Exam 2 Ch. 4-7
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
Where does adaptive immunity occur?
First in secondary lymphoid tissue, then throughout the body
When does the adaptive immune response occur?
4-7 days after infection, usually subsides 2-3 weeks later
T and B cells develop from what progenitor?
common lymphoid progenitor
Antigen receptor of B cells
immunoglobulins
Antigen receptor for T cells
T-cell receptor
How does T-cell activation work?
dendritic cell takes up antigen and is activated by PRRs
dendritic cell travels to lymph node
antigen is processed and presented by MHC
dendritic cell interacts with naive T cells, causing them to proliferate and perform their specific functions
Structure of the T-cell receptor
heterodimer whose chains each have membrane-distal variable domains, membrane-proximal constant domains, transmembrane domains, and cytoplasmic tails
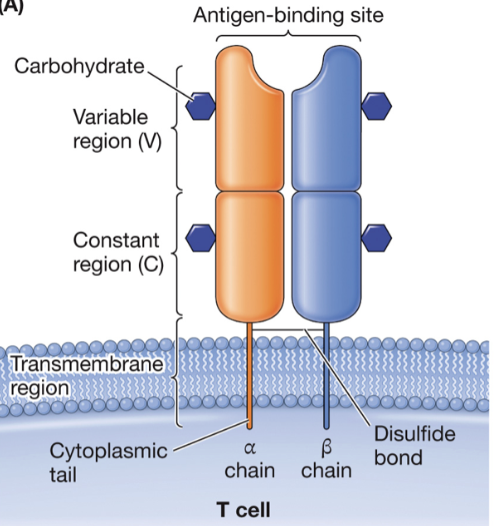
What are the TCR loci?
alpha, beta, gamma, and delta
What forms the structure of antigen binding sites?
combination of two variable domains
Somatic recombination
V, J, and sometimes D regions of DNA recombine to produce a new exon for a new protein, increasing diversity dramatically with a small amount of DNA
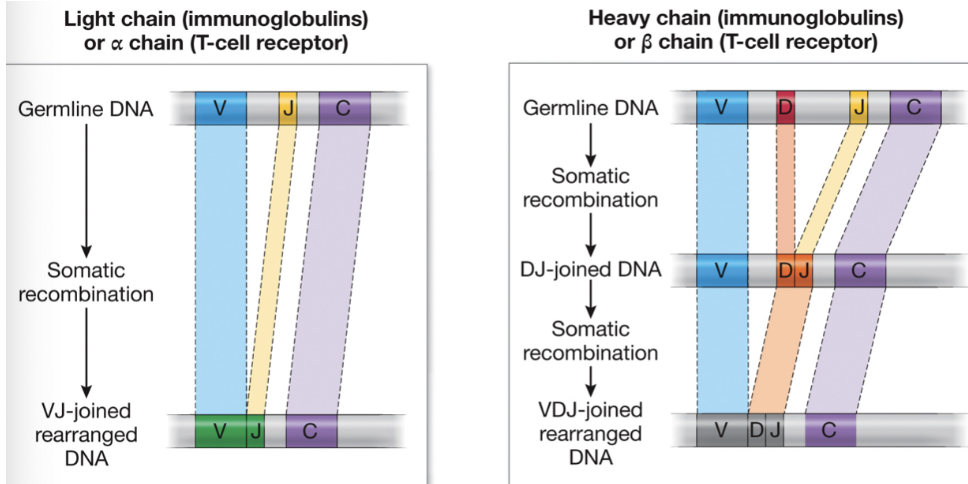
Which chains have D segments in addition to V and J segments?
heavy chain in immunoglobulins and beta chains in TCRs
TCR signaling happens by association with what?
several additional polypeptides containing ITAMs
Signaling motifs
small polypeptides that help in the signaling pathways
MHC molecules
peptide binding specialists that bind a variety of different peptides, not stable when empty
Beta2 microglobulin
invariant polypeptide found in all class I MHC molecules
What is the difference in peptide binding ability between class I and II MHCs?
class I can bind to peptides ~9 amino acids long
class II can bind to peptides ~14-20 amino acids long
Is MHC class I or class II more common on cells?
class I is on all cells
CD8
coreceptor for T cells that associates with MHC class I
CD4
coreceptor for T cells that associates with MHC class II
What is the difference between the structure of antigen binding grooves on MHC class I and class II?
class I groove is made only from the alpha chain
class II groove is made from both alpha and beta chains
MHC equivalent in mice
H-2
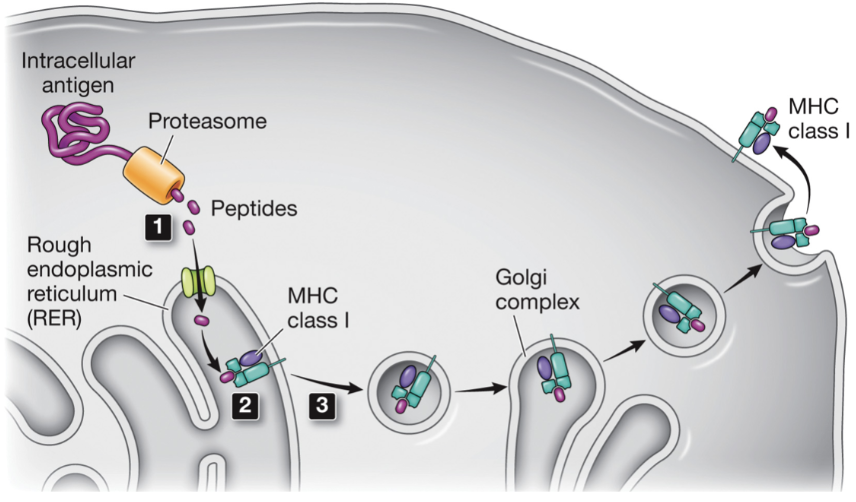
Mechanism of MHC class I peptide presentation
cytoplasmic proteins digested by the proteasome
peptides transported to the ER where they bind to the peptide-binding site
the complex leaves the ER and travels through the secretory pathway to the plasma membrane where it is presented to T cells
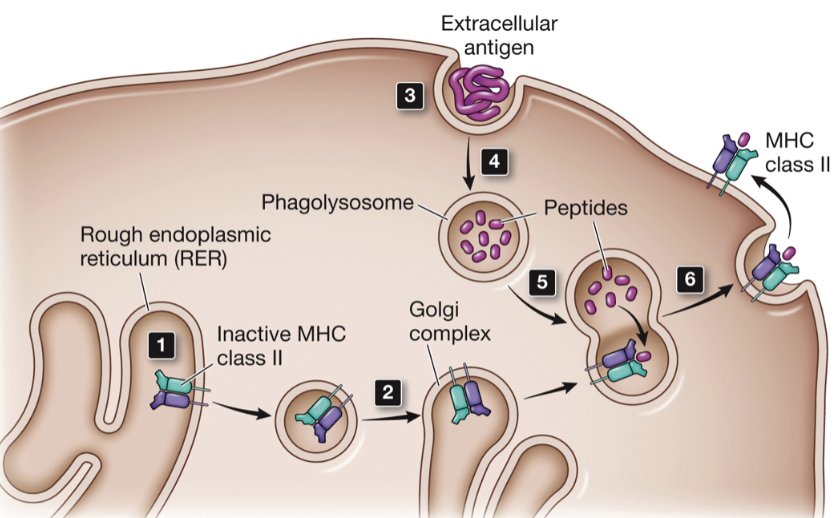
Mechanism of MHC class II peptide presentation
MHC class II are translated and transported to the rough ER where they remain in an inactive state
travel through the secretory pathway to a vesicle where they wait for further action by a phagolysosome
extracellular molecules and pathogens are endocytosed by professional APCs
endosome containing extracellular material matures into a phagolysosme
lysosomal proteases digest proteins
phagolysosome fuses with secretory vesicles containing MHC class II molecules
travel to cell surface where they present peptides generated by digestion
Proteasome
proteolytic enzyme that degrades intracellular proteins
What chains are in surface immunoglobulins?
surface immunoglobulins contain 2 heavy chains and 3 light chains
Structure of B-cell receptor complexes
contain 2 heavy and 3 light chains, transmembrane domains, and small cytoplasmic domains
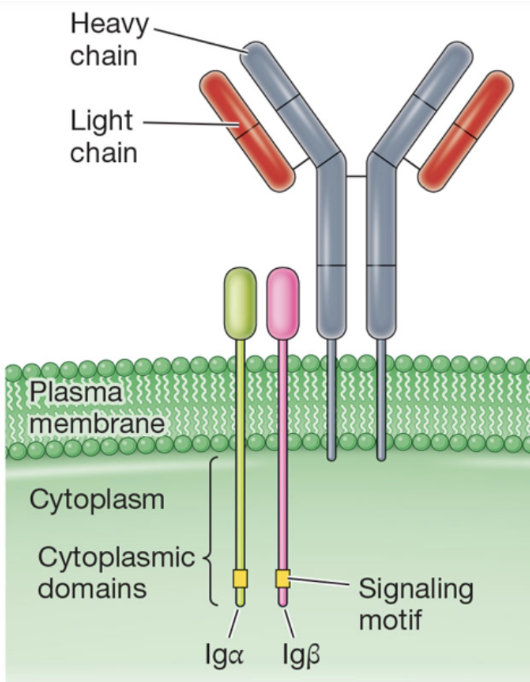
What makes up the antigen binding site of antibodies?
combination of V domains of the heavy and light chains
Contents of the chains of an antibody
each has a single variable domain, one constant domain in the light chain, and 3-4 constant domains in the heavy chain
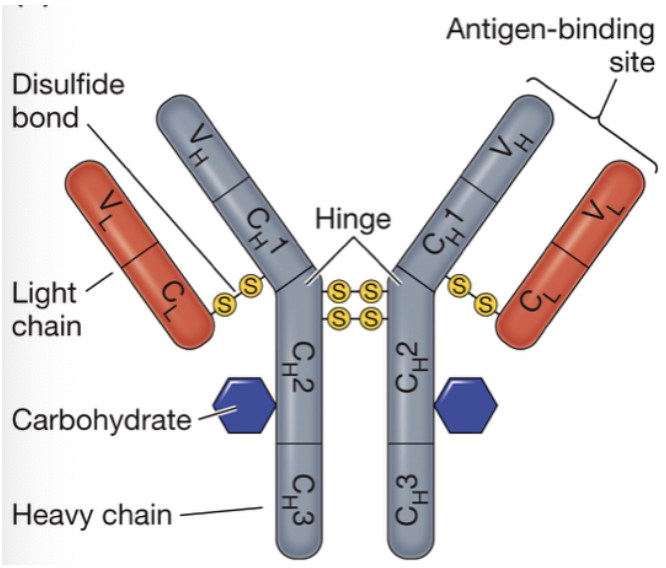
Hinge region
flexible angle on antibodies that can adapt to bind to a large or small structure
Where do proteases cleave immunoglobulins?
just above the hinge or just below the hinge
Fab
fragment of immunoglobulin that binds antibody
Fc
constant fragment of immunoglobulin
Fab2
antibody binding fragment resulting from cleavage below the hinge, does not have the constant region and its signaling capabilities
Other than somatic recombination, what genetic mechanism increases diversity of Ig and TCR genes?
addition of N nucleotides by TdT
addition of P nucleotides
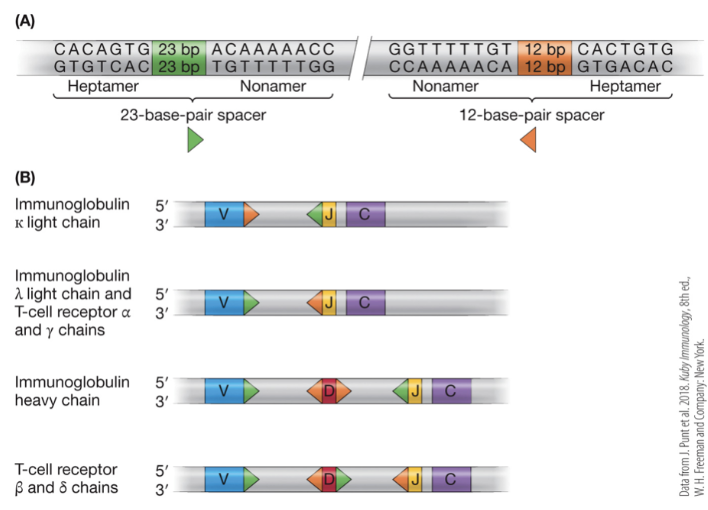
RAG1 and RAG2
recombination genes in the immune system that recognize heptamer and nonamer sequences with spacers of either 23 or 12 base pairs
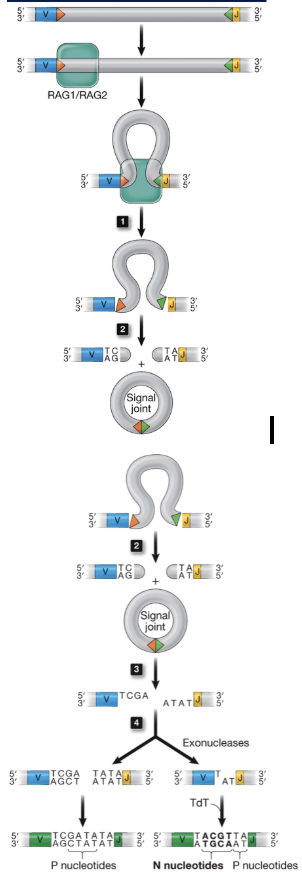
Mechanism of V(D)J Recombination
recombinase recognizes recombination signal sequence (RSS)
recombinase brings the 12 and 23 RSS together
recombinase cuts the DNA to produce a hairpin and a circular byproduct by covalently attaching ends
hairpin cleaved randomly by another nuclease
exonucleases, polymerases, and TdT modify the ends until DNA is reconnected by ligase
imprecision leads to addition and deletion of nucleotides
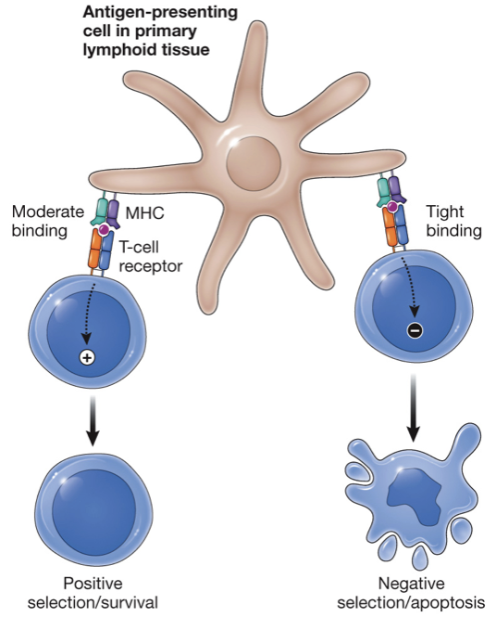
Positive selection of T lymphocytes
only T cells that have moderate affinity for self-MHC + peptide recieve a survival signal
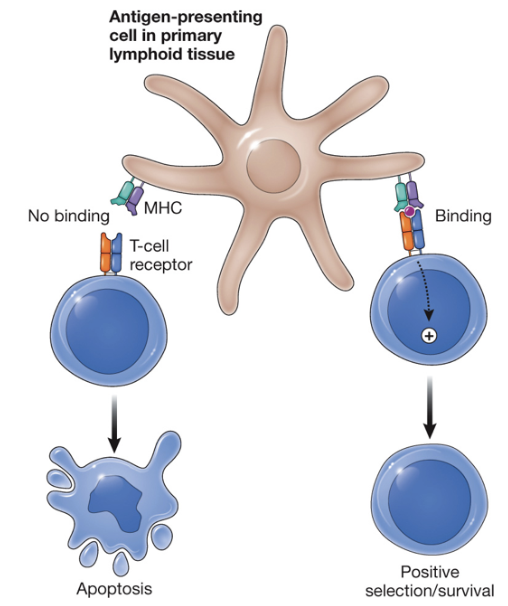
Death by neglect
cell dies because it does not receive a signal to survive
Negative selection of T lymphocytes
T cells that have high-affinity for self-MHC + peptide receive a death signal to produce tolerance
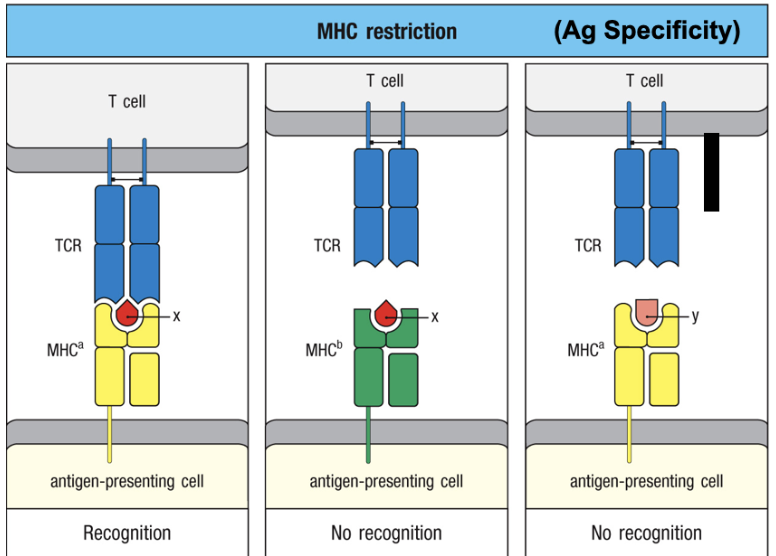
MHC restriction
T-cells only recognize peptides + MHC molecules matching their own self-MHC type
Allogeneic response
immune system attack by a recipient against foreign antigens from a donor of the same species
Syngeneic
no response when donor A T cells are mixed with donor A APCs
Allogeneic
strong response when donor A T cells mixed with donor B APCs
B-cell negative selection
self-reactive B cells are deleted or become anergic
Anergic
not killed but non-responsive
Clonal selection
T cells with receptors that recognize the specific pathogen are activated
Clonal expansion
T-cell proliferation and differentiation results in effector cells that work to eliminate pathogens
Function and activation of cytotoxic T cells
recognize target, and destroy cells infected with an intracellular pathogen
activated upon engagement of a T cell containing a CD8 corecpetor with an MHC class I APC
Function and activation of TH1 helper cells
aid in combatting extracellular pathogens by activating macrophages
activated upon engagement of a T cell containing CD4 coreceptor with MHC class II APC
Function and activation of TH2 helper cells
combat extracellular pathogens by activating B cells, good at combating helminths
activated upon engagement of a T cell containing a CD4 coreceptor with MHC class II APC
Follicular helper T cell
within secondary lymphoid tissue to promote isotype switching and somatic hypermutation
isotype switching
B cell changes the type of antibody it produces without changing the target specificity
Function and activation of TH17 helper cells
combat extracellular pathogens by activating neutrophils
activated upon engagement of a T cell containing CD4 coreceptor with MHC class II APC
Regulatory T cells
Inactivate self-reactive T cells to promote peripheral tolerance
Memory T cells
long-lived T cells that promote an adaptive immune response to a pathogen upon subsequent exposure
Secreting cells and function of IL-2
T cells
T-cell activation
Secreting cells and function of IL-4
T cells, ILC2s
B-cell activation, T cell activation (TH2)
Secreting cells and function of IL-10
monocytes, macrophages, T cells
anti-inflammatory
Secreting cells and function of IL-12
dendritic cells, macrophages
TH1 helper T-cell and NK cell activation
Secreting cells and function of IL-17
T cells, ILC3s
neutrophil activation
Secreting cells and function of IFN-γ
T cells, macrophages, NK cells, ILC1s
macrophage activation
IFN-a/IFN-B
macrophages, dendritic cells, virally infected cells
activation of NK cells, prevents viral replication
Secreting cells and function of TGF-β
regulatory T cells
anti-inflammatory, peripheral tolerance, T-cell inactivation
Antibody effector functions
neutralization, opsonization, complement activation, antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity
Neutralization (antibody effector function)
inactivation, prevents binding to cells
Opsonization (antibody effector function)
binds to pathogens to facilitate phagocytosis
Complement activation (antibody effector function)
activates the complement system to facilitate membrane attack and opsonization
Antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (antibody effector function)
activates NK cells to trigger killing, triggers degranulation of other granulocytes
Function and production of IgM
antibody isotype that acts as a B-cell receptor on the surface of naive B-cells, neutralizer, complement activator
produced by activated B cells in conjunction with IgD through alternative splicing
Function and production of IgD
antibody isotype acting as a B-cell receptor on the surface of naive B cells, activates mast cells and basophils
produced by activated B cells in conjunction with IgM through alternative splicing
Function of IgG
antibody isotype: neutralizes, opsonizes, complement activator, helps form and clear soluble immune complexes, helps activate NK cells in ADCC
Function of IgE
antibody isotype: binding to antigen causes mast cell degranulation and release of inflammatory mediators, activates mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils
Function of IgA
antibody isotype: found on mucosal surfaces, neutralizes, delivers pathogens to mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue
How do we measure cytotoxic T-cell activity?
incubate target cells with radioactive chromium which gets taken up into the cytoplasm
mix effector cells and target cells at different ratios
after a few hours, collect and measure radioactivity in the supernatant
calculate specific lysis
What cells are in the thymus?
bone-marrow derived cells and radiation resistant epithelial cells
C-kit
receptor for stem cell factor cytokine
CD34
marker for stem cells
CD25
receptor for T cell growth factor IL-2
AIRE
autoimmune regulator
Instructive model of MHC restriction
CD8 ligation produces a different signal than CD4 ligation and the signal generated tells the cell what it should become
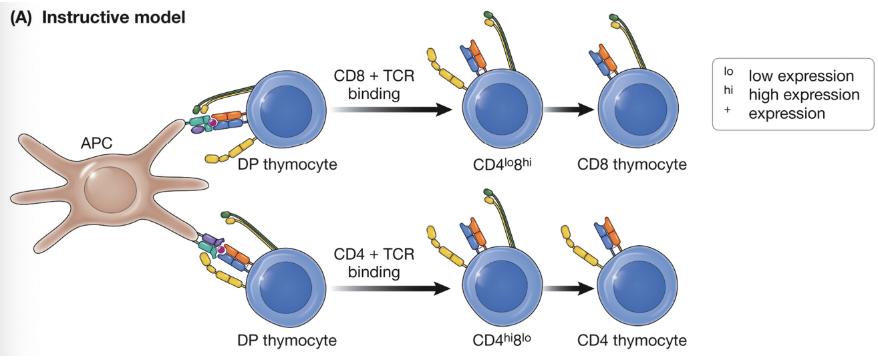
Kinetic signaling model of MHC restriction
all cells reduce CD8 expression on DP thymocytes, TCRs seeing MHC class I signal less and respond by increasing CD8 and turning off CD4, while TCRs seeing class II have unchanged signaling and loss of CD8 continues
Transgenic
injecting DNA into an embryo results in those embryos sometimes incorporating that DNA
Function of CD8 cells
become cytotoxic T-cells
Function of CD4 T-cells
become helper T cells
Which coreceptor is favored when TCRs recognize class I MHC?
CD8
Which coreceptor is favored when TCRs recognize class II MHC
CD4
What type of antigens are presented by MHC class I?
intracellular
What type of antigens are presented by MHC class II?
extracellular
Complementarity determining region
where molecules bind to their specific antigen
CD28
costimulatory molecule on T cells that binds a ligand on APCs
Function of αβ or δγ subunit
recognize antigen presented to T cell
Function of CD4
recognize MHC class II molecule, transduction of antigen-binding signal
Function of CD8
recognize MHC class I molecule, transcution of antigen-binding signal
Function of CD3δ, CD3ε, CD3γ, CD3ζ
transduction of antigen-binding signal
Function of CD28
required for co-stimulation of T-cell activation during primary immune response
Function of CD45
transduction of antigen-binding signal and preferentially activating memory T cells
Function of CTLA4
downregulate T-cell activation by dampening costimulatory signal
Mechanism of class I peptide processing and loading
phagolysosome and β-microglobulin find each other to facilitate peptide binding
TAP transports peptides in
ERAP trims peptides so they fit better into the grooves of MHC class I molecules
stable vesicle buds off and is secreted
Mechanism of class II peptide processing and loading`
MHC class II binds invariant chain
CLIP produced
antigen is phagocytosed to a phagolysosome which fuses with MHC class II vesicle
HLA-DM pulls out any peptides it can, so you are left with high-affinity binding peptides
How do naive T cells become anergic?
encounter MHC-peptide complexes in the absence of CD28 co-stimulation