Chapter 9: The Joints
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What is a joint (aka an articulation)?
a point of contact between bones, cartilage and bones, and teeth and bones.
What two major functions do joints serve?
they provide mobility/flexibility and they hold the skeleton together
What is joint classification based on?
the presence/absence of a space between the articulating bones and/or the degree of movement allowed at the joint
What are synostosis (bony joints)?
immovabale joints formed when two bones join together and ossify into one single bone
What is an example of a synostosis?
the fetal ilium, ischium, and pubis fuse to form the pelivic griddle/hip bones
What are synarthroses (fibrous joints)?
joints where bones are connected by fibrous connective tissue. these joints are immovable or allow slight movement
What are 3 examples of a synarthroses?
sutures (in skull)
gomphoses (tooth socket)
syndesmosis (bone linked together by ligament)
What are cartilaginous joints?
joints where the bones are connected entirely by cartilage (either hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage)
What are the two types of cartilaginous joints?
synchondoses and symphysis
What is a synchondroses?
a type of cartilaginous joint where the bones are joined together by hyaline cartilage
What is a symphysis?
a type of cartilaginous joint where the bones are joined together by fibrocartilage.
What is an example of synchondroses?
the epiphyseal plate
What is an example of symphysis?
the pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs
What are diarthroses (synovial joints)?
the most common and most movable type of joint in the human body. these joints have a fluid-filled joint synovial cavity that allows for a wide range of motion.
What are the major parts of diarthroses?
a synovial cavity
articular (hyaline) cartilage
ligaments
a synovial membrane
bursa
tendons
What is a synovial cavity?
a space that separates the articulating bones in this synovial joint
What is articular (hyaline) cartilage?
cartilage that covers the ends of the articulating bones that prevents friction between the bones
(in some joints, the cartilage forms pads between bones known as menisci)
What are ligaments?
connective tissue cords that join bones together
What is a synovial membrane?
membrane that covers the surface of the articular capsule (a protective sleeve that surrounds the synovial joint and encloses the synovial cavit)
the cells in this membrane secrete synovial fluid
What does synovial fluid do?
it nourishes and lubricates articular cartilage
What is a bursa?
a liquid filled pad in diarthroses that further reduce friction and stress at the ends of articulating bones
What is bursitis?
inflammation of the bursa pads
What are tendons?
connective tissue cords that attach muscles to bone
What is tendinitis?
inflammation of the tendon sheaths that surround the tendons
What are the types of synovial joints?
gliding joints
hinge joints
pivot joints
condyloid joints
saddle joints
ball and socket joints
What are gliding joints?
a type of synovial joint where bones only move side to side past each other
example: between the bones of the foot
What is a hinge joint?
a type of synovial joint that works like a hinge door, it allows movement in one plane only, bending and straightening
one bone is shaped like a rounded bump and the other bump is has a matching dip for the bump to fit in
example: the elbow joint between humerus and ulna
What are pivot joints?
a type of synovial joint where the rounded portion of one bone articulates with a bone or ligament ring of another bone and allows for some rotational movement
example: atlas/axis joint allows you to rotate head no (side to side)
What are condyloid joints?
a type of synovial joint where an oval, convex surface of one bone fits into a shallow, oval-shaped concave surface of another bone
example: wrist joint
What are saddle joints?
a type of synovial joint where both bone surfaces are shaped like a saddle—each surface is concave in one direction and convex in the other. They fit together like a rider sitting in a saddle.
What are ball and socket joints?
a type of synovial joint where a spherical (ball-shaped) head of one bone fits into a cup-like (concave) socket of another bone.
example: shoulder joint
What is a flexion?
bending of a joint
What is an extension?
straightening of a joint
What is an abuduction?
movement of a limb away from the midline of the body
What is an adduction?
movement of a limb towards the midline of the body
What is elevation?
raising a body part vertically
What is depression?
lowering a body part vertically
What is a supination?
rotation of the forearm that results in the palm facing upward or forward
What is a pronation?
rotation of the forearm that results in the palm facing downward or out
What is rotation?
when a bone turns around its own longitudinal axis
What is dorsiflexion?
bending the foot upward to the knee
What is plantarflexion?
bending the foot downward away from the shin
What is range of motion?
the degrees through which on ebone can move relative to another
What are 3 factors that affect the ROM and stability of joints?
structure of the aritculating bones
strength of ligaments and joint capsules
action of the muscles and tendons
What is the temporomandibular joint?
the jaw joint
What makes up the temporomandibular joint?
the mandibular condyle attaches to the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone and is held together by the lateral ligament and sphenomandibular ligament
What is the largest joint in the human body?
the knee joint, it is composed of three joints connecting the femur, tibia, and patella
What are the parts of the knee?
articular capsule
menisci
collateral ligaments (medial and lateral)
cruciate igaments (anterior and posterior)
What is the articular capsule of the knee?
an open space around the articulating bones of the knee
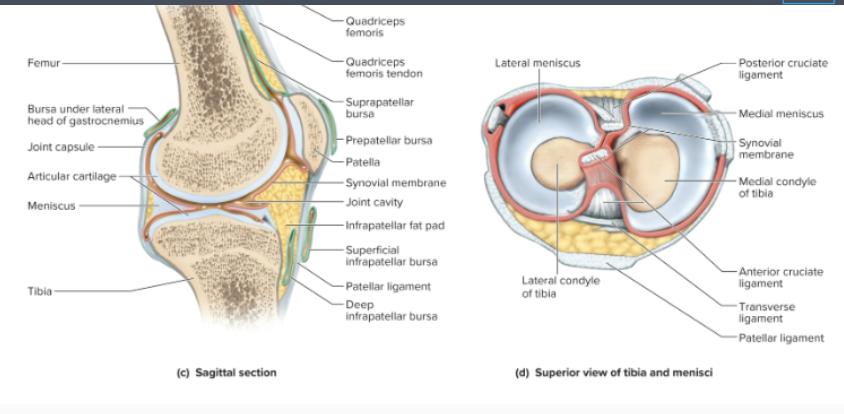
What is the menisci? (plural forms of meniscus)
fibrocartilage pads located between the tibial and femoral condyles that reduce friction between the articulating bones
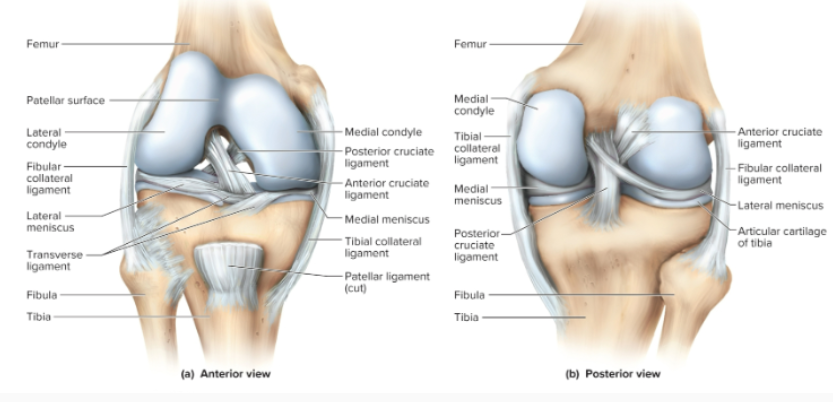
What do the medial and lateral collateral ligaments of the knee do?
ligaments that hold the tibia and the femur together as well as the fibula to the femur
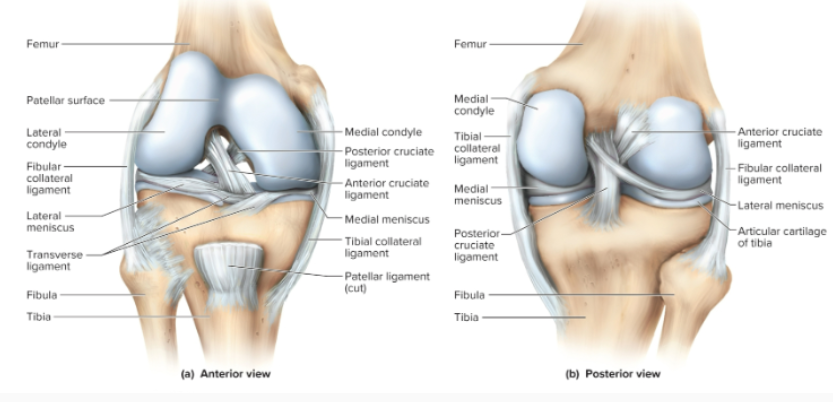
What do the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments of the knee do?
they form an x under the patella and hold the fibia and femur together
What is arthroscopy?
a procedure that is used to examine the internal protion of a joint using an arthroscope, it is used because it greatly reduces the tissue damage to the joint
What is arthroplasty?
the surgical replacement of a joint
What is the glenohumeral joint?
the shoulder
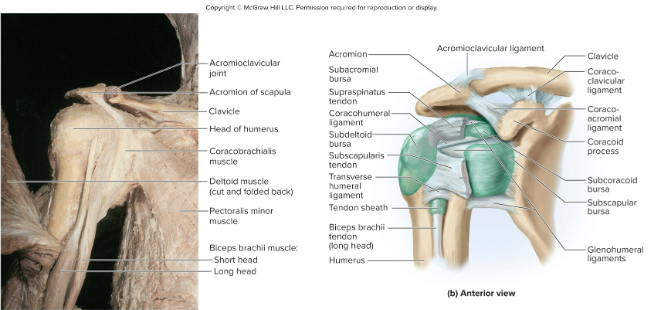
Anatomy of the glenohumeral joint:
the head of the humerus attaches to the glenoid cavity of the scapula and the gelnoid labrum cartilage layer surrounds the attachment site
How is the glenohumeral joint held in place?
by the coracohumeral ligament and the glenohumeral ligament
What is the rotator cuff?
a collection of muscles that surrounds and protects the shoulder joint
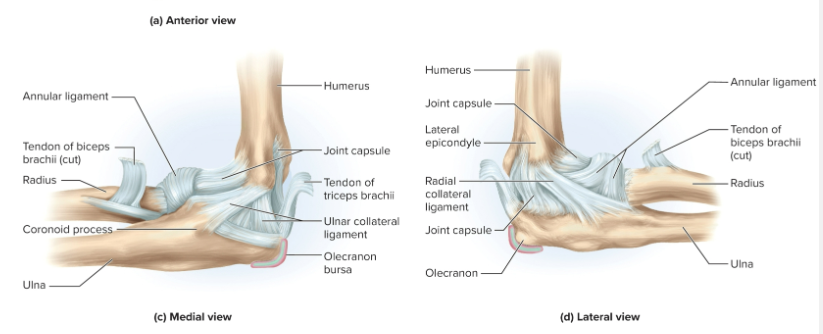
Anatomy of the elbow joint:
the joint involves attachment of the radius and ulna to the humerus
What holds the elbow joint together?
the ulnar collateral ligament and the radial collarteral ligament
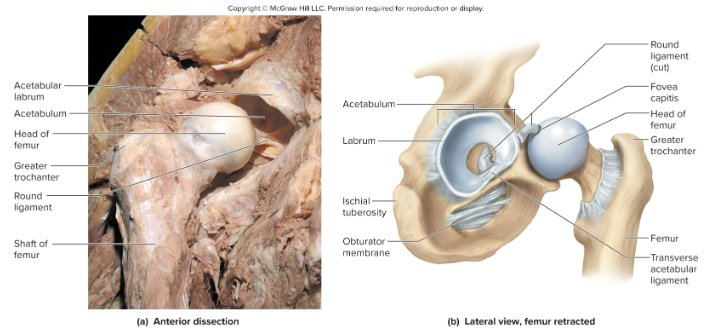
anatomy of the hip joint:
the head of the femur attaches to the acetabulum of the ox coxa and it surrounded by the acetabular labrum
What ligaments hold the hip joint together?
the iliofemoral ligament, the pubofemoral ligament, and the ischiofemoral ligament
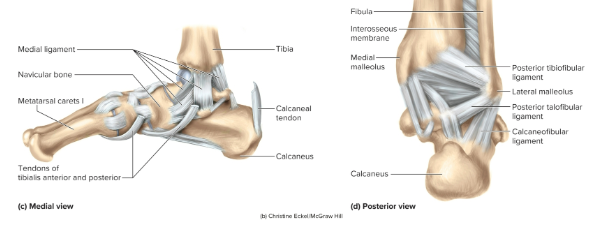
Anatomy of the ankle joint:
the tibia articulates medially with the talus of the foot and the fibula articulates laterally with the talus
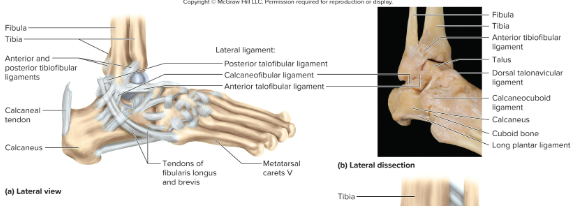
What ligaments hold the ankle joint together?
a variety of ligametns, including the anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments
What is rheumatism?
any painful state of the body’s support structures
What is arthritis?
inflammation of a joint
What is osteoarthritis?
joint degeneration characterized by deterioration of articular cartilage
What is gouty arthritis?
occurs when sodium urate crystals deposit in and destory joints
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
autoimmune disease in which the person's antibodies attack and destroy joint tissue
What is lyme disease?
joint disorder characterized by joint stiffness, pain, headache, fever, and chills that is caused by the bacterium, borrelia borgdorferi
What is a sprain?
the forcible wrenching or twisting of a joint with partial rupture to its attachments without disslocation occuring
What is a strain?
overstretching of a muscle
What is dislocation?
the displacement of a bone from a joint with tearing of ligaments, tendons, and articular capsules
What is arthralgia?
pain in a jointW
What is arthrosis?
disease of a joint
What is bursectomy?
surgical removal of a bursa
What is chondritis?
inflammation of cartilage in a joint
What is synovitis?
inflammation of a synovial membrane in a joint