420 Casts / Crystals /Other
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Urinalysis Microscopics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Significance of RBCs in urine
Glomerular membrane damage
Vascular Injury
Vaginal Contamination
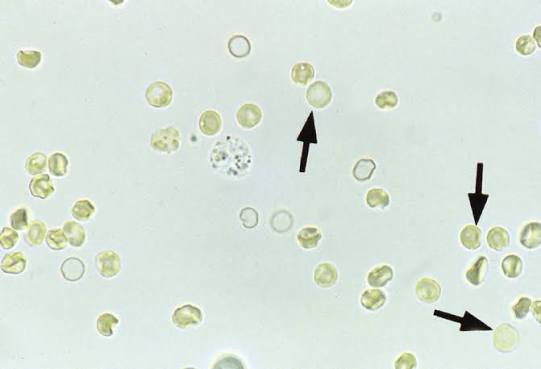
Ghost Cells happen when
RBCs absorbing water in diluted urine
Crenated RBCs happen when
loss of water in concentrated urine
How does acidic urine affect RBCs/WBCs?
Preservation of morphology
How does alkaline urine affect WBC/RBCs?
May lyse cells
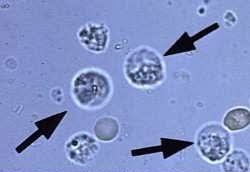
what are most of these cells
RBC
Glitter cells
WBCs that have been in diluted or alkaline urine and lyse, losing nuclear detail.
Significance of WBCs in urine
Inflammation, infection
Glomerular or capillary trauma
what dis
WBC
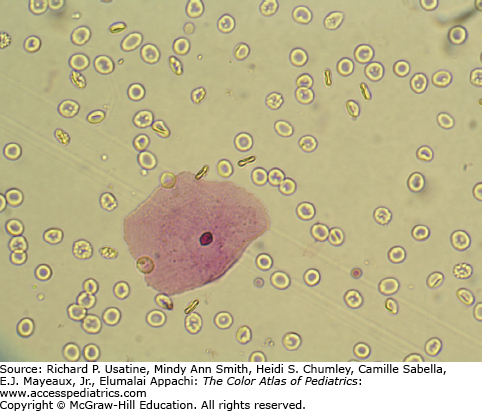
Large and flat cell with a small single nucleus
Squamous epithelial
what dese
Squamous Epithelial Cell
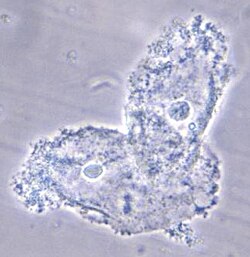
Clue cells are:
Bacteria adhering to squamous epithelial cells, which extend beyond the cell border
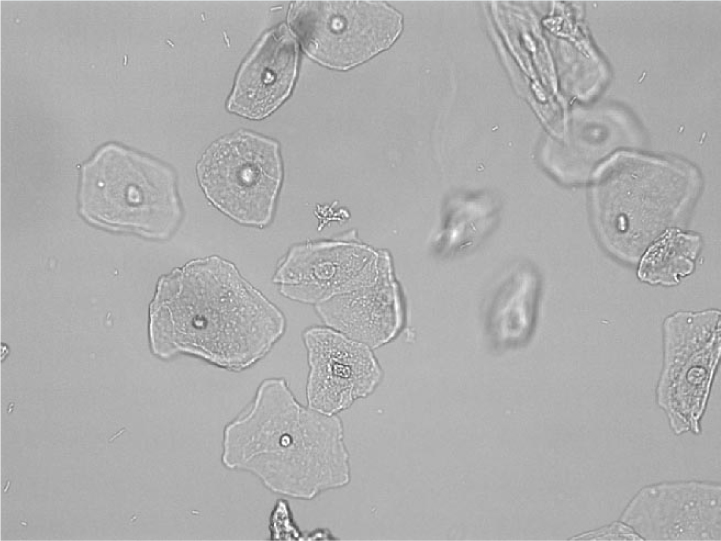
Round, central nuclear cells which line the ureters, bladder, and upper urethra
Transitional Epithelial cells
Why might we see transitional epithelial cells in the urine?
Normal sloughing, catheterization, malignancy, or infection
Round, larger than WBC cells with an eccentric nucleus that line the renal tubules
RTEs
Significance of RTEs in the urine
Exposure to toxins, viral infections, pyelonephritis, or transplant rejection.
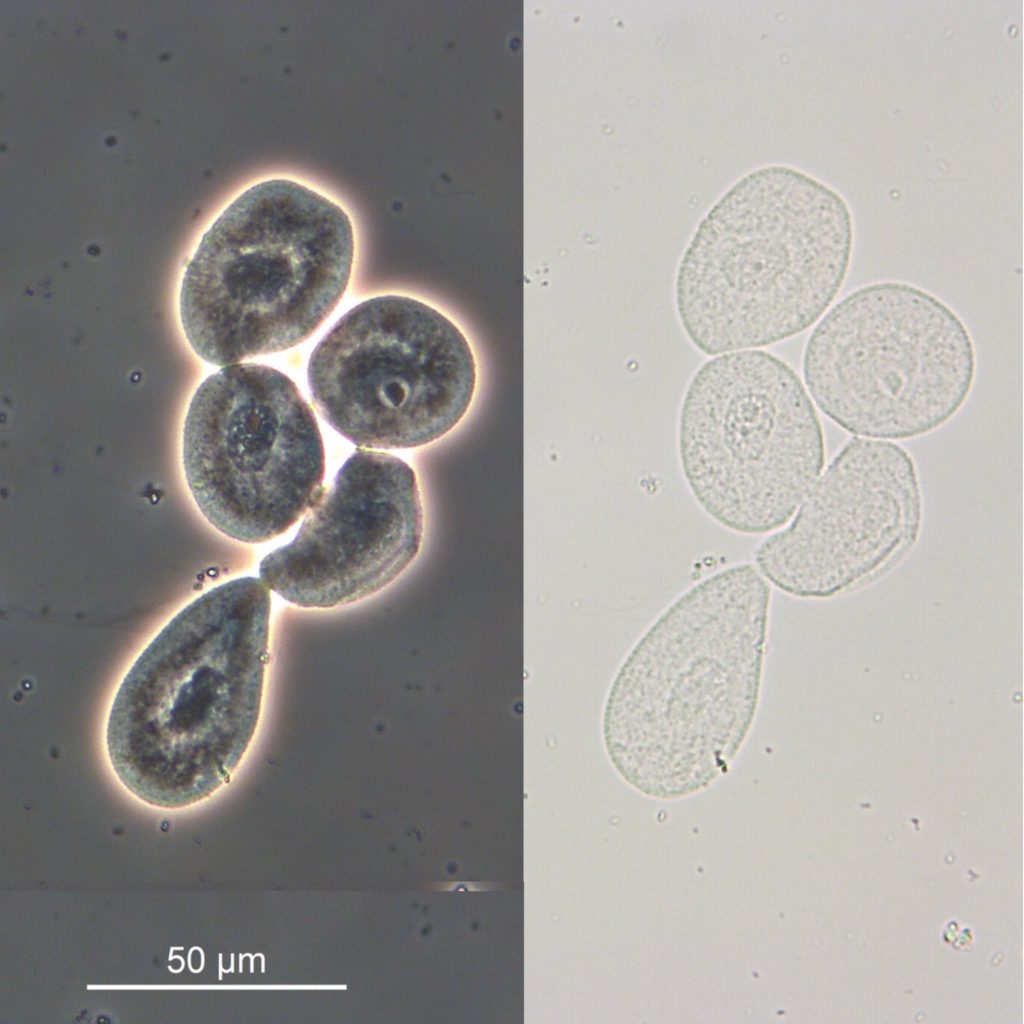
what these
RTE
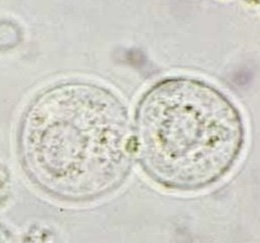
identify
Transitional Epithelial
What is an oval fat body?
RTE with adsorbed lipids
How do we confirm oval fat bodies?
Polarized Microscopy or Stains for Fat (Sudan / Oil Red)
Significance of oval fat bodies
Nephrotic syndrome
How are casts formed? What protein
Precipitation of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein (uromodulin) That cells/proteins in the renal tubules can become conglutinated with.
What conditions favor cast formation?
Slow flow, concentrated, and acidic urine.
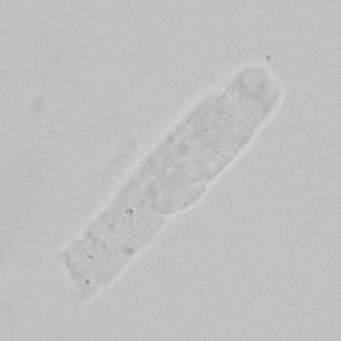
what
Hyaline Cast
Hyaline significance
Strenuous exercise, stress, dehydration, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, chronic renal disease
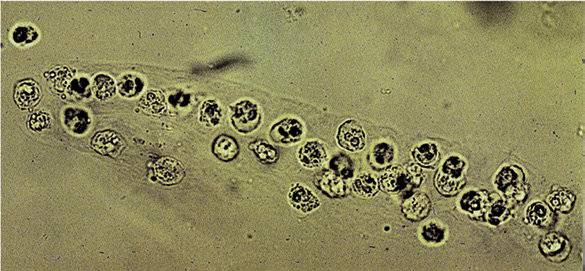
this is:
RBC cast
Significance of RBC cast
Bleeding in the nephron
(acute glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis, pyelonephritis, strenuous exercise) verify with positive blood on reagent strip + free standing RBCs on slide
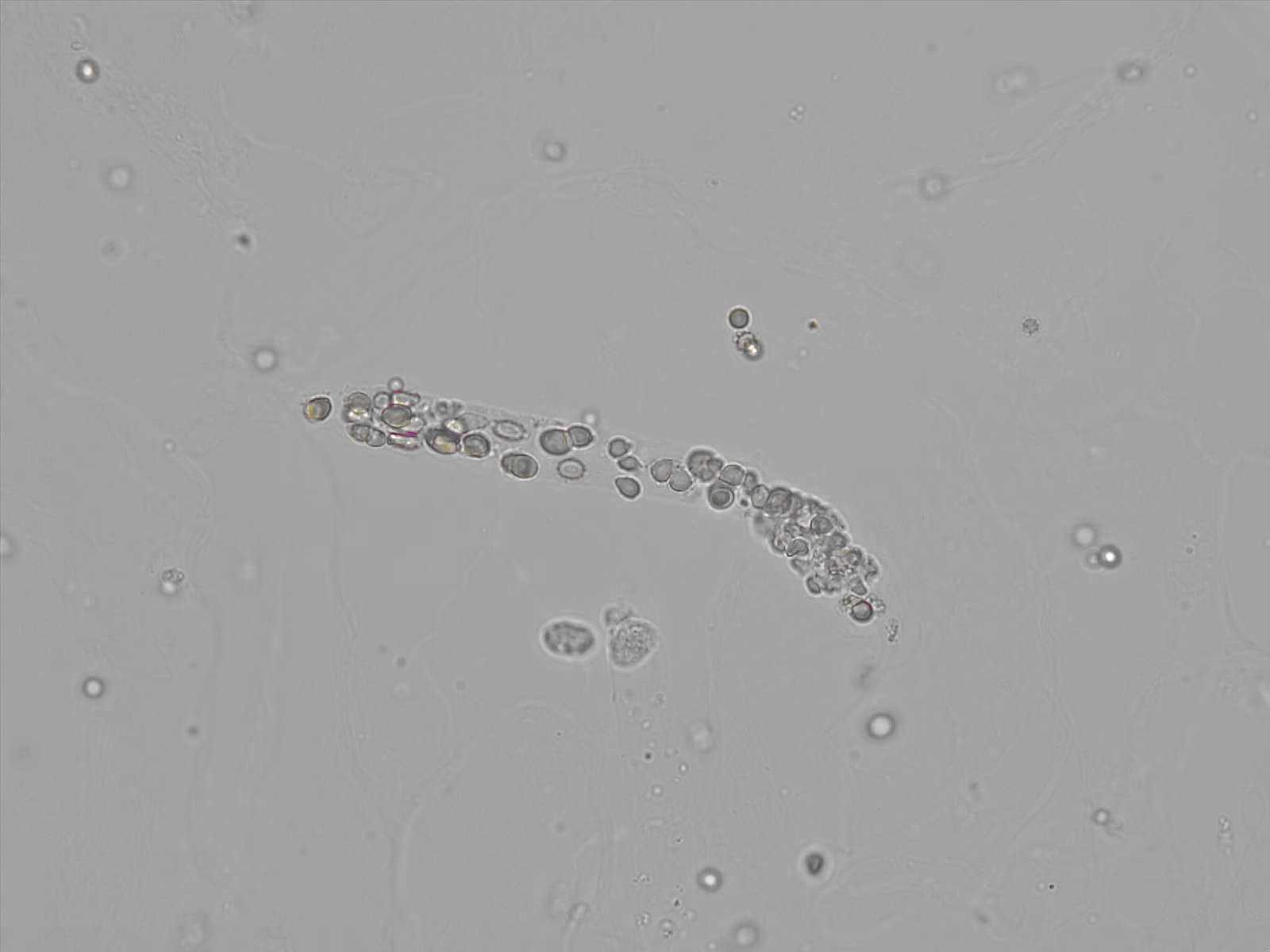
what this
WBC cast
Significance of WBC casts
Pyelonephritis, Lupus nephritis, Glomerulonephritis
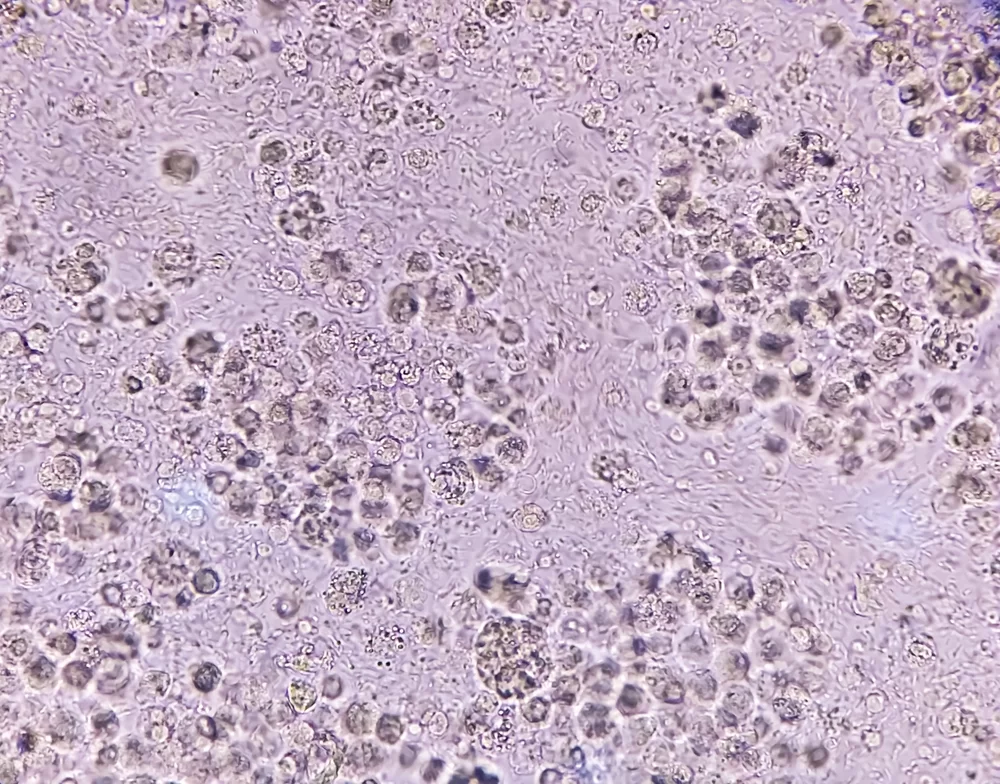
what hapepend here
WBC clump
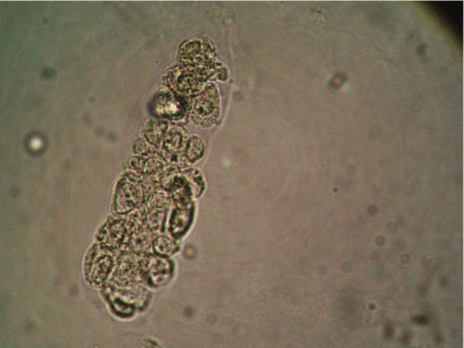
what
Epithelial cell cast
What do epithelial cell casts suggest?
Excessive desquamation (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, renal vascular disease, exposure to toxin, viral infections, and allograft rejection)
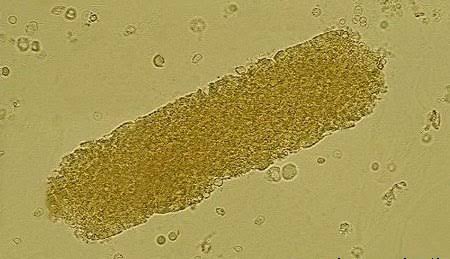
?
Granular Cast
Significance of Granular Casts
Glomerulonephritis
Pyelonephritis
Strenuous exercise
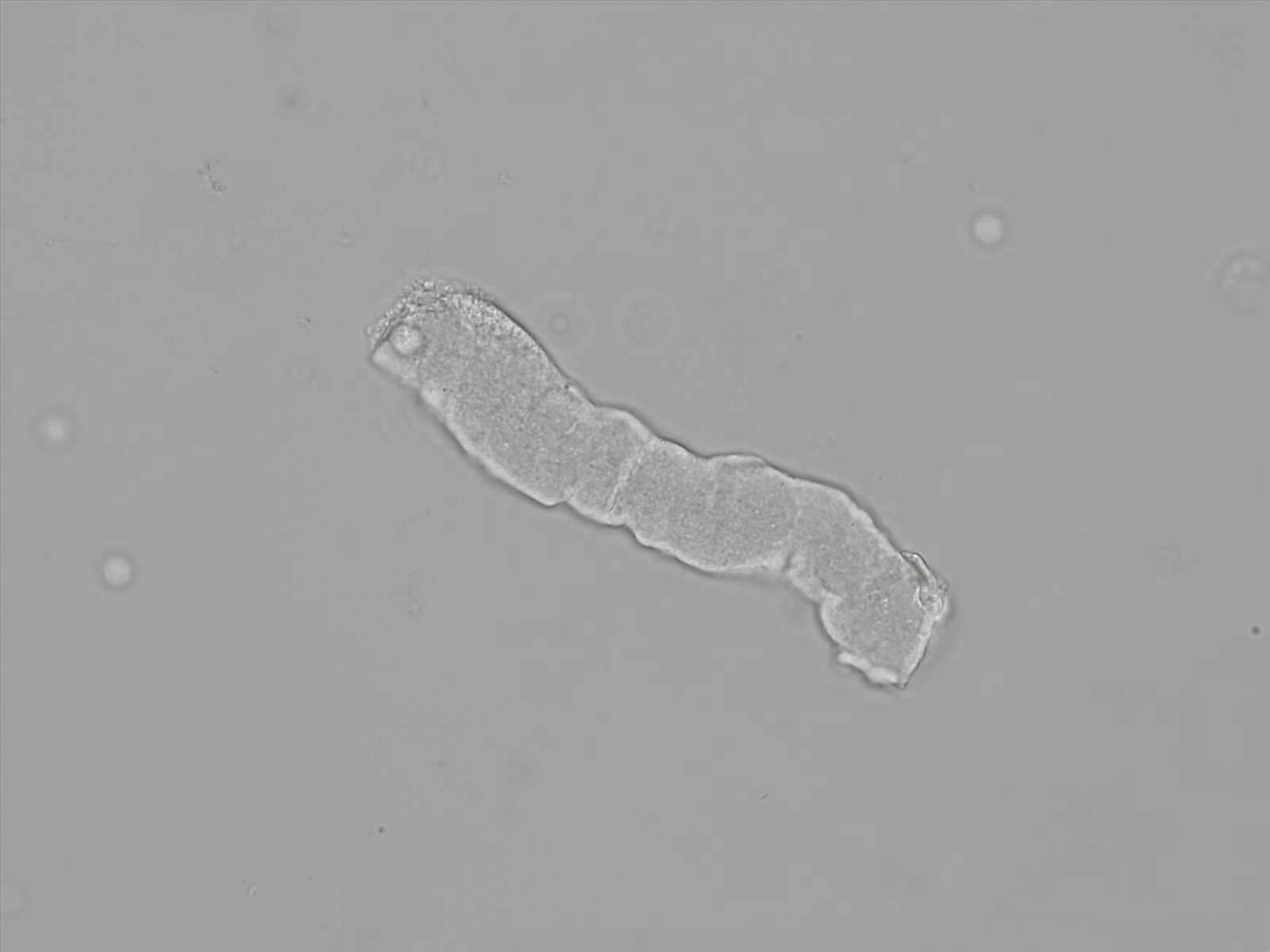
this is what
Waxy cast
What significance do Waxy casts have?
Extreme stasis of urine flow
Chronic Renal Failure
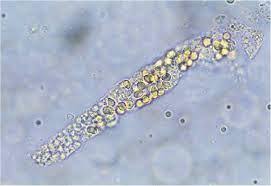
?
Fatty cast
Significance of fatty casts
Chronic renal disease, nephrotic syndrome
How do we confirm fatty casts?
Polarized microscopy or fat stains.
Amorphous Cystals in acidic and alkaline urine
Acidic = urates
Alkaline = phosphates
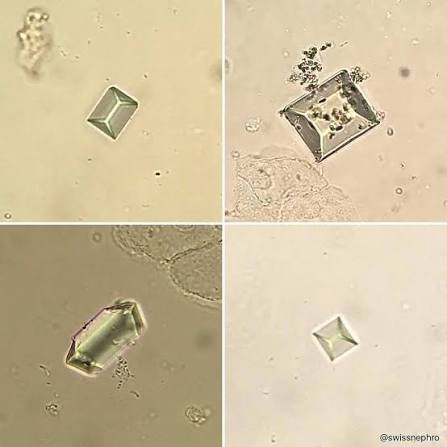
“Coffin Lids” AKA
Triple Phosphate (alkaline)
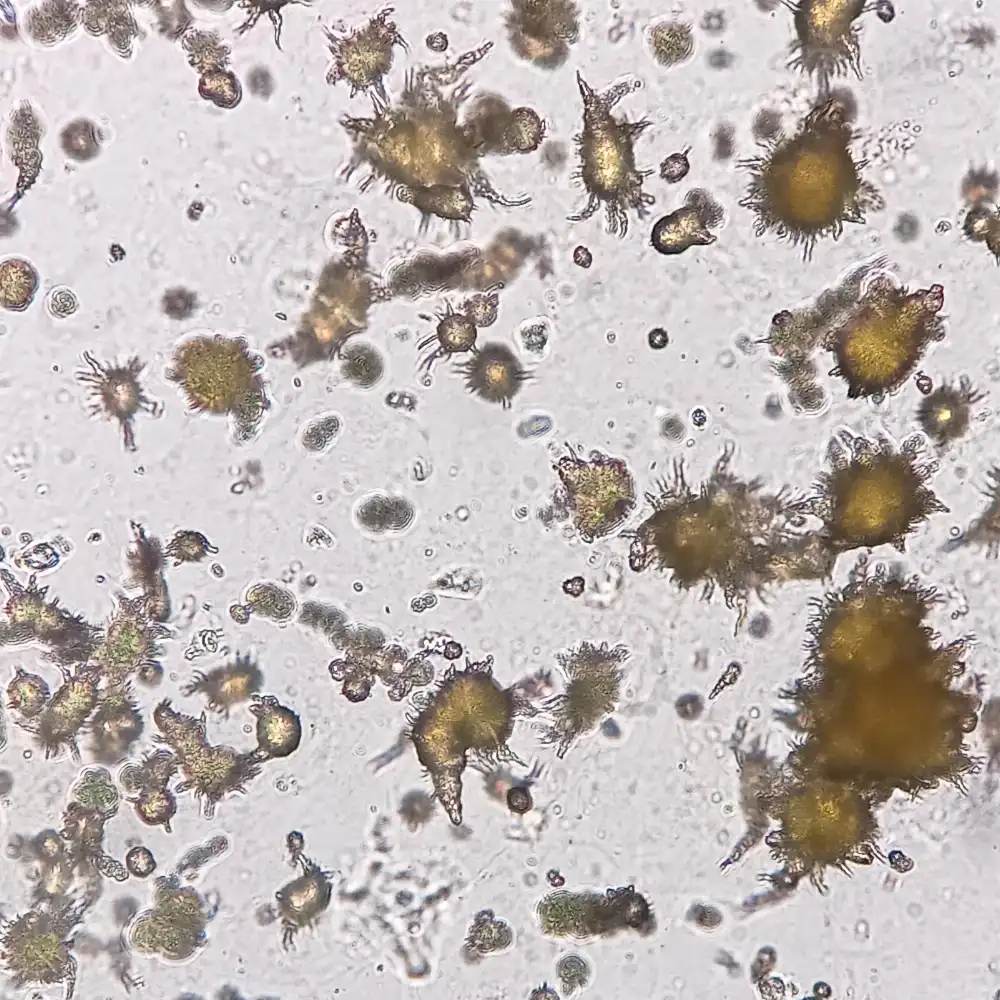
“Thorny Apples”
AKA
Ammonium biurate (alkaline)
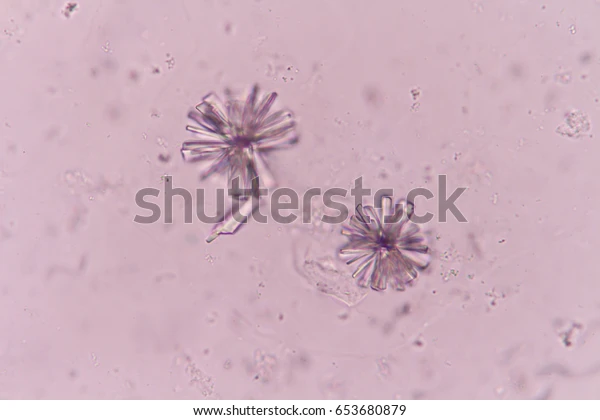
This is:
Calcium phosphate (alkaline)
Alkaline normal crystals
Triple Phosphate
Ammonium Biurate
Calcium phosphate
Normal Acidic Crystals
Calcium oxalate and uric acid
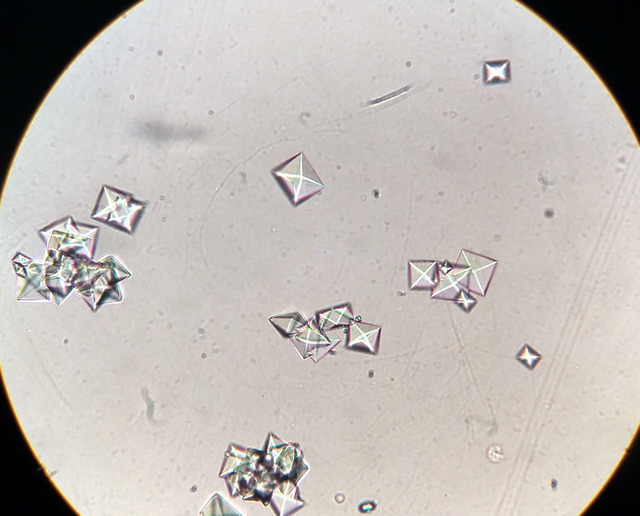
the envelope ones aka
Calcium oxalate
What causes calcium oxalate?
Foods high in oxalic acid, antifreeze posioning, main culprit of renal calculi

and these r:
Uric Acid
3 forms of calcium oxalate
envelope, oval, dumbbell
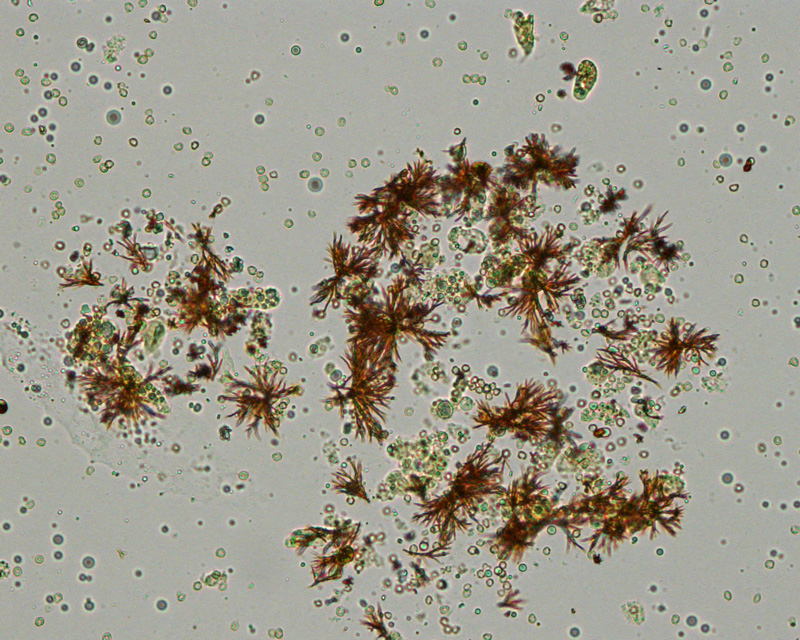
dis is:
Bilirubin
Liver disease

this one is tricky
Cholesterol
Nephrotic Syndrome (may see fatty casts)
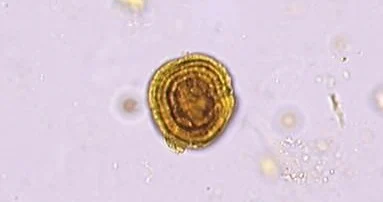
this one might be my favorite
Leucine
Liver disease
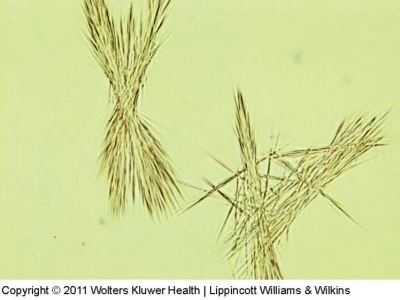
ts Is:
Tyrosine
Liver disease
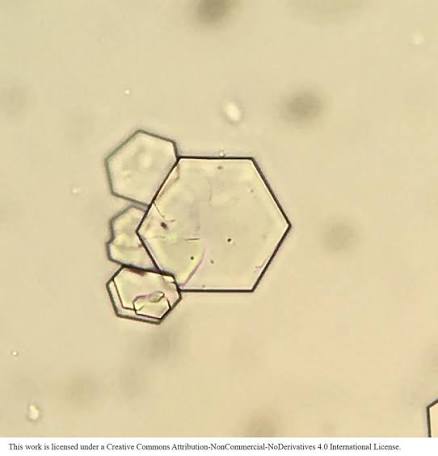

this one might also be a top 3
Cystine
Cystinuria/Cystinosis
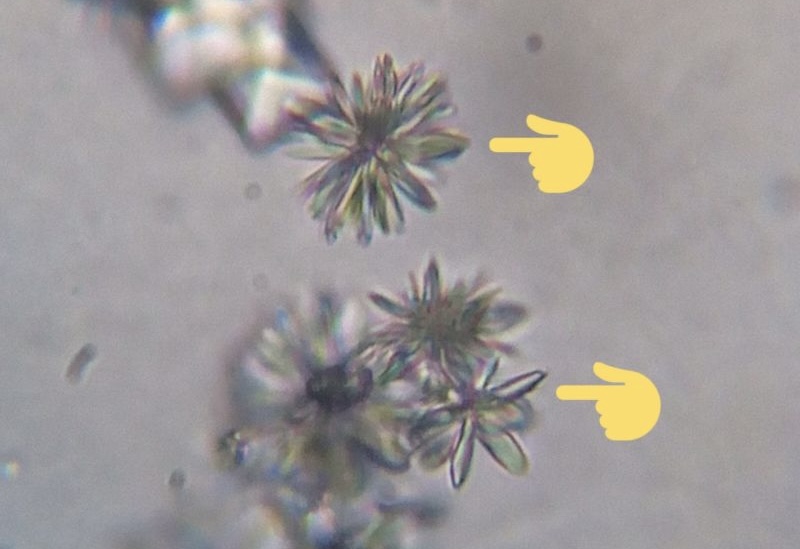

emojis pointing at
Sulfonamide
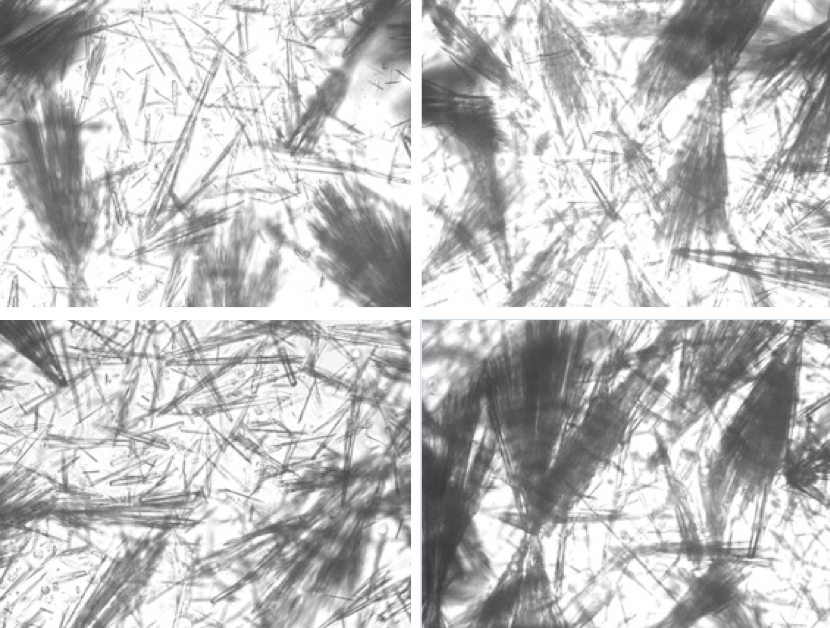
I do not like this one
Ampicillin
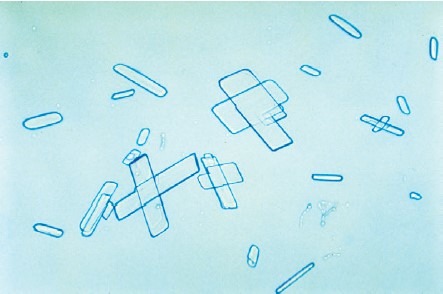
tricky pt 2.
Renografin
How to distinguish renografin from cholesterol crystals?
Look at specific gravity and patient history
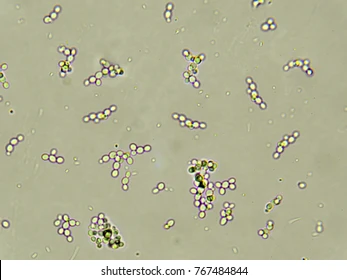
wash urself or u will get:
Yeast
Diabetics, immunocompromised, infections
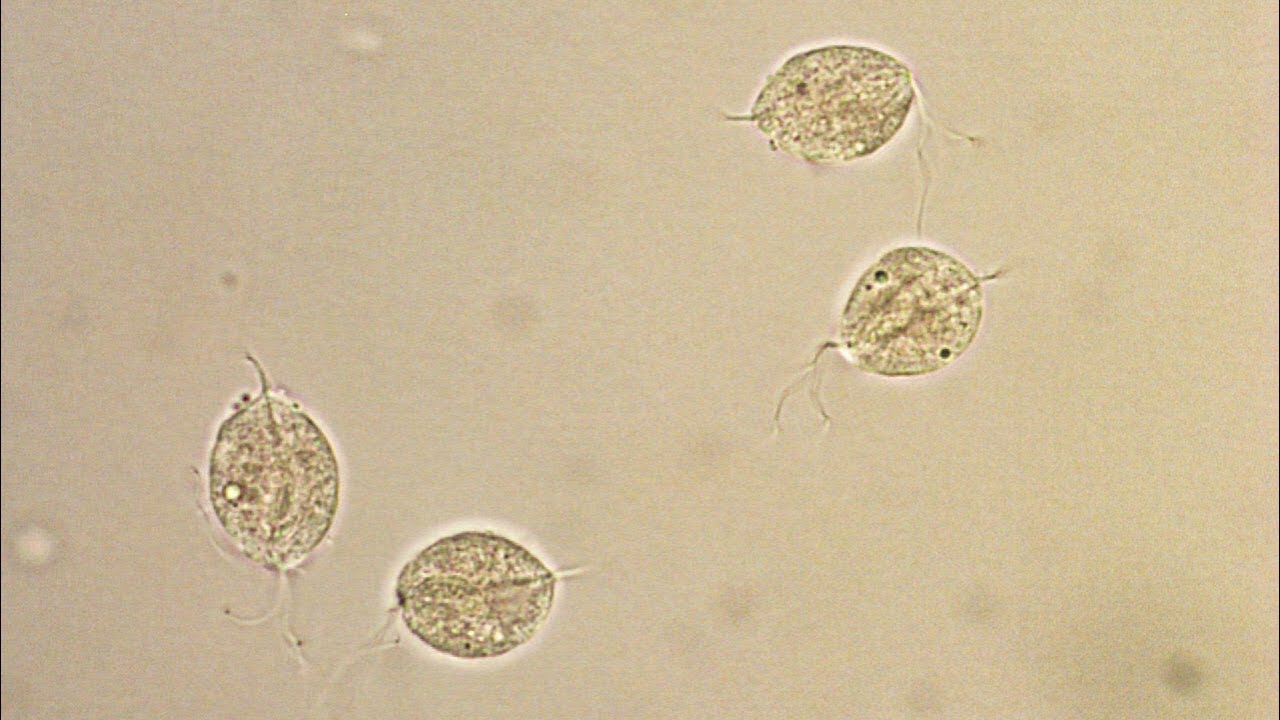
wrap it up or you will get:
Trichomona
Sexually transmitted parasite
Usual kind of bacteria found in urine
gram negative rods
How to tell apart yeast vs RBC?
Look for budding pattern
Can lyse RBCs with acetic acid
Why might we question a UTI diagnosis if bacteria are visible on the microscopic exam?
If there’s not WBCs, it may be due to contamination or poor preservation.