Hematology Exam 2 (Chapter 10)
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
The following data were reported by an instrument: RBC = 5.00 × 1012/L, hemoglobin = 8.5 g/dL and hematocrit = 32%. Calculate the MCHC.
A. 64.0
B. 26.6
C. 17.0
D. 29.5
B. 26.6
Remnants of DNA inside an RBC produce which type of inclusion?
A. Basophilic stippling
B. Pappenheimer bodies
C. Howell-Jolly bodies
D. Cabot rings
C. Howell-Jolly bodies
A patient sample has an RBC count of 4.30 × 1012/L and a reticulocyte count of 4%. What is the absolute retic count?
A. 90 × 109/L
B. 172 × 109/L
C. 350 × 109/L
D. 142 × 109/L
B. 172 × 109/L
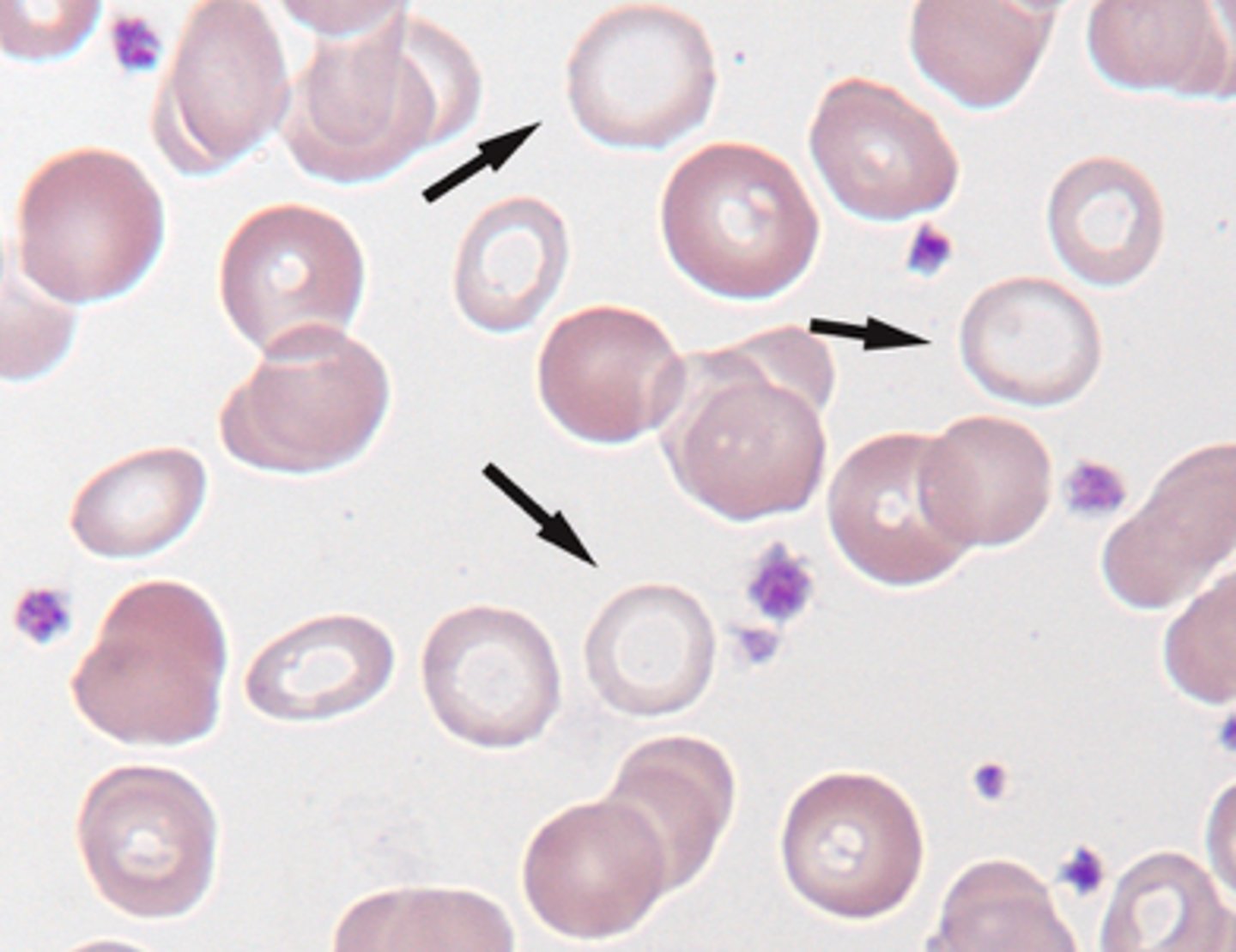
What should be reported about the RBCs indicated by the arrows in the following image?
A. Macrocytes
B. Hypochromasia
C. Ovalocytes
D. Drepanocytes
B. Hypochromasia
Which of the following laboratory values would best correlate with moderate polychromasia on a peripheral blood smear?
A. A low PLT count
B. A retic count of 8%
C. Schistocytes on the PB smear
D. A low RBC count
B. A retic count of 8%
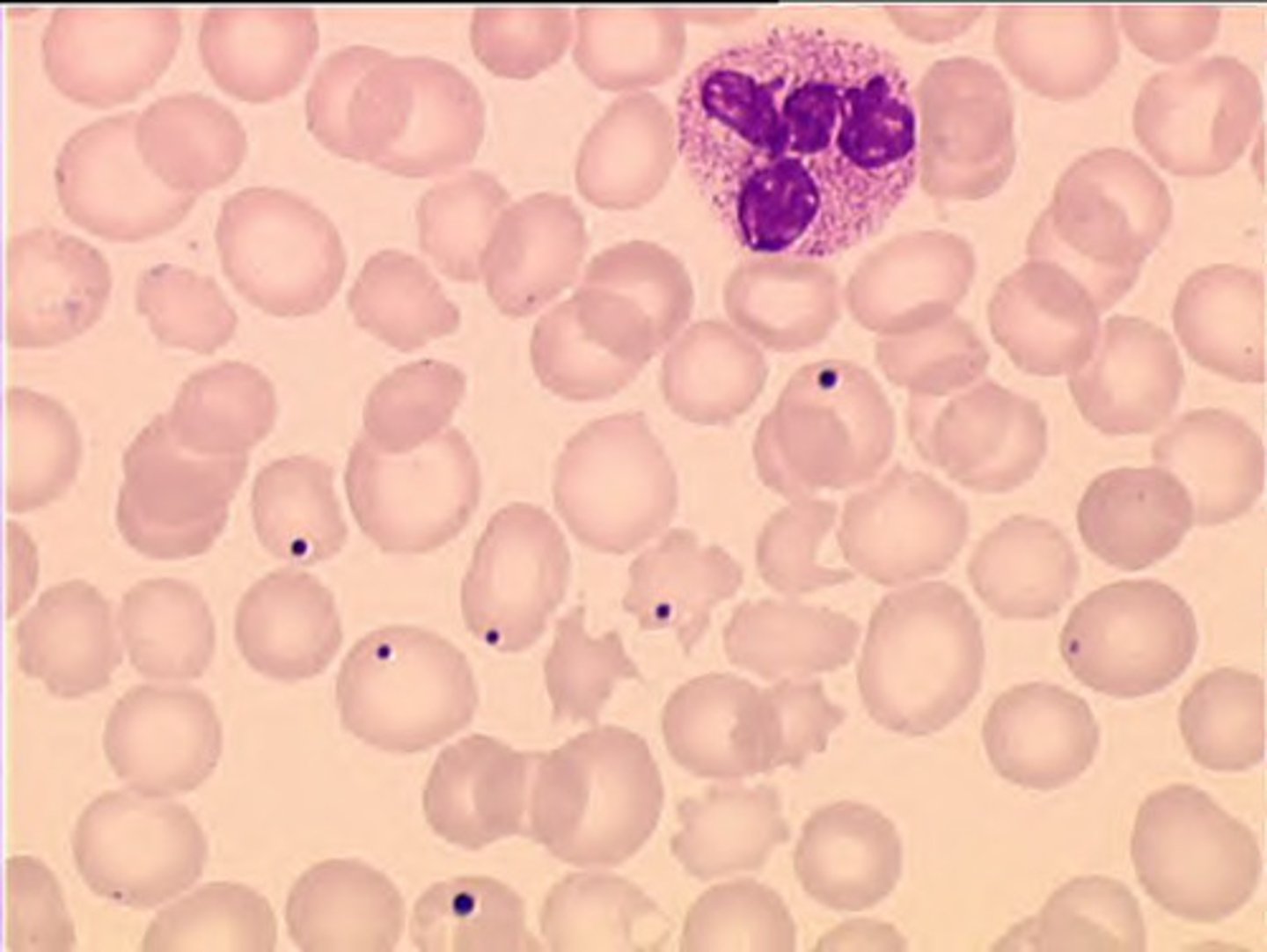
Identify the RBC inclusion in the following image.
A. Siderotic granule
B. Heinz body
C. Howell Jolly body
D. Basophilic stippling
C. Howell Jolly body
A peripheral blood smear has an even distribution of both normocytic normochromic cells and microcytic hypochromic cells. What is this phenomenon called?
A. Extramedullary hematopoiesis
B. Nuclear-cytoplasmic asynchrony
C. Dimorphic cell population
D. Monoclonal cell population
C. Dimorphic cell population
What is one of the disease states associated with the presence of target cells?
A. Thalassemia
B. Hemolytic anemia
C. Uremia
D. Sickle cell anemia
A. Thalassemia
Acanthocytes or spur cells have membranes with irregular distribution of spikes. What other significant feature does this cell possess?
A. Increased size
B. Presence of Pappenheimer bodies
C. Lack of central pallor
D. Decreased life span
C. Lack of central pallor
Platelet estimates are usually performed on a blood smear using which microscopic magnification?
A. 1000x
B. 100x
C. 400x
D. 10x
A. 1000x
What staining method can be used to differentiate Pappenheimer bodies from reticulocytes?
A. PAS
B. Phase microscopy on wet prep
C. New methylene blue
D. Perl's Prussian blue
D. Perl's Prussian blue
Codocytes are associated with all of the following conditions except:
A. Iron-deficiency anemia
B. Thalassemias
C. Hemolytic anemia
D. Hemoglobinopathies
C. Hemolytic anemia
Calculate the MCV from the results of a patient′s CBC:
RBC = 3.50 × 10 12/L
Hemoglobin = 12.0 g/dL
Hematocrit = 40%
A. 30
B. 114
C. 100
D. 31
B. 114
Which RBC parameter describes the variation in the volume of the RBCs in a blood sample?
A. MCHC
B. Reticulocyte count
C. MCV
D. RDW
D. RDW
Howell-Jolly bodies are red cell inclusions associated with what disease state?
A. G6PD deficiency
B. Lead poisoning
C. Normal reticulocytes
D. Megaloblastic anemia
D. Megaloblastic anemia
Which of the following are the correct units for reporting the absolute RBC count using the SI system?
A. x 10^9/L
B. x 10^12/L
C. x 10^3/mcL
D. x 10^9.fL
B. x 10^12/L
Which erythrocyte inclusions are composed of DNA and stain blue on Romanowsky stains?
A. siderotic granules
B. Heinz bodies
C. Howell-Jolly bodies
D. basophilic stippling
C. Howell-Jolly bodies
Which of the following RBC indices indicates how filled the average RBC is with hemoglobin in terms of weight per unit volume?
A. MCV
B. MCH
C. MCHC
D. RDW
B. MCH
A blood smear reveals uneven distribution of red blood cells, and the red blood cells appear to be stacked together like a stack of coins. How would you describe this distribution?
A. agglutination
B. rouleaux
C. anisocytosis
D. poikilocytosis
B. rouleaux
How would you classify the red cell population with the following indices: MCV 110 fL, MCH 38 pg, MCHC 33 g/dL?
A. normocytic, normochromic
B. macrocytic, normochromic
C. microcytic, normochromic
D. microcytic, hypochromic
B. macrocytic, normochromic
If the cell population in the question above were homogeneous (absence of anisocytosis), the RDW might show:
A. false increase
B. false decrease
C. normal reference interval
D. true increase
C. normal reference interval
A peripheral blood smear that has an erythrocyte mixture of macrocytes, microcytes, and normocytes present can best be described as:
A. poikilocytosis
B. polychromatophilia
C. megaloblasts
D. anisocytosis
D. anisocytosis
Which of the following erythrocyte inclusions cannot be stained and visualized with Romanowsky stains?
A. Pappenheimer bodies
B. Howell-Jolly bodies
C. Heinz bodies
D. basophilic stippling
C. Heinz bodies
If there is an increase in macrocytic, polychromatophilic erythrocytes on the Romanowsky stained blood smear, which laboratory test result would correlate with this?
A. platelet count
B. reticulocyte count
C. leukocyte count
D. MCHC
B. reticulocyte count
A routine CBC is to be performed on a blood sample that arrives in the laboratory from an outside clinic 4 hours after it is drawn. The sample is frozen. The sample is:
A. acceptable
B. acceptable but must be warmed before performing the CBC
C. unacceptable due to improper sample temperature
D. unacceptable due to improper time restraints
C. unacceptable due to improper sample temperature
A 53-year old patient had hemoglobin of 70 g/L. The reticulocyte count is 15%. Which of the following would you expect on the blood smear?
A. poikilocytes
B. polychromatophilia
C. agglutination
D. Howell-Jolly bodies
B. polychromatophilia
Numerous schistocytes in the patient in the question above were identified on the blood smear. How could this finding affect the RDW?
A. increase it
B. decrease it
C. have no effect
D. invalidate it
A. increase it
Some of the RBCs on a petient's smear contain numerous small blue inclusions. What should be done next to determine what to report about the inclusions?
A. perform an iron stain for identification of siderocytes
B. perform a screen for sickle cell anemia
C. use new methylene blue stain to confirm an increase in reticulocytes
D. check the CBC data for an indication of the presence of Howell-Jolly bodies
A. perform an iron stain for identification of siderocytes
The RDW is found to be 19.5% on a patient. Which of the following should you find increased on the smear?
A. macrocytosis
B. microcytosis
C. anisocytosis
D. poikilocytosis
C. anisocytosis
Rouleaux is found on a smear of a patient with multiple myeloma. How will this affect the CBC results?
A. RBC count will be decreased.
B. Hematocrit will be increased.
C. MCHC will be increased.
D. There will be no effect.
C. MCHC will be increased.
A CBC is ordered on a 3-day-old infant with a fever of 100F. The laboratory professional notes nucleated RBCs on the peripheral blood smear but is not alarmed by this finding. Why not?
A. Nucleated RBCs are a common occurrence during infection
B. The fever promoted an increase in RBC production
C. Nucleated RBCs are commonly observed in the first 7 days of life.
D. The nucleated RBCs are likely to be artifacts.
C. Nucleated RBCs are commonly observed in the first 7 days of life.
A CBC is performed for a patient who has been treated for anemia. The laboratory professional notes an increase in polychromatophilic macrocytes. Which of the following is speculated about the patient from the peripheral blood smear?
A. responding to an infection
B. needs further treatment for the anemia
C. is responding to the treatment for the anemia
D. has a decreased RBC count
C. is responding to the treatment for the anemia
The presence of dacryocytes on a peripheral blood smear is most likely suggestive of which of the following?
A. artifact
B. young RBCs
C. RBC destruction
D. splenic removal of RBC inclusions
D. splenic removal of RBC inclusions
The MCHC result is extremely elevated in a patient's CBC results. Which of the following is a likely cause of this result?
A. microcytic RBCs
B. agglutination of the RBCs
C. increased hemoglobin and RBC count
D. high RDW
B. agglutination of the RBCs
Which of the following poikilocytes are frequently artifacts, not a pathologic finding?
A. drepanocytes
B. echinocytes
C. spherocytes
D. schistocytes
B. echinocytes