Types of Reactions in Organic Chemistry Model Questions & Answers (Mechanism description not included).
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1. State and explain the effect of adding a little tetraethyllead to a mixture of methane and chlorine exposed to weak sunlight
The reaction rate increases for the substitution reaction as tetraethyllead is a catalyst.
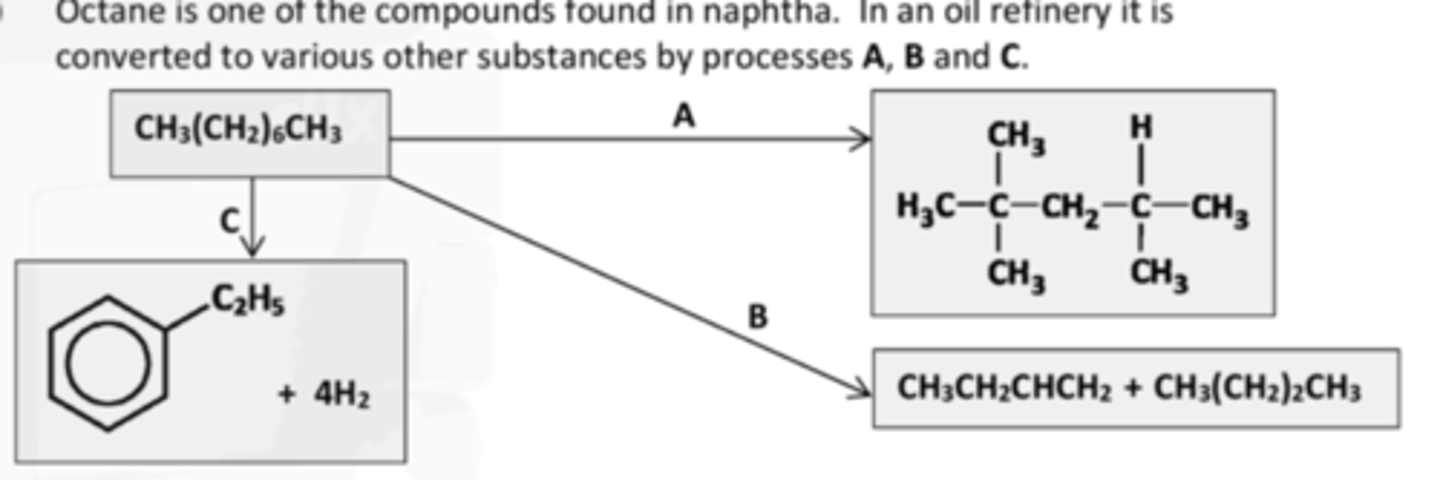
give the IUPAC names for the four hydrocarbon products shown above
2,2,4-trimethylpentane
butane
but-1-ene
ethylbenzene
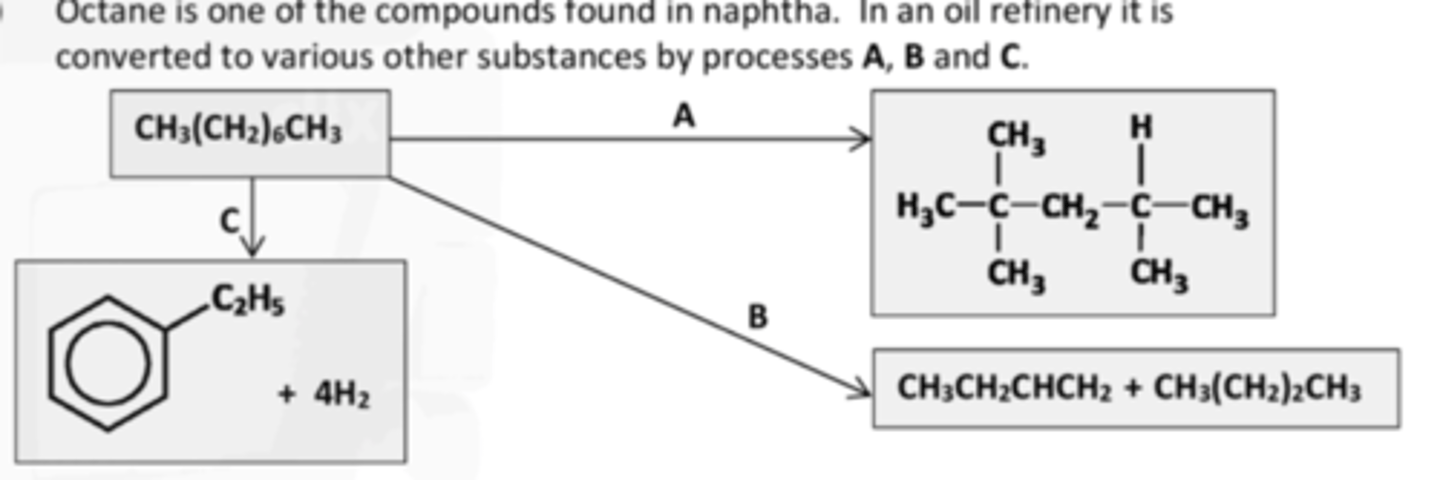
IDENTIFY PROCESS B
Catalytic cracking,
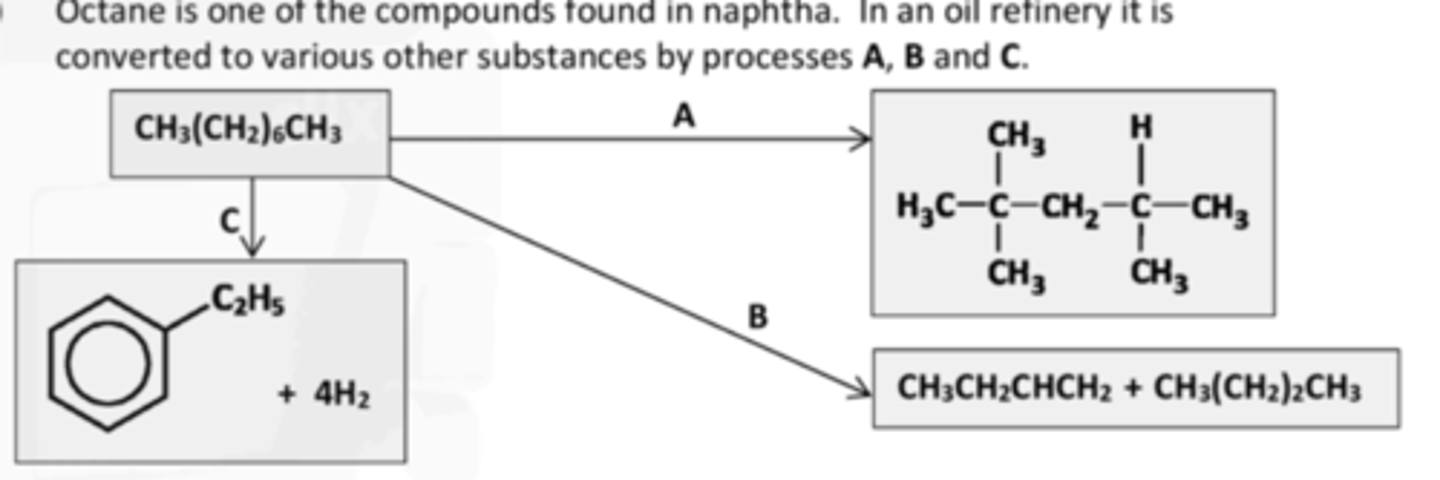
IDENTIFY PROCESS C
Dehydrocylisation
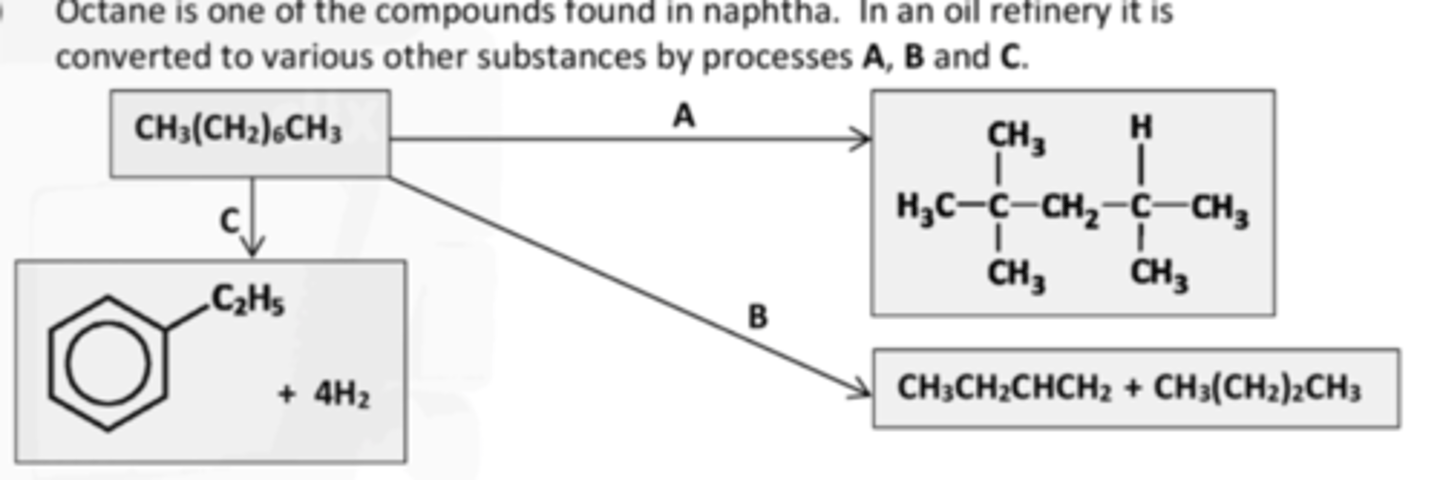
why are ABC carried out
To increase the octane number.
2. Petrol contains 5-10 carbon atoms per molecule whereas diesel contains 14-19 carbon atoms. How would you expect boiling points to between the two to compare?
Diesel would have the higher boiling point as it contains more carbon atoms.
Give the IUPAC names for A and B
A = Propanal
B = Propanone
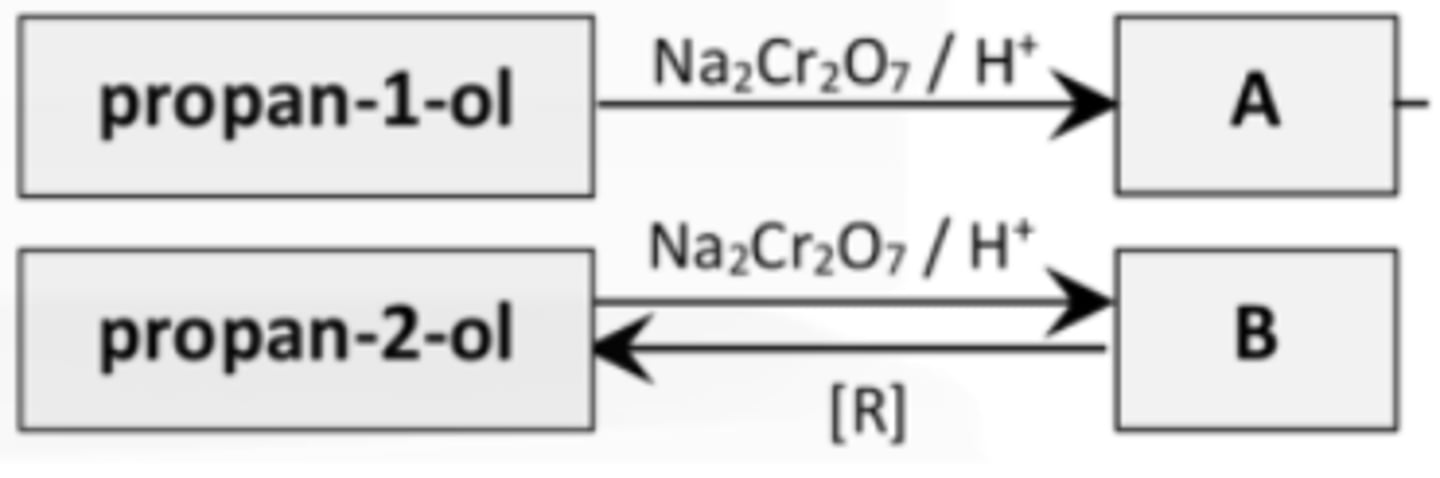
4. Identify reactant and catalyst required to reduce propanone to propanol
Hydrogen with a Nickel catalyst
5. How could one distinguish between propanone and propanal?
Heat with Tollens reagent. Silver mirror forms for aldehydes and nothing for ketones.
6. What type of reaction is involved in the conversion of ethane to
chloroethane?
Substitution
Ester C is formed when A (ethanol) is heated with methanol acid and a few drops of sulfuric acid acting as a catalyst. Name C and draw its structure. Circle the carbonyl group.
Ethyl methanoate
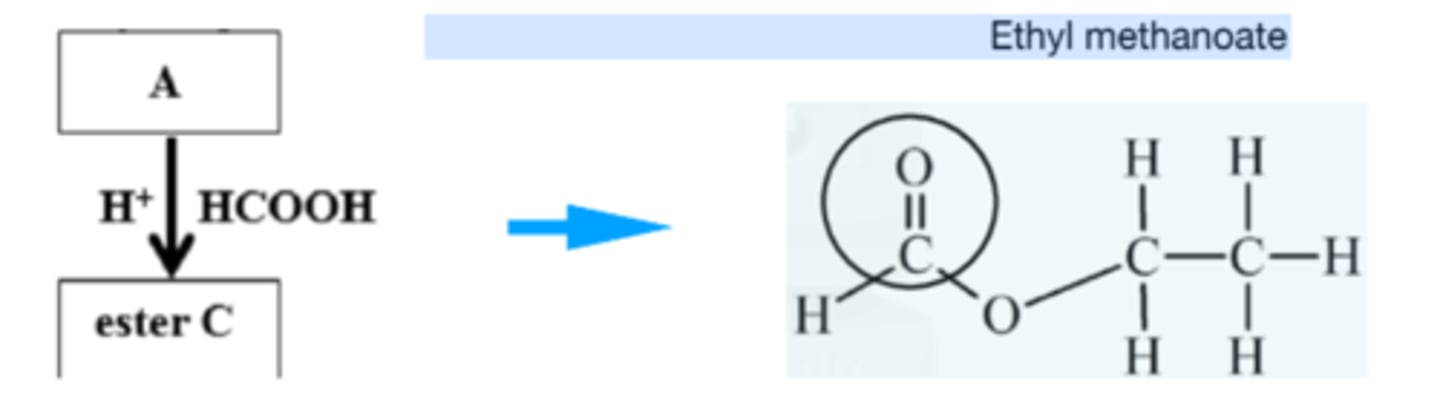
8. What name is given to the type of reaction that occurs between sodium hydroxide and ethyl methanoate?
Base hydrolysis
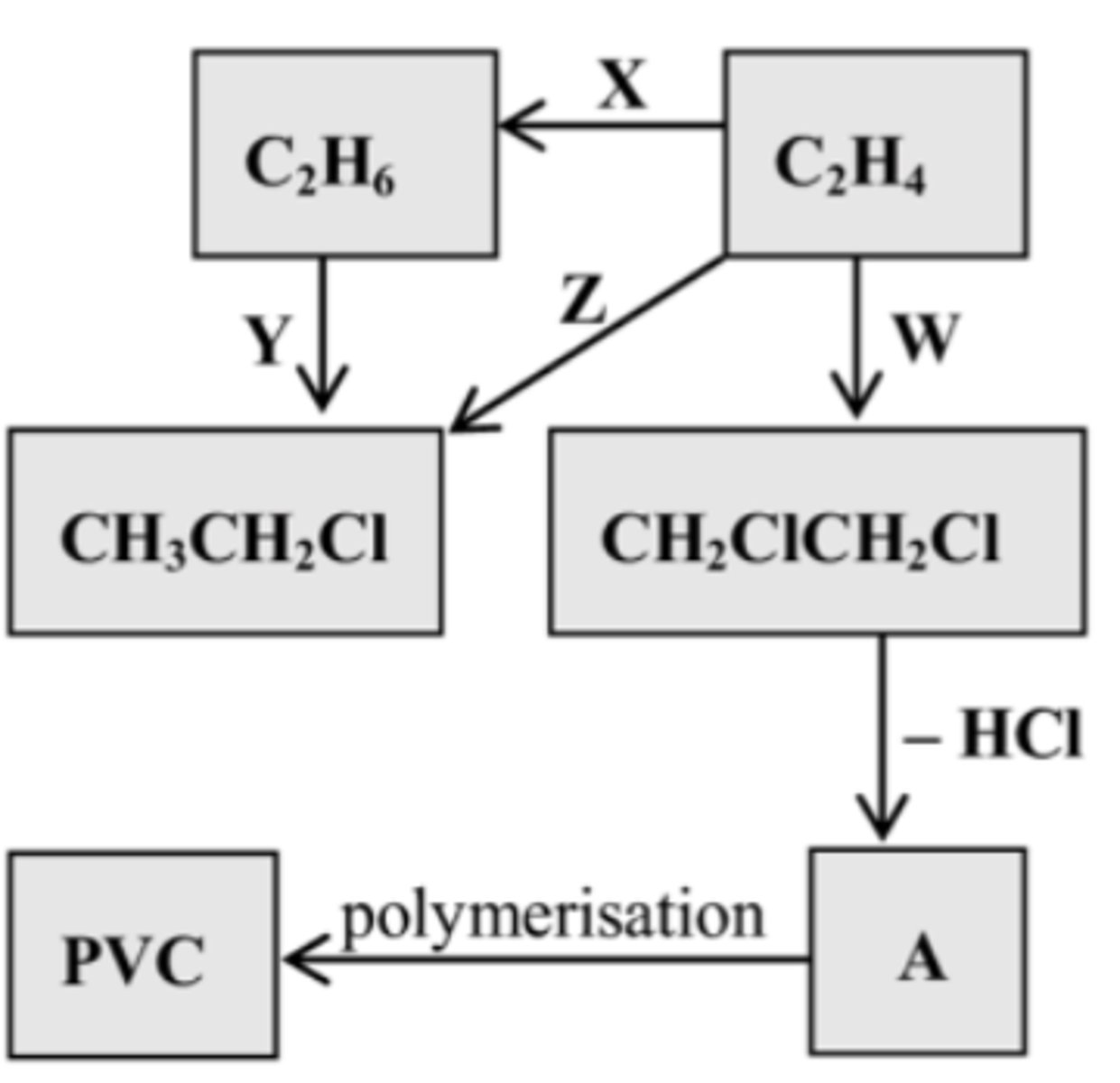
Identify the regents/catalysts for X,
State the type of reaction
H2
Addition
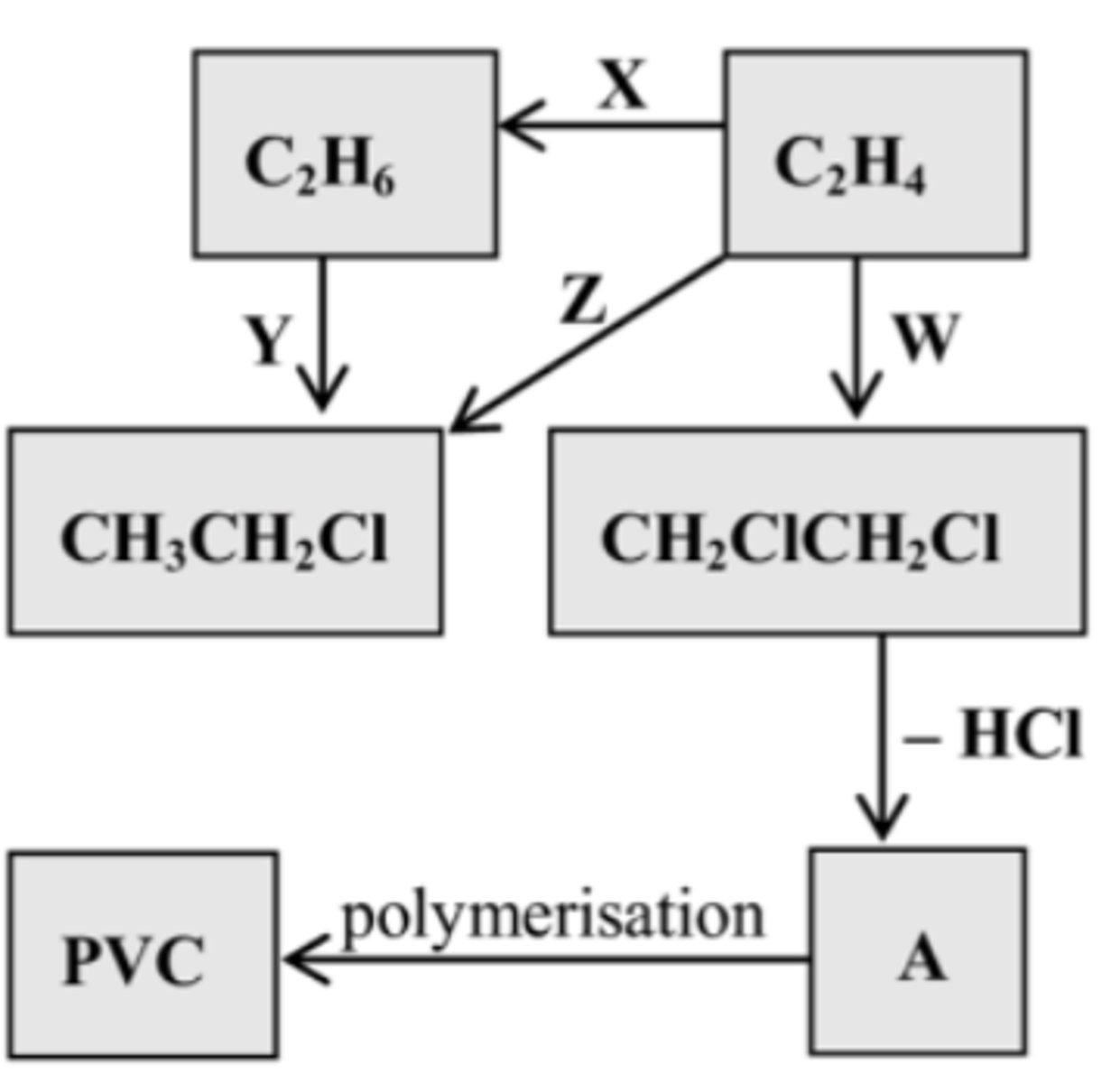
Identify the regents/catalysts for Y,
State the type of reaction
Cl2
Substitution
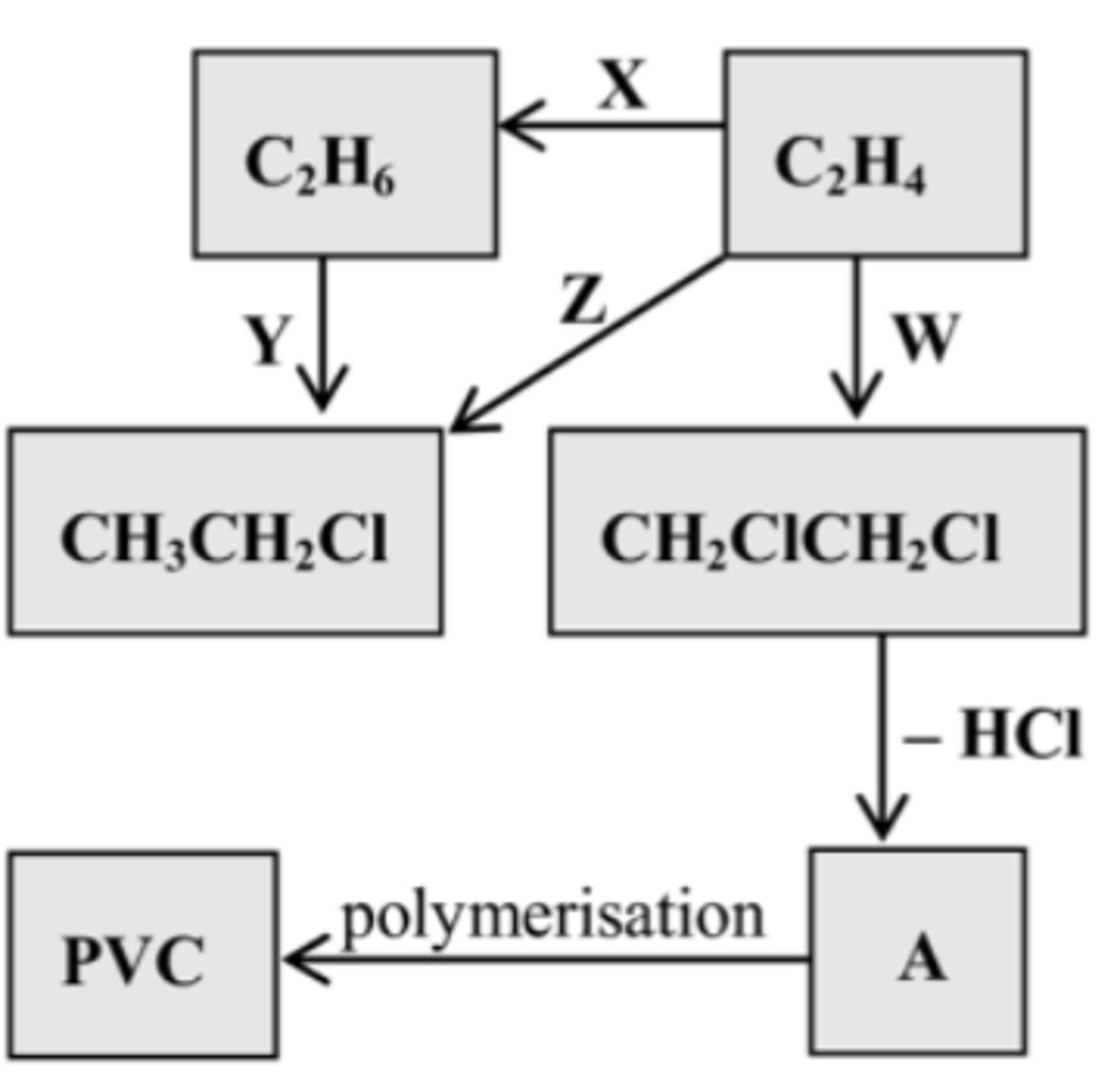
Identify the regents/catalysts for W,
State the type of reaction
HCl
Addition
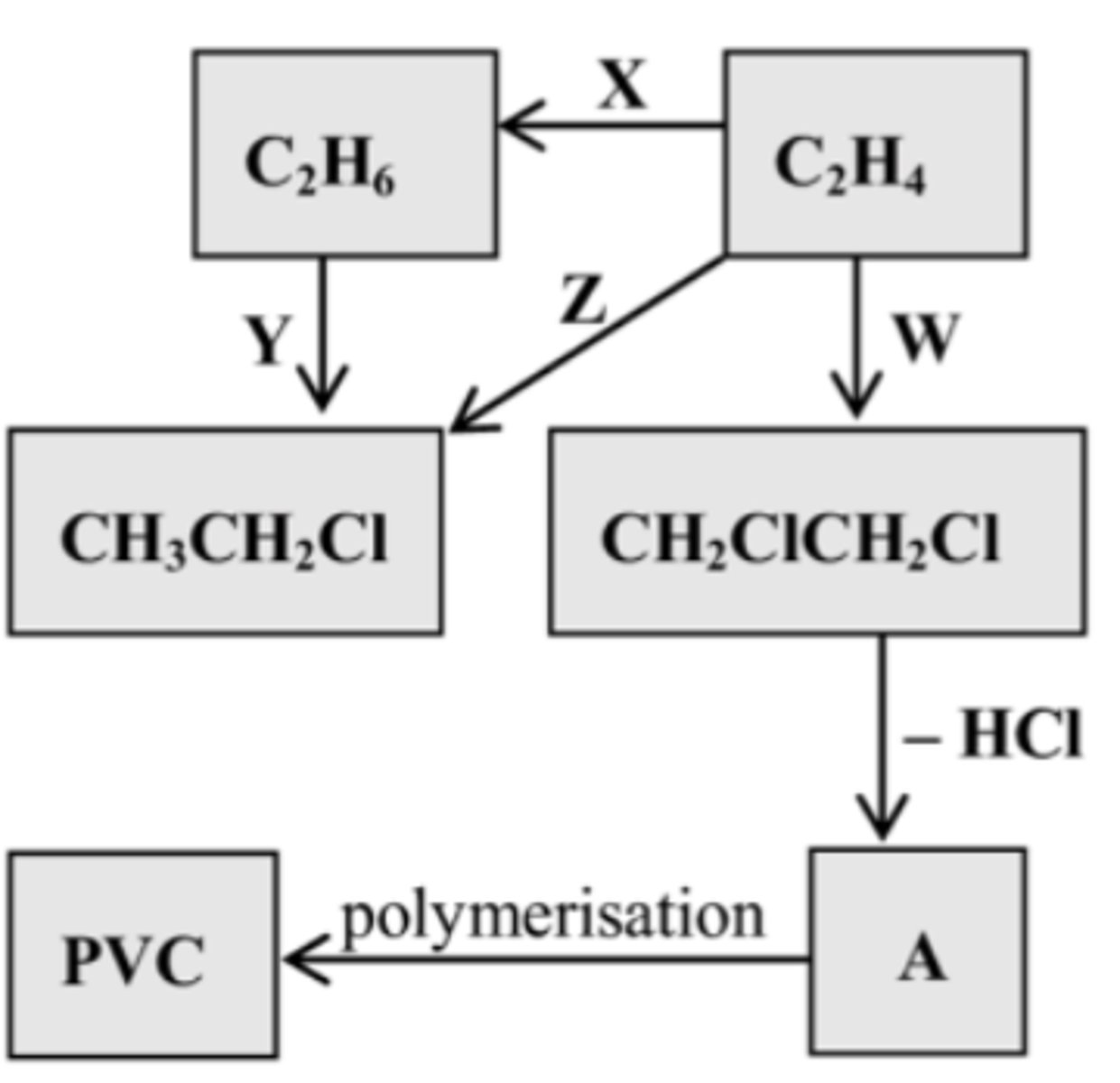
Identify the regents/catalysts for Z
State the type of reaction
Cl2
Addition
State a piece of evidence for the "bromine and ethene" addition
mechanism
2-bromoethanol is formed if bromine water is present.
13. State three pieces of evidence for the "chlorine and methane + UV light" substitution mechanism
1. ? is produced in the reaction due to ?
Ethane
two methane free radicals reacting.
13. State three pieces of evidence for the "chlorine and methane + UV light" substitution mechanism
2. The ? of ? speeds up the reaction
addition
tetraethyl lead
13. State three pieces of evidence for the "chlorine and methane + UV light" substitution mechanism
3. Only works in the presence of UV due to ?
free radicals being involved.
14. State two substances that could be formed if ethanol is oxidised
Ethanal and then ethanoic acid. Ethanoic acid would only be formed if a very strong oxidising agent was used.
16. Give the names of the three products that form if bromine water is used instead of sodium chloride in the addition mechanism evidence
1,2-dibromoethane
2-bromoethanol
1-bromo-2-chloroethane
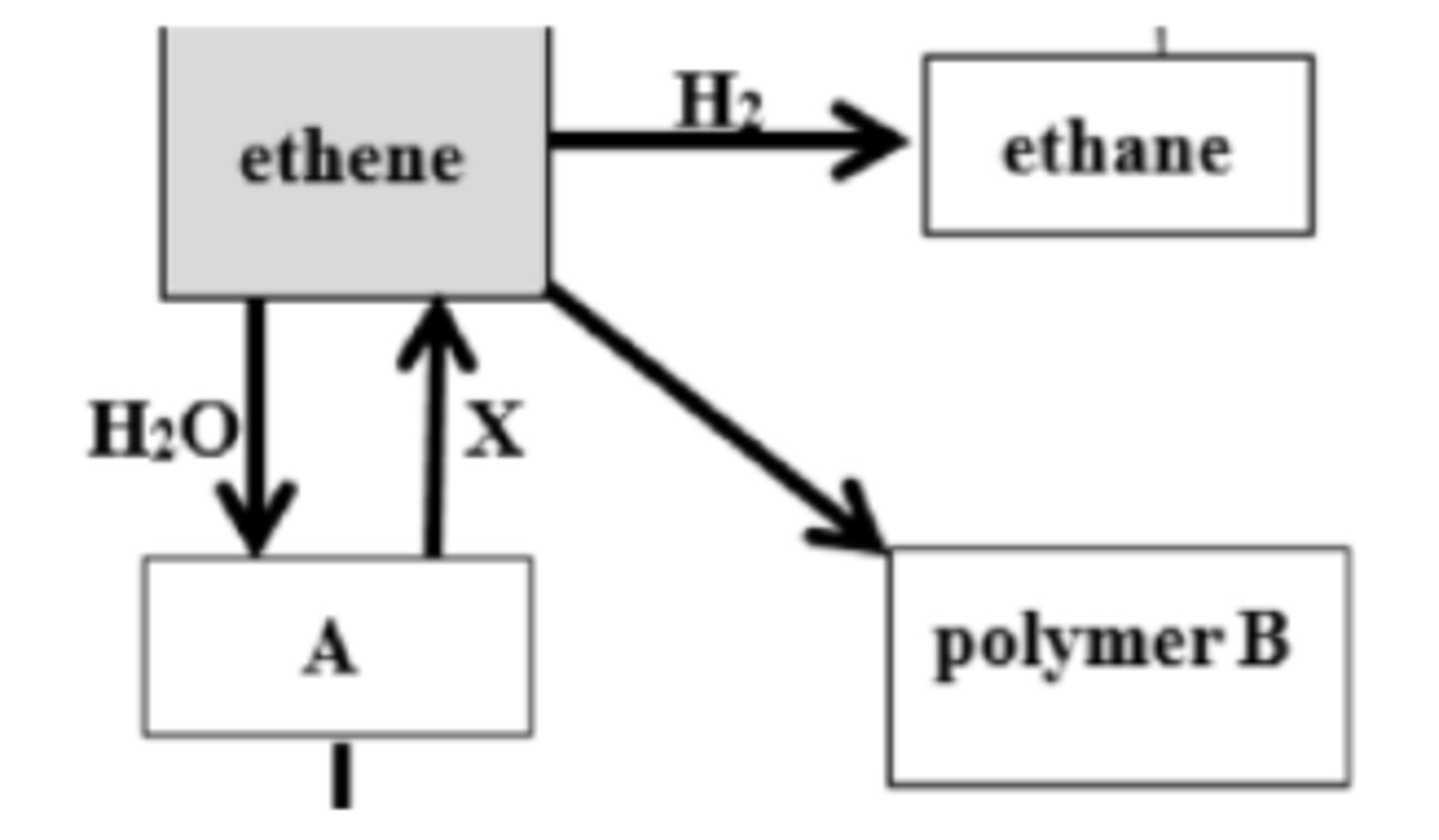
17. Name A and polymer B
A = Ethanol
B = Polythene