MS 3605 VARIABLE COSTING MAY
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
If a firm produces more units than it sells, absorption costing, relative to variable costing, will result in
a. higher income and assets
b. lower income but lower assets
c. higher income but lower assets
d. lower income and assets
a. higher income and assets
Under absorption costing, if sales remain constant from period 1 to period 2, the company will report a larger income in period 2 when
a. period 2 production exceeds period 1 production
b. period 1 production exceeds period 2 production
c. variable production costs are larger in period 2 than period 1
d. fixed production costs are larger in period 2 than period 1
a. period 2 production exceeds period 1 production
The variable costing format is often more useful to managers than the absorption costing format because
a. costs are classified by their behavior
b. it is required for external reporting
c. costs are always lower
d. it justifies higher product prices
a. costs are classified by their behavior
When a firm prepares financial reports using absorption costing
a. profits will always increase with increase in sales
b. profits will always decrease with decreases in sales
c. profits may decrease with increased sales even if there is no change in selling prices and costs
d. decreased output and constant sales result in increased profits
c. profits may decrease with increased sales even if there is no change in selling prices and costs
Which of the following statements is true for a firm that uses variable costing?
a. The cost of a unit of product changes because of changes in the number of units manufactured
b. Profits fluctuate with sales
c. An idle facility variation is calculated
d. None of the given choices
b. Profits fluctuate with sales
Net income determined using full absorption costing can be reconciled to net income determined using variable costing by computing the difference between:
A. fixed manufacturing overhead costs deferred in or released from inventories.
B. inventoried discretionary costs in the beginning and ending inventories.
C. gross margin (absorption costing method) and contribution margin (variable costing method).
D. sales as recorded under the variable costing method and sales as recorded under the absorption costing method.
A. fixed manufacturing overhead costs deferred in or released from inventories.
Which of the following statements is correct?
A. When production is higher than sales, absorption costing net income is lower than variable costing net income
B. If all products manufactured during the period are sold in that period, variable costing net income is equal to absorption costing net income.
C. When production is lower than sales, variable costing net income is lower than absorption costing net income
D. When production and sales level are equal, variable costing net income is lower than absorption costing net income.
B. If all products manufactured during the period are sold in that period, variable costing net income is equal to absorption costing net income.
As compared with total absorption costing profit over the entire life of a company, total variable costing profit will be
A. less
B. greater
C. equal
D. substantially greater or less depending upon external factors
C. equal
Using absorption costing, fixed manufacturing overhead costs are best described as
a. Direct period costs.
b. Indirect period costs.
c. Direct product costs.
d. Indirect product costs.
d. Indirect product costs.
Which of the following groups prefer variable costing for their reporting?
A. Internal decision maker
B. Bureau of Internal Revenue
C. Stockholders
D. Securities & Exchange Commission
A. Internal decision maker
How will a favorable volume variance affect net income under each of the following methods?
Absorption - Variable
a. Reduce - No effect
b. Reduce - Increase
c. Increase - No effect
d. Increase - Reduce
a. Reduce - No effect
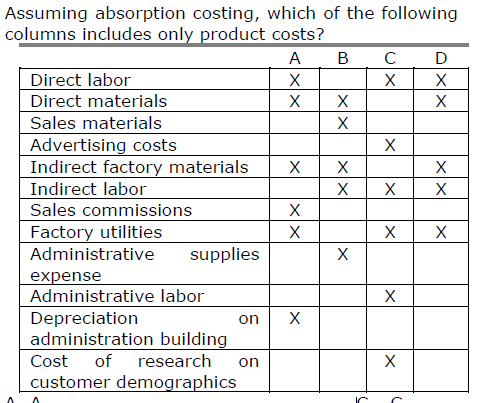
Assuming absorption costing, which of the following columns includes only product costs?
A. A.
B. B.
C. C.
D. D.
D. D.
Which of the following is(are) closely related to variable costing than to absorption costing?
1. Predetermined fixed overhead
2. Unit sales
3. Production units
4. Contribution margin
5. Gross margin
6. Volume variance
7. Cost behavior
8. Management accounting
A. 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8
B. 2, 4, 7, 8
C. 1, 3, 4, 7, 8
D. 1, 3, 5, 6
B. 2, 4, 7, 8
At its present level of operations, a small manufacturing firm has total variable costs equal to 75% of sales and total fixed costs equal to 15% of sales. Based on variable costing, if sales change by P1.00, income will change by
a. P0.25
b. P0.10
c. P0.75
d. Undeterminable
a. P0.25
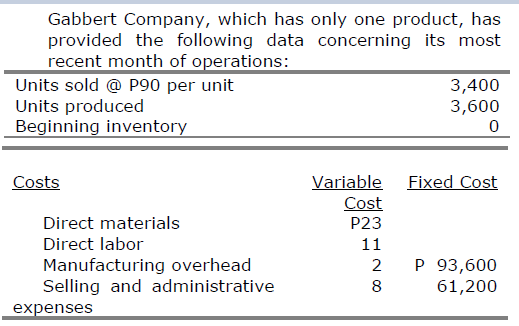
What is the total period cost for the month under the variable costing approach?
a. P93,600
b. P154,800
c. P88,400
d. P182,000
d. P182,000
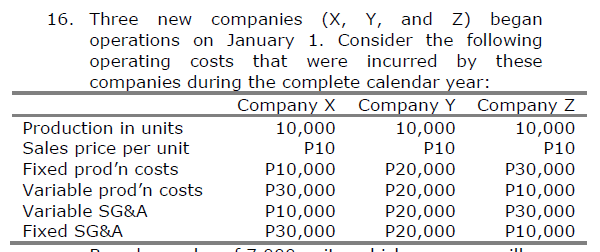
Based on sales of 7,000 units, which company will report the greater income before income taxes under variable costing?
a. Company X
b. Company Y
c. Company Z
d. All of the companies will report the same income.
a. Company X
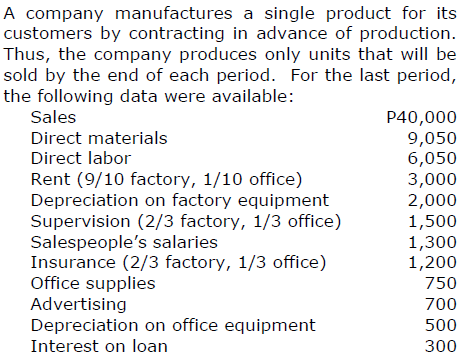
The gross profit margin percentage (rounded) was
a. 34% c. 44%
b. 41% d. 46%
d. 46%
Lauder Company produces a single product. During March, the company had net operating income under absorption costing that was P3,500 lower than under variable costing. The company sold 7,000 units in March, and its variable costs were P7 per unit, of which P3 was variable selling expense. If fixed manufacturing overhead was P2 per unit under absorption costing, then how many units did the company produce during March?
a. 5,250 units c. 6,500 units
b. 8,750 units d. 6,125 units
a. 5,250 units
Company B produces a single product. The company had 16,000 units in its beginning inventory. During the year, the company's variable production costs were P6 per unit and its fixed manufacturing overhead costs were P4 per unit. The company's net operating income for the year was P24,000 higher under absorption costing than it was under variable costing.
Given these facts, the number of units in the ending inventory must have been:
a. 22,000 units c. 6,000 units
b. 10,000 units d. 4,000 units
a. 22,000 units
This year, Roberts Company's income under absorption costing was P2,000 lower than its income under variable costing. The company sold 8,000 units during the year, and its variable costs were P8 per unit, of which P2 was variable selling expense.
If production cost was P10 per unit under absorption costing, then how many units did the company produce during the year?
A. 7,500 units.
B. 7,000 units.
C. 9,000 units.
D. 8,500 units.
A. 7,500 units.
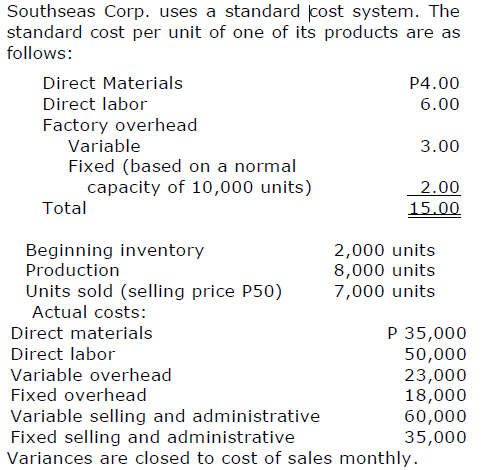
How much are the net income under absorption costing and variable costing methods?
Absorption - Variable
a. 144,000 - 143,000
b. 143,000 - 144,000
c. 144,000 - 142,000
d. 142,000 - 144,000
c. 144,000 - 142,000

What would X Co. have reported as its income before tax if it had used variable costing?
a. P30,000 c. P67,500
b. P(7,500) d. P45,000
b. P(7,500)

What was the total amount SG&A expense incurred by X Co.?
a. P30,000 c. P6,000
b. P62,500 d. P45,000
b. P62,500
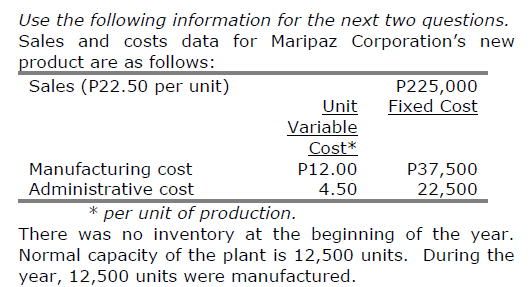
The total fixed cost charged to expense for the year under the absorption costing shall be
a. P48,000
b. P52,500
c. P55,500
d P60,000.
b. P52,500
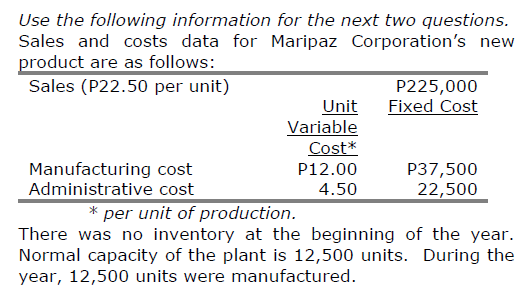
The cost of ending inventory under the direct costing and absorption costing shall be as follows:
Direct Costing - Absorption Costing
a. 30,000 - 37,500
b. 30,000 - 30,000
c. 37,500 - 30,000
d. 37,500 - 37,500
Direct Costing - a. 30,000
Absorption Costing - a. 37,500
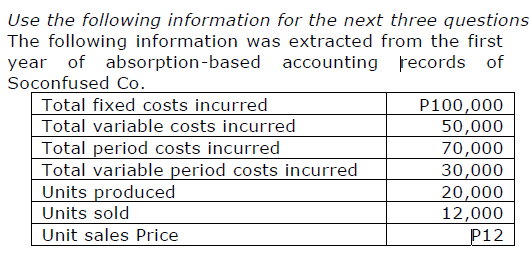
What is Cost of Goods Sold for Soconfused Co.’s first year?
a. P80,000 c. P48,000
b. P90,000 d. Undeterminable
c. P48,000
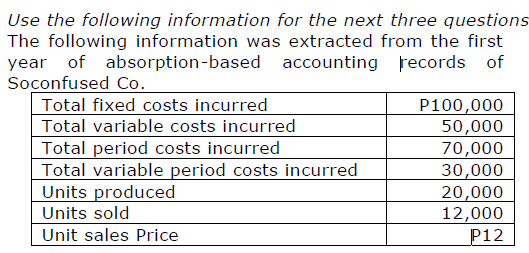
If Soconfused Co. had used variable costing in its first year of operations, how much income (loss) before taxes would they have reported?
a. P(6,000) c. P26,000
b. P54,000 d. P 2,000
d. P 2,000
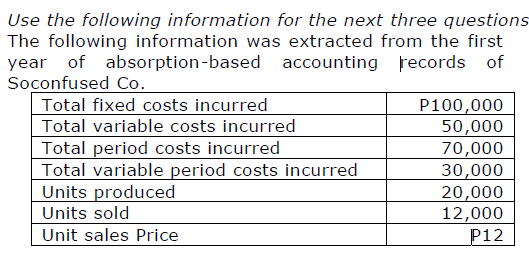
Based on variable costing, if Soconfused had sold 12,001 units instead of 12,000, its income before taxes would have been
a. P9.50 higher c. P8.50 higher
b. P11.00 higher d. P8.33 higher
c. P8.50 higher
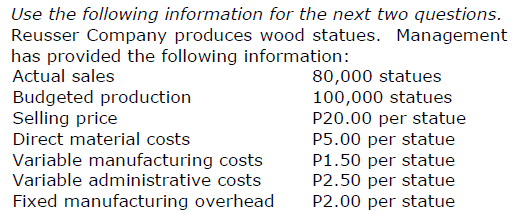
What is the cost per statue if throughput costing is used?
a. P11.00 c. P7.50
b. P9.50 d. P5.00
d. P5.00
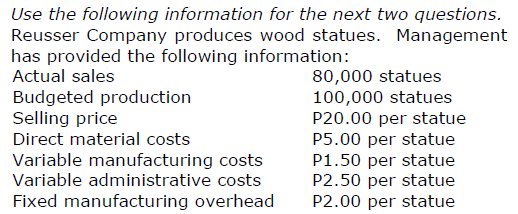
What is the total throughput contribution?
a. P1,500,000 c. P720,000
b. P2,000,000 d. P1,200,000
d. P1,200,000