HMI 102 – Foundational Principles and Application of Medical Imaging
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A collection of vocabulary flashcards detailing key terms and their definitions related to the abdominal cavity and medical imaging principles.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Abdominal Cavity
The space within the abdomen that contains digestive organs and other structures.
Peritoneum
A membranous connective tissue layer that lines the abdominal cavity and covers the abdominal organs.
Intraperitoneal
Refers to organs that are fully covered by peritoneum and located within the peritoneal cavity.
Retroperitoneal
Describes organs that are located behind the peritoneum and are not fully wrapped by it.
McBurney’s point
A point in the right lower quadrant that is a common site for appendicitis pain and is located 1/3 along the line linking the ASIS and umbilicus.
Quadrant Division
A method of dividing the abdomen into four parts using the median and transumbilical planes.
9-fold division
Right mid clavicular line
left mid-clavicular line
transpyloric plane
trans-tubercular plane
Gallbladder
An organ that stores and concentrates bile produced by the liver.
Spleen
An organ responsible for processing blood, immune function, and recycling red blood cells.
9 divisions names
R hypochondriac
Epigastric
L hypochondriac
R lumbar
Umbilical
L lumbar
R iliac
Hypogastric (pubic)
L iliac
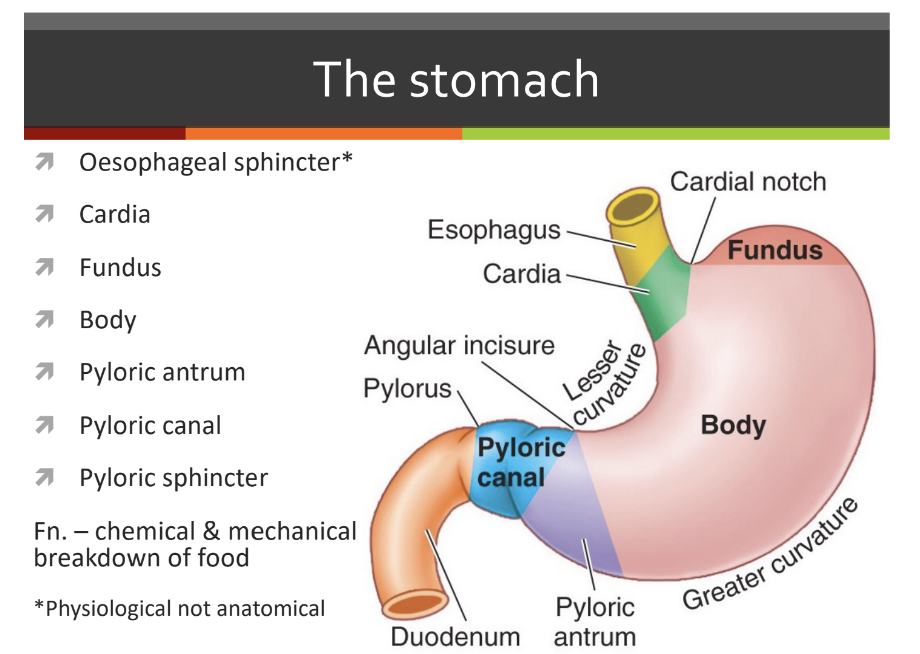
the stomach
Small intestine
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
function:
mixing/neutralising digestive contents
absorption of nutrients
Large intestine
The large intestine, also known as the colon, is responsible for the absorption of water and electrolytes, and the formation and excretion of feces. It consists of several sections including the cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum.
right corner = hepatic flexure
left corner = splenic flexure
Liver
An essential organ that detoxifies chemicals, metabolizes drugs, and produces bile for digestion. It also plays a key role in nutrient storage and blood filtration.
Pancreas
An organ that produces digestive enzymes and hormones, including insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels, playing a vital role in digestion and metabolism.