Nurse 3110 Exam 4
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
184 Terms
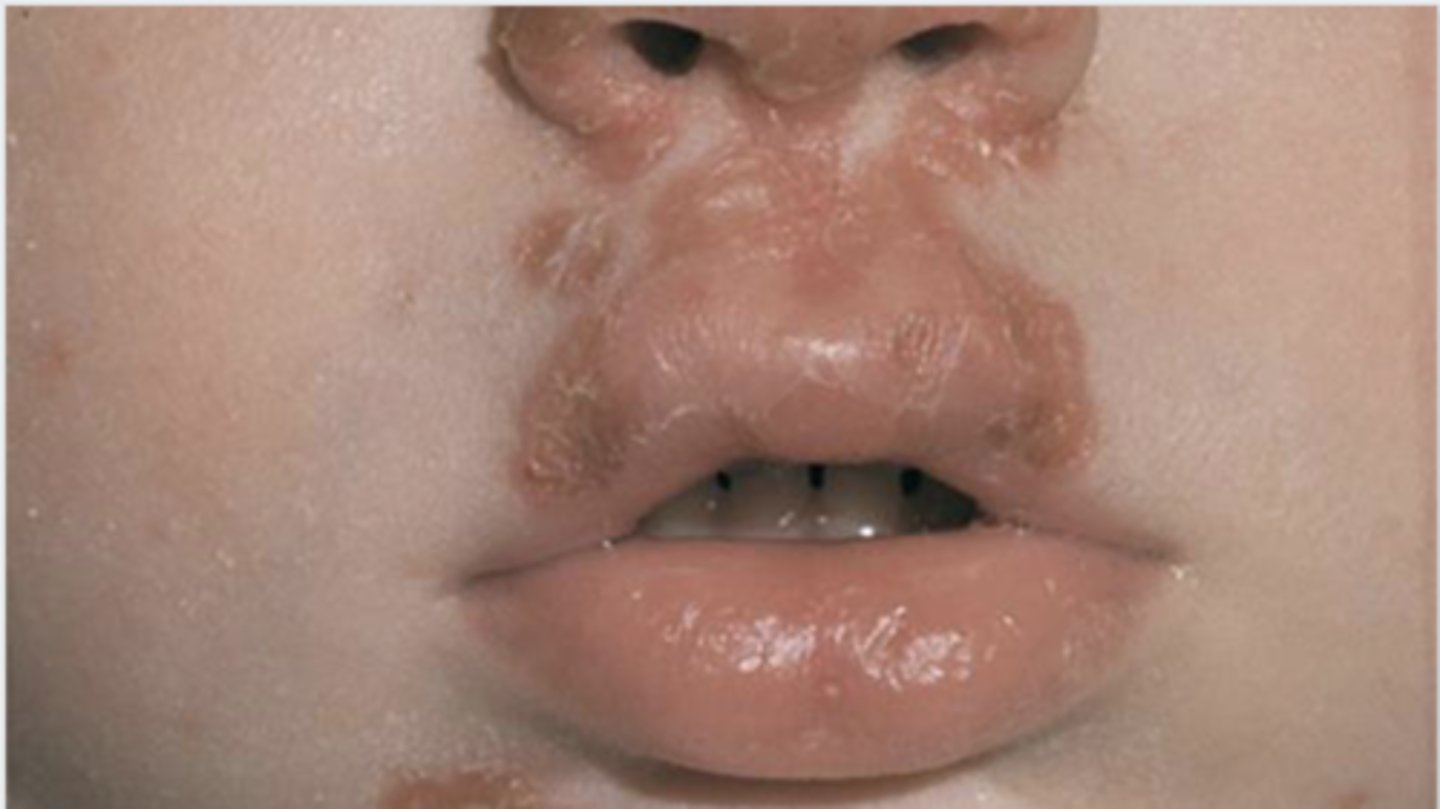
What's this rash?
A. Impetigo
B. Fever blisters
C. Thrush
D. Cellulitis
impetigo
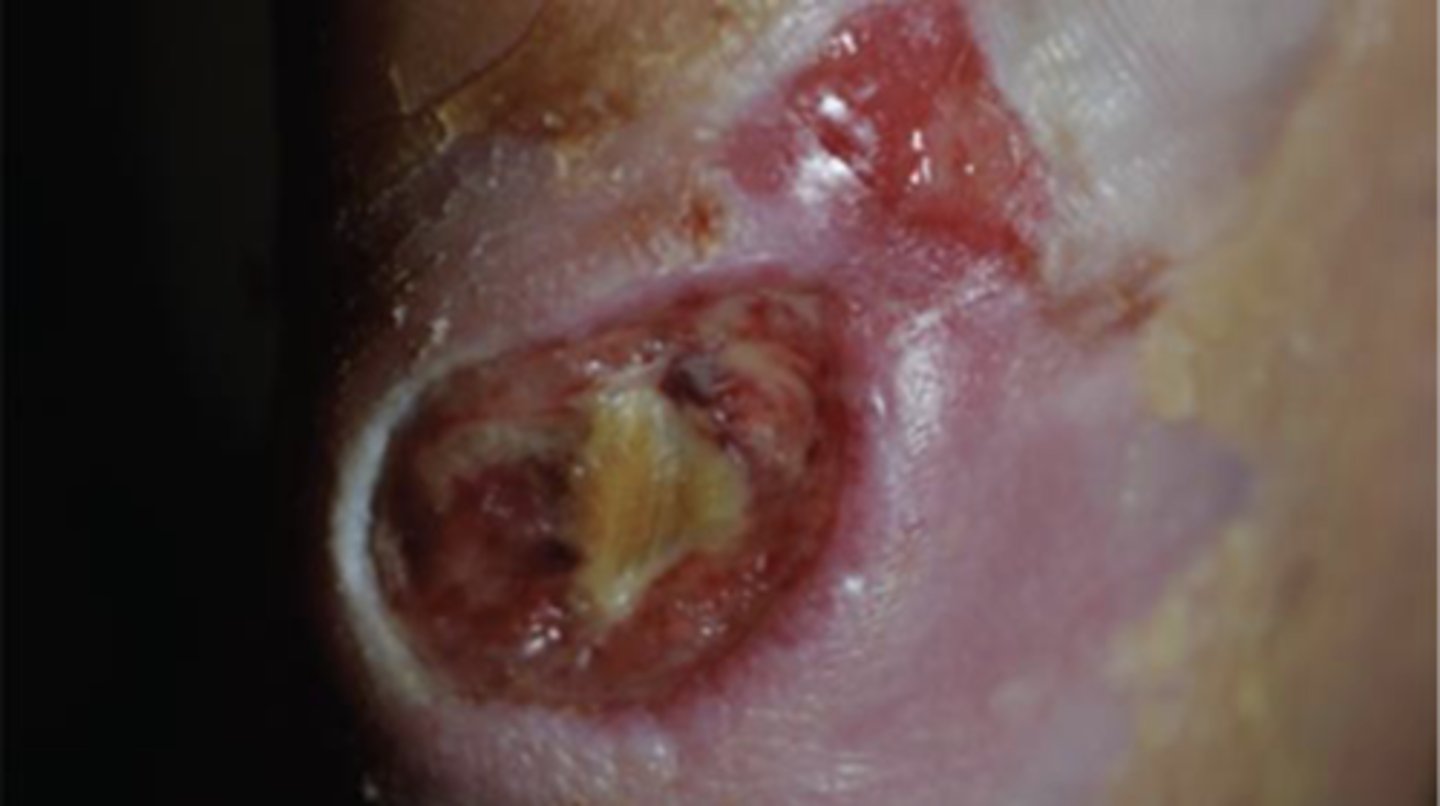
What's this on the heel of the foot?
A. Decubitus ulcer
B. Diabetic foot ulcer
C. Basal cell carcinoma
D. Infected corn/callus
B. Diabetic foot ulcer
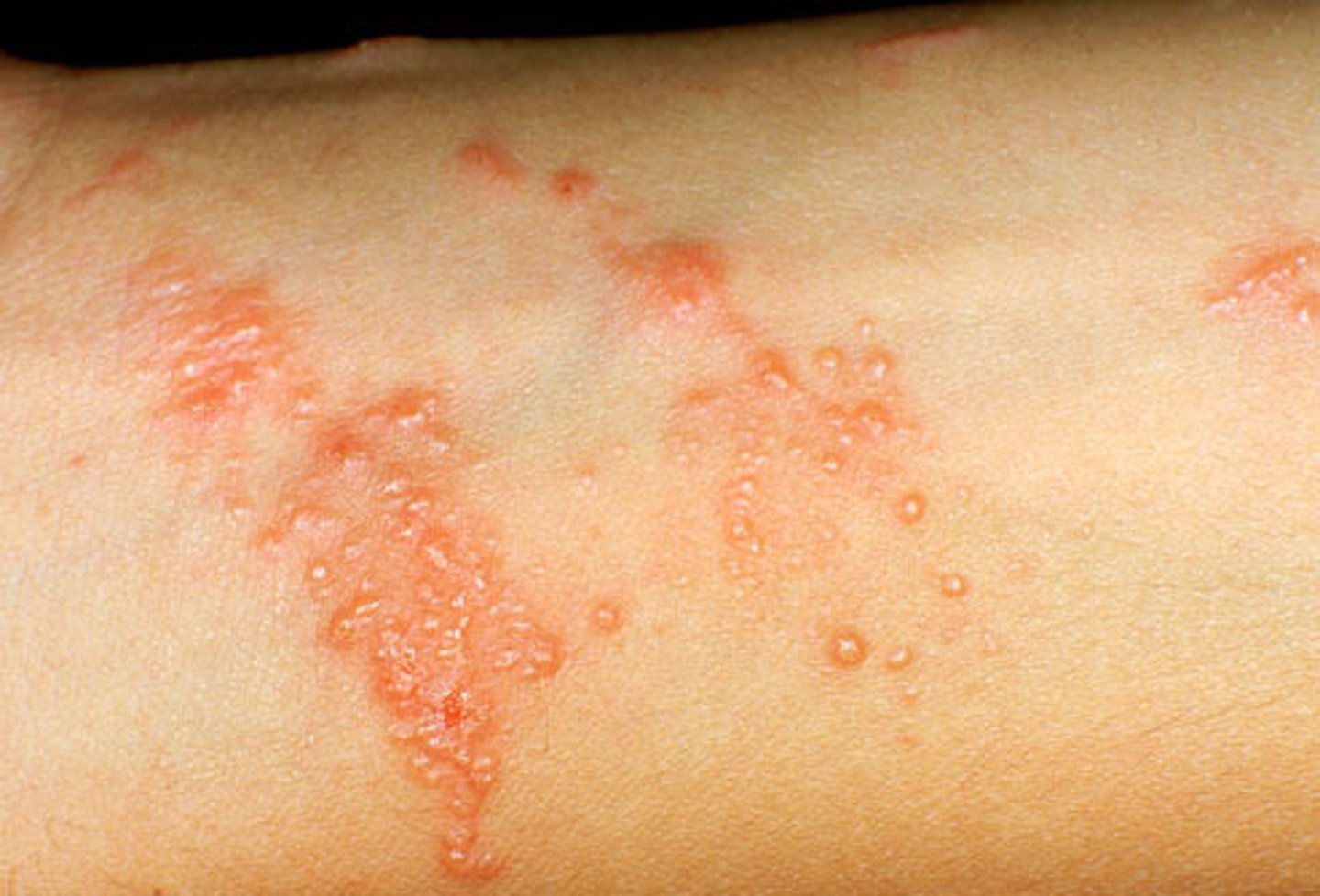
What is this rash?
A. Shingles
B. Psoriasis
C. Poison ivy
D. Eczema
C. Poison ivy
Which of the following areassociated with open angleglaucoma? Select all that apply.
1.Acute onset
2.Surgical emergency
3.Amenable to pharmacologictherapy
4.Most common type of glaucoma
5.Gradual onset
Gradual onset, Amenable to pharmacologic therapy, Most common type of glaucoma
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following areassociated with Closed angleglaucoma? Select all that apply.
1.Acute onset
2.Surgical emergency
3.Amenable to pharmacologictherapy
4.Most common type of glaucoma
5.Gradual onset
Acute onset, Surgical emergency, Amenable to pharmacologic therapy
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following classes of medications would youexpect a patient to be taking with a Conjunctivitis?
A. Topical antihistamine
B. Topical beta blocker
C. Topical antibiotic
D. Topical sympathomimetic
Topical beta blocker, Topical sympathomimetic
2 multiple choice options
Which of the following classes of medications would youexpect a patient to be taking with a diagnosis of closedangle glaucoma? Conjunctivitis?
A. Topical antihistamine
B. Topical beta blocker
C. Topical antibiotic
D. Topical sympathomimetic
Topical antibiotic, Topical antihistamine
2 multiple choice options
A nurse in an urgent care facility is preparing to administer a stat dose of medication to a toddler who is accompanied by their parent. The child is not wearing an ID band. How should the nurse identify the patient?
1. Ask the child to say their name.
2. Say the child's name and ask them if that iscorrect.
3. Ask the parent to identify the child by name.
4. Hold the medication until the child receives an IDband.
Ask the parent to identify the child by name.
A nurse is reviewing a new prescription by a provider. The nurse should verify that which ofthe following components of a prescription arepresent? Select all that apply.
1. Date and time of prescription
2. Patient's diagnosis
3. Dosage of medication
4. Route of medication
5. Generic name of medication
6. Prescriber's signature
Prescriber's signature, Date and time of prescription, Dosage of medication, Route of medication, Generic name of medication
3 multiple choice options
A nurse is administeringmedications to a patient. Which ofthe following actions should thenurse perform during the planningstep of the nursing process? Selectall that apply.
1.Identify patient allergies.
2.Calculate the dose.
3.Explain the purpose of the medication tothe patient.
4.Observe for adverse effects of the medication.
5.Verify the dose.
Verify the dose, Calculate the dose.
A nurse is asked to administer a medication to a patient because acoworker must help with an emergency. The coworker gives the nursea syringe labeled furosemide 20 mg. The label also includes thepatient's name and hospital ID number. Which of the followingresponses by the nurse is appropriate?
1. "I'll go and give the medication to the patient right away."
2. "Go with me to identify the patient properly, and then I'll give the medication for you."
3. "You should ask the charge nurse to administer this medication."
4. "I'll go help with the emergency situation while you administer themedication."
"Go with me to identify the patient properly, and then I'll give themedication for you."
A nurse receives a telephoneprescription from a prescriber. Theprescriber states, "Administer three-tenths of a milligram of nitroglycerinorally to the patient." How shouldthe nurse transcribe "three-tenths ofa milligram" in the medicationadministration record (MAR)?
1. .3 mg
2. 3/10's mg
3. 0.30 mg
4. 0.3 mg
0.3 mg
What is the primary function of the skin in the integumentary system?
Producing new blood cells
Regulating body temperature
Supplying energy for the body
Acting as a protective barrier
Acting as a protective barrier
A nurse in an urgent care facility is preparing to administer a stat dose of medication to a toddler who is accompanied by their parent. The child is not wearing an ID band. How should the nurse identify the patient?
Ask the parent to identify the child by name.
Hold the medication until the child receives an ID band.
Ask the child to say their name.
Say the child's name and ask them if that is correct.
Ask the parent to identify the child by name.
A nurse is preparing to administer medication to the client. Which of the following client information should the nurse use to identify the client?
Select all that apply.
A
Date of birth
B
Full name
C
Hospital room number
D
Photograph
E
Medical record number
Date of birth, full name, medical record number, photograph
A nurse is asked to administer a medication to a client because a coworker needs to assist another client. The coworker gives the nurse a syringe labeled furosemide 20 mg. The label also includes the client's name and hospital identification number. Which of the following responses by the nurse is appropriate?
A
“I’ll go and give the medication to the client right away.”
B
“Go with me to identify the client properly, and then I’ll give the medication to you.”
C
“You should ask the charge nurse to administer this medication.”
D
“I’ll help the other client while you administer the medication.”
"I'll help the other client while you administer the medication."
A nurse is administering medications to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse perform during the planning step of the nursing process?
Select all that apply.
A
Identify client allergies.
B
Calculate the dose.
C
Explain the purpose of the medication to the client.
D
Observe for adverse effects of the medication.
E
Verify the dose.
Calculate the dose, Verify the dose
Match the error-prone abbreviation on the left with the correct way to write the information on the MAR on the right.
Drag the options on the left to the corresponding category on the right (or select the option on the left and then the corresponding category on the right).
HS
IU
QD
SC
Unit
Subcutaneously
Once daily
At bedtime
HS- At bedtime
IU- Unit
SC- Subcutaneously
QD- Once daily
A provider prescribes clonidine 300 mcg PO daily. Available is 0.3 mg/tablet. How many tablets should the nurse administer?
Round the answer to the nearest whole number.
1 tablet
A nurse is reviewing instructions with a client who has a new prescription for furosemide 20 mg PO daily. Available is 8 mg/mL. The nurse should instruct the client to take how many tsp daily?
Round the answer to the nearest tenth.
.5 tsp
A provider prescribes cephalexin 0.5 g PO every 12 hr. The amount available is 250 mg/capsule. How many capsules should the nurse administer?
Round the answer to the nearest whole number.
2 capsules
Which type of solid medication should not be crushed but may be opened?
Tablet
Caplet
Enteric-coated tablet
Capsule
Capsule
A nurse is preparing to administer a unit-dose medication. Which of the following information should the nurse expect to find on the medication label?
Select all that apply.
A
Administration times
B
Generic name
C
Storage instructions
D
Client diagnosis
E
Expiration date
Storage instructions, generic name, expiration date
Use the above image to answer the following question below.A nurse is reviewing a client’s electronic medication administration record. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to administer orally?
Select all that apply.
A
Metoprolol
B
Enoxaparin
C
Prilosec
D
Fluticasone propionate
E
Sodium chloride
Metoprolol, Prilosec
A nurse is reviewing instructions with a client about how to take a sublingual medication. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
A
Swallow the medication whole.
B
Allow the medication to dissolve completely.
C
Take the medication with a glass of water.
D
Chew the medication carefully.
Allow the medication to dissolve completely
A nurse is preparing to administer medications. Which of the following forms of medication should the nurse instruct the client to swallow?
Select all that apply.
A
Sustained-release capsule
B
Enteric-coated tablet
C
Caplet
D
Troche
Sustained-release capsule, Enteric-coated tablet, Caplet
A nurse is administering medications to four clients using an automated dispensing system. Which of the following actions should the nurse take to prevent medication administration errors?
Select all that apply.
A
Compare the medication label with the medication administration record.
B
Take out medications for more than one client at once.
C
Check the expiration date on the medication label.
D
Document the medication immediately after administering it.
E
Remove the medication from the unit-dose package immediately after removing it from the automated dispensing system.
Compare the medication label with the medication administration record, Check the expiration date on the medication label, Document the medication immediately after administering it
A nurse is preparing to administer methylprednisolone. The prescribed dose is 125 mg IV every 6 hr. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose?
Round the answer to the nearest whole number. Enter only the number for your response.
2 mL
A nurse is preparing to administer ceftriaxone 250 mg IM. How many mL should the nurse administer?
.71 mL
A nurse is preparing to administer azithromycin. The prescribed dose is 500 mg via IV bolus. How many mL should the nurse administer?
5
A nurse is preparing to administer ampicillin 500 mg IM. How many mL should the nurse administer?
2 mL
A nurse is preparing to administer doxycycline oral suspension PO. The prescribed dose is 80 mg. How many mL should the nurse administer?
16 mL
Which of the following is a common name for the IV solution 0.9% sodium chloride?
A
Half normal saline
B
Normal saline
C
Lactated Ringer's
D
Sodium lactate
Normal saline
A nurse is administering lactated Ringer’s (LR), which contains lactate. LR can be used to treat a client who has which of the following disorders?
A
Acidosis
B
Alkalosis
C
Caloric deficit
D
Caloric excess
Acidosis
Which of the following is the abbreviation for the IV solution half normal saline?
A
0.25% NaCl
B
0.45% NaCl
C
0.5% NaCl
D
0.9% NaCl
Which of the following is the abbreviation for the IV solution half normal saline?
A
0.25% NaCl
B
0.45% NaCl
C
0.5% NaCl
D
0.9% NaCl
0.45% NaCl
How many calories does 1 L of 5% dextrose in water (D5W) provide?
170 Calories
Which of the following IV solutions should a nurse use when preparing to administer a blood transfusion?
A
5% dextrose in water (D5W)
B
Lactated Ringer’s (LR)
C
5% dextrose in 0.9% sodium chloride (D5NS)
D
0.9% sodium chloride (0.9% NaCl or NS)
0.9% sodium chloride (0.9% NaCl or NS)
Match the type of IV solution with its description.
Hypotonic- moves fluid from the veins to the cells and interstitial
Hypertonic- Pulls fluid out of the cells into the veins
Isotonic- Remains in the intravascular space
Hemolysis can occur with the administration of which of the following types of solution?
A
Isotonic
B
Hypotonic
C
Hypertonic
Hypotonic
A nurse administers a solution of 3% NaCl to a client. Which of the following types of solution is this?
A
Isotonic
B
Hypotonic
C
Hypertonic
Hypertonic
A nurse administers lactated Ringer’s by continuous IV infusion. Which of the following types of solution is this?
A
Isotonic
B
Hypotonic
C
Hypertonic
Isotonic
A nurse administers dextrose 5% in water (D5W) IV solution. After the dextrose is metabolized, which of the following types of solution is this?
A
Isotonic
B
Hypotonic
C
Hypertonic
Hypertonic
5 lbs., 4 oz. = ? lbs
5.25 lbs
5.25 / 2.2
2.4kg
21 lbs., 14 oz. = ? Lbs.
Divide 14 by 16 = 0.875 = 21.875 lbs.
21.875 / 2.2 = ? kg
9.9kg
175 lbs., 7 oz. = ? Kg
79.58 kg
100 lbs., 15 oz. = ? Kg
45.88 kg
49 lbs., 2 oz. = ? Kg
22.33 kg
Which type of injection is administered below the dermis but above the muscle?
Subcutaneous (SC)
Intravenous (IV)
Intradermal (ID)
Intramuscular (IM)
Subcutaneous (SC)
Which of the following best represents a standing order?
1.Atorvastatin 10 mg one tablet PO daily.
2.Acetaminophen 500 mg two tablets every 8 hours PRN pain or fever greater than 100.5 degrees F.
3.Midazolam 1 mg IV 30-60 minutes preoperatively.
4.Hepatitis B vaccine 1 mL IM
2.Acetaminophen 500 mg two tablets every 8 hours PRN pain or fever greater than 100.5 degrees F.
Which of the following best represents a Routine order?
1.Atorvastatin 10 mg one tablet PO daily.
Which of the following best represents a One time order?
.Atorvastatin 10 mg one tablet PO daily.
2.Acetaminophen 500 mg two tablets every 8 hours PRN pain or fever greater than 100.5 degrees F.
3.Midazolam 1 mg IV 30-60 minutes preoperatively.
4.Hepatitis B vaccine 1 mL IM
3.Midazolam 1 mg IV 30-60 minutespreoperatively.
Administer filgrastim 5 mcg/kg/day SCfor 14 days. The patient weighs 127 lb.You have filgrastim 480 mcg/0.8 mL
Administer 0.48 mL of filgrastim subcutaneously once daily for 14 days.
Administer cyanocobalamin 100 mcg.You have cyanocobalamin 1 mg/mL.
Administer 0.1 mL of cyanocobalamin.
Administer gentamicin 1 mg/kg for apatient weighing 168 lbs. You havegentamicin 40 mg/mL
Administer 1.91 mL of gentamicin.
Administer adalimumab 20 mg. Youhave adalimumab 40 mg/0.8 mL.
Administer 0.4 mL of adalimumab.
Administer heparin 7,000 units SC. Youhave heparin 10000 units/mL.
Administer 0.7 mL of heparin subcutaneously.
Administer digoxin 400 mcg IVP. Youhave digoxin 0.25 mg/mL
Administer 1.6 mL of digoxin IV push.
Administer atropine 0.6 mg IM. You have0.4 mg/mL
Administer 1.5 mL of atropine intramuscularly.
A patient is admitted with hypocalcemia. Which assessment finding should the nurse expect?
A. Bradycardia and facial flushing
B. Muscle cramps and positive Chvostek's sign
C. Lethargy and decreased reflexes
D. Warm, dry skin and hypotension
Muscle cramps and positive Chvostek's sign
A patient with osteoporosis is prescribed alendronate. Which instruction is most important for the nurse to give?
A. Take at bedtime with food
B. Lie down for 30 minutes after taking
C. Take with a full glass of water on an empty stomach
D. Avoid dairy products when taking this drug
Take with a full glass of water on an empty stomach
A patient receiving IV calcium gluconate reports tingling and weakness. Which action should the nurse take first?
A. Stop the infusion immediately
B. Check the patient's calcium level
C. Assess the IV site for infiltration
D. Notify the healthcare provider
Stop the infusion immediately
A patient is at risk for bone demineralization due to long-term corticosteroid use. What is the best nursing intervention?
A. Encourage low-calcium diet
B. Promote bed rest
C. Recommend daily weight-bearing exercise
D. Limit vitamin D supplements
Recommend daily weight-bearing exercise
The nurse is reviewing lab results for a patient taking vitamin D and calcium. Which finding requires follow-up?
A. Calcium level of 9.4 mg/dL
B. Phosphate level of 3.2 mg/dL
C. Calcium level of 11.5 mg/dL
D. Vitamin D level of 40 ng/mL
Calcium level of 11.5 mg/dL
A nurse is caring for a patient with hypocalcemia. Which of the following assessments is most concerning and requires immediate action?
A. Mild abdominal cramping
B. Positive Chvostek's sign
C. Tingling in fingers
D. New-onset laryngospasm
New-onset laryngospasm
Which of the following nursing instructions is most appropriate when educating a patient taking oral calcium carbonate?
A. Take on an empty stomach for best absorption
B. Take with a full glass of water and food to improve absorption
C. Avoid vitamin D supplements to prevent toxicity
D. Take with milk of magnesia to prevent constipation
Take with a full glass of water and food to improve absorption
A patient is receiving IV calcium gluconate for symptomatic hypocalcemia. Which nursing intervention is a priority?
A. Monitor hourly urine output
B. Administer rapidly for quick correction
C. Monitor cardiac rhythm continuously
D. Assess for pedal pulses before infusion
Monitor cardiac rhythm continuously
The nurse knows that vitamin D is essential in calcium regulation because it:
A. Stimulates PTH release to increase serum calcium
B. Promotes GI absorption of calcium
C. Suppresses renal reabsorption of calcium
D. Inhibits calcitonin production
Promotes GI absorption of calcium
A patient with osteoporosis is prescribed alendronate (a bisphosphonate). Which nursing instruction is most important to include?
A. Take at bedtime for best bone absorption
B. Remain upright for at least 30 minutes after taking
C. Avoid dairy products when taking the drug
D. Take with orange juice for best effect
Remain upright for at least 30 minutes after taking
A nurse is reviewing labs. Which calcium level would prompt the nurse to hold a scheduled dose of IV calcium and notify the provider?
A. 7.8 mg/dL
B. 9.2 mg/dL
C. 10.8 mg/dL
D. 11.5 mg/dL
11.5 mg/dL
Which patient is most at risk for developing osteomalacia?
A. A postmenopausal woman taking calcium daily
B. A child who plays outside daily and drinks fortified milk
C. An older adult with chronic kidney disease and limited sun exposure
D. A middle-aged man taking vitamin D supplements
An older adult with chronic kidney disease and limited sun exposure
A patient asks, "Why do I need vitamin D with my calcium supplement?" The nurse's best response is:
A. "Vitamin D helps soften bones so calcium can be absorbed."
B. "It enhances calcium absorption in your intestines."
C. "It reduces stomach upset from calcium."
D. "Vitamin D decreases calcium levels to prevent toxicity."
"It enhances calcium absorption in your intestines."
Which of the following findings is most important to report immediately in a patient receiving calcium IV therapy?
A. Mild constipation
B. Decreased urine output
C. Complaints of metallic taste
D. Fatigue
Decreased urine output
The nurse is administering ergocalciferol to a patient. The patient asks what it’s for. Which is the best explanation?
A. "It helps dissolve kidney stones made of calcium."
B. "It prevents your body from losing too much calcium in urine."
C. "It is a form of vitamin D that helps your body absorb calcium."
D. "It increases the strength of your heart muscle."
"It is a form of vitamin D that helps your body absorb calcium."
A patient with Paget’s disease asks why their bones are weakening. The nurse’s best explanation is:
A. “Your bones are absorbing too much calcium from your diet.”
B. “Bone breakdown and bone formation are happening too slowly.”
C. “Your bones are being broken down and rebuilt abnormally fast and unevenly.”
D. “Your bones are lacking enough red blood cells to stay strong.”
"Your bones are being broken down and rebuilt abnormally fast and unevenly."
A nurse is teaching about risk factors for osteoporosis. Which of the following statements indicates a need for further teaching?
A. “I drink two glasses of wine every day.”
B. “I walk 20 minutes daily to stay active.”
C. “I take a daily calcium and vitamin D supplement.”
D. “My mom had osteoporosis, so I should be screened early.”
"I drink two glasses of wine every day."
A nurse is preparing a patient for a DEXA scan. Which statement by the nurse is correct?
A. “This test uses sound waves to measure calcium in your blood.”
B. “It measures your bone strength by comparing it to other people’s x-rays.”C. “It’s a special type of x-ray that measures bone density in your hip and spine.”
D. “It will determine the level of vitamin D in your bones.”
"It's a special type of x-ray that measures bone density in your hip and spine."
A patient's DEXA scan T-score is –2.7. The nurse recognizes this as:
A. Normal bone density
B. Osteopenia
C. Osteoporosis
D. Paget’s disease
Osteoporosis
A nurse is teaching a group of postmenopausal women about osteoporosis prevention. Which recommendation is most appropriate?
A. Avoid all dairy products to reduce fat intake
B. Take calcium and vitamin D supplements daily
C. Begin high-impact exercise like jumping rope
D. Avoid sun exposure to protect your bones
Take calcium and vitamin D supplements daily
Which medication works by inhibiting bone resorption and is a first-line treatment for osteoporosis?
A. Teriparatide
B. Raloxifene
C. Bisphosphonates
D. Calcitonin
Bisphosphonates
A nurse is administering alendronate (a bisphosphonate) to a patient. Which instruction is most important?
A. “Take with milk to reduce stomach upset.”
B. “Stay upright for 30 minutes after taking the medication.”
C. “Take it right before bedtime to increase absorption.”
D. “You should lie down if you feel nauseated.”
"Stay upright for 30 minutes after taking the medication.
Which lab result should the nurse monitor closely in a patient taking calcitonin for osteoporosis?
A. Serum potassium
B. Blood glucose
C. Serum calcium
D. Serum sodium
Serum calcium
A nurse is educating a patient prescribed teriparatide (Forteo). What is the best explanation of its mechanism of action?
A. “It blocks calcium from being absorbed into the bone.”
B. “It stimulates new bone formation by activating osteoblasts.”
C. “It replaces missing estrogen to reduce bone loss.”
D. “It slows down your metabolism to preserve bone tissue.”
"It stimulates new bone formation by activating osteoblasts."
Which patient is at highest risk for developing osteoporosis?
A. A 40-year-old African American male who lifts weights daily
B. A 72-year-old Caucasian woman with a sedentary lifestyle
C. A 30-year-old woman who takes birth control pills
D. A 55-year-old Asian man who takes calcium supplements
A 72-year-old Caucasian woman with a sedentary lifestyle
A nurse is teaching a patient prescribed alendronate (Fosamax). Which of the following statements by the patient requires correction?
A. “I’ll take it with a full glass of water.”
B. “I’ll remain upright for 30 minutes after taking it.”
C. “It’s okay to lie back down if I feel tired.”
D. “I’ll take it first thing in the morning before eating.”
"It's okay to lie back down if I feel tired."
A serious adverse effect of bisphosphonate therapy that the nurse should monitor for is:
A. Tinnitus
B. Osteonecrosis of the jaw
C. Hypotension
D. Pulmonary embolism
Osteonecrosis of the jaw
A nurse is caring for a patient with Paget’s disease who is prescribed zoledronic acid (Reclast). What is the priority nursing assessment before administration?
A. Liver enzyme panel
B. ECG
C. Serum calcium and renal function
D. Blood glucose
Serum calcium and renal function
Which common side effect of calcitonin (Miacalcin) should the nurse include in teaching?
A. Chest pain
B. Constipation
C. Runny nose
D. Diarrhea
Runny nose
The nurse is giving denosumab (Prolia) to a patient. Which of the following findings would require provider notification?
A. Fatigue
B. Muscle pain
C. Calcium level of 7.1 mg/dL
D. Mild injection site redness
Calcium level of 7.1 mg/dL
Which statement about teriparatide (Forteo) indicates the patient understands the medication?
A. “This helps prevent estrogen-related cancers.”
B. “It may help rebuild bone through PTH-like effects.”
C. “It blocks estrogen in the breast and uterus.”
D. “It’s a bisphosphonate that reduces stomach acid.”
"It may help rebuild bone through PTH-like effects."
A black box warning associated with teriparatide is:
A. Liver toxicity
B. Osteosarcoma risk
C. Anaphylaxis
D. Renal failure
Osteosarcoma risk
The nurse is administering raloxifene (Evista). What is the most common side effect the nurse should assess for?
A. Hypertension
B. Hot flashes
C. Depression
D. Nausea
Hot flashes
Which medication requires dental clearance before starting due to risk of jaw complications?
A. Raloxifene
B. Denosumab
C. Teriparatide
D. Alendronate
Denosumab
A patient with gout is receiving care. Which lab value is most important for the nurse to monitor?
A. Serum potassium
B. Serum uric acid
C. Blood glucose
D. Vitamin D
Serum uric acid
Which finding is most consistent with osteoarthritis (OA)?
A. Symmetrical joint involvement
B. Autoimmune markers in the blood
C. Morning stiffness that improves with activity
D. Joint pain with systemic fever and fatigue
Morning stiffness that improves with activity
A patient has rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The nurse knows which is true?
A. RA involves cartilage only and is non-inflammatory
B. RA affects a single joint and is self-limiting
C. RA involves systemic inflammation and joint deformity
D. RA improves with cold therapy and immobility
RA involves systemic inflammation and joint deformity
Which of the following medications can increase uric acid levels, worsening gout?
A. Metformin
B. Thiazide diuretics
C. Calcium supplements
D. NSAIDs
Thiazide diuretics
A patient taking long-term corticosteroids is at increased risk for which bone-related condition?
A. Osteomalacia
B. Paget’s disease
C. Osteoporosis
D. Hyperparathyroidism
Osteoporosis