Anatomy Unit 3 Exam
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Functions of Vertebral Column
Protection of spinal cord and support of trunk
Number of Cervical vertebrae
7
Number of Thoracic Vertebrae
12
Number of Lumbar vertebrae
5
Number of Sacral vertebrae
5 fused
Number of Coccygeal vertebrae
2-5 Fused
Number of total vertebrae
33
Where are primary vertebral curvatures located?
Thoracic and Sacral
Where are secondary vertebral curvatures located?
Cervical and Lumbar
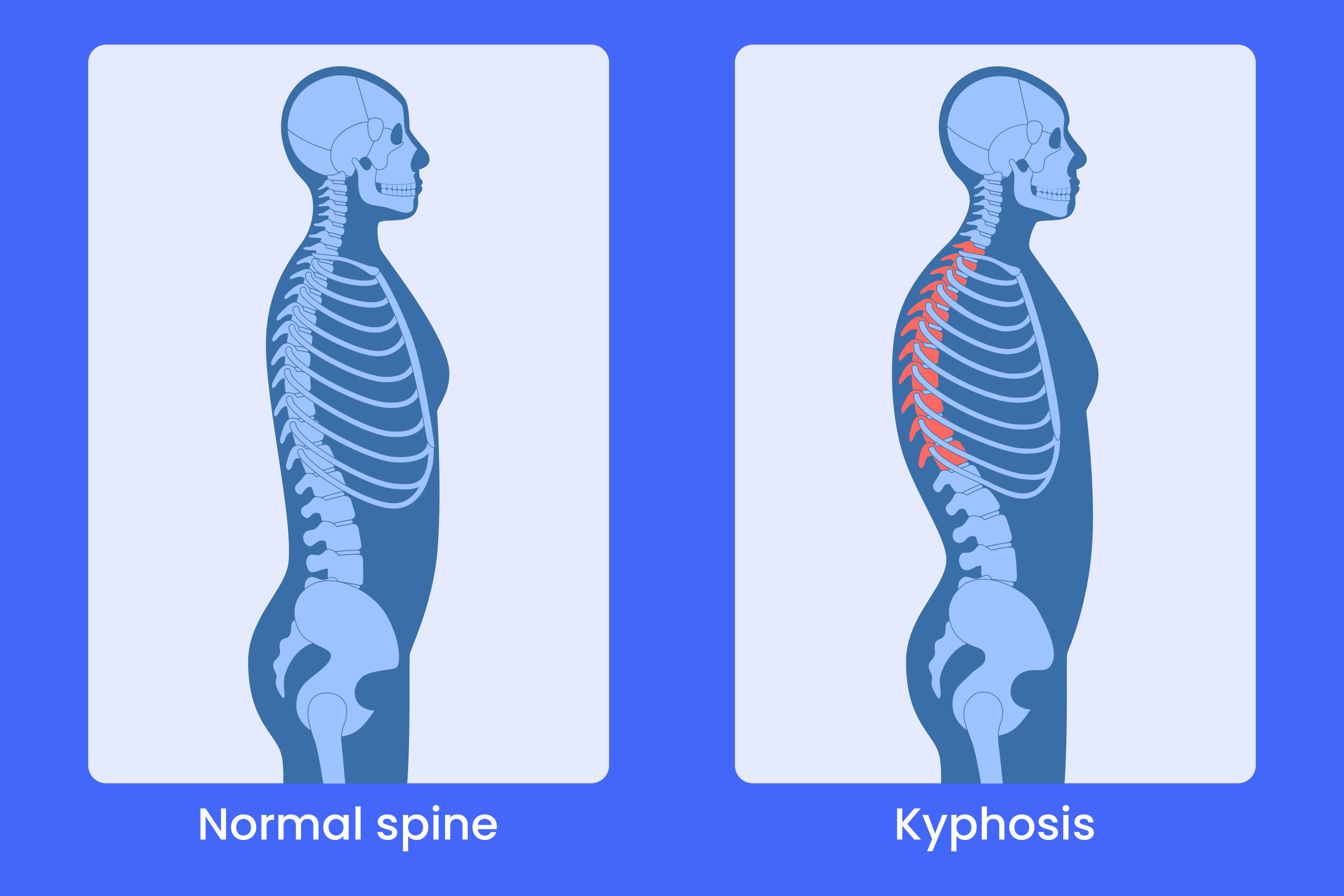
kyphosis
“Hunchback”, Posterior deviation in thoracic primary curvature
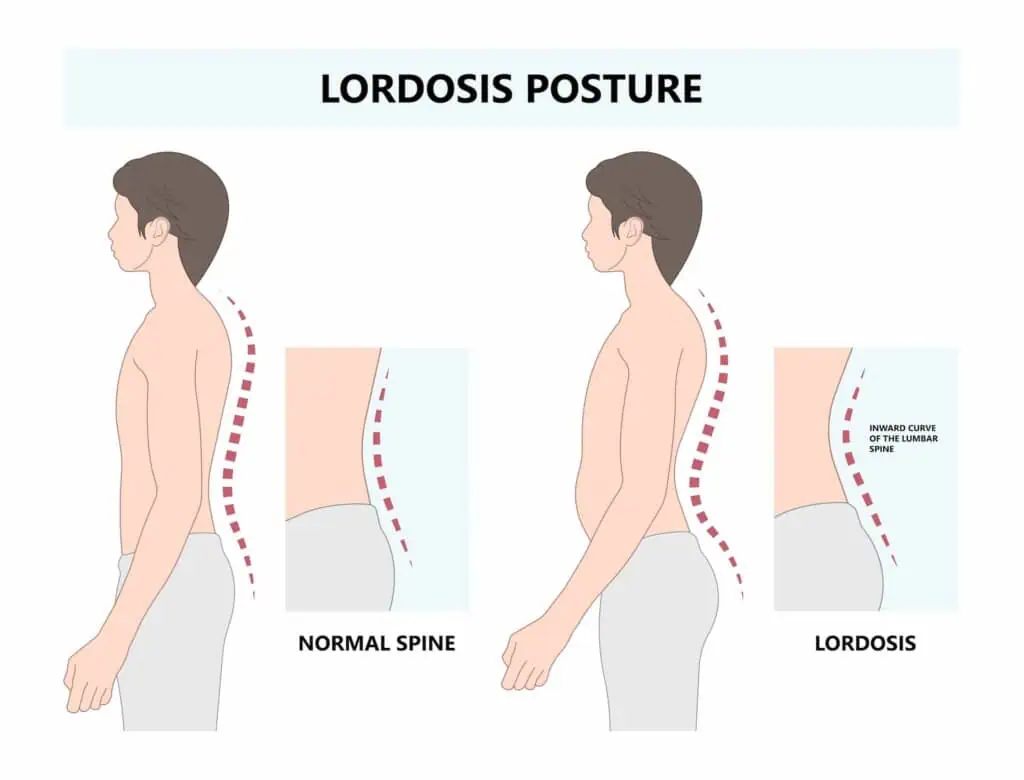
lordosis
Happens from pressure from big belly on lower back, Anterior deviation in lumbar secondary curvature
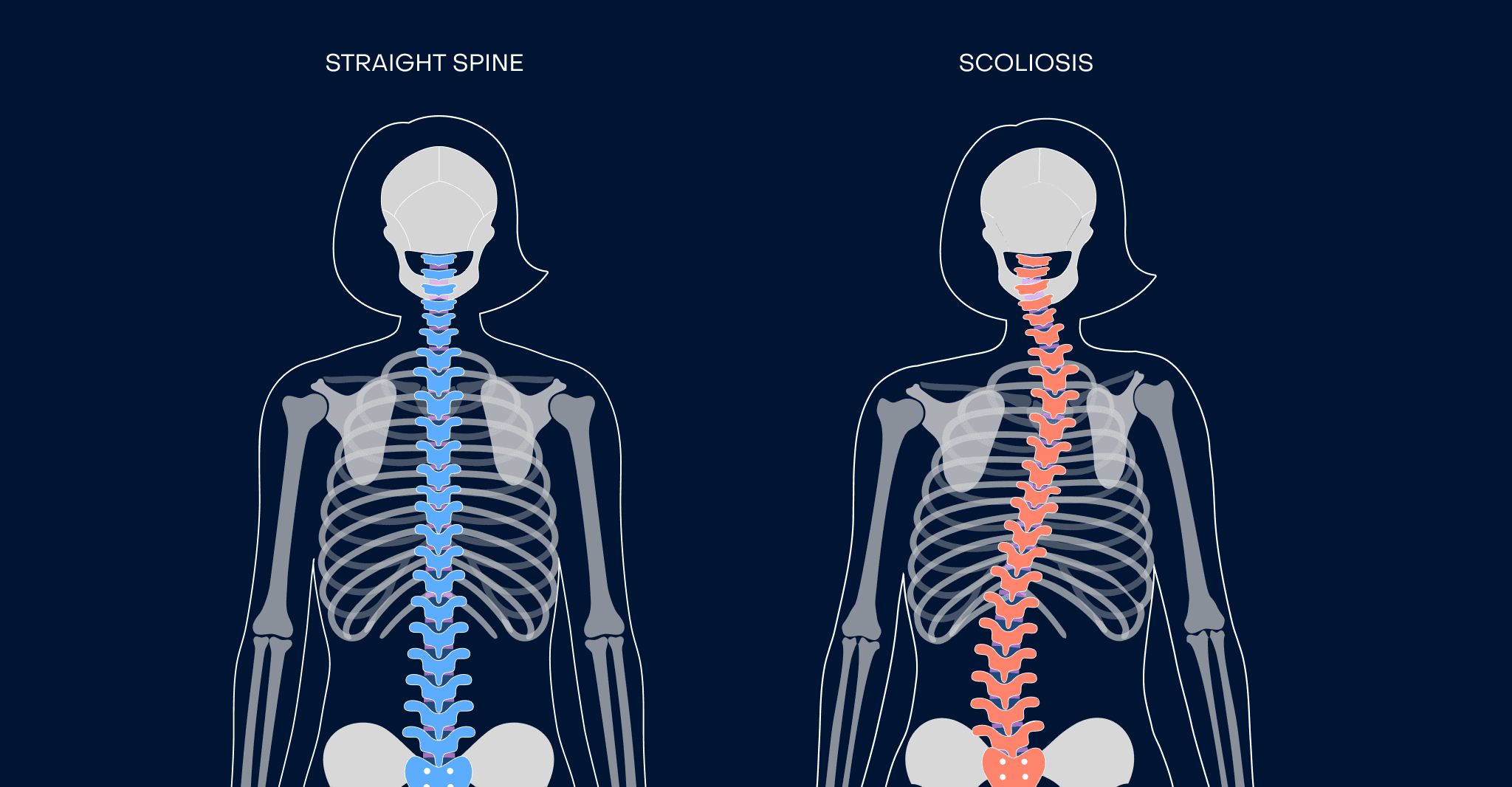
Scoliosis
Right or left lateral deviation in either thoracic or lumbar vertebrae
What is the purpose of the vertebral body?
Holds up body weight!
What is the purpose of intervertebral discs?
to absorb shock and allow movement between vertebrae
What is the purpose of the vertebral canal?
To protect the spinal cord and nerve roots.
Which vertebrae are “functional discs”?
The vertebrae between which intervertebral discs are present, excluding the sacrum and coccyx, because they are fused
What is the purpose of intervertebral foramen?
Nerves exit in between each vertebrae!
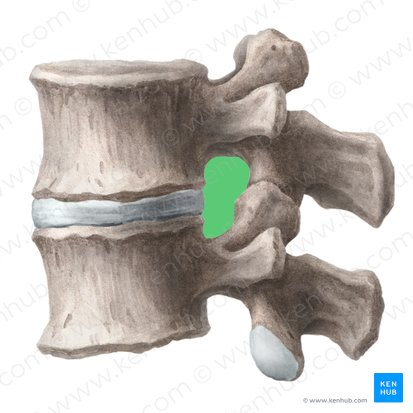
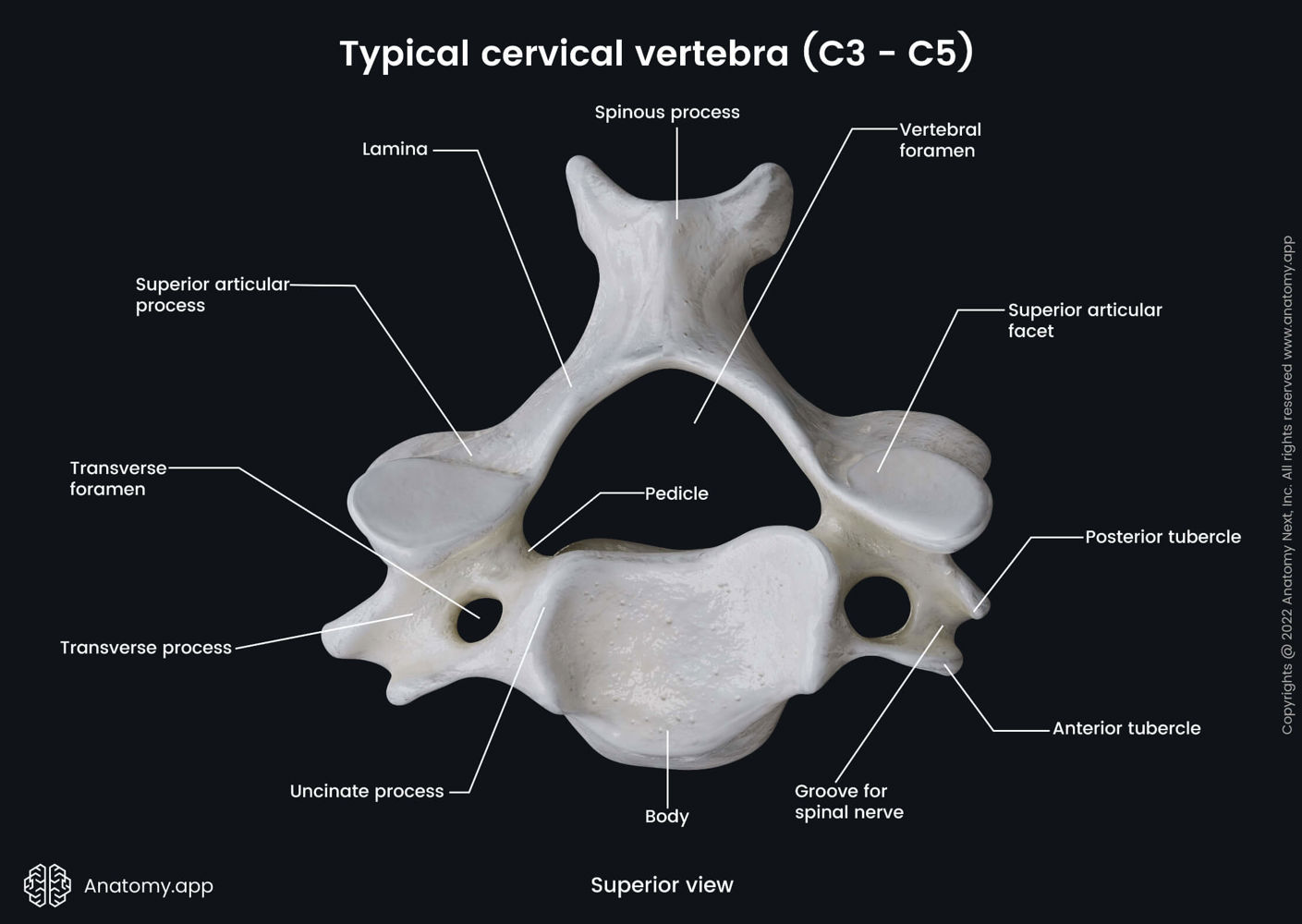
Distinct characteristics of cervical vertebrae? (C3-C7)
The presence of transverse foramina, which allow for the passage of vertebral arteries.
A large and triangular vertebral canal
Bifid spine
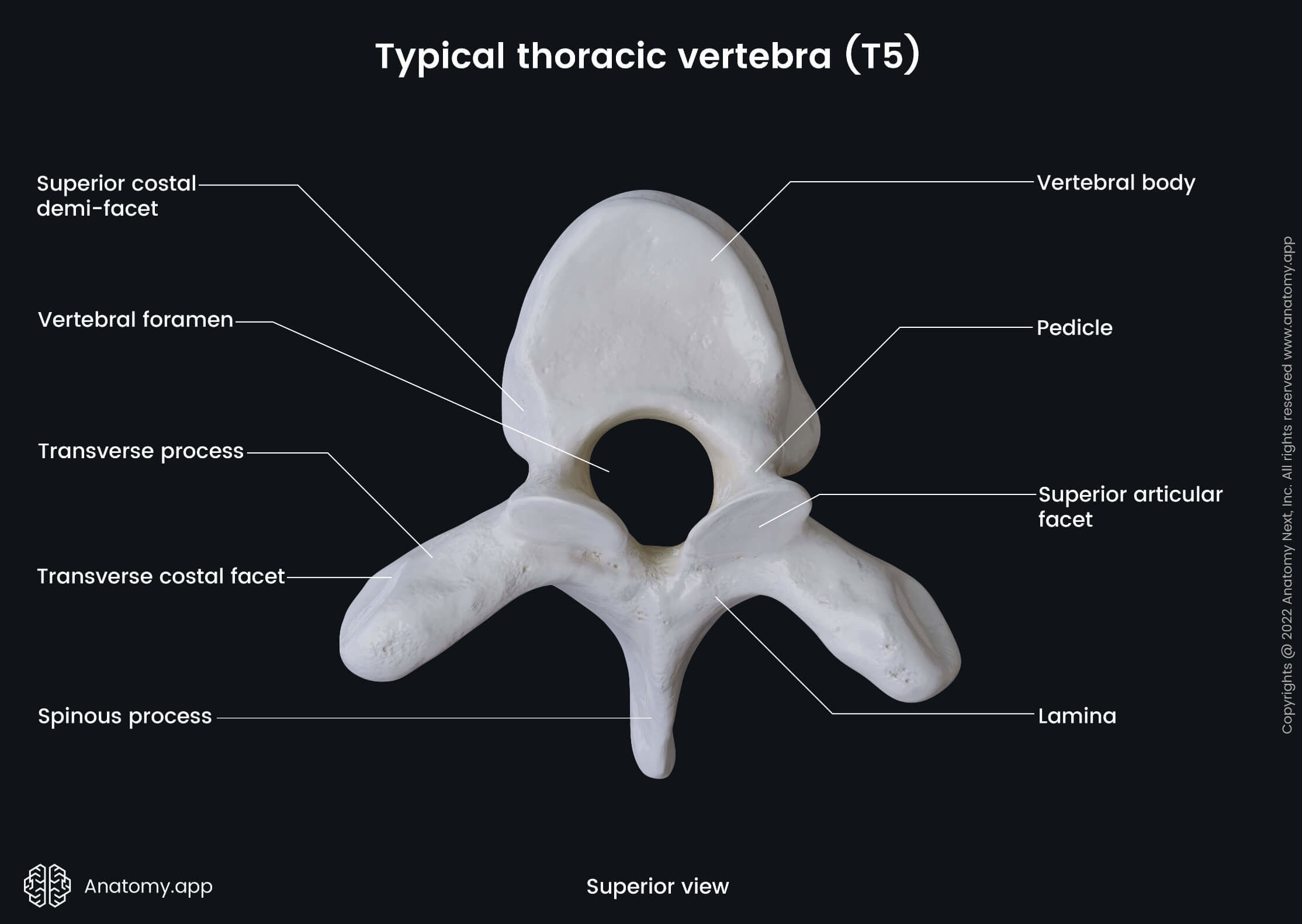
Distinct characteristics of thoracic vertebrae?
Costal facets for rib articulation
A medium-sized vertebral canal
A long and pointed spinous process
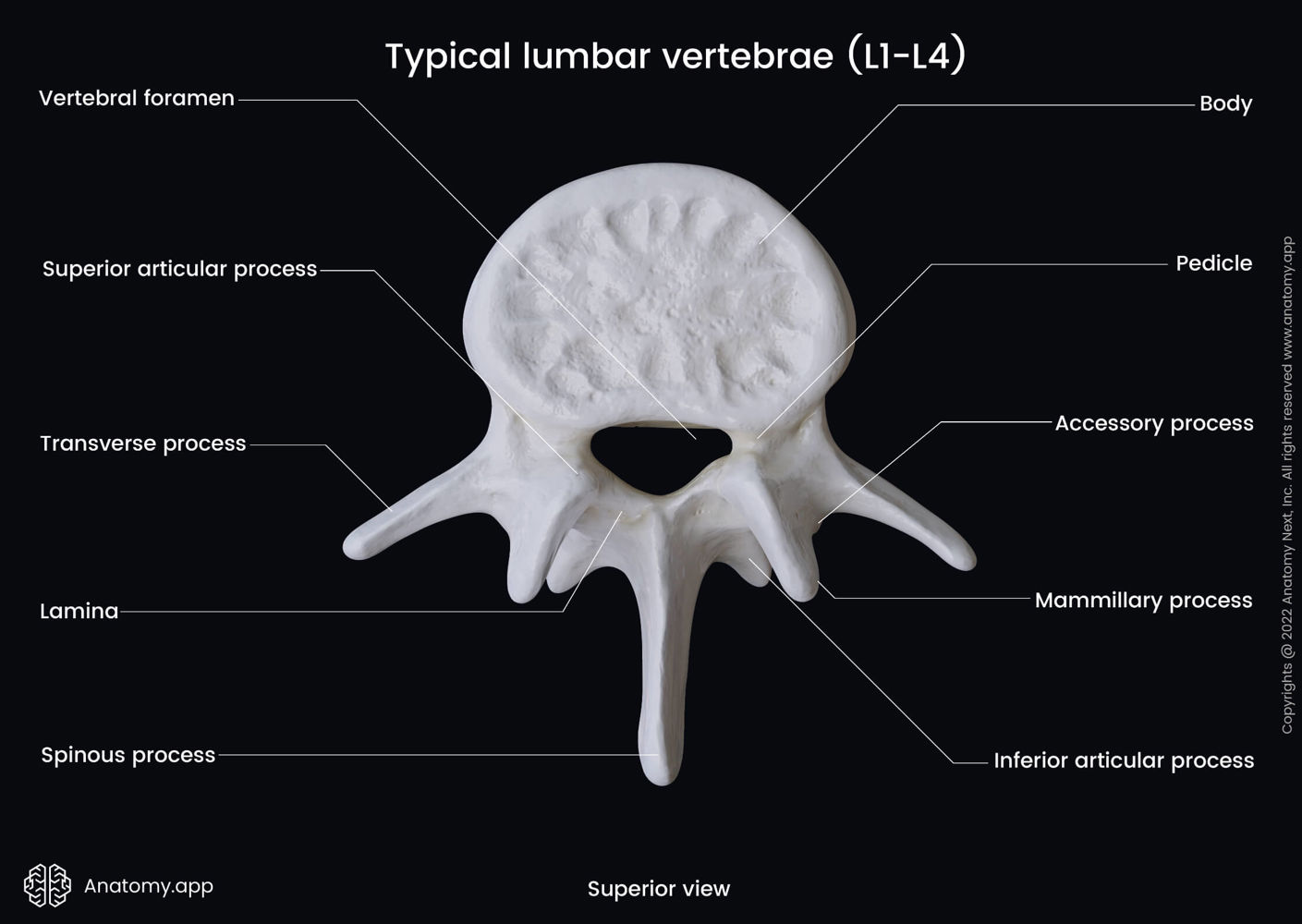
Distinct characteristics of Lumbar vertebrae?
A giant vertebral body (because most of the body weight is supported here)
Smallest vertebral canal
A blunt spinous process
Trend for articular processes as you move down vertebral collumn
Vertical ——> Horizontal
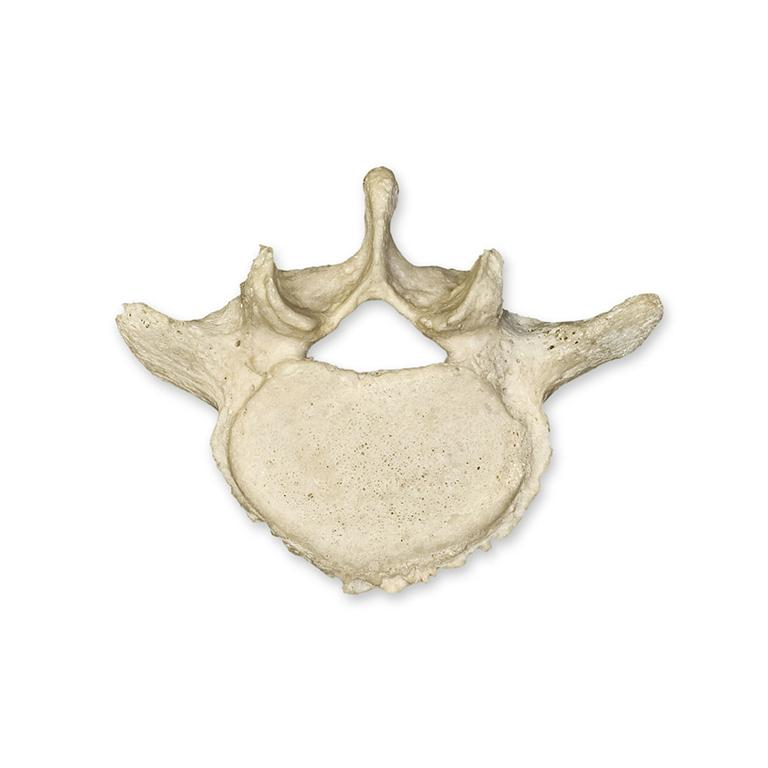
What kind of vertebrae is this?
Lumbar
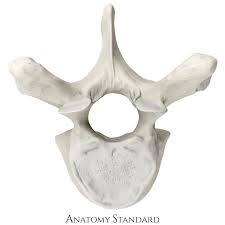
What kind of vertebrae is this?
Cervical
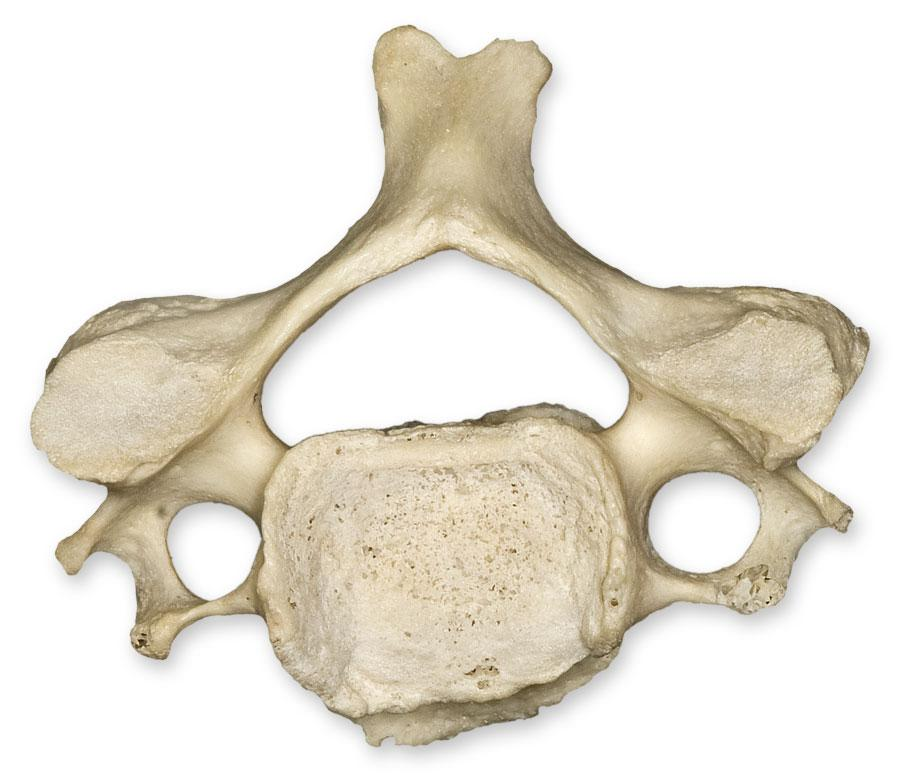
What kind of vertebrae is this?
Thoracic
What is the name for the first cervical vertebrae? (C1)
Atlas
What is the name for the second cervical vertebrae? (C2)
Axis
Distinct features of Atlas (C1)
No vertebral body
No Bifid spine
Holds head up —- large facets
Helps nod “yes”
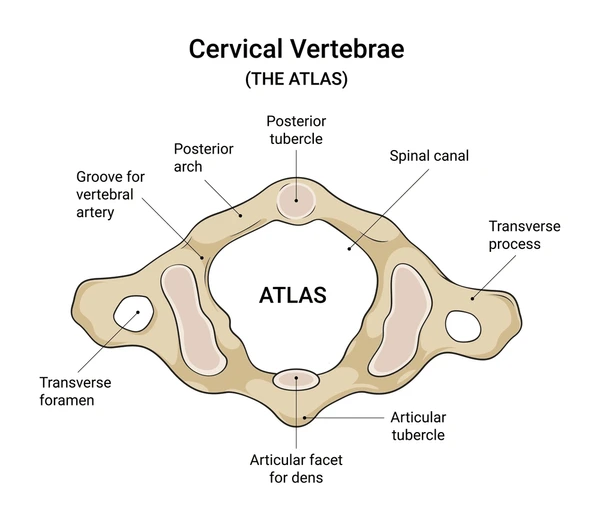
Distinct features of Axis (C2)
Dens — where we swivel the head “no”, atlas spins on.
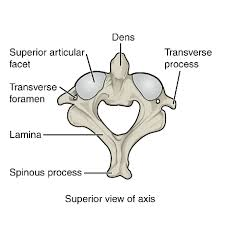
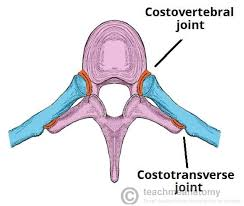
2 places ribs and vertebrae articulate
Head of rib + Body of vertebrae
Tubercle of rib + Transverse process of vertebrae
Purpose of rib cage?
protect heart and lungs
Bones in sternum
1) Manubrium
2) Body
3) Xiphoid Process
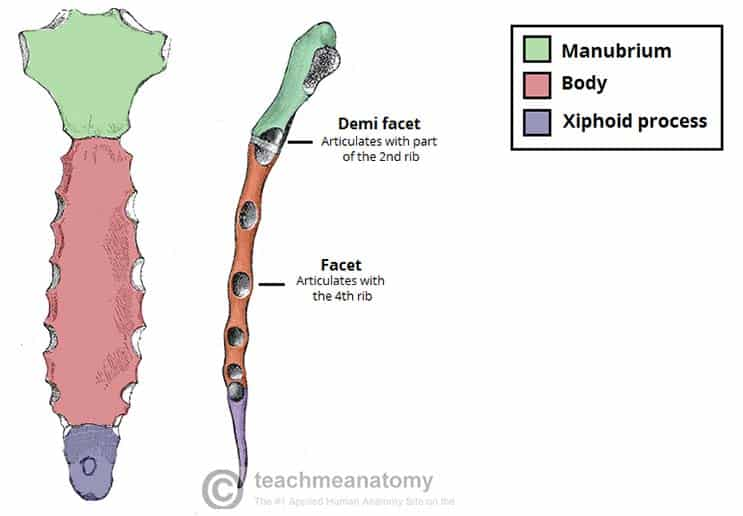
Where do the clavicles meet the sternum?
Clavicular notch

How many attachment points for ribs on the sternum?
7
How many ribs total?
12
What is a true rib?
attach directly to the sternum via their own costal cartilage
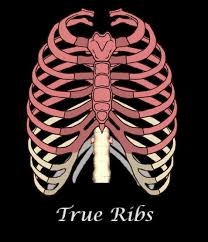
How many true ribs?
7
What is a False rib?
Costal cartilage is attached to the costal cartilage of rib just above it
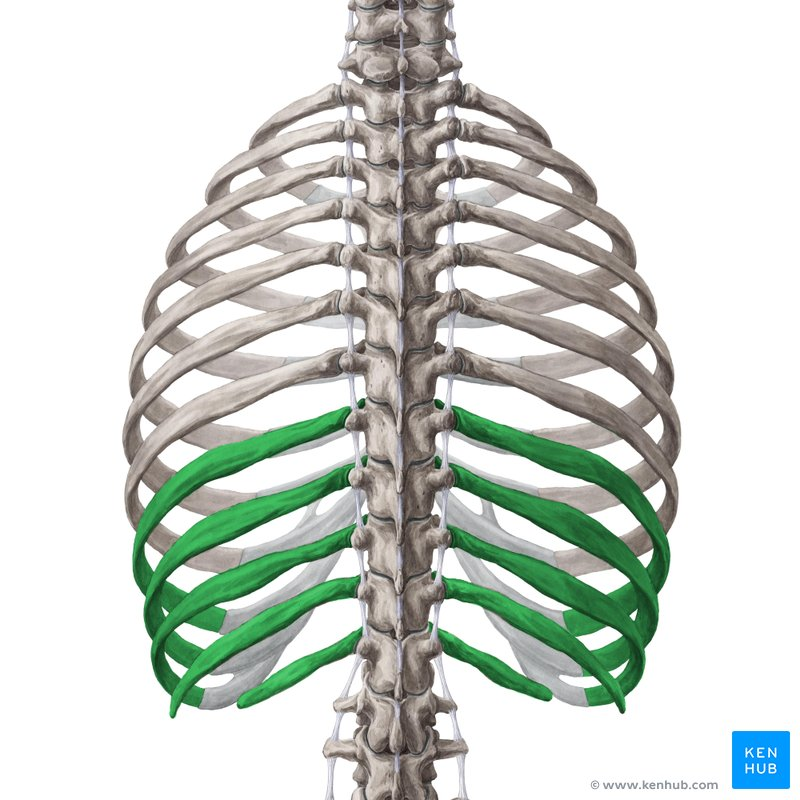
How many false ribs/what pairs?
8-10
3 false ribs
What is a floating rib?
ribs that do not have a connection to the sternum
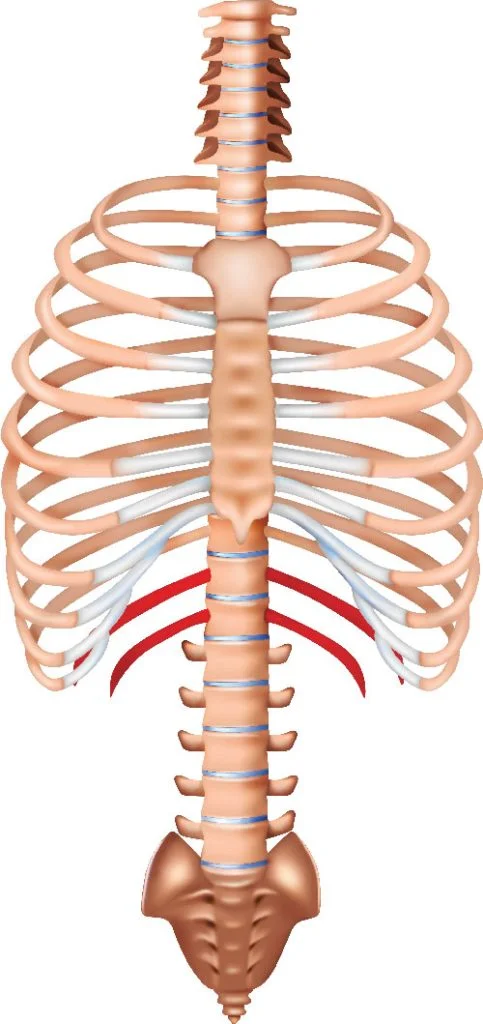
How many / which ribs are floating
pairs 11 and 12
2 floating ribs
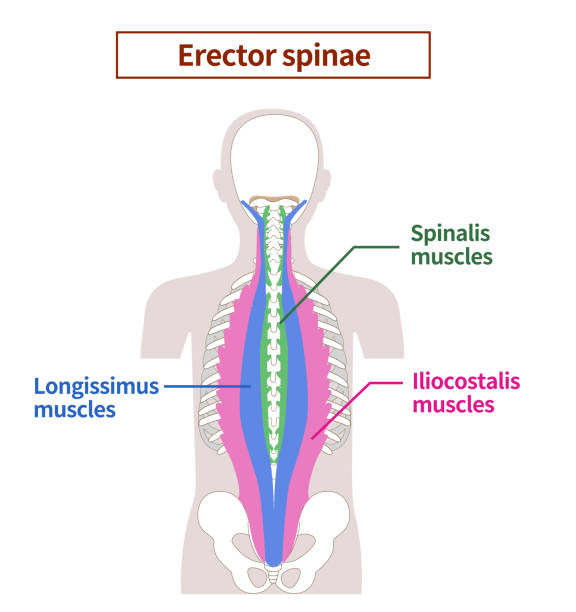
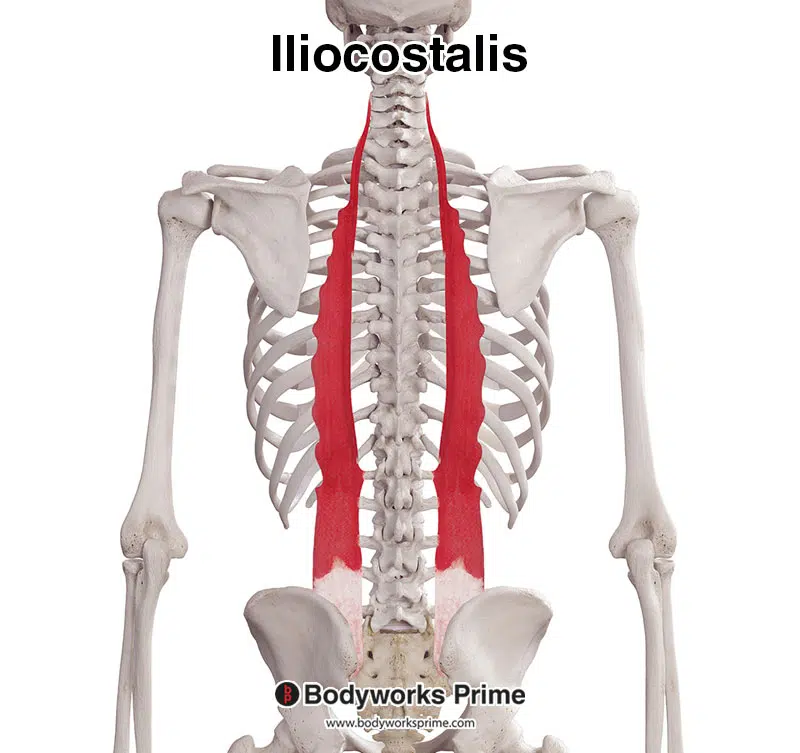
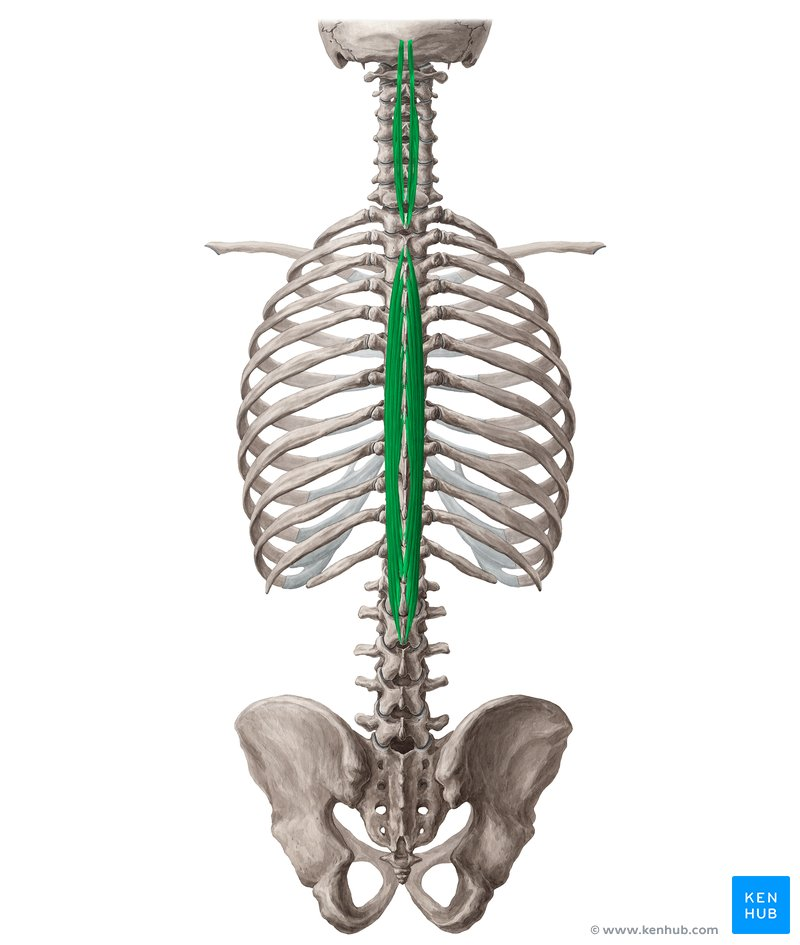
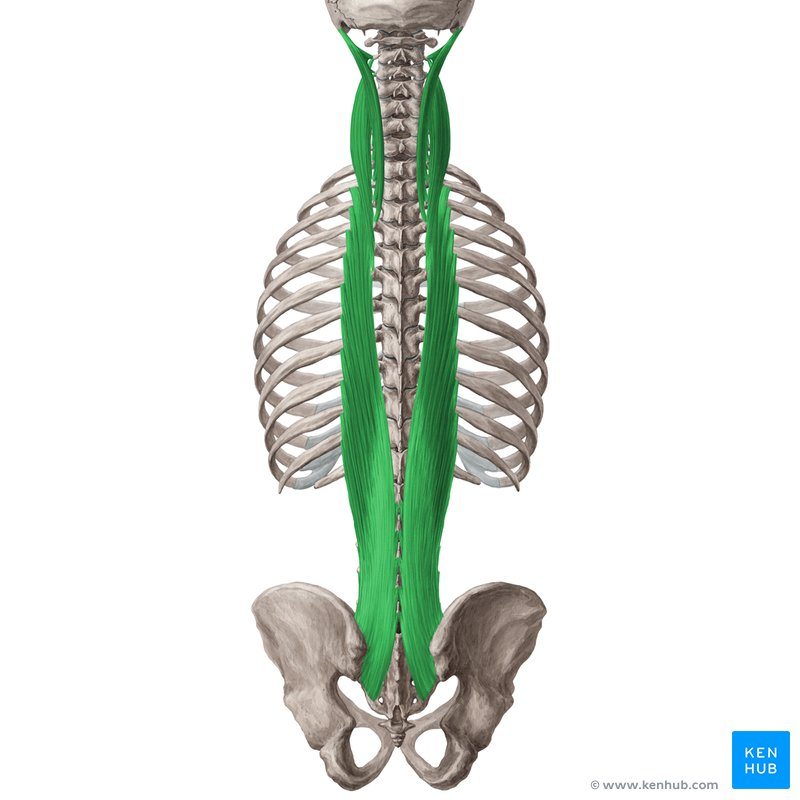
What are the 3 erector spinae muscles?
Iliocostalis
Longissimus
Spinalis
I LOVE STANDING!!!!!
Lat —> Med
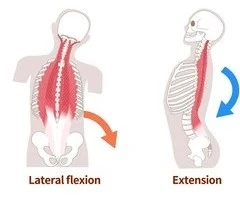
Action of erector spinae mm.
Erect (hold up) spine
Unilateral contraction → Lateral flexion of head and vertebral column
Bilateral contraction → Extend head and vertebral column
Lateral most Erector Spinae m.
Iliocostalis m.
Medial most Erector Spinae m.
Spinalis m.
Innervation of erector spinae mm.
Dorsal rami of spinal nn.
Intermediate (middle) muscle of erector spinae mm.
Longissimus m.
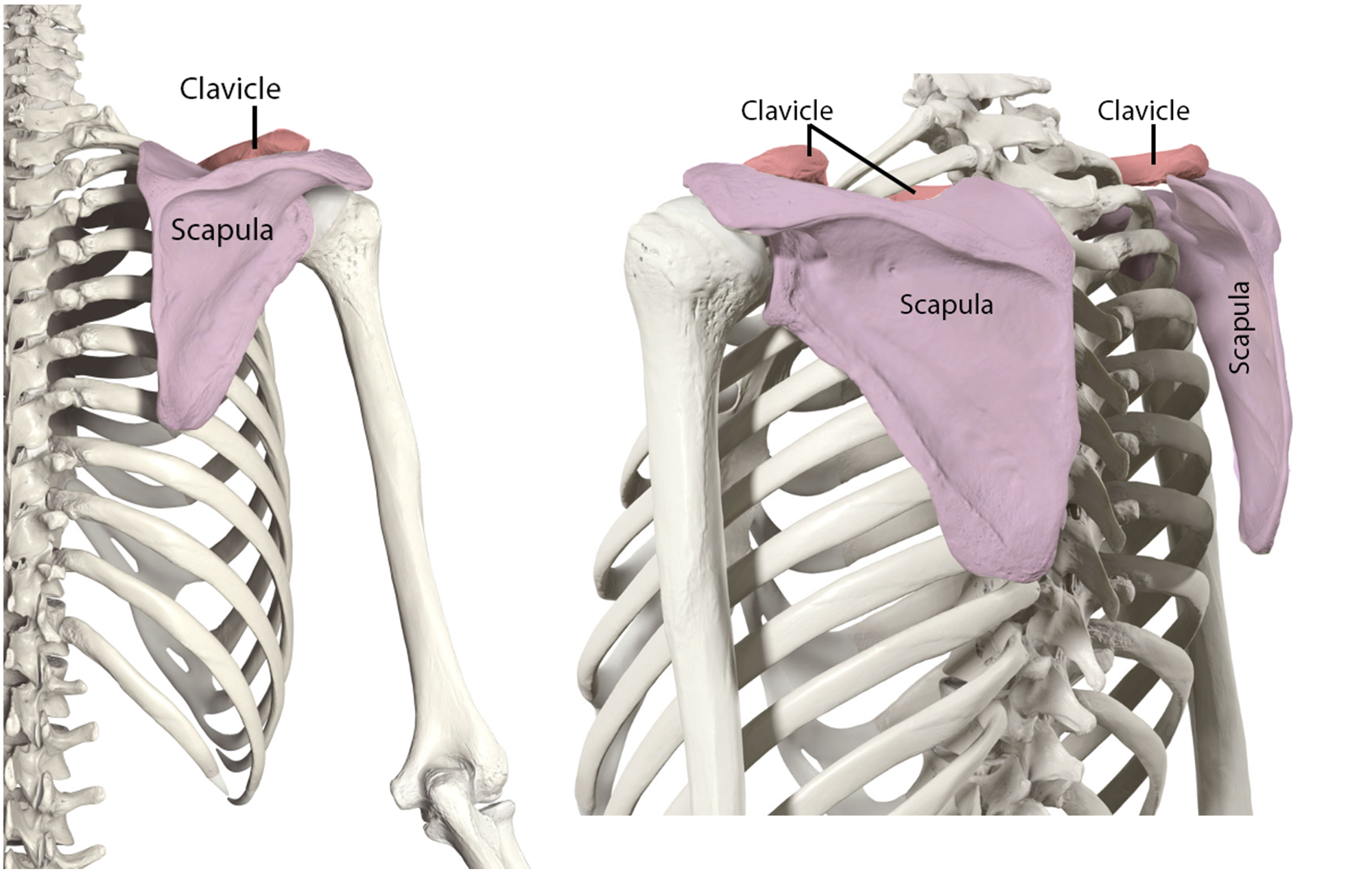
What 2 bones make up the Pectoral Girdle
Clavicle and Scapula!
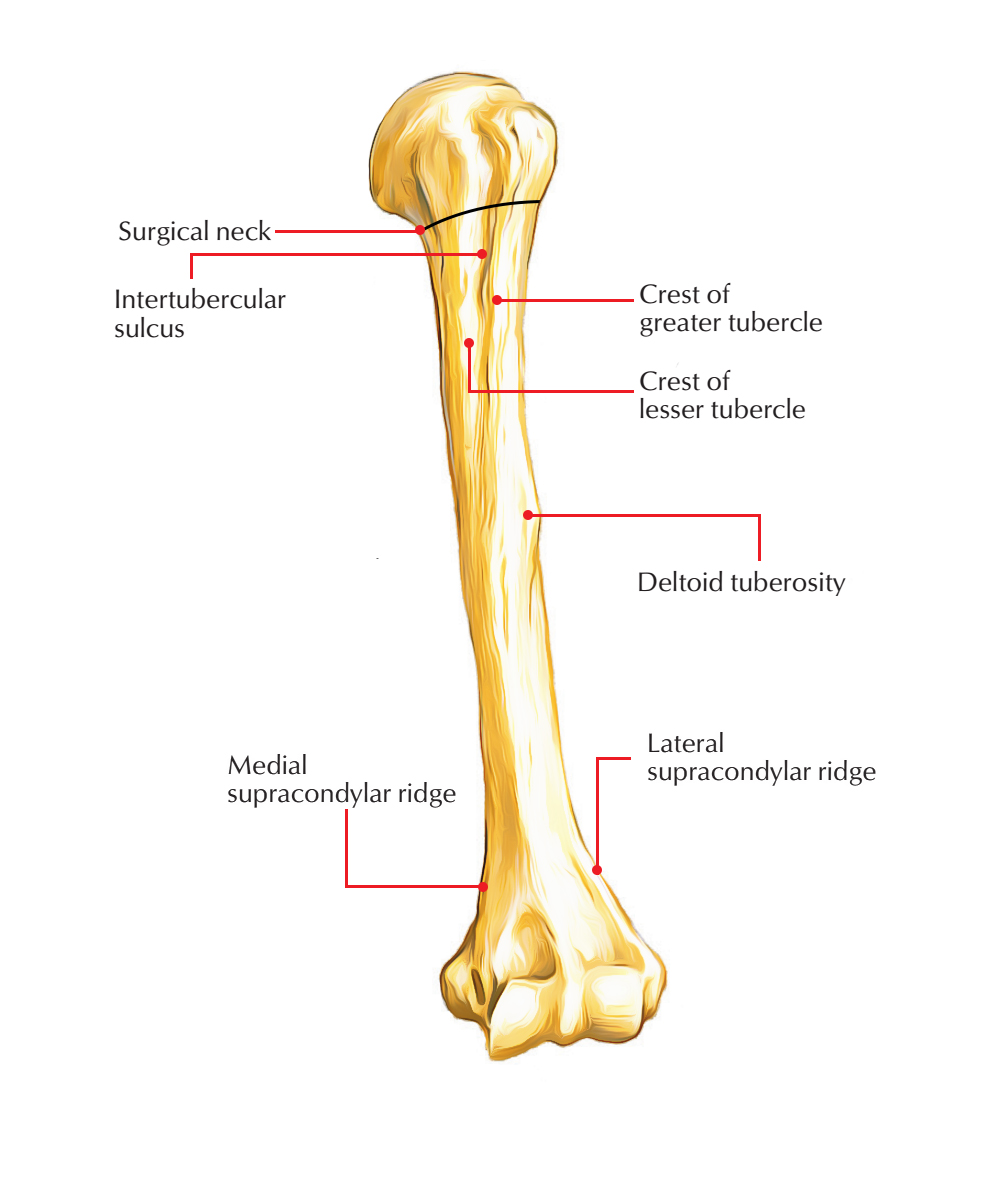
What bone is the “arm”
The humerus
What 2 bones make up the forearm?
Radias and Ulna
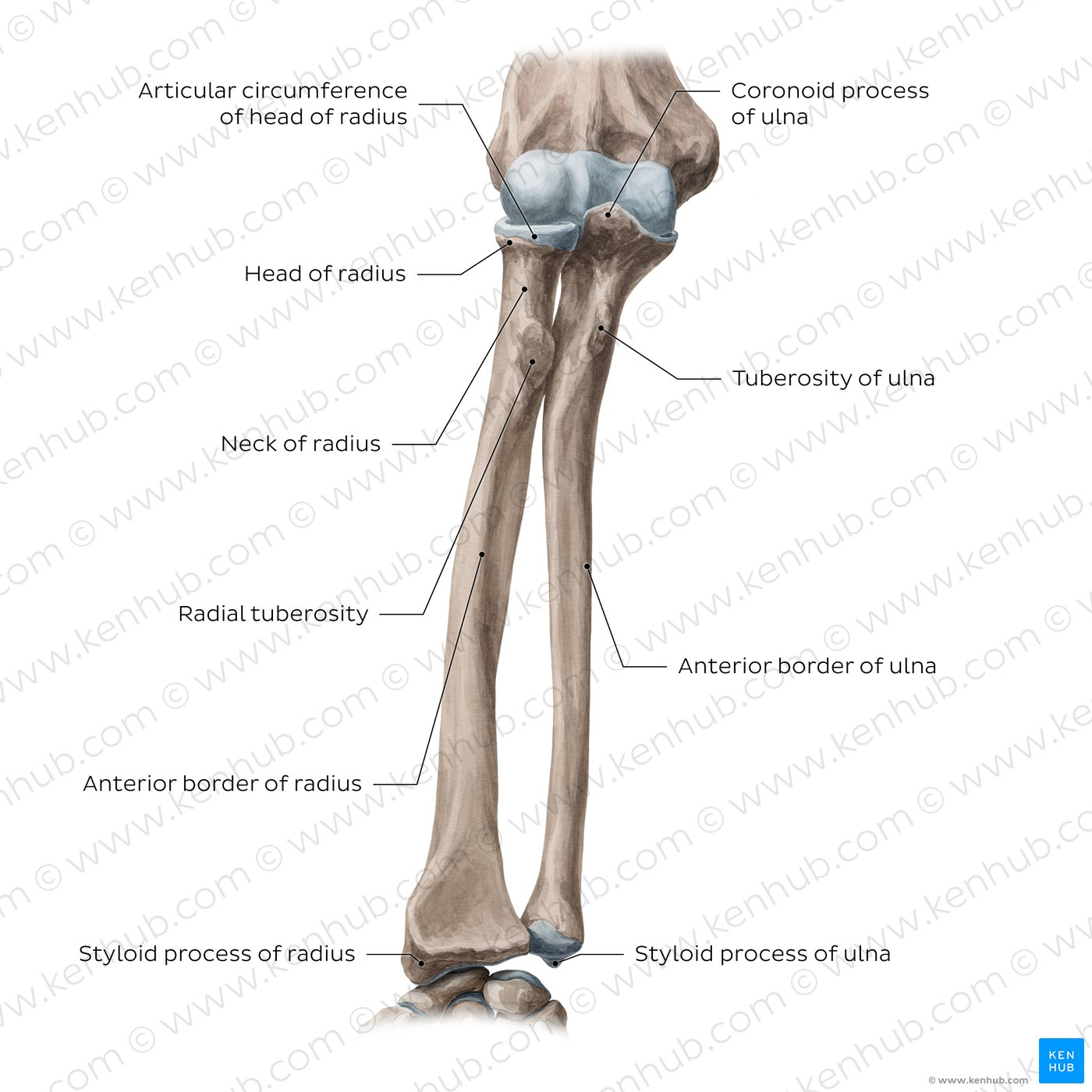
Where is the Ulna is relation to the Radius
Medial
What are the two ends of the clavicle called?
The acromial end (articulates with scapula)
The sternal end (articulates with manubrium of sternum)
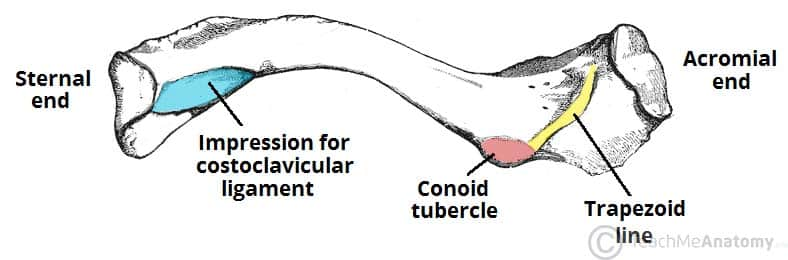
Difference between superior and inferior surfaces of clavicle?
Smooth on a superior view, groovy/rough inferiorly
Borders of scapula
Superior
Medial
Lateral
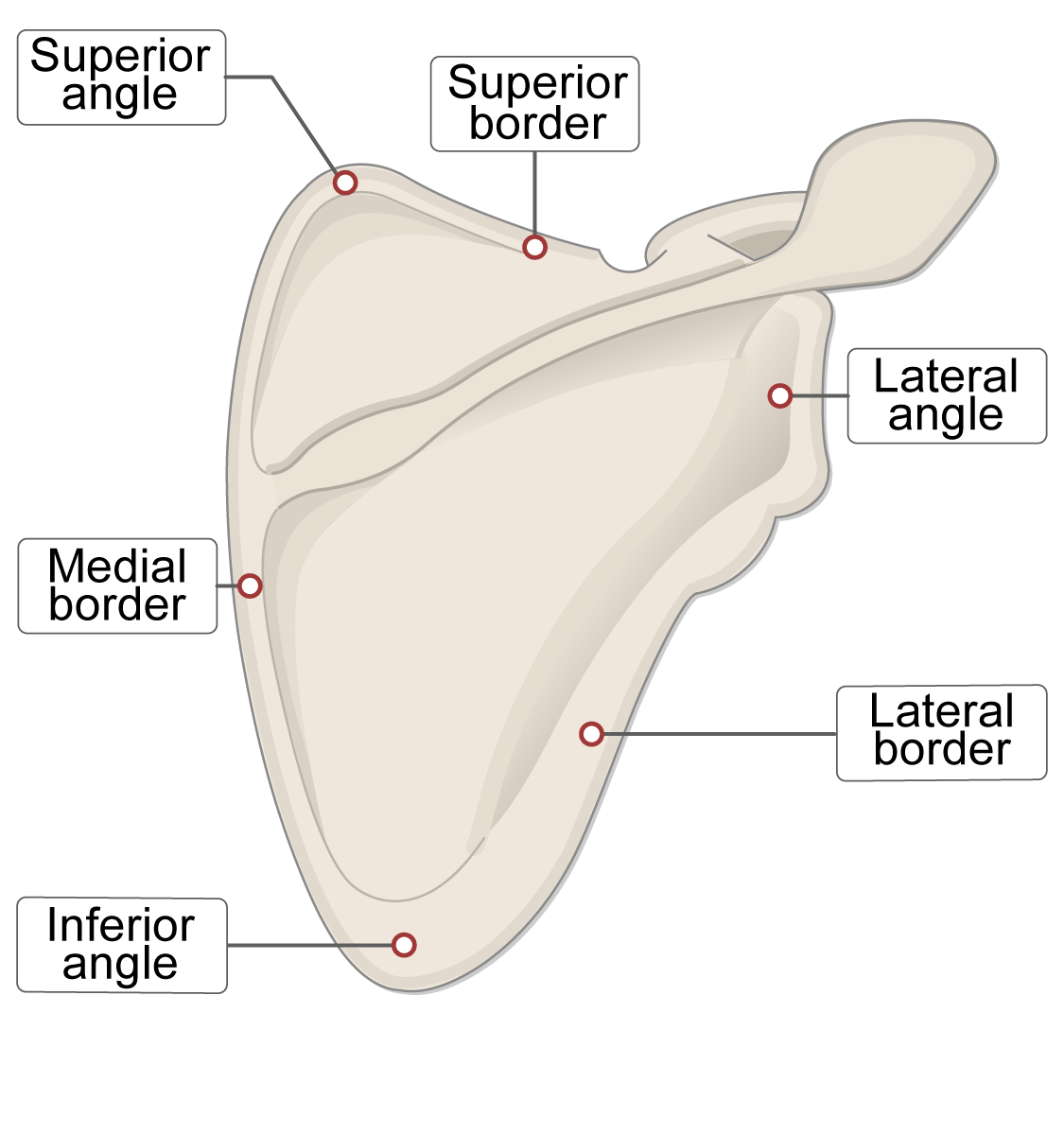
How do you know when you are looking at a posterior scapula?
If you see the spine!
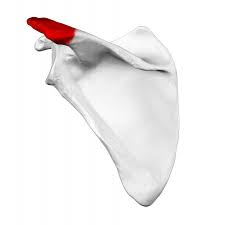
What is this structure on the scapula?
The acromion process
This is where the clavicle articulates
End of the spine of the scapula
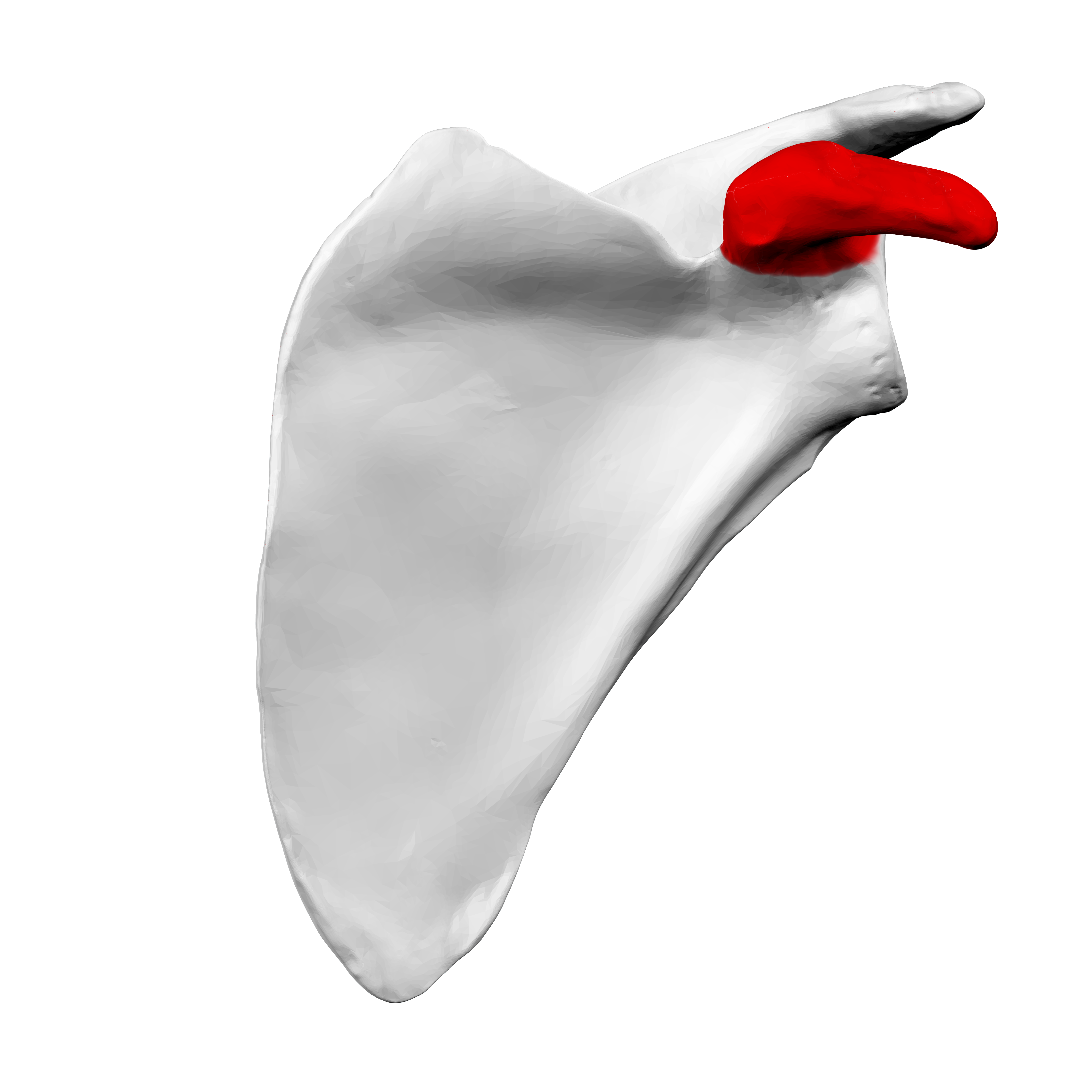
What is this structure on the scapula?
The coracoid process
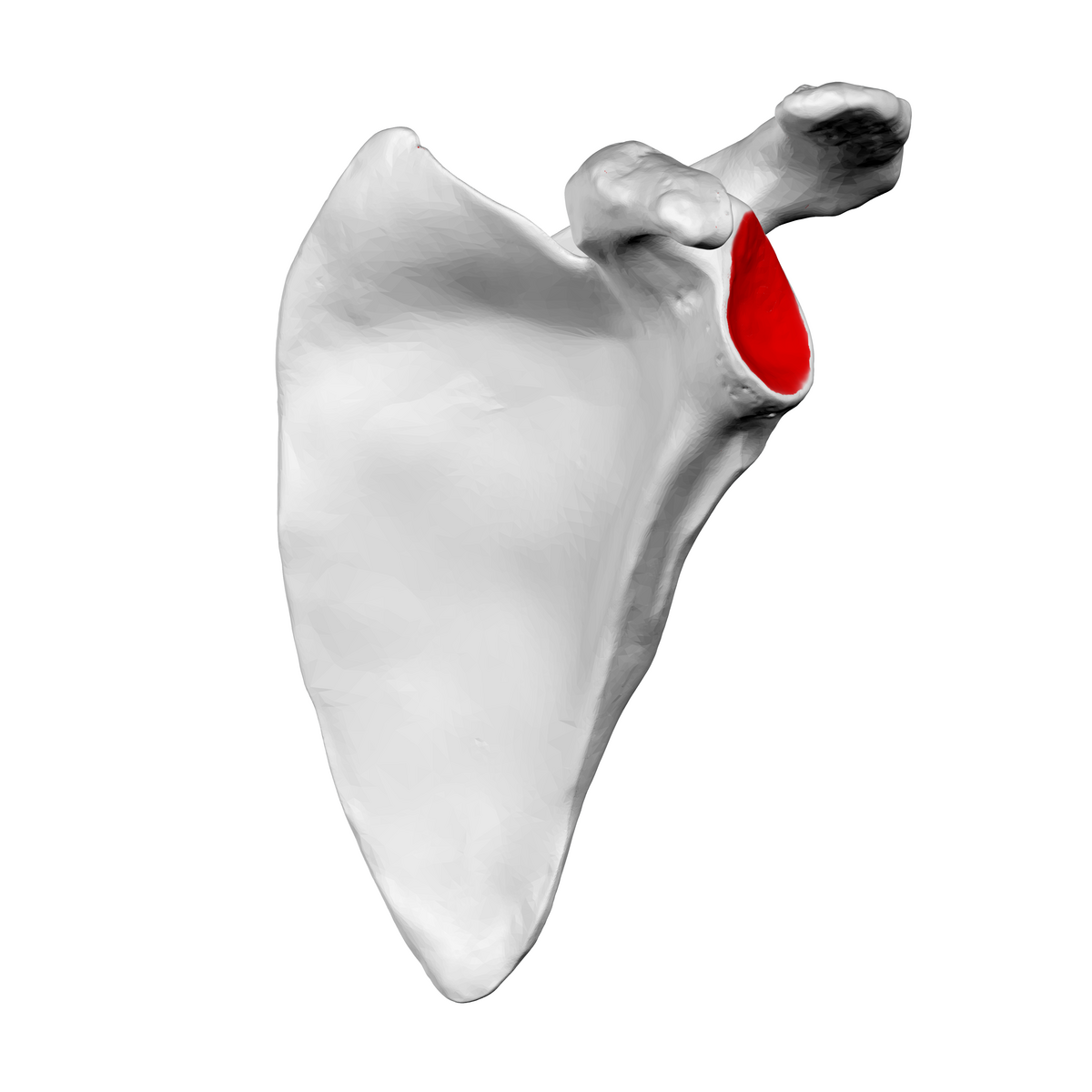
What is this structure on the scapula?
This is the glenoid cavity
This is the socket for the ball and socket joint
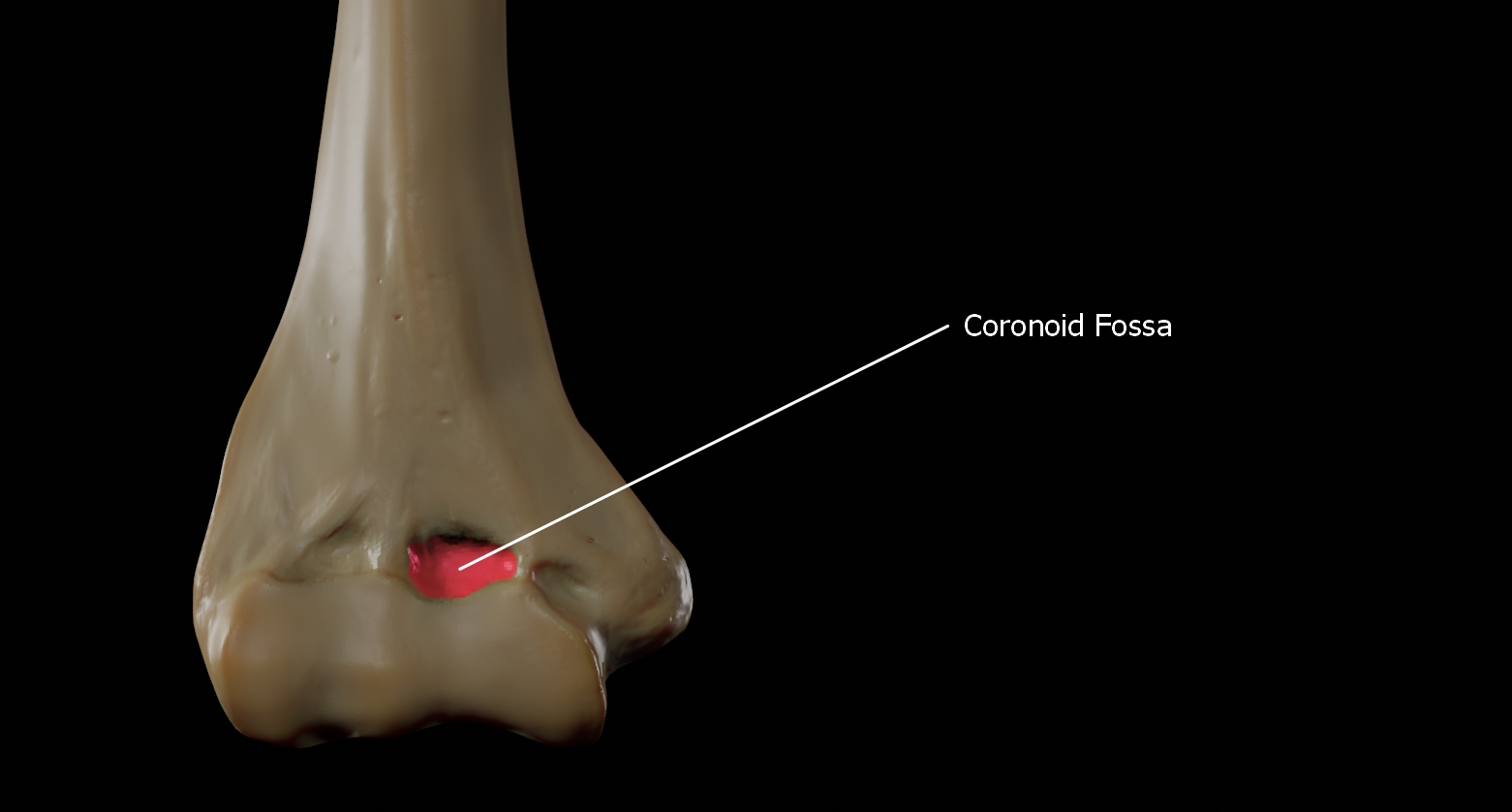
Where is the coroNoid fossa located?
the humerus!!!
This is where the ulna head comes in when the arm is flexed!
What is the significance of the capitulum?
It is a smooth “cap” that sits on the head of the radius
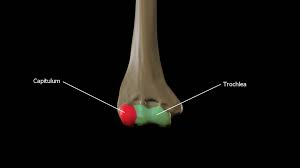
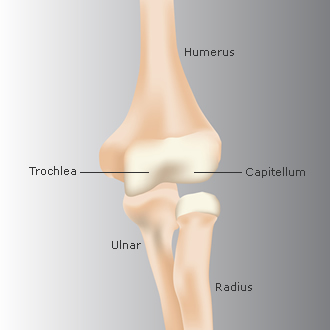
Where do the Ulna and Humerus articulate?
the trochlea of the humerus articulates with the trochlear notch of the ulna.
How can we tell the different between posterior and anterior views of the humerus?
The posterior side only has one fossa (olecranon), whereas the anterior side has two (the radial and coronoid fossas)
What is the medial bone on the forearm?
Ulna
On ya!
Which bone is lateral on the forearm?
The radius
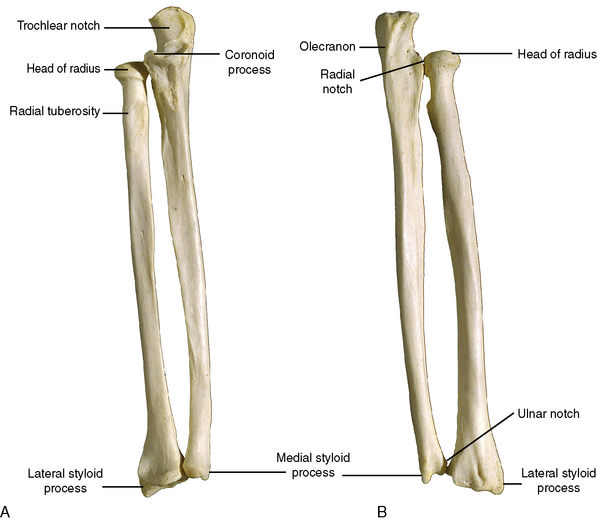
How can we tell tell if we are looking at a anterior or posterior view of the forearm?
The radius is bumpy (for tendon attachment) posteriorly and smooth anteriorly
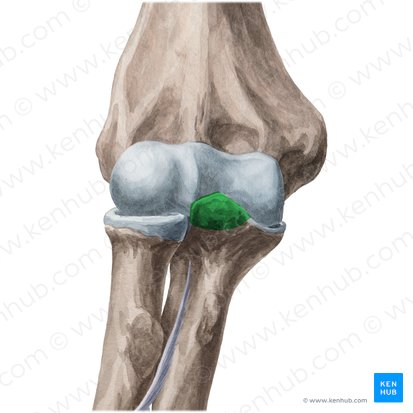
What is the structure highlighted?
The coronoid process of the ulna!
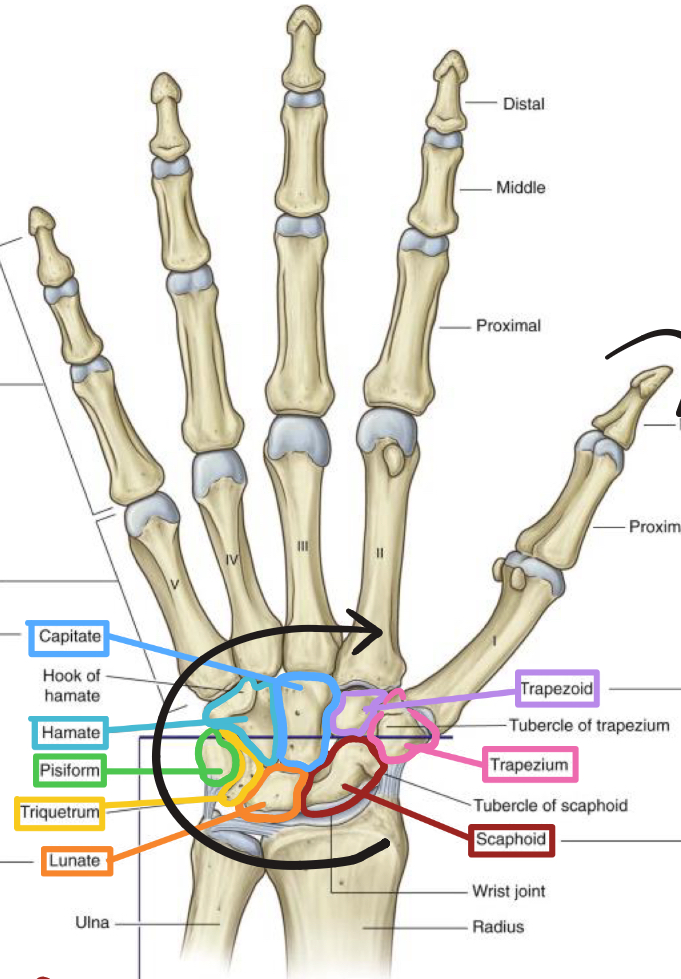
How many carpal bones are there?
eight!
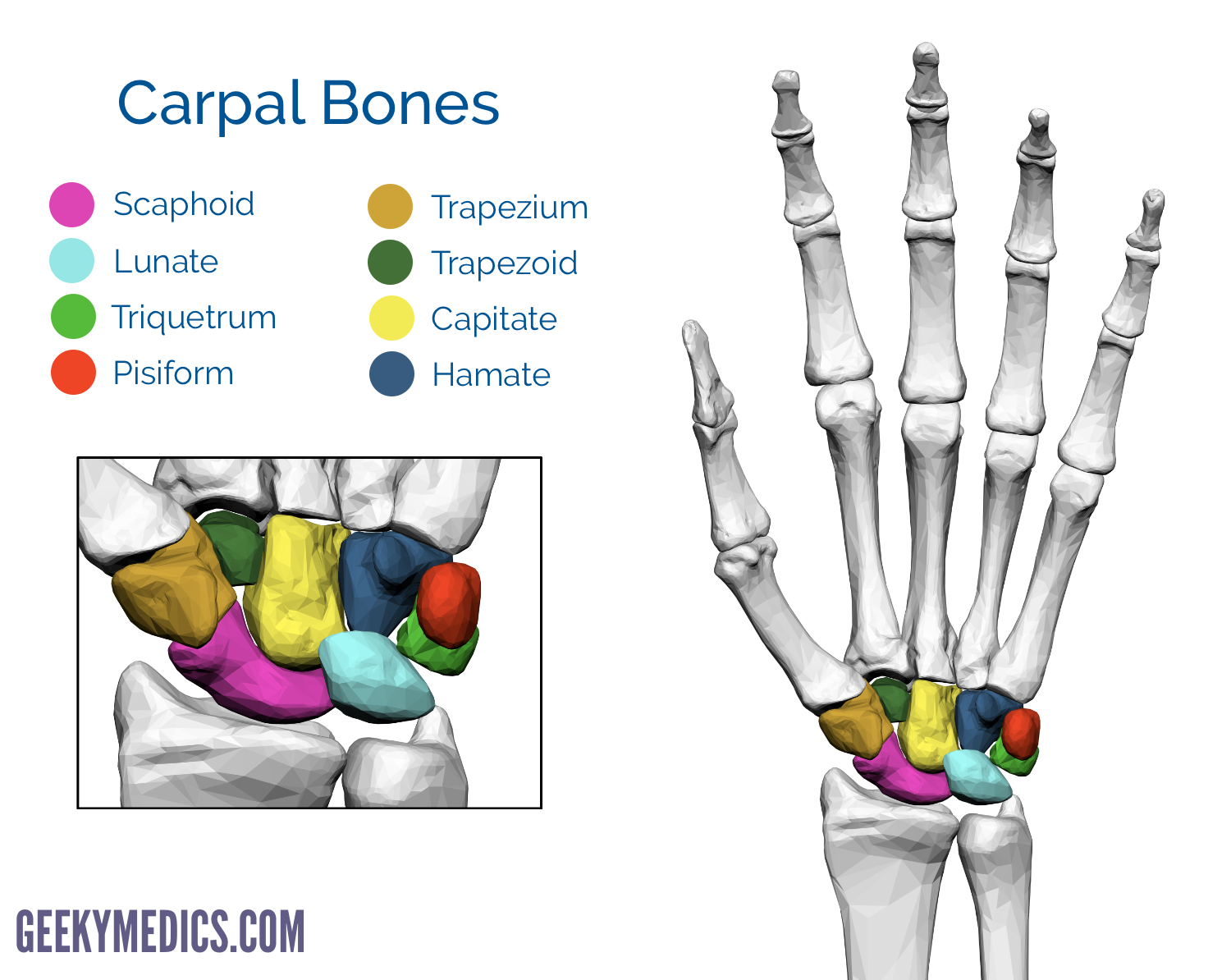
Name the carpal bones in order of lateral to medial from the proximal row to the distal row
Scaphoid
Lunate
Triquetrum
Pisiform
So long to pinkie
Hamate
Capitate
Trapezoid
Trapezium
Here comes the thumb!
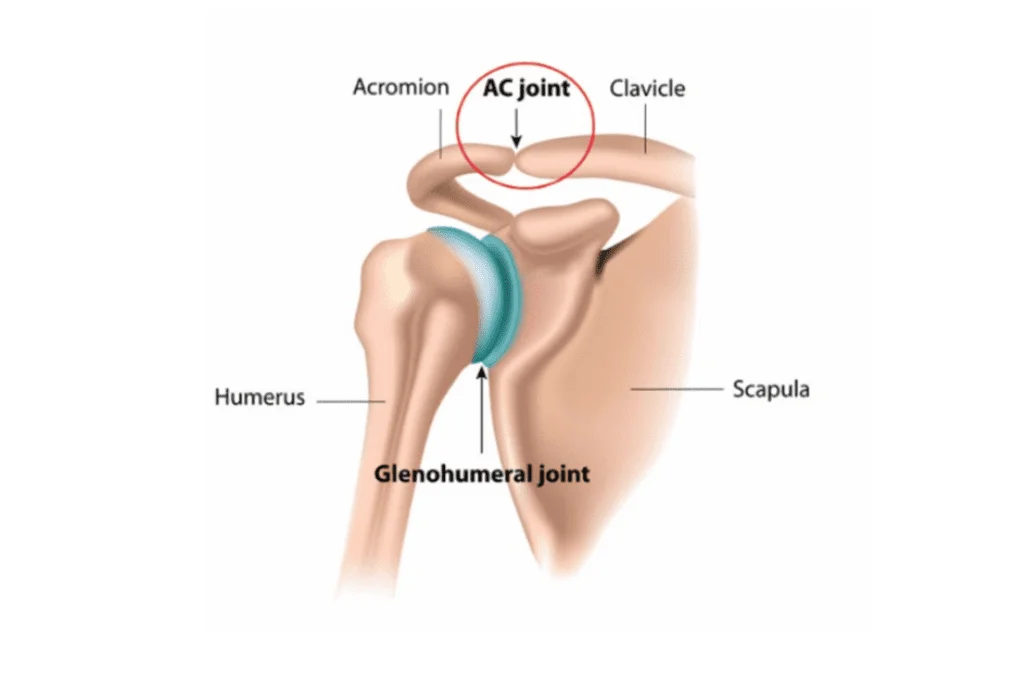
What bones articulate at the Acromio-clavicular joint?
The Scapula (the acromion) and the clavicle