PHED 4507 Nutrition Final Exam
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
What is a Macronutrient
Nutrients required in larger amounts they provide energy to our bodies and consist of proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids
What is a Micronutrient
Nutrients that are required in smaller amounts consist of vitamins and minerals
What is Psychological Hunger
occurs when you have a desire to eat but feel no physical signs that your body needs food.
Physiological Hunger
When our stomachs are empty, they contract, causing both hunger pangs and the secretion of chemical messages that travel to the brain to serve as a signal to initiate feeding behavior.
What is RDA
Recommended Dietary Allowances which is the average daily intake lvl required to meet the needs of 97-98% of healthy people in a particular life stage or gender group
What is AI for nutrition
Adequate Intake
What is DRI
Dietary Reference Intake they are used to assess and plan nutrient intakes of individuals and population
Measuring the % of total calories from a certain nutrient
calculate the nutrients calories then divide it by the total amount of calories in that food
What are the non essential nutrients early in life
The non-essential nutrients include nutrients that can be manufactured by the body. They include biotin, cholesterol, vitamin K, and vitamin D.
What are the Dehydration Mechanisms
ADH, thirst, and the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
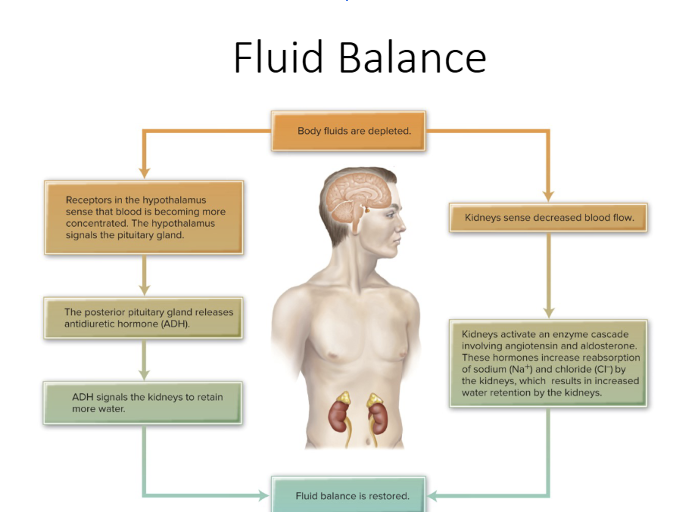
Where is water lost from
perspiration, urine, feces, and breathing
What is the role of calcium in electrolytes
The electrolyte calcium is needed for muscle contraction
What is the role of potassium w/ electrolytes
carry an electric charge when dissolved in body fluids such as blood.
What is the role of chloride w/ electrolytes
Chloride is, after sodium, the most abundant electrolyte in serum, with a key role in the regulation of body fluids, electrolyte balance, the preservation of electrical neutrality, acid-base status and it is an essential component for the assessment of many pathological conditions.
What is the role of Sodium w/ electrolytes
It has a critical role in helping your cells maintain the right balance of fluid. It's also used to help cells absorb nutrients. It's the most abundant electrolyte ion found in the body.
What mechanisms regulate blood calcium levels
parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, calcitriol
What is the kcal count for 1 gram of carbs
4kcal
What is the kcal count for 1 gram of protein
4kcal
What is the kcal count for 1 gram of lipids
9kcal
Which macronutrient is the most energy dense
Lipids
What is the one vitamin that is stored in the body
Vitamin D
Which vitamins/minerals are antioxidants
vitamins C and E, selenium, carotenoids, anthocyanins, and polyphenols
What nutrients are essential in the first trimester of pregnancy
Folic acid.
Iron.
Calcium.
Vitamin D.
DHA.
Iodine
What nutrients are essential in the Second Trimester of Pregnancy
iron, vitamin B12, choline, iodine, vitamin A, and folate
What nutrients are essential in the third trimester of pregnancy
Folate, Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12, Vitamin D, Calcium, Choline, Iron, Iodine, Folate, Omega-3 Fatty Acids
What is vitamin B 1 and how does it work
Vitamin B 1 is thiamin and it helps to turn food into energy and to keep the nervous system healthy
What do the B vitamins do
help the process your body uses to get or make energy from the food you eat
What is vitamin B2 and what does it do
Vitamin B2 is riboflavin and it help the body to convert food (carbohydrates) into fuel (glucose), which is used to produce energy
What is viatmin B3 and what does it do
Vitamin B3 is Niacin and it helps with maintaining the health of your heart, blood vessels, and metabolism
What is vitamin B5 and what does it do
vitamin B5 is called pantothenic acid and it is critical to the manufacture of red blood cells
What is vitamin B6 and what does it do
vitamin B6 is called pyridoxine and it is important for normal brain development and for keeping the nervous system and immune system healthy.
What is B7 and what does it do
vitamin B7 is called biotin and it helps the body metabolize fats, carbohydrates, and protein. It also helps maintain a healthy nervous system, nails, hair and skin, among other functions.
What is vitamin B9 and what does it do
It is called folate or folic acid and it helps the body metabolize fats, carbohydrates, and protein. It also helps maintain a healthy nervous system, nails, hair and skin, among other functions.
What is vitamin B12 and what does it do
it is called cyanocobalamin and it helps keep your body's blood and nerve cells healthy and helps make DNA, the genetic material in all of your cells
What are the proteins that are crucial for bodily function
antibodies, contractile proteins, enzymes, hormonal proteins, structural proteins, storage proteins, and transport proteins
What are the different types of saccharides
monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides
What are the different types of monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose and galactose
What are the different types of disaccharides
maltose, sucrose, lactose
What are complex saccharides
consists of starches, glycogen, and fiber. They have 10+ carbohydrate molecules
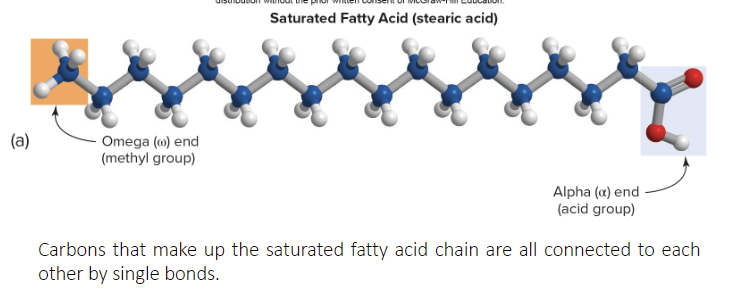
What does a Saturated fatty acid structure look like
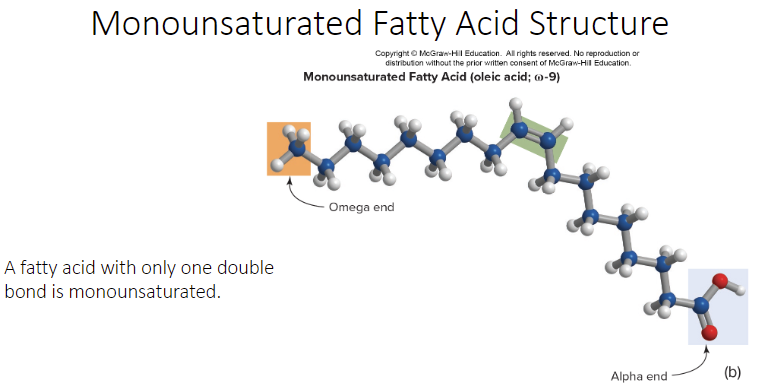
What does a monosaturated fatty acid structure look like
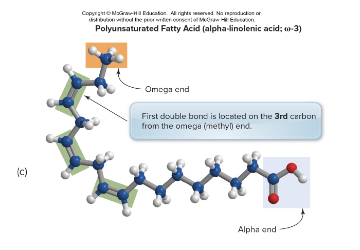
What does a polyunsaturated fatty acid structure look like (Omega-3)
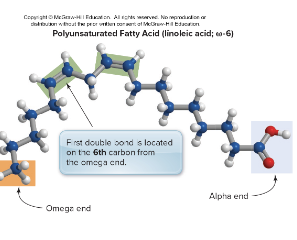
What does a polunsaturated fatty acid structure look like (Omega-6)
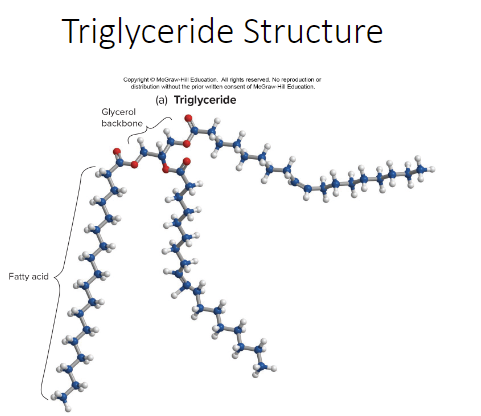
What does a triglyceride structure look like
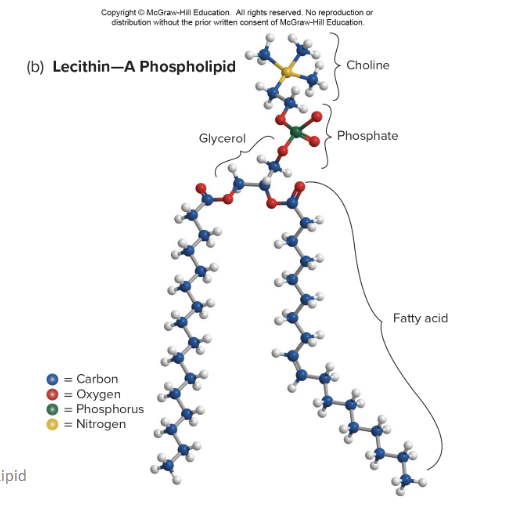
What does a phospholipid look like
Vitamin D deficiency/toxicity can lead to
Rickets in children and osteoporosis in adults for deficiency and hypercalcemia+ kidney failure for toxicity
Main vitamin B1 deficiency symptom
Beriberi
Main B-6 deficiency
anemia
the primary symptom of vitamin B-12 deficiency
megaloblastic anemia
Vitamin A deficiency/toxicity
you lose your ability to see under low-light conditions, and xerophthalmia for deficiency, and bone pain, + birth defects for toxicity
Vitamin K deficiency/toxicity
hemorrhages for deficiency, and toxicity can lead to the disruption of anticlotting medications
What micronutrients help w/ bone health
Calcium, Phosphorus, Vitamin D, magnesium, fluoride, vitamin C, iron, zinc, copper and silicon, vitamin K, and Boron
How do you analyze a food label
by looking at what micronutrients are on it and how they relate to your daily intake
What are some symptoms of PCOS syndrome
High testosterone, excess hair growth on face, acne, and a tendency to deposit fat around the waistline, there is also insulin resistance, higher chance of type 2 diabetes high blood pressure cardiovascular disease, and low glycemic-index eating pattern imrpoves fertility for women w/ PCOS
What is PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome; tiny cysts that surround the ovaries
What do women w/ PCOS have
Irregular or absent periods, difficulty becoming pregnant, and a higher than average rate of spontaneous abortions.
What are the key nutrients for a women to have during their pregnancy
Folate, antioxidants such as vitamin E+C, iron, zinc, and limited sources of saturated and trans fat
What organ exchanges nutrients for oxygen b/t the mother and the baby
The placenta
What is the glycemic index
is a rating system that ranks carbohydrates on a scale of 1-100 based on how much they raise blood sugar
What is the gestation period for a healthy infants
40 weeks
What enzyme helps digest carbohydrates
amylase
What enzyme helps digest protein
protease
What enzyme helps digest lipids
lipase
How are lipids digested
begins in the mouth then moves to the stomach and small intestine, where the majority of lipid digestion takes place
How are proteins digested
Once the protein reaches your stomach hydrochloric acid and enzymes called proteases break it down into smaller chains of amino acid
How are carbohydrates digested
begins in the mouth, where salivary amylase starts the breakdown. After breaking down throughout the digestive system, monosaccharides are absorbed into the bloodstream. As carbohydrates are consumed, the blood sugar levels increase, stimulating the pancreas to secrete insulin
What are the water-soluble vitamins
Vitamins B and C
What are the fat-soluble vitamins
Vitamins A,D,E,K
What breaks down Sucrose
Sucrase
What breaks down Lactose
Lactase
What breaks down Maltose
Maltase
What are lipoproteins
any of a group of soluble proteins that combine with and transport fat or other lipids in the blood plasma.
How do lipoproteins work
They carry cholesterol through your bloodstream to your cells
What are the different lipoproteins
Chylomicron, VLDL, LDL, HDL
What is the primary role of Chylomicrons
THey carry dietary fat from the small intestine to the cells
What is the primary role of VLDL
VLDL (Very Low density Lipoprotein) Carries lipids made and taken up by the liver to the cells
What is the primary role of LDL
LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein), it carries cholesterol made by the liver and from other sources to cells
What is the Primary role of HDL
HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein), Contributes to cholesterol removal from cells and, in turn, the excretion of it from the body
What is lipoprotein lipase
Is an enzyme that breaks down triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol
What is Low-Density Lipoprotein
Bad cholesterol
Originates from the liver
Oxidized LDL particles are taken up by scavenger cells (WBC) to form atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels
Primary risk of high LDL lvls:
Promotes atherosclerosis
Increased risk of cardiovascular disease
How does HDL remove cholesterol from the blood
May block the oxidation of LDL
Reduces formation of atherosclerotic plaque
Reduces risk of cardiovascular disease
What factors influence infertility in nutrition
Energy balance, excessive alcohol consumption, Excess body fat, a low glycemic index eating pattern, diets low in antioxidants, people who are low in iron and zinc, and a maternal iodine deficiency
What non nutrition-related factors can inhibit fertility
Exercise levels, smoking, genetic factors to name a few
How many essential amino acids are there
There are 9 essential amino acids
How many non-essential amino acids are there
There are 11 non-essential amino acids
What is the process for antioxidants
The supply free radicals w/ a electron, this helps break a chain reaction that can affect other molecules in the cell and other cells in the body.
What are the 5 areas in the world that have the lowest levels of chronic disease
Italy, Greece, Japan, Costa Rica, and USA*** bias article
What are the elements that make up Carbohydrates
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
What are the elements that make up proteins
Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen
What are the elements that make up lipids
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
What is a food allergy
an immune system reaction that happens soon after eating a certain food
What is a food intolerance
occurs when the body has a chemical reaction to eating a particular food or drink
What are the symptoms of dehydration
Headache, delirium and confusion.
Tiredness (fatigue).
Dizziness, weakness and lightheadedness.
Dry mouth and/or a dry cough.
High heart rate but low blood pressure.
Loss of appetite but maybe craving sugar.
Flushed (red) skin.
Swollen feet.
What factors can influence a persons decision on what to eat
money, culture, friends/family, current lifestyle habits, amount they exercise, among other things
How do people develop an iron deficiency
not getting enough iron in your diet, chronic blood loss, pregnancy and vigorous exercise
What can chronically low Iron levels lead to
anemia
What can you change an anemic blood level
By taking supplements for iron and vitamin B9, and increase the amount of iron-rich foods that are in your diet
What are some symptoms of an iron deficiency
Abnormal paleness or lack of color of the skin.
Irritability.
Lack of energy or tiring easily (fatigue)
Increased heart rate (tachycardia)
Sore or swollen tongue.
Enlarged spleen.
A desire to eat peculiar substances such as dirt or ice (a condition called pica)
What are the essential fatty acids
2 fatty acids must be supplied to by the diet to maintain health
These are called linoleic acid which is an omega-6 fatty acid, and Alpha-linolenic acid which is an omega-3 fatty acid
What are the function of essential fatty acids
Forms body structures, performs important functions for the immune and nervous systems, and produce regulatory compounds, such as eicosanoids and hormones