Chapter 16: Development of Economic Thinking
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
core principles of classical thinking
laissez-faire
free trade
sound finance
long-run equilibrium
laissez-faire
minimal government intervention in the economy, free markets are self-regulating and lead to efficient outcomes
free trade
unrestricted international trade benefits for all countries involved
sound finance
the government’s primary role is to maintain price stability, ensuring a stable financial environment for businesses to operate
long-run equilibrium
the economy naturally gravitates towards full employment equilibrium, with only frictional unemployment
Say’s Law
production generates income, which is then used to purchase goods and services, ensuring that aggregate supply and aggregate demand remains in balance
Equation of Exchange (MV = PY)
used by classic economists to argue that changes in the money supply only affect the price level, not real output
MV = PY
M: Money supply
V: velocity of money
P: price level
Y: real GDP
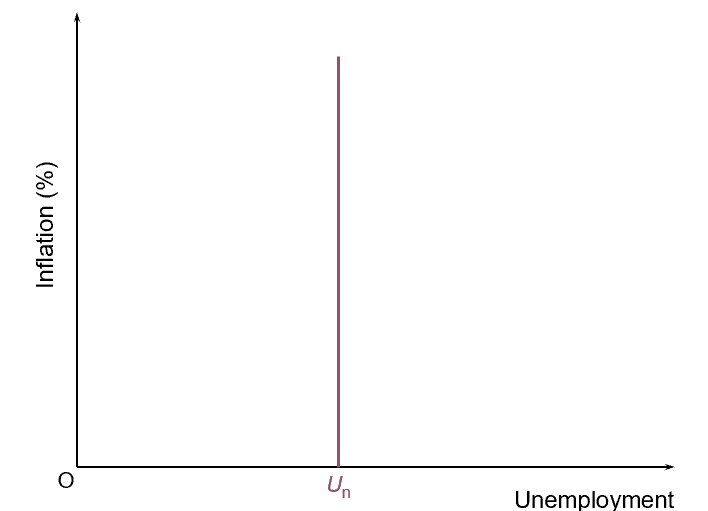
monetarist version of the long-run phillips curve