Molecules to Metabolism
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Metabolism
Sum of all enzyme catalysed reactions in an organism
Intracellular - within the cell
Extra cellular - outside the cell
Carbon
-the 15th most abundant element on earth
-forms 4 covalent bonds with other nonmetals
-covalent bonds produce strong compounds
-variety of bonds with variety of elements producing highly diverse properties and structures
Carbon can form double bonds and triple bonds (number of electron pairs two atoms are sharing)
Ethylene has double bonds
Acetylene has triple bond
Biochemical macromolecules
4 types: - carbohydrates -lipids - proteins -nucleic acids
All contain carbon
All are organic
Organic compounds: contain carbon and hydrogen atoms together
Macromolecules
Polymer: Large unit made up of smaller subunits
Monomer: subunits
Monomers are linked together to form polymers
Linkage occurs by condensation reaction aka dehydration synthesis
Dehydration synthesis is when water molecule is lost
Condensation Reaction
joining two monomers through removal of a water molecule
ANABOLIC: building things up
monomer + monomer = polymer + water
Hydrolysis
Opposite of condensation reaction
Uses water molecule to break down polymer
CATABOLIC : breaks down
Polymer + water —> monomer + monomer
Functional groups
positions on a molecule most likely to undergo a reaction
H and OH are often involved
C is not
6 functional groups
Hydroxyl
OH
Often found in alcohols
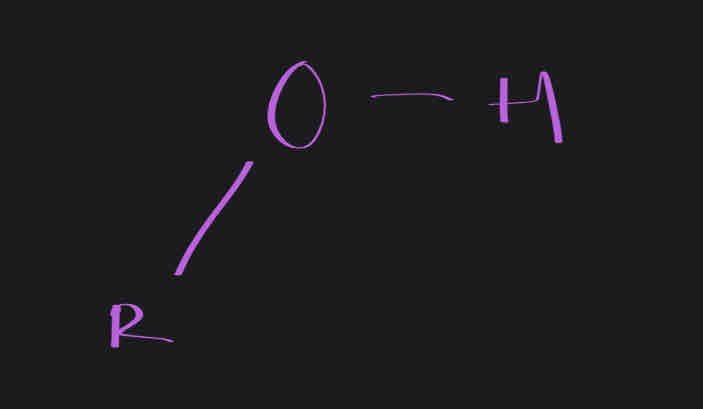
Sulfhydrl
SH
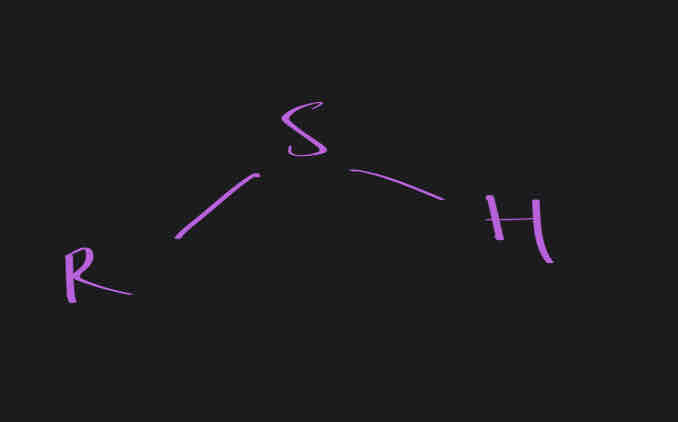
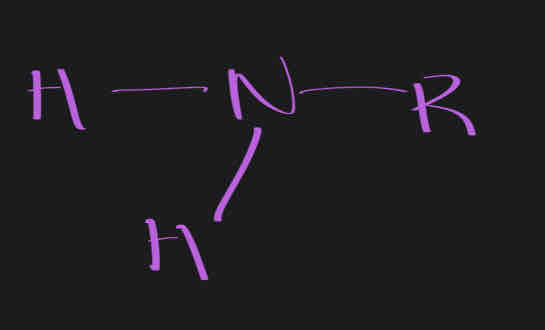
Amine / NH, NH2 , NH3
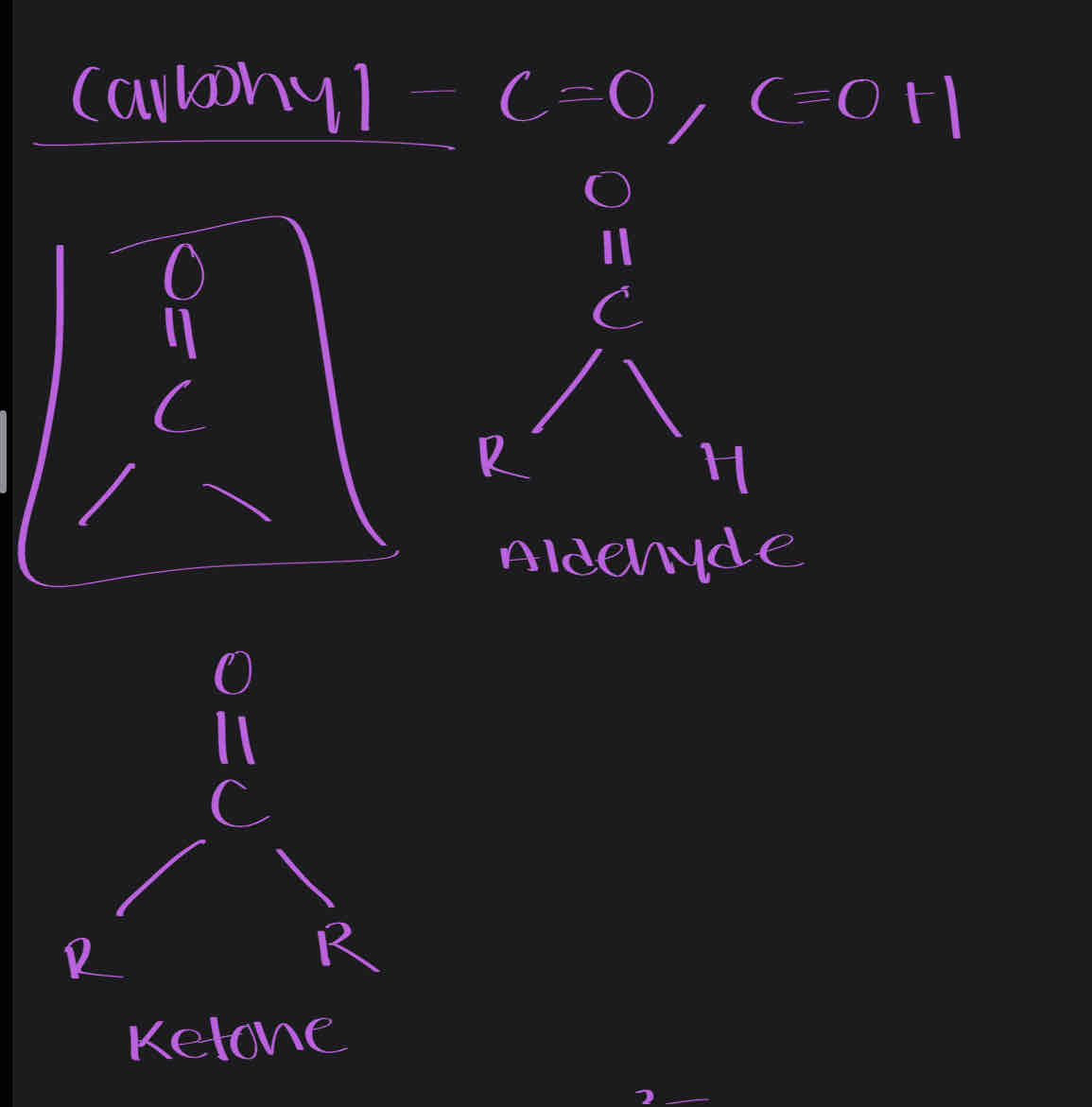
Carbonyl- C=O, C=OH
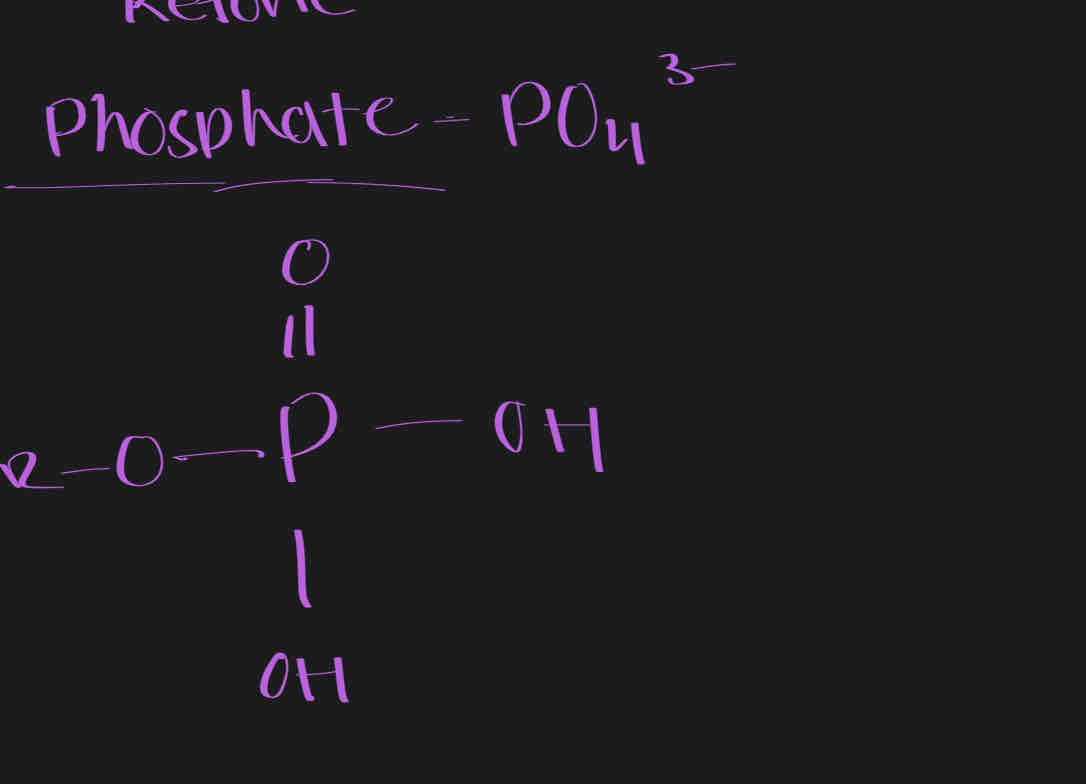
Phosphate - PO4-3
Bonding Capacity
Number of bonds an atom can form with a neighbouring atom —> or ionic charge
C-4
H-1
O-2
S-2 or 6
N-3 or 5
P - 5 (phosphate)