Behavioral Science II Lesson 1: Needs, Motivation, and Attitude
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
CRB Fill in the blanks: There are two main classes of motivation that depend on where the motivation comes from. A motivation coming from internal forces would be _________ motivation, whereas motivation from external forces would be ____________ motivation.
(A) Extrinsic, Intrinsic
(B) Intrinsic, Extrinsic
(C) Ego, Id
(D) Internal, External
(B) Intrinsic, Extrinsic
There are two main classes of motivation that depend on where the motivation comes from. A motivation coming from internal forces would be Intrinsic motivation, whereas motivation from external forces would be Extrinsic motivation.
CRB Shashank is lacking motivation to study for his SAT, so his parents want to extrinsically motivate him. Which of the following would be extrinsic motivators?
I. Praise from his parents when he studies.
II. Setting up an SAT competition with his neighbor.
III. Offering a monetary reward for a high practice exam score.
(A) III only
(B) I and III
(C) II and III
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Each of the following would be examples of extrinsic motivation.
I. Praise from his parents when he studies.
II. Setting up an SAT competition with his neighbor.
III. Offering a monetary reward for a high practice exam score.
Sarah is motivated to go to work because she knows that it is the responsible thing to do. When asked why she doesn't skip work to party, she replies that it makes rational sense to go to work so that she can pay the bills and not end up living on the streets. Which theory of motivation is Sarah relying upon to make this explanation?
(A) Maslow's Hierarchy
(B) Evolutionary Approach
(C) Cognitive Approach
(D) Optimal Arousal Theory
(C) Cognitive Approach
Sarah is relying on logical thinking to explain her motivation. The Cognitive Approach focuses on rationality and decision-making abilities.

CRB Social Cognitive Theory emphasizes interactions, including observational learning and modeling. Which of the following are factors considered in Social Cognitive Theory for how our attitudes and behaviors are impacted?
I. Personal Factors
II. Environment
III. Behavior
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III only
(D) I, II and III only
Social Cognitive Theory sees a person's behavior as being influenced or defined by three factors:
I. Personal Factors
II. Environment
III. Behavior
CRB Because the personal factors and environmental factors and behaviors all interact, they are able to influence and alter each other. Which of the following terms best describes this concept?
(A) Reciprocal Determinism
(B) Reciprocal Bias
(C) Reciprocal Alteration
(D) Correlational Adjustment
(A) Reciprocal Determinism
Reciprocal Determinism is the interaction between someone's behaviors, personal factors and environmental factors. A person both shapes and is shaped by their environment.
Elizabeth has always dreamed about being a doctor, but she is not studying hard for the MCAT because she needs to work her hourly job at Walmart in order to pay the bills and afford groceries. Which theory of motivation is best able to explain Elizabeth's situation?
(A) Maslow's Hierarchy
(B) Evolutionary Approach
(C) Cognitive Approach
(D) Optimal Arousal Theory
(A) Maslow's Hierarchy
According to Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, we fulfill basic needs before higher-level needs just as Elizabeth is doing in this situation.
John enjoys being a physician. He finds it to be much more mentally stimulating than his last job cleaning toilets and much less scary than his old job cleaning windows on 100-story skyscrapers. He feels like he is motivated to be at work because it is exciting to the right level. Which theory of motivation is John relying upon to make this explanation?
(A) Maslow's Hierarchy
(B) Evolutionary Approach
(C) Cognitive Approach
(D) Optimal Arousal Theory
(D) Optimal Arousal Theory
John has found the optimal level of arousal and it is motivating him to perform his job. In accordance with this, the Optimal Arousal Theory would suggest that John is also performing his job well due to a balanced level of arousal.
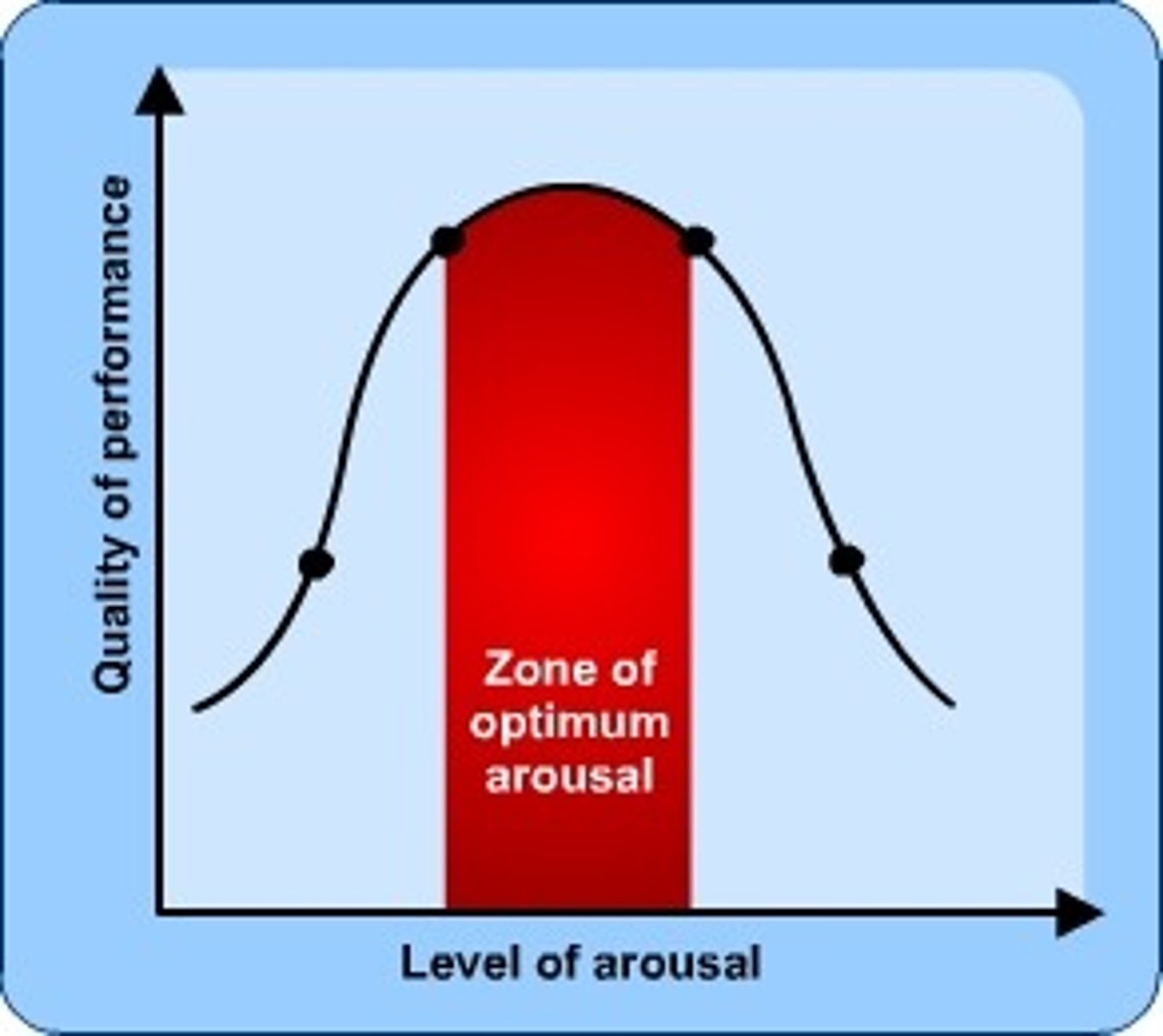
Max explains his desire to eat lasagna at dinner as resulting from his innate need for food. Which theory of motivation is Max relying upon to make this explanation?
(A) Maslow's Hierarchy
(B) Evolutionary Approach
(C) Cognitive Approach
(D) Optimal Arousal Theory
(B) Evolutionary Approach
The Evolutionary Approach focuses on the role instincts play in motivation. Max is explaining his motivation in terms of innate instincts that make him want to eat.
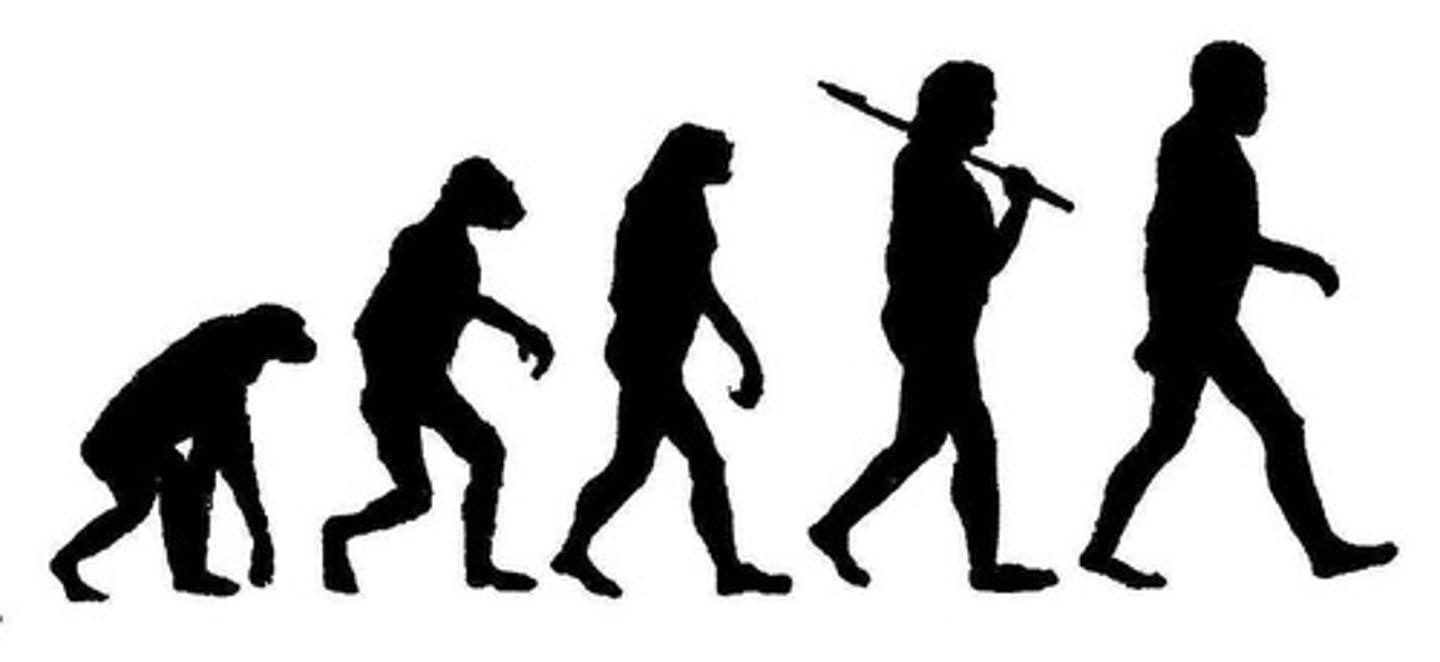
Jacob walked on the carpet with muddy shoes on. His Mom told him that before he could eat any dinner, he would need to clean the carpet. How might this situation relate to the Drive-Reduction Theory of Motivation?
Jacob's need for food is driving him to clean the carpet. Once he finishes cleaning the carpet and eats his dinner, his need is fulfilled and his drive is reduced.
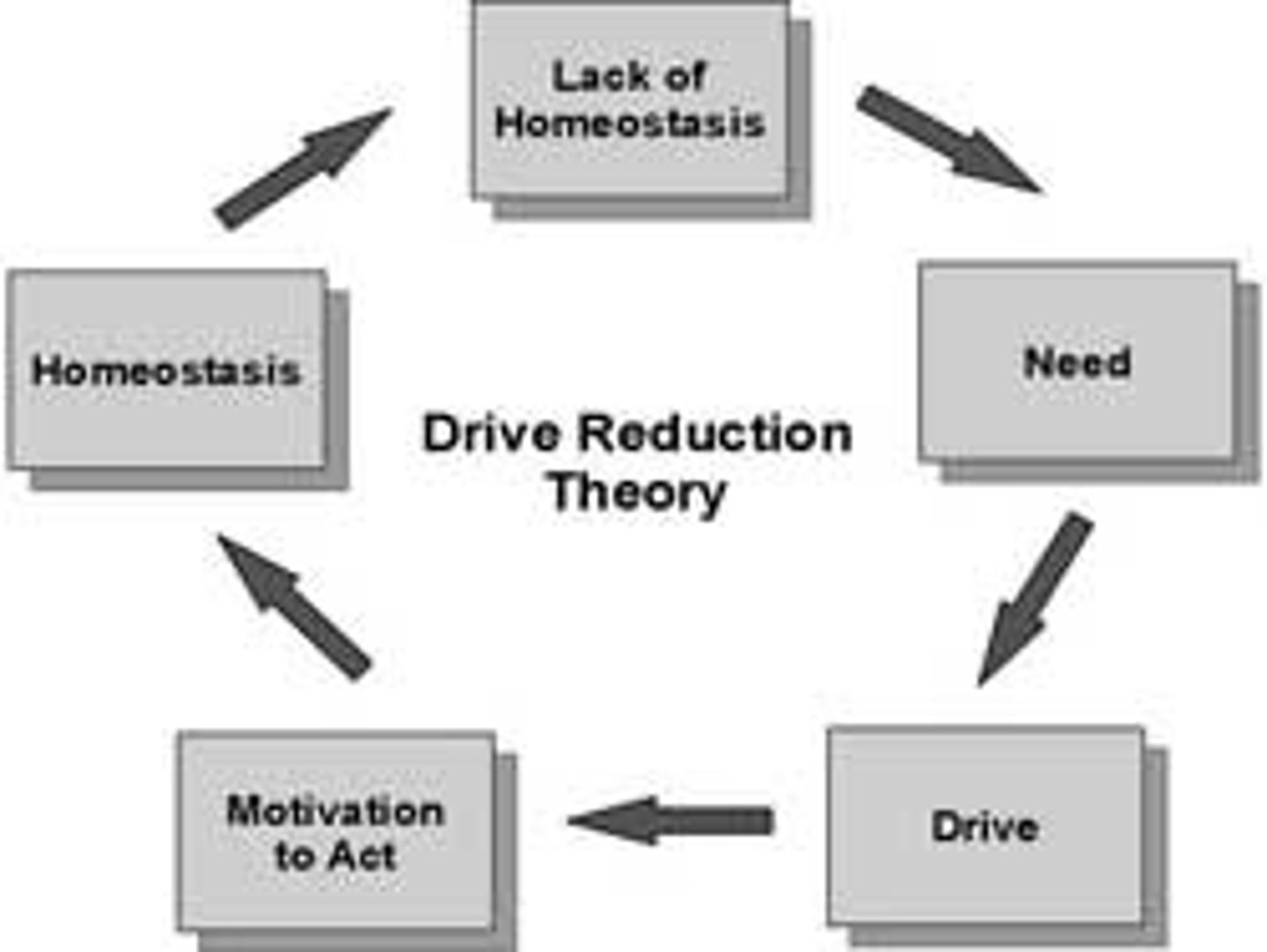
CRB Is Capital one of the primary drives of Drive reduction theory?
No. Primary Drives in Drive Reduction Theory include the need for food, water, warmth, and generally to promote processes responsible for homeostasis.
Capital would be a Secondary Drive, since it had to be learned to be valuable.

CRB True or false? Instincts, like naturally holding breath underwater, represent the contributions of behavior in Motivation.
False. Instincts, like naturally holding breath underwater, represent the contributions of Genes in Motivation.
These instincts are innate, unlearned behaviors, so they must have been encoded somewhere!
Draw Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Pyramid, including the 5 major levels of needs.
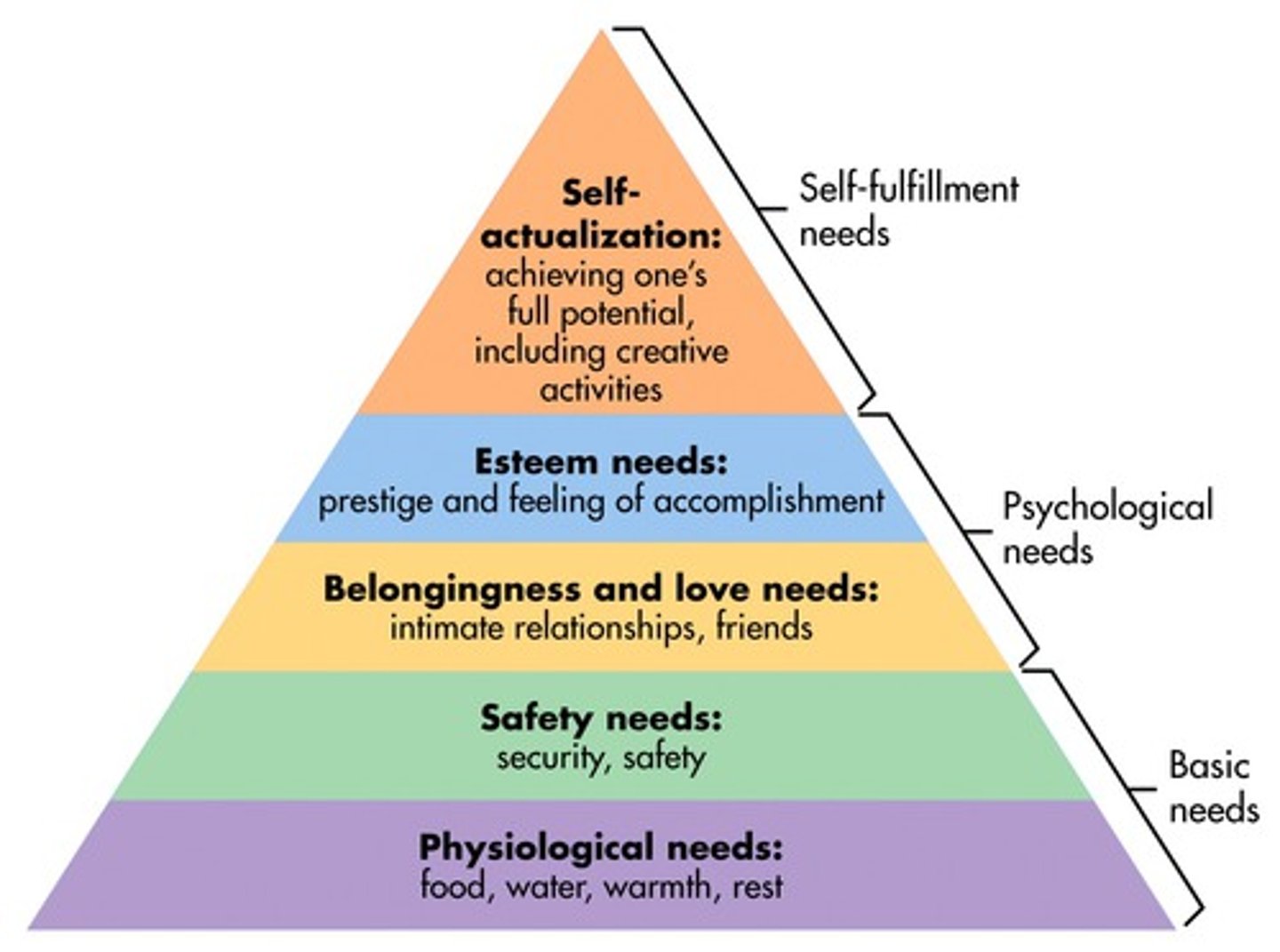
Jim is working out because he likes the respect he gets from his friends when they see his six-pack at the beach. Which level of Maslow's Hierarchy is Jim relying upon?
(A) Safety
(B) Physiological
(C) Self-esteem
(D) Belongingness/Love
(C) Self-esteem
The need for Self-esteem is closely related to our desiring of respect from others, just as is the case with Jim the muscle man.
Fred is the father of three little children. They are a very poor family and instead of buying food for his family to eat, Fred pays the bill for his household security system. Safety is more important to Fred than food. Is Fred's behavior supported by Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs?
Fred's behavior contradicts Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs because Maslow argues that Physiological needs are more basic than safety needs; thus, a father would be expected to try and fulfill his personal and family's need for food first and need for security second.
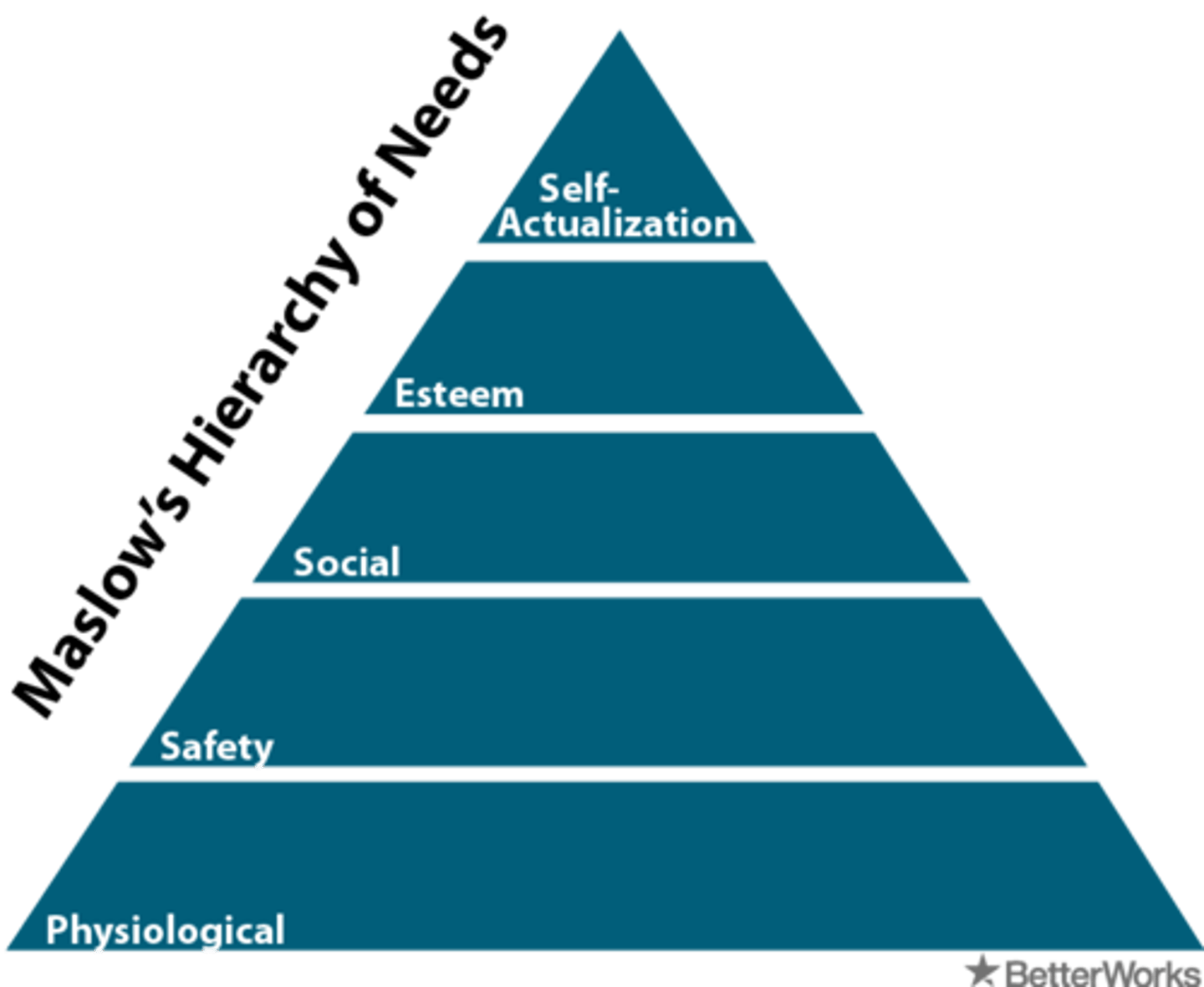
Jacob says he has reached self-actualization after winning an Olympic Gold medal in the high jump. He used steroids to achieve this feat and was really only doing it for the fame and fortune. Would Maslow agree with Jacob?
Self-actualizers are those who reach their full potential and these individuals are true to their own moral principles. Jacob is not focused on reaching his full potential or on obeying his own moral principles. He is most likely trying to meet needs of self-esteem, and is not actually self-actualizing.

CRB Self-Determination Theory is another motivational theory based on needs. Which of the following is NOT one of the three universal needs outlined in this theory?
(A) Competence
(B) Autonomy
(C) Belonging
(D) Relatedness
(C) Belonging
The three universal needs outlined by Self-Determination Theory are Autonomy, Competence and Relatedness.
Incentive theory is based on the idea that if a behavior is rewarded, it will result in what?
Incentive theory is based on the idea that if a behavior is rewarded, it will result in the behavior occurring again.

John often quotes Yoda as saying, "It is not the destination, but in the journey." Is Incentive Theory in line with this popular mantra?
Incentive Theory stipulates that it is the reward at the end of doing something that motivates us to do it. For this reason, Incentive Theory would not agree with this saying.
CRB Expectancy-Value theory claims that which factor does NOT determine how much motivation is needed to reach a goal?
(A) The individual's expectation of success in reaching this goal.
(B) How much the individual values reaching this goal.
(C) How attainable the process of reaching the goal is.
(C) How attainable the process of reaching the goal is.
According to Expectancy-Value Theory, the amount of motivation needed to reach a goal depends on how much the individual expects to succeed at the goal and how much they value reaching that goal.
True or False. The sooner a reward is given after an accomplishment/action, the less likely it is to occur again. Behavior is best rewarded at random and inconsistently as in variable-ratio conditioning.
False. The sooner a reward is given after an accomplishment/action, the more likely it is to occur again.
True or False. The removal of a negative factor can replace a reward in Incentive Theory, similar to negative reinforcement and positive reinforcement in operant conditioning achieving similar outcomes.
False. The removal of a negative factor (negative reinforcement) cannot replace a reward (positive reinforcement) in Incentive Theory
When you are hungry, your ______________ will signal to you that you are hungry. Once you've eaten enough and are full, your ____________ will signal to you to stop eating.
(A) Lateral Hypothalamus, Ventromedial Hypothalamus
(B) Ventromedial Hypothalamus , Lateral Hypothalamus
(C) Ventromedial Hypothalamus , Ventromedial Hypothalamus
(D) Lateral Hypothalamus, Lateral Hypothalamus
(A) Lateral Hypothalamus, Ventromedial Hypothalamus
When you are hungry, your Lateral Hypothalamus will signal to you that you are hungry. Once you've eaten enough and are full, your Ventromedial Hypothalamus will signal to you to stop eating.
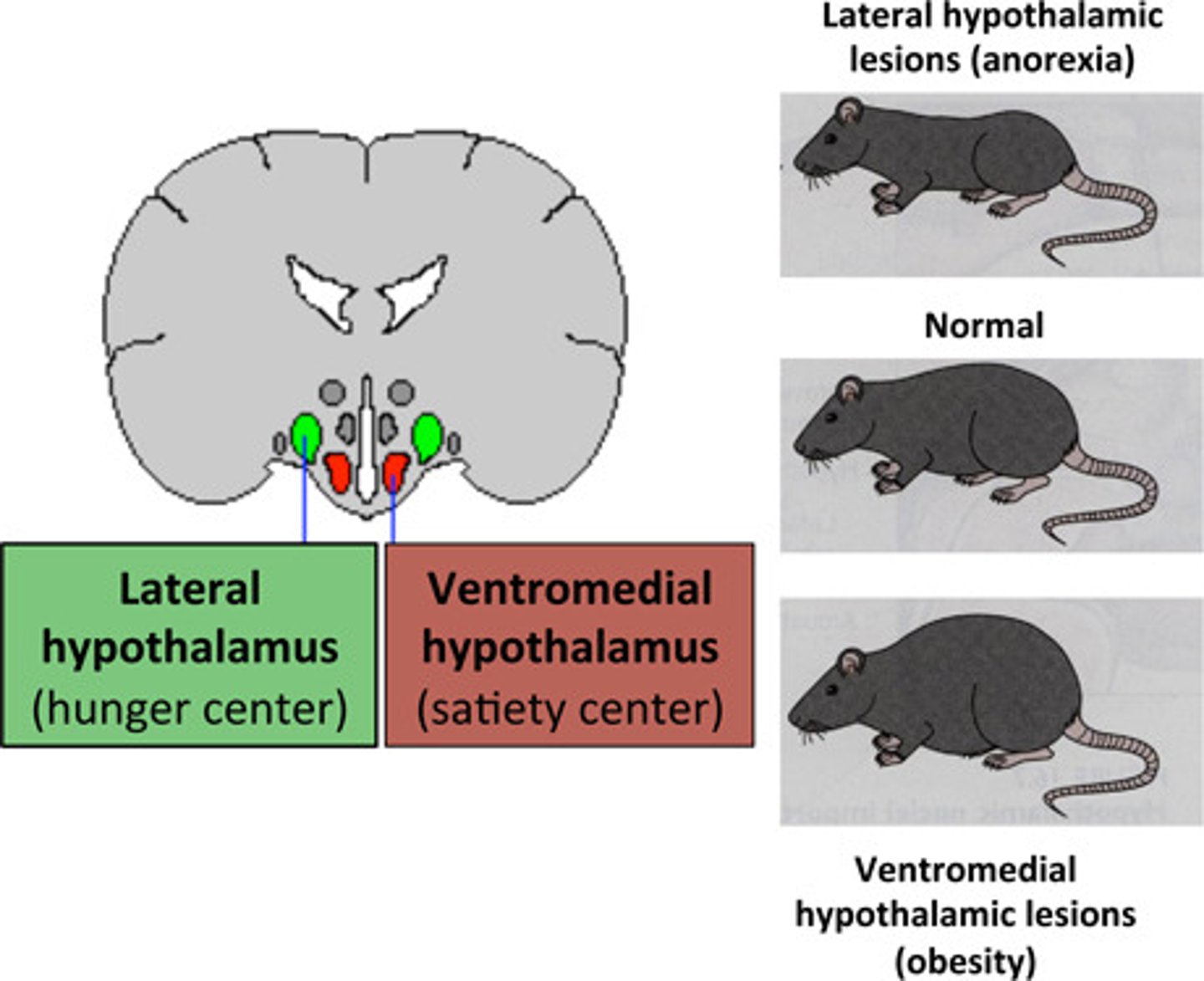
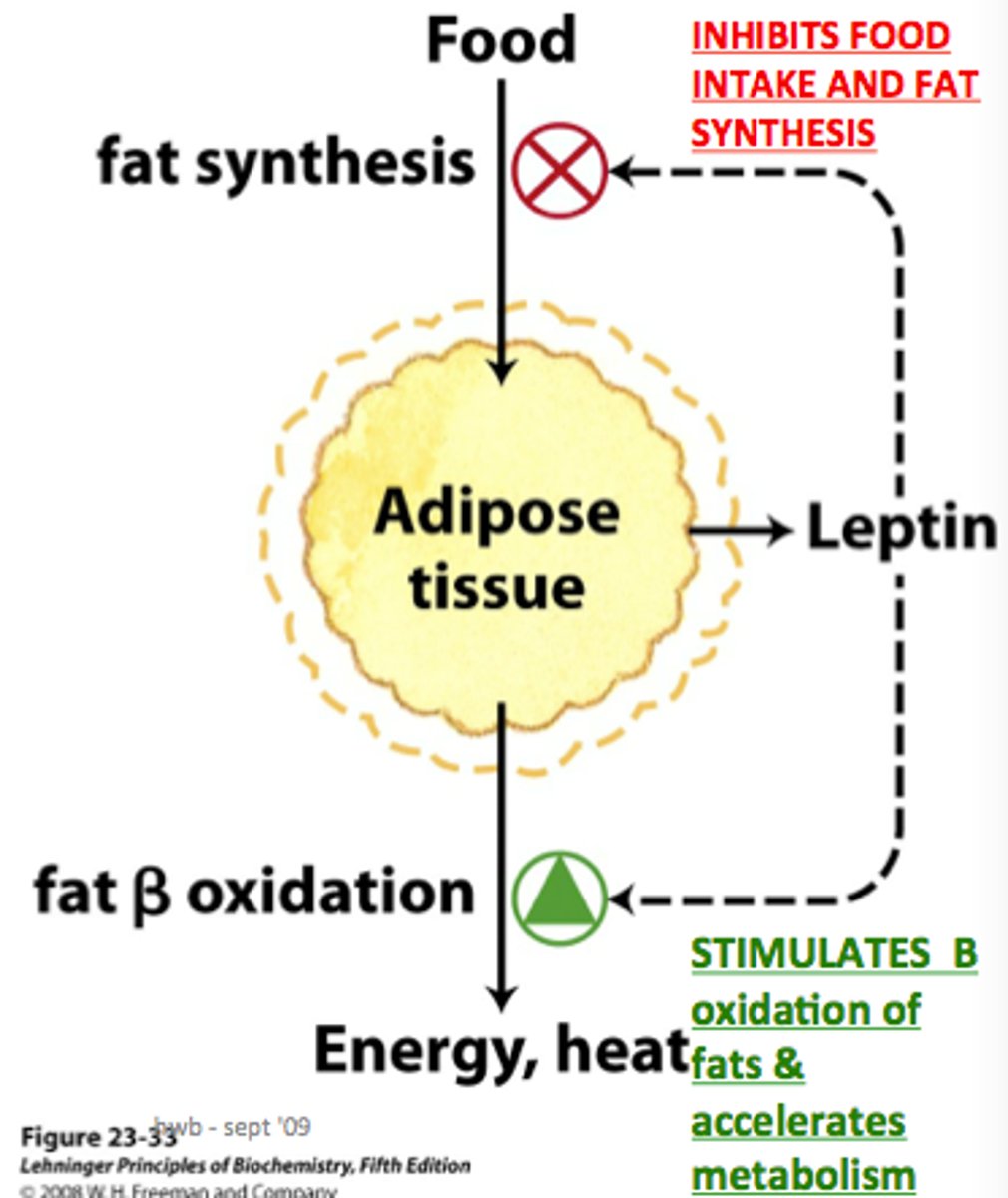
True or False. When you are hungry, Leptin is found in high amounts in your blood as it is a hunger-stimulating hormone.
False. When you are full, Leptin is found in high amounts in your blood as it is an appetite-suppressing hormone.
Which of the following is not a sociocultural factor for eating habits?
(A) Time of day
(B) Insulin levels
(C) Occasions
(D) Appeal
(B) Insulin Levels
Common sociocultural factors affecting eating habits include occasions, time, desire, appeal, and availability.
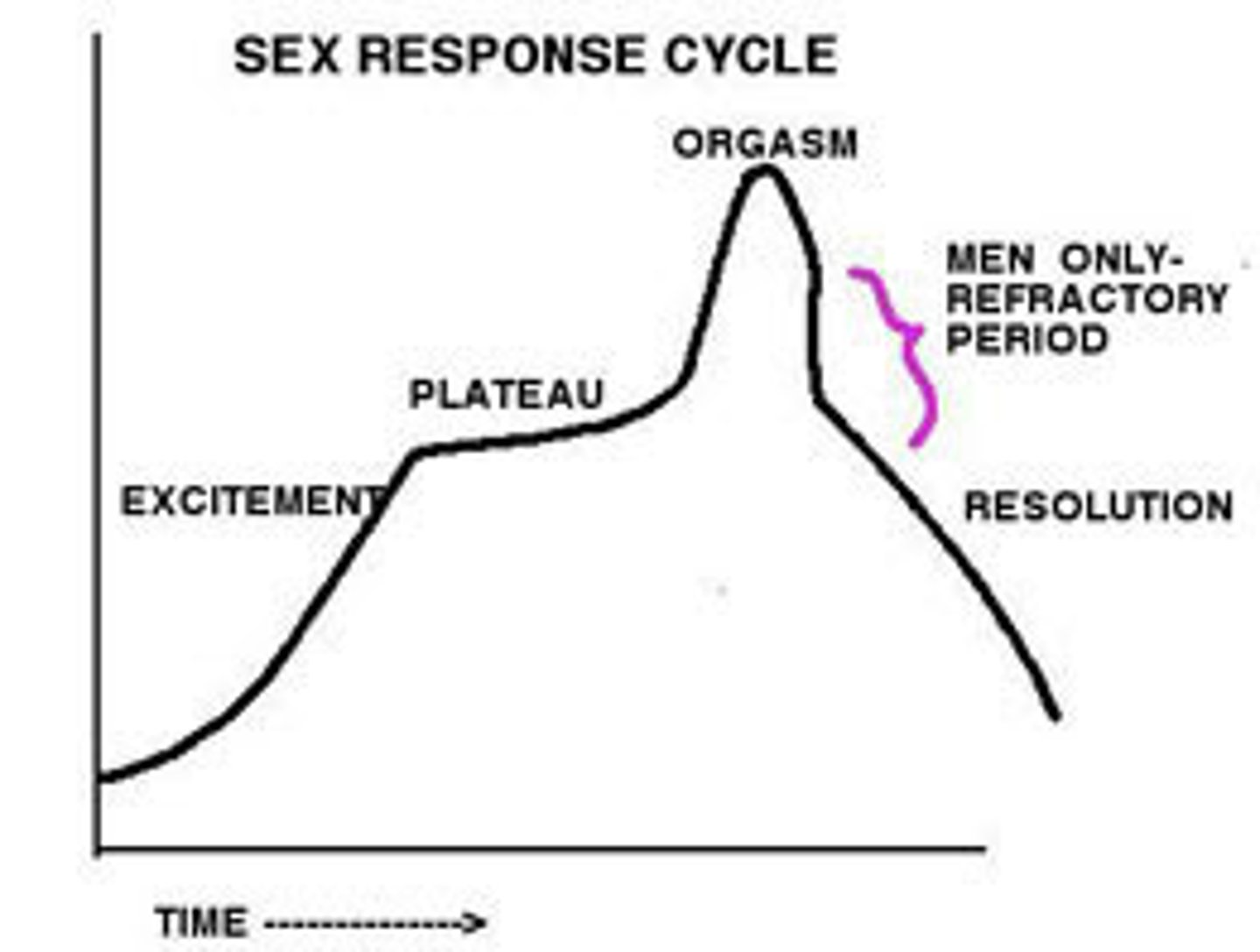
Put the following phases of the Sexual Response Cycle in order from first to last:
I. Plateau
II. Orgasm
III. Excitement
IV. Refractory Period
(A) I > III > II > IV
(B) II > I > III > IV
(C) III > I > II > IV
(D) I > III > IV > II
(C) III > I > II > IV
In order from first to last, the order of the phases of the Sexual Response Cycle are as follows: Excitement > Plateau > Orgasm > Refractory Period.
Which of the following can be affected by genetics?
I. Drug Use
II. Sexual Activity
III. Hunger Levels
(A) I and II Only
(B) I and III Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Drug Use, Sexual Activity, and Hunger Levels are all affected by genetics.
CRB One manipulation of genetics is to use Transgenesis to alter genotypes of samples. This allows them to alter and study phenotypes while still controlling the environment. Which of the following are examples of Transgenesis?
I. "Knockout" Genes
II. Exogenous Genes being transcribed
III. Endogenous Genes being transcribed
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and II only
"Knockout Genes" and Introducing Exogenous ("outside") Genes both are altering the genotypes of the sample. The sample would already have its endogenous genes (genes belonging to the natural genome) being transcribed, so this would not be Transgenetic.
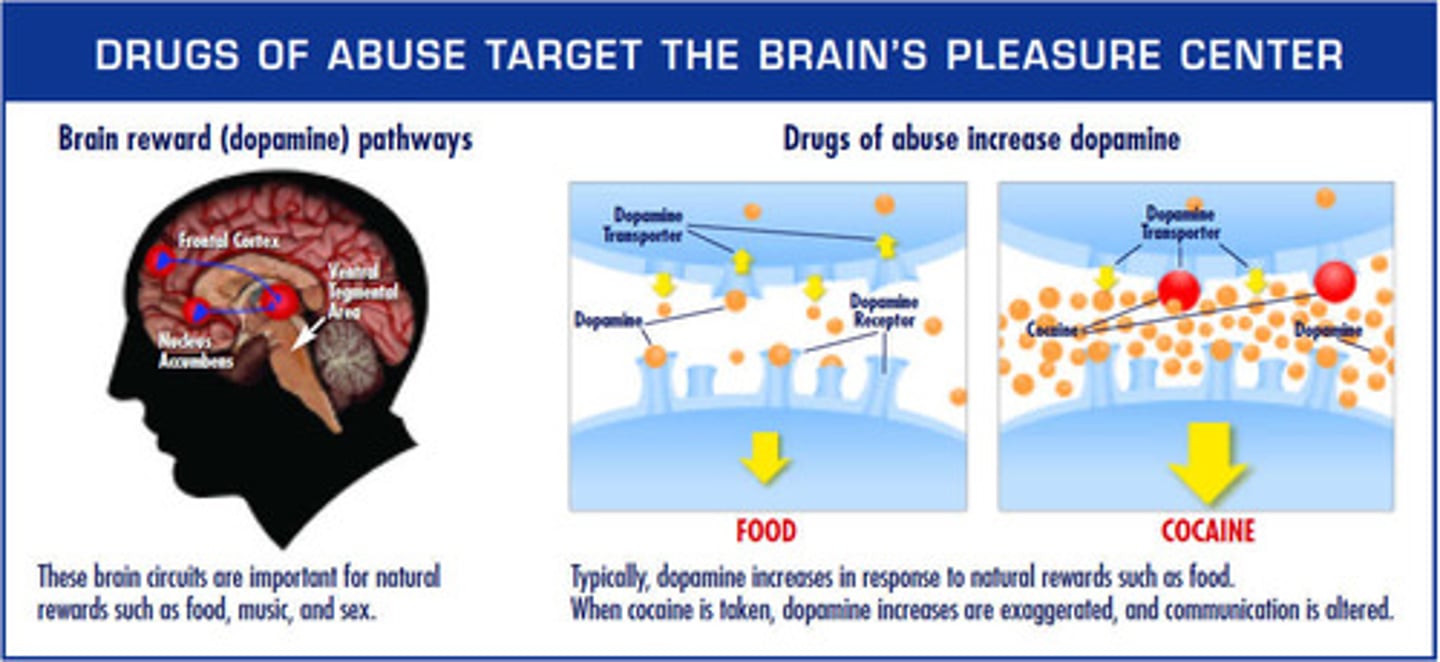
While taking illicit drugs, Mary-Kate experienced a state of euphoria. Which of the following nervous system structures was most likely affected?
(A) Limbic System
(B) Frontal Cortex
(C) Lateral Hypothalamus
(D) Ventromedial Hypothalamus
(A) Limbic System
The limbic system is known for controlling emotion, cognition, motivation and pleasure, and is a common target for illicit drugs.
True or False. Attitudes are something innate and unchangeable as they are closely intertwined with one's personality.
False. Attitudes are defined as "learned tendencies."

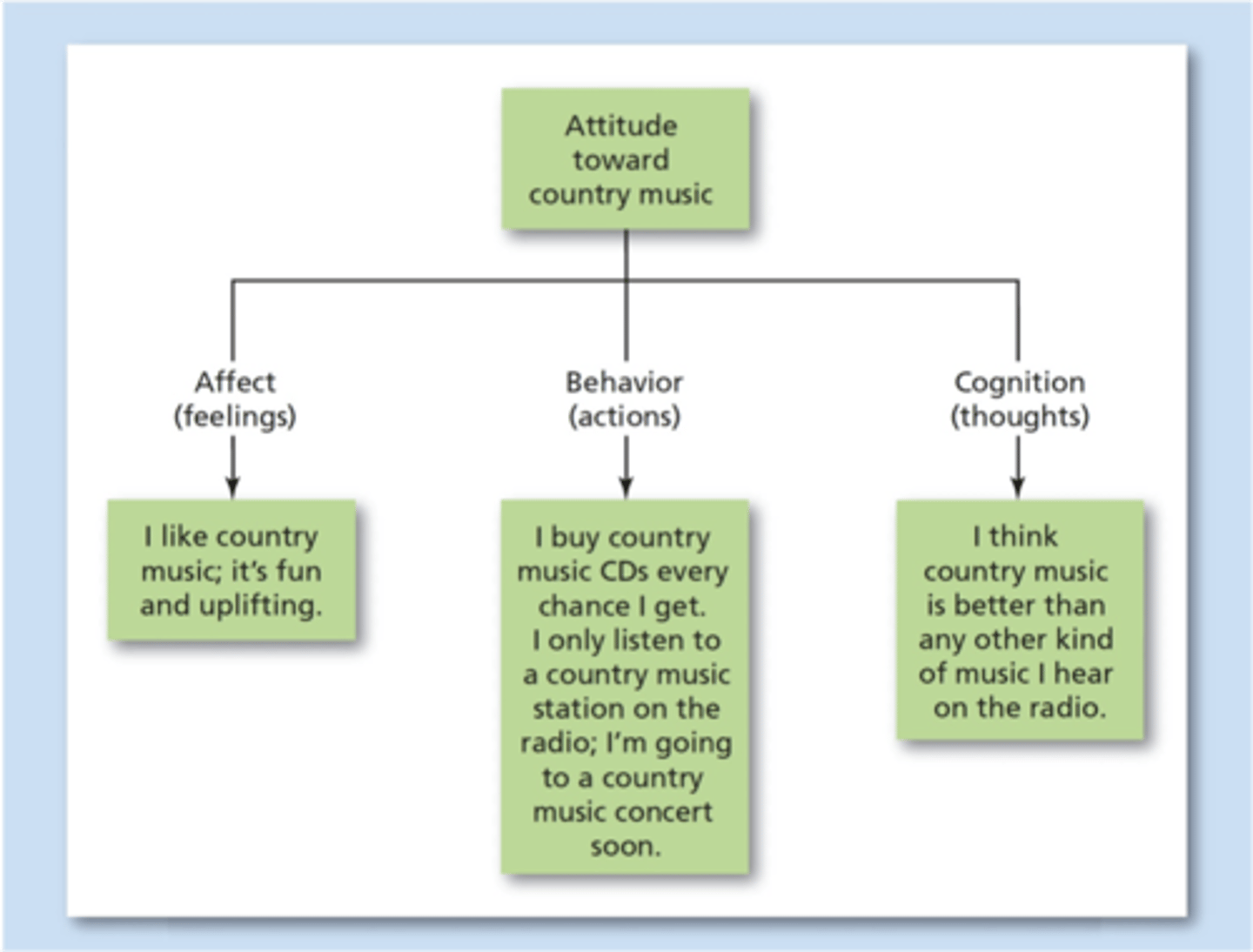
When Sarah sees spiders, she immediately starts screaming, " I AM SO SCARED OF SPIDERS! I AM SO AFRAID OF SPIDERS! AGHHAHGAH!!!" Which component of attitude best describes Sarah in this situation?
(A) Behavioral
(B) Cognitive
(C) Affective
(D) Neurological
(C) Affective
Sarah screams that she is SCARED of spiders. Fear is an emotion, and thus this related most closely to the affective component of attitude.
The cognitive component would focus more on how she is thinking about spiders (i.e. "I am afraid of spiders because I KNOW they are poisonous.")
The Behavioral component is focused more on actions (i.e. She RUNS away from the spider).
Neurological is not a component of attitude.
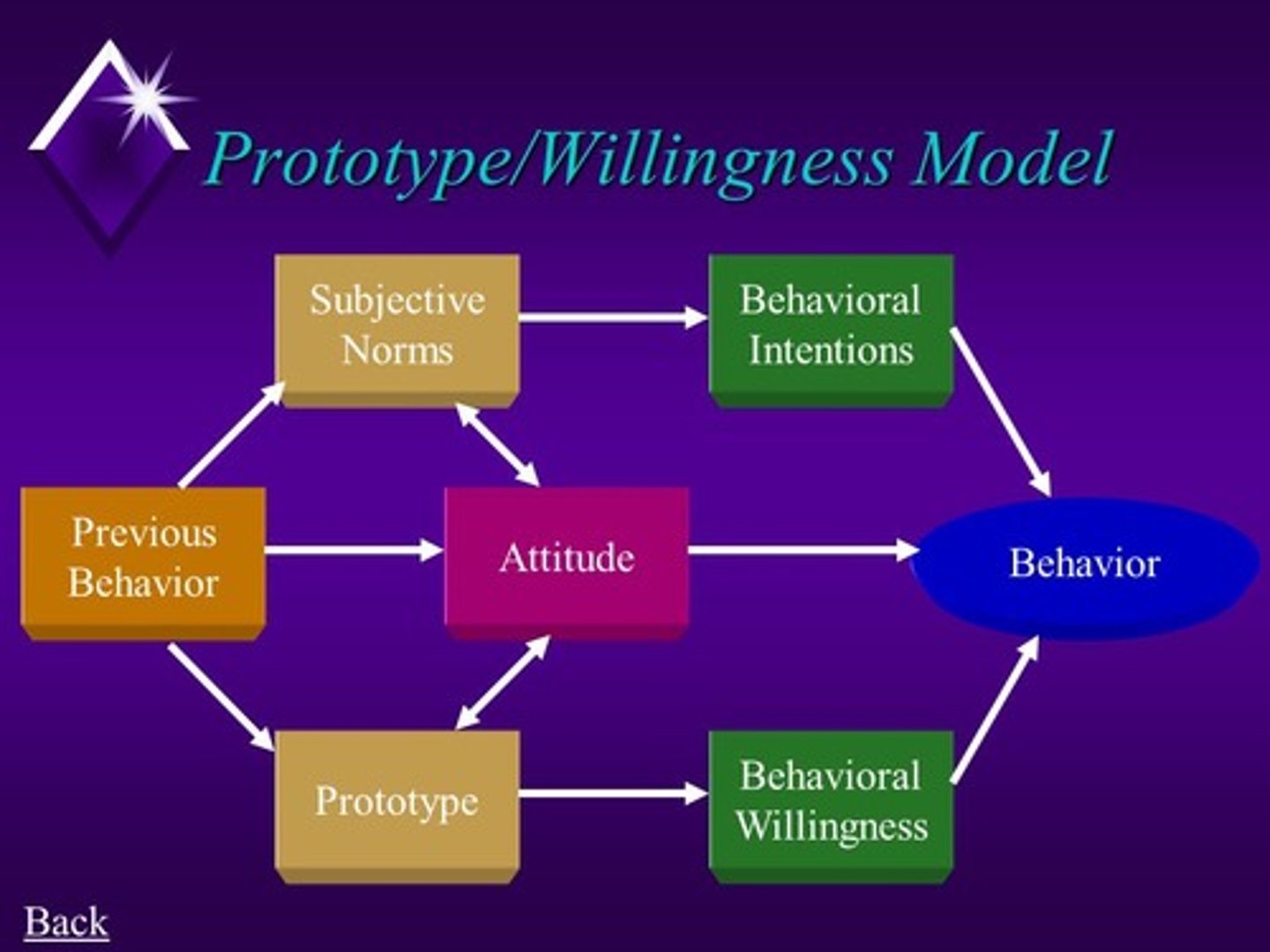
Natalie knows people who drink and they are cool in her mind. She has also always been someone to try something new. Therefore, she started drinking and going to parties at the age of 13. Which attitude theory best explains Natalie's thought process?
(A) Theory of Planned Behavior
(B) Elaboration Likelihood Model
(C) Attitude-to-behavior Process Model
(D) Prototype Willingness Model (PWM)
(D) Prototype Willingness Model (PWM)
The Prototype Willingness Model takes into account the role models one has and one's willingness to engage in risky behavior, as is the case here with Natalie.
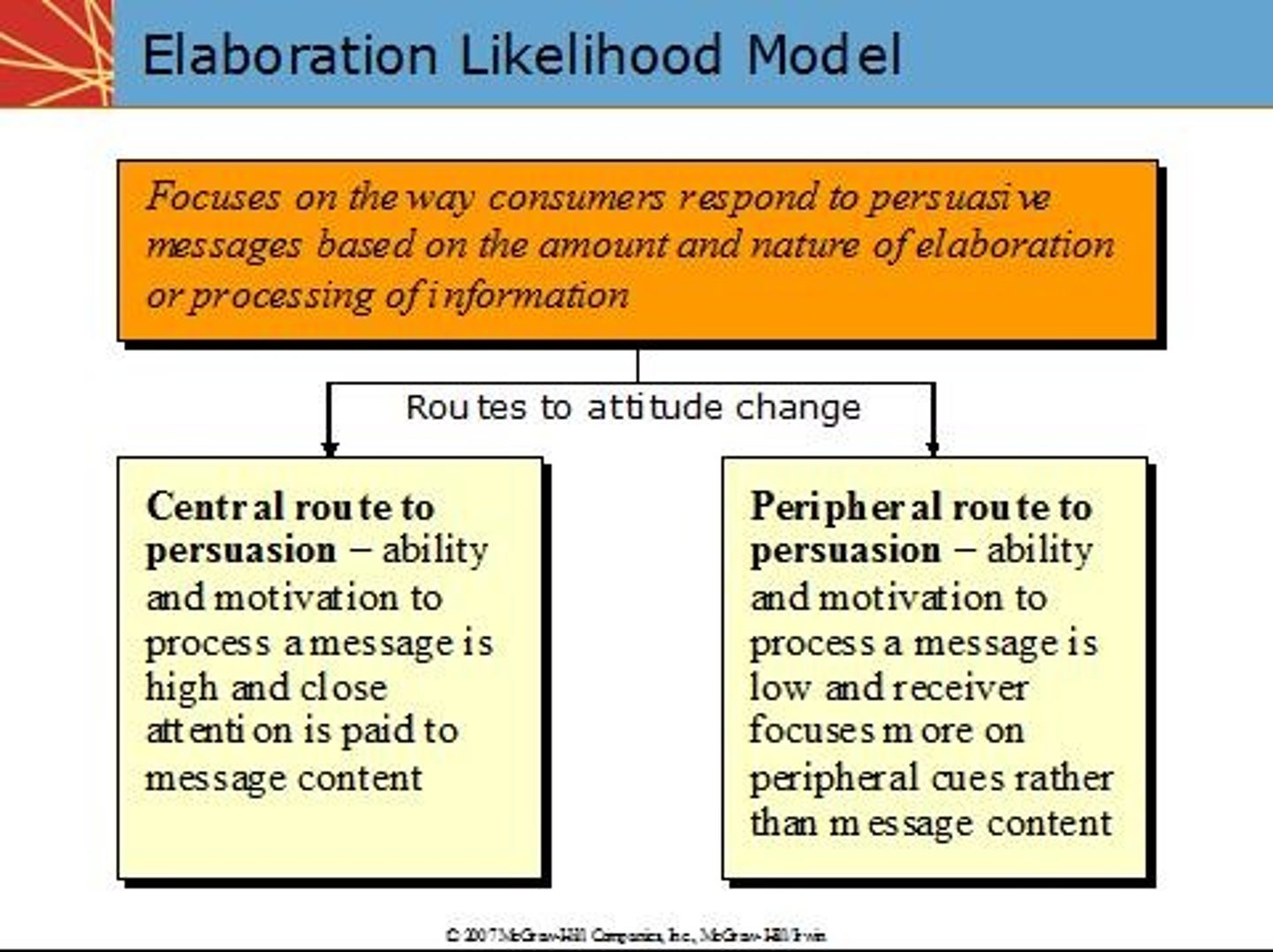
Sam goes to a car dealership to buy a car, and while he is impressed with the cars and the prices, he does not like the way the salesman is dressed or the way he talks to Sam. Which attitude theory best explains Sam's thought process?
(A) Theory of Planned Behavior
(B) Elaboration Likelihood Model
(C) Attitude-to-behavior Process Model
(D) Prototype Willingness Model (PWM)
(B) Elaboration Likelihood Model
Sam is persuaded by quality (Central Route Processing) but distracted and put off by the superficial cues (Peripheral Route Processing). This is closely related to the Elaboration Likelihood Model.
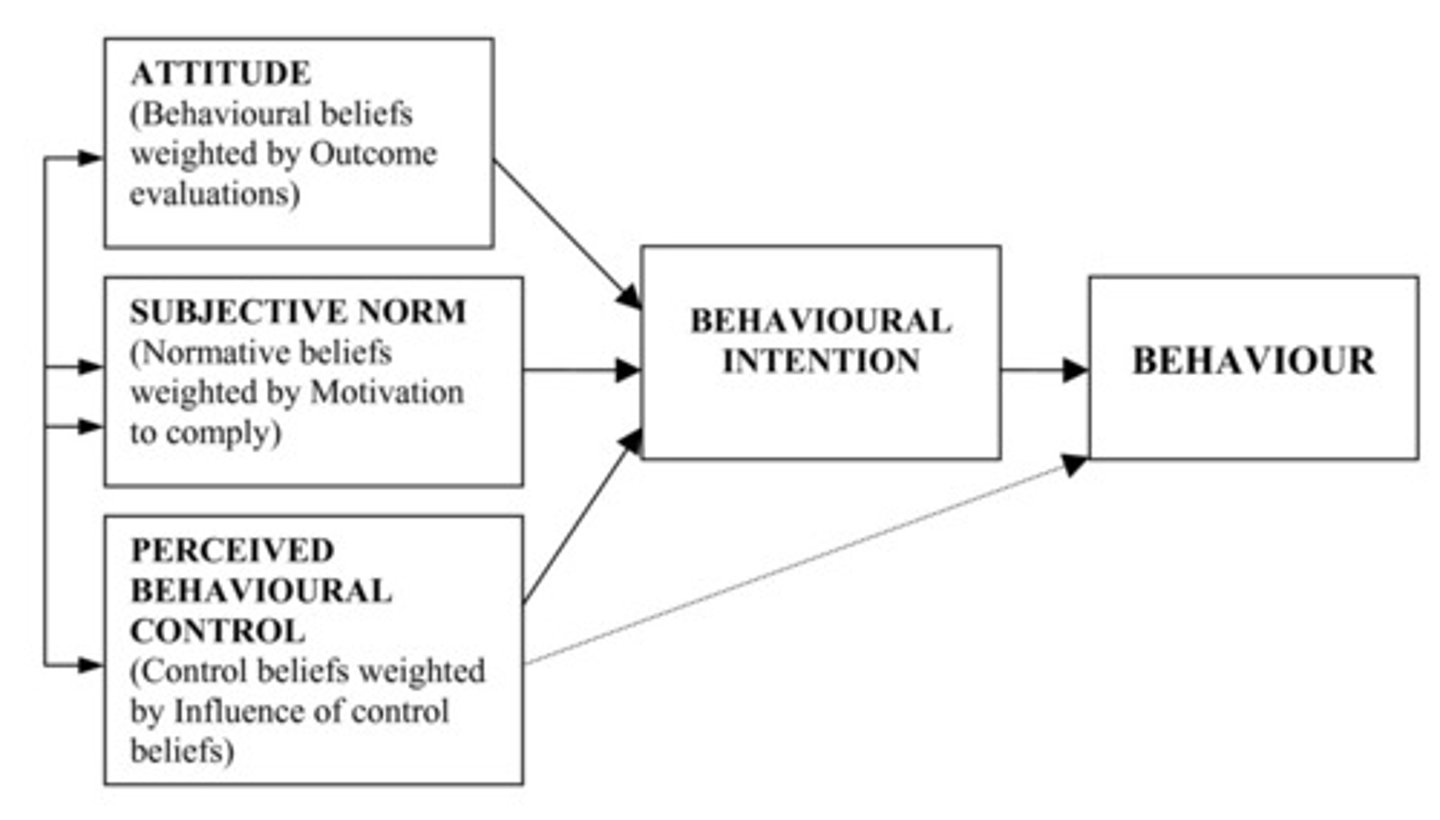
In deciding whether or not she should go on a trip, Eliza decides not to go because she feels that the weather is out of her control and may ruin her vacation. Which attitude theory best explains Eliza's thought process?
(A) Theory of Planned Behavior
(B) Elaboration Likelihood Model
(C) Attitude-to-behavior Process Model
(D) Prototype Willingness Model (PWM)
(A) Theory of Planned Behavior
The Theory of Planned Behavior is focused on people making decisions based on the implications and intentions of their actions. Those intentions are affected by 3 factors, including perceived behavior control, and in this case Eliza feels she does not have control over her vacation's weather.
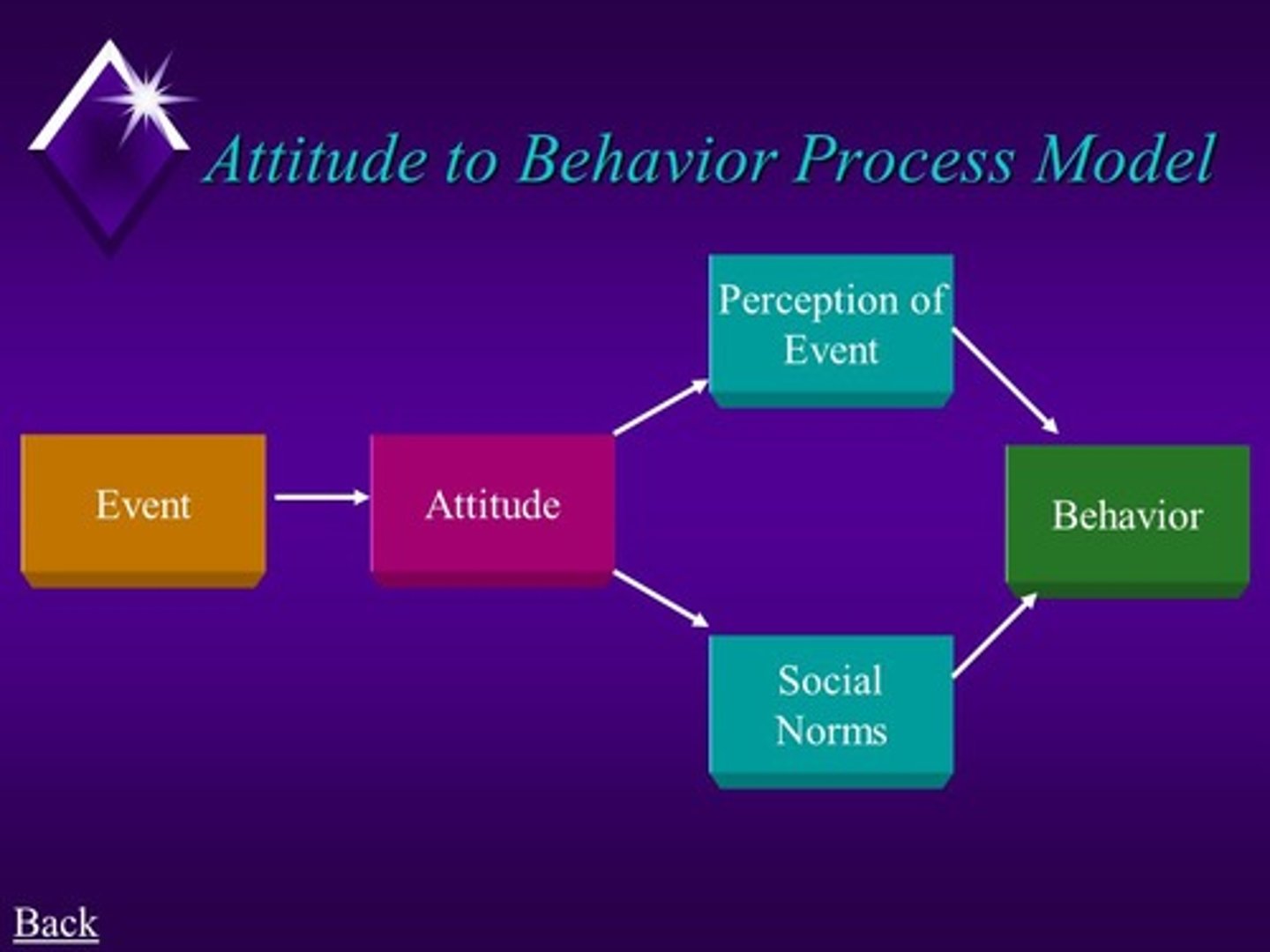
Mohammad was on a roller coaster when it broke down. Ever since then, he has had a bad attitude toward riding roller coasters and no longer rides on them. Which attitude theory best explains Mohammad's thought process?
(A) Theory of Planned Behavior
(B) Elaboration Likelihood Model
(C) Attitude-to-behavior Process Model
(D) Prototype Willingness Model (PWM)
(C) Attitude-to-behavior Process Model.
According to the Attitude-to-behavior Process Model, an event will influence our attitude, which will then influence our behavior.
CRB The Functional Attitudes theory claim that attitudes serve each of the following functions EXCEPT for:
(A) Knowledge
(B) Ego Suppresion
(C) Adaptation
(D) Ego Defense
(B) Ego Suppresion
The Functional Attitudes Theory claims attitudes serve each of the following functions:
I. Knowledge
II. Ego Expression
III. Adaptation
IV. Ego Defense
The Theory of Planned Behavior states that our behavior is determined by how we think about an action before we do it, specifically our implications and intentions. Our intentions are influenced by 3 things - attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavior control. Describe how your intention to study for the MCAT might be influenced by these three things.
If you have a negative attitude toward studying ("I hate studying"), others think your studying is a waste of time (subjective norms), and you feel like you can't control how much time you have for studying, you would be less likely to study.
Read this abstract about the Prototype WIllingness Model: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0273229707000512
What does it mean to say that the Prototype WIllingness Model is a Dual-processing Model? Can you relate this to a child who decides to smoke for the first time?
Basically, this theory says that there are two paths of influence on this child's behavior. The first path is rational and analytical (i.e. "It is okay to smoke because I've never been taught the consequences") . The second path is the social reaction path, which involves prototypes ("I know people who smoke and they are cool") and willingness to engage in the risky behavior ("I'm a daredevil, risk-taker kind of person").
A girl scout comes to your door and sells you girl scout cookies. The next week, she stops by again, and asks you to donate $1,000 so that she can attend girl scout camp. You agree. Which theory would best explain your willingness to do this?
(A) Role-Playing
(B) Door-in-the-face
(C) Foot-in-the-door
(D) Situational Approach
(C) Foot-in-the-Door
You likely agreed because you already agreed to support her in a small way before. This enhanced your willingness to support her in a bigger way now. This is perfectly in line with the Foot-in-the-door theory.
Jack is a medical student. He is trying his best to act like a doctor. Over time, he starts to truly feel like a doctor. Which theory best explains Jack's change?
(A) Role-Playing
(B) Door-in-the-Face
(C) Foot-in-the-Door
(D) Situational Approach
(A) Role-Playing
Jack is role-playing being a doctor until he starts feeling like one.

Shaq is listening to Barack Obama speak about how we need to crack down on terrorists. Shaq believes that Obama is sharing a good message because Shaq has always believed that terrorists need to be punished. Which characteristics is Shaq relying upon as he evaluates Obama's speech?
(A) Message Characteristics
(B) Source Characteristics
(C) Background Characteristics
(D) Target Characteristics
(D) Target Characteristics
Target Characteristics describe one's innate characteristics such as attitude or beliefs that influence how they receive a message. This is the case here as Shaq is using his innate beliefs to evaluate Obama's message.
Message Characteristics describe the properties of the message. For instance, if Obama was using big vocabulary and the argument was sound.
Source Characteristics are the characteristics of the speaker. An example is if Obama were known for being kind to all people and very wise.
Background Characteristics are not one of the three properties of a message according to Persuasion Theory.
CRB A pre-med student stumbles across an anti-vaccine journal and starts to read it. Within a few minutes, the student tosses aside this journal, realizing every source was a social media post and there were no peer-reviewed studies supporting this. Which type of characteristics did the student judge this journal off of?
(A) Message Characteristics
(B) Source Characteristics
(C) Background Characteristics
(D) Target Characteristics
(B) Source Characteristics
The lack of peer-reviewed studies and the only citations coming from social media both indicate that the student is thinking about where this information came from, including its expertise and credibility. These are all classic Source Characteristics.
CRB The famous chess players Viswanathan Anand and Magnus Carlson were in a debate over who the best golfer ever was. Magnus focused his argument on the emotional appeals and how Tiger Wood's famous red shirt excited crowds on Sundays and consciously tried to keep his pitch short, but Vishy was not persuaded. Which type of characteristics describe the focus of Magnus' approach?
(A) Message Characteristics
(B) Source Characteristics
(C) Background Characteristics
(D) Target Characteristics
(A) Message Characteristics
By focusing on emotions as the foundation of of argument, conscientiously planning the length of the message, and the illogical conclusion drawn from Tiger's red shirt, Magnus really built his argument on Message Characteristics.
CRB Which of the following are Message Characteristics that could have been used by Magnus to improve his argument?
I. Incorporating Logic
II. Carefully choosing the number of key points
III. Altering the grammatical complexity of his argument.
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Three Message Characteristics that could have been utilized by Magnus to improve his case include:
I. Incorporating Logic
II. Carefully choosing the number of key points
III. Altering the grammatical complexity of his argument.
Jack is listening to Donald Trump give a speech. He is persuaded to vote for him because of Trump's exciting personality. Jack is using ___________ Route Processing.
Jim listens to the same speech and decides to vote for Trump because he finds his arguments to be compelling and of high-quality. Jim is using _____________ Route Processing.
(A) Central, Peripheral
(B) Indirect, Direct
(C) Direct, Indirect
(D) Peripheral, Central
(D) Peripheral, Central
Jack is listening to Donald Trump give a speech. He is persuaded to vote for him because of Trump's exciting personality. Jack is using Peripheral Route Processing.
Jim listens to the same speech and decides to vote for Trump because he finds his arguments to be compelling and of high-quality. Jim is using Central Route Processing.
This is in line with the Elaboration Likelihood Model.
A salesman approaches your door and proceeds to try and convince you to buy their pest control product. You have little interest in pest control, have no desire to listen to a salesman, and see pest control as useless. According to the Elaboration Likelihood Model, are you going to more closely follow Central or Peripheral Root Processing?
According to the ELM, you are most likely to engage in Peripheral Root Processing as your interest, motivation, and importance are all low.