taste
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
what are the 5 “well accepted” tastes
slaty
bitter
sour
sweet
umami
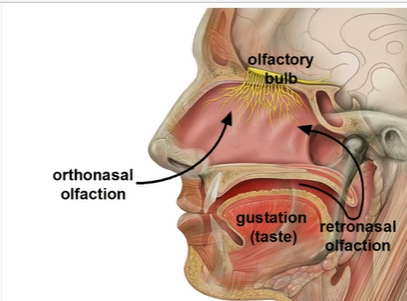
what are the two types of olfaction we experience in our sensory world
orthonasal olfaction
retronasal olfaction
what are the requirements for a basic taste
has a defined class of effective stimuli
has specialized transduction mechanisms
the signal is conveyed by the gustatory system
what is gustation
taste
what structures play a part in flavor
gustation
retronasal
what are the taste receptors that recognize umami
T1R
what are the taste receptors that recognize salty
ENaC: epithelium sodium channels
what are the taste receptors that recognize bitter
T2Rs
what are the taste receptors that recognize sour
Otopetrin-1 (OTOP1)
what are the taste receptors that recognize sweet
T1R
where was OTOP1 first identified
in the vestibular system
what specifically is OTOP1
a proton-selective ion channel
what is included in the chemosensory perceptual systems
gustation
olfaction
chemesthesis, including burning sensation
what CN caries chemosensation
trigeminal- V
if a receptor is not carried by the gustatory system…
it is NOT considered a basic taste
which cranial nerves are responsible for taste
7, 9, 10
where does CN VII carry taste from
the anterior 2/3 of tongue via chorda tympani and the palate- greater superficial petrosal branch of VII
where does CN IX carry taste from
the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
where does the CN X carry taste from
larynx
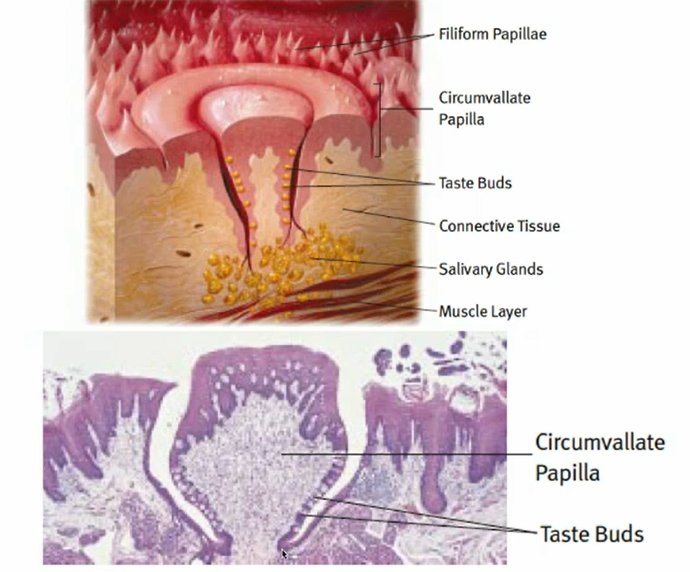
where is taste recognized on the tongue
fungiform papillae on anterior 2/3
foliate papillae in the folds in the rear/lateral
circumvallate papillae in the rear that form a ‘V’
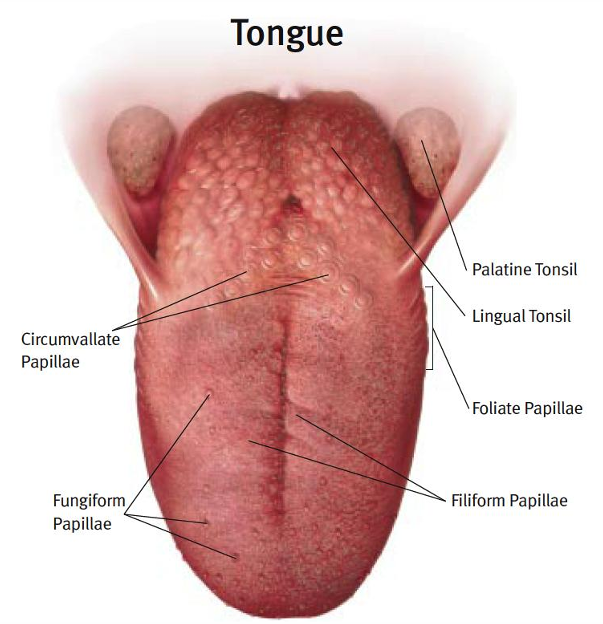
what papillae on the tongue do NOT recognize taste
filiform papillae
where does food dissolve to enter the taste bud
food will impinge on the taste receptor cells at the taste pore- only at the apical portion
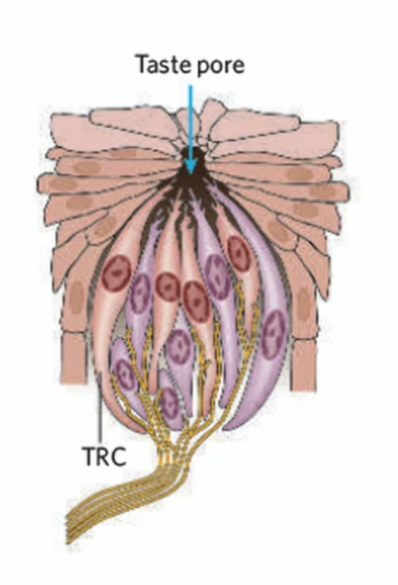
what is the ratio of pores and taste buds per papillae
many pores and taste buds per papillae in humans; unlike rats- 1:1
what are the cell types found in taste buds
type I
type II
type III
what innervates the anterior 2/3 of the tongue
chorda tympani and lingual nerve
lingual nerve has what type of nerve fibers
trigeminal- sensation for pain and touch
chorda tympani nerve has what type of nerve fibers
facial- taste, lingual cold and tactile
what does the chorda tympani specifically innervate
the taste receptor cells on the inside of the fungiform papilla
what type of nerve fibers does the glossopharyngeal nerve carry to the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
touch and pain information to the circumvallate papillae
what does the glossopharyngeal nerve specifically innervate
the para gammel area; outside the taste bud
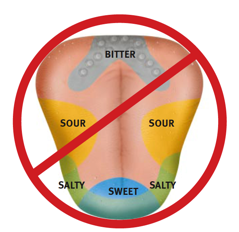
why is this wrong
we do NOT perceive just one taste quality on each part of the tongue; taste buds from all regions of the oral cavity contain cells that respond to all five basic tastes
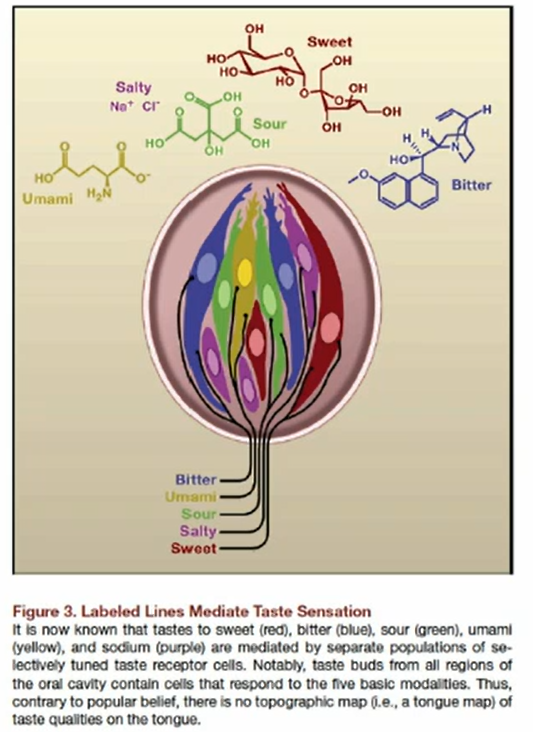
what is a type IV cells
is a progenitor cell for type I, II, and III
what is type I cell also known as
glial-like
what type of taste are type I cells responsible for
salty
what is type II cells also known as
receptor cell
what are type III cells also known as
presynaptic cell
which cell type is the only one where you see true vesical synapses w the nerve fibers
type III
which cell type has these features: round nucleus, come close to the nerve fiber to release ATP to stimulate nerve fibers and to communicate with type III cells
type II cells
what are the two major types of taste receptor proteins expressed by type II cells
contain G-protein coupled receptors for:
T1Rs: involved in detection of sweet and umami
T2Rs: involved in detection of bitter
for the sweet and umami receptors on type II cells, what does it need to have to function properly
need to have 2 functional units: heterodimer
what do type II cells release
ATP
what do type III cells release
serotonin
which cells type contains the otopetrin I receptor
type III
what do G-protein coupled receptors do in T1rs and T2rs
initiate a cascade of intracellular messaging system involving PLCbeta2, IP3R3, and TrpM5
T2Rs are what type of receptor
transmembrane
T1Rs are what type of receptors
have a venus-flytrap domain- where sweetness is capture
what effect does the miraculous berry have on taste
makes sour things taste really sweet
MOA of miraculous berry
binds to sweet receptors during low pH levels (during reg pH, tastes blah)
what can drugs for treating cancer- like BCC cause
taste loss
what can progenitor cells in the basement membrane outside of the tastebuds differentiate into
non-taste keratinocytes
precursors for type I/II/III
what pathway will determine what the progenitor cells will become
the sonic hedgehog pathway
what will form based if the sonic hedgehog pathway is activated vs not activated
activated: form taste cells- type I/II/II
not activated: non-taste keratinocytes
what affect do BCC drugs have on the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway
one will act at SMO and others will act on the Shh binding PTCH → will block gene production → no formation of taste cells
how often do taste cells turnover
10-14 days
when can radiation cause permanent taste lost
when there is damage to the salivary glands (if no damage, taste can return)
how can dental injections cause taste loss
can be blunt nerve injury w the needle or some cytotoxicity from the the local anesthetic
what is the most common way to the lingual nerve is damaged → damaging taste
3rd molar extractions
what is happening on the tongue when you damage the lingual nerve
there is an atrophy of fungiform papillae
how can you cause taste loss during an ear surgery
chorda tympani travels along tympanic membrane of inner ear → can damage during surgery → will lose taste on the same side of damage ONLY
how can salivary issues cause taste loss
saliva is necessary to dissolve food
saliva protects taste cells from dehydration
has growth factors necessary for the regeneration of the taste cells
how can viruses cause taste loss
shingles in the facial nerve →loss of taste on affected side
SARS-COV-2 → can directly enter cells via ACE2 receptors → directly will kill taste cells → can get complete taste loss
according to Sue how can you loose smell
whiplash → can shear axonos going through cribriform plate