CS110 FINAL EXAM
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
carbon footprint
used to describe the amount of carbon dioxide a person or machine emits
UAV/drone
remote controlled/operated either by a remote control or a flight plan
digital divide
the gap between those who have access to internet service and those who do not. also used to describe the people who are able to functionally use the internet/tech and those who cannot. these divides are usually caused by location, and/or socioeconomic status.
cloud computing
using servers remotely over the internet to store/access one’s data/programs instead of using a computer drive
chatgpt
AI created from an open source AI program, it has been programmed to answer questions/tell stories in a human-like manner
artificial intelligence (AI)
used to describe human-like intelligence in computers and other automated machines; it, like numbers, can learn and become smarter the more information they are exposed to.
algorithmic bias
when computer programs create unfair results that benefit one group through systematic errors
citizen science
when the general public helps games information, conduct experiments, and interpret results voluntarily
crowdfunding
a way for companies or individuals to raise money for projects. popular way for startup developers to raise funds to create video/computer games
private cloud
best for companies or individuals who deal with sensitive data and need extra security. it’s only used by said company/person and does not share information
public cloud
best for companies or individuals who do NOT need extra security and are NOT dealing with sensitive data. used a shared infrastructure.
crowdsourcing
utilizes the online community for contributions to a project. it allows the person/company to draw from a wider pool of talent and instead of having to pay a salary/hourly wage, you can utilize a commission based pay model
scalability
in cloud computing, it is used to describe the ability to add or take away resources as needed
elasticity
in cloud computing, it is used to describe the ability to compress or expand resources as needed
redundancy
in cloud computing, it is used to describe the ability to copy functions of a computer system to help with availability and reliability
open-source software
distributed software that has its source code available, that allows it to be modeled, used, and distributed
hybrid cloud
a combination of private and public clouds, with the provider managing the public cloud and the consumer utilizing the private cloud
name at least 2 cloud computing applications that you regularly use
instagram, amazon, netflix, facebook
describe how the increase in the production of technological devices negatively impacts our environment
with the increase in production in technology we see that this industry alone creates 1% of the whole world’s energy consumption, in addition to creating massive amounts of harmful waste as chip designs are not utilizing the materials in an eco-friendly manner
what is meant by a carbon footprint?
every time we use our electronic devices, or even creating nanotechnologies, we are contributing to increasing our carbon footprint or the amount of carbon dioxide that is being created by one person or a community/country as a whole
list the 3 dangers of deep fakes
1) political issues - making it seem like a politician said something
2) extortion
3) national security - terrorism
list 3 examples of how drones are used for commercial, industrial, or military use
1) deliveries
2) surveying hard to reach areas
3) border surveillance
what is meant by open-source software and how is it different from (or related to) crowdsourcing and crowdfunding?
open source software is software that has the code readily available for people who purchase the software, and is related to crowdsourcing because it allows a group to make changes to a program/game and then upload changes to the public for free (ex: modding games like skyrim)
give one example of algorithmic bias
facial recognition software
what steps can be taken to eliminate the digital divide?
using social media ads to help fund closing the gap through “romer taxes”
removing the bureaucracy that allows internet service providers to throttle, overcharge, and underserve
ISP’s should be held accountable for their promises to help the underserved while accepting government funding
there should be a bigger push for public-private partnerships that would quickly help those who need it the most, while giving private companies incentives to participate
improve the quality of assistance programs already in place
implement policies that would protect broadband services as our needs increase in the future
fund digital literacy programs
what is the purpose of captcha-recaptcha?
captcha is used to prove that a human and not an automated system is using the site, while recaptcha is used to digitize old publications that cannot be read by a computer
how can the text that is presented in recaptcha be used?
the text that is presented in recaptcha is used to prove that you are human and not an automated system trying to access the site while at the same time; by typing the words shown, we help the computer identify words from old texts that they are unable to recognize
application software
any program, group of programs, designed to be used directly by the end user (ex: word processors, firefox, google chrome, web browsers)
abstraction
the process of picking out (abstracting) common features of objects and procedures. a programmer would use abstraction, for example, to note that 2 functions perform almost the same task and can be combined into a single function
hardware
refers to objects that you can actually touch, like disks, disk drives, display screems, keyboards, printers, boards, and chips
software
set of instructions, data, or programs, used to operate a computer and execute specific tasks (aka tells a computer how to function). used to refer to applications, scripts, and programs that run on devices such as PCs, mobile phones, tablets, and other smart devices
bit
unit of measuring data. a single bit is the smallest unit of information on a machine and can only hold one of two values: 0 or 1. these values can represent a variety of binaries, including yes/no, positive/negative, on/off, true/false, and positive/negative.
byte
unit of digital information used in computer processing and storage. a standard byte is made of eight binary digits, which are called bits.
BIOS
basic input output system, the “spine” of the computer. a chip that is a special kind of ROM that handles interactions between the software running on the computer and the machine’s hardware components
volatile
memory that loses its contents when the power is turned off
nonvolatile
memory that does NOT lose its contents when the power is turned off
random access
data file that enables you to read or write information anywhere in the file
sequential access
you can only read and write information sequentially, starting from the beginning of the file
input/output devices
any hardware that allows a human operator or other systems to interface with a computer
peripherals
a computer device, such as a keyboard or printer, that is not part of the essential computer (i.e. the memory and microprocessor). these auxillary devices are intended to be connected to the computer and used
device drivers
a software program without a user interface (UI) that manages hardware components or peripherals attached to a computer and enables them to function with the computer smoothly
computer malware
short for malicious software, malware is any program or file designed to harm or exploit any programmable device or network. umbrella term for viruses, worms, trojans, and ransomware, among others, used to cause destruction or gain access to sensitive information
operating systems
the software the supports a computers’ basic functions, such as scheduling tasks, executing applications, and controlling peripherals
DDOS
distributed denial of service, a mass attack from malware
what is the difference between ROM and RAM?
ROM is read only memory that can’t write new data to it but remains even after the computer is turned off. RAM is random access memory that can have new data written to it but is deleted after the computer is turned off (temporary)
how does RAM affect a computer’s performance?
RAM affects a computer’s performance by allowing it to surf the web then quickly change to downloading an app or writing in word
how many bytes in a gigabyte? in a kilobyte?
gigabyte = 1,073,741,824 bytes
kilobyte = 1,024 bytes
list from smallest to largest: kilobyte, megabyte, byte, bit, terabyte, gigabyte
bit, byte, kilobyte, megabyte, gigabyte, terabyte
alice has 600MB of data, bob has 2000MB of data, will it all fit in alice’s 4GB thumb drive?
600MB = 0.6GB
2000MB = 2GB
2.6GB < 4GB (YES!)
alice has 200 small images, each of which is 600KB. how much space do they take up overall in MB?
200 × 600 = 120000KB
120000KB = 120MB!
how is data represented in a computer?
binary format
what is the job of an operating system? list 3 operating systems
the job of an operating system is to manage all of the software and hardware in the computer
microsoft windows, macOS, linux
when we refer to an operating system, are we referring to hardware or software?
software
list from most general (most abstract) to most specific (least abstract): USB flash drive, byte, secondary storage
secondary storage, byte, USB flash drive
list from most general to most specific: microsoft office, software, excel
software, microsoft office, excel
what are the advantages of a multi-core processor?
can work on more than one problem at a time as well as a larger problem more efficiently
what is the difference between a modem and a router?
router is a small box that allows multiple computers to join the same network. most are now wireless. modem connects to your ISP (internet service provider) and connects you to either cable or DSL internet services
list the following in device connection order of their connections to each other. assume that the modem and router are 2 separate devices: modem, ISP, router, laptop, computer, internet
laptop → computer —> router —> modem —> ISP —> internet
what units are used to measure:
a) RAM? how much would be a reasonable choice when purchasing a computer?
b) hard drive capacity? how much would be a reasonable choice when purchasing a computer?
c) processor speed? what’s good here?
a) megabytes and gigabytes; 8GB when purchasing a computer
b) gigabytes; 256-500GB is enough for the average user
c) 2.4GHz is good
what is the difference between a hard disk drive (HDD) and a solid state drive (SSD)?
SSDs store data in flash memory, while HDDs store data in magnetic drives
how do you delete files from your computer? how are you sure that no one can access your deleted files (or any files?)
to completely delete files on a computer after you delete the items and empty out your trash can, you need a third party tool (for windows) which will overwrite the vacant space on your drive with random data so the original files and folders can’t be brought back. without that short of destroying your computer, there is no way to completely erase files.
binary representation of data
a type of data that is represented or displayed in the binary numeral system. binary data is the only category of data that can be directly understood and executed by a computer. numerically represented by a combination of zeros and ones.
octal
refers to base-8 number system, which uses just 8 unique symbols (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7) programs often display data in octal format translated into binary format easily
octal number: 3456
binary: 011 100 101 110
hexadecimal
refers to the base-16 number system, which consists of 16 unique symbols: the numbers 0 to 9 and the letters A to F. for example, the decimal number 15 is represented as F in the hexadecimal system. the hexadecimal system is useful because it can represent every byte (8 bits) as 2 consecutive hexadecimal digits
hexadecimal: 0x3F7A
binary: 0011 1111 0111 1010
ASCII
american standard code for information interchange - code representing 128 english characters as numbers, with each letter assigned a number from 0 to 127. for example, the ASCII code for uppercase M is 77. most computers use ASCII codes to represent text, which makes it possible to transport data from one computer to another.
unicode
a standard for representing characters as integers. unlike ASCII, which uses 7 bits for each character, unicode uses 16 bits, which means that it can represent more than 65,000 unique characters
data
any sequence of one or more symbols; datum is a single symbol of data. data requires interpretation to become information. digital data is data that is represented using a binary number system of ones and zeros instead of analog representation
metadata
describes how and when and by whom a particular set of data was collected and how the data is formatted. metadata is essential for understanding information stored in data warehouses and has become increasingly important in the XML-based web applications.
RGB
refers to a system representing the colors used on a digital display screen. red, green, blue, can be combined in various proportions to obtain any color in the visible spectrum.
steganography
practice of hiding or concealing a message within a message that is not a secret, such as hiding a secret script inside of a microsoft word document. goal is to practice secrecy or deceit.
how does a computer distinguish between a photo and a text file if everything is stored as bits?
the computer distinguishes between different types of files through file extensions. an extension such as .doc, .txt, or .rtf indicates a text. an extension of .jpeg, .jpg, or .psd indicates a picture. these extensions tell the operating system what file it is and how to open it.
how does the computer distinguish between lossy and lossless compression? which would be most appropriate for each of the following?
a) an image saved to be studied by brain surgeons while performing delicate surgery
b) an image uploaded to use on a personal webpage
c) a sound file used as background music for a home video where the song and video are to be uploaded to youtube
d) a .zip file used to store a directory of documents
e) an image used as a thumbnail on your computer
lossy is usually used for video, sound, and photos. lossless is usually used for text, spreadsheets, or gifs
a) lossless
b) lossy
c) lossy
d) lossless
e) lossy
classify each of the following file types as lossy compression, lossless compression, or not compressed: JPEG, BIG, BMP, MP3, WAV, AND PNG
JPEG: lossy compression
GIF: lossless compression
BMP: not compressed
MP3: lossy compression
WAV: lossless compression
PNG: lossless compression
an RGB color represented by the triplet (220, 65, 43) is closest in color to red, green, or blue?
red - uses 220 bits, green only 65, blue only 43.8
network interface card (NIC)
a hardware component that enables a device to connect to a network by providing a physical interface for communication, typically via ethernet cables or wireless signals
circuit switching
establishes a dedicated communication path between 2 nodes before the actual data transfer. the path remains reserved for the duration of the communication session
packet switching
breaks data into packets, which are then individually routed over a shared network. each packet can take a different route to reach its destination, and they are reassembled upon arrival
asynchronous transmission
data transmission method where individual characters or data blocks are sent independently of one another, typically with the sender and receiver using their own clocks to time the transmission
synchronous transmission
data transmission method where data is sent in a continuous stream and is synchronized by a clock signal shared between the sender and receiver, ensuring data integrity and reliable timing
BPS
“bits per second” - a unit of measurement used to quantify the rate of data transmission in a network or commuication channel
ethernet
a widely used networking technology for connecting devices in a local area network (LAN), characterized by its speed and reliability. ethernet typically uses twisted pair of fiber optic cables
bluetooth
a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances between devices, commonly used for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, and headphones to computers and mobile devices
broadband
refers to high speed internet access that is always on and provides faster data transmission rates compared to traditional dial-up connections
DSL/cable
DSL (digital subscriber line) - a technology that uses existing telephone lines to provide high-speed internet access. DSL allows for simultaneous voice and data transmission over the same line
cable - high-speed internet service provided through the same coaxial cables that deliver cable television. cable internet typically offers faster speed than DSL
internet protocols
set of rules and conventions that govern how data is transmitted over the internet. this includes protocols like TCP/IP (transmission control protocol/internet protocol), which define how data is broken down into packets, routed, and reassembled at the destination
define the term network and list 3 advantages provided
network: a collection of interconnected devices and systems that can communicate and share resources with each other
advantages: resource sharing, communication, and collaboration
compare and contrast peer-to-peer networks with client server networks
peer-to-peer: each device in the network can act as both a client and a server, sharing resources directly with other devices
client-server: devices are divided into clients and servers, with servers providing resources and services to clients upon request
tdlr: in peer-to-peer, there’s no centralized control, while client-server networks have a centralized server managing resources. peer-to-peer is simpler and cheaper to set-up, while client-server offers better security and scalability
a school with 20 stand alone PCs is considering networking them together and adding a file server. give 3 possible benefits.
1) centralized storage
2) data backup
3) improved collaboration
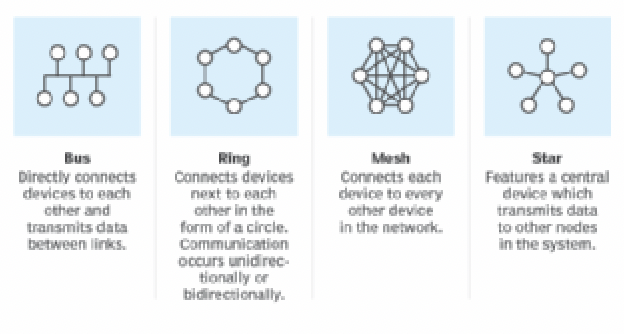
draw examples of the following LAN configurations: ring, star, mesh, bus, give an advantage or disadvantage of each configuration.
ring:
advantage: simple to install and maintain
disadvantage: failure of one device can disrupt the entire network
star:
advantage: centralized management and easy troubleshooting
disadvantage: dependency on the central hub; failure can disrupt the entire network
mesh:
advantage: redundancy and fault tolerance
disadvantage: complex and expensive to implement
bus:
advantage: simple and inexpensive
disadvantage: susceptible to cable failure, which can disrupt the entire network
what is the difference among LAN, MAN, WAN, and PAN? list them in order of size from smallest to largest.
LAN (local area network) - within a small area such as buildings or campus
WAN (wide area network) - covers a much larger geographic area, such as a state, or a country
PAN (personal area network) - interconnection of your personal digital devices
MAN (metropolitan area network) - public high speed network with range of about 50 miles; covers a town or city
PAN —> LAN —> MAN —> WAN
describe the process followed by packet switching in transfer
at each interconnected node, packets are received, stored briefly, and then forwarded based on the routing information in the header. upon reaching their destination, packets are reassembled into the original data stream. this process allows for efficient use of network resources and enables data to take different paths to reach its destination, enhancing reliability and speed
list 4 essential pieces of information contained in a packet
1) source address
2) destination address
3) payload/data
4) header information
list the necessary components of a wireless network
1) network interface card (NIC)
2) access point (AP)
3) router
what is the difference between bandwidth and latency?
bandwidth represents the measure of computer network used. latency refers to delays incurred in processing data. low latency is desirable.
open standards
specifications or protocols that are publicly available and not owned by any single company or organization. they promote interoperability and compatibility among different systems and software.
hotspot
a physical location, typically in public areas like cafes, airports, or hotels, where wireless internet access is available to all users with compatible devices
internet
a global network of interconnected computers and devices that use standardized communication protocols to exchange data and info
WWW (world wide web)
an information space on the internet that allows users to access websites and web pages linked by hyperlinks. it’s one of the many services available on the internet
static ip address
an IP address that remains constant and does not change over time. manually configured and assigned to a device
dynamic ip address
an ip address that is automatically assigned to a device by a DHCP server and may change periodically