Unit C: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Heterotroph
organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes; also called a consumer
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food
Metabolic Pathway
A series of chemical reactions that either builds a complex molecule or breaks down a complex molecule into simpler compounds.
Oxidation
an atom or molecule loses an electron (this is a LOSS of energy)
Reduction
an atom or molecule gains an electron (this is a GAIN of energy)
A compound that gains electrons also gains __________
energy
Reducing agent
Gives electrons to another compound to reduce it (gets oxidized)
Oxidizing agent
Takes electrons from another compound to oxidize it (gets reduced)
Gaining electrons stores ___________ ___________
chemical energy
Energy Carrier for Photosynthesis
NADPH (short term), ATP (long term)
Parts of ATP
A nitrogen base (adenosine) and three phosphates attached with high energy bonds
Metabolism
any chemical reaction that happens in your cells that either breaks down molecules or builds them.
Anabolic reactions
build larger molecules from smaller ones and require energy
Catabolic reactions
break down larger molecules into smaller ones and release energy
4 types of energy carries in this unit
NADH, NADPH, FADH2, ATP
Products of Photosynthesis and their jobs
Fruit: containing reproductive structure, purpose is to reproduce and help to colonize elsewhere
Plant bodies: cell walls and structural support
Poisons: used to repel or kill predators.
Part of the chloroplast
Stroma: liquid matrix ("goopy gunk with stuff in it" [basically the cytoplasm for the chloroplast]{where Calvin Cycle happens})
Thylakoids: membranes embedded with chlorophyll & accessory pigments
Granum: stack of thylakoids (pancakes)
![<p>Stroma: liquid matrix ("goopy gunk with stuff in it" [basically the cytoplasm for the chloroplast]{where Calvin Cycle happens})</p><p>Thylakoids: membranes embedded with chlorophyll & accessory pigments</p><p>Granum: stack of thylakoids (pancakes)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b2c60d43-c6da-46b5-a483-3d792c4316a5.jpg)
Light dependent reactions: Definition
use sunlight directly to reduce energy carriers (store energy)
Light independent reactions (dark): Definition
use the products of the light reactions to make glucose out of carbon dioxide
How is ATP made from the light dependent reactions?
Chemiosmosis: The process of using a hydrogen gradient to make ATP
Hydrogen moves into the thylakoid using energy made by the electron as it moves down the Electron Transport System. It is too squished inside, and it needs to get out. It moves with the help of the ATP synthase (like a channel protein). As it moves through the ATP synthase, ADP combines with a inorganic phosphate to make ATP.
Final Electron Acceptor of the Light Reactions
NADP+
Final Product of the Light Reactions
NADPH
What is the point of the light reactions?
To create energy carriers
Where do the light reactions take place?
Thylakoid Membrane
What happens to the electron that is lost by a compound that is oxidized?
Gets accepted by the oxidizing agent (there can't be and oxidation without a reduction)
Explain what is meant by 'photolysis of water' and state the destination of the water components.
Breaking water down with sunlight. The oxygen is a waste product and gets released in the air. The hydrogen is used in chemiosmosis and helps reduce NADP+ to NADPH. The electrons released from the water are used to replace the electrons in Photosystem 2 (PS2).
What are photopigments? What do they do? AND where are they found in a plant cell.
Photopigments absorb and reflect different wavelengths of light, determining the colour of the plant. They are found in the reaction centers in the membrane of the thylakoid, which is in the chloroplast.
How is the electron in PS1 replaced?
Replaced with electron from PS2
3 phases of calvin cycle
carbon fixation, reduction, regeneration
What happens to ADP and NADP+ after they have been oxidized in the calvin cycle.
Used again when light reactions take place to make ATP and NADPH.
Why is it beneficial to have more than one photopigment?
To have a wider variety of light that can be absorbed
How do we calculate Rf values (in chromotography)?
distance pigment travelled/distance solvent travelled
What is PGA? How is formed?
Three carbon molecule formed in the Calvin Cycle. Two of them are formed when breaking down 6 carbon molecule.
What is RuBP? What does it do in the Calvin Cycle?
5 carbon carbohydrate. Bonds with CO2, then broken down into two PGA's in Calvin Cycle
What is PGAL? What is it's other name? What is its purpose?
High energy 3 carbon molecule. PGA that is activated by ATP, the reduced by NADPH. Also called G3P. Used to make glucose and other products for the plant.
Why do the dark reactions need the light reactions?
To use energy from ATP and oxidize NADPH
Why does RuBP need to be regenerated?
So that the Calvin cycle can continue happening
How many times does the Calvin cycle need to happen to generate glucose?
6 times (all at same time)
Where does the Calvin Cycle take place?
stroma of the chloroplast
What is ATP used for the regeneration process of the Calvin cycle?
Break and reform bonds to make more 5-carbon RuBP molecules out of the G3P that is left
True or False: During chemiosmosis, ATP synthase uses active transport of H+ ions across the membrane to make ATP.
False: Uses passive transport. Uses active transport to move H+ ions in the thylakoid space, but is passive when it moves through the ATP synthase, creating ATP, since it's moving from high conc. to a low conc.
Why do we need to breath?
Cellular Respiration needs oxygen.
Why do we need cellular respiration?
We need energy. Without energy, we die.
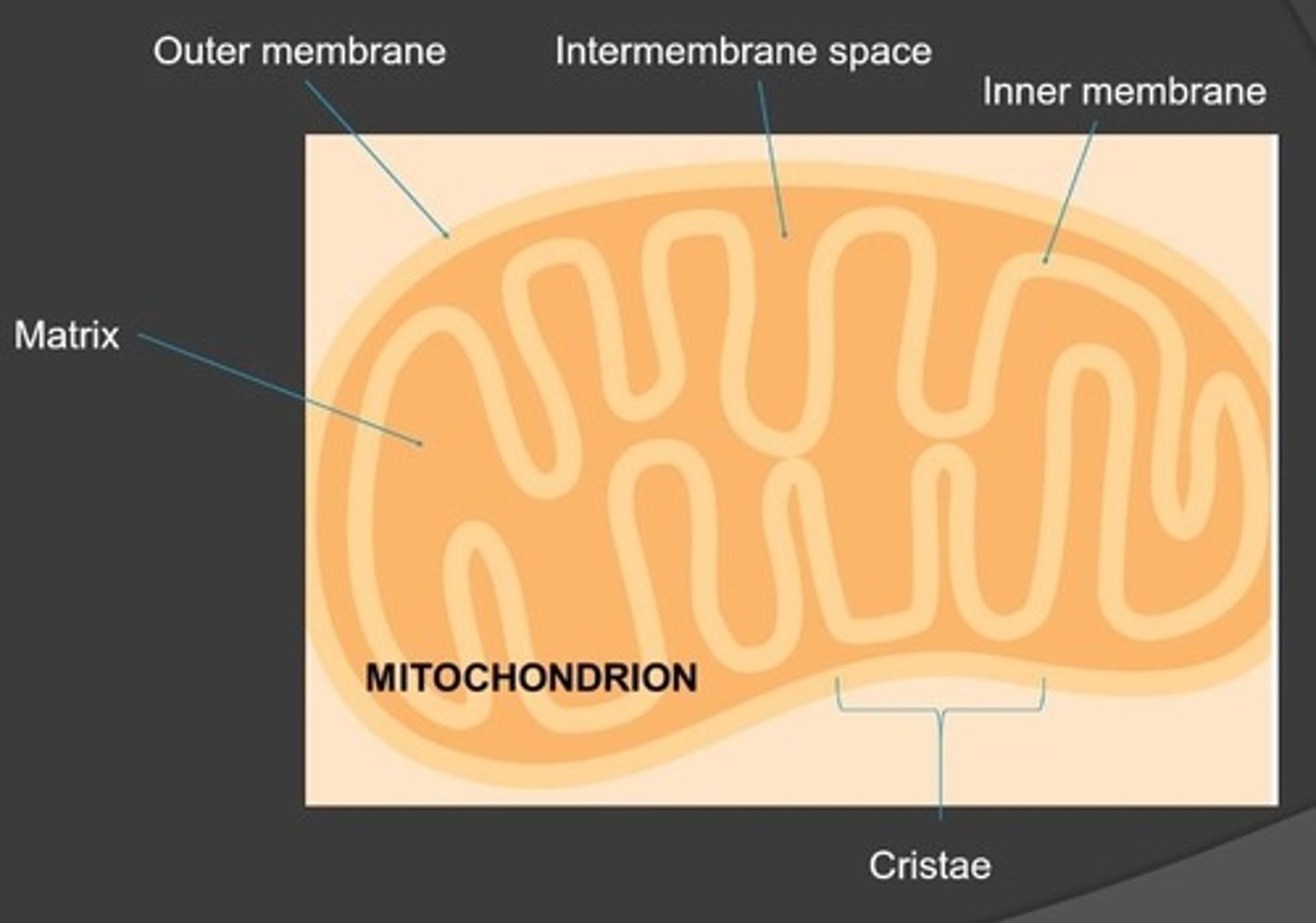
Parts of the Mitochondria
Matrix: fluid-filled space
Cristae: folds of inner membrane (large surface area)
Intermembrane space: between inner and outer membrane
Aerobic respiration
O2 present
Anaerobic respiration
O2 absent
2 Types of Anaerobic respiration
Lactate fermentation, Ethanol fermentation
4 Parts of Aerobic Cellular Respiration (and where each piece happens)
1. Glycolysis (happens in the cytoplasm)
2. Krebs Cycle Prep (happens in the Matrix)
3. Krebs Cycle (happens in the Matrix)
4. Electron Transport System (Happens in the inner membrane)
2 Parts of Anaerobic Cellular Respiration (and where each piece happens)
1. Glycolysis (happens in the cytoplasm)
2. Fermentation (either Lactate or Ethanol) [happens in the cytoplasm]
True or False: Glycolysis requires oxygen
False: Glycolysis is anaerobic
What is happening during glycolysis? (What is being done)
Glucose is breaking down
What are the products of Glycolysis?
2 pyruvate, 4 ATP (Net Gain: 2), 2 NADH
What compound derived from glucose enters the krebs cycle?
Acetyl-CoA
Does the Krebs Cycle require O2?
Needs it, but does not use it
What is produced by the Krebs Cycle?
- 6 NADH
- 2 ATP
- 2 FADH2
- 4 Carbon Dioxide (waste product)
(these are the amounts for when it happens twice)
At the end of the Glycolysis, Krebs Prep & the Krebs cycle, how many NADH, FADH2 and ATP have been produced in total?
- ATP: 4 ATP (Remember, the Net gain of ATP in glycolysis is 2 + the two created in the krebs cycle)
- NADH: 10 NADH
- FADH2: 2 FADH2
How many times does the krebs cycle and krebs prep happen?
Twice (for both pyruvate)
Where in the mitochondria does the ETC take place?
The Inner Membrane
What is the source of the high energy electrons for the ETC in the mitochondria?
NADH & FADH2
Describe the function of O2 in cellular respiration
Final electron acceptor. Combines with H+ ions t make water
Why must we complete fermentation in the absence of Oxygen?
To continue regenerate NAD+ and energy for the body
What is the Net Gain for glycolysis?
2 ATP
Kreb Cycle Prep. process
Pyruvate Combines with CoA and is oxidized by NAD+ (creating NADH) to make Acetyl-CoA + Carbon Dioxide
Lactate Fermentation: Organisms that perform it
Muscle Cells & Bacteria
Lactate Fermentation: Final electron acceptor
Lactate
Lactate Fermentation: Products
2 ATP (happens twice, once for each pyruvate) & lactate, NAD+
Lactate Fermentation: Process
Pyruvate get's reduced by NADH to create lactate
Ethanol Fermentation: Organisms that perform it
Some bacteria & yeast
Ethanol Fermentation: Final electron acceptor
Ethanol
Ethanol Fermentation: Products
CO2, ethanol, NAD+ & 2 ATP (happens twice, once for each pyruvate)
Ethanol Fermentation: Process
Pyruvate creates CO2 to be released to make a C2 compound which gets reduced by NADH to create ethanol
Electron Transport Chain (Aerobic Cellular respiration) process
- NADH and FADH2 donate their energetic electrons to the carriers of the transport chain.
- As the electrons pass through the transport chain, some of their energy is used to pump hydrogen ions from the matrix into the intermembrane space.
- This creates a hydrogen ion gradient that is used to drive ATP synthesis.
- At the end of the electron transport chain, the energy-depleted electrons combine with oxygen and hydrogen ions in the matrix to form water.