L9 - Life and the Atmosphere
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is life?
‘Life is a sustaining chemical system capable of Darwinian evolution’ - NASA 2021
Darwinian evolution relies on natural selection: organisms that produce offspring that have heritable variation that gives rise to competitive advantage for a limited resource.
What 4 compounds are all life forms reliant on?
Carbohydrates - all life forms use to store energy
Lipids - all life forms use to store energy
Amino acids - produce proteins: all life forms use ‘left-handed’ amino acids
Nucleic acids - RNA (more primitive version of DNA), DNA, etc.
Where did life originate on the planet? Why?
Water is very good at absorbing Ultraviolet Light - UV light breaks up organic molecules.
Life is unlikely to have been formed on the terrestrial surface of the planet because it would have been subjected to UV.
Life must have formed in water, which protects it from UV light
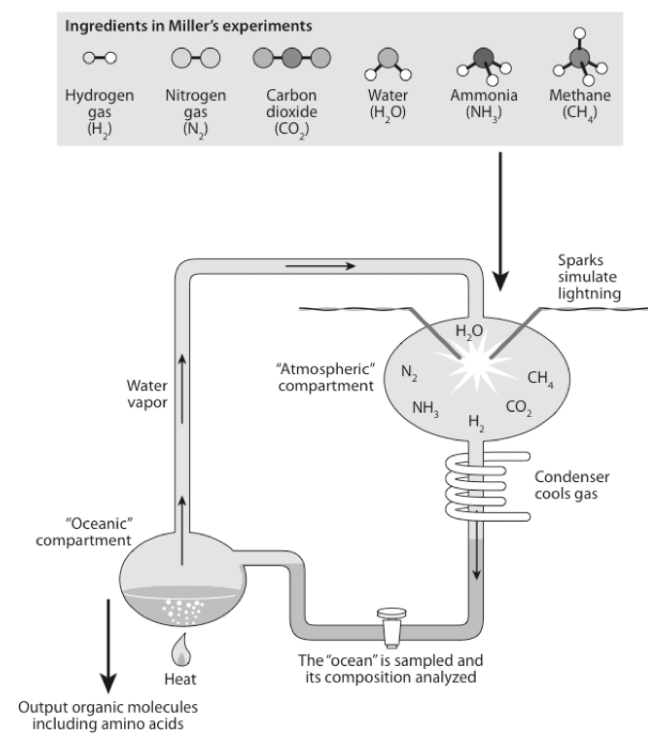
What was discovered in Miller’s experiments?
In this simple organic experiment, they were able to produce amino acids and, later, nucleic acids. And they were able to do this abioeically.
You could produce the molecules necessary for life, without life
These molecules have also been found on asteroids: possible that the first organic compounds present on the Earth came from space.
How do black smokers work?
Occur when the oceanic crust is thin, near oceanic ridges, and where the asthenosphere is relatively close to the surface.
The oceanic crust cracks, cold water seeps through, is heated up, and flows upwards due to low density.
How do black smokers and hydrothermal vents provide evidence for life formation?
As the water reacts with the oceanic crust, it loses sodium and magnesium that is removed from the water.
The minerals in the ocean crust (pyroxene, plagioclase, olivine) react to from sheet silicates to release iron, manganese, copper, lead, etc.
The metals acts as catalysts, lowering the activation energy, making it easier for things to from.
The metal-enriched water flows out of the cracks and the metals precipitate with sulphide ions to create metal sulphides.
How can the influence of black smokers be traced?
3H is released through black smokers.
These plumes of 3H can be tracked for thousands of kilometres.
The seawater percolates through the crust, sodium, and magnesium is removed from the seawater, and other elements are released (strontium)
It is possible that life originated from black smokers.
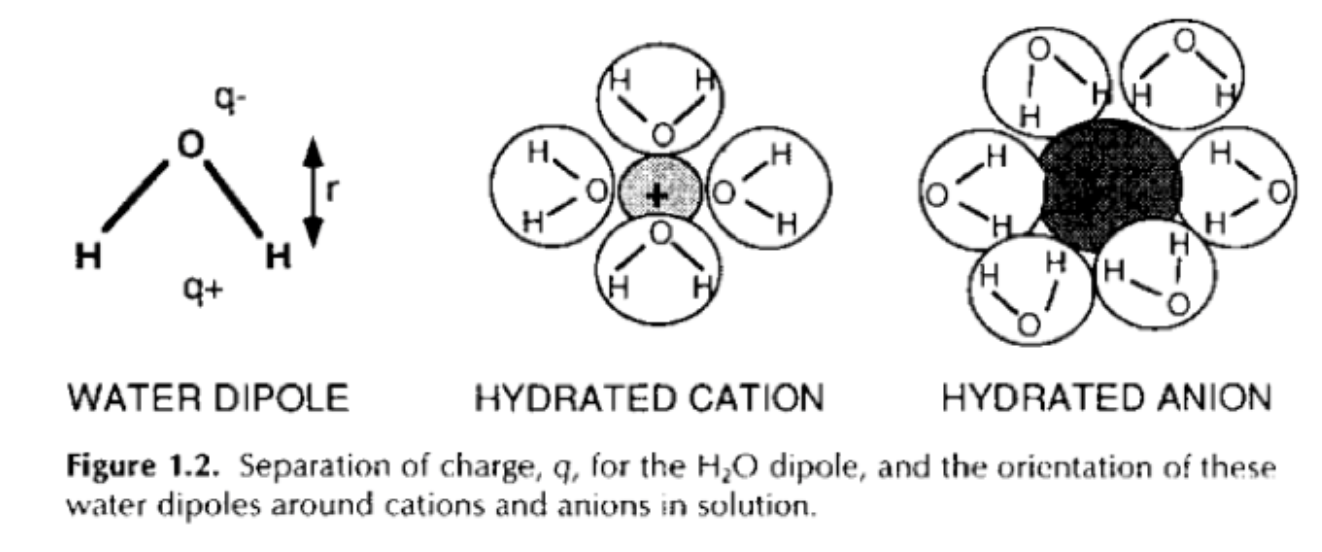
What is polarity?
A cell membrane collects and protects these molecules, and it is thought that cell membranes are formed through abiotic processes.
This depends on a property called polarity
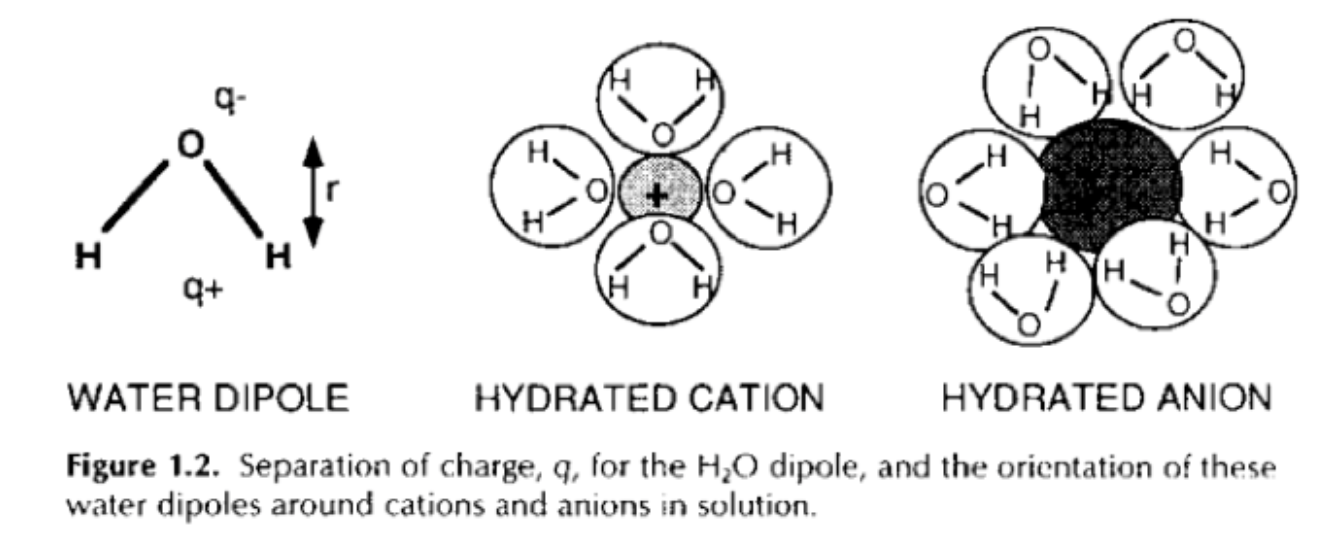
What is a water dipole?
Water molecules have polarity
Oxygen is slightly negatively charged and the hydrogen is slightly positively charged
The molecule has a zero change.
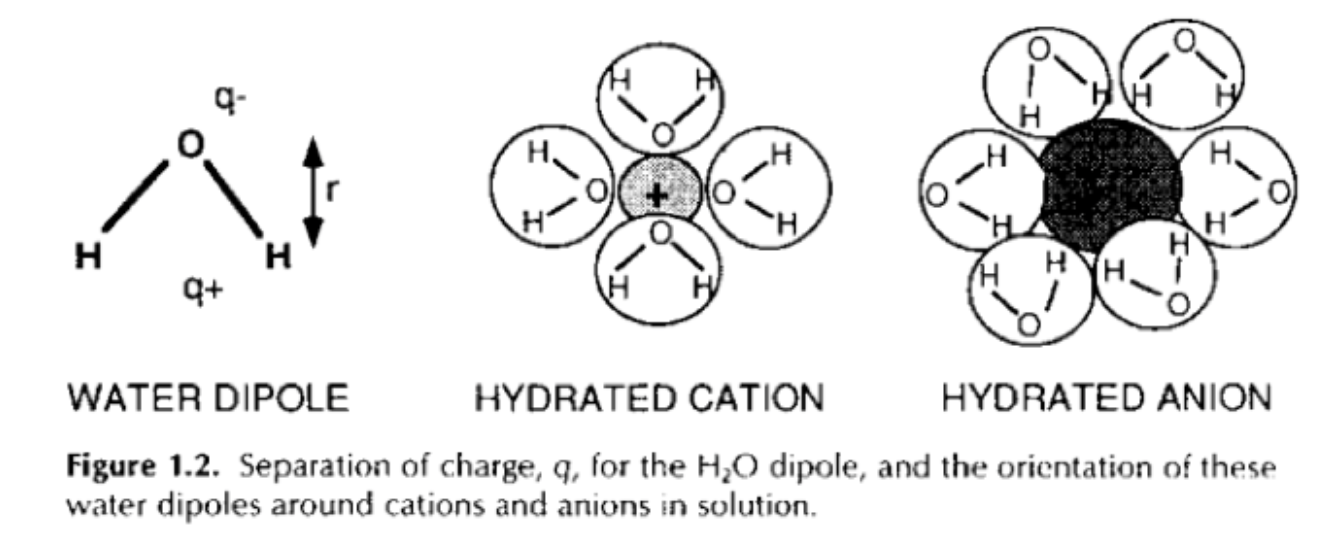
What is a hydrated cation?
Positively charged atom that dissolves in water
Positively charged ions can dissolve in water because the water molecules cluster around them
What is a hydrated anion?
Negatively charged ion
The hydrogen atoms in the water are attracted towards it.
Negatively charged ions dissolve in water because water molecules cluster around them.
What does polarity explain?
Polarity explains why organic molecules do not dissolve in water
Polar molecules (e.g. water molecules) are attracted to the opposite charges.
Non polar molecules do not have charges so water does not cluster around; the non polar molecules are shunted over to one side
They do not mix
What is self-organisation and why does it happen?
Polarity gives rise to self-organisation: a natural property where some structure appears driven by thermodynamics
How could self-organisation have given rise to cellular membranes?
If fatty acids are together, they line up according to polarity: polar molecules clump together and nonpoalar clump together.
Once this layer is formed, it will flip over on itself to produce a double layer
They then form spheres: if water and fatty acids are combined, water will be trapped by the spheres.
So, a cellular membrane can be formed where water is in its centre with dissolved organic compounds which can protect those organic molecules
Therefore, cellular membranes may have originated as self-organising phenomena which can be produced abiotically.
Why is RNA thought to be a form of primitive life?
Primitive life (prokaryotes) are a source of heritable material
RNA, a nucleic acid, can form by inorganic processes and can self replicate.
RNA can produce proteins; thought to be initial heritable material of life, but then somehow began to form DNA, which became the heritable material as well as producing proteins.
RNA World = hypothesis that life started using RNA rather than DNA as its heritable material.
Why could clay minerals be considered initial life forms?
If there is a clay material, it is capable of growing and breaking up (having offspring).
These individual fragments may be different to each other, therefore have variation.
Once these fragments start to grow, they might preserve this variation - so that it is heritable variability.
Fragments of minerals with different structures can be more or less favourable to their growth.
These clay ‘offspring’ can be viewed as having heritable variation - which could affect their fitness for survival
Is life inevitable?
Thermodynamics suggests it is.
The 2nd Law of Thermodynamics suggests that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred.
Whenever a reaction occurs, some of the energy is converted into entropy (unusable energy).
Life is very good at converting energy to unusable forms of energy and accelerating the development of entropy.
Ultimately, the universe will eventually die because all of the energy would have been converted to entropy.
What happens if an atom (A) loses an electron to another atom (B)?
Atom A loses an electron and B has gained an electron
A has been oxidised (oxidation = loss)
B has been reduced (reduction = gain)
How is energy converted into ATP?
If you burn sugar in the presence of oxygen, it is an incredibly efficient way of converting energy into ATP
What is the significance of energy being converted to ATP?
Thought to be significant step in the evolutionary process because suddenly a lot more energy became available to organisms (used to reproduce and colonise planet)
This would only happen once levels of oxygen had built up, after billions of years, oxygen would have accumulated in the atmosphere and be utilised by life.
Left with an oxidised surface layer (Earth’s crust and atmosphere = oxygen rich).
In the mantle, it is still very reduced but has lots of Fe2+ - sets a massive energy potential because of the reduced phase in the mantle and oxidised mantle on the crust.