fong - osteomyelitis
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
osteomyelitis
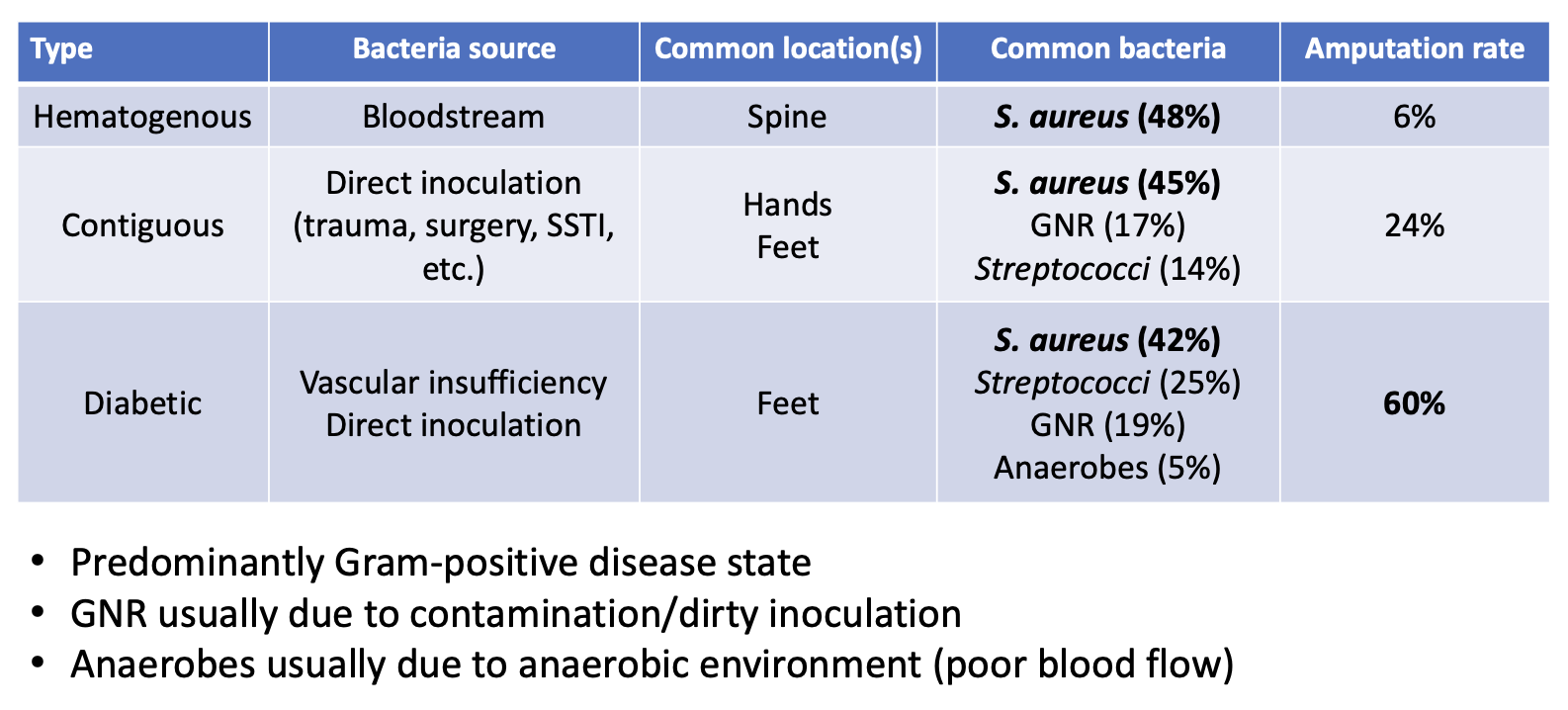
inflammation of the bone caused by an infecting organism (monomicrobial > > > polymicrobial)
contiguous (trauma, surgery, SSTI progression)
hematogenous (bacteremia from another source)
vascular insufficiency (diabetic foot infection — polymicrobial)
epidemiology and risk factors
diabetes
recent injury (broken bones)
orthopedic surgery (bone/joint repair)
IVDU (IV drug use)
dialysis
catheter use
immunosuppression (malignancy, liver disease, etc)
anything that increases gram-positive bacteremia risk
microbiology
S. aureus
up to 1/3 MRSA
group B Streptococcus
newborns
GNR’s
contiguous > hematogenous
fungal (rare)
mycobacterial (rare)
osteomyelitis pathophysiology
clinical presentation
diagnostic tools (imaging)
X-ray:
helps rule out other diagnoses but not very sensitive
CT scan:
can reveal extent of destruction and guide bone biopsies
less useful than MRI but less costly
imaging:
MRI is most sensitive and specific
can detect infection days after onset
diagnostic/monitoring tests
WBC
not reliably elevated, especially in chronic osteomyelitis
C-reative protein (CRP)
produced by liver in response to any infection (non-specific)
elevated within hours of infection
should return to normal within a week after appropriate antibiotics
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
generally elevated in osteomyelitis, but slower responder than CRP
*NOT very useful diagnostics, but helpful for monitoring
diagnostic cultures
recommend withholding antibiotics until cultures obtained
osteomyelitis usually not acute illness presenting with hemodynamic instability
blood culture
unlikely positive unless systemic signs of infection (SIRS)
bone biopsy
gold standard to identify organism + bone destruction, but difficult to obtain
wound culture (e.g, diabetic foot)
very limited utility, can capture the wrong bugs unless done in sterile surgery
good quality cultures are crucial for appropriate treatment
surgery (source control)
must eliminate dead bone (mainly chronic osteomyelitis)
difficult for vertebral (spinal) osteomyelitis
radical debridement until down to living bone
inadequate debridement leads to recurrence
may require reconstruction if it results in large dead space
bone grafts, antibiotic beads, muscle flaps
last resort is amputation
treatment

landmark trial: OVIVA
RCT of 1054 patients with osteomyelitis to receive IV or oral antibiotics within 7 days of surgery or start of therapy
primary outcome: treatment failure at 1 year
oral antibiotics noninferior to IV antibiotics
treatment duration
acute (uncommon in adults):
antibiotics alone may be sufficient
treatment duration: 4-6 weeks
subacute/chronic:
surgery likely required for tissue/bone removal
treatment duration: ≥ 6 weeks
treatment duration for subacute/chronic begins when removal of necrotic bone/tissue is complete (if possible)
takes 6 weeks for bone to be covered by vascularized tissue
can monitor normalization of CRP/ESR ± repeat imaging
presence of foreign material/hardware may require lifetime suppression
osteomyelitis with hardware
highest risk of infection within 2 years of hardware implantation
most likely organism: S. aureus or S. epidermidis
add rifampin 450 mg IV/PO BID
rifampin to penetrate biofilm formation on prosthetic material
if no cultures, what do you do?
cover for likely pathogens
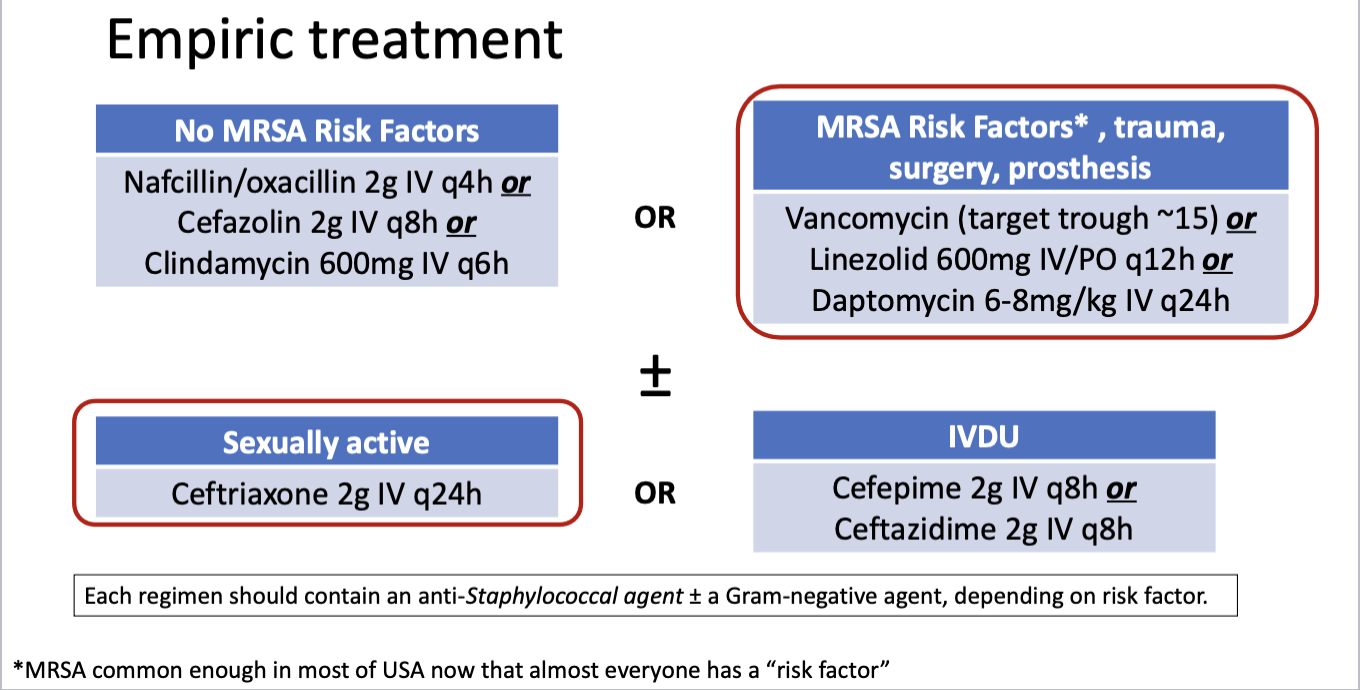
S. aureus (consider MRSA risk factors)
Streptococci spp.
gram-negatives if contaminated/trauma or immunocompromised
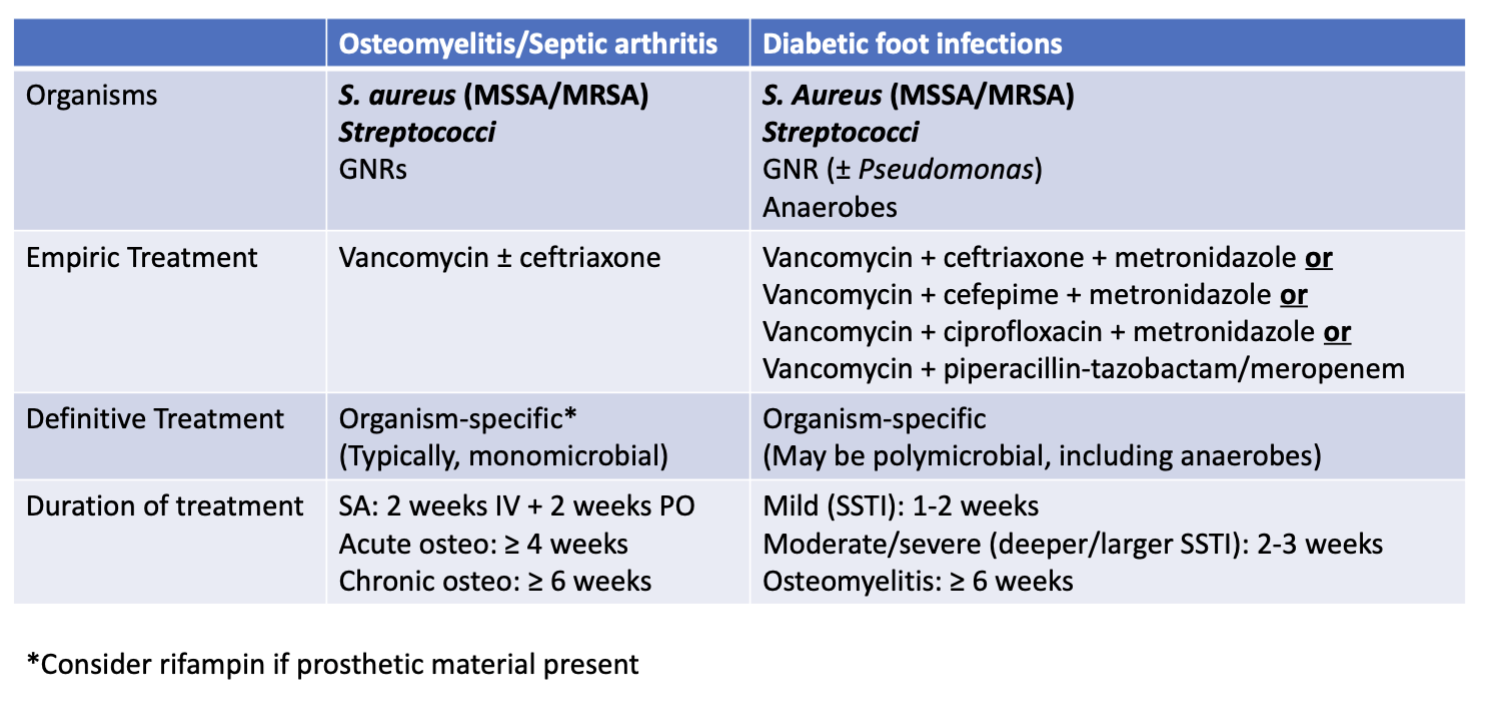
if diabetes-related (foot infection):
consider adding gram-negative and anaerobic coverage
potentially requiring ≥ 6 weeks of vancomycin ± ceftriaxone or piperacillin-tazobactam?
osteomyelitis monitoring
clinical improvement
symptoms decrease (pain, tenderness, warmth, etc)
improved movement
CRP, ESR to monitor inflammatory response (WBC likely not helpful)
imaging to demonstrate improvement/completion of treatment
must monitor antibiotics considering long duration, to name a few:
vancomycin: levels, AKI
nafcillin/oxacillin: AKI (AIN), hepatoxicity, blood dyscrasias
daptomycin: rhabdomyolysis
fluroquinolones: separate from divalent cations
all antibiotics: C. difficile
septic arthritis
infection of joint
bacteria > fungi/mycobacteria
hematogenous or direct
4-10 per 100,000 patients-years
risk factors:
rheumatoid or osteoarthritis
joint prosthesis
IV drug use
alcholoism
diabetes
intra-articular corticosteroid use
SSTI
complications: osteomyelitis, mortality (up to 10%)
septic arthritis: symptoms and diagnosis
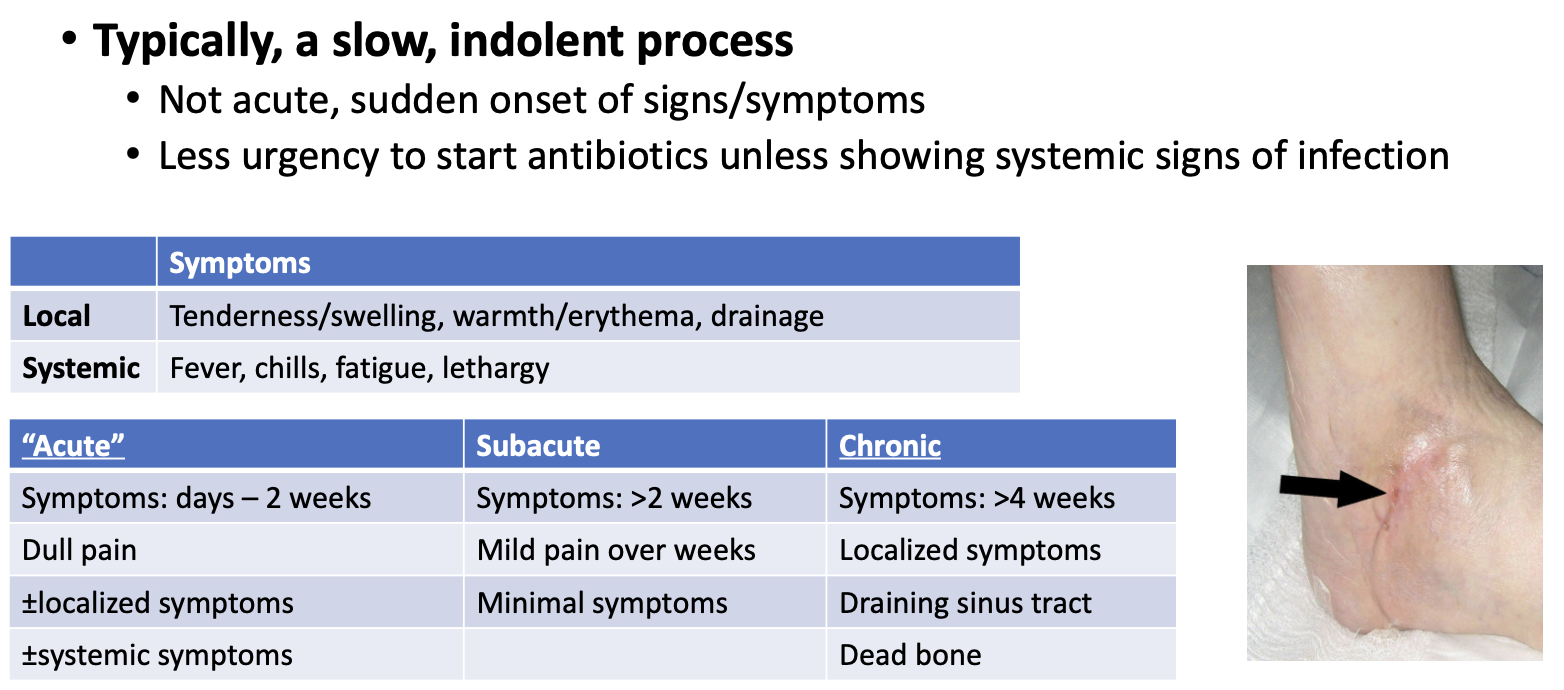
1-2 weeks of erythema, pain, fever, and restricted joint movement
“hot joint”
less common: sweats, rigors
blood cultures positivity: < 20%
get synovial (joint) fluid aspirate, but can be difficult
WBCs > 50,000/microliter highly suggestive of infection
antibiotics should be withheld prior to cultures unless patient is hemodynamically unstable
microbiology

empiric treatment
no MRSA risk factors = uncommon
most likely: vancomycin + ceftriaxone
*any MRSA + ceftriaxone
definitive treatment and management
de-escalate based on cultures (blood or synovial)
if culture negative, likely stuck with vancomycin ± ceftriaxone
duration of treatment
2 weeks of IV therapy THEN at least 2 weeks of oral therapy
monitoring
like osteomyelitis
diabetic foot infections (DFI) pathophysiology
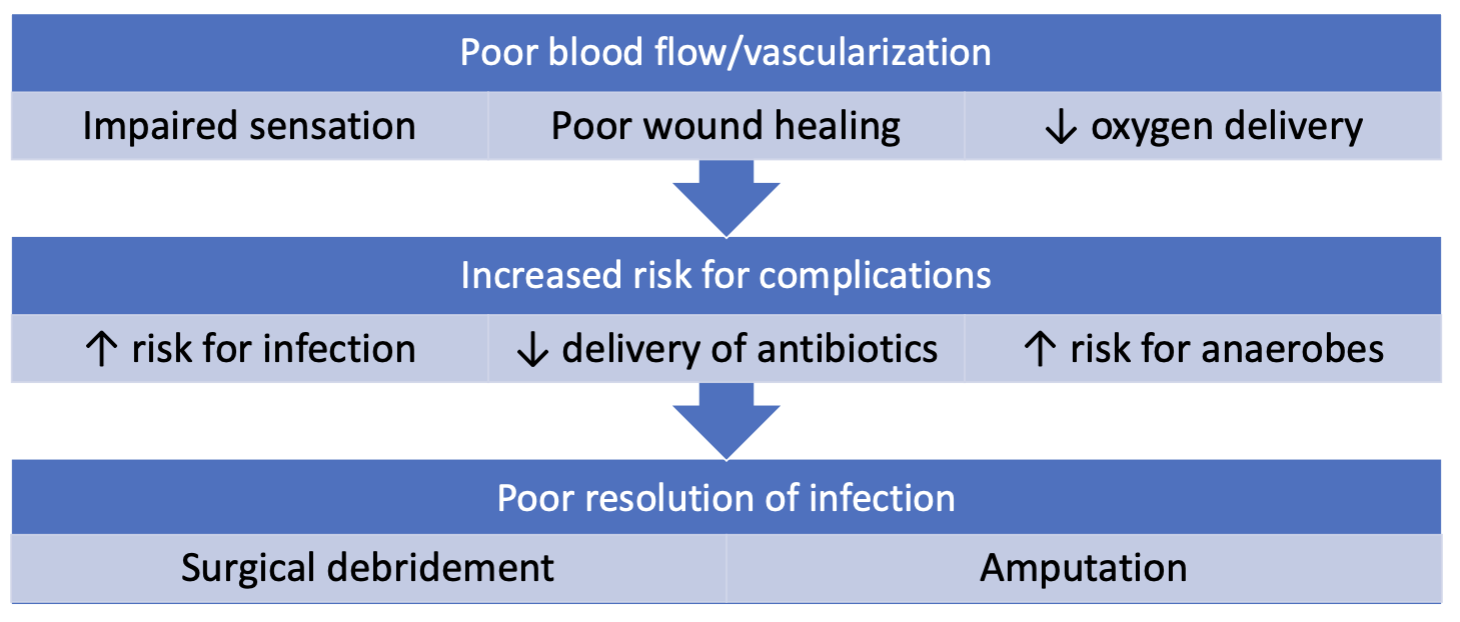
diabetic food infections (DFI) management
goal: cure infection without amputation
antibiotics alone often fail and amputation often required due to:
poorly controlled diabetes
poor blood flow —> poor drug delivery
impaired immune system
necrotic tissue
osteomyelitis
prolonged therapy (adherence)
location (foot) increases chance of polymicrobial infection
skin, dirty, less oxygenation
anaerobes: often covered, especially if dead tissue present
DFI empiric therapy
cover: MSSA/MRSA + GNR (± Pseudomonas) ± anaerobes (B. fragilis+)
vancomycin OR linezolid OR daptomycin AND
ceftriaxone OR ciprofloxacin OR cefepime OR pip-tazo OR meropenem AND
metronidazole (unless using piperacillin-tazobactam or meropenem)
DFI definitive therapy
treat cultured organisms ± anaerobes (B. fragilis, etc)
if adequate debridement of dead tissue, anaerobic coverage NOT required
can use oral antibiotics
DFI antibiotic duration
adequate source control: 0-5 days
e.g. amputation with clean margins
mild (SSTI): 1-2 weeks
no bone involvement
moderate/severe (deeper/larger SSTI): 2-3 weeks
osteomyelitis: ≥ 6 weeks
try to avoid this duration by doing amputation
treatment take home points