Biochemistry Class 10 - Muscular, Skeletal, and Respiratory Systems
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
What are general characteristics of skeletal muscles? Control, location, nuclei, microscopic appearance
Voluntary
On the bones
Multinucleate
Striated under microscope
What is the hierarchy of muscle cells?
Protein filaments (actin and myosin) → sarcomere → myofibril (organelle) (string of sarcomeres) → muscle cell (myofibers) (bundle of myofibrils) → fascicle (bundle of muscle cells) → whole muscle (bundle of fascicles)
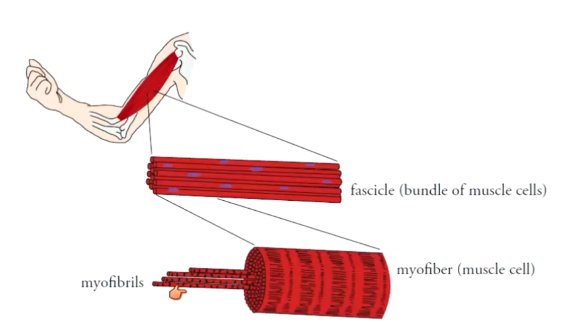
What are parts of a muscle cell?
Myofibrils, mitochondria, sarcoplasmic reticulum, T-tubules, mitochondria, nuclei
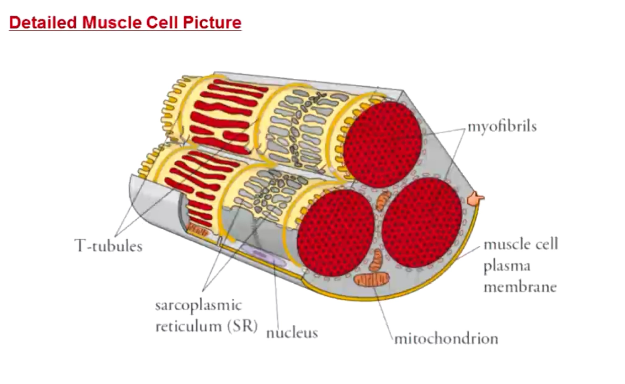
What is the SR?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Storage of calcium in muscle cells
What are T-tubules?
Invaginations of muscle cell plasma membrane
Allows action potentials to travel to the interior of the cell
What gets shorter when muscles contract?
Sarcomere and larger get shorter
Proteins (actin and myosin) themselves do not
How are sarcomeres structured?
Ended on either side by Z-lines
Actin (thin filament) attached to Z-lines
Myosin filaments (thick filaments) overlap with actin
I-band: where only actin and Z-line is
A-band: myosin and actin
H-zone: only myosin
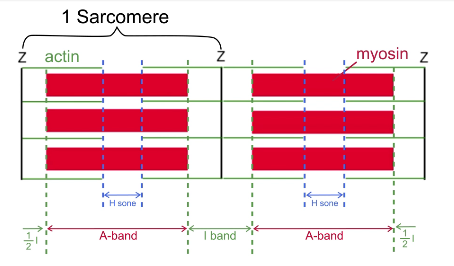
Why do skeletal muscles look striped
H band and I band are lighter in color → alternates with A-band, which is darker → striped
What is the sliding filament theory? 4 steps.
Myosin heads bind to actin filaments
Myosin pulls actin towards center of the sarcomere
Myosin releases actin
Myosin resets to high energy conformation
How does myosin bind to actin?
Called “cross-bridge formation”
Uses calcium
Not all myosin heads bind and release at once → net movement only happens when some myosins are attached to actin
How does myosin pull actin towards the center of the sarcomere?
AKA “power stroke”
Uses no ATP
Myosin returns to low energy state
How does myosin release actin?
Requires ATP to be present
How does myosin reset to its high energy form?
Requires hydrolysis of ATP
What is the part of muscle contraction first affected by a lack of ATP?
Muscle relaxation → why there is rigor mortis
What is the thin filament? How is it structured?
Actin, tropomyosin, troponin
Actin forms bundles → tropomyosin covers myosin binding sites on actin → troponin sits on top of tropomyosin and binds Ca2+
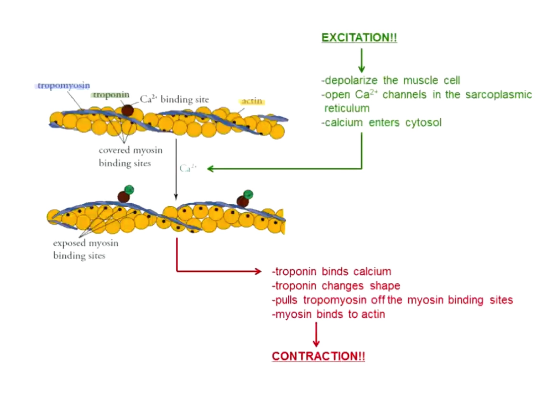
What is excitation-contraction coupling?
Excitation: muscles innervated by neurons → action potentials → depolarization of muscle cell → open calcium channels in the SR → calcium released into cytosol
Contraction: troponin binds to calcium → pulls tropomyosin off of myosin binding site → myosin binds to actin → sliding filament theory picks up here
Why does contraction of muscle cells require so much ATP?
Must use active transport to get calcium out of cytosol and back into SR
Sliding filament theory uses ATP to relax muscles
What are motor units?
Neurons and all of the muscle cells it controls
All muscle cells in a motor unit contract as one
Large: 1000s of muscle cells per neuron
Small: 10-20 muscle cells per neuron
How are muscle contractions controlled in a graded fashion (how do you contract strongly vs softly)?
Contract different numbers of motor units
More = stronger
How is gross motor control innervated?
A few large motor units
How is fine motor control innervated?
Many small motor units
How does your body know how many motor units to use for movements?
This is what you learn as a baby
Or by practicing motor movements
What are sources of ATP for muscles? From fastest to slowest.
Creatine-P + ADP → creatine + ATP
Glycolysis: 2 net ATP, lactic acid
Aerobic metabolism: 30 ATP, CO2, H2O
In very long-term movements, switch between aerobic and glycolysis
What is myoglobin?
Stores one oxygen
In muscles that are used for super long-term endurance
Allows for aerobic respiration
Myoglobin is dark, makes dark meat
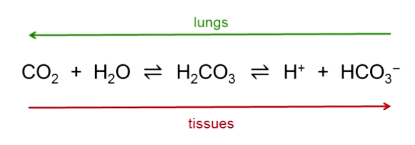
What is oxygen debt?
Extra oxygen needed after exercise to replenish oxygen stored on myoglobin and convert lactic acid into something useful
Why is oxygen required to convert lactic acid to something useful?
Must be oxygenated back to pyruvate first → to do other things with it requires ATP → need oxygen to make ATP
Where does the oxygen come from to repay the oxygen debt?
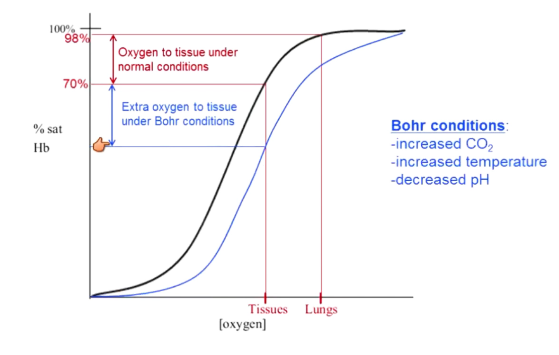
Pull more oxygen off of hemoglobin
Increased CO2, increased temperature, and decreased pH shift hemoglobin curve right → this stuff happens when exercising (Bohr conditions) → Hb has a lower affinity to oxygen
These conditions do not shift in lungs due to oxygen
What are types of skeletal muscles?
Slow twitch
Type IIA
Type IIB
What are slow twitch muscle characteristics? AKA, myoglobin content, capillary network, speed of contraction, # of mitochondria, fatigue resistance, force generated, example
AKA: slow oxidative fibers
Myoglobin content: high
Capillary network: very dense
Speed of contraction: slow
# of mitochondria: high
Fatigue resistance: high
Force generated: low
Example: thigh muscles of marathon runners
What are type IIB skeletal muscle characteristics? AKA, myoglobin content, capillary network, speed of contraction, # of mitochondria, fatigue resistance, force generated, example
AKA: fast twitch
Myoglobin content: none
Capillary network: very few
Speed of contraction: very fast
# of mitochondria: very low
Fatigue resistance: low
Force generated: high
Example: thigh muscles of sprinters
What are type IIA skeletal muscle characteristics? AKA, myoglobin content, capillary network, speed of contraction, # of mitochondria, fatigue resistance, force generated, example
AKA fast oxidative
Myoglobin content: low
Capillary network: medium
Speed of contraction: medium
# of mitochondria: some
Fatigue resistance: medium
Force generated: medium
Example: thigh muscles of 5k runners
What are characteristics of cardiac muscles? Function, location, nuclei, microscopic appearance
Involuntary, autorhythmic (can generate own contraction)
Only in the heart
Uninucleate
Striated
How does the functioning of skeletal and cardiac muscle contractions differ?
Skeletal: calcium comes exclusively from SR
Cardiac: calcium from both SR and extracellular environment
What are characteristics of smooth muscles? Function, location, nuclei, microscopic appearance
Involuntary, neurally stimulated, hormonally stimulated, mechanically stimulated
Walls of hollow organs
Uninucleate
Non-striated
What is connective tissue?
Lots of extracellular material, but not many cells
Cells in a matrix
Connects other tissues
What types of cells are in connective tissues?
“___ blast”
“____ cyte”
What are fibroblasts?
Generic connective tissue cells
What are “____ blast” cells?
Immature cells
Still divide
Produces the matrix of connective tissue
What are “____ cyte” cells?
Mature cells
Usually do not divide
Maintain connective tissue matrix
What is the matrix of connective tissue made of?
Fibers and glop (ground substance)
What are fibers and their roles in connective tissues?
Collagen: strength (triple helix protein → super strong)
Elastic: recoil (regain shape after stretch)
What is the glop (ground substance) in the connective tissue matrix?
Liquid (blood plasma)
Solid (bone)
Can be anywhere between bone and liquid
What is the main role of connective tissue?
Plays a supporting role
What are four functions of the skeletal system?
Support and movement
Protection
Blood cell formation
Mineral storage of calcium and phosphate
What is the anatomy of long bones?
Well defined shaft (diaphysis)
Two well defined ends (epiphysis)
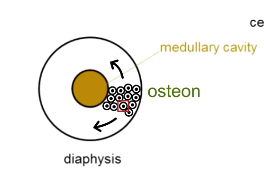
What is the anatomy of the diaphysis?
Medullary cavity filled with yellow bone marrow (fat)
Compact bone (relatively non-porous and inflexible)
Osteons surround medullary cavity
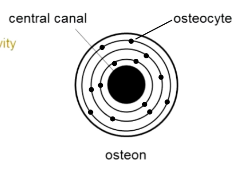
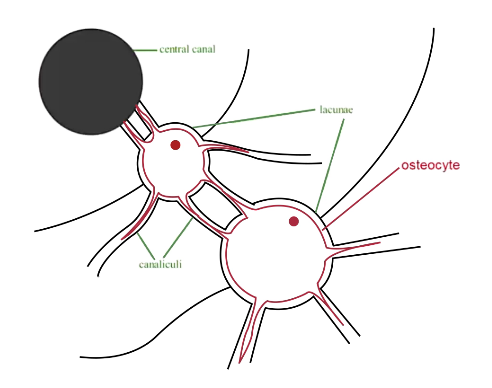
What is the structure of an osteon?
Central canal with blood vessels, nerves, some fat
Bone grows around central canal in rings
Osteocytes all along rings (dormant cells)
How do osteocytes get nutrients?
Have a cavity system that connects them to each other and back to the central canal
Called canaliculi
Joined by gap junctions
What is bone made of?
Solid calcium phosphate matrix
What is the anatomy of the epiphysis?
Outer shell is compact bone
Inner core is spongy bone (more porous and flexible)
Spongy bone is made of red bone marrow (blood cell formation)
What is the epiphyseal plate?
Cartilage between epiphysis and diaphysis → can grow and push them apart to allow for bone growth → rate of ossification is larger than rate of growth → ultimately your bones are all bone
What does parathyroid hormone do?
Increases blood calcium
Stimulates bone breakdown (osteoclasts dissolve bones)
Increased absorption of calcium in intestines
Increases reabsorption of calcium in kidneys
Can do calcium regulation on its own if it needs to
What does calcitonin do?
Decreases blood calcium
Stimulates bone formation (osteoblasts build bones)
Decreases absorption of calcium in intestines
Decreases reabsorption of calcium in kidneys
What are the functions of the respiratory system?
Gas exchange
pH regulation (fast)
What is ventiallation?
Moving air in/out of a system
What is respiration?
Gas exchange
Where does respiration happen? What do you call each?
Between lungs and blood = external
Between blood and body cells = internal
What do the organs of the conduction zone do?
Ventilation
What organs are in the conduction zone?
Nose/nasal cavity
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Primary bronchi, secondary bronchi (lobar) → → → terminal bronchioles
What is the role of the nose/nasal cavity?
Warms air
Humidifies air
Filters air
What is the structure of the nose/nasal cavity?
Lined with respiratory epithelium and mucus cells
Lots of cilia that can push mucus (and stuff trapped within it) out
What are the parts of the pharynx? What they do? What are they lined wiht?
Nasopharynx (behind nose): moves air, lined with respiratory epithelium
Oropharynx (behind mouth cavity): lined with protective layers of cells
Laryngopharynx (behind larynx): moves air and food, lined with protective layer of cells
What is the role of the larynx? Made out of?
Made entirely of cartilage (so trachea does not collapse)
Keeps trachea open, separates food and air (controls epiglottis), voice production
What does the trachea do? Structure?
Alternating bands of cartilage and connective tissue membrane
Trachealis muscle controls the diameter
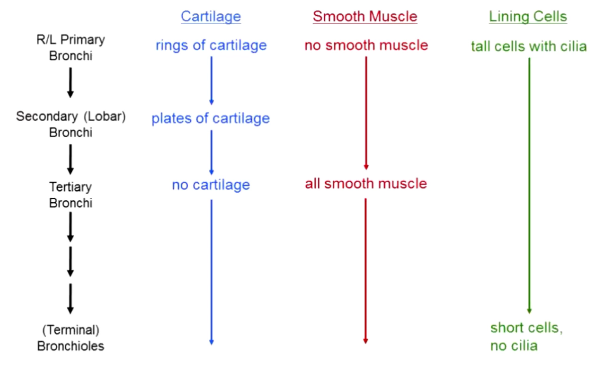
What is the structure of the bronchi and bronchioles?
Primary bronchi have rings of cartilage, no smooth muscle → as you go to second → plates of cartilage and some smooth muscle → as you move past tertiary → no cartilage, all smooth muscle
Start off lined with tall cells with cilia → eventually go to short cells with no cilia
How are secondary bronchi and below controlled?
Sympathetic nervous system relaxes the muscles → more air
Epinephrine is the major hormone of the SNS → relaxes muscles → why epipen injections open airways
Inhalers work similarly
What are the organs of the respiratory zone?
Bronchial tubes (respiratory bronchioles that branch off of terminal bronchioles of conduction zone)
Alveolar ducts
Alveolar sacs
Alveoli
What is the structure of alveoli?
Made of super thin cells for easy diffusion (type I cells)
Have some type II cells lining them
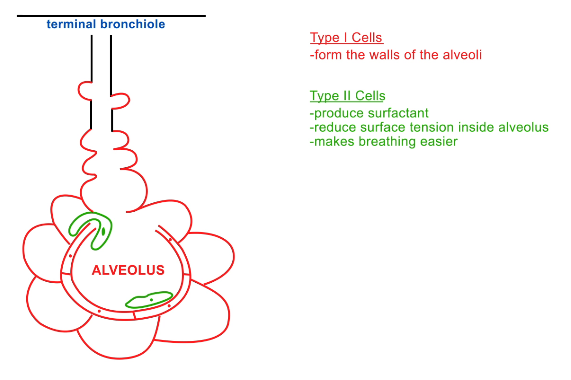
What do type II cells do in alveoli?
Produces surfactant
Reduces surface tension inside alveolus → so alveoli can be separated again if they contact one another
Makes breathing easier
What is the structure of respiratory bronchioles?
All smooth muscle
Includes some alveoli so it can do gas exchange
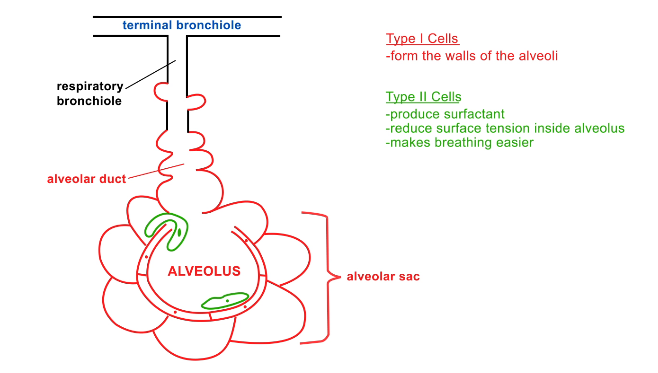
What is the alveolar duct?
Connects respiratory bronchiole to alveolar sac
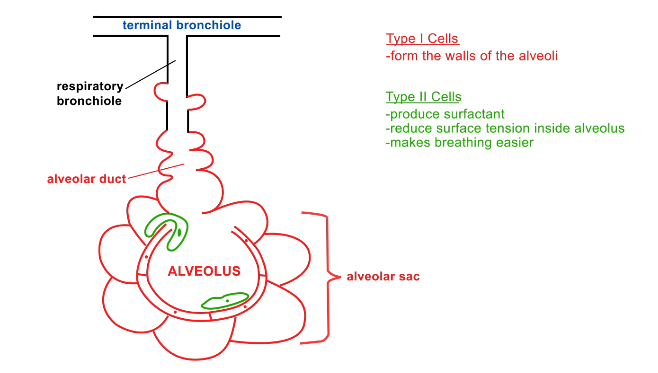
What are alveolar sacs?
Surround an alveolus
How are alveoli expanded/contracted?
Alveolar sac stuck to side of chest cavity → change size of chest cavity → change size of alveolar sac, thus alveoli
How is ventilation controlled?
Lungs stuck to inside of chest cavity → expand chest cavity → expand lungs → air comes in → contract chest cavity → contract lungs → air goes out
Why are lungs stuck to the chest cavity walls?
Surface tension
Slight negative pressure in the space between lungs and chest wall → lungs and chest wall push together
Losing negative pressure → cannot breathe
What is inspiration? Relaxed expiration? Forced expansion?
Inspiration (active): diaphragm contracts down → increase size of chest cavity → pressure decrease in lungs → air in
Relaxed expiration (passive): relax diaphragm → lungs elastically recoil → decrease size of chest cavity → pressure increases → air out
Forced expiration (active): contract abdominal muscles → increased pressure in abdominal cavity → diaphragm pushed up past resting position → air forcefully pushed out
What is ventilation rate based on?
Need to regulate pH
Ventilation increases pH → why we breathe faster after exercise
Cell functions decrease pH
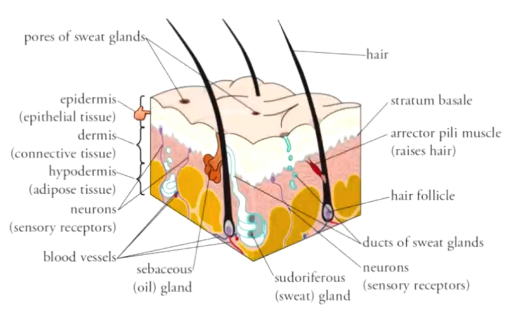
What are the three layers of the skin? What are they made of?
Epidermis: epithelial tissue
Dermis: connective tissue
Hypodermis: fat
How does skin help with thermoregulation?
Cold: deactivate sweat glands, shivering, vasoconstriction
Hot: activate sweat glands, no shivering, vasodilation