(3, 4) Magnetic Circuits + Electromagnetic induction
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is the difference between magnetising force and magnetomotive force? (A, At/m, m) (At/m, A, m)
Magnetomotive force = current * coil windings amount (Fm=IN).
Magnetising force = magnetomotive force / length of magnetic circuit (H=IN/l)
What is magnetic reluctance?
A material opposing the formation of magnetic flux (resisting being magnetised), determines amount of magnetising force required to create given amount of flux
How does the length of a magnetic circuit affect its reluctance?
(Like electrical wire resistance) reluctance is proportional to length
How does cross-sectional area of magnetic circuit affect reluctance?
(Like electrical wire resistance) reluctance is inversely proportional to cross-sectional area (reduces when larger)
How does permeability affect reluctance?
reluctance is inversely proportional to permeability (reduces when more permeable)
Compare Ohms Law to Hopkinson's Law
Ohms Law = V=IR, Hopkinsons Law = mmf = Φ*Rm. Very similar, except one's for electrical circuits and one's for magnetic circuits
What are the names of the two magnetic quantities shown on a hysteresis loop?
B = Flux Density, H = Magnetising Force
What does it mean when a magnetic material is saturated?
When the flux density has almost reached its maximum for the material. Attempting to apply more mmf will have negligible effects (like capacitor)
What are the saturation regions of a hysteresis loop?
Pre-saturation: from start where magnetising force increases in near-linear fashion
Saturation region: where curve turns to form "knee", increase in flux density starts having negligible effects
Post-saturation region: negligible increase in saturation from higher mmf
What happens to permeability of a magnetic material as flux density increases?
Permeability effectively increases at high flux densities
What is coercive force?
Magnetising force required to reduce flux to zero
What axis on a hysteresis loop is for coercivity?
X axis
What is remanence?
(residual magnetism) A measure of the remaining magnetisation when driving field is zero
What is the relationship between area of a hysteresis loop and energy loss due to hysteresis?
Greater area in loop means more energy required to magnetise material in opposite direction
For a transformer on AC with flux direction being reversed every 20ms, what size hysteresis loop area is better?
Small, less energy to switch
For a material that needs to stay magnetised after magnetising force has been removed, what size hysteresis loop would be better?
Large, needs to retain more magnetising force
What is hysteresis/iron loss?
Energy lost due to the oscillation of magnetic saturation on a hysteresis loop, larger area means more loss
Magnetic circuits on AC have voltages and therefore unwanted currents induced in the iron circuit called eddy currents, which heat up the iron core. How can this be reduced?
Laminating the iron core to produce electrical resistance
What is magnetic leakage?
Useless magnetic force leaking into alternate paths from intended design
What is magnetic fringing?
Flux that spreads out and becomes less compact when passing through high reluctance air gaps
How does hysteresis contribute to energy losses in magnetic circuit?
Hysteresis is energy required to overcome residual magnetism in an iron circuit, creating heat loss from constantly realigning iron molecules
How does magnetic leakage contribute to energy losses in a magnetic circuit?
Magnetic leakage causing stray eddy current losses in surrounding materials
What are eddy currents?
Currents induced in the core material by alternating flux which can generate waste heat energy
With pickup and dropout voltages of a relay, why is dropout voltage lower than pickup voltage?
Dropout voltage is required to de-energise the relay, but is lower because an energised circuit has lower reluctance (easier to keep energised than to initially energise)
(Faraday's Law) What are 3 things required for electromagnetic induction to occur?
Conductor, magnetic field, relative motion between the two
(Faraday's Law) what is the relationship between the number of turns being cut by a changing magnetic field and the value of EMF produced?
EMF produced is proportional to number of turns being cut (more turns cut, more emf produced)
(Faraday's Law) What is the relationship between change in value of flux and value of EMF produced?
EMF produced is proportional to change in flux (more flux change, more EMF)
What three parameters determine magnitude of a generated EMF in a magnetic field?
Flux density of magnetic field, length of conductor cutting through magnetic field, velocity of conductor cutting relative to magnetic field
What is the relationship between flux density of the field and value of EMF produced?
Higher flux density, more lines of flux cut (higher flux density = more EMF)
What is the relationship between length of conductor and value of EMF?
Longer conductor, more EMF
What is the relationship between velocity of relative motion and EMF produced?
Relative velocity between conductor/turns and field is proportional to EMF produced (higher velocity, greater EMF)
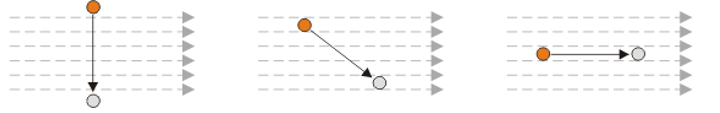
How many lines of force are cut in each pic and how do they affect the voltage generated?
In first diagram, conductor cuts 6 lines of force, and the maximum amount of voltage is generated. In the second, 4 lines cut, which creates less voltage (sin part of e=Blvsin(θ)), third cuts no lines of force so no voltage generated
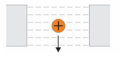
Using Fleming’s Right Hand Rule for Generators, what direction are the magnetic dipoles?
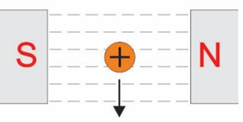

Using Fleming’s Right Hand Rule for Generators, what direction is the motion?
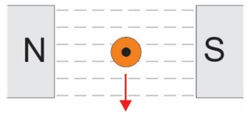

Using Fleming’s Right Hand Rule for Generators, is the current running into the page or out?
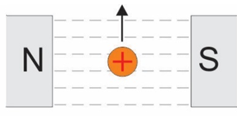

What is relationship between current through the conductor and the magnetic field around the conductor? Also how does changing amount of current affect magnetic field?
As current increases, conductor’s magnetic field’s range increases. This flux cuts through conductor material inducing emf in conductor. Using Flemings’s right hand rule, induced emf opposes change in current
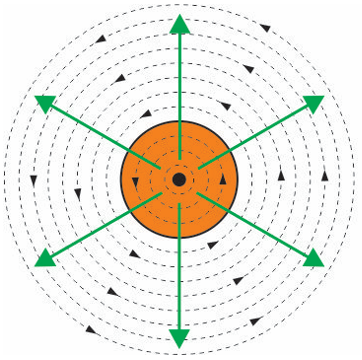
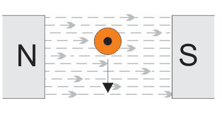
Using right-hand grip rule and fleming’s right hand rule, show how the magnetic field is distorted by the field around the conductor and what force is exerted on the conductor
When conductor is moved down through the field, induced EMF produces flux opposing downward force (drives conductor upwards)
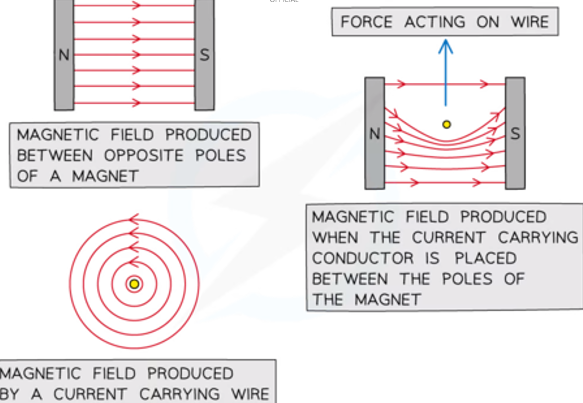
How does an AC current clamp meter work?
Changing conductor flux cuts clamp conductors, inducing EMF measured by meter
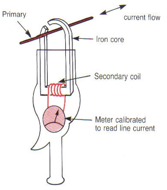
How does an AC transformer work?
AC Current supplied to primary winding, changing flux induces EMF in second winding, EMF generates changing magnetic field in secondary winding, generating current