Hematology
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Neutrophil maturation process
Myeloblast
Promyelocyte
Myelocyte
Metamyelocyte
Band
Neutrophil
how long does it take a neutrophil to mature
5-7 days
Abnormal lymphocyte morphology
Reactive lymphocytes
Granulated lymphocytes
Lymphoproliferative and myeloproliferative disease
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Acute lymphocytic leukemia
the most consistent morphologic abnormality observed in reactive lymphocytes
Increased blue staining of the cytoplasm
Which animal species may show the presence of Döhle bodies within their neutrophil cytoplasm without the presence of toxicity or inflammatory disease?
feline and equine
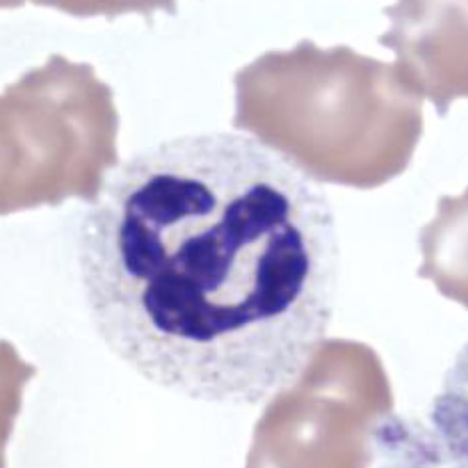
Which cytologic description matches this image?
Platelet clumps
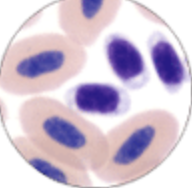
Which classification best describes this image?
Nonmammalian platelet
What are the two types of reticulocytes dogs and cats both have
aggregate reticulocytes
Punctate reticulocytes
What is the most common cause of decreased RETIC-HGB?
inflammation
What is RETIC-HGB?
reflects amount of hemoglobin in the reticulocyte
measures “quality” reticulocyte
sensitive and specidc indicator of iron availibitliy for normal RBC production
Which type of reticulocytes do automated analyzers count for the absolute reticulocyte count?
Aggregate reticulocytes
Whole blood is composed of ________ & __________
fluid & cells
3 types of blood cells are
RBC, WBC, and thrombocytes
fluid portion of blood =
plasma
agranuloctyes
lymphocytes, monocytes
granulocytes
Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
RBC maturation process
Rubriblast
Prorubricyte
Basophilic rubricyte
Polychromatophilic rubricyte
Metarubricyte
Reticulocyte
Erythrocyte
A red blood cell count measures
number or red blood cells circulating in the blood, indicating potential anemia or dehydration
Hemoglobin (HGB) measures the
oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells; low level can indicate anemia
Hematocrit demtermines the
% of red blood cells in the blood, another indicator of anemia or hydration status
mean corpuscular volume indicates
average size of red blood cells, which can help differentiate types of anemia
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
average hemoglobin concentration per red blood cell
White blood cell count measures the
total # of white blood cells, which are important for fighting infection
Leukocyte differential determines the
different types of white blood cells to identify specific types of infections or inflammatory conditions.
Platelet count measures the
number of platelets which are essential for blood clotting
hematopoietic stem cell gives rise to
common myeloid precursor and common lymphoid precursor
common myeloid precursor gives rise to
megakaryocyte
erythrocyte precursor / rubriblast
granulocyte precursor
Monocyte precursor
common lymphoid precursor gives rise to
t lymphocyte/NK cells
b lymphocytes
organs involved in hematopoisesis
liver, spleen, thymus, red bone marrow
which organ releases erythropoietin into the blood stream
kidneys
Erythroid progenitor cells respond yo EPO and stimulates
proliferation and differentiation of RBCs precursors
increased oxygen levels tell kidneys to ____ producing erythropoietin, maintaing hemostasis
stop
monocytes have a ____ appearance
grey
leukocyte maturation process
myeloblast
promyelocyte
Myelocyte
Band
Granulocyte
Proliferation pool
cells capable of mitosis
Maturation pool
cells no longer capable of mitosis
maturation pool consists of
band cells and segmented granulocytes
dog common blood collection sites
cephalic, jugular, saphenous vein
Cat common blood collection sites
cephalic, jugular, femoral vein
horse common blood collection sites
jugular vein
cattle common blood collection sites
coccygeal and jugular vein
Bird common blood collection sites
jugular and medial metatarsal
Rabbit common blood collection sites
ear vein
Rodent common blood collection sites
tail vein
Heparin is
antithrombin
EDTA is
chelates calcium
oxalates
chelates calcium
Citrates
chelates calcium
most abuntant type of WBC
Granulocyte
Neoplastic blood in the cells in blood or bone marrow
Leukemia
which species are known for larger platelets
cats
anticoagulants are used when _____ ____ or ______ samples are needed
whole blood or plasma
plasma is
liquid minus blood cells
Heparin works by preventing the
conversion of prothrombin to thrombin
______ should NOT be used for WBC morphology
heparin
Preferred anticoagulant because it does not alter cell morphology
EDTA