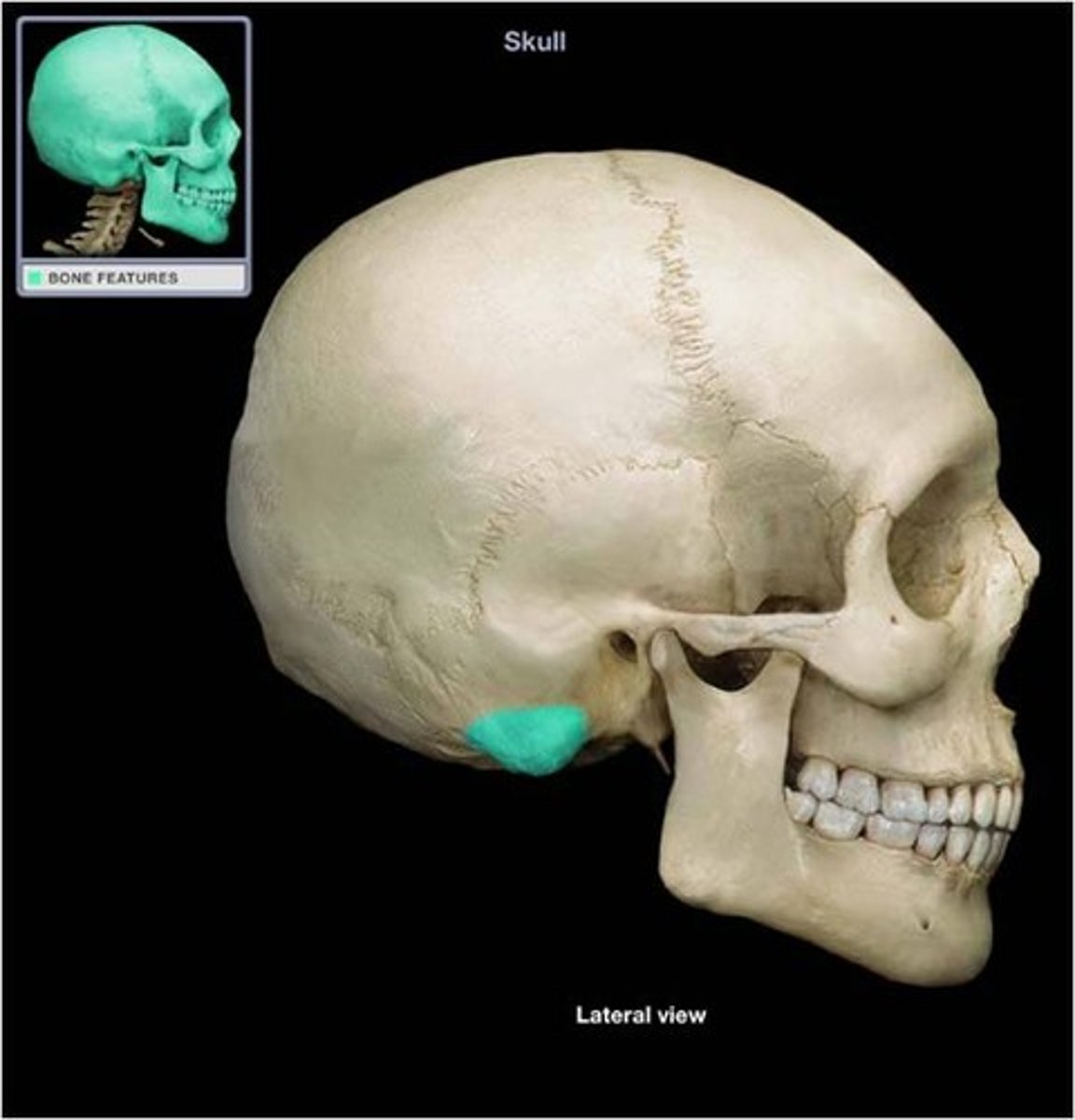
which portion of the temporal bone holds the organs of hearing and equilibrium?
the petrous portion (AKA the petrous pyramid or pars petrosa)
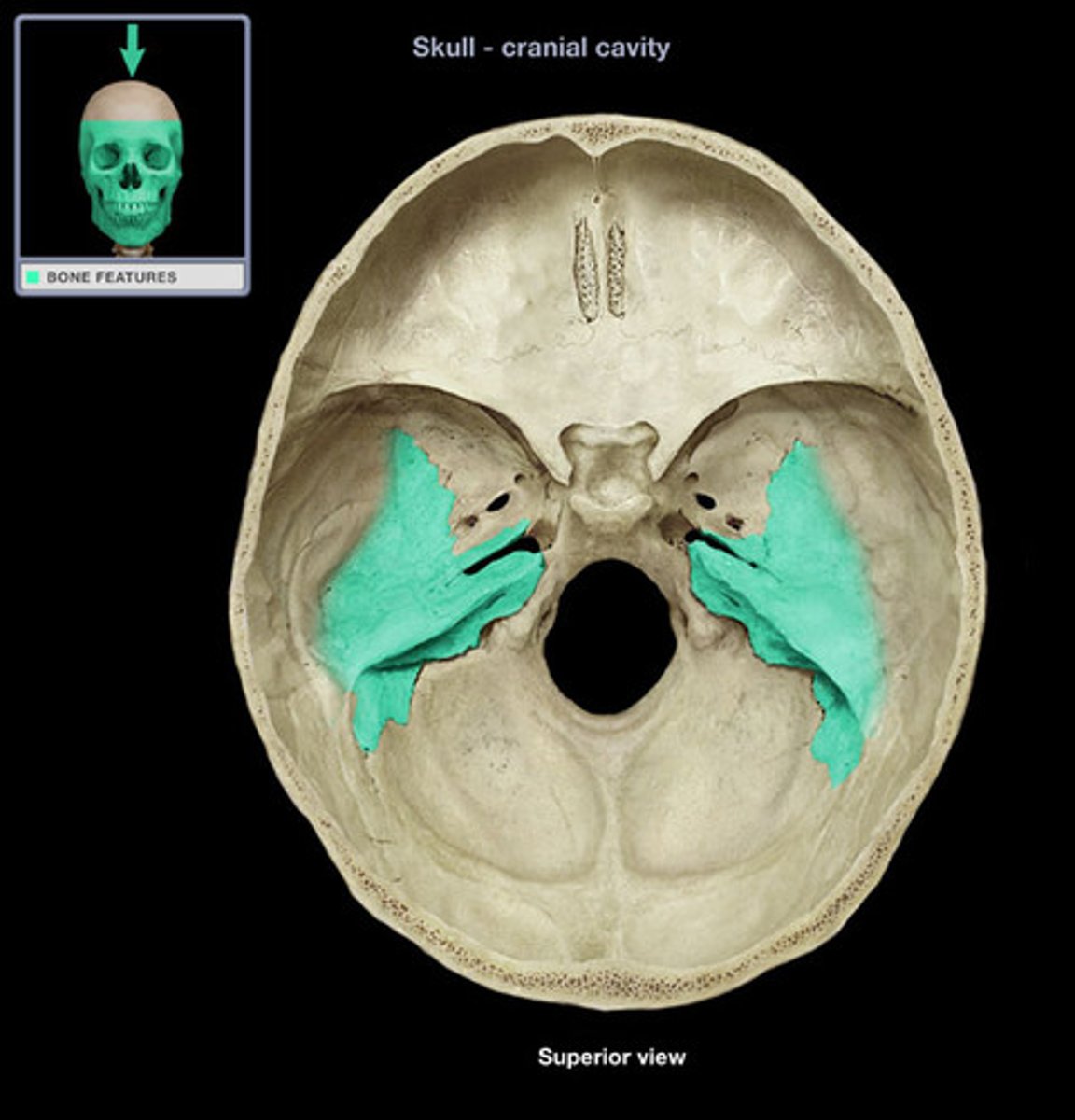
the upper border of the petrous pyramid is called the _________ _________
petrous ridge (B in the image)
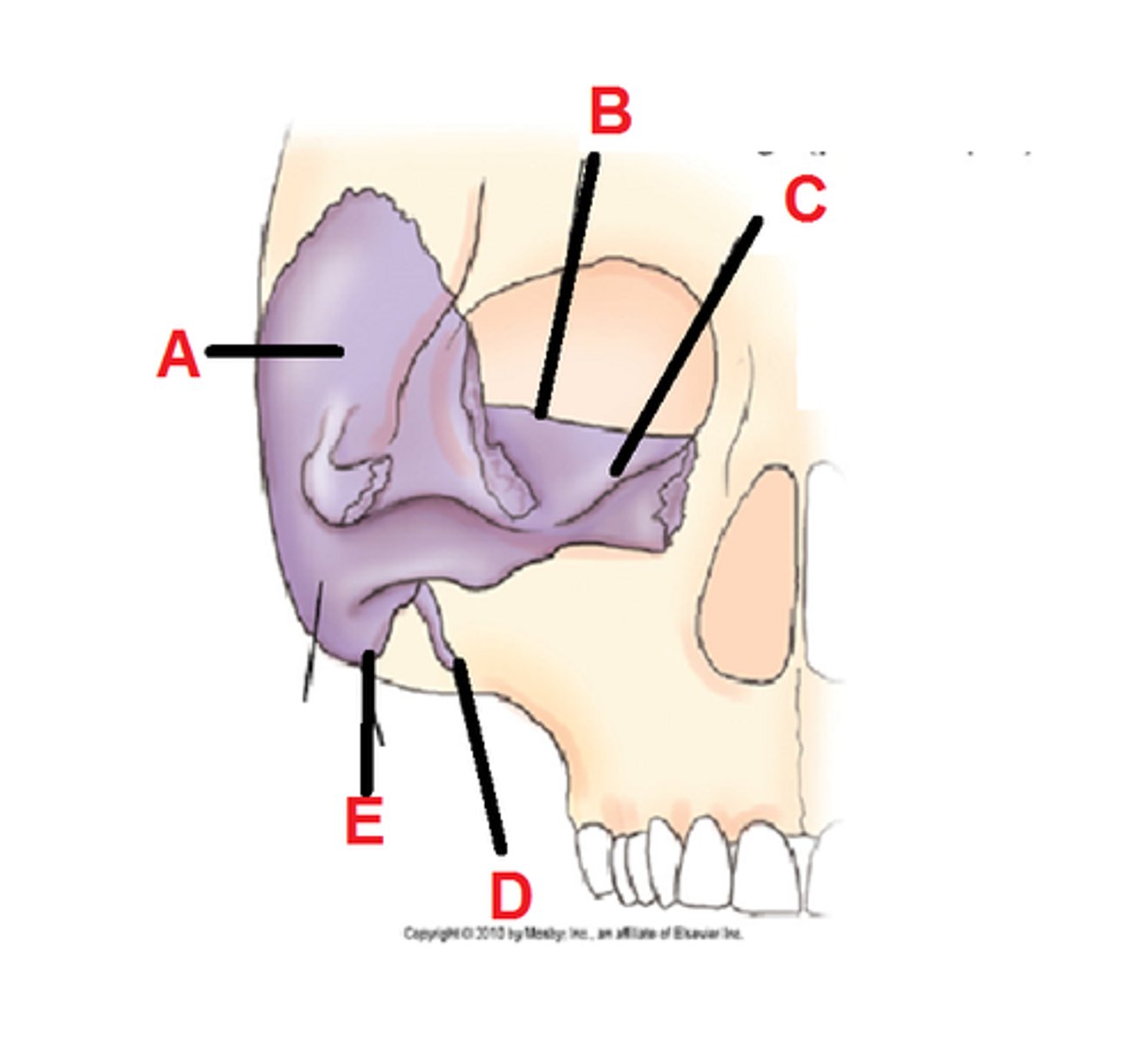
the petrous ridge corresponds to the level of the ______________
TEA (top of ear attachment)
the _________ ___________ _________ serves to transmit the nerves of hearing and equilibrium
internal acoustic meatus
what 3 cranial bones does the temporal bone articulate with?
the parietal, occipital, and sphenoid bones
which cranial bone forms the anchor for the other 7 cranial bones?
the sphenoid bone
what is contained within the body of the sphenoid bone?
the sphenoid sinus
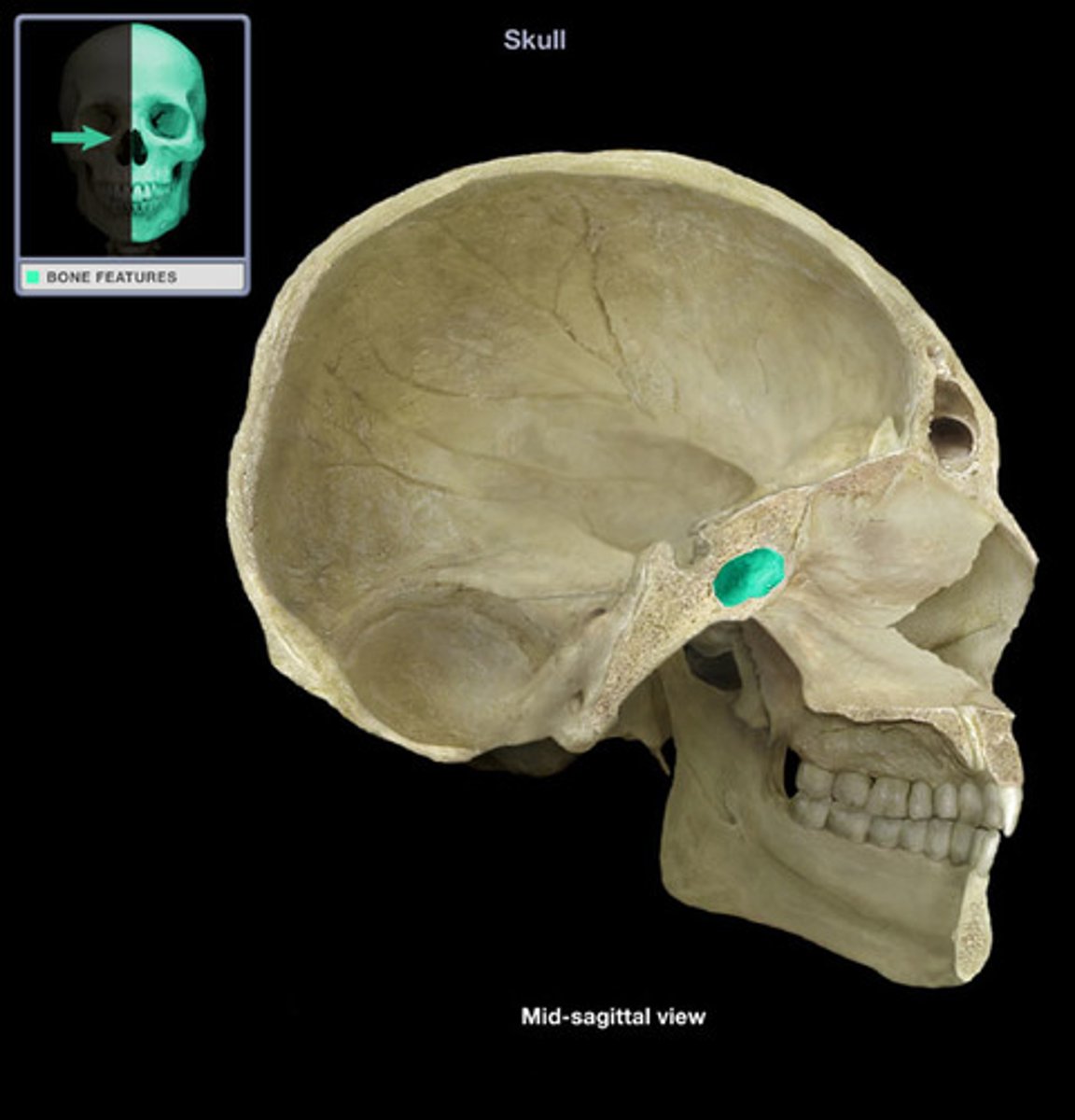
what cranial bone is the sella turcica a part of and what does it protect?
sphenoid bone, the pituitary gland
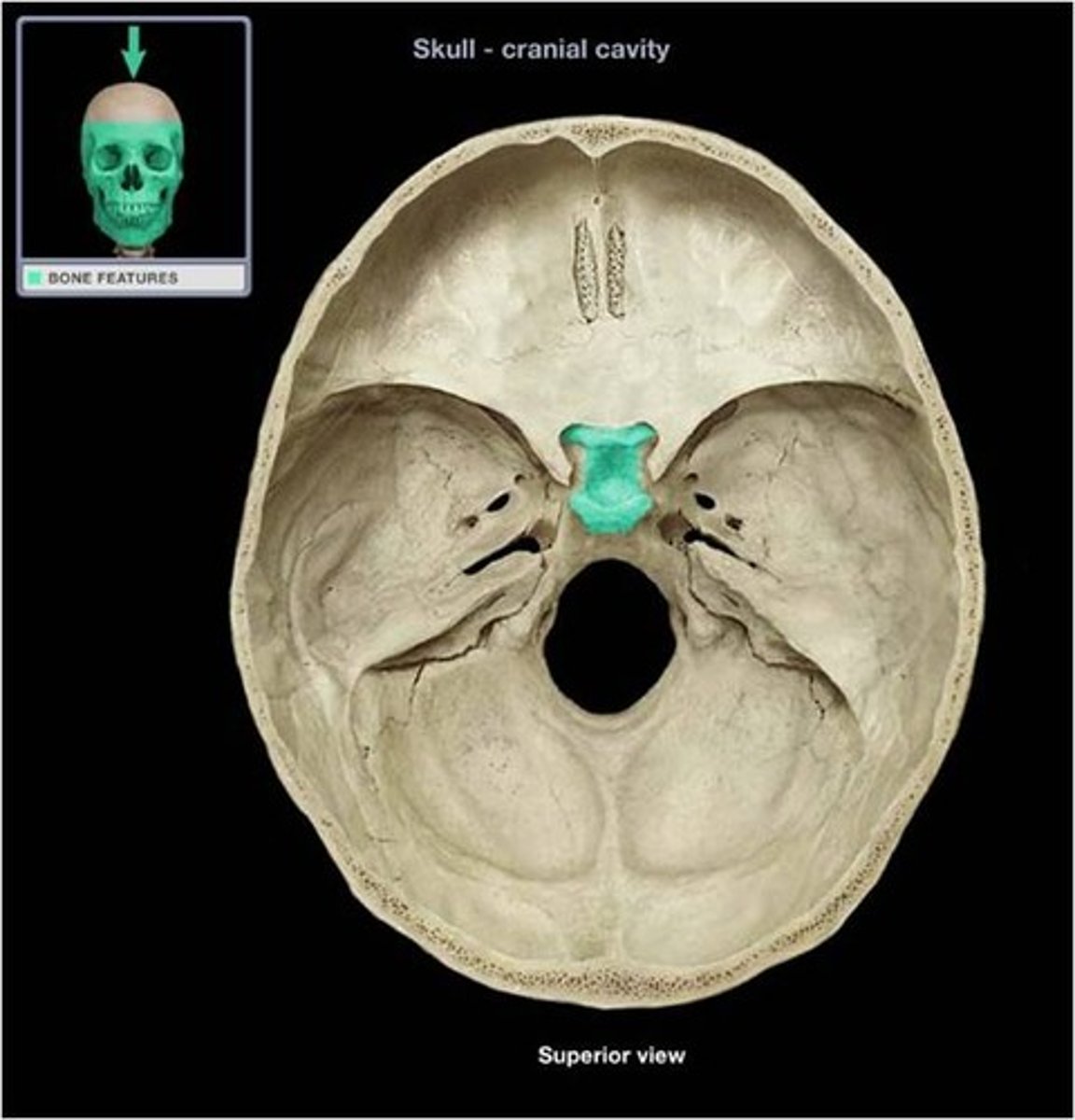
the posterior aspect of the sella turcica is known as what?
dorsum sellae
what cranial bone is the clivus a part of and what does it for a base of support for?
sphenoid bone, the pons and basilar artery
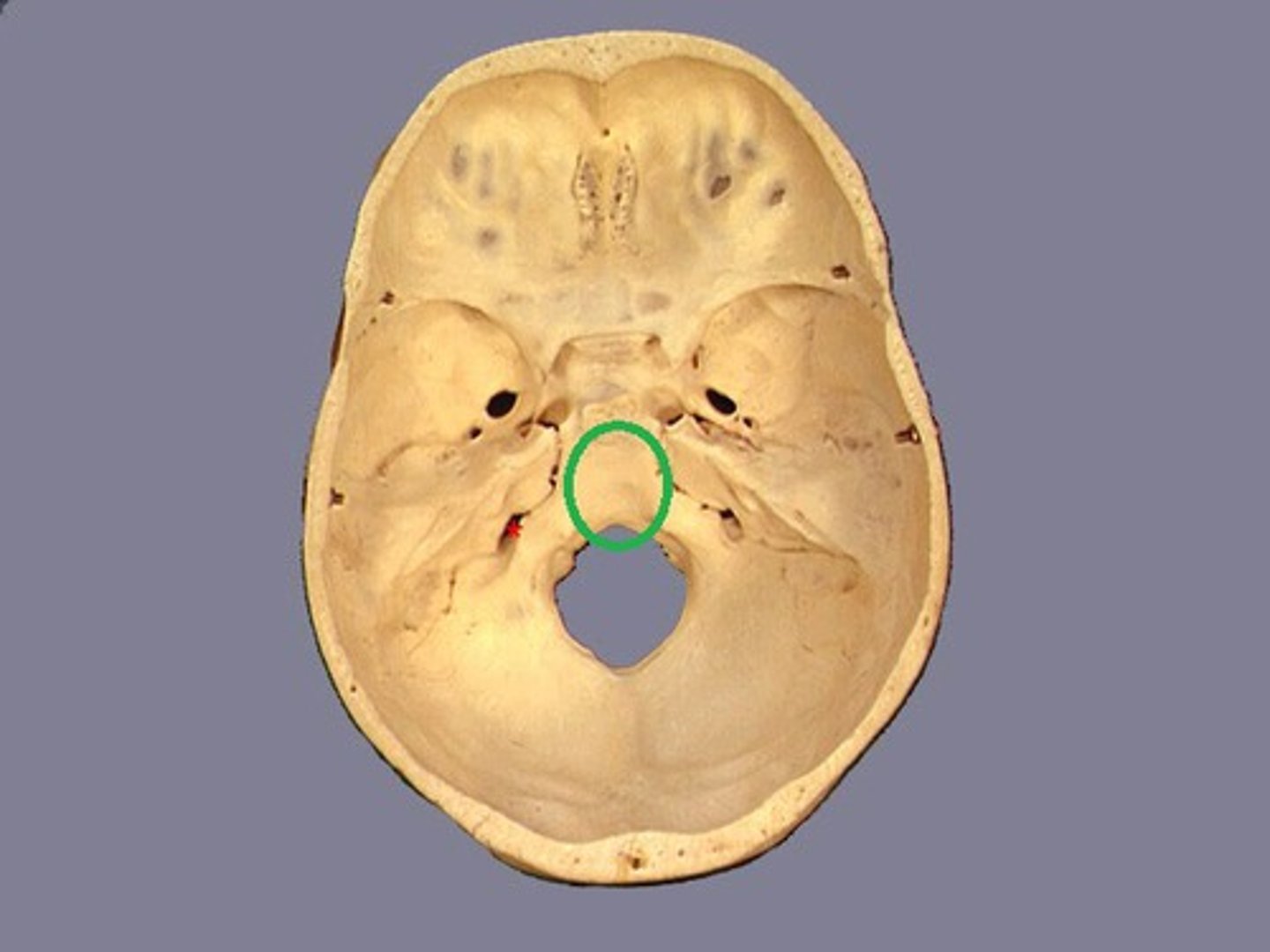
the bilateral lesser wings of the sphenoid bone end medially as what?
the anterior clinoid processes
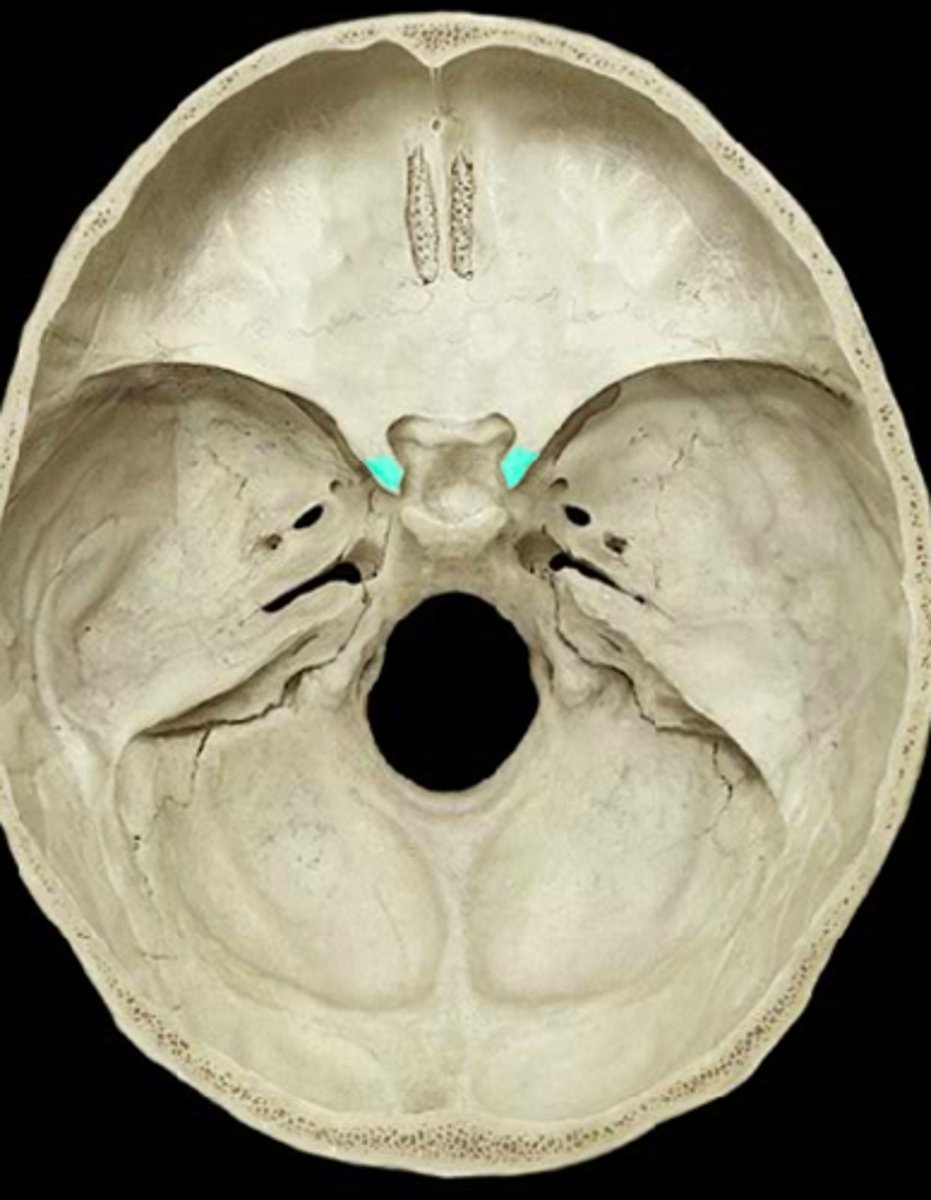
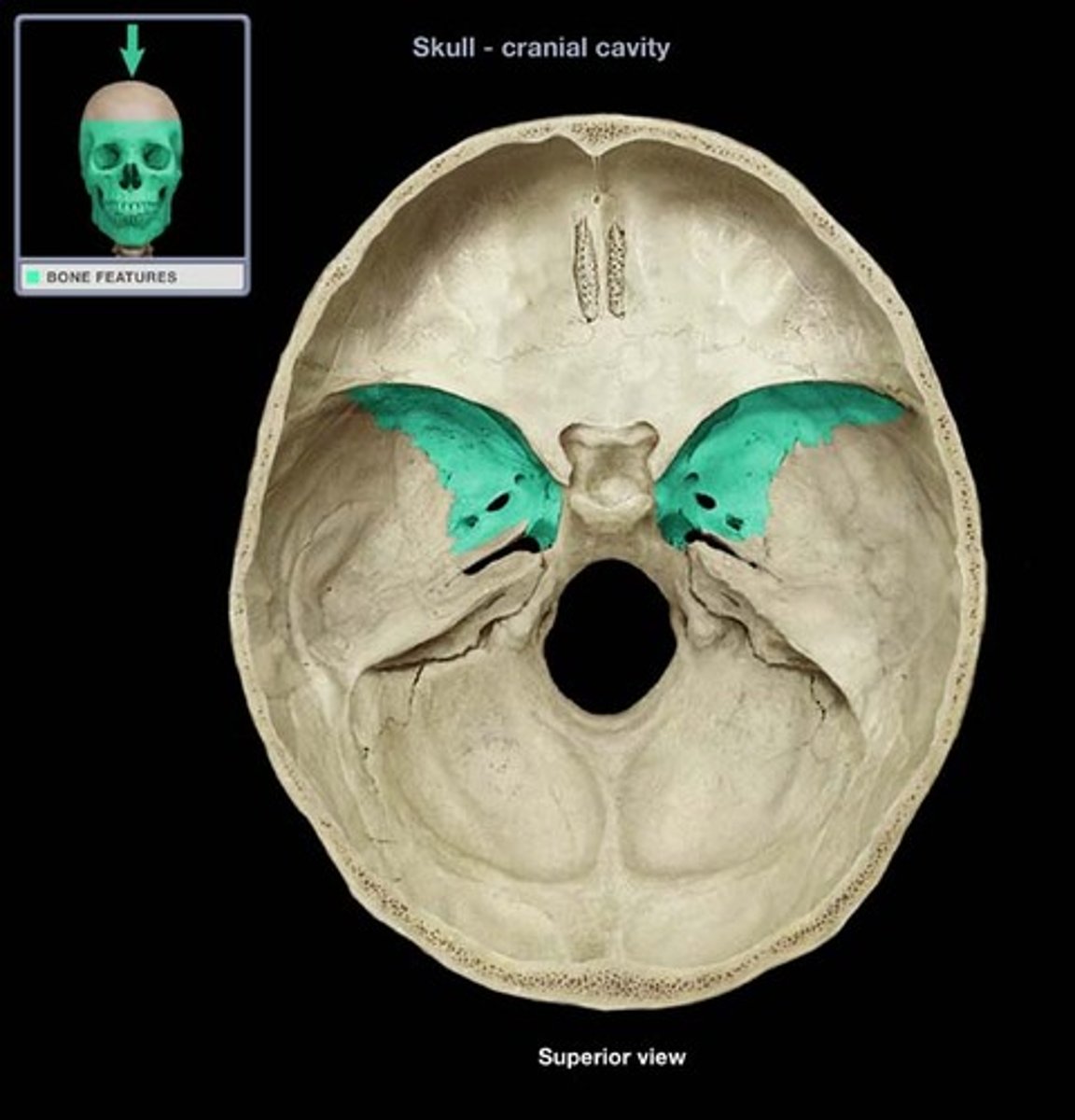
the ____________ __________ of the sphenoid bone extend laterally and form a portion of the floor and sides of the cranium
greater wings
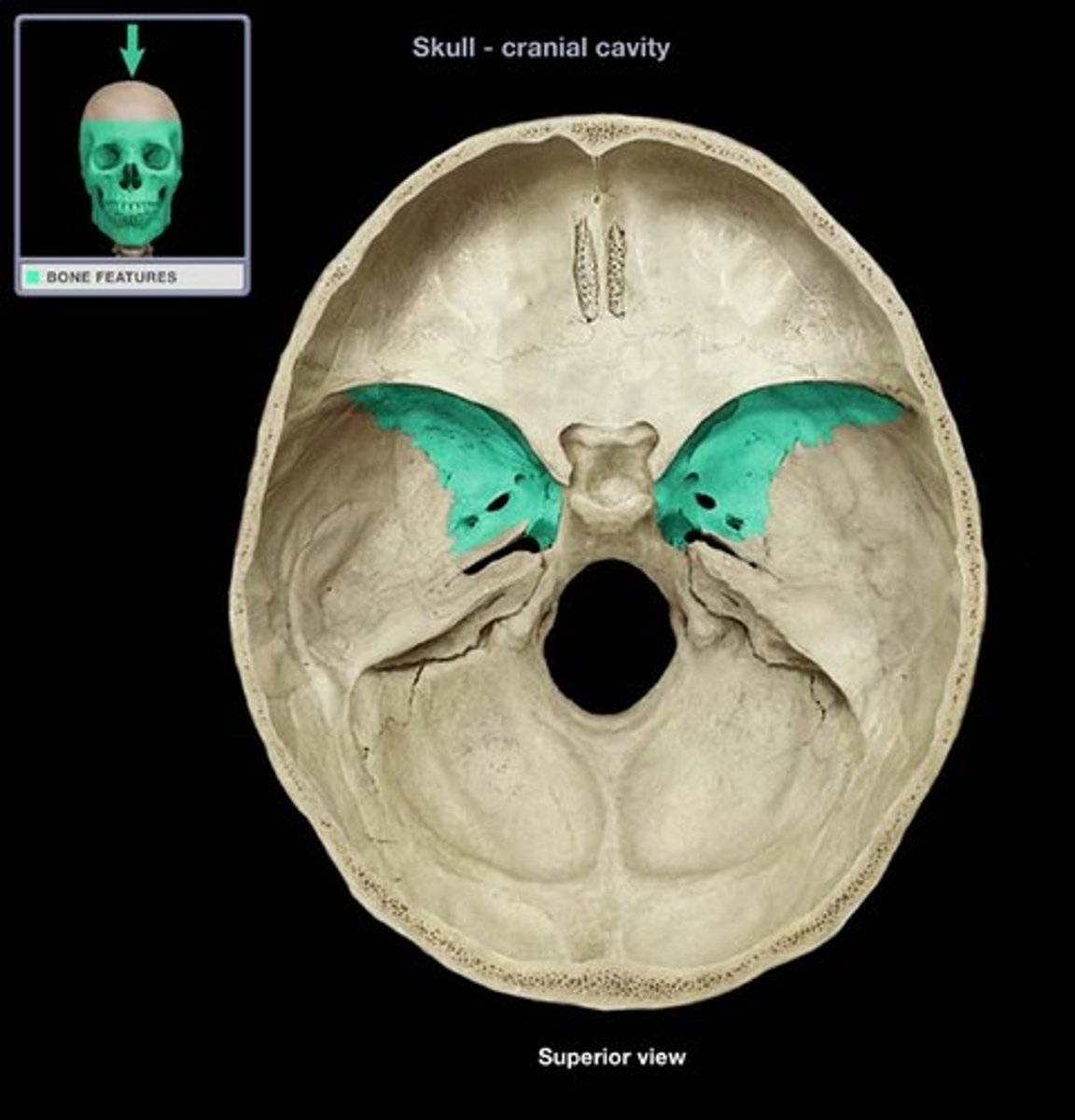
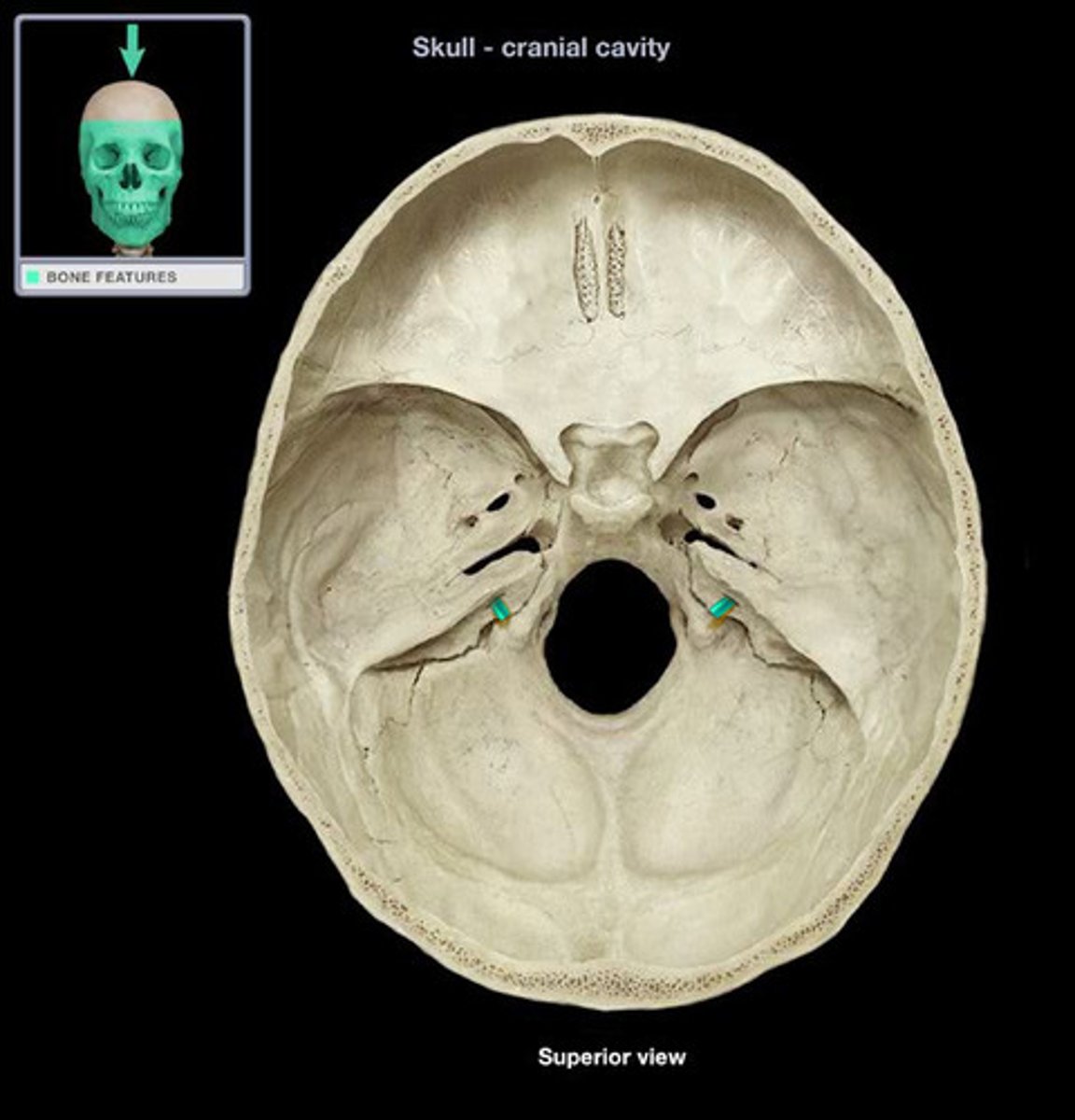
what are the 3 small foramina in the greater wings of the sphenoid bone, allowing passage of cranial nerves?
foramen rotundum, foramen ovale, foramen spinosum (3 small openings in the image)
the __________ clinoid processes are larger and spread farther apart than the _________ clinoid processes that extend superiorly from the dorsum sellae
anterior, posterior
the ________________ ________ leads to the optic canal and opening into the orbit for the passage of the optic nerve and certain arteries.
chiasmatic (optic) groove
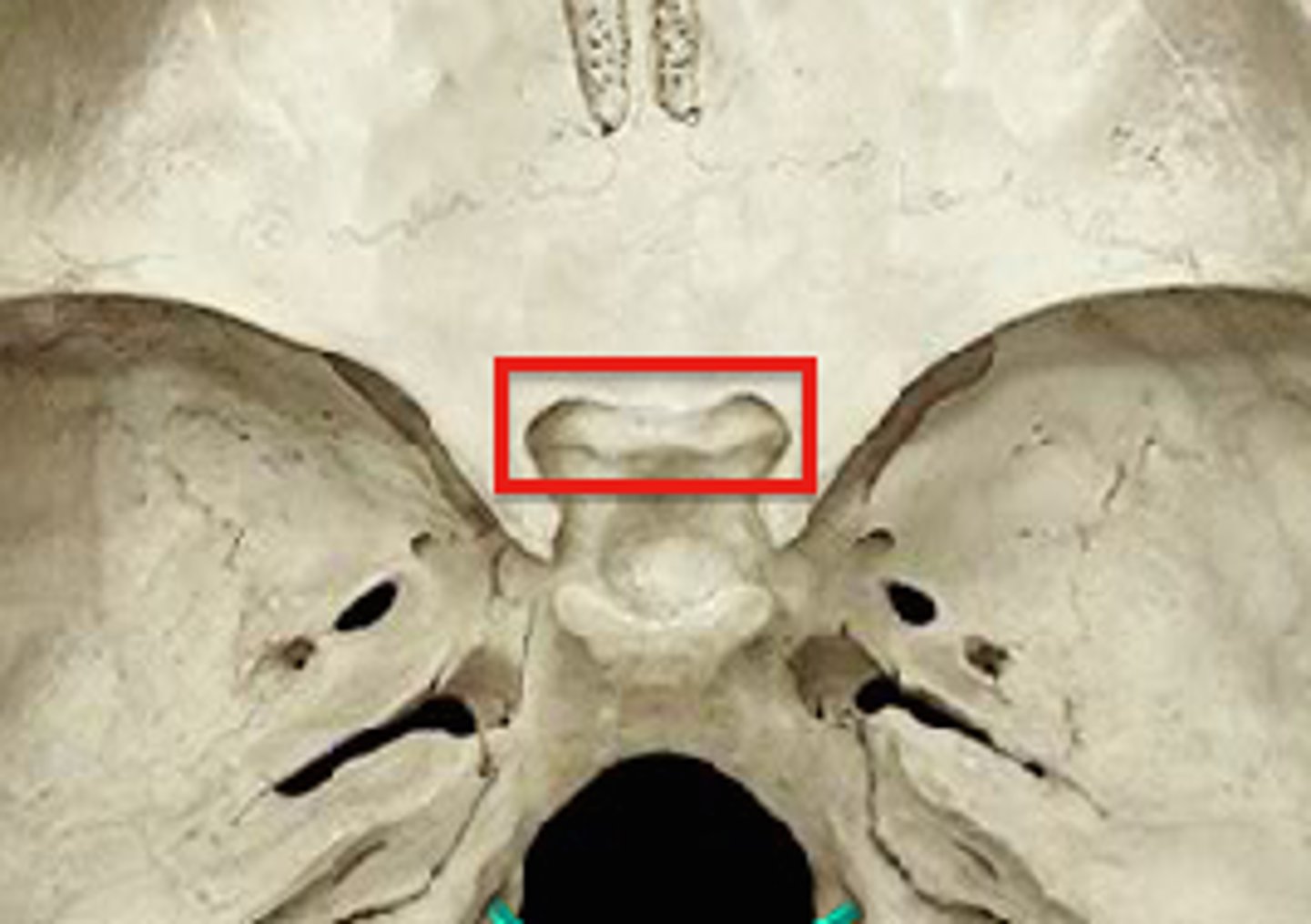
what cranial bone are the superior orbital fissures part of and what do they provide for?
the sphenoid bone, communication with the orbits for numerous cranial nerves and blood vessels
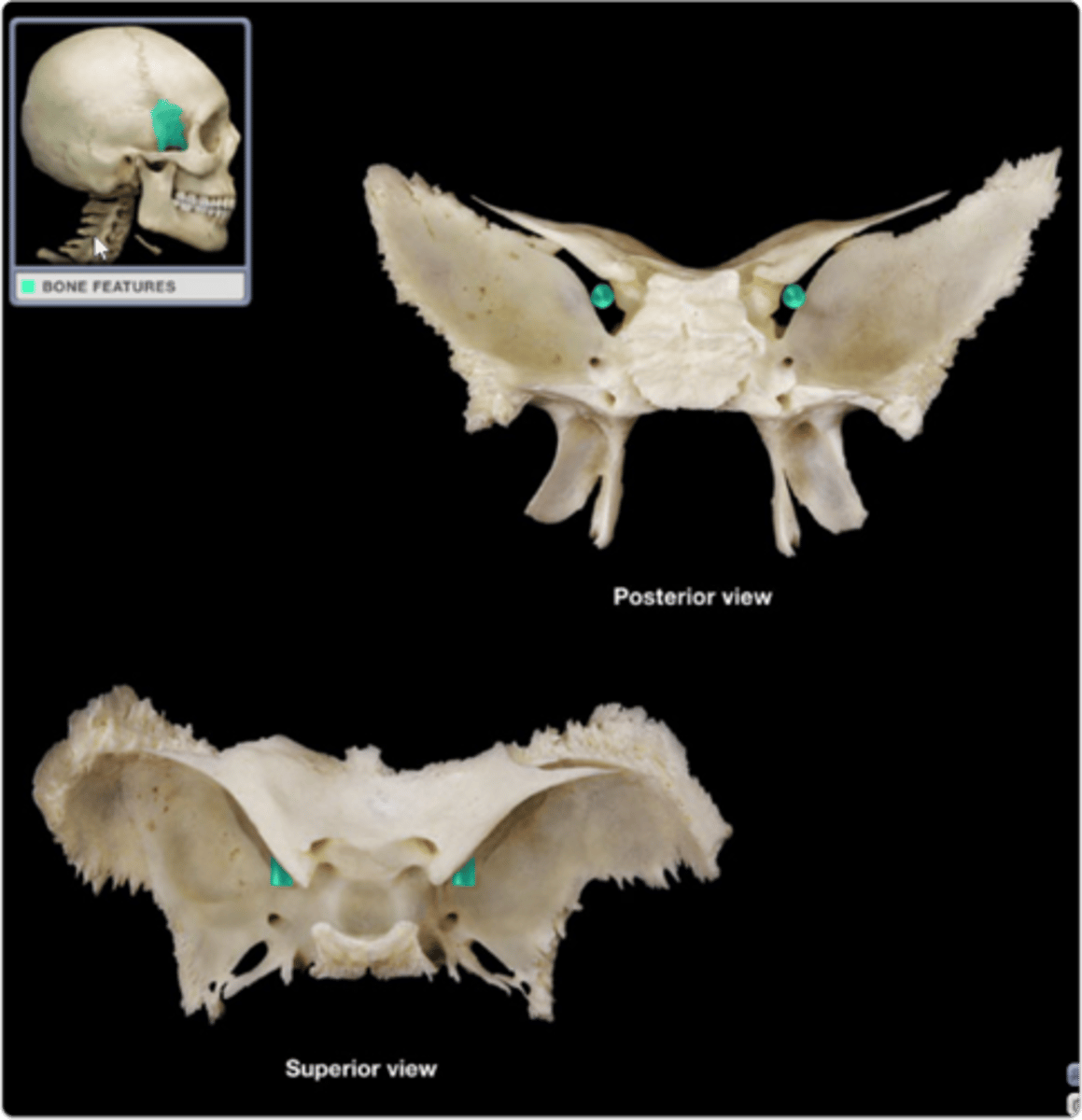
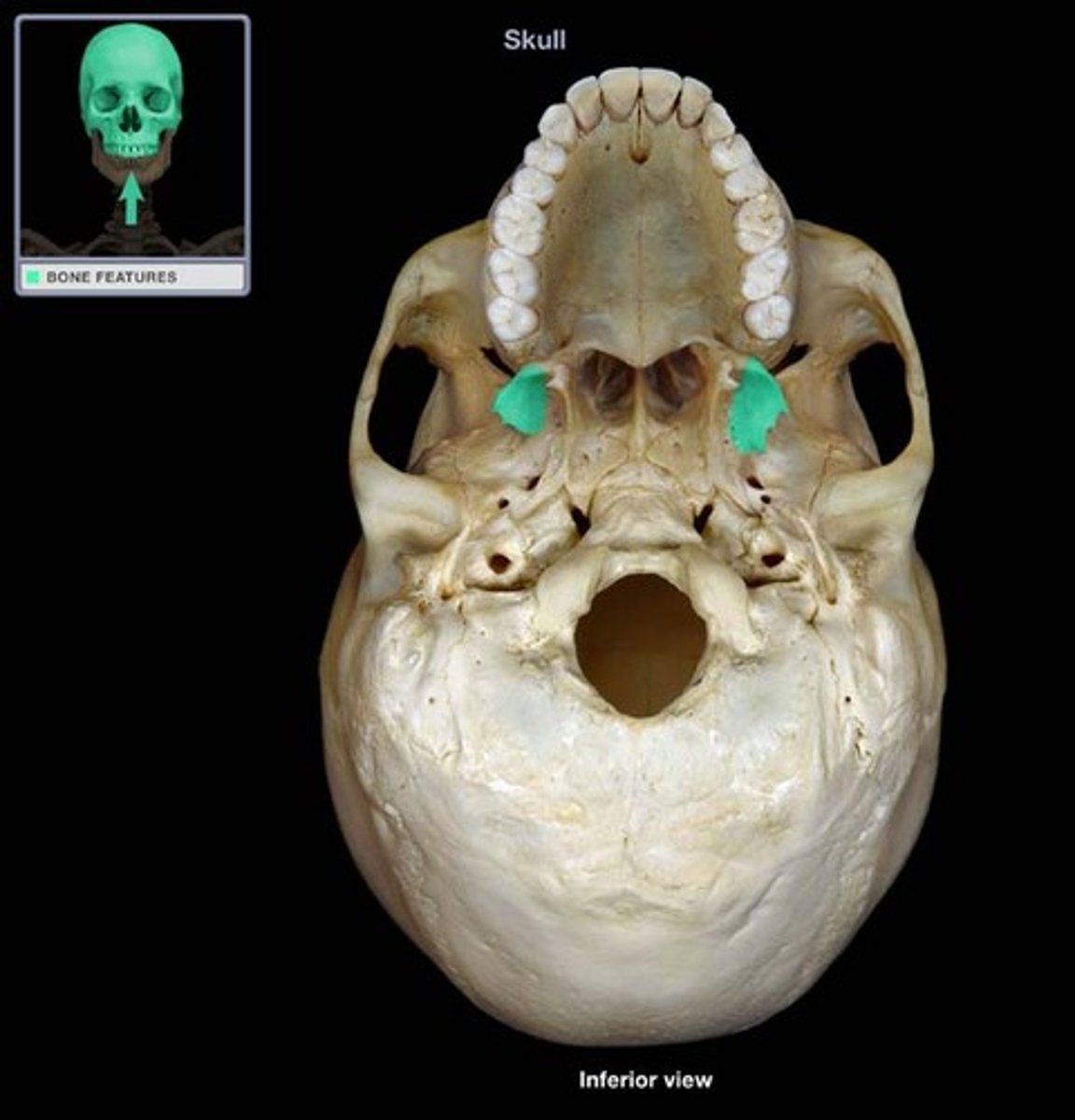
the projections from the inferior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone are 4 processes known as the medial and lateral __________ __________
pterygoid processes (or plates)
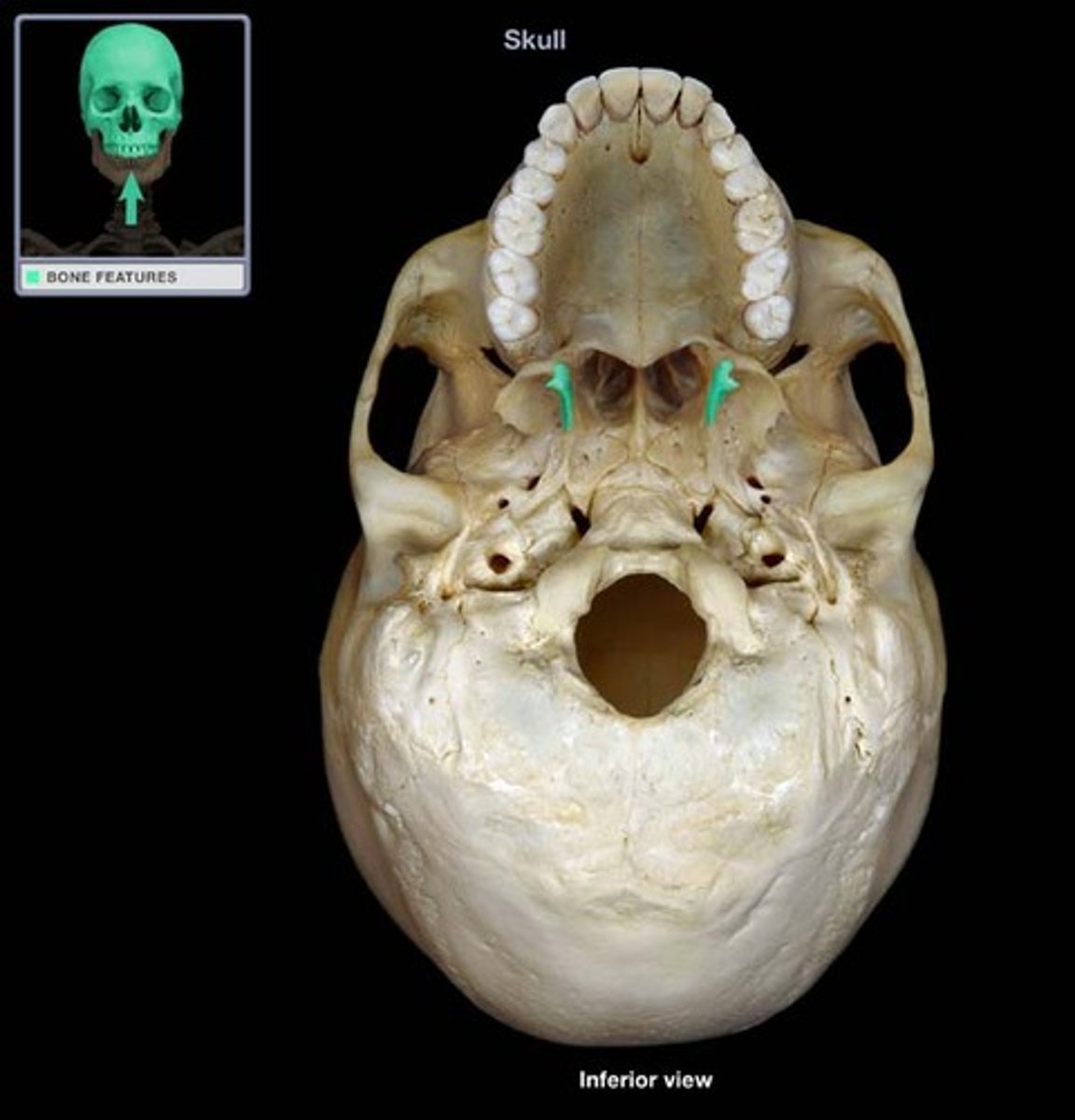
the medial pterygoid processes end inferiorly in small hook-like processes called ____________ _____________
pterygoid hamuli
what cranial bones articulate with the sphenoid bone?
all of the other 7
which cranial bone lies below the floor of the cranium?
the ethmoid bone
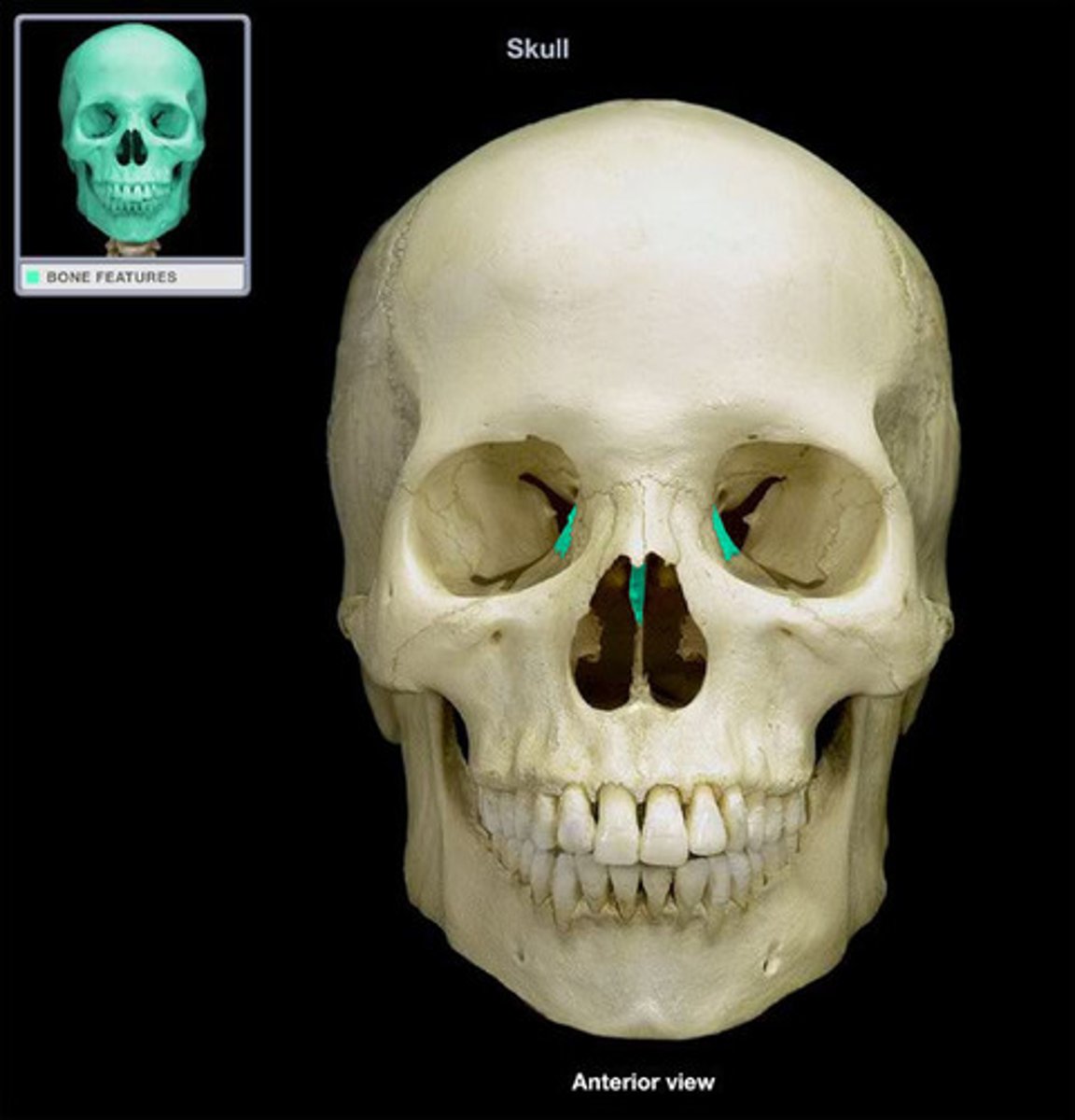
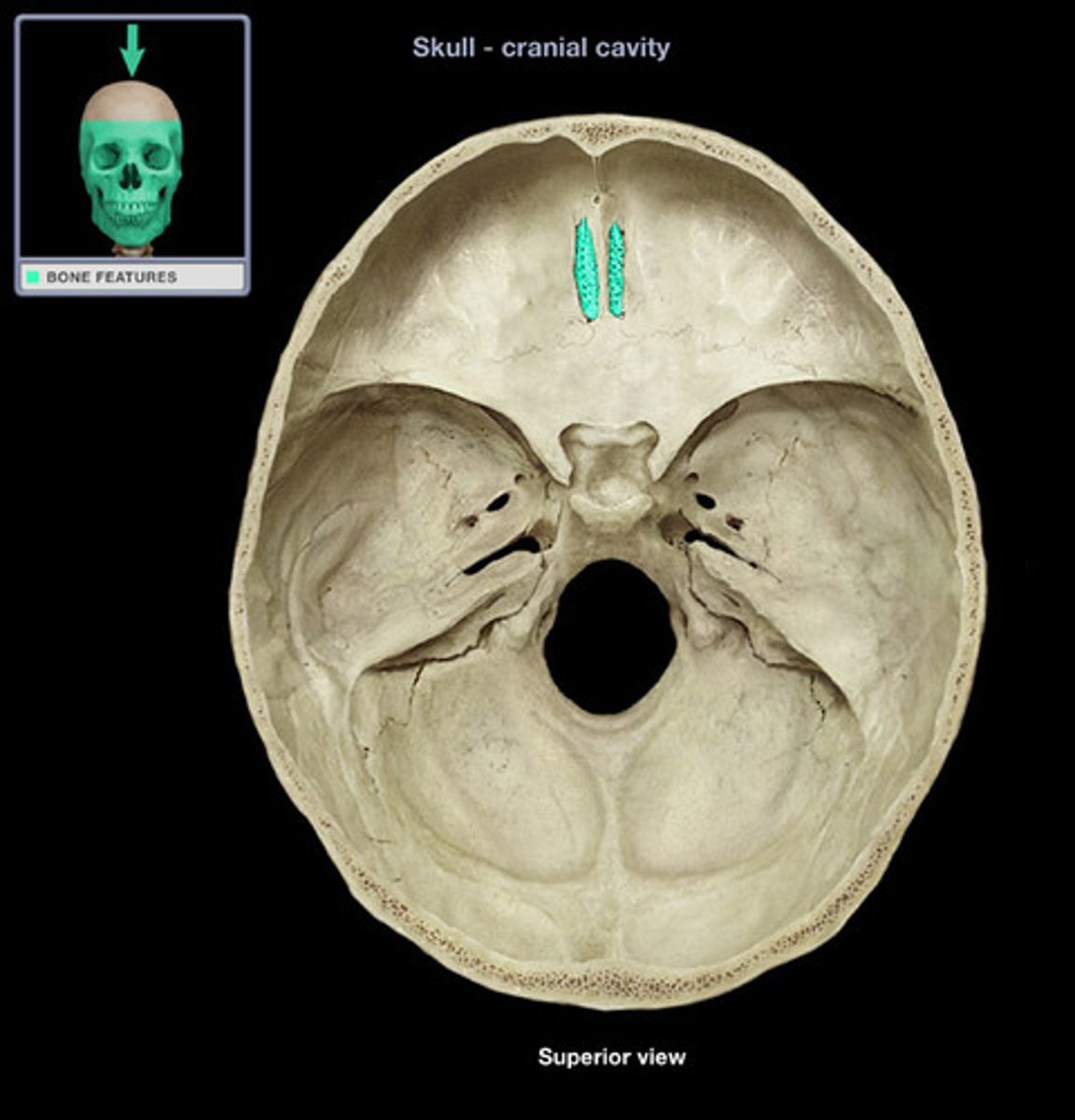
what part of the ethmoid bone contains small openings or foramina through which segmental branches of the olfactory nerves pass?
the cribriform plate
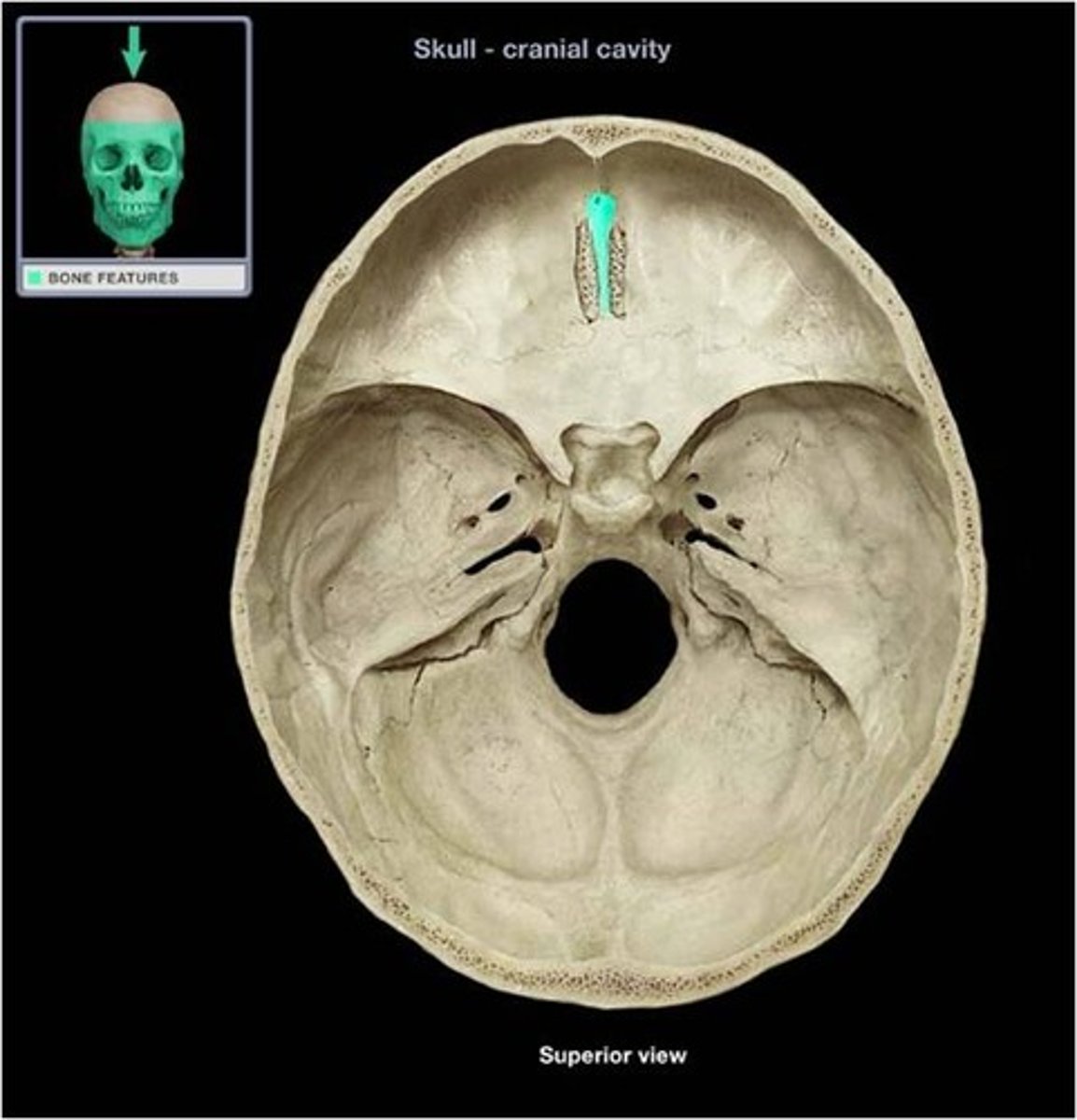
what projects superiorly from the cribriform plate?
the crista galli
what part of the ethmoid bone projects downward midline to help form the bony nasal septum?
perpendicular plate
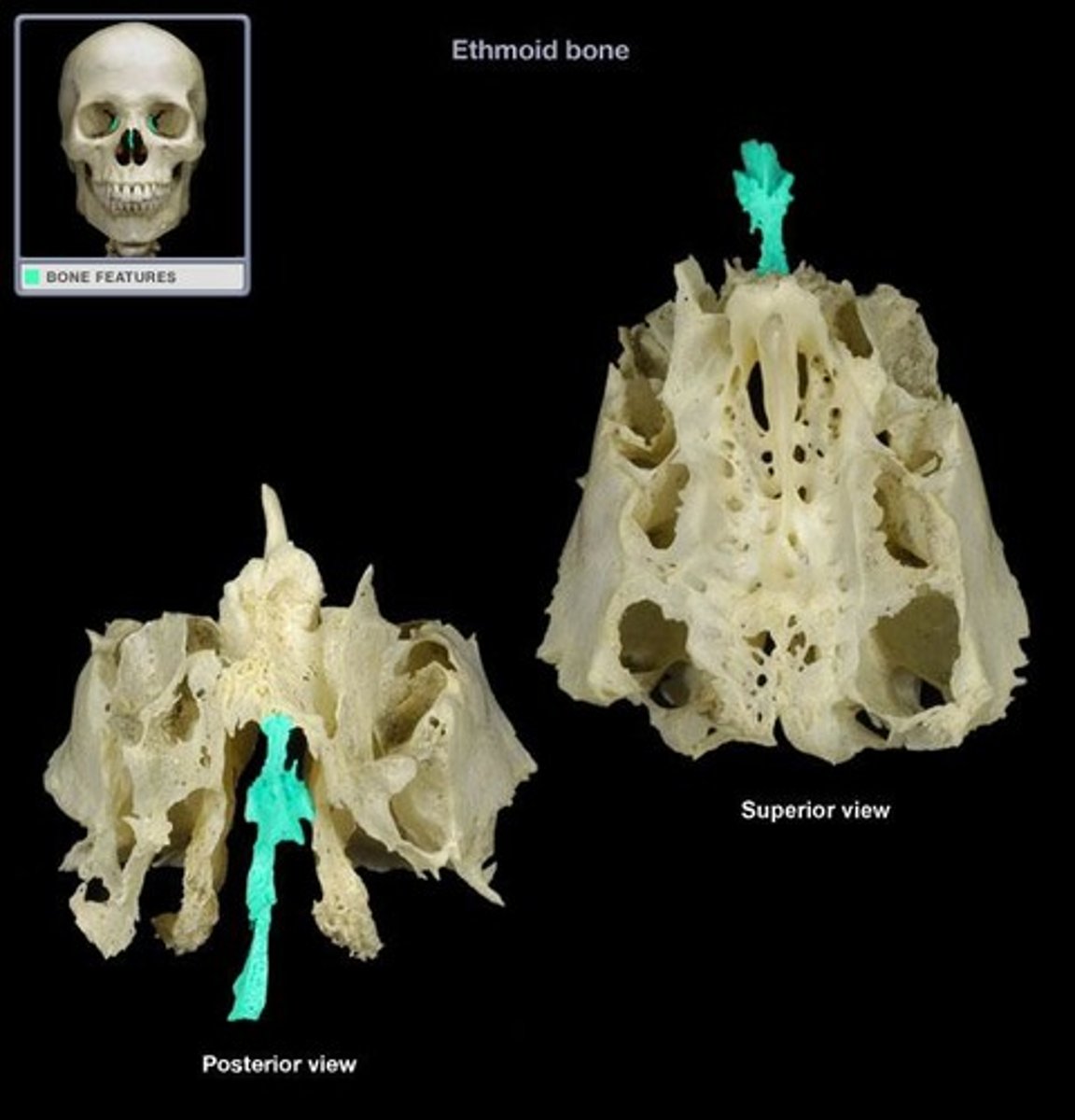
the __________ ___________ are suspended from the cribriform plate on either side of the perpendicular plate
lateral labyrinths
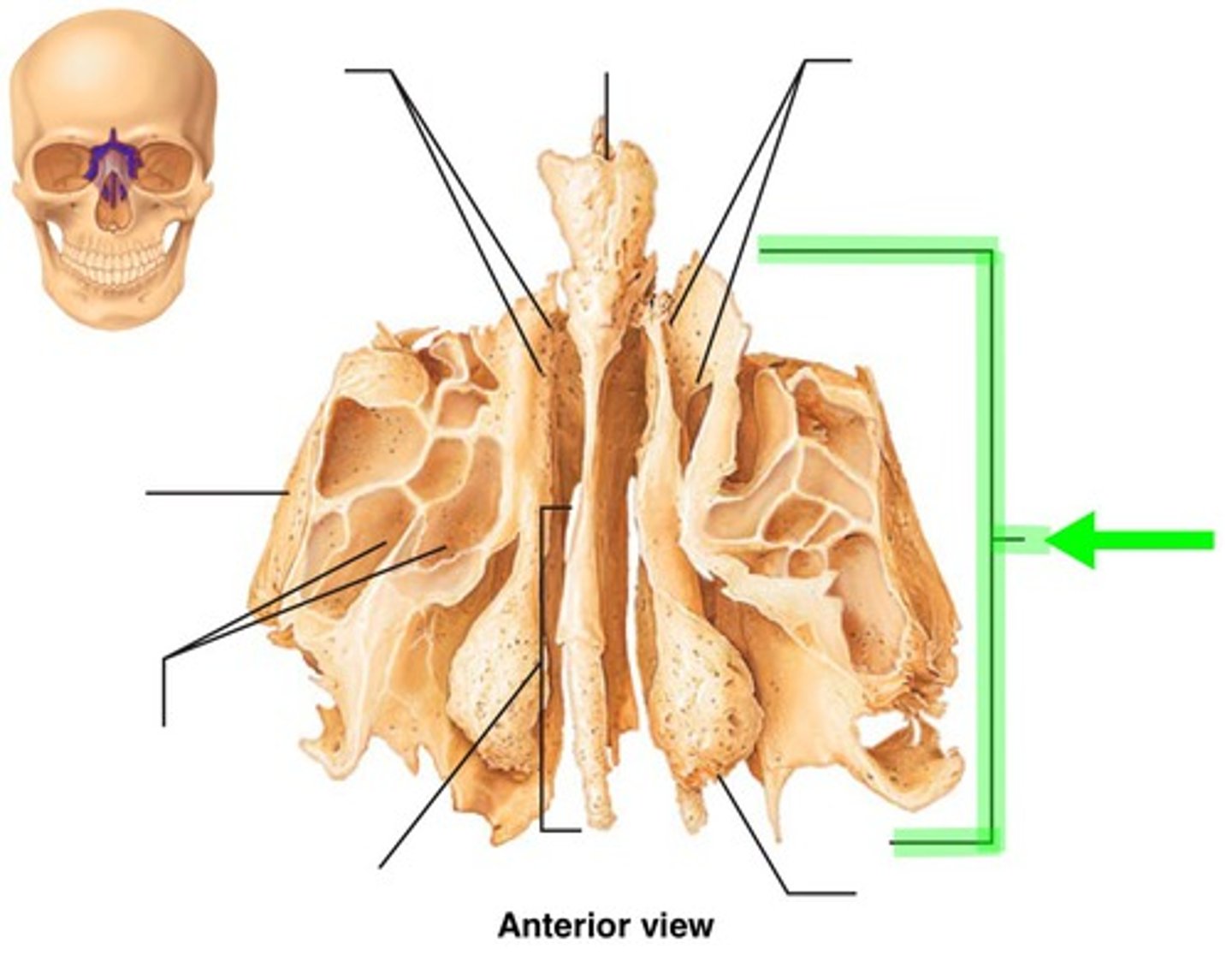
the lateral labyrinths (or masses) contain what? what do they help to form?
ethmoid air cells/sinuses, help form the medial walls of the orbits and the lateral walls of the nasal cavity
the thin, scroll-shaped projections of bone extending medially and downward from the medial wall of each labyrinth are the superior and middle __________ __________
nasal conchae (or turbinates)
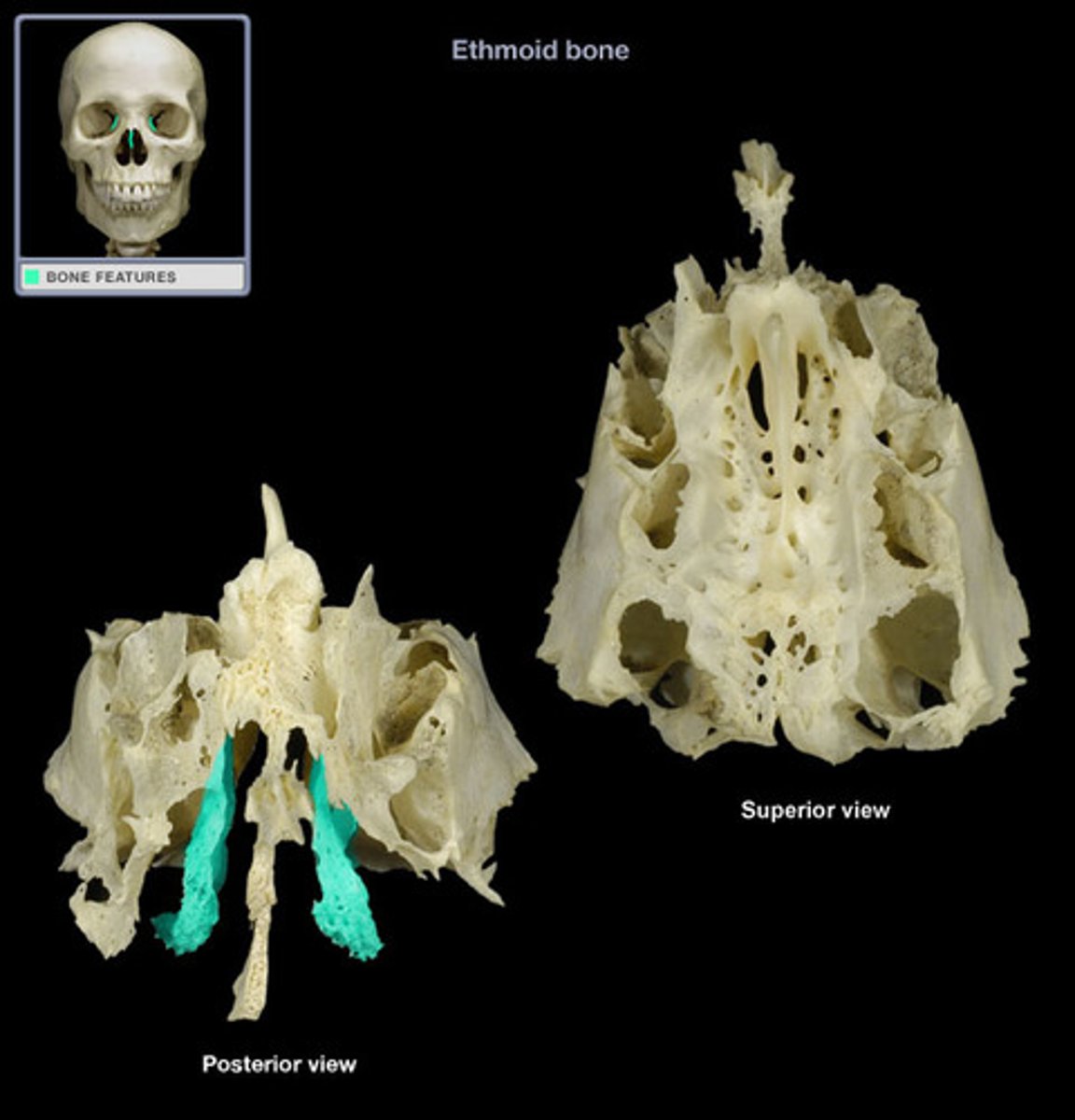
what 2 cranial bones does the ethmoid bone articulate with?
frontal and sphenoid
the frontal bone has a cavity directly posterior to the glabella containing the _________ _________
frontal sinus
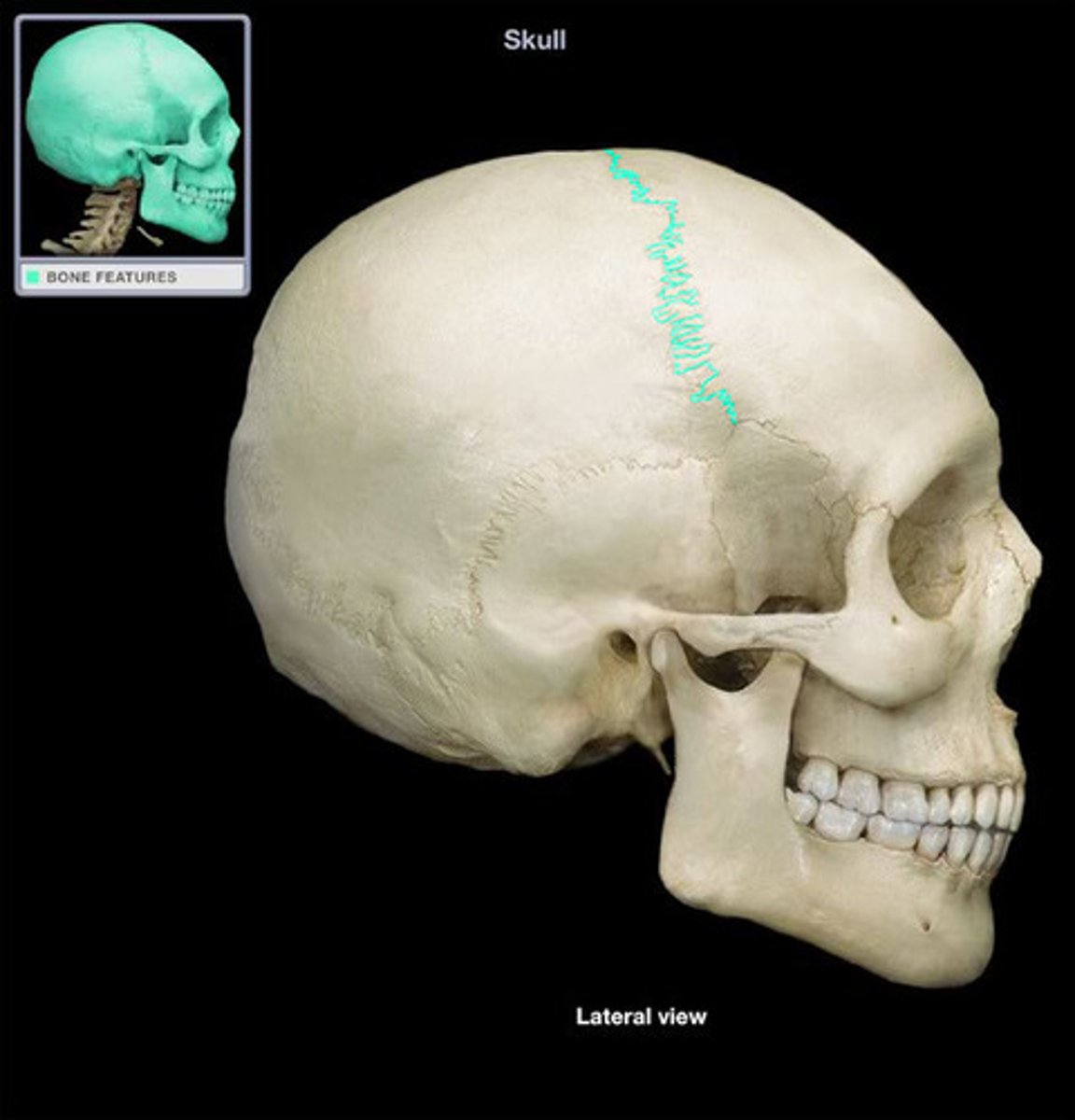
the articulations of the cranium are called __________ and are classified as _______________ _________ joints
sutures, synarthrodial fibrous joints
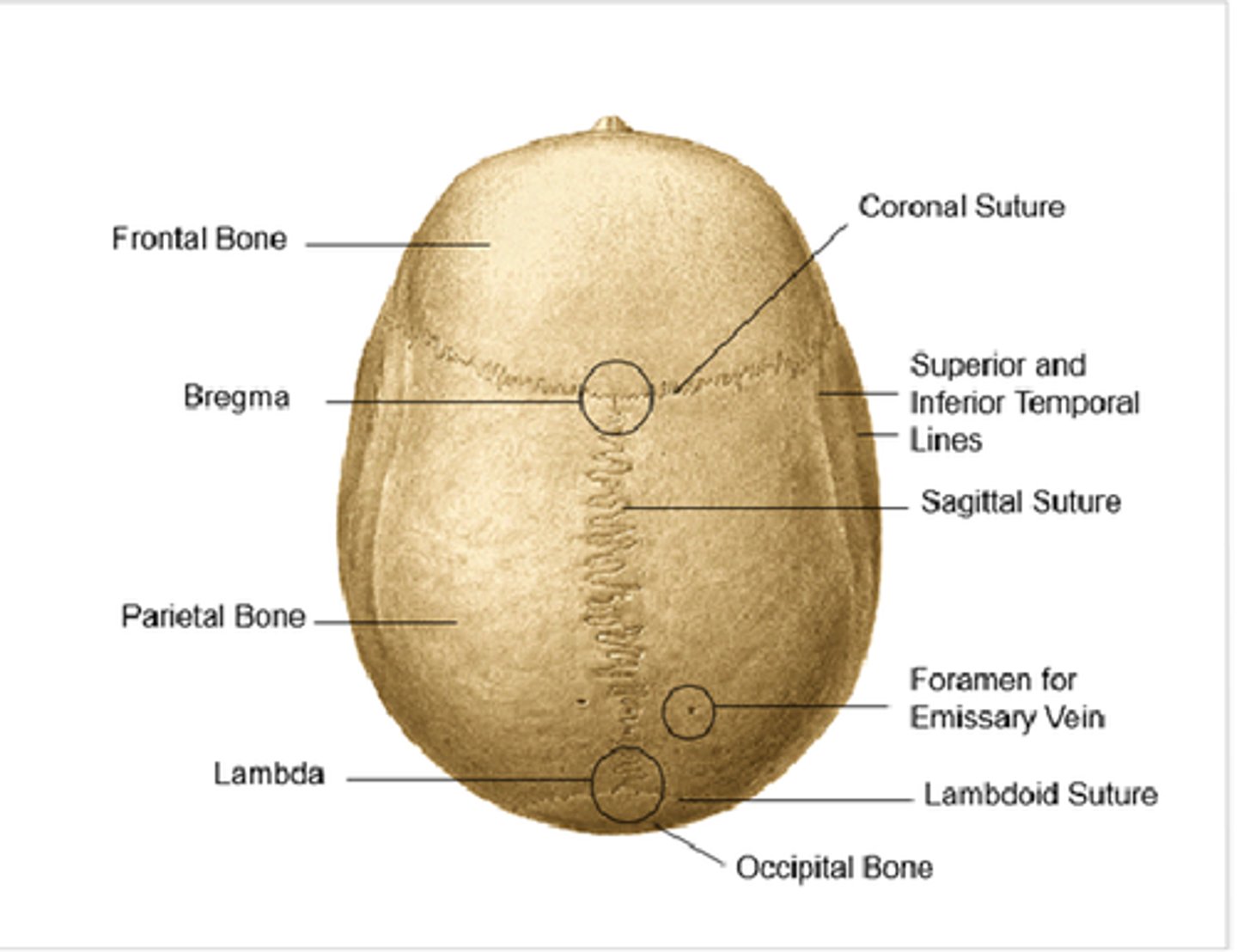
the ___________ suture separates the frontal bone from the two parietal bones
coronal
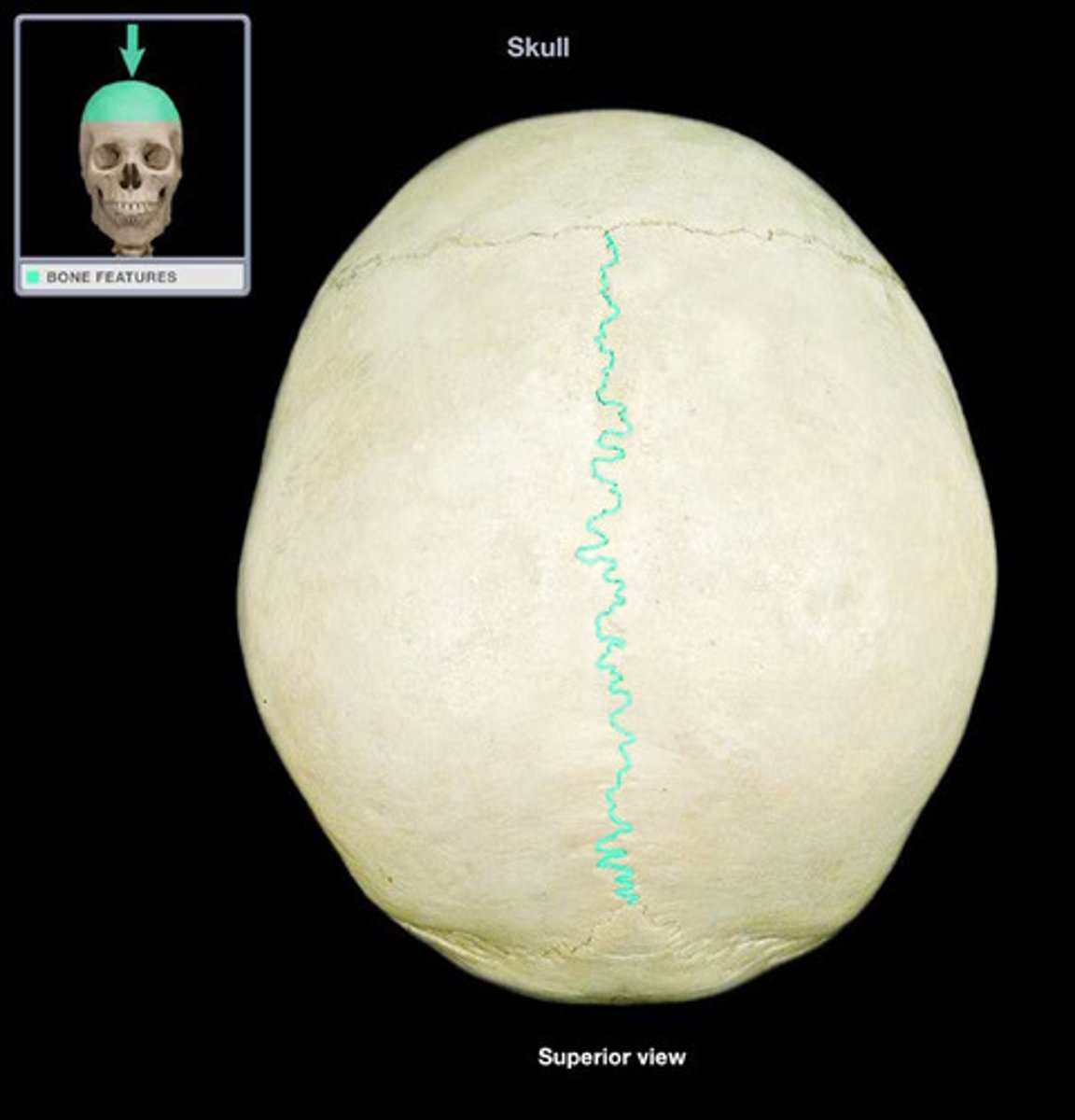
the ___________ suture separates the two parietal bones at midline
sagittal
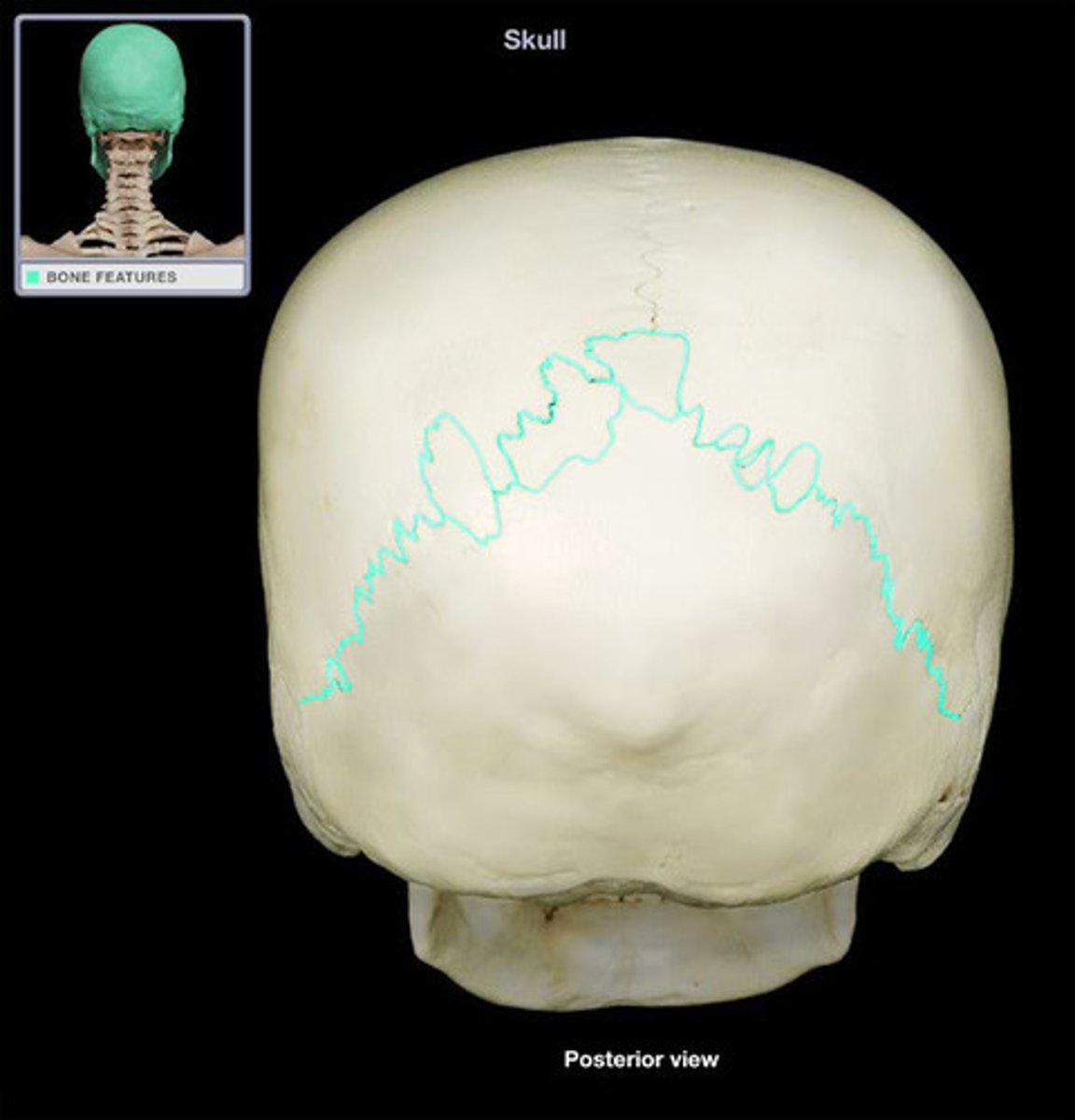
the ____________ suture separates the two parietal bones from the occipital bone
lambdoidal
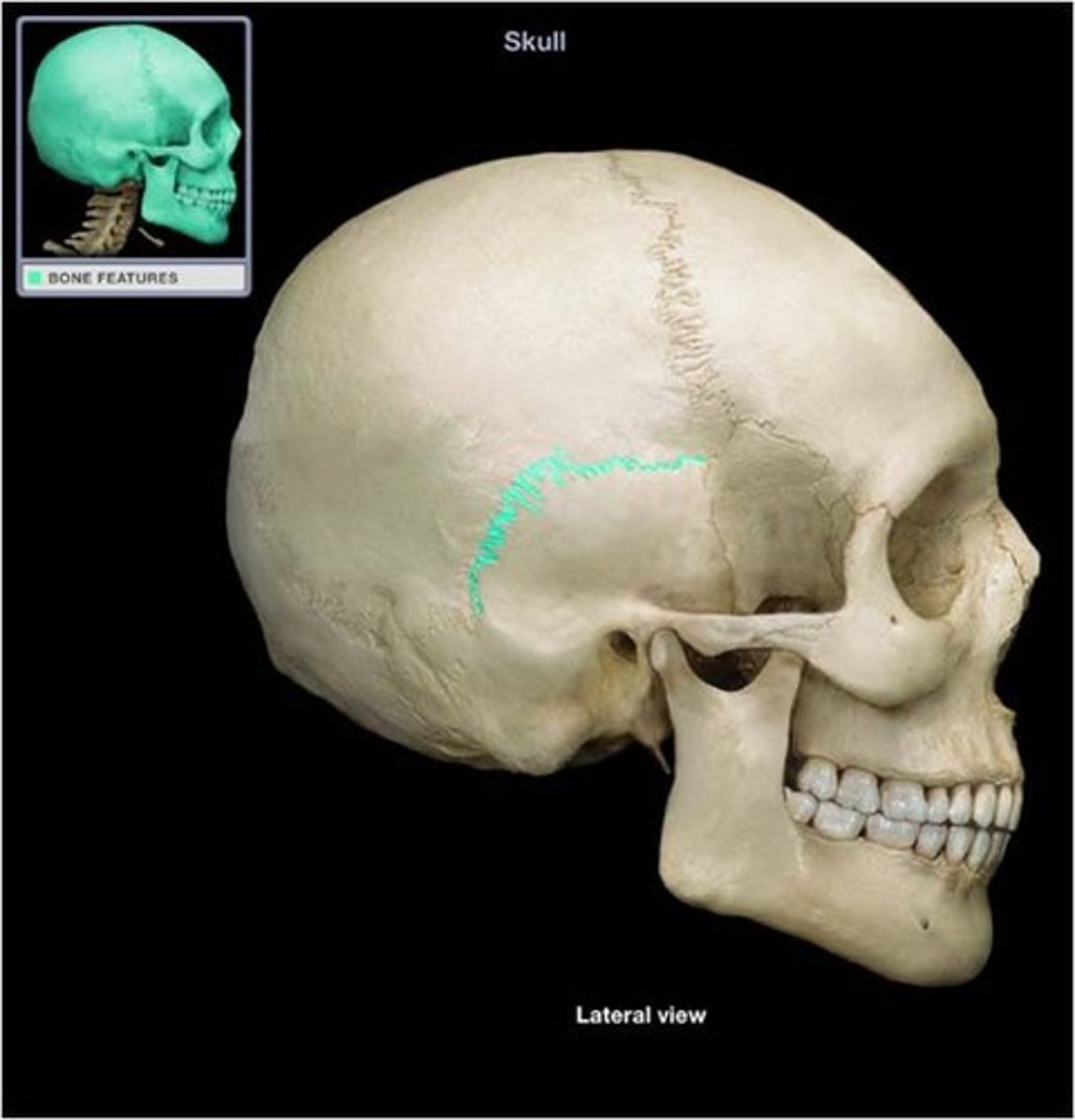
the __________ sutures are formed by the inferior junctions of the two parietal bones with their respective temporal bones
squamosal
the anterior end of the sagittal suture is the _________ and the posterior end is the ___________
bregma, lambda
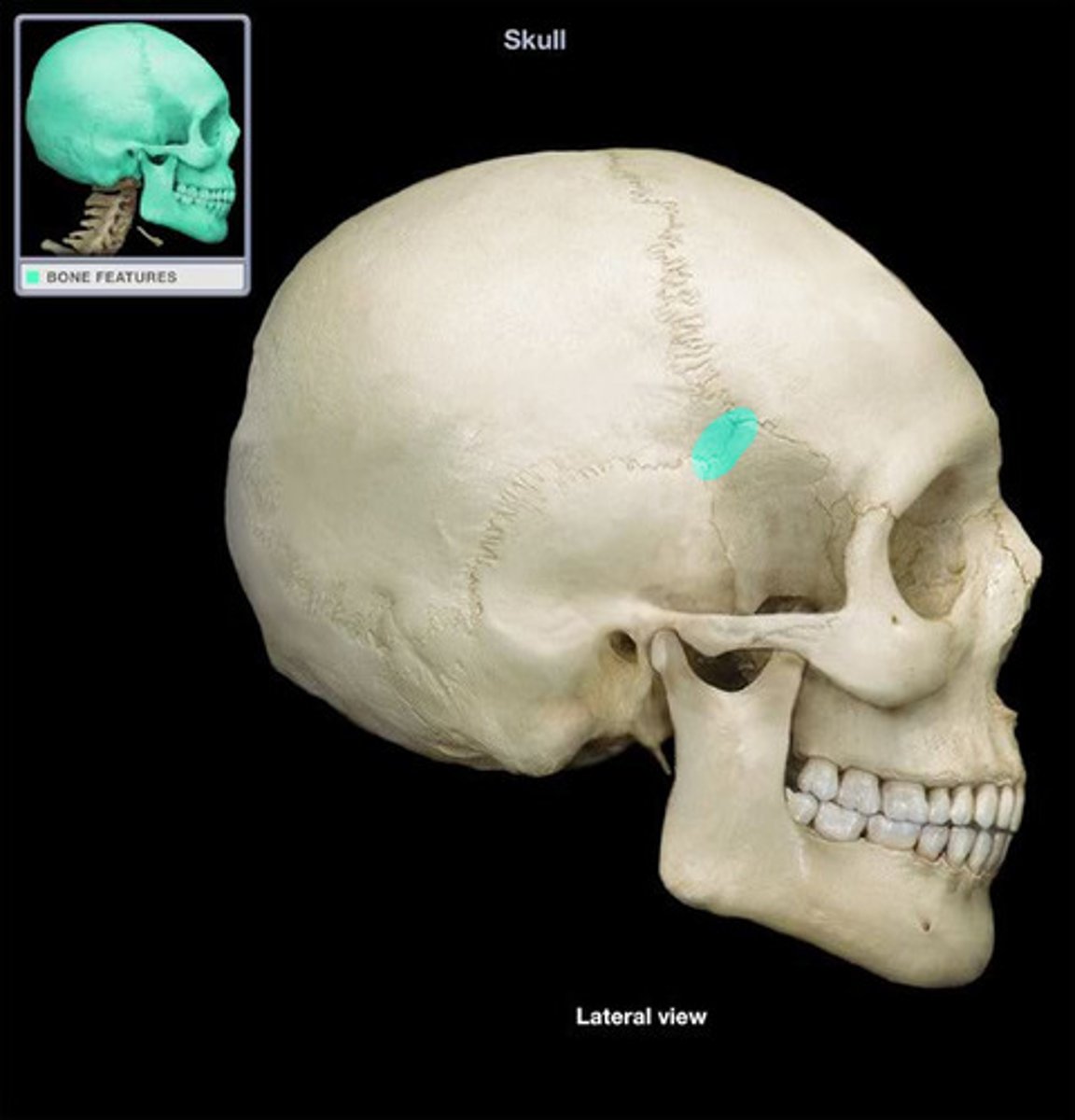
the right and left __________ are points at the junction of the frontal, parietals, temporals, and the great wings of the sphenoid
pterions
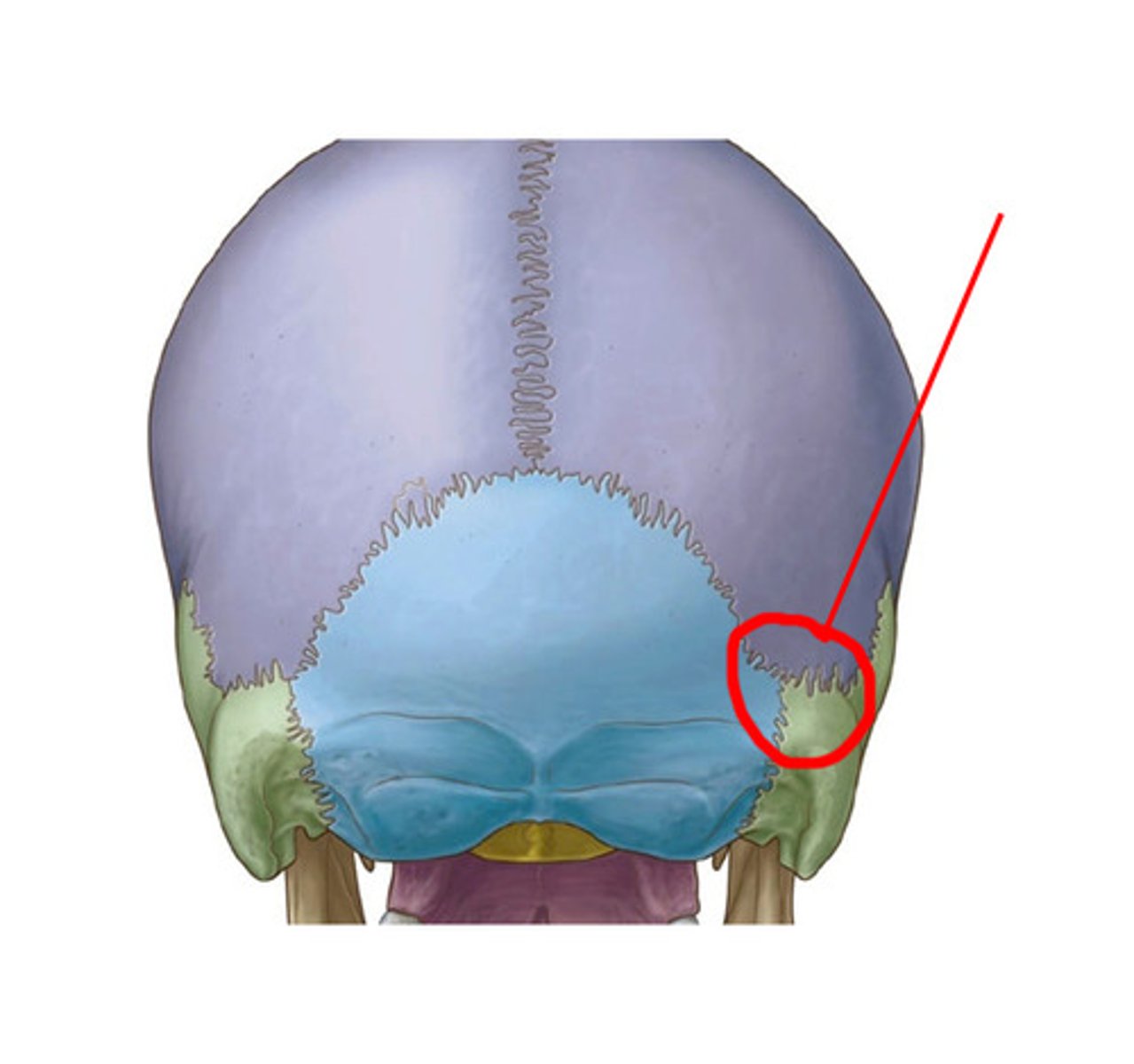
the right and left ___________ are points posterior to the ear when the squamosal and lambdoidal sutures meet
asterions
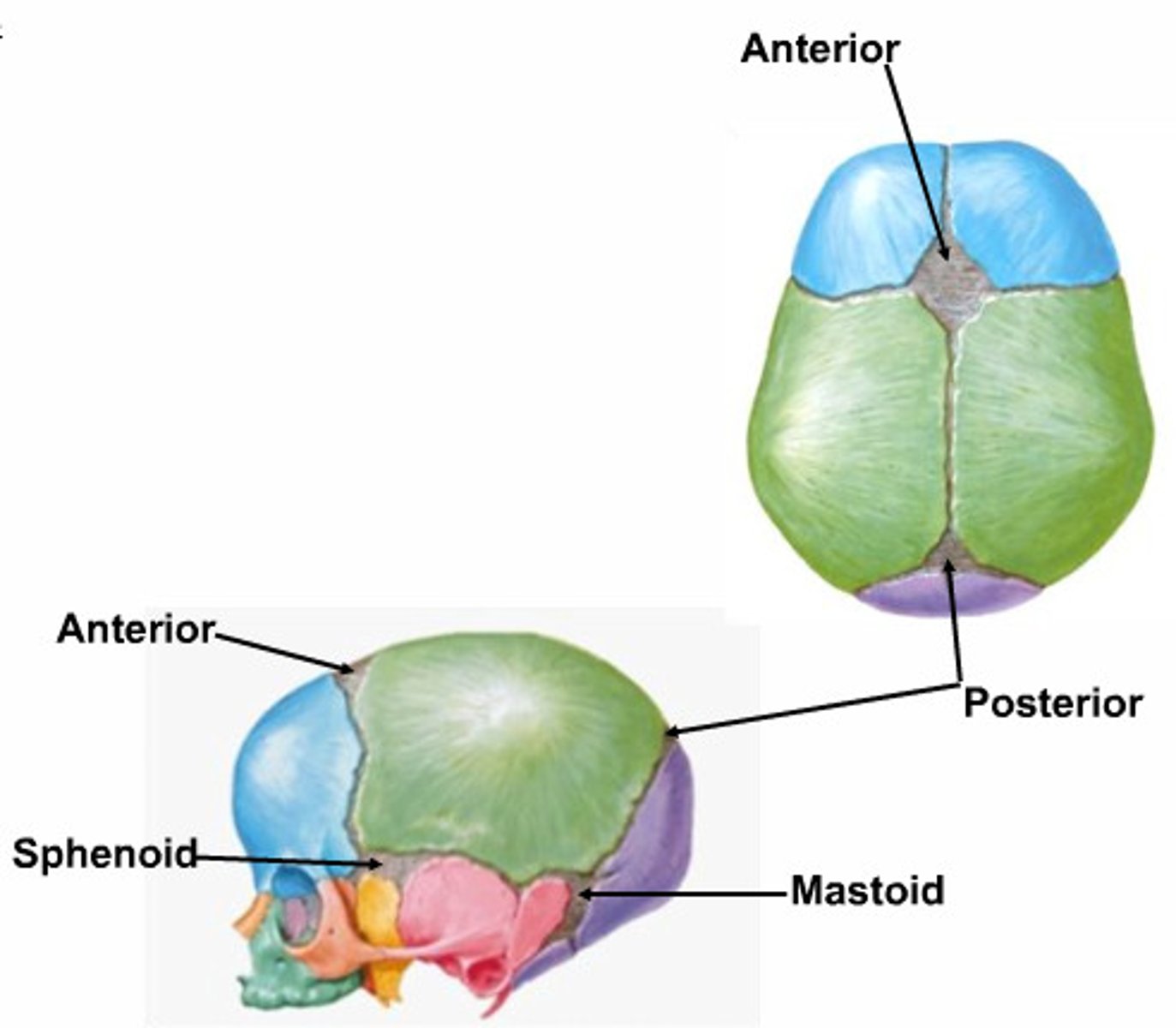
what are the regions where sutures join that are slower in their ossification called? when do cranial sutures ossify completely?
fontanels, mid-to-late 20's
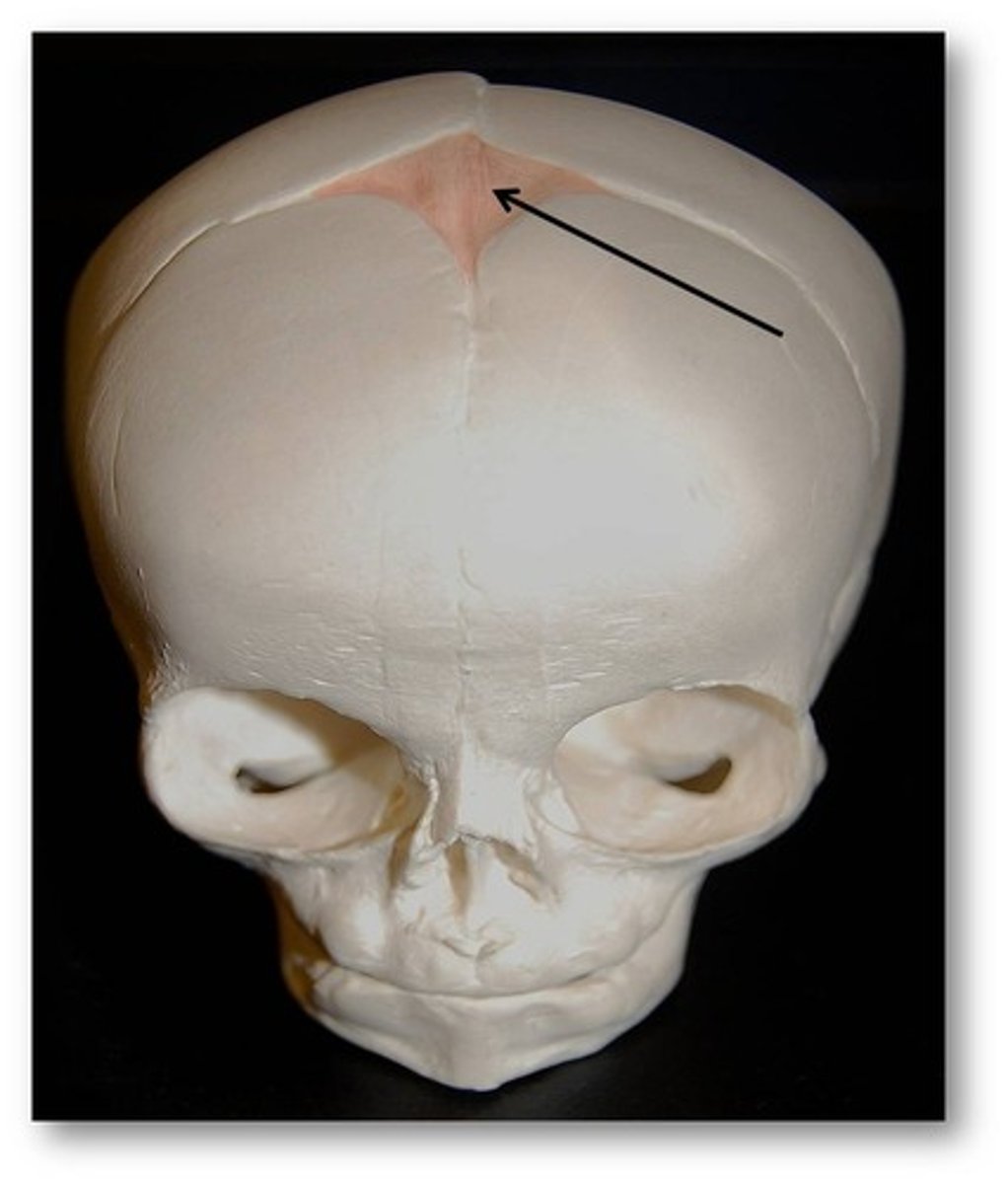
the bregma and lambda in the adult are termed the ____________ and ____________ ____________ in an infant
anterior and posterior fontanels
which fontanel is the largest?
the anterior fontanel
the pterions in an adult are the ____________ fontanels in infants
sphenoid
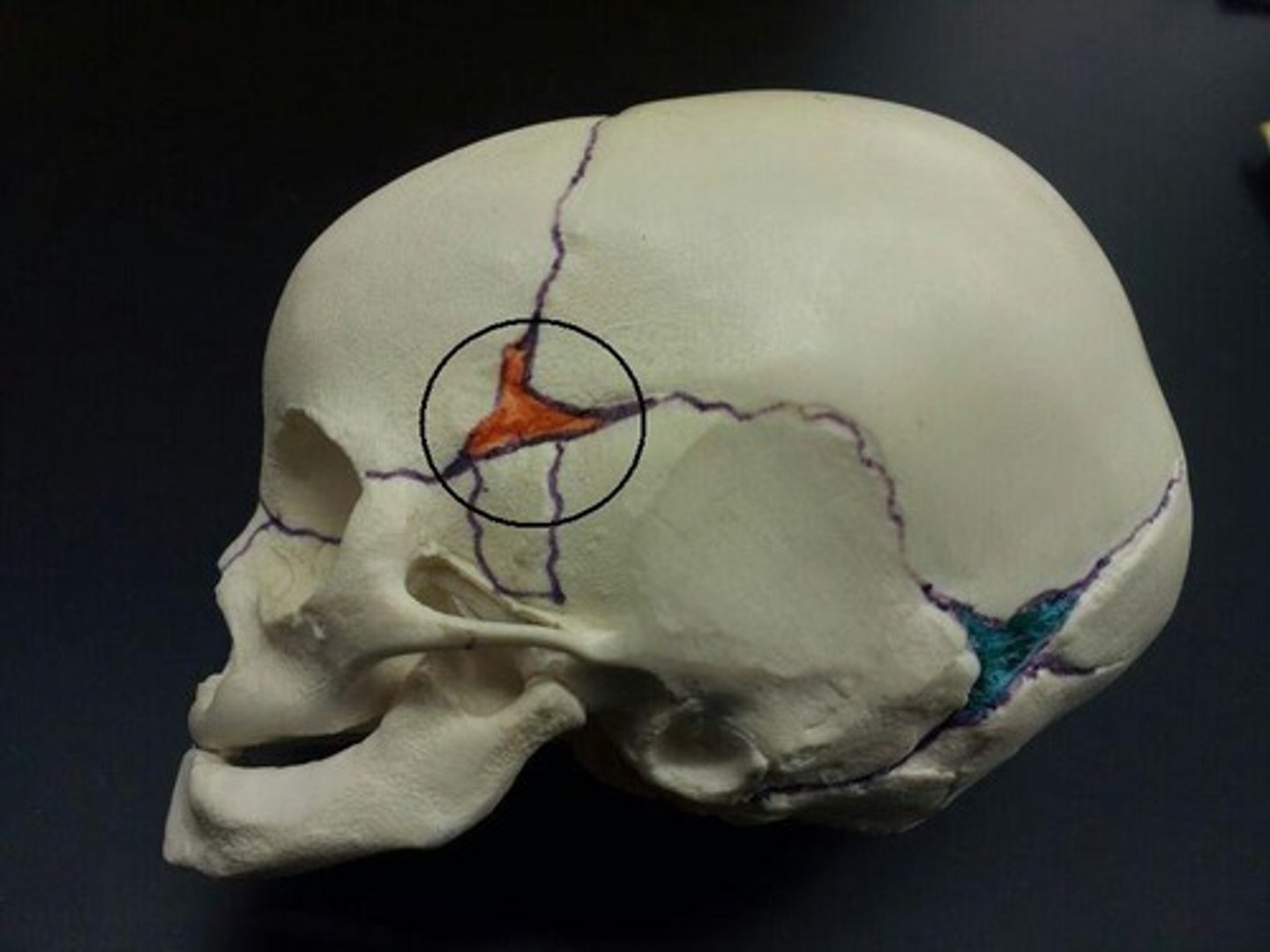
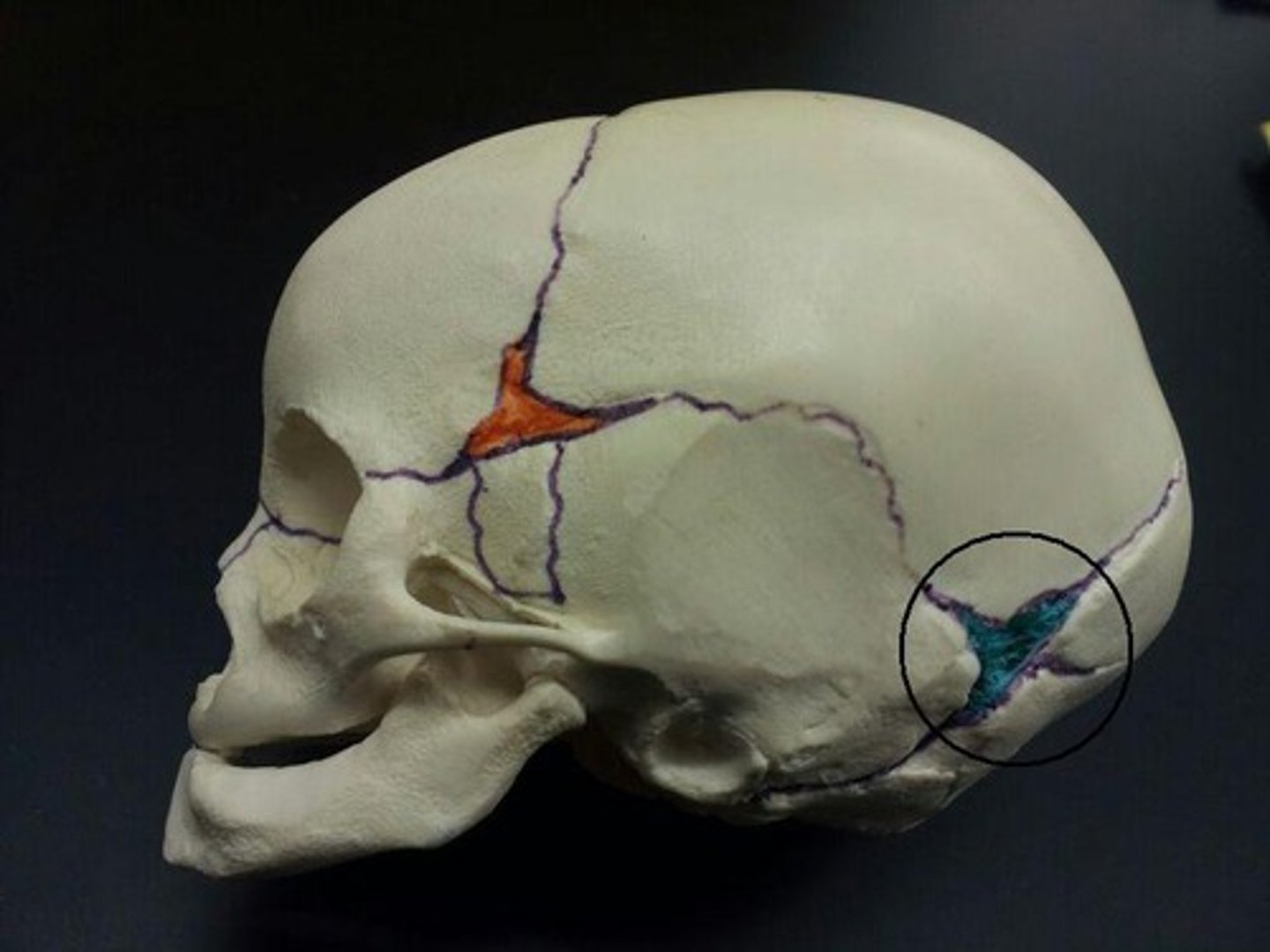
the asterions in an adult are the ____________ fontanels in infants
mastoid
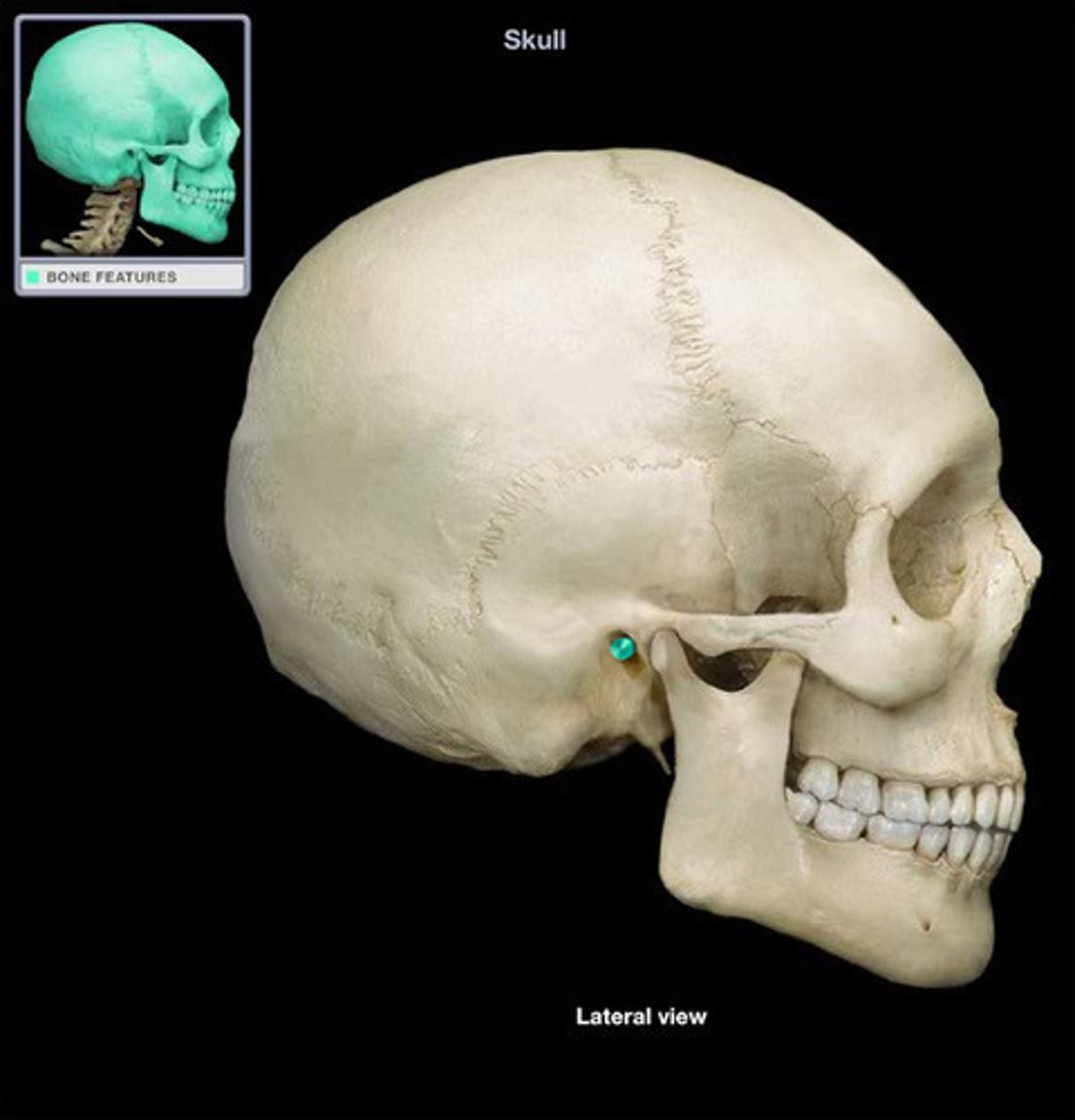
the external ear begins with the _________ or _________ on each side of the head
auricle, pinna
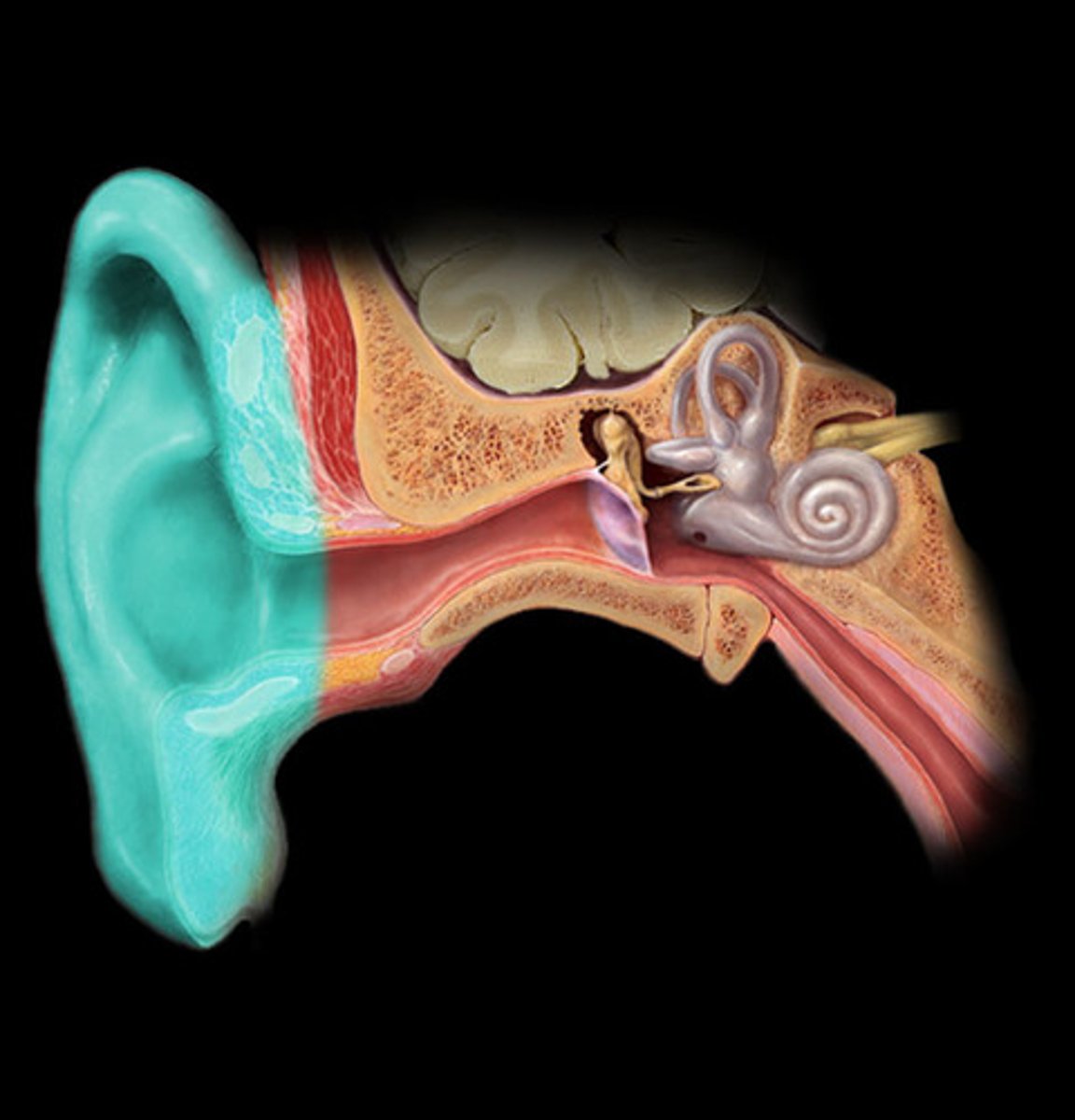
the _________ is a small liplike structure located anterior to the EAM acting as a partial shield to the ear opening
tragus
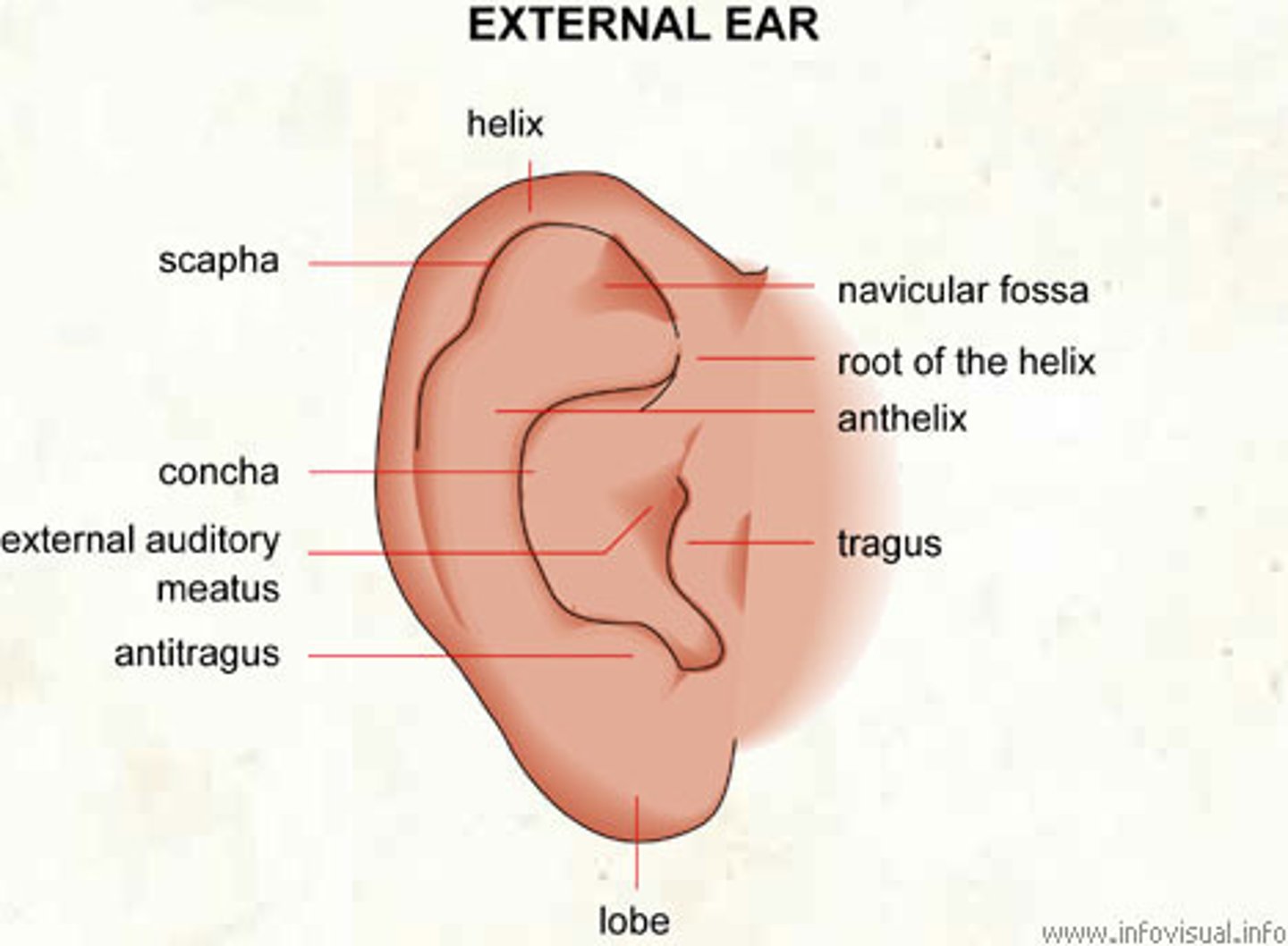
the opening or canal of the external ear is termed what?
external auditory meatus (EAM)
-approximately 1 inch long
-half bony, half cartilaginous
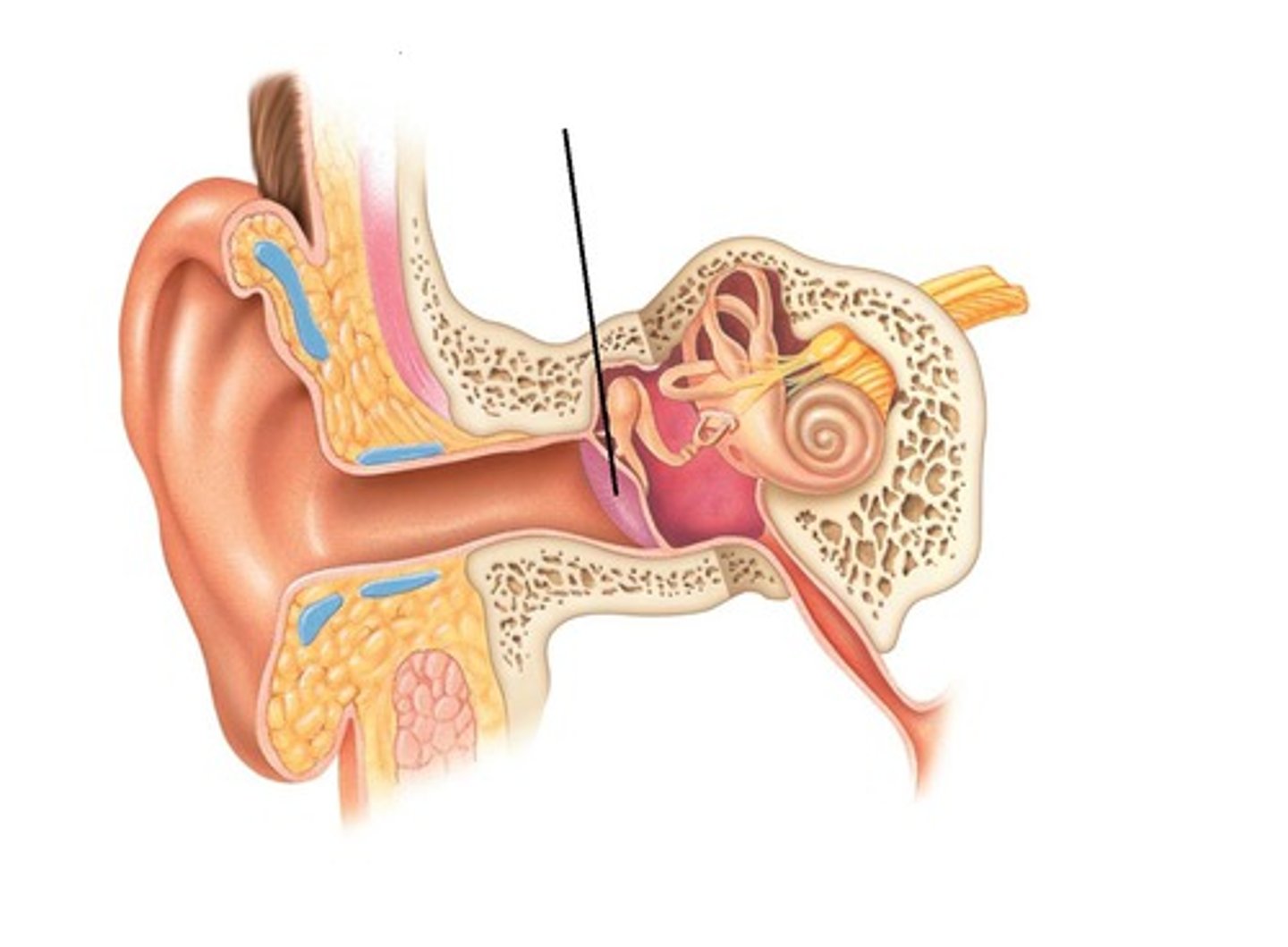
the mastoid process and mastoid tip of the temporal bone are posterior and inferior to the ________
EAM
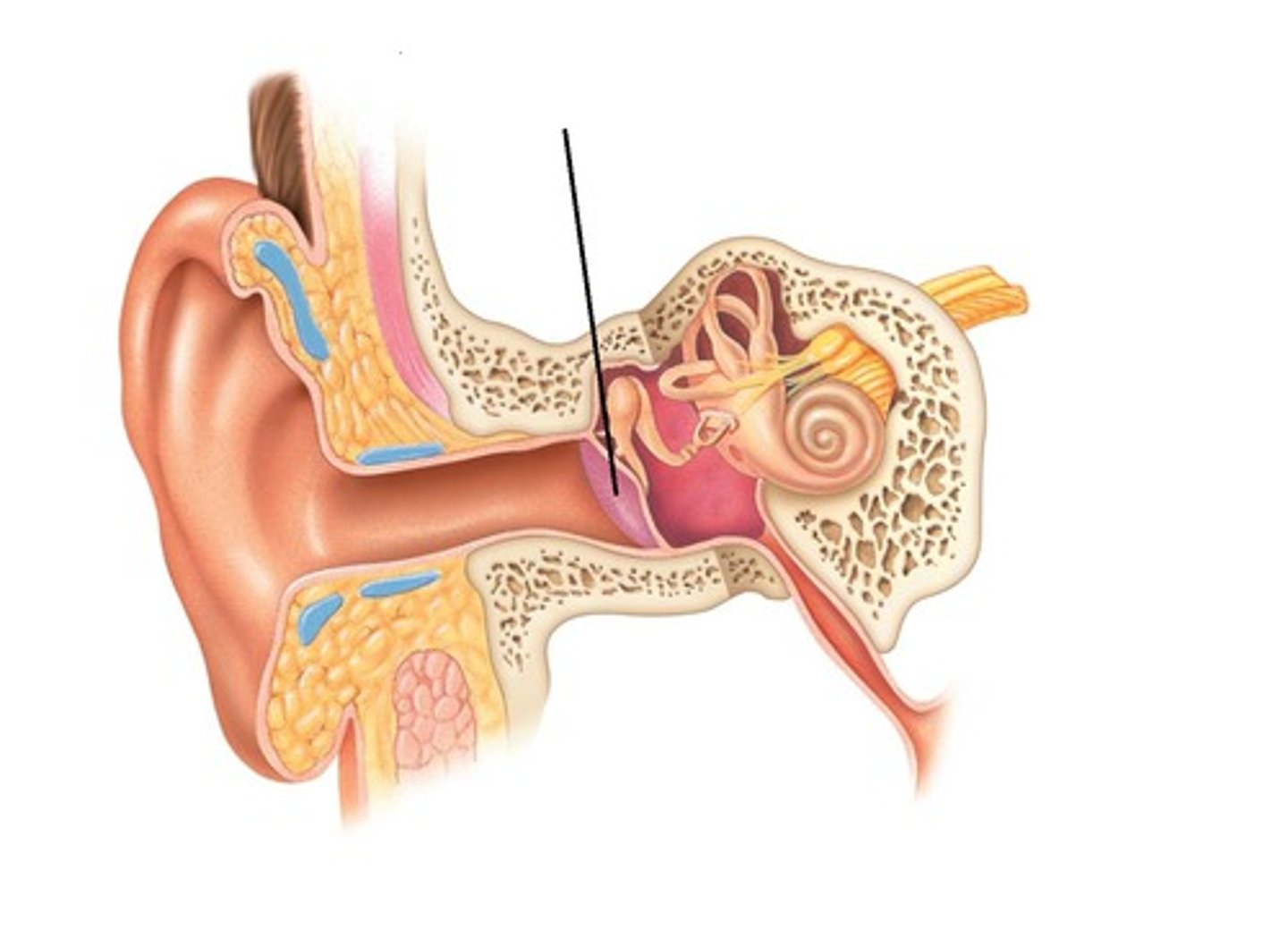
the meatus narrows as it meets the ___________ ___________
tympanic membrane (eardrum)
how is the eardrum situated?
at an oblique angle, forming a depression at the lower medial end of the meatus
what are the 3 main parts of the middle ear?
tympanic membrane, the 3 auditory ossicles, and the tympanic cavity
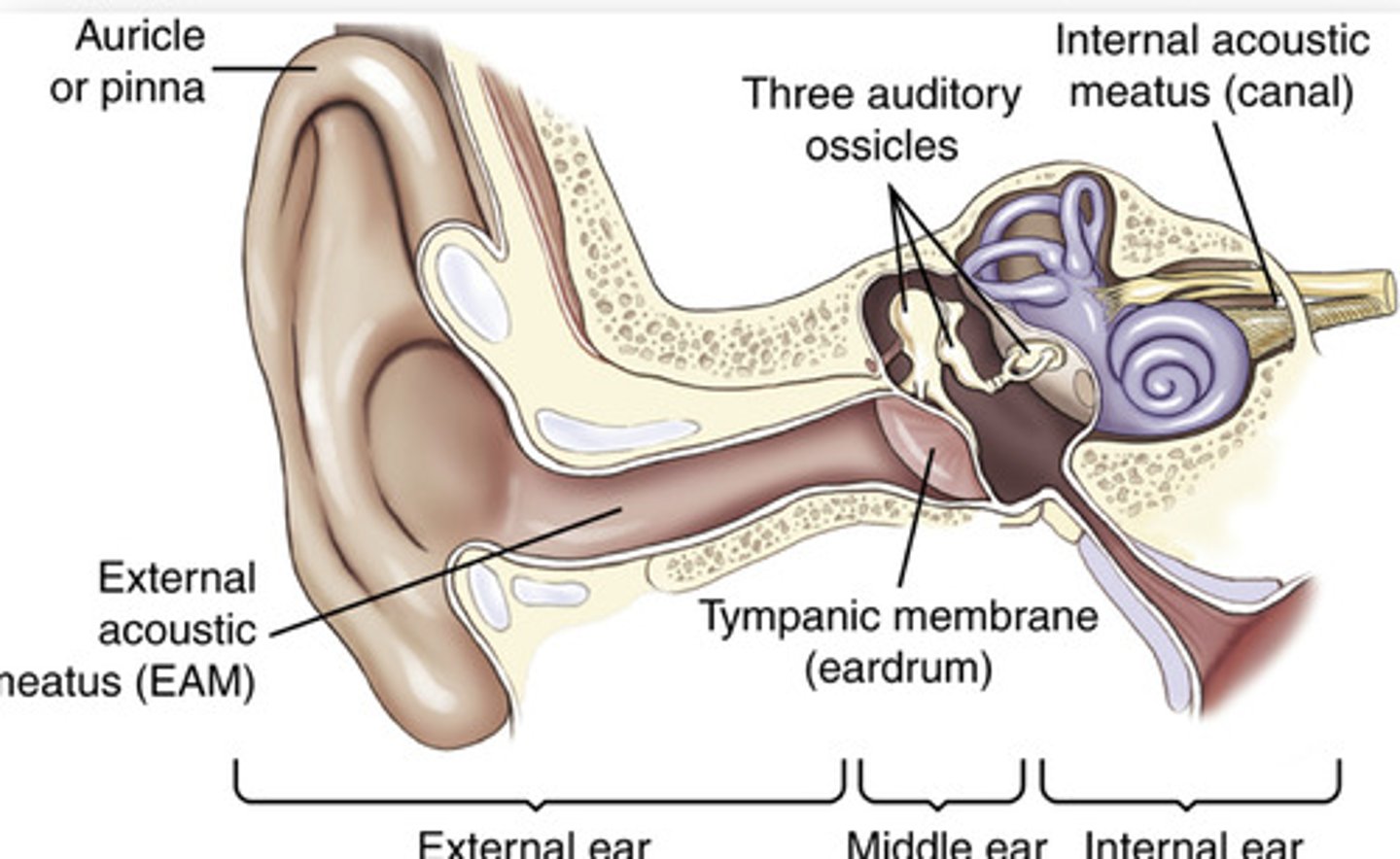
the tympanic cavity is divided into what 2 parts?
tympanic cavity proper and the epitympanic recess (attic)
the drum crest/spur separates the EAM from what?
the epitympanic recess
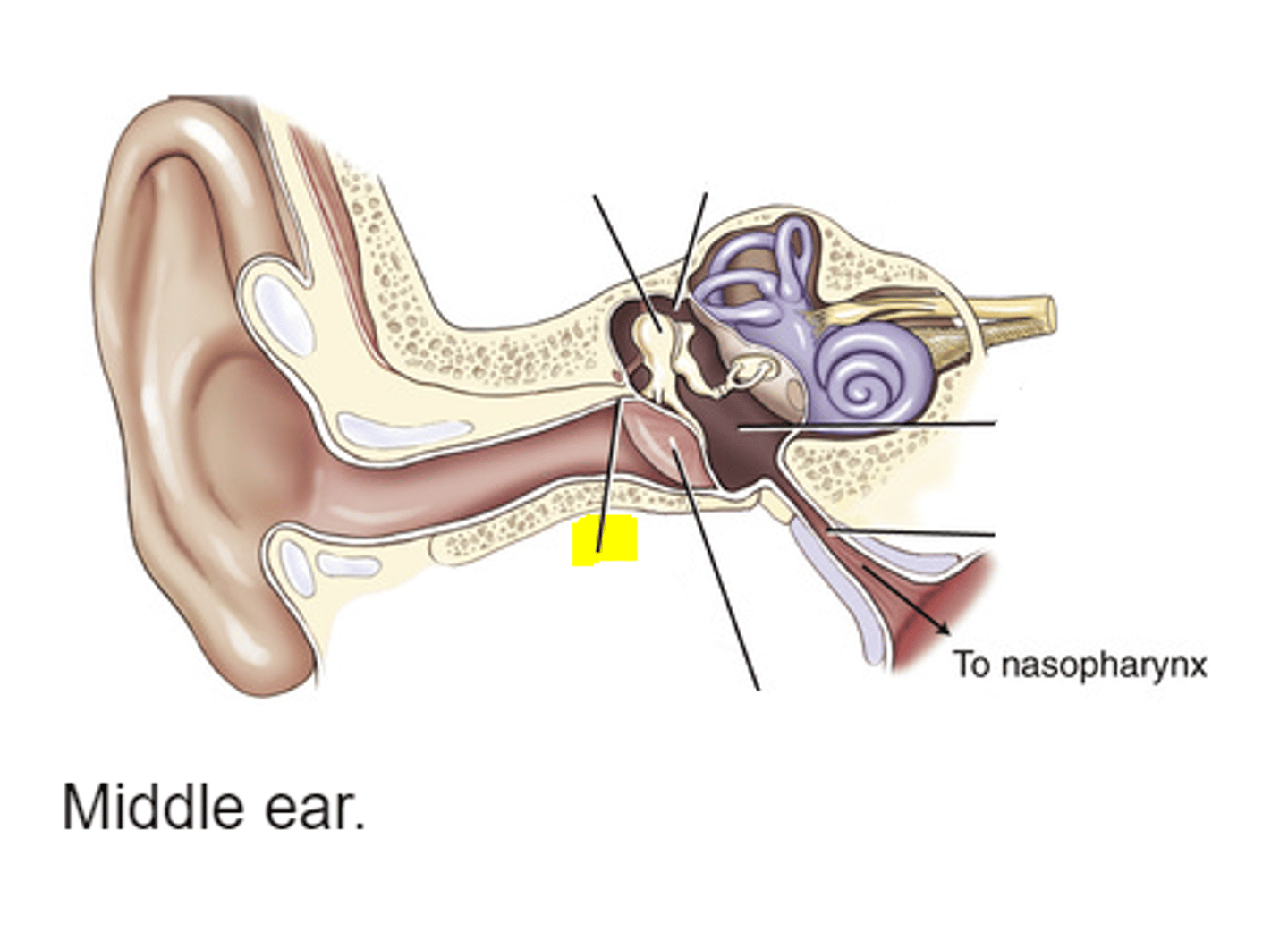
the _______________ _______ is the passageway between the middle ear and the nasopharynx
eustachian (auditory) tube
-approximately 1.5 inches long
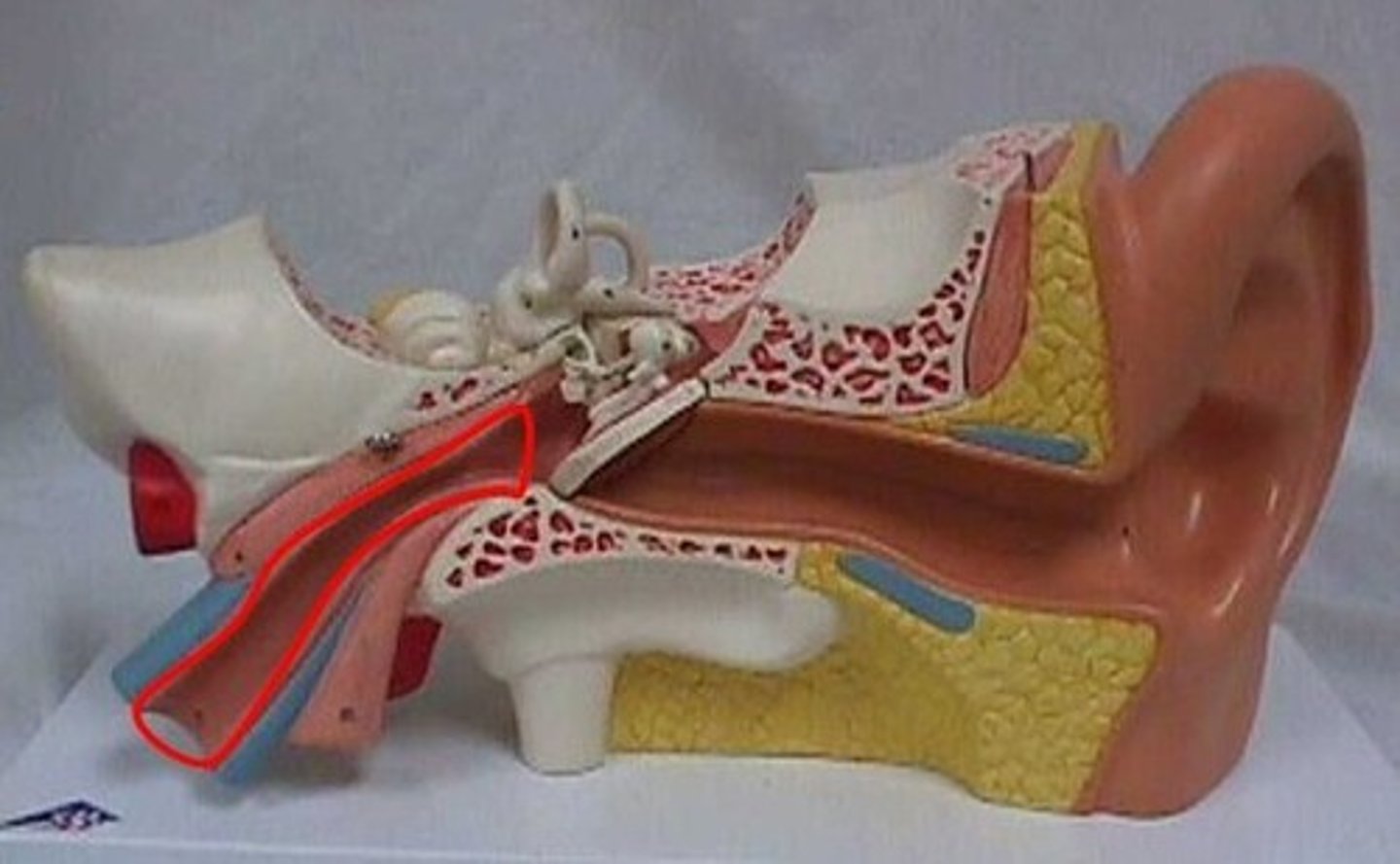
what is the function of the eustachian tube?
equalizes pressure in the middle ear with atmospheric pressure through the nasopharynx
the lateral portions of the petrous ridges are at approximately the level of the _______
TEA (top of ear attachment)
the ________ is the opening between the epitympanic recess and the mastoid portion
aditus
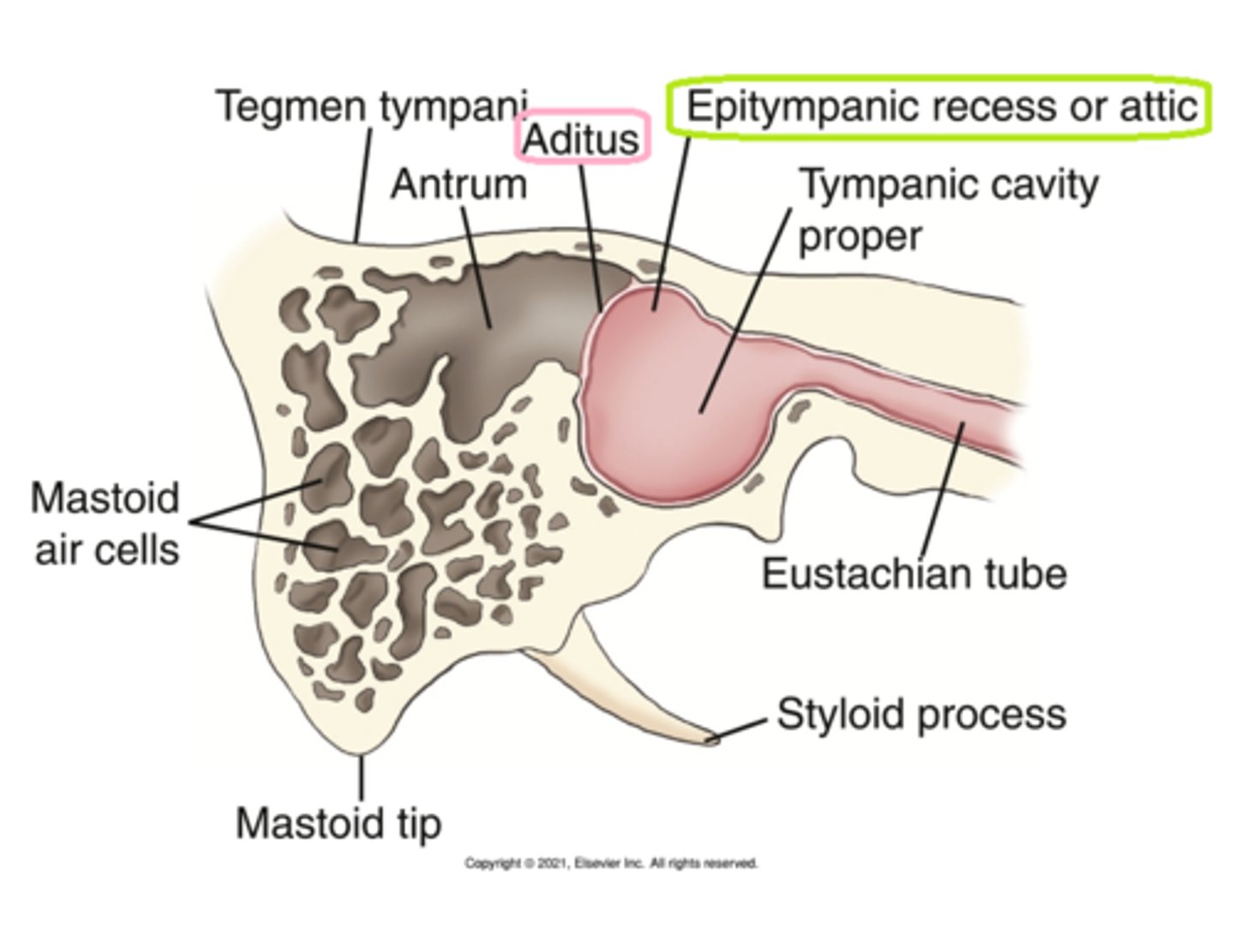
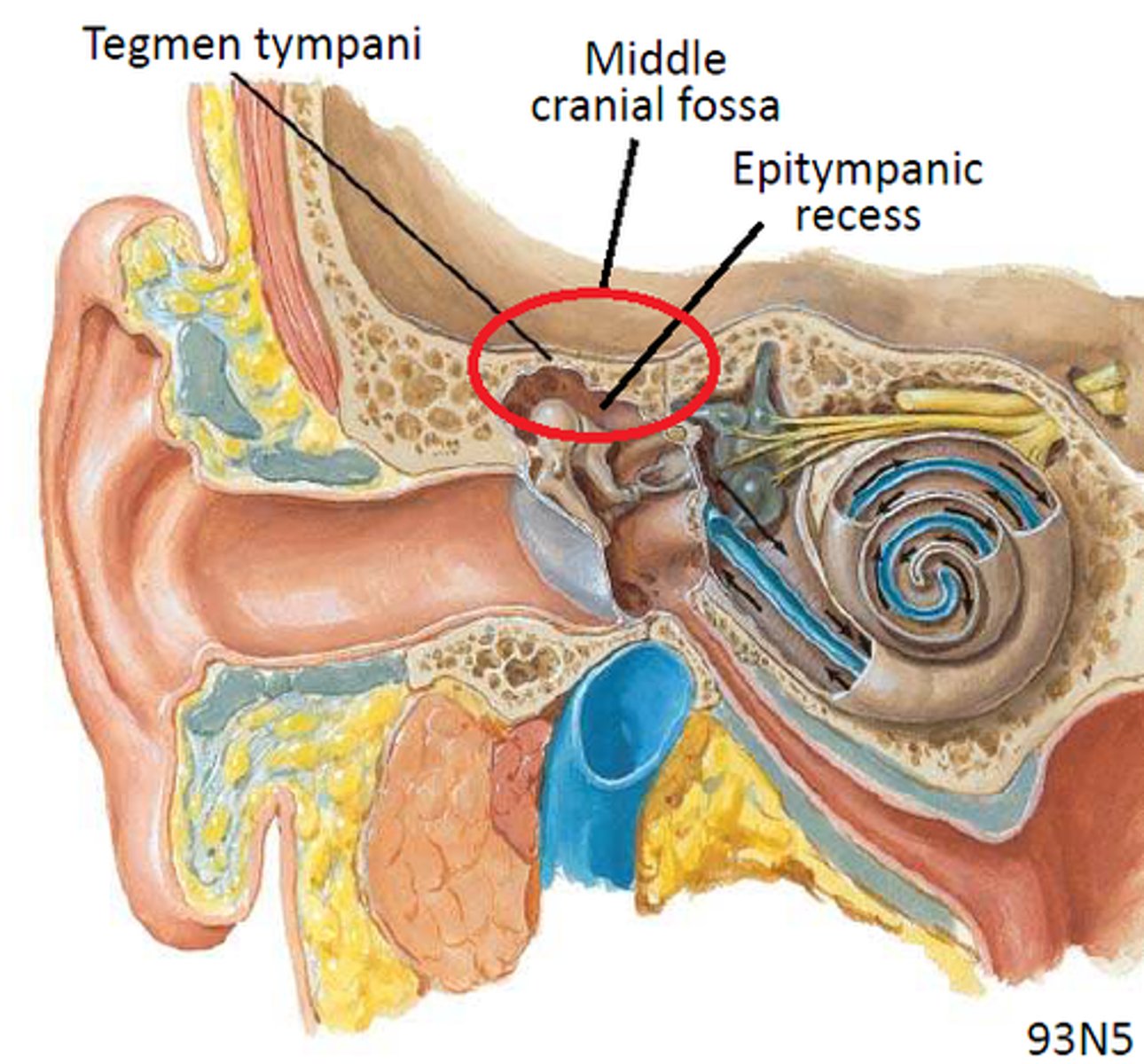
the __________ __________ is the thin plate of bone that forms the roof of the antrum, aditus, and attic area of the tympanic cavity
tegmen tympani
what are the 3 auditory ossicles?
malleus, incus, stapes
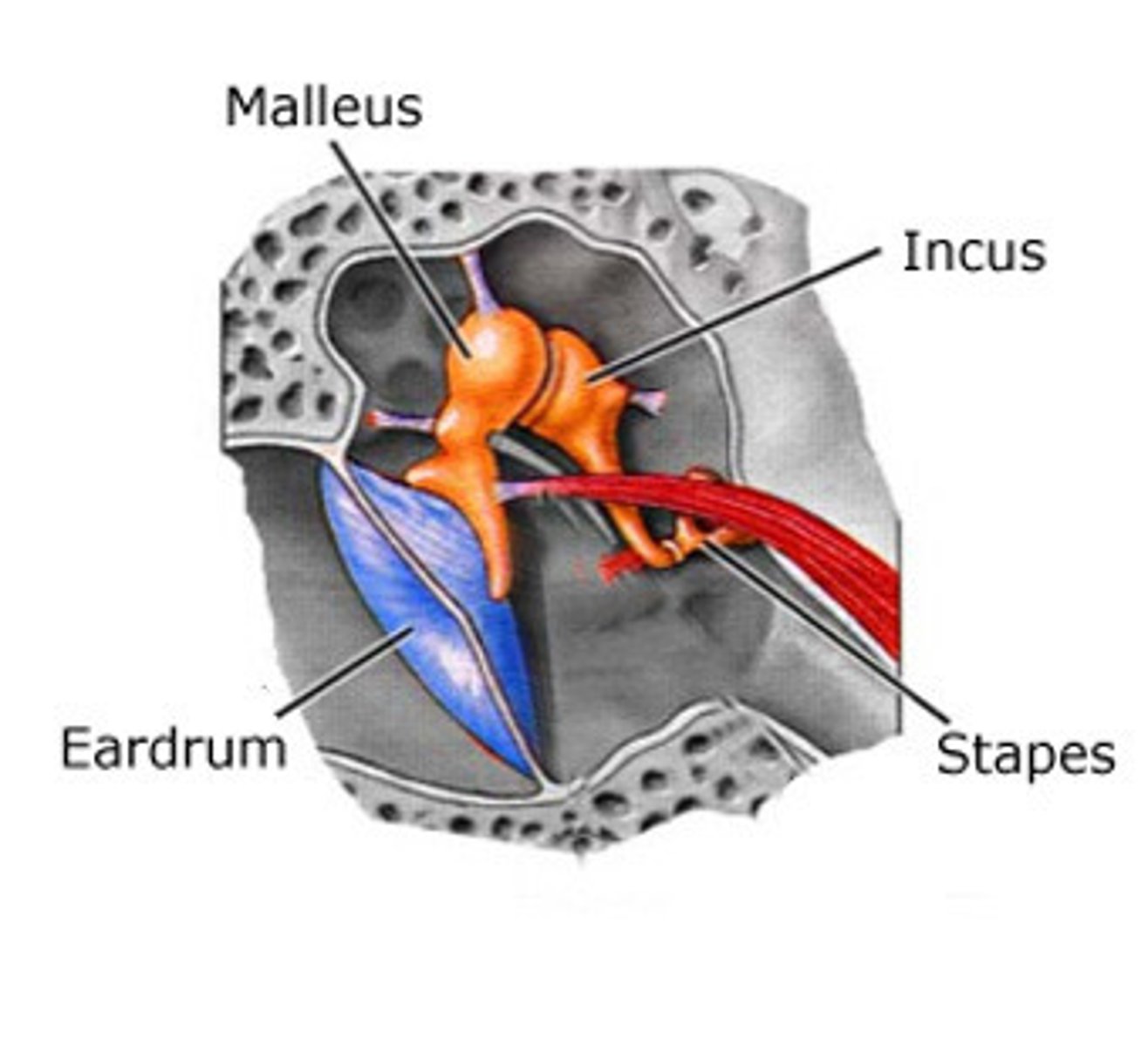
which of the auditory ossicles is attached directly to the inside surface of the tympanic membrane and picks up vibrations first?
the malleus
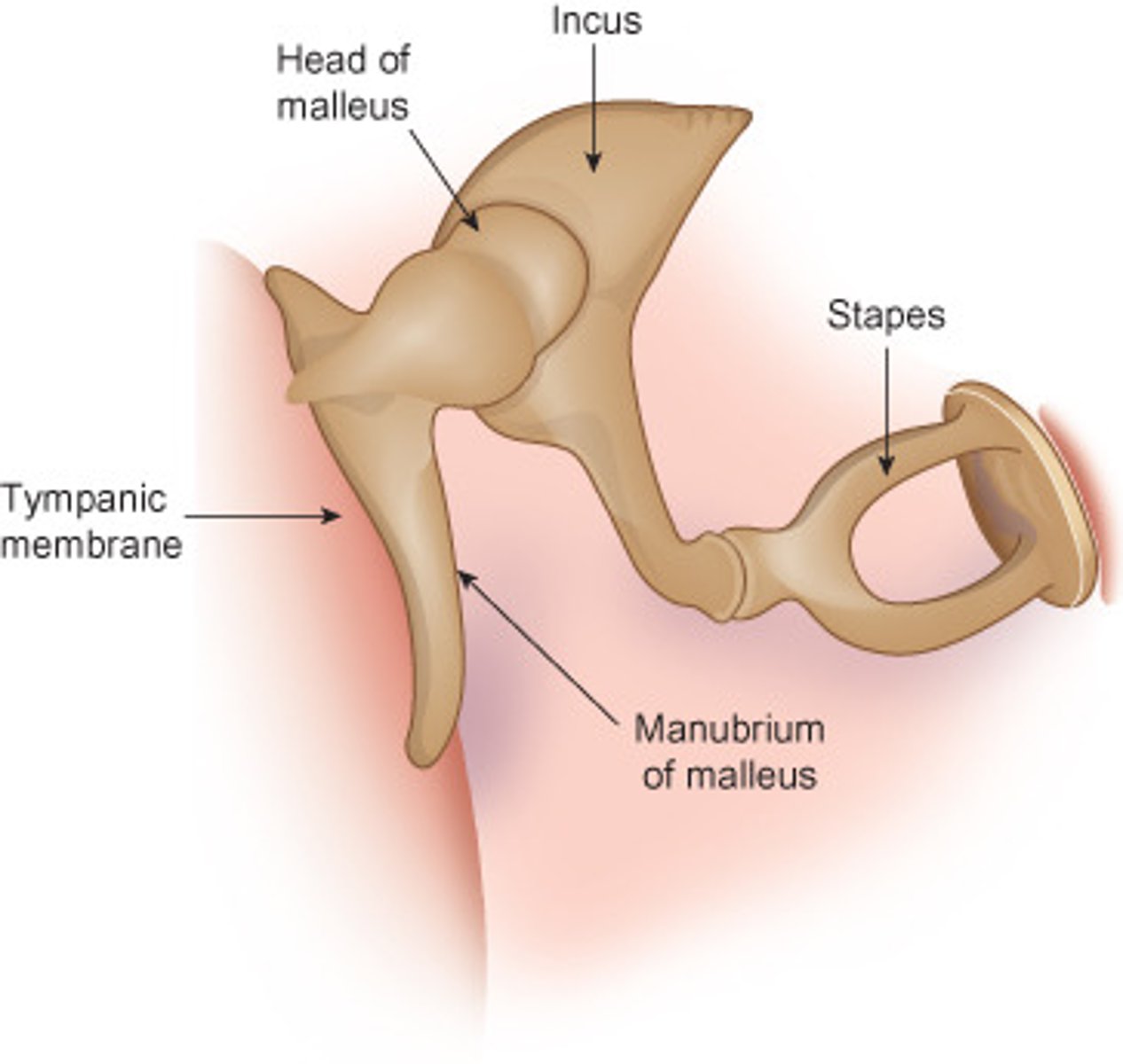
the head of the malleus articulates with the central ossicle, the _________
incus
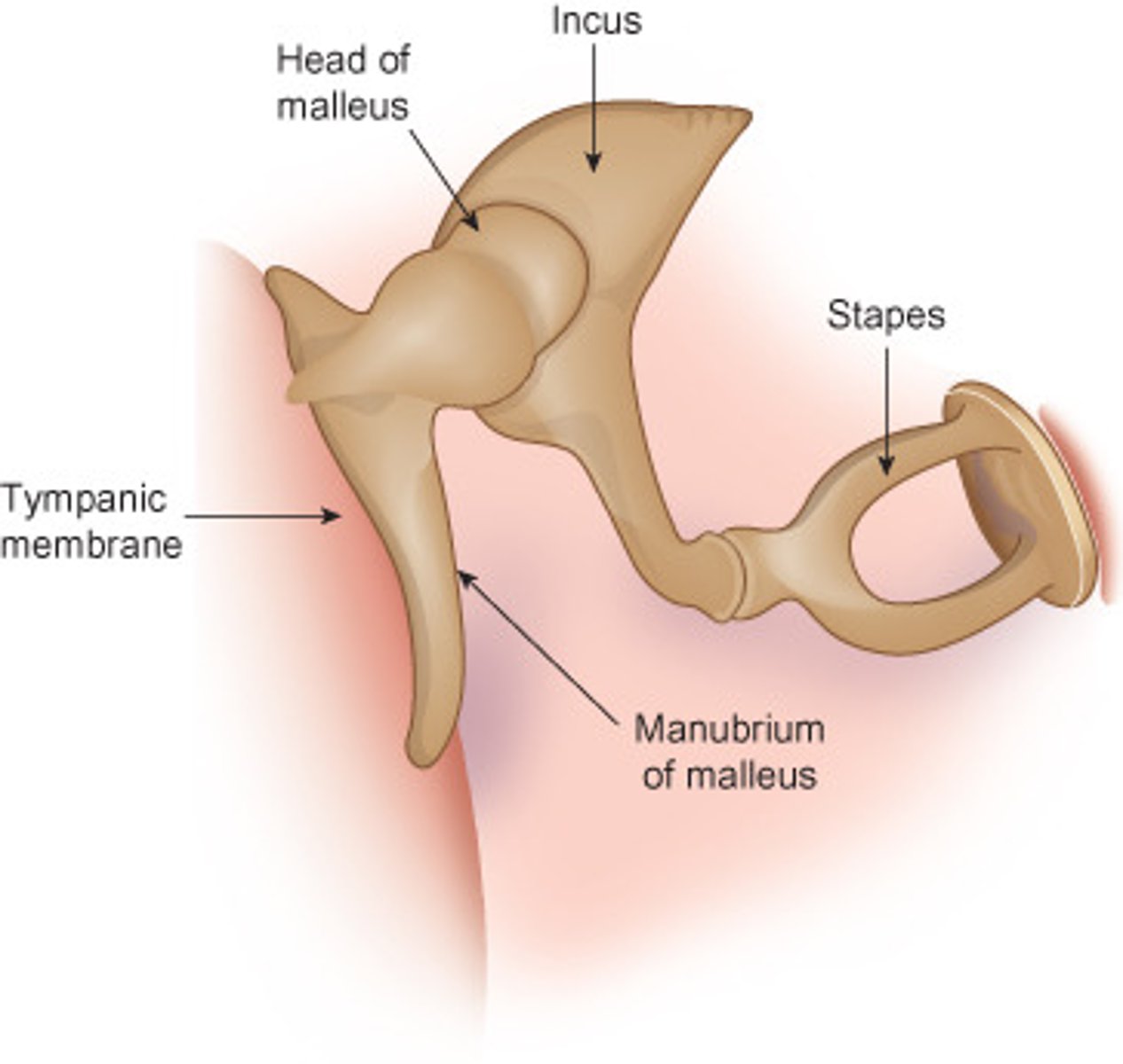
which of the auditory ossicles is the smallest and is attached to the oval window of the cochlea?
the stapes
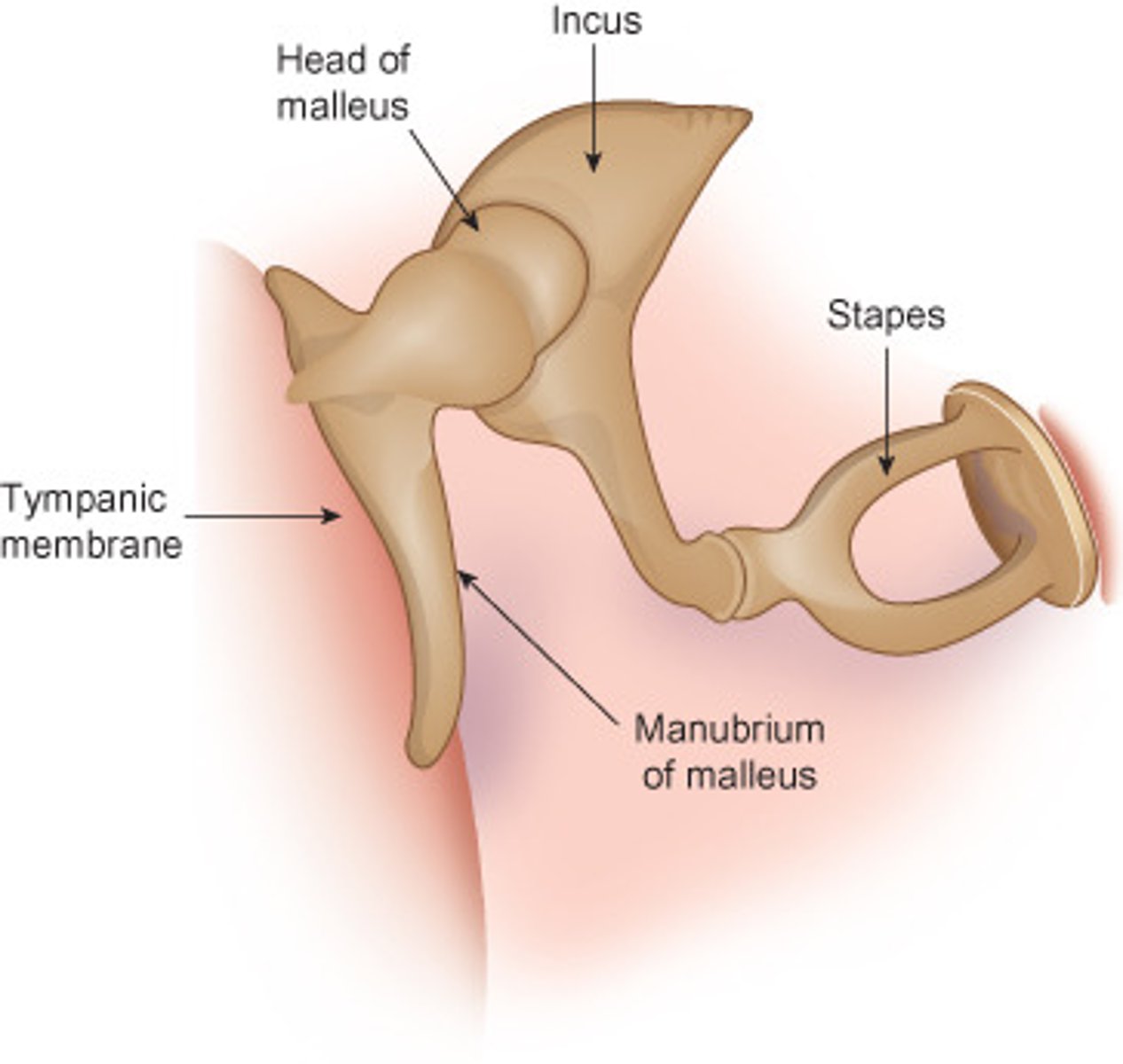
what is the most lateral auditory ossicle? which is the most medial?
malleus, stapes
what two parts is the internal ear divided into?
the osseous (bony) labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth
the ___________ labyrinth is a series of intercommunicating ducts and sacs
membranous
what duct is a blind pouch or closed duct contained in a small, canal-like, bony structure? ****
endolymphatic duct
the osseus labyrinth is divided into what 3 parts?
the cochlea, vestibule, and semicircular canals
what are the 3 semicircular canals?
superior, posterior, and lateral semicircular canals
the semicircular canals relate to the sense of _____________ and the cochlea relates to the sense of ____________
direction (equilibrium), hearing
what are the 2 facial bones that are unpaired?
the vomer and mandible
what are the largest immovable bones of the face?
the two maxillae
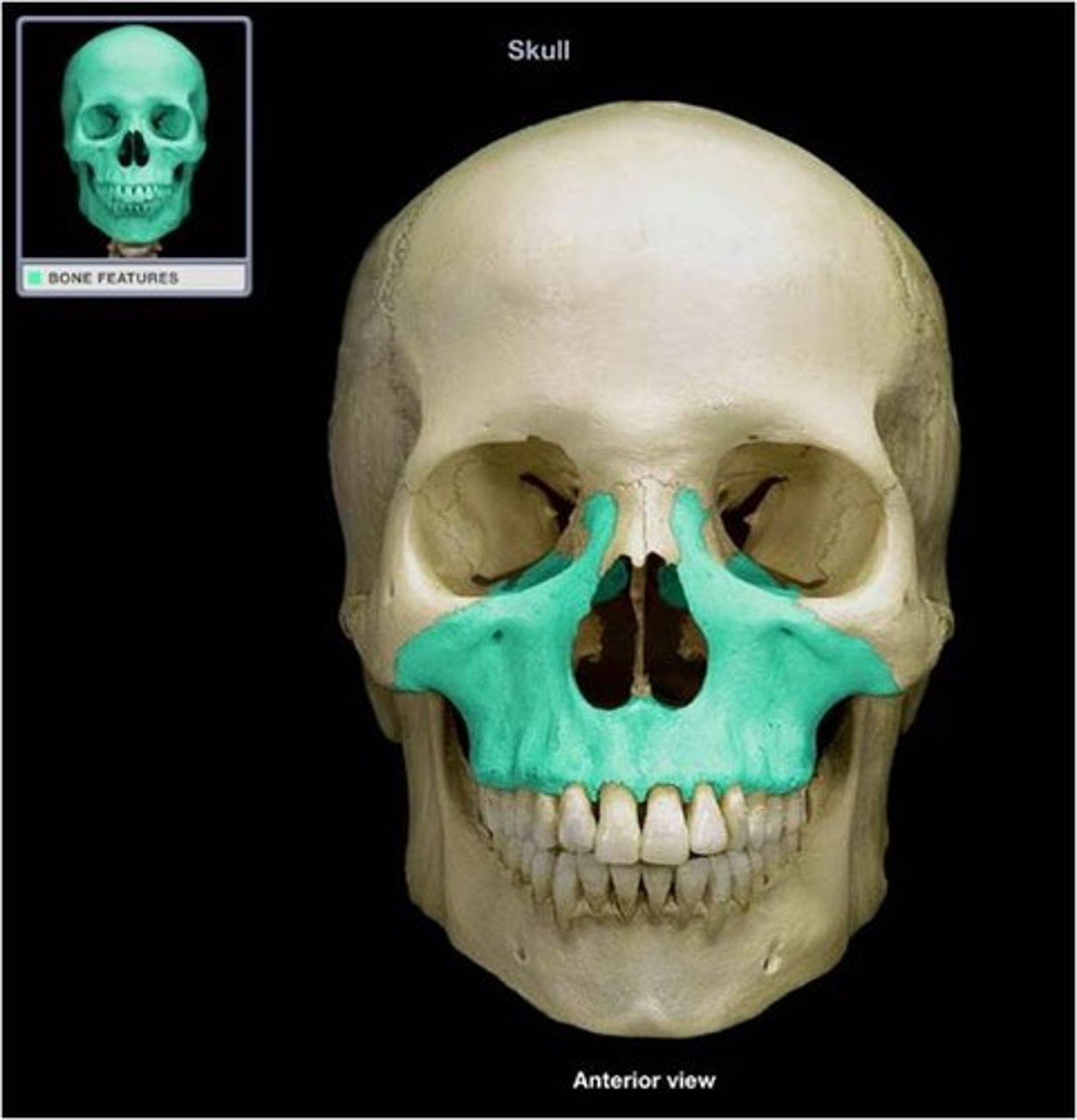
the right and left maxillary bones unite where?
midline below the nasal septum
what 3 cavities are assisted in formation by the maxillae?
the mouth, nasal cavity, and orbits
what does each maxilla consist of?
a centrally located body and 4 processes
which process of the maxilla projects upward along the lateral border of the nose toward the frontal bone?
the frontal process
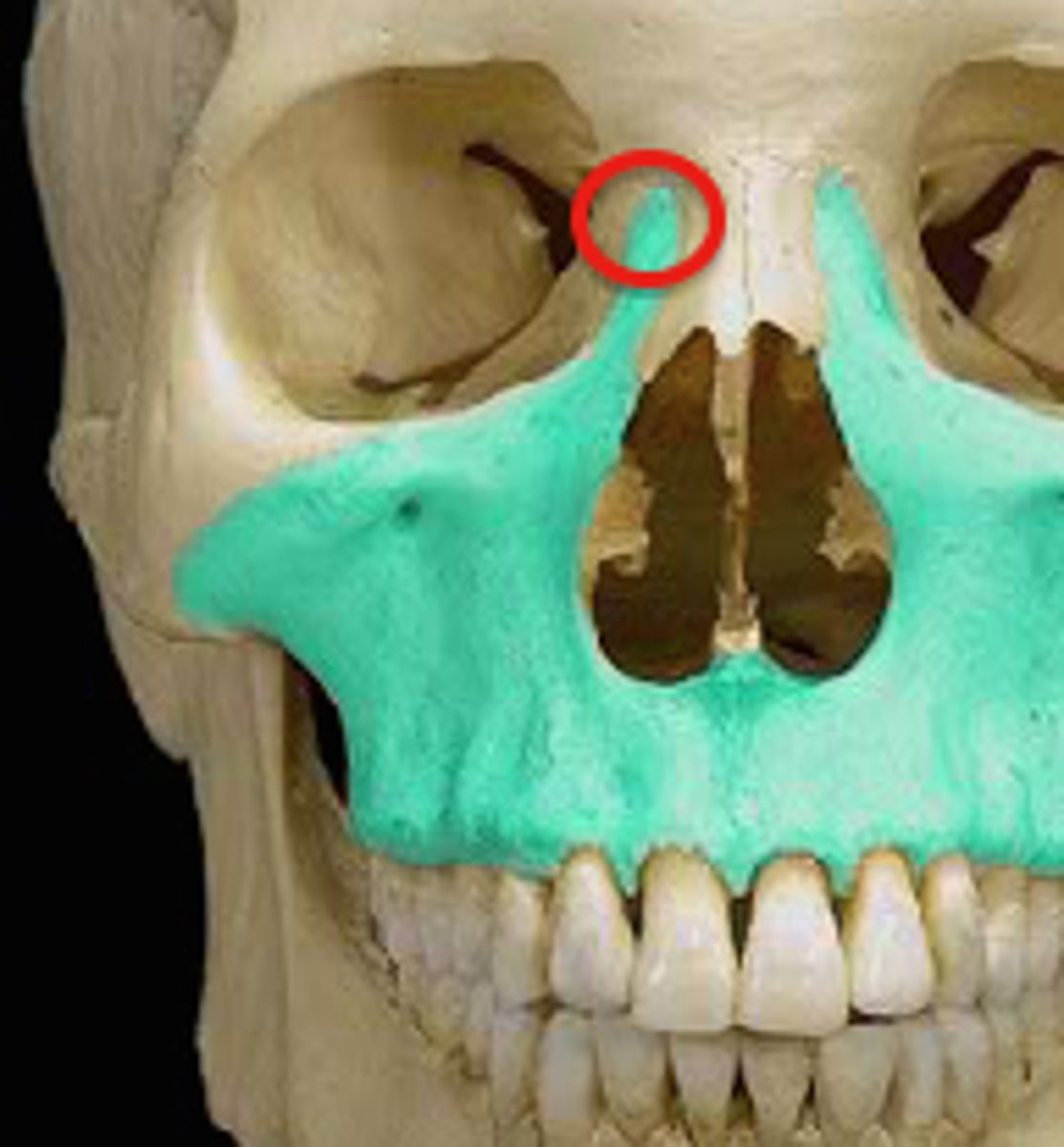
which process of the maxilla projects laterally to unite with the zygoma?
the zygomatic process