physics - light & the EM spectrum (5.1 - 5.24)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
5.1 Ray diagrams
arrows show direction of light travel
normal: imaginary line perpendicular to surface
all angles measured from normal
angle of incidence: angle ray enters at
angle of reflection: angle ray exits at
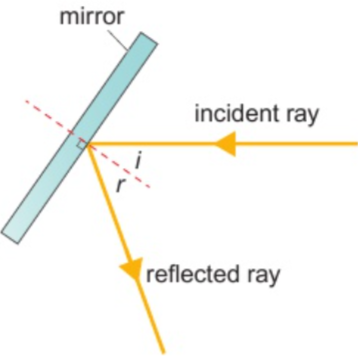
5.1 reflection
angle of incidence = angle of reflection (law of reflection)
5.1 refraction
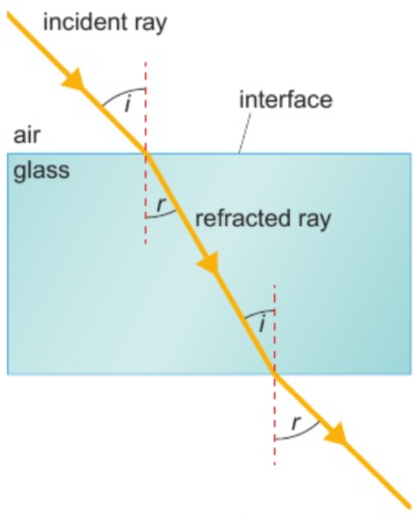
light ray → material where it travels at diff. speed: changes direction
light → medium where travels slower: bends towards normal
light → medium where travels faster: bends away from normal
(light meets interface at right angle - no change in direction)
5.1 total internal reflection
when angle of incidence > critical angle
light from water/glass → air with small angles of incidence - most light passes through interface, some reflected
angle of incidence increases - angle of refraction increases until refracted light passes along interface
angle of incidence increases more - light completely reflected inside glass
5.1 critical angle
angle of incidence TIR starts to occur at
5.2 specular vs diffuse reflection
specular: very smooth surfaces reflect light evenly
diffuse: rough surfaces scatter reflected light in all directions
5.3 colour of light - differential absorption at surfaces
white light: from sun/lamps; mix of diff. colours eyes see white
white light hits coloured surface - some colours that make it up absorbed & reflected
e.g. red object looks red - reflects red light, absorbs all other colours
e.g. white object looks white - reflects all colours
5.3 colour of light - transmission of light through filters
white light made into coloured light using filter
filter: transparent material, absorbs some colours in white light
e.g. blue filter - transmits blue light, absorbs all other colours
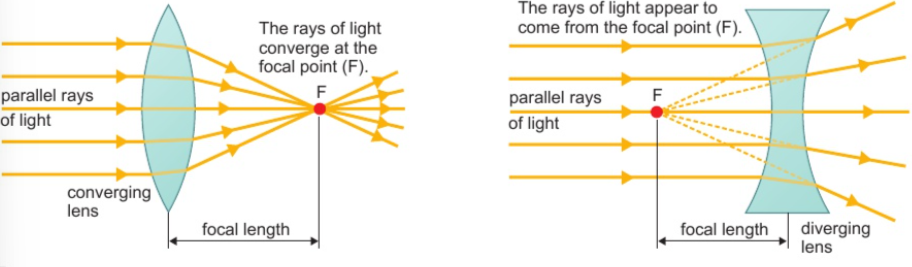
focal point
where parallel rays of light meet after passing through lens
focal length
distance between focal point & centre of lens
5.4 power of lens related to focal length & shape
more curved lens = shorter focal length = more powerful lens
5.5 similarities & differences in refraction of light by converging & diverging lenses (ray diagrams)
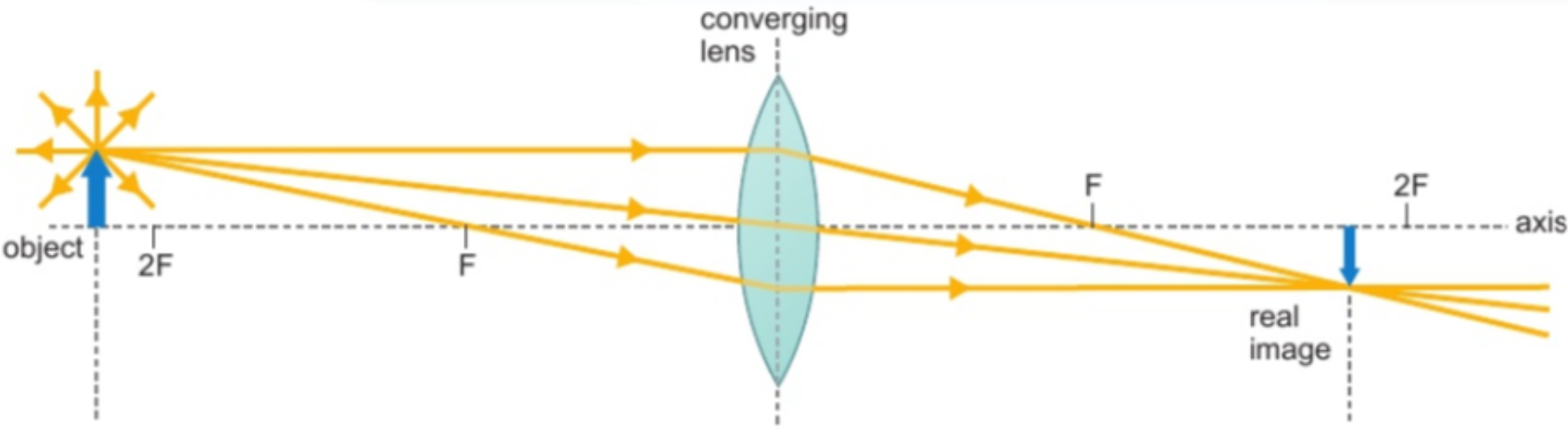
5.6 different types of lenses producing real images
can be projected onto screen - light rays converge
image on opposite side of lens to object
image inverted & smaller than object
produced by converging lenses
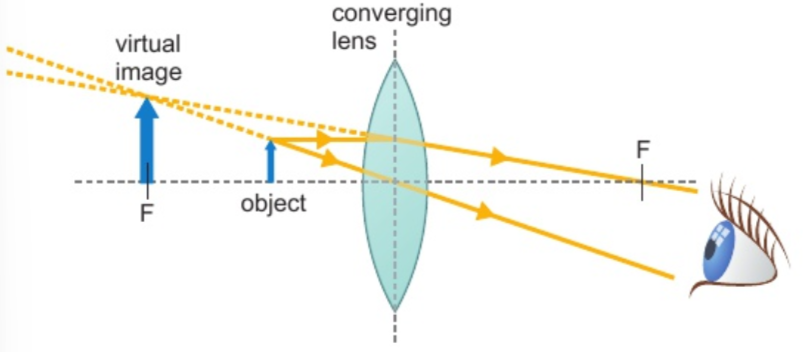
5.6 different types of lenses producing virtual images
cannot be projected onto screen - light rays don’t converge
image appears on same side of lens as object
image upright & bigger than object
produced by converging/diverging lenses
5.7 EM waves (type & speed)
transverse
travel at same speed in vacuum
5.8 EM waves transfer energy from source → observer - e.g.
e.g. light travels from source & reflected by object into eyes - light transfers energy from source → eyes (observer)
5.9 core practical: investigate refraction into rectangular glass blocks in terms of interaction of EM waves with matter
place piece of plain paper on desk; set up power supply, ray box & single slit so you can shine single light ray across paper
place rectangular glass block on paper & draw around it
shine ray of light into block, mark where light rays go with small crosses
take block off paper; use ruler to join crosses to show path of light & extend lines so they meet outline of block; join points where light entered & left block to show where it travelled inside block
measure angles of incidence & refraction where light entered & left block
repeat step 3-5 with ray entering block at diff. angles
move ray box to light ray reaches interface at right angles; note what happens to light as it enters & leaves block
5.10 EM spectrum order
radio waves
microwaves
infrared
visible
UV
x-rays
gamma rays
5.10 visible spectrum order
red
orange
yellow
green
blue
indigo
violet
5.11 EM spectrum (continuity, frequency & wavelength)
continuous
increasing frequency
decreasing wavelength
5.12 eyes detecting EM radiation
our eyes can only detect limited range of frequencies of EM radiation
5.13 what do diff. substances do?
absorb/transmit/refract/reflect EM waves in ways that vary with wavelength
5.14 effects of differences in velocities of EM waves in diff. substances
waves travel in straight lines unless reflected/refracted (bending of path of wave due to change in velocity)
EM waves travel at diff. speeds in diff. substances - causes reflection/refraction
5.15 bodies emitting radiation (intensity & wavelength - temp.)
all bodies emit radiation
object at higher temp. = greater intensity & shorter wavelength of radiation emitted
5.16 what is needed for body to be at constant temp.?
needs to radiate same average power it absorbs
power = amount of energy transferred in certain time
1W = 1J/s
5.17 what happens to body if average power it radiates is less/more than average power it absorbs?
radiates less power than absorbs = temp. increases
radiates more power than absorbs = temp. decreases
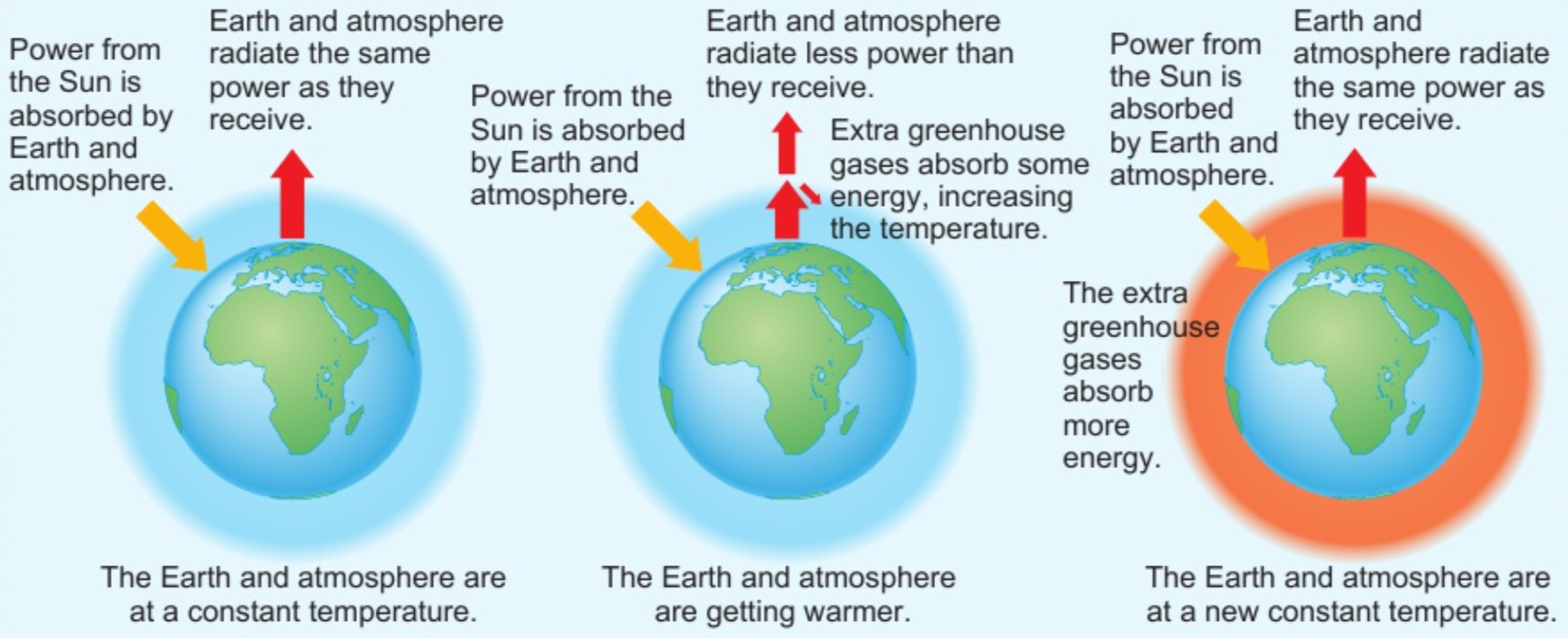
5.18 how is earth’s temp. affected by factors controlling balance between incoming emitted radiation?
earth’s surface absorbs about half of radiation from sun
re-radiates energy as infrared radiation (warms atmosphere)
greenhouse effect: some gases (greenhouse gases) in atmosphere naturally absorb some energy - keep earth at higher temp. than if no atmosphere
5.19 core practical: investigate how nature of surface affects amount of thermal energy radiated/absorbed
cover 4 boiling tubes in diff. coloured materials - shiny silver, dull grey, shiny black, dull black
pour same volume of hot water from kettle into each
inert bung with thermometer into each tube
measure temp. of water in each tube & start stop clock
record temp. of water in each tube every 2 mins for 20 mins
5.20 potential danger associated with EM wave
increases with increasing frequency
5.21 microwaves - harmful effects on people of excessive exposure
internal heating of body cells
5.21 infrared - harmful effects on people of excessive exposure
skin burns
5.21 UV - harmful effects on people of excessive exposure
damage to surface cells & eyes - leads to skin cancer & eye conditions
5.21 x-rays & gamma rays - harmful effects on people of excessive exposure
mutation/damage to body cells
5.22 radio waves - uses
broadcasting
communications
satellite transmissions
5.22 microwaves - uses
cooking - microwaves transfer energy → food, food heats up
communications
satellite transmissions
5.22 infrared - uses
cooking - grill/toaster transfers energy → food, food absorbs radiation & heats up
thermal imaging - shows amounts of infrared radiation emitted by diff. objects
short range communications
optical fibres
TV remote controls
security systems - detect infrared radiation emitted by intruders
5.22 visible light - uses
vision
photography - cameras detect visible light & record images
illumination
5.22 UV - uses
security marking - fluorescent materials only visible when UV light shines on them
fluorescent lamps - gas in lamps produces UV radiation when electric current passes through, coating inside glass absorbs UV & emits visible light
(fluorescence: some materials absorbs UV radiation & re-emit it as visible light)
detecting forged bank notes
disinfecting water - kills microorganisms
5.22 x-rays - uses
observing internal structure of objects - pass through materials visible light can’t
airport security scanners
medical x-rays - pass through muscles & fat, absorbed by bone
5.22 gamma rays - uses
sterilising food & medical equipment - transfer lots of energy & can kill cells (kill potentially harmful microorganisms)
detecting cancer - chemical that emits gamma rays injected into blood, collects in cancer cells, scanner outside body finds source of gamma rays & locates cancer
treating cancer - kills cells (radiotherapy)
oscillation definition
variation in current & voltage
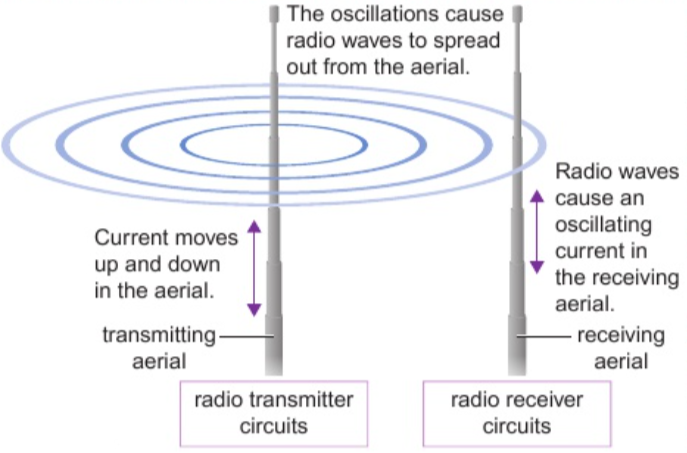
5.23 radio waves & electrical circuits
radio waves produced by/themselves induce oscillations in electrical circuits
5.24 what can changes in atoms & nuclei do?
generate radiations over wide frequency range (e.g. EM radiation produced by changes in electrons/nuclei in atoms)
be caused by absorption of range of radiations (e.g. makes atoms lose electrons)