populations, individuals and gene pools
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
antibiotic resistance
the ineffectiveness of an antibiotic that results if a bacterial cell has alleles that make it resistant to being destroyed by antibiotics
Each dose of antibiotics will allow these bacteria to survive and pass on their resistant traits to the next generation—more of each generation are resistant until the resistant allele is the most common; at this point, the antibiotic is no longer effective.
behavioural defences
actions and gestures that are meant to communicate that the organism is dangerous and should be avoided or is harmless and not threatening
biotechnology
manipulation of genes or traits
biotic potential (r)
highest per capita growth rate possible
bottleneck effect
a type of genetic drift similar to the founder effect; occurs when a natural disaster thins the population to a small group that happens to be unrepresentative of the original group
Allele frequencies of the two groups will be dissimilar.
carrying capacity (K)
the theoretical maximum population size that the environment can sustain over an extended period of time; may change as the quality of the habitat changes; the population is at carrying capacity when it levels off during logistic growth
chemical defences
toxic, bad-tasting, or bad-smelling chemicals secreted by an organism that either discourage consumers from eating it, poison consumers, or prevent competitors from growing or living nearby
climax species
the last species of plant in the succession; is used to name the succession
clumped distribution:
organisms grouped together; occurs in highly competitive environments
commensalism
a type of symbiosis in which one species benefits and the other is not affected one way or another
cryptic colouration (camouflage)
colours or patterns that allow an organism to blend into its environment and avoid being seen
density (Dp)
the number of individuals in a given unit of area (land) or volume (air or water)
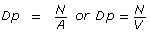
density-dependent limiting factors
biotic factors that limit a habitat’s carrying capacity (e.g., parasites, disease, increase in predators, lack of water, food, or territory); the impact increases with the density of the population
density-independent factors
abiotic factors that limit a habitat’s carrying capacity (e.g., fire, flood, frost); the impact is not affected by the density of the population
emigration
number of individuals that leave the population; due to the same reasons as immigration
environmental resistance
the combined effects of factors that limit population growth; prevents a population from growing at its biotic potential; determines the carrying capacity of the environment
exponential growth
a growth pattern exhibited by a population that doubles with each generation; results in a J-shaped curve; begins with a lag phase, followed by a steep rise
exponential phase
the second phase of a growth graph in which population size increases significantly because limiting factors are not yet significant
fecundity
fertility; the ability of an organism to be fertile or to reproduce
founder effect
a type of genetic drift that occurs when a small population that is not representative of the main population migrates away
Allele frequencies of the two groups will be dissimilar.
frequency
number/total; how common something is; usually expressed as a decimal percentage; e.g., an incidence of “2 in 5” gives the same information as a frequency of 0.4 or 40%
gene flow
movement of alleles into or out of a population by immigration or emigration
genetic drift
a change in allele frequencies caused by chance events in a small gene pool, such as inbreeding caused by isolation of a small non-representative group or a few non-breeding individuals (bachelors)
Founder effect and bottleneck effect are examples of genetic drift.
Growth rate
the change in the number of individuals in a unit of time
![]()
will be positive if the population size is increasing, and negative if it is decreasing.
Hardy-Weinberg equation
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
a principle that states that allele frequencies in a population will remain the same over time as long as the population is large, there is no gene flow, natural selection is not occurring, there is no change in mutation rate, and no mate selection is occuring
If allele frequencies do change, it indicates that microevolution is occurring in the population.
host
the organism in a type of symbiotic relationship that provides food or a means to complete reproduction for the parasitic organism of another type of species
immigration
number of individuals entering the population from outside; can be due to abiotic factors (e.g., escape from fire, drought, flood, climate change) or biotic (e.g., increased competition)
interspecific competition
when members of two different species compete for scarce resources and survival; competition only occurs when there are too many organisms and not enough resources
intraspecific competition
when members of the same species compete against each other for scarce resources and survival; causes microevolution because one phenotype or allele will have better survival than another
The scarcer the resources, the more extreme the competition and the faster microevolution occurs
invasive species
species that are introduced to an area and that out-compete the indigenous species in its trophic level for nutrients and/or prey; are less affected by limiting density-dependent and density-independent factors
J curve
population growth with a brief lag phase and a steep increase in the growth curve
K-selected strategy
takes advantage of stable conditions; characterized by few offspring with much investment and nurturing to increase offspring survival
K-selected organisms
species that have K-selected strategies, such as longer life span, later reproductive age, few offspring, and parental care
lag phase
the first phase of a growth graph showing little increase in population numbers
logistic growth:
a population increase resulting in an S-shaped curve; begins with slow growth, steepens to exponential growth, and then levels to a carrying capacity due to competition because of environmental resistance
mate selection (non-random mating)
the process of choosing mates based on the presence of certain traits or phenotypes and, thus, genotypes
Traits are usually displayed in some form of courtship ritual.
microevolution
a change in the frequency of alleles in the gene pool that results in a change in the characteristics of the population; does not result in a new species
mimicry
when a harmless organism has the same bright colouration of an organism that has protective colouration
monoculture
the cultivation of a single crop
mortality
death; may be due to kill-off (predation) or die-off (disease, starvation, or exposure)
mutualism
a type of symbiosis involving two organisms of different species in which both benefit or depend on the relationship to survive
natality
number of births; tends to increase with food supply and decrease with competition
natural selection
the process by which organisms with heritable traits survive in a particular environment, passing on their successful traits to the next generation
Those selected have greater reproductive fitness that either increases fertility or decreases mortality.
niche
a position or role taken by an organism within its community
parasite
the organism in a symbiotic relationship that benefits by living on or in another organism (host) as a source of food or means of reproduction
The host is harmed in this relationship.
per capita growth rate (cgr)
the rate of change per individual; the amount of change each individual in the initial population is responsible for
![]()
cgr can be positive or negative depending on what the initial N is.
pioneer species
the first species of plant to invade a cleared site in a succession
population
organisms of a particular species in a particular place at a particular time
population determiners
four factors that change the numbers of individuals in the population: natality, mortality, immigration, and emigration
predator-prey
a relationship in which one organism (predator) hunts and kills another organism (prey) for food
primary succession
a succession that begins with bare rock; soil-building organisms (e.g., lichen) are pioneers
protective colouration
bright colours that give clear warning to potential attackers
random distribution
no pattern exists in organism distribution; occurs in environments with little competition
reproductive strategy
the strategies used in reproduction to ensure survival of a species; may be r- or K-selected strategies
r-selected strategy
takes advantage of favourable conditions; characterized by early reproduction and high reproductive rate with little investment in offspring survival
r-selected organisms
species that have r-selected strategies, such as a short life span, early reproductive age, large numbers of offspring, and little parental care
S curve
a logistic growth pattern with a lag phase, growth phase, and stationary phase in which limiting factors become significant
secondary succession
a succession that begins with soil
stationary phase
the third stage of a population growth graph in which population size stabilizes because of the balance between environmental resistance and biotic potential
structural defences
physical parts of the organism that either protect the organism from being consumed or allow the organism to compete better for scarce resources
succession
the orderly replacement of one species with another over time; occurs after a disruption, such as fire
symbiotic relationship
any close relationship in which individuals of different species live together in a feeding or protective relationship
transgenic organism
an organism that has genes from more than one species
uniform distribution
organisms are equally spaced apart; occurs in artificial environments (e.g., agricultural crops)
wildlife corridor
a route used by wildlife to move from one territory to another
Wildlife corridors are often part of a migratory pattern.