Topic 4 - Natural Selection & Genetic Modification
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Define: Evolution
Gradual change in a species over time.

Use words from the box to complete the sentences.
Natural, Mutate.
Which scientist believed evolution occurs by natural selection?
Charles Darwin.

Pick A, B, C or D.
A - Charles Darwin.
D - New species evolve over many generations.
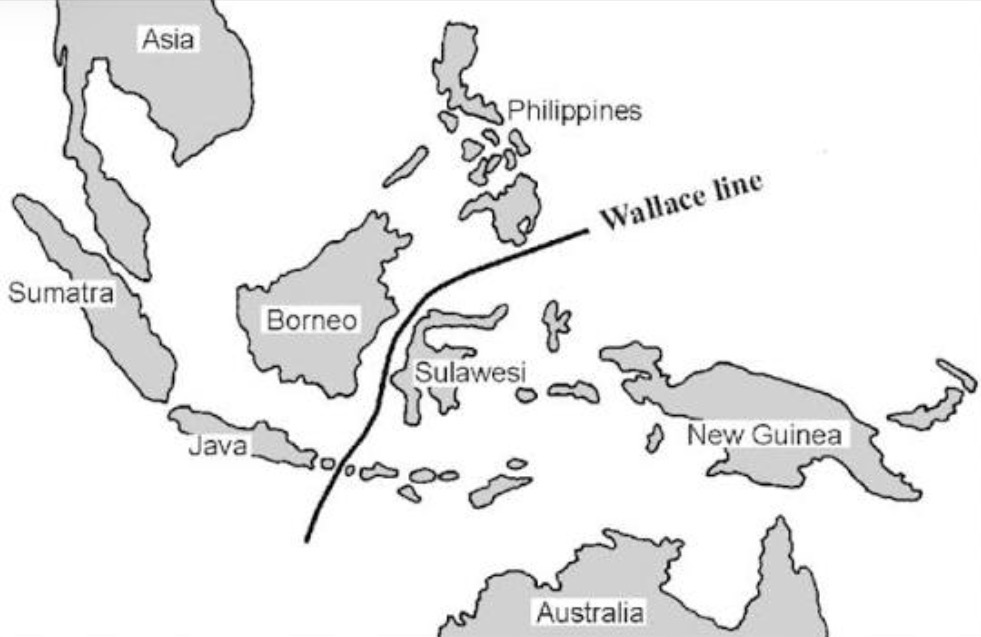
Suggest two possible reasons why animals to the west of the Wallace line are different from animals to the east of the Wallace line.
Different environments/climate/habitats/ecosystems.
Different mutations.
Different selection pressure.
Different prey and predators.
Different diseases present.
Give one reason why the work of Alfred Wallace encouraged Charles Darwin to publish his theory of evolution.
More evidence.
He showed that animals have adapted to their environments and evolved from common ancestors.
Describe the role of Wallace in the development of the theory of evolution by natural selection.
Proposed a theory of natural selection that was similar to Darwin’s but with more evidence to support the theory.
What is natural selection?
Organisms within a species with certain characteristics are more likely to survive than others as they are better suited to their environment. This means that they have the beneficial allele.
Describe the theory of evolution by natural selection.
Organisms in a species have genetic variation.
There is a selection pressure such as change in environment or diseases.
Random mutation gives an organism a selective advantage.
These organisms adapt to survive and then reproduce to pass on their beneficial alleles/characteristics to the offspring.
Repeated over many generations so frequency of advantageous allele increases.
Which mnemonic do we use to answer a question about natural selection?
G enetic variation.
E nviromental change.
N atural selection.
I nheritance.
E volution.

Describe how the thinner beak of species A is as a result of evolution.
Variation in beak shape/mutations occurred that changed the shape of the beak.
Thinner beaks are more suited to catching insects for food.
Birds with thinner beaked are more likely to survive because they can obtain more food than those with thicker beaks.
Birds with thinner beaks reproduce and pass on alleles for thinner beaks.
Occurs over many generations until all birds have thin beaks.

Explain how natural selection could have caused an increase in beak length because of the use of bird feeders.
Population of great tits show variation where some birds have longer beaks.
Bird feeders exert a selection pressure.
Birds with longer beaks are more likely to survive because they can obtain more food than those with shorter beaks.
Birds with longer beaks reproduce and pass on alleles for long beaks to their offspring.
Occurs over many generations so the beak length of the bird population increases.
Darwin believed that male birds have feathers that are brightly coloured to make them more attractive to female birds. Wallace thought that female birds have feathers that are less brightly coloured so they are more likely to survive.
Explain why having feathers that are less brightly coloured increases the survival rate of females.
Fewer bright feathers are less noticeable and makes it easier for birds to camouflage.
Therefore they are less likely to be eaten by predators and may find it easier to get food from their prey.
Darwin believed that male birds have feathers that are brightly coloured to make them more attractive to female birds. Wallace thought that female birds have feathers that are less brightly coloured so they are more likely to survive.
Suggest why it is important for type survival of the species that survival rate is higher in female birds that males.
Female birds lay eggs to produce offspring whereas males do not reproduce. Therefore, even if lots of males die, one male can still reproduce with many female birds.
Why did many people doubt Charles Darwin’s theories?
It challenged the belief that God created all living things.
Little evidence - not many fossils + no knowledge of antibiotic resistance.
Little understanding of genes, inheritance etc.
Define: Classification
Organising living things into groups according to similar characteristics.
What is taxonomy?
Classification of organisms into taxa; kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species.
Name the 7 groups to classify animals into from largest to smallest.
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
Name the 7 groups to classify animals into from smallest to largest.
Species, Genus, Family, Order, Class, Phylum, Kingdom.
What happens not the number of organisms in each taxonomy as you move down the hierarchy?
Decreases.
Define: Species
A group of similar organisms that can breed to produce fertile offspring.
Name the 5 kingdoms organisms can be organised into
Animal, Plant, Fungi, Bacteria/Prokaryotes, Protist.
Name the 3 domains organisms can be organised into
Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya.
Which domain contains ancient bacteria?
Archaea.
Which domain contains true bacteria?
Bacteria.
Which domain contains animals, plants, fungi and protists?
Eukarya.
Which domain do eukaryotic organisms belong to?
Eukarya.
Which domains do prokaryotic organisms belong to?
Archaea and bacteria.

Birds are classified in the domain Eukarya. Why are the cells from birds described as eukaryotic?
A - Membrane bound organelles.
What is the name of the domain that plants belong to?
Eukarya.
Is the domain or kingdom system more accurate? Why?
Domains because it uses genetic analysis to show the similarities and relationships between animals.
Give one reason why the three domain classification system was proposed.
It’s uses improved genetic analysis.
Based on genetics and DNA.
Describe organisms in the animal kingdom.
Multicellular, Nuclei, No cell wall, Eat other organisms.
Describe organisms in the plant kingdom.
Multicellular, Nuclei, Cellulose cell wall, Makes food via photosynthesis.
Describe organisms in the fungi kingdom.
Mainly multicellular but some such as yeast are unicellular, Nuclei, Chitin cell wall, Digest dead materials.
Describe organisms in the bacteria kingdom.
Unicellular, No nucleus, Cell wall.
Describe organisms in the protist kingdom.
Mainly unicellular, some multicellular, Some have cell walls.
Who is the oldest human fossil and when were they discovered?
Ardi - 4.4 million years ago.
How was Ardi similar to humans?
Walked upright.
How was Ardi similar to apes?
Long arms and legs.
More body hair.
Shorter.
Smaller head.
Big toes.
Describe the fossil of Ardi.
Walks up right.
Long arms and legs.
More body hair.
Shorter.
Smaller head.
Big toes.
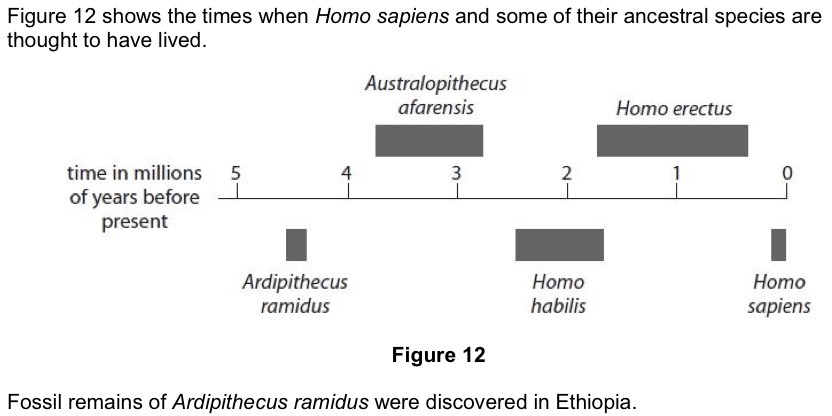
Calculate the number of years Ardipithecus ramidus is thought to have inhabited the Earth.
200,000 years because 4.6 - 4.4 million is 0.2 million.
Describe the evidence that scientists may have used to show that Ardipithecus ramidus inhabitated the Earth earlier than Homo habilis.
Looked at differences in the structural features of the fossil.
Ardipithecus ramidus would be deeper in the rock than Homo habilis.
When was Lucy discovered?
3.2 million years ago.
Describe the fossil of Lucy.
Walks more upright than Ardi.
More human like feet - smaller, arched.
Small head still but slightly bigger than Ardi.
Order the human fossils from oldest to newest.
Ardi.
Lucy.
Homo habilis.
Homo erectus.
Homo sapiens.
Suggest an explanation for the extinction of Homo habilis.
Likely to be outcompeted by the Homo erectus.
Struggled to survive due to the presence of a new selection pressure like environmental change or disease.
What are the common evolution trends in humans?
Decease in body hair.
Decrease in limb size/proportion.
Increase in height.
Increase in skull volume.
Describe two structural changes that have cured during human evolution.
Skull volume has increased.
Walking upright.
Taller.
Shorter arms and longer legs.
Are rock layers containing older rocks found closer or further away from the Earths surface?
Further away.
Are rock layers containing newer rocks found closer or further away from the Earths surface?
Closer.
Will more complex tools be found in older or newer rock?
Newer
What type of tools are found in newer rock?
Complex, sophisticated, sharp, specialised tools.
Will more simple tools be found in older or newer rock?
Older.
What type of tools are found in older rock?
Simple, blunt tools.
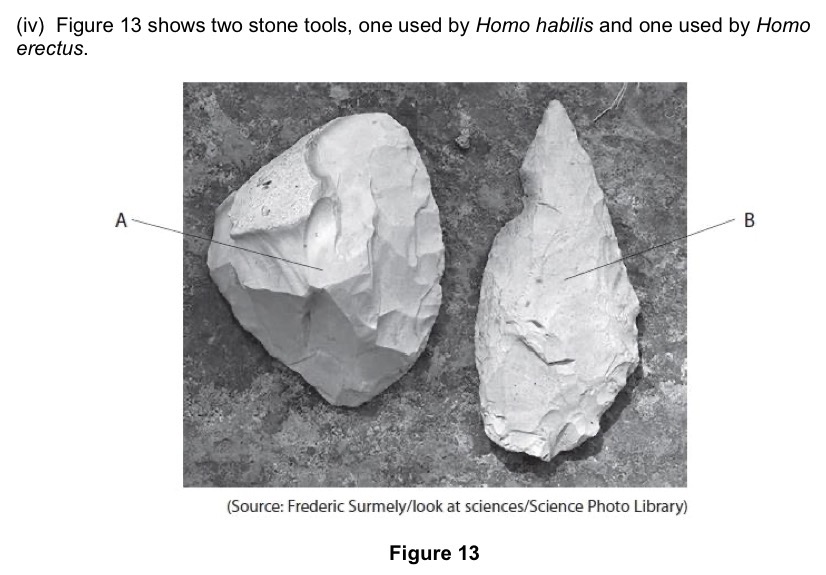
Explain which stone tool was most likely to be used by Homo erectus.
Stone tool B because it is more sophisticated and sharper. Home erectus lived the quite recently out of all fossils.
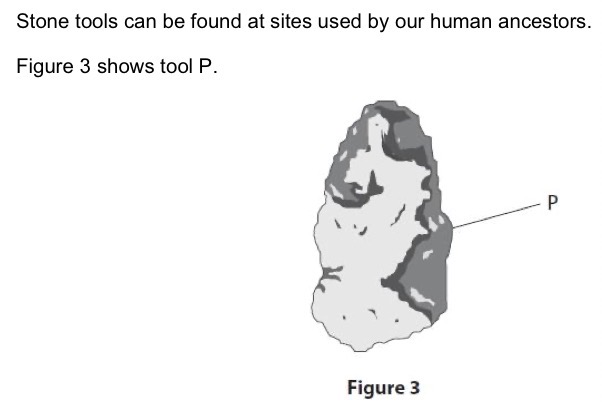
Describe how tool P was made.
By hitting it with another rock/something hard to knock flakes and chips off.
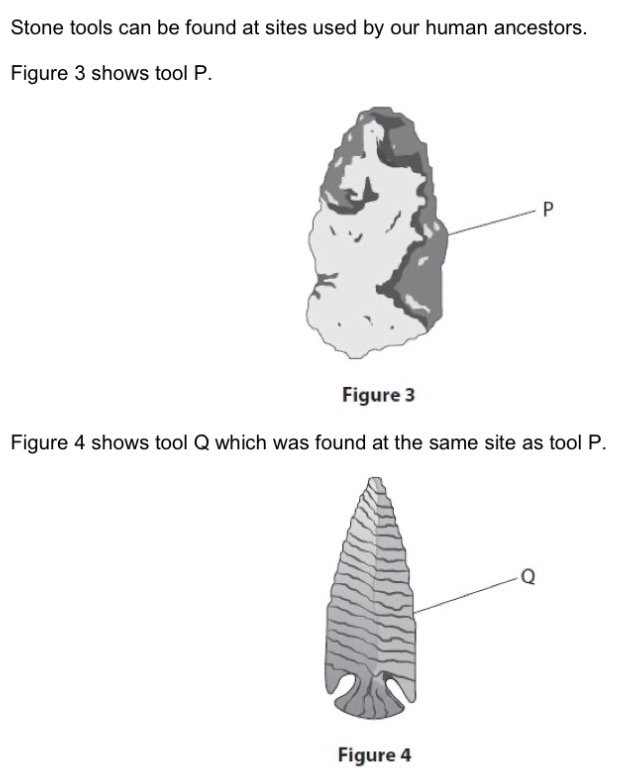
A scientist stated that tool Q was made by a more evolved human ancestor than tool P. Suggest why.
Tool Q is sharper/more pointed than tool P.

Give one reason why scientists believed that tool Q was used by a more recent human ancestor.
It is more sophisticated and sharper.
If a fossil is found in a 200,000 year old rock, how old is the fossil?
200,000 - always the same age.
Describe two ways that stone tools and fossils can be dated to find out how old they are.
From the layer of rock in which they found.
How deep the tool is found.
Compare to other finds of known age from the same layer of rock.
Compare with other tools/fossils that have already been dated.
Radiometric dating of the rock layer.
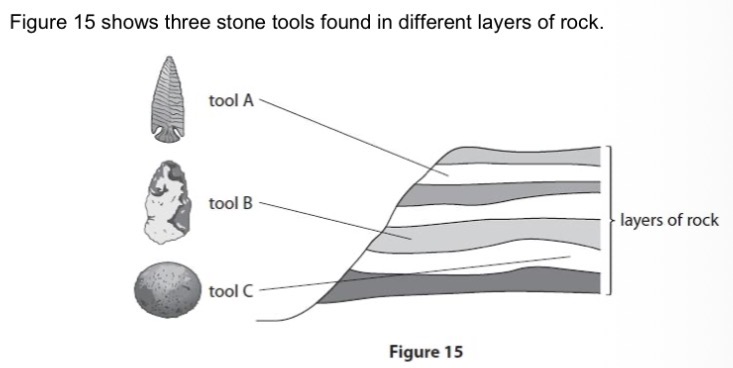
Explain how the information in Figure 15 provides evidence for human evolution.
Age of tools - Younger rock layers towards top and older rock
layers lower down so C is older than B which is older than A. Rocks can be dated by radiometric dating.
Quality of tools - A is the most sophisticated/specialised/ refined. C most basic/simple and less sophisticated. B shows some evidence of being worked but is still rough.
Skills and intelligence - Recent tools like A show that humans have greater human manipulation, greater skill and higher intelligence compared to when C was made.
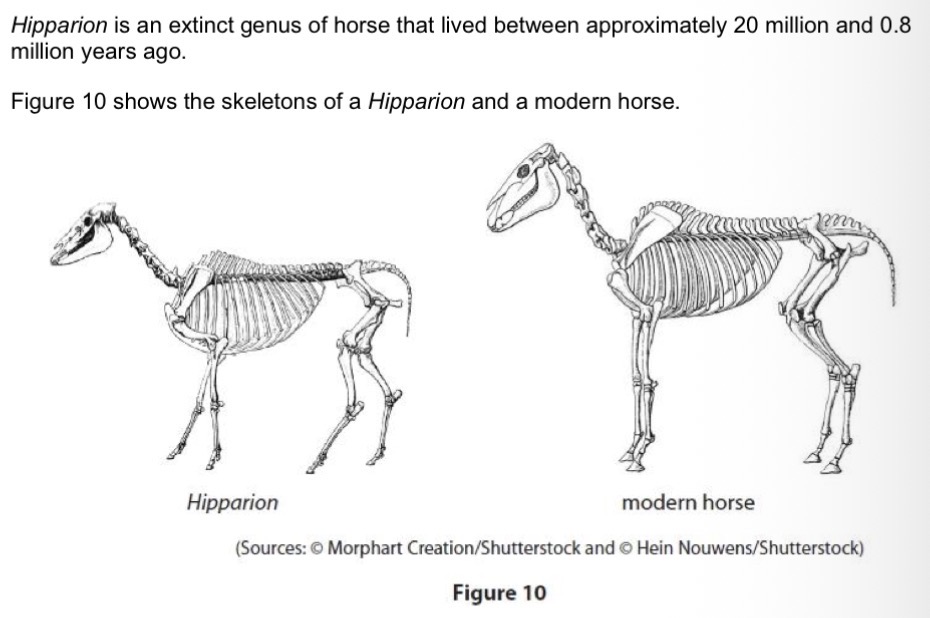
Give one method that can be used to date a fossil of a Hipparion.
Radiometric dating.
Location in rock layer.
Age of fossils surrounding it.
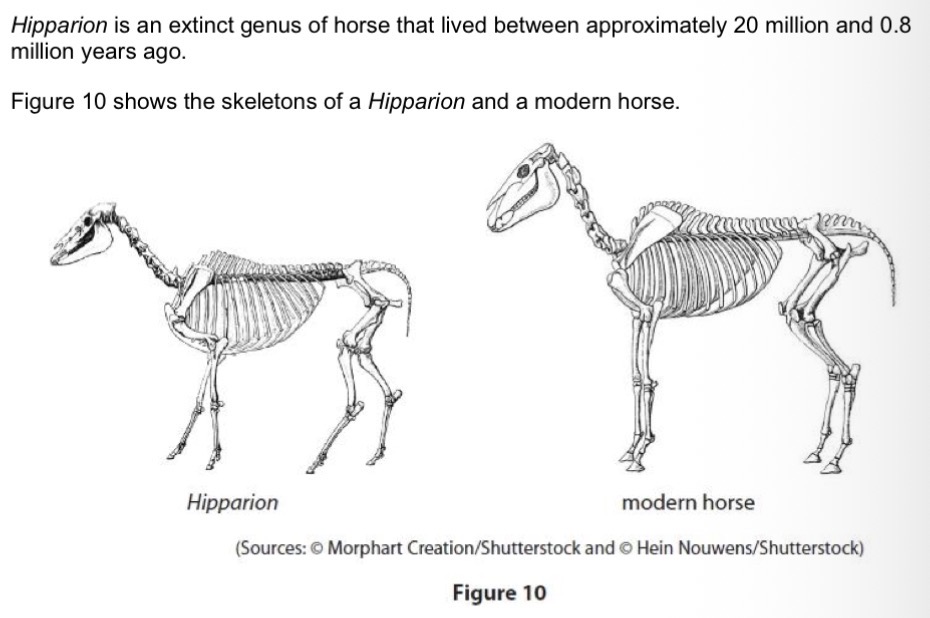
Give one reason why scientists have concluded that the modern horses evolved from Hipparion.
They have a similar pentadactyl limb structure.
What is a pentadactyl limb?
A limb with 5 units.
How does the pentadactyl limb provide evidence for evolution?
Suggests all species with it have descended from a common ancestor.
How does many species having a pentadactyl limb prove evolution?
Despite looking externally different; this similarity shows that they all evolve from the same species or have a common ancestor.
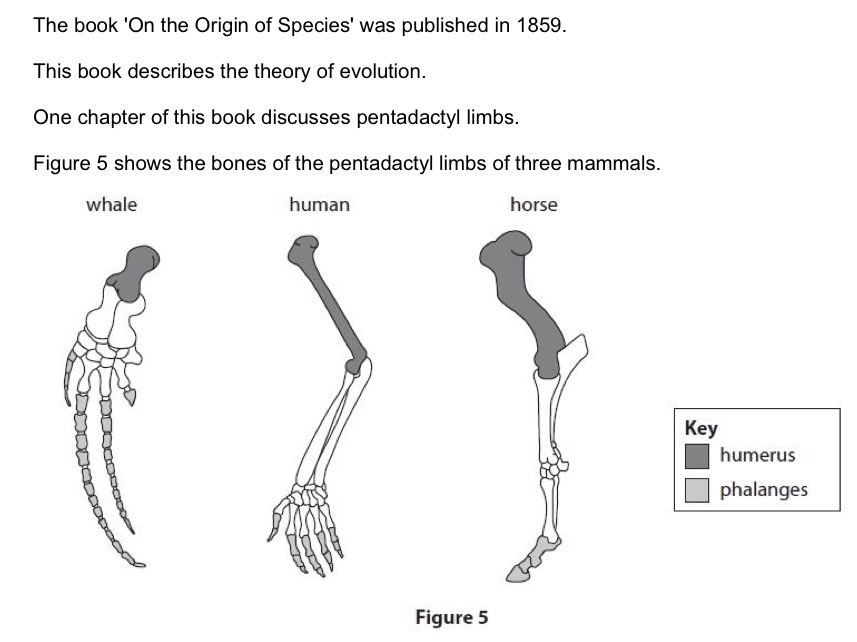
Describe one difference between the humerus of the whale and human.
The whale humerus is shorter and wider.
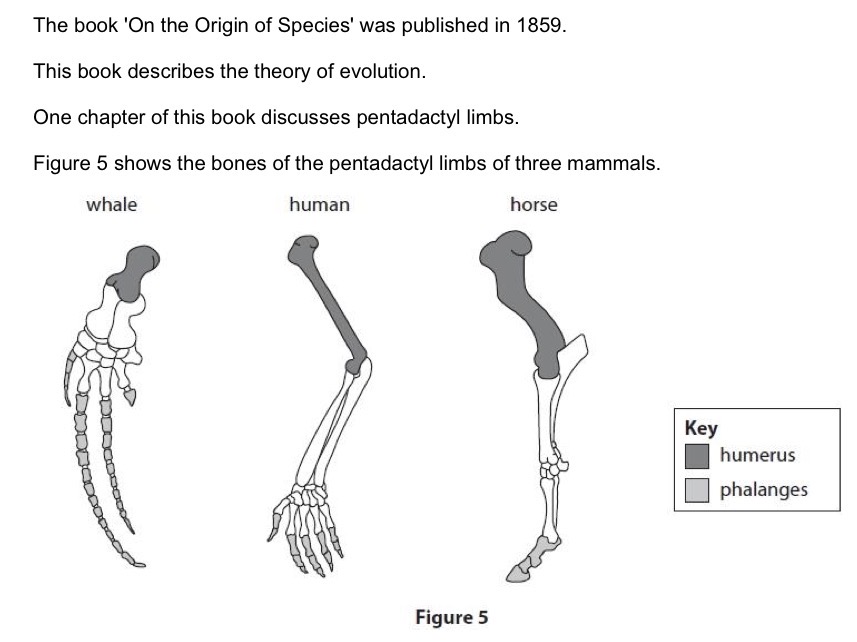
Describe one difference between the phalanges of the horse and human.
The horse has fewer phalanges with 3 whereas the human has 14. The horse also has thicker phalanges.
Describe how the structure of these limbs provides scientists with evidence for evolution.
They have a pentadactyl limb to suggest a common ancestor. This limb structure has been adapted for different functions.
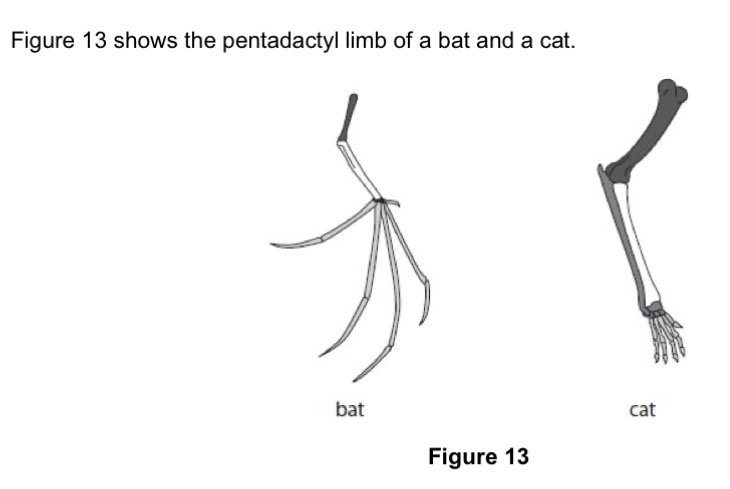
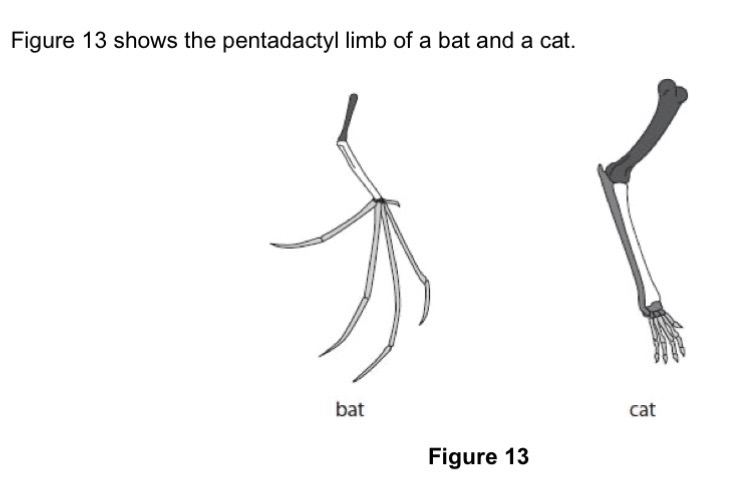
Describe the reasons why the anatomy of the pentadactyl limb suggests that bats and cats evolved from a common ancestor.
Same bone structure is unlikely to have occurred more than once during evolution, suggesting that they have a common ancestor.
Genetic analysis also provides evidence for evolution. Scientists can sequence genes from different organisms.
Describe how this type of genetic analysis provides evidence for evolution.
Genetic analysis provides evidence for evolution because scientists can compare the DNA sequences of different organisms. Species that are closely related have more similarities in their DNA and gene sequences, showing that they share a recent common ancestor.
Explain how bacteria can become resistant to antibiotics.
Bacteria have a high, medium or low resistance to antibiotics.
Antibiotics are introduced to an environment.
Antibiotics will first kill low resistance then medium resistance but if a person doesn’t continue to take antibiotics/doesn’t finish the course, high resistance bacteria remains.
High resistant bacteria will breed and divide, passing on their beneficial allele to the offspring.
Now antibiotics don’t work as all bacteria is highly resistant to it.
MRSA is a bacterium that has evolved to become resistant to antibiotics. With reference to Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection, explain how MRSA bacteria have evolved to become resistant to antibiotics.
Bacteria rapidly reproduce to generate a large population.
Bacteria have genetic variation. Some bacteria develop a high resistance to antibiotics through mutation.
Antibiotic treatment exerts a selection pressure.
Antibiotics will kill low and medium resistance bacteria and high resistance bacteria will survive.
High resistant bacteria will breed and divide, passing on their beneficial allele of high resistance to the offspring.
Colistin is an antibiotic used to treat infections in the bloodstream. Some bacteria are resistant to Colistin. Explain how these bacteria have become resistant to Colistin.
People do not finish their Colistin course.
Natural selection/evolution occurs.
Bacteria have genetic variation of genes/alleles with a high, medium or low resistance to antibiotics.
Bacteria are introduced to an environment.
Antibiotics will kill low and medium resistance bacteria and high resistance bacteria will survive.
High resistant bacteria will breed and divide, passing on their beneficial allele of high resistance to the offspring.
Explain how Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria developed resistance to antibiotics.
By natural selection/evolution.
Bacteria have genetic variation of genes/alleles with a high, medium or low resistance to antibiotics.
Bacteria are introduced to an environment.
Antibiotics will kill low and medium resistance bacteria and high resistance bacteria will survive.
High resistant bacteria will breed and divide, passing on their beneficial allele of high resistance to the offspring.
State how the use of antibiotics could contribute to Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteria developing resistance to ntibiotics.
People may not complete their course or may overuse the antibiotics.
How can we reduce antibiotic resistance?
Patients should always take full course every time.
Reduce use of antibiotics in farm animals.
Reduce the prescription of antibiotics for viral infractions.
Disease is an example of a selection pressure. Give another example of a selection pressure that leads to survival of the fittest.
Change in environment.
Competition.
Increase in predators.
What is selective breeding?
Humans artificially select organisms with desirable characteristics and breed them to produce offspring with the similar characteristic.
Outline the main steps involved in selective breeding.
Select parent organisms with desired characteristics and breed together.
Select offspring with desirable characteristics and breed together.
Repeat process over many generations until all offspring have desired characteristics.
In which fields is selective breeding useful?
Horse racing.
Agriculture.
Medical research.
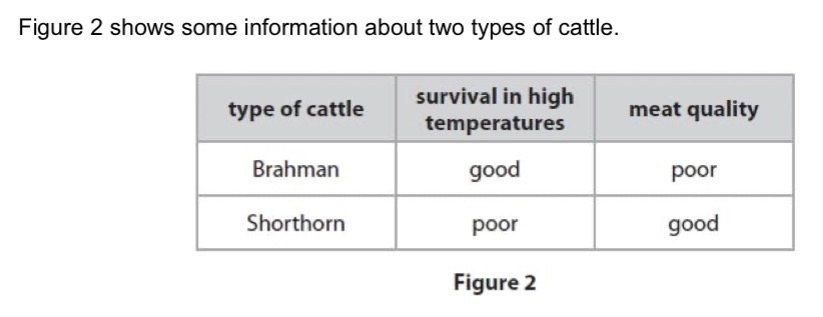
Describe how these types of cattle could be selectively bred to produce cattle that can survive high temperatures and have good meat quality.
Breed/cross Brahman cattle with Shorthorn cattle.
Select the offspring with the desired characteristics and cross/breed them together.
Repeat over many generations.
Describe how race horses alive today have been selectively bred to run faster.
Breed two animals with the beneficial characteristic for running fast.
Select offspring that can run fast and cross/breed them together.
Repeat over many generations.
Describe how drought resistant crops can be produced.
Genetic variation means that some plant will be tolerant of drought conditions.
Select these plants.
Cross pollinate these plants and grow the seeds under drought conditions.
Select offspring with desired characteristics and cross/breed them together. Repeat over many generations.
What are the advantages of selective breeding?
Provides higher yields of crops.
Leads to more profit; more wool, milk, meat produced.
Creates a higher resistance to disease.
Can be used for medical research.
What are the disadvantages of selective breeding?
Can cause random genetic mutations.
Inbreeding can cause health problems and genetic disorders.
Potential to unknowingly select harmful recessive alleles.
No variation/Decrease in gene pool - more likely to suffer from environment changes or exposure to new diseases. Less chance of resistant alleles.
Define: Clone
A genetically identical copy.
What is tissue culture?
Cells grown on or in an artificial medium.
Why is tissue culture used in plants?
To preserve rare plants.
Explain how to clone plants using tissue culture.
Take a cutting of the parent plant/Remove tissue.
Place cutting/tissue into growth medium (contains nutrients + growth hormones) under aseptic conditions.
Wait until roots and shoots form.
Put into soil.
What is added to the growth medium to help plants/animals to grow?
Nutrients + Growth Hormones.
Why are hormones and nutrients added to the growth medium?
To stimulate the growth of shoots and roots.
What must be ensured when preparing tissue cultures?
Ensure aseptic conditions prevent contamination by microorganisms.
Why do we sterilise everything during tissue culture?
To kill pathogens and microbes that could harm the plant or be cloned on to the new plant.
Why is tissue culture used in animals?
Medical research.
Explain how to clone animals using tissue culture.
Take sample of tissue.
Separate individual cells from tissue using enzymes.
Place cells into a culture vessel and bathe in a growth medium. Store sample.
Cells begins to split via osmosis.
Then, split cells into different vessels to encourage more growth and division for larger samples.
State the advantages of using a tissue culture or plant cuttings.
Preserves rare plants.
Plants and animals can be used in medical research.
Plant cuttings can produce clones quickest and cheapest.
Fast and simple process.
Requires little space.
Enables the growth of plants with same desirable characteristics.
Define: Genetic Engineering
Transfer of DNA from one organism to another, giving it desirable characteristics.
Which enzyme is used to cut the target gene out of the chromosome?
Restriction Enzyme.