viruses
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
non-cellular
no nucleus or other cell organelles but do have nucleic acid
living
contain genetic material
can be replicated
have protein coat
non-living
obligate parasite
non-cellular
contains DNA or RNA (not both)
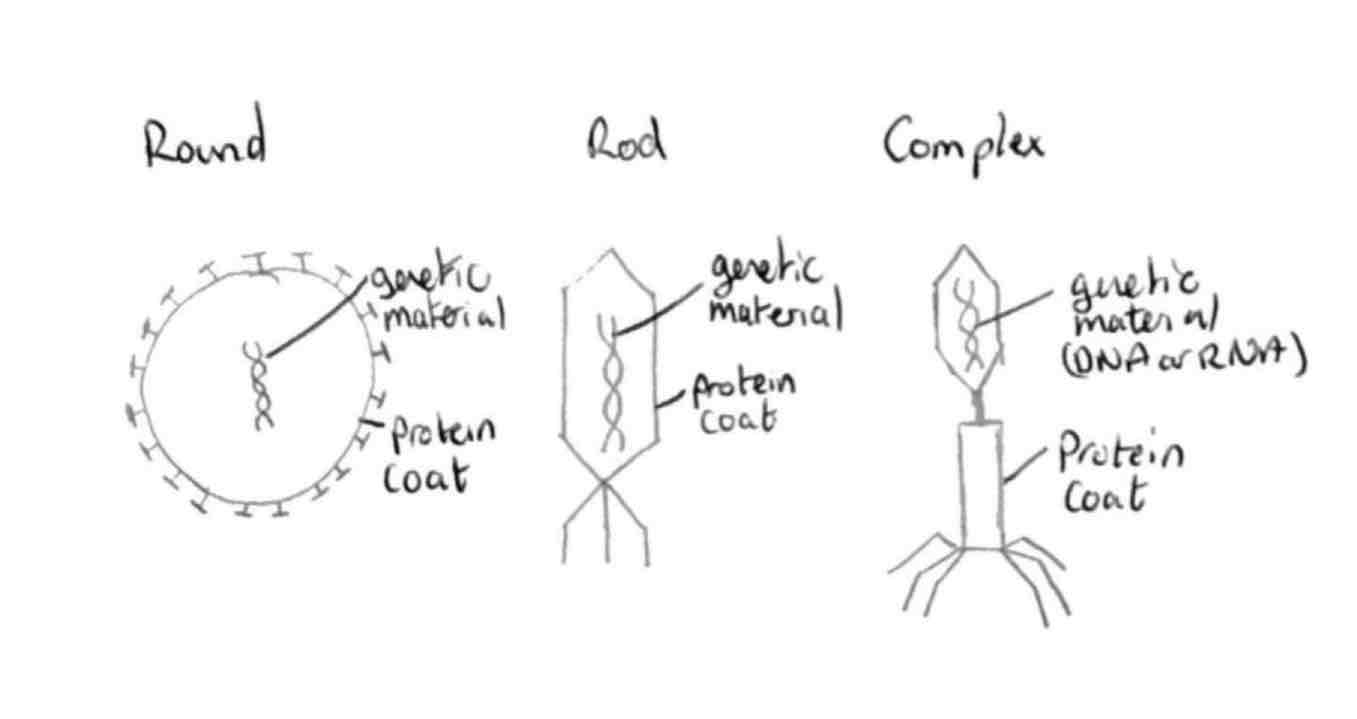
structure of viruses
protein coat and DNA or RNA
shapes of viruses
Rod, round, complex
obligate parasite
Can only live and reproduce on or inside a living host cell while causing harm to the host cell
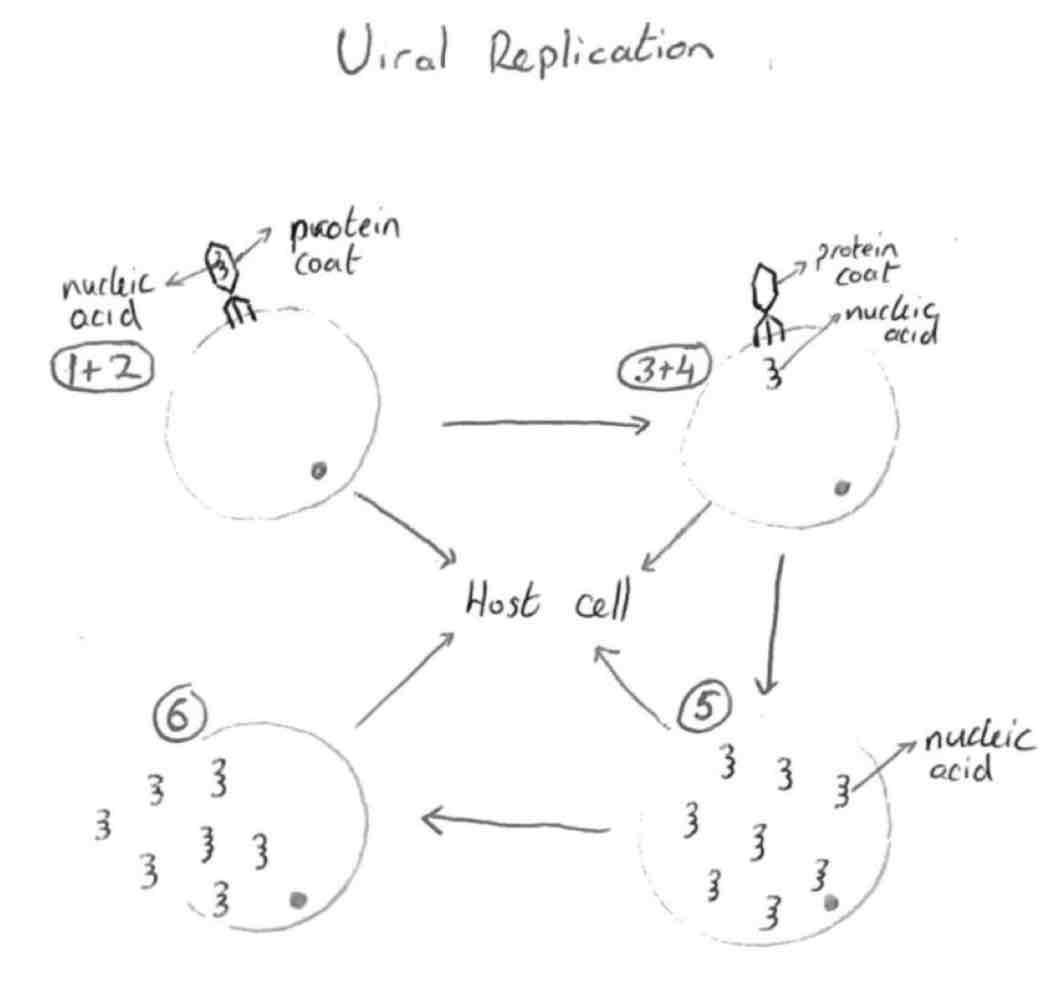
Viral Reproduction
virus attaches itself to the surface of the host cell
virus pierces a hole in the membrane of the host cell
DNA or RNA enters host cell
Protein coat remains outside
DNA/RNA replicates inside the host cell using host cell machinery. Synthesis of a new protein coat also occurs
Host cell bursts and releases the replicated virus and the process repeats
economic importance of viruses
advantage: production of vaccines
disadvantage: causes harmful diseases
HIV
AIDS
influenza virus
flu/cold
poliovirus
polio
HPV
cervical cancer
Virus X
plant virus
antibiotics
artificial antibodies that are made up by micro-organisms used to kill other micro-organisms
antibiotic resistance
bacteria do not die in the presence of an antibiotic
antibiotic misuse
using antibiotics to treat a viral infection/ not finishing course of antibiotics
antibiotic overuse
taking to many courses of antibiotics
antibiotic misuse/overuse result
causes the surviving bacteria to to adapt through mutations and will not die when treated with an antibiotic in the future
vaccines
introducing and inactive form of the virus that will stimulate an immune response
sensitive bacteria
bacteria that die in the presence of an antibiotic